Insert HTML-Formatted RichText into Excel Cell in C#
Some time back, one of registered members on our Forum had a requirement to display the value of HTML code in Excel cell. This article is aimed to provide a fine way to manage this issue using Spire.Doc and Spire.XLS.
Main Method:
At present, we have to use Document.LoadHTML() method which is available in Spire.Doc.Document class to load HTML string to a Word document, this way, HTML formatted text will be save in specific paragraphs. Then, get the paragraph with rich text style and return a RichTextString object, save RichText to a specified CellRange. Besides, the paragraph text style must be applied to this CellRange.
Detailed Steps:
Step 1: Create a new Workbook and Word document.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook(); Document doc = new Document();
Step 2: Save the HTML code to StringReader and load the HTML string to Word document.
StringReader sr = new StringReader("<span style=\"border-width:thin;border-color:#FFFFFF;\"><font color=#000000 size=8><b>U = Unchanged rate</b></font></span>");
doc.LoadHTML(sr, XHTMLValidationType.None);
Step 3: Get the formatted text from Word document and save to cell 'A4' in the first worksheet.
foreach (Section section in doc.Sections)
{
foreach (Paragraph paragraph in section.Paragraphs)
{
if (paragraph.Items.Count > 0)
{
workbook.Worksheets[0].Range["A4"].RichText.Text += paragraph.Text;
}
}
}
Step 4: Apply text style including font color and font size to cell 'A4'.
int index = 0;
foreach (var item in paragraph.Items)
{
if (item is Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange)
{
for (int i = index; i < (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).Text.Length + index; i++)
{
ExcelFont excelFont = workbook.CreateFont();
excelFont.FontName = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.FontName;
excelFont.Size = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.FontSize;
excelFont.IsBold = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.Bold;
excelFont.IsItalic = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.Italic;
excelFont.Underline = (FontUnderlineType)(item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.UnderlineStyle; excelFont.Color = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.TextColor;
workbook.Worksheets[0].Range["A4"].RichText.SetFont(i, i, excelFont);
}
}
index += (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).Text.Length;
}
Step 5: Change the width and height of the row to achieve the best fit.
workbook.Worksheets[0].Range["A4"].AutoFitRows();
Step 6: Save changes to the workbook in a new file.
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
HTML-Formatted Text in Excel would be shown as:
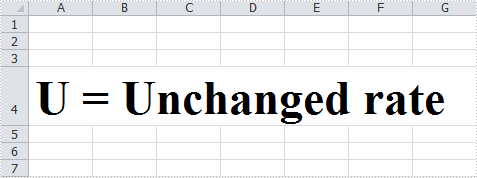
Full Code:
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Document doc = new Document();
StringReader sr = new StringReader("<span style=\"border-width:thin;border-color:#FFFFFF;\"><font color=#000000 size=8><b>U = Unchanged rate</b></font></span>");
doc.LoadHTML(sr, XHTMLValidationType.None);
int index = 0;
foreach (Section section in doc.Sections)
{
foreach (Paragraph paragraph in section.Paragraphs)
{
if (paragraph.Items.Count > 0)
{
workbook.Worksheets[0].Range["A4"].RichText.Text += paragraph.Text;
foreach (var item in paragraph.Items)
{
if (item is Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange)
{
for (int i = index; i < (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).Text.Length + index; i++)
{
ExcelFont excelFont = workbook.CreateFont();
excelFont.FontName = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.FontName;
excelFont.Size = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.FontSize;
excelFont.IsBold = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.Bold;
excelFont.IsItalic = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.Italic;
excelFont.Underline = (FontUnderlineType)(item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.UnderlineStyle;
excelFont.Color = (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).CharacterFormat.TextColor;
workbook.Worksheets[0].Range["A4"].RichText.SetFont(i, i, excelFont);
}
}
index += (item as Spire.Doc.Fields.TextRange).Text.Length;
}
}
}
}
workbook.Worksheets[0].Range["A4"].AutoFitRows();
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Set Excel View Mode in C#, VB.NET
Users can change the Excel view mode according to reading habit. By default, there are several view modes we can choose, including Normal View, Page Layout View, Page Break Preview, Full Screen View and Custom Views. Besides, Microsoft Excel also enables us to zoom in/out the document to a specified level. In this article, I'll make a brief introduction about how to set Excel view mode using Spire.XLS in C# and VB.NET.
In this sample, the Excel view mode will be set as Page Break Preview with zoom in 80 percent. Download the Spire.XLS for .NET, add the Spire.Xls.dll as a reference into assemblies, then we can use the following code snippet to achieve this end goal.
Detailed Steps
Step 1: Create a new instance of Workbook and load the sample file.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Step 2: Get the first the worksheet from the Excel workbook.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Step 3: Set view mode as Page Break Preview and Zoom in the sheet with 80 percent.
sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Preview; sheet.ZoomScalePageBreakView = 80;
Step 4: Save the changes to workbook in a new file.
workbook.SaveToFile("Result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Output:
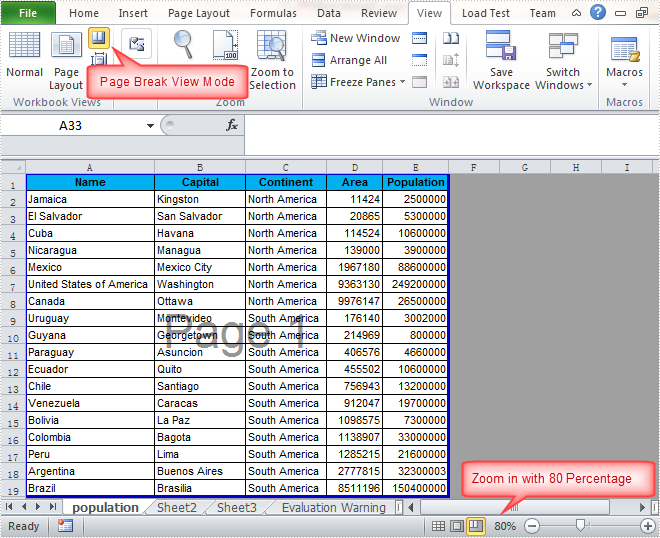
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetExcelViewMode
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
////Page Layout
//sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Layout;
//sheet.ZoomScalePageLayoutView = 80;
////Normal View(Default)
//sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Normal;
//sheet.ZoomScaleNormal = 80;
//Preview
sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Preview;
sheet.ZoomScalePageBreakView = 80;
workbook.SaveToFile("Result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace SetExcelViewMode
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'''/Page Layout
'sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Layout;
'sheet.ZoomScalePageLayoutView = 80;
'''/Normal View(Default)
'sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Normal;
'sheet.ZoomScaleNormal = 80;
'Preview
sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Preview
sheet.ZoomScalePageBreakView = 80
workbook.SaveToFile("Result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Get information of pagination in Excel document
When we print Word and PDF documents which have regular page size, we can clearly know the pagination information for Word and PDF by delimiters. Excel document is different since Excel pagination is based on its content when we print Excel document or convert to Pdf. So get Excel pagination information is important to developer. Below would introduce a solution to get pagination information in Excel document.
The solution call book.GetSplitPageInfo() method to obtain information of excel document and return this information to the List<Dictionary<int, PageColRow>> object via Spire.XLS. By the object we can get this information about: sheet count, page count and the start and end column and row of every page in excel document. Below is effect screenshots:
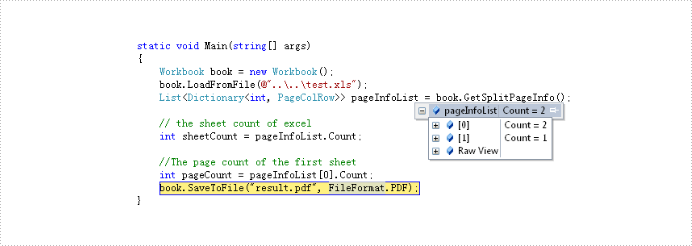
The main steps of the solution are:
Step 1: Create and load an excel document.
Workbook book = new Workbook(); book.LoadFromFile(@"test.xlsx");
Step 2: Call GetSplitPageInfo() method to Excel information.
List> pageInfoList = book.GetSplitPageInfo();
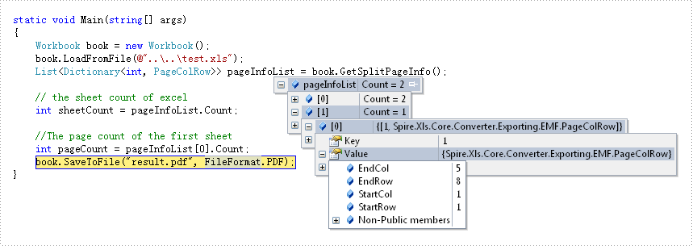
The full code:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Core.Converter.Exporting.EMF;
namespace GetPageInformation
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// create and load Excel document
Workbook book = new Workbook();
book.LoadFromFile(@"test.xlsx");
// get the Excel document information and save in pageInfoList object
List> pageInfoList = book.GetSplitPageInfo();
// the sheet count of excel
int sheetCount = pageInfoList.Count;
//The page count of the first sheet
int pageCount = pageInfoList[0].Count;
book.SaveToFile("result.pdf", FileFormat.PDF);
}
}
}
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports Spire.Xls.Core.Converter.Exporting.EMF
Module Module1
Sub Main()
'create and load Excel document
Dim book As New Workbook()
book.LoadFromFile("test.xlsx")
' get the Excel document information and save in pageInfoList object
Dim pageInfoList As List(Of Dictionary(Of Integer, PageColRow)) = book.GetSplitPageInfo()
' the sheet count of excel
Dim sheetCount As Integer = pageInfoList.Count
'The page count of the first sheet
Dim pageCount As Integer = pageInfoList(0).Count
book.SaveToFile("result.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
End Sub
End Module
C#/VB.NET: Print Excel Documents
Excel documents are easy to print, but it would be a bit tricky if you have some special printing requirements. For example, printing only selected range of a sheet, repeating the header row on each page, or fitting a worksheet on one page. This article covers how to set Excel print options via page setup and how to send an Excel document to printer in C# and VB.NET by using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Set Excel Print Options via Page Setup in C# and VB.NET
- Print Excel Documents Using Print Dialog in C# and VB.NET
- Silently Print Excel Documents in C# and VB.NET
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Set Excel Print Options via Page Setup in C# and VB.NET
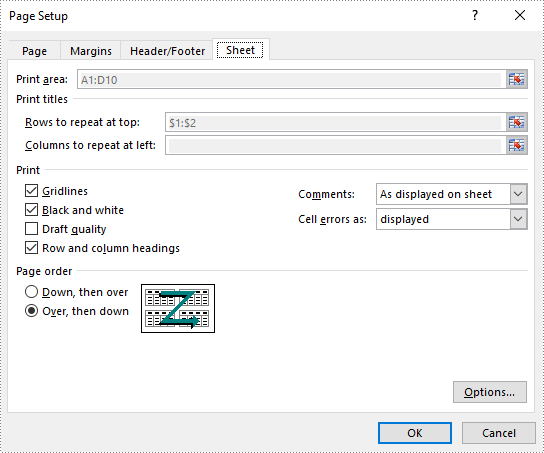
Excel Page Setup provides options to control how a worksheet will be printed, such as whether to print comments, whether to print gridlines and specify the cell range to print. Spire.XLS offers the PageSetup object to deal with these things. The following are the steps to set Excel print options through PageSetup using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get PageSetup object through Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set page margins, print area, pint title row, print quality, etc. through the properties under PageSetup object.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace PrintOptions
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Get the PageSetup object of the first worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = worksheet.PageSetup;
//Set page margins
pageSetup.TopMargin = 0.3;
pageSetup.BottomMargin = 0.3;
pageSetup.LeftMargin = 0.3;
pageSetup.RightMargin = 0.3;
//Specify print area
pageSetup.PrintArea = "A1:D10";
//Specify title row
pageSetup.PrintTitleRows = "$1:$2";
//Allow to print with row/column headings
pageSetup.IsPrintHeadings = true;
//Allow to print with gridlines
pageSetup.IsPrintGridlines = true;
//Allow to print comments as displayed on worksheet
pageSetup.PrintComments = PrintCommentType.InPlace;
//Set printing quality (dpi)
pageSetup.PrintQuality = 300;
//Allow to print worksheet in black & white mode
pageSetup.BlackAndWhite = true;
//Set the printing order
pageSetup.Order = OrderType.OverThenDown;
//Fit worksheet on one page
pageSetup.IsFitToPage = true;
//Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("PagePrintOptions.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Print Excel Documents Using Print Dialog in C# and VB.NET
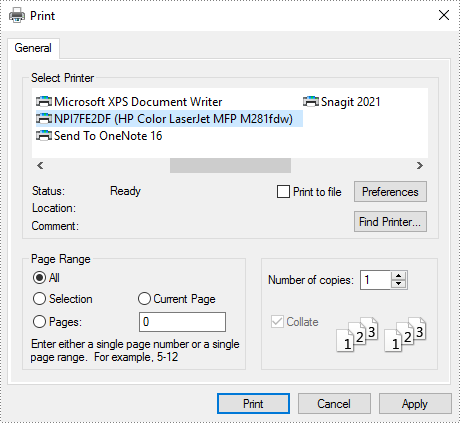
A Print Dialog box lets users to select options for a particular print job. For example, the user can specify the printer to use. The following are the steps to send an Excel document to a print dialog using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PrintDialog object.
- Specify printer settings through the properties under PrintDialog object.
- Apply the print dialog to workbook.
- Get PrintDocument object from the workbook through Workbook.PrintDocument property.
- Invoke the print dialog and start printing using PrintDocument.Print() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using System;
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing.Printing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace PrintExcelUsingPrintDialog
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\sample.xlsx");
//Fit worksheet on one page
PageSetup pageSetup = workbook.Worksheets[0].PageSetup;
pageSetup.IsFitToPage = true;
//Create a PrintDialog object
PrintDialog dialog = new PrintDialog();
//Specify printer settings
dialog.AllowCurrentPage = true;
dialog.AllowSomePages = true;
dialog.AllowSelection = true;
dialog.UseEXDialog = true;
dialog.PrinterSettings.Duplex = Duplex.Simplex;
//Apply the dialog to workbook
workbook.PrintDialog = dialog;
//Create a PrintDocument object based on the workbook
PrintDocument printDocument = workbook.PrintDocument;
//Invoke the print dialog
if (dialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
printDocument.Print();
}
}
}
}
Silently Print Excel Documents in C# and VB.NET
If you do not want to see the print dialog or the print process, you can silently print Excel documents to a specified printer. The following are the steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the print controller to StandardPrintController, which will prevent print process from showing.
- Get PrinterSettings object from the workbook through Workbook.PrintDocument.PrinterSettings property.
- Specify printer name, duplex mode and print pages through the properties under PrinerSettings object.
- Print the workbook using Workbook.PrintDocument.Print() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing.Printing;
namespace SilentlyPrint
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\sample.xlsx");
//Fit worksheet on one page
PageSetup pageSetup = workbook.Worksheets[0].PageSetup;
pageSetup.IsFitToPage = true;
//Set the print controller to StandardPrintController, which will prevent print process from showing
workbook.PrintDocument.PrintController = new StandardPrintController();
//Get PrinterSettings from the workbook
PrinterSettings settings = workbook.PrintDocument.PrinterSettings;
//Specify printer name, duplex mode and print pages
settings.PrinterName = "HP LaserJet P1007";
settings.Duplex = Duplex.Simplex;
settings.FromPage = 1;
settings.ToPage = 3;
//Print the workbook
workbook.PrintDocument.Print();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#: Dynamically Create, Load, and Save Excel Files via Stream
Using stream operations in C#, developers can dynamically create, load, and save Excel files, enabling flexible and efficient data handling. This approach eliminates the need for physical file storage, improving application performance and responsiveness. Ideal for real-time data manipulation or environments with storage limitations, it streamlines data exchange and system integration. This article demonstrates how to create, load, modify, and save Excel files using streams in C# with Spire.XLS for .NET, offering agile and scalable data management solutions.
- Dynamically Create an Excel File and Save It to Stream
- Load and Read Excel Files from Stream with C#
- Modify an Excel File in Stream with C#
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Dynamically Create an Excel File and Save It to Stream
Using Spire.XLS for .NET, developers can dynamically create Excel files in memory by initializing a Workbook object, populating it with data and formatting, and then saving the workbook to a stream using the Workbook.SaveToStream() method. This approach eliminates the need for physical file storage, enhancing both application performance and responsiveness.
Below are the steps for creating an Excel file and saving it to a stream with C#:
- Create an instance of the Workbook class to generate a new Excel workbook, which includes three default worksheets.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Define the data to write to the worksheet, such as using a DataTable to organize the data.
- Insert the data into the worksheet using the Worksheet.InsertDataTable() method or the Worksheet.Range[].Value property for individual cell values.
- Format the worksheet cells, applying styles like colors, fonts, and borders, or adjusting column widths as needed.
- Save the workbook to a memory stream using the Workbook.SaveToStream() method. The stream can then be used for further processing, such as saving it to a file or transmitting it over a network.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
namespace CreateExcelStream
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Access the first worksheet in the workbook
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Create and populate a DataTable with sample data
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable("Data");
dataTable.Columns.Add("ID", typeof(int));
dataTable.Columns.Add("Name", typeof(string));
dataTable.Columns.Add("Age", typeof(int));
dataTable.Columns.Add("Country", typeof(string));
dataTable.Columns.Add("Salary ($)", typeof(decimal));
dataTable.Rows.Add(101, "John Smith", 28, "USA", 54000m);
dataTable.Rows.Add(102, "Maria Garcia", 34, "Spain", 65500m);
dataTable.Rows.Add(103, "Liam Johnson", 22, "Canada", 48000m);
dataTable.Rows.Add(104, "Emma Brown", 30, "Australia", 72300m);
dataTable.Rows.Add(105, "Wei Zhang", 40, "China", 58700m);
dataTable.Rows.Add(106, "Sofia Lopez", 26, "Mexico", 45200m);
// Insert data from the DataTable into the worksheet
sheet.InsertDataTable(dataTable, true, 1, 1);
// Format the worksheet
// Style the header row
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Color = Color.LightGreen;
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Font.FontName = "Arial";
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Font.Size = 12f;
sheet.Rows[0].BorderAround(); // Apply borders around the header row
sheet.Rows[0].Borders.Color = Color.Blue;
// Style the data rows
for (int i = 1; i < sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.Count(); i++)
{
sheet.Rows[i].Style.Color = Color.LightGray;
sheet.Rows[i].Style.Font.FontName = "Arial";
sheet.Rows[i].Style.Font.Size = 11f;
}
// Adjust the column widths to fit the content
for (int j = 1; j <= sheet.AllocatedRange.Columns.Count(); j++)
{
sheet.AutoFitColumn(j);
}
// Save the workbook to a memory stream
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
workbook.SaveToStream(stream, FileFormat.Version2016);
// Write the stream content to a file
File.WriteAllBytes("output/CreateExcelByStream.xlsx", stream.ToArray());
// Release resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Load and Read Excel Files from Stream with C#
Spire.XLS for .NET simplifies loading Excel files directly from a stream using the Workbook.LoadFromStream() method. Once the file is loaded, developers can easily access and read cell data, optimizing memory usage and enabling fast, flexible data processing without requiring file I/O operations.
The steps for loading and reading Excel files from streams with C# are as follows:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Create a MemoryStream or FileStream object.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromStream() method to load the Excel file from the stream into the workbook.
- Retrieve the first worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Loop through the rows and columns of the worksheet to extract the cell through the Worksheet.AllocatedRange[].Value property.
- Print the extracted data, or use the data for further operations.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace LoadExcelStream
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Create a memory stream
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
File.OpenRead("Sample.xlsx").CopyTo(stream);
// Load the Excel file from the stream
workbook.LoadFromStream(stream);
// Access the first worksheet in the workbook
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Initialize a list to store the data retrieved from the worksheet
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.Count(); i++)
{
// Create a list to hold each row of data
List<string> lines = new List<string>();
for (int j = 0; j < sheet.AllocatedRange.Columns.Count(); j++)
{
// Retrieve the cell text and add it to the row
lines.Add(sheet.AllocatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Text);
}
// Add the row to the data list
data.Add(lines);
}
// Print the retrieved data or use it for further operations
foreach (List<string> lines in data)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" | ", lines));
}
}
}
}

Modify an Excel File in Stream with C#
With Spire.XLS for .NET, developers can modify an Excel file in memory by first loading it into a Workbook object with the LoadFromStream() method. After making updates (such as changing cell values or formatting), the file can be saved back to a stream using the Workbook.SaveToStream() method. This approach allows seamless real-time changes without relying on physical storage.
Follow the steps below to modify Excel files in streams with C#:
- Create a Workbook instance to represent the Excel file.
- Create a MemoryStream or FileStream instance.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromStream() to load the Excel file from the stream.
- Access the first worksheet through the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Modify the header row and the data rows' styles (font, size, background color, etc.) through the properties in CellRange.Style.
- Autofit the columns to adjust their width based on the content using the Worksheet.AutoFitColumn() method.
- Save the changes to the stream using the Workbook.SaveToStream() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ModifyExcelStream
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Create a memory stream
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
File.OpenRead("Sample.xlsx").CopyTo(stream);
// Load the Excel file from the stream
workbook.LoadFromStream(stream);
// Access the first worksheet in the workbook
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Modify the style of the header row
CellRange headerRow = sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows[0];
headerRow.Style.Font.FontName = "Times New Roman";
headerRow.Style.Font.Size = 12f;
headerRow.Style.Color = Color.LightBlue;
// Modify the style of the data rows
for (int i = 1; i < sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.Count(); i++)
{
CellRange dataRow = sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows[i];
dataRow.Style.Font.FontName = "Arial";
dataRow.Style.Font.Size = 10f;
dataRow.Style.Color = Color.LightGray;
// Alternate row coloring (even rows)
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
dataRow.Style.Color = Color.LightSlateGray;
}
}
// Autofit columns to adjust their width based on content
for (int k = 1; k <= sheet.AllocatedRange.Columns.Count(); k++)
{
sheet.AutoFitColumn(k);
}
// Change the border color
sheet.AllocatedRange.Style.Borders.Color = Color.White;
// Save the modified workbook back to the stream
workbook.SaveToStream(stream);
// Write the stream content to a new file
File.WriteAllBytes("output/ModifyExcelByStream.xlsx", stream.ToArray());
// Release resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Add Document Properties in Excel
Document properties, also known as metadata, are a set of data that describe a document. In Excel, you can add built-in document properties such as author, title, and keywords to quickly locate and identify documents in a folder. Or you can also add custom properties to provide more information about the Excel document. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically add built-in and custom document properties to an Excel document using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Add Built-in Document Properties in Excel in C# and VB.NET
- Add Custom Document Properties in Excel in C# and VB.NET
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Add Built-in Document Properties in Excel in C# and VB.NET
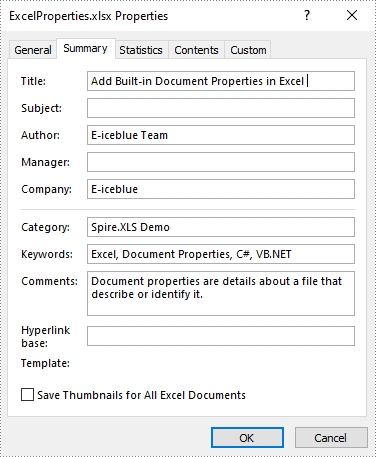
Built-in document properties are basic information about a document such as title, subject, author, category, etc. The names of these properties are predefined that cannot be edited, but Spire.XLS for .NET allows you to set specific values for these properties. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the built-in document properties of the document using Workbook.DocumentProperties property.
- Set specific document properties such as title, author, keywords and comments using the properties of BuiltInDocumentProperties class.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ExcelProperties
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
//Set built-in document properties for the Excel workbook
workbook.DocumentProperties.Author = "E-iceblue Team";
workbook.DocumentProperties.Title = "Add Built-in Document Properties in Excel ";
workbook.DocumentProperties.Keywords = "Excel, Document Properties, C#, VB.NET";
workbook.DocumentProperties.Category = "Spire.XLS Demo";
workbook.DocumentProperties.Company = "E-iceblue";
workbook.DocumentProperties.Comments = "Document properties are details about a file that describe or identify it.";
//Save the result document
workbook.SaveToFile("ExcelProperties.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
}
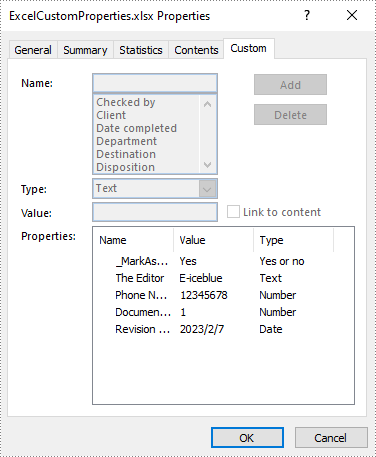
Add Custom Document Properties in Excel in C# and VB.NET
Custom document properties are additional properties that you can define for an Excel document. Spire.XLS for .NET allows you to add custom properties with specified names and values using ICustomDocumentProperties.Add() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the custom document properties of the document using Workbook.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Add custom document properties with different data types to the document using ICustomDocumentProperties.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using System;
namespace CustomExcelProperties
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
//Add custom document properties to the document
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("_MarkAsFinal", true);
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("The Editor", "E-iceblue");
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("Phone Number", 12345678);
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("Document ID", 1);
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("Revision Date", DateTime.Now);
//Save the result document
workbook.SaveToFile("ExcelCustomProperties.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Merge Excel Files into One
Sometimes, we may get annoyed when we have to open many Excel files simultaneously. Merging Excel files of the same type or category can help us avoid the trouble and save us much time. This article will demonstrate how to merge Excel files into One in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET library.
- Merge Multiple Excel Workbooks into One in C# and VB.NET
- Merge Multiple Excel Worksheets into One in C# and VB.NET
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Merge Multiple Excel Workbooks into One in C# and VB.NET
The following are the steps to merge multiple Excel workbooks into one:
- Create a string array from the Excel file paths.
- Initialize a Workbook object to create a new Excel workbook, and clear the default worksheets in the workbook using Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Initialize another temporary Workbook object.
- Loop through the string array, load the current workbook into the temporary Workbook object using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- loop through the worksheets in the current workbook, then copy each worksheet from the current workbook to the new workbook using Workbook.Worksheets.AddCopy() method.
- Save the new workbook to file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace MergeExcelFiles
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a string array from Excel file paths
string[] inputFiles = new string[] { "April.xlsx", "May.xlsx", "June.xlsx" };
//Initialize a new Workbook object
Workbook newWorkbook = new Workbook();
//Clear the default worksheets
newWorkbook.Worksheets.Clear();
//Initialize another temporary Workbook object
Workbook tempWorkbook = new Workbook();
//Loop through the string array
foreach (string file in inputFiles)
{
//Load the current workbook
tempWorkbook.LoadFromFile(file);
//Loop through the worksheets in the current workbook
foreach (Worksheet sheet in tempWorkbook.Worksheets)
{
//Copy each worksheet from the current workbook to the new workbook
newWorkbook.Worksheets.AddCopy(sheet, WorksheetCopyType.CopyAll);
}
}
//Save the new workbook to file
newWorkbook.SaveToFile("MergeWorkbooks.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
}
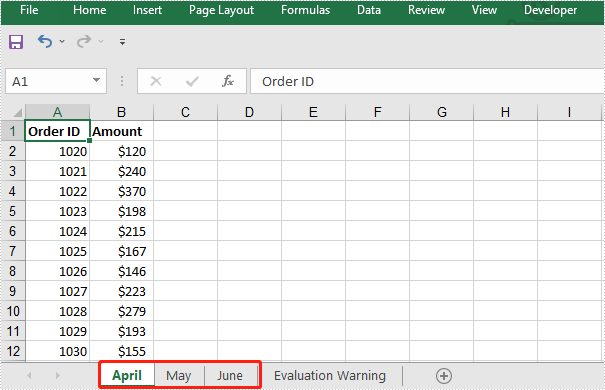
The input Excel workbooks:

The merged Excel workbook:
Merge Multiple Excel Worksheets into One in C# and VB.NET
We can merge multiple worksheets in the same or different workbooks into one. The following steps show how to merge two Excel worksheets in the same workbook into a single worksheet:
- Initialize a Workbook object and load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the two worksheets that need to be merged using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property. Note the sheet index is zero-based.
- Get the used range of the second worksheet using Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Specify the destination range in the first worksheet using Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex] property. Note the row and column indexes are 1-based.
- Copy the used range of the second worksheet to the destination range in the first worksheet using CellRange.Copy(destRange) method.
- Remove the second worksheet using XlsWorksheet.Remove() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace MergeExcelWorksheets
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Get the second worksheet
Worksheet sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1];
//Get the used range in the second worksheet
CellRange sourceRange = sheet2.AllocatedRange;
//Specify the destination range in the first worksheet
CellRange destRange = sheet1.Range[sheet1.LastRow + 1, 1];
//Copy the used range of the second worksheet to the destination range in the first worksheet
sourceRange.Copy(destRange);
//Remove the second worksheet
sheet2.Remove();
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("MergeWorksheets.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
}
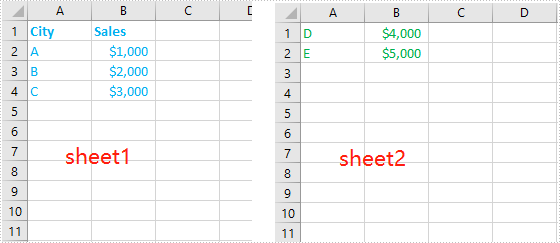
The input Excel worksheets:
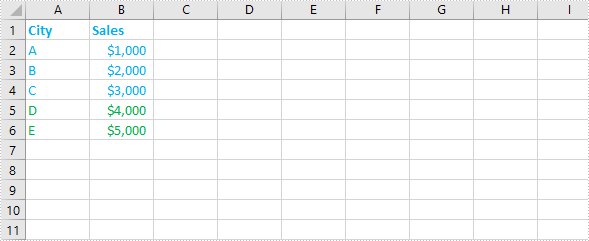
The merged Excel worksheets:
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Create, Read, or Update Excel Documents
Excel spreadsheet is a widely used file format that enables users to organize, analyze, and present data in a tabular format. The ability to interact with Excel files programmatically is highly valuable, as it allows automation and integration of Excel functionality into software applications. This capability is particularly useful when working with large datasets, performing complex calculations, or when data needs to be dynamically generated or updated. In this article, you will learn how to create, read, or update Excel documents in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Create an Excel File in C#, VB.NET
- Read Data of a Worksheet in C#, VB.NET
- Update an Excel File in C#, VB.NET
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Create an Excel File in C#, VB.NET
Spire.XLS for .NET offers a variety of classes and interfaces that you can use to create and edit Excel documents. Here is a list of important classes, properties and methods involved in this article.
| Member | Description |
| Workbook class | Represents an Excel workbook model. |
| Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method | Adds a worksheet to workbook. |
| Workbook.SaveToFile() method | Saves the workbook to an Excel document. |
| Worksheet class | Represents a worksheet in a workbook. |
| Worksheet.Range property | Gets a specific cell or cell range from worksheet. |
| Worksheet.Range.Value property | Gets or sets the value of a cell. |
| Worksheet.Rows property | Gets a collection of rows in worksheet. |
| Worksheet.InsertDataTable() method | Imports data from DataTable to worksheet. |
| CellRange class | Represents a cell or cell range in worksheet. |
The following are the steps to create an Excel document from scratch using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Add a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Write data to a specific cell through Worksheet.Range.Value property.
- Import data from a DataTable to the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertDataTable() method.
- Save the workbook to an Excel document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
namespace CreateExcelSpreadsheet
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Remove default worksheets
wb.Worksheets.Clear();
//Add a worksheet and name it "Employee"
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets.Add("Employee");
//Merge the cells between A1 and G1
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Merge();
//Write data to A1 and apply formatting to it
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Basic Information of Employees of Huanyu Automobile Company";
sheet.Range["A1"].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
sheet.Range["A1"].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Font.Size = 13F;
//Set row height of the first row
sheet.Rows[0].RowHeight = 30F;
//Create a DataTable
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
dt.Columns.Add("Name");
dt.Columns.Add("Gender");
dt.Columns.Add("Birth Date");
dt.Columns.Add("Educational Background");
dt.Columns.Add("Contact Number");
dt.Columns.Add("Position");
dt.Columns.Add("ID");
dt.Rows.Add("Allen", "Male", "1990-02-10", "Bachelor", "24756854", "Mechanic", "0021");
dt.Rows.Add("Patrick", "Male", "1985-06-08", "Master", "59863247", "Mechanic", "0022");
dt.Rows.Add("Jenna", "Female", "1989-11-25", "Bachelor", "79540352", "Sales", "0023");
dt.Rows.Add("Tommy", "Male", "1988-04-16", "Master", "52014060", "Mechanic", "0024");
dt.Rows.Add("Christina", "Female", "1998-01-21", "Bachelor", "35401489", "HR", "0025");
//Import data from DataTable to worksheet
sheet.InsertDataTable(dt, true, 2, 1, true);
//Set row height of a range
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].RowHeight = 15F;
//Set column width
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].Columns[2].ColumnWidth = 15F;
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].Columns[3].ColumnWidth = 21F;
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].Columns[4].ColumnWidth = 15F;
//Set border style of a range
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium);
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].BorderInside(LineStyleType.Thin);
sheet.Range["A2:G2"].BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium);
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].Borders.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Black;
//Save to a .xlsx file
wb.SaveToFile("NewSpreadsheet.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016);
}
}
}
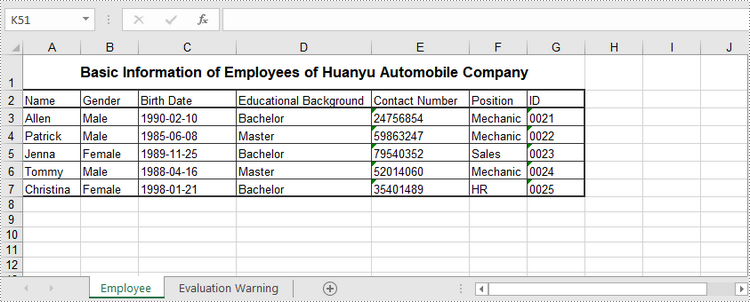
Read Data of a Worksheet in C#, VB.NET
The Worksheet.Range.Value property returns number value or text value of a cell as a string. To get data of a whole worksheet or a cell range, loop through the cells within it. The following are the steps to get data of a worksheet using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the cell range containing data though Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Iterate through the rows and columns to get cells within the range, and return the value of each cell through CellRange.Value property.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ReadExcelData
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\NewSpreadsheet.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
//Get the cell range containing data
CellRange locatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange;
//Iterate through the rows
for (int i = 0;i < locatedRange.Rows.Length;i++)
{
//Iterate through the columns
for (int j = 0; j < locatedRange.Rows[i].ColumnCount; j++)
{
//Get data of a specific cell
Console.Write(locatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
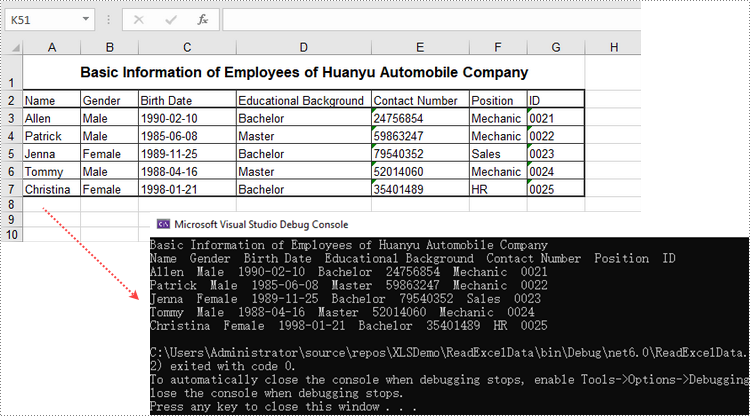
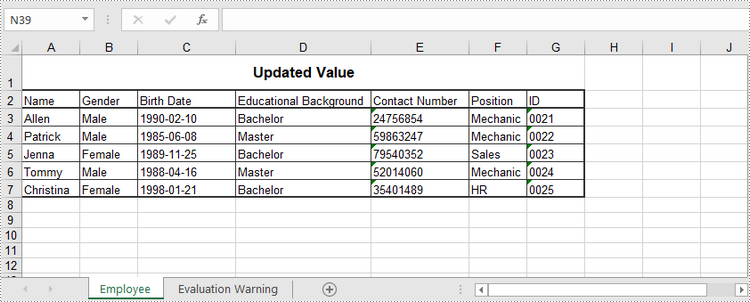
Update an Excel Document in C#, VB.NET
To change the value of a certain cell, just re-assign a value to it through Worksheet.Range.Value property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Change the value of a particular cell though Worksheet.Range.Value property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace UpdateCellValue
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\NewSpreadsheet.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
//Change the value of a specific cell
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Updated Value";
//Save to file
wb.SaveToFile("Updated.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Load/Save Excel VBA in C#, VB.NET
By running VBA within the Office applications, developers/programmers can build customized solutions and programs to enhance the capabilities of those applications. The VBA function of Excel is very powerful. Below I will show you how to use VBA by Spire.XLS.
VBA is the acronym for VB.NET for Applications. It is an implementation of Microsoft's event-driven programming language VB.NET 6 and its associated integrated development environment (IDE), which are built into most Microsoft Office applications. VBA is closely related to VB.NET and uses the VB.NET Runtime Library, but can normally only run code within a host application rather than as a standalone program. It can be used to control one application from another via OLE Automation.
Spire.XLS for .NET is a professional Excel .NET component that can be linked into any type of .NET 2.0, 3.5 or 4.0 projects, either ASP.NET web sites or Windows Forms application. Spire.XLS for .NET offers a combination of APIs and GUI controls for speeding up Excel programming in .NET platform-create new Excel documents from scratch, edit existing Excel documents and convert Excel files. At the same time, Spire.XLS supports VBA and it can load/Save Excel VBA.
Here comes to the steps:
- Write a template with VBA program with which you can execute your work in Excel.
- Create another workbook to load the VBA template.
In this demo, it generates a new worksheet named "test" with the VBA template we provide.
Please check the codes as below:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace NumberFormat
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Initailize worksheet
workbook.LoadFromFile("VBASample.xls");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//VBA function
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "test";
//Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("Sample.xls",ExcelVersion.Version97to2003);
//Launch the file
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Sample.xls");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Module Module1
Sub Main()
'Create a workbook
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
'Initailize worksheet
workbook.LoadFromFile("VBASample.xls")
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'VBA function
sheet.Range("A1").Text = "test"
'Save doc file.
workbook.SaveToFile("Sample.xls",ExcelVersion.Version97to2003)
'Launching the MS Word file.
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Sample.xls")
End Sub
End Module
Marker Designer
Introduction
A Marker Designer represents a single data point or value that gives a mean to Spire.XLS to place relevant data into different cells of the worksheet in a workbook. We make use of Designer spreadsheets in which we write marker designers into different cells. Normally a marker designer consists of DataSource and a Field Name and starts with "&=". The DataSource can be a DataSet, DataTable, DataView or an Object variable etc. You can also make use of dynamic formulas that allows you to insert MS Excel's formulas into cells even when the formula must reference rows that will be inserted during the export process. Moreover, you may calculate totals and sub totals of any data field too.
Marker designer is a way to let Spire.XLS know that what information you wish to place in an Excel designer spreadsheet. Marker designers allow you to create templates that contain only relevant information and are formatted to meet your needs.
Designer Spreadsheet and Marker Designers
Designer spreadsheets are standard Excel files that contain the visual formatting, formulas and marker designers. They can contain marker designers that reference one or more data sources such as information from a project and information for related contacts. Marker designers are written into cells where you want information to be filled in.
All marker designers start with "&=", without the quotes. An example of a data marker is &=Party.FullName. If the data marker results in more than one item, i.e. row then following rows will be moved down automatically to make room for all of the new information. Thus sub-totals and totals can be placed on the following row after the data marker to make calculations based on inserted data. In order to make calculations on the rows that are inserted, you must use Dynamic Formulas.
Marker designers consist of the Data Source and Field Name parts for most information. Special information may also be passed with variables and variable arrays. Variables always fill only one cell whereas variable arrays may fill several ones. You may only use one data marker per cell. Unused marker designers will be removed.
Marker designer may also contain parameters. Parameters allow you to modify how the information will be laid out. They are appended to the end of marker designer in parenthesis as a comma separated list.
Marker designer Options
&=DataSource.FieldName &=[Data Source].[Field Name] &=VariableName
Formulas
Formulas allow you to insert Excel's formulas into cells even when the formula must reference rows that will be inserted during the export process. And they can repeat for each inserted row or use only the cell where the data marker is placed for it.
If value of a cell referred to other cells, such as (copy:rc6), it means the value of the cell will be referred by cells of column 6. Multiple refer can be used like this: (copy:rc5,copy:rc7).
Note: Separate them with comma
Cell "G6" contains the formula = D6*E6, cell "G7" contains = D7*E7 and cell "G8" contains = D8*E8, etc.
The following illustrates a repeating dynamic formula and the resulting Excel worksheet.
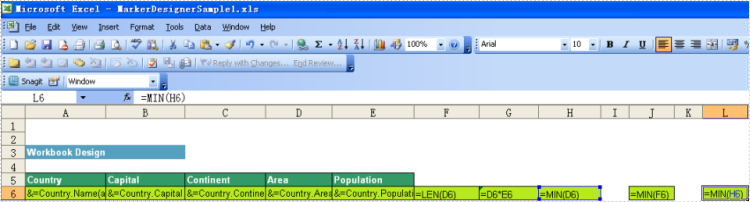
Result:
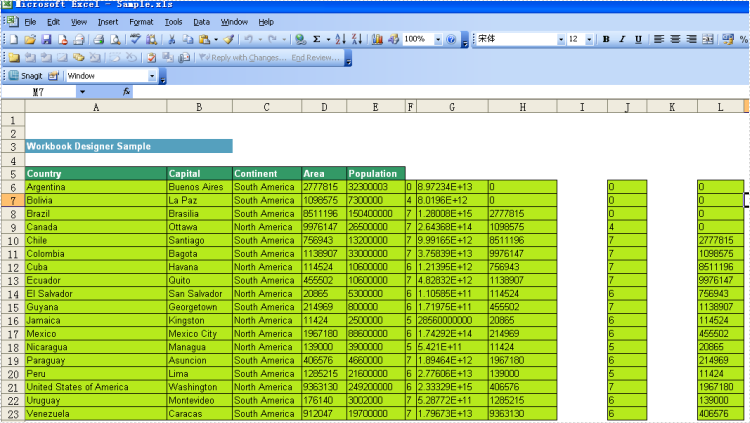
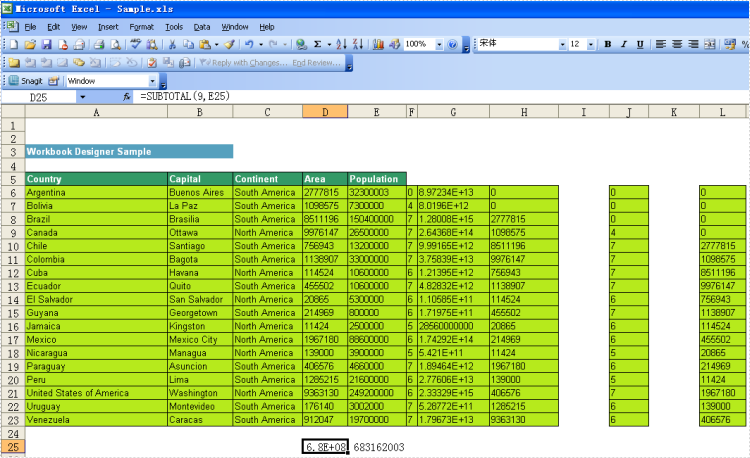
Sum and Subtotal
Below is showing you how to use these 2 formulas:
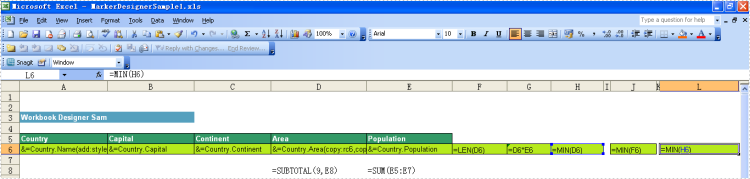
Result:
Code:
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"..\..\..\..\..\..\Data\MarkerDesignerSample1.xls");
DataTable dt = (DataTable)dataGrid1.DataSource;
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//fill parameter
workbook.MarkerDesigner.AddParameter("Variable1", 1234.5678);
//fill DataTable
workbook.MarkerDesigner.AddDataTable("Country",dt);
workbook.MarkerDesigner.Apply();
//AutoFit
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitRows();
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
workbook.SaveToFile("Sample.xls",ExcelVersion.Version97to2003);