
Data (10)
A Slicer in Excel is an interactive filtering tool that simplifies data analysis in pivot tables and tables. Unlike traditional dropdown menus, slicers present intuitive, clickable buttons, each representing a distinct value in the dataset (e.g., regions, product categories, or dates). With slicers, users can filter datasets to focus on specific subsets with just a single click, making analysis faster and more visually intuitive. In this guide, we will explore how to create new slicers, update existing slicers, and remove slicers in Excel using Java and the Spire.XLS for Java library.
- Add Slicers to Tables in Excel
- Add Slicers to Pivot Tables in Excel
- Update Slicers in Excel
- Remove Slicers from Excel
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add Slicers to Tables in Excel
Spire.XLS for Java provides the Worksheet.getSlicers().add(IListObject table, String destCellName, int index) method to add a slicer to a table in an Excel worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets.get(0) method.
- Add data to the worksheet using the Worksheet.getRange().get().setValue() and Worksheet.getRange().get().setNumberValue() methods.
- Add a table to the worksheet using the Worksheet.getIListObjects().create() method.
- Add a slicer to the table using the Worksheeet.getSlicers().add(IListObject table, String destCellName, int index) method.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.core.IListObject;
import com.spire.xls.core.spreadsheet.slicer.*;
public class AddSlicerToTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an object of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Add data to the worksheet
worksheet.getRange().get("A1").setValue("Fruit");
worksheet.getRange().get("A2").setValue("Grape");
worksheet.getRange().get("A3").setValue("Blueberry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A4").setValue("Kiwi");
worksheet.getRange().get("A5").setValue("Cherry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A6").setValue("Grape");
worksheet.getRange().get("A7").setValue("Blueberry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A8").setValue("Kiwi");
worksheet.getRange().get("A9").setValue("Cherry");
worksheet.getRange().get("B1").setValue("Year");
worksheet.getRange().get("B2").setNumberValue(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B3").setNumberValue(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B4").setNumberValue(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B5").setNumberValue(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B6").setNumberValue(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B7").setNumberValue(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B8").setNumberValue(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B9").setNumberValue(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("C1").setValue("Sales");
worksheet.getRange().get("C2").setNumberValue(50);
worksheet.getRange().get("C3").setNumberValue(60);
worksheet.getRange().get("C4").setNumberValue(70);
worksheet.getRange().get("C5").setNumberValue(80);
worksheet.getRange().get("C6").setNumberValue(90);
worksheet.getRange().get("C7").setNumberValue(100);
worksheet.getRange().get("C8").setNumberValue(110);
worksheet.getRange().get("C9").setNumberValue(120);
// Create a table from the specific data range
IListObject table = worksheet.getListObjects().create("Fruit Sales", worksheet.getRange().get("A1:C9"));
// Add a slicer to cell "A11" to filter the data based on the first column of the table
XlsSlicerCollection slicers = worksheet.getSlicers();
int index = slicers.add(table, "A11", 0);
// Set name and style for the slicer
XlsSlicer slicer = slicers.get(index);
slicer.setName("Fruit");
slicer.setStyleType(SlicerStyleType.SlicerStyleLight1);
// Save the resulting file
workbook.saveToFile("AddSlicerToTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
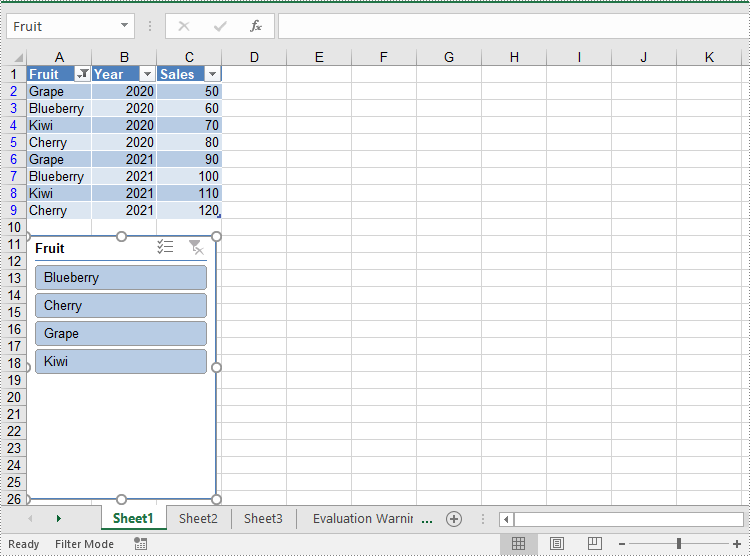
Add Slicers to Pivot Tables in Excel
Spire.XLS for Java also supports adding slicers to pivot tables using the Worksheet.getSlicers().add(IPivotTable pivot, String destCellName, int baseFieldIndex) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets.get(0) method.
- Add data to the worksheet using the Worksheet.getRange().get().setValue() and Worksheet.getRange().get().setNumberValue() methods.
- Create a pivot cache from the data using the Workbook.getPivotCaches().add() method.
- Create a pivot table from the pivot cache using the Worksheet.getPivotTables().add() method.
- Drag the pivot fields to the row, column, and data areas. Then calculate the data in the pivot table.
- Add a slicer to the pivot table using the Worksheet.getSlicers().add(IPivotTable pivot, String destCellName, int baseFieldIndex) method.
- Set the properties, such as the name, width, height, style, and cross filter type for the slicer.
- Calculate the data in the pivot table.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.core.IPivotField;
import com.spire.xls.core.IPivotTable;
import com.spire.xls.core.spreadsheet.slicer.*;
public class AddSlicerToPivotTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an object of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Add data to the worksheet
worksheet.getRange().get("A1").setValue("Fruit");
worksheet.getRange().get("A2").setValue("Grape");
worksheet.getRange().get("A3").setValue("Blueberry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A4").setValue("Kiwi");
worksheet.getRange().get("A5").setValue("Cherry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A6").setValue("Grape");
worksheet.getRange().get("A7").setValue("Blueberry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A8").setValue("Kiwi");
worksheet.getRange().get("A9").setValue("Cherry");
worksheet.getRange().get("B1").setValue("Year");
worksheet.getRange().get("B2").setNumberValue(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B3").setNumberValue(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B4").setNumberValue(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B5").setNumberValue(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B6").setNumberValue(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B7").setNumberValue(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B8").setNumberValue(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B9").setNumberValue(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("C1").setValue("Sales");
worksheet.getRange().get("C2").setNumberValue(50);
worksheet.getRange().get("C3").setNumberValue(60);
worksheet.getRange().get("C4").setNumberValue(70);
worksheet.getRange().get("C5").setNumberValue(80);
worksheet.getRange().get("C6").setNumberValue(90);
worksheet.getRange().get("C7").setNumberValue(100);
worksheet.getRange().get("C8").setNumberValue(110);
worksheet.getRange().get("C9").setNumberValue(120);
// Create a pivot cache from the specific data range
CellRange dataRange = worksheet.getRange().get("A1:C9");
PivotCache cache = workbook.getPivotCaches().add(dataRange);
// Create a pivot table from the pivot cache
PivotTable pt = worksheet.getPivotTables().add("Fruit Sales", worksheet.getRange().get("A12"), cache);
// Drag the fields to the row and column areas
IPivotField pf = pt.getPivotFields().get("Fruit");
pf.setAxis(AxisTypes.Row);
IPivotField pf2 = pt.getPivotFields().get("Year");
pf2.setAxis(AxisTypes.Column);
// Drag the field to the data area
pt.getDataFields().add(pt.getPivotFields().get("Sales"), "Sum of Sales", SubtotalTypes.Sum);
// Set style for the pivot table
pt.setBuiltInStyle(PivotBuiltInStyles.PivotStyleMedium10);
// Calculate the pivot table data
pt.calculateData();
// Add a Slicer to the pivot table
XlsSlicerCollection slicers = worksheet.getSlicers();
int index_1 = slicers.add(pt, "F12", 0);
// Set the name, width, height, and style for the slicer
XlsSlicer slicer = slicers.get(index_1);
slicer.setName("Fruit");
slicer.setWidth(100);
slicer.setHeight(120);
slicer.setStyleType(SlicerStyleType.SlicerStyleLight2);
// Set the cross filter type for the slicer
XlsSlicerCache slicerCache = (XlsSlicerCache)slicer.getSlicerCache();
slicerCache.setCrossFilterType(SlicerCacheCrossFilterType.ShowItemsWithNoData);
// Calculate the pivot table data again
pt.calculateData();
// Save the resulting file
workbook.saveToFile("AddSlicerToPivotTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
workbook.dispose();
}
}

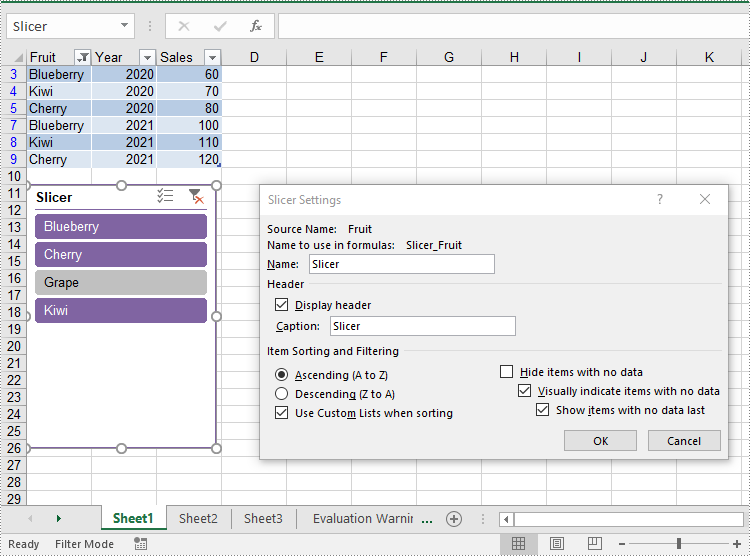
Update Slicers in Excel
The XlsSlicer class in Spire.XLS for Java provides methods for modifying slicer attributes such as name, caption, style, and cross filter type. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get a specific slicer from the worksheet by its index using the Worksheet.getSlicers().get(index) property.
- Update the properties of the slicer, such as its style, name, caption, and cross filter type using the appropriate methods of the XlsSlicer class.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import com.spire.xls.core.spreadsheet.slicer.*;
public class UpdateSlicer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an object of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("AddSlicerToTable.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the first slicer in the worksheet
XlsSlicer slicer = worksheet.getSlicers().get(0);
// Change the style, name, and caption for the slicer
slicer.setStyleType(SlicerStyleType.SlicerStyleDark4);
slicer.setName("Slicer");
slicer.setCaption("Slicer");
// Change the cross filter type for the slicer
XlsSlicerCache slicerCache = slicer.getSlicerCache();
slicerCache.setCrossFilterType(SlicerCacheCrossFilterType.ShowItemsWithDataAtTop);
// Deselect an item in the slicer
XlsSlicerCacheItemCollection slicerCacheItems = slicerCache.getSlicerCacheItems();
XlsSlicerCacheItem xlsSlicerCacheItem = slicerCacheItems.get(0);
xlsSlicerCacheItem.isSelected(false);
// Save the resulting file
workbook.saveToFile("UpdateSlicer.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Remove Slicers from Excel
Developers can remove a specific slicer from an Excel worksheet using the Worksheet.getSlicers().removeAt() method, or remove all slicers at once using the Worksheet.getSlicers().clear() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Remove a specific slicer from the worksheet by its index using the Worksheet.getSlicers().removeAt() method. Or remove all slicers from the worksheet using the Worksheet.getSlicers().clear() method.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class RemoveSlicer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an object of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("AddSlicerToTable.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Remove the first slicer by index
worksheet.getSlicers().removeAt(0);
// Alternatively, remove all slicers
// worksheet.getSlicers().clear();
// Save the resulting file
workbook.saveToFile("RemoveSlicer.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Java without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Subtotal is a built-in function in Microsoft Excel that enables you to quickly calculate a range of data using a summary function, such as SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, or MIN. This article will demonstrate how to add subtotals to a data range in Excel in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add Subtotals to a Data Range
The XlsWorksheet.subtotal() method is used to add subtotals to a data range. It accepts the following parameters:
- IXLSRange: the specific data range.
- int: the column index (zero-based) that you want to base the subtotals on.
- int[]: an array of column indexes (zero-based) on which the subtotals are calculated.
- SubtotalTypes: the function (SUM, AVERAGE etc.) used to calculate the subtotals.
- boolean: Indicates whether to replace existing subtotals.
- boolean: Indicates whether to insert page breaks between groups.
- boolean: Indicates whether to add summary rows below data.
The following are the steps to add subtotals to a data range:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Access the range that you wish to subtotal using Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Add subtotals to the range using XlsWorksheet.subtotal() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class AddSubtotalsToDataRange {
public static void main(String []args){
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Report.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Access the range that contains data you wish to subtotal
CellRange range = sheet.getCellRange("A2:C11");
//Add subtotals to the range, the function is Sum and it will be applied to the 3rd column in the range
sheet.subtotal(range, 0, new int[] { 2 }, SubtotalTypes.Sum, true, false, true);
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("AddSubtotal.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When manipulating Excel data, the "Text to Columns" feature in MS Excel is a handy tool that allows users to separate text in a single cell into multiple columns. This functionality is extremely useful when dealing with data that imported in a less structured format. For Java developers, being able to replicate this operation programmatically can significantly enhance the automation of data processing tasks involving Excel spreadsheets.
This guide will walk you through how to utilize the Spire.XLS for Java library to split text into multiple columns in Excel in Java.
- Java Library for Working with Excel
- Step-by-Step Guide to Splitting Excel Text to Columns
- Handling Different Delimiters
Java Library for Working with Excel
The Spire.XLS for Java library is a practical solution for reading, writing and converting Excel XLS or XLSX files in Java. To start using it, you need to add the appropriate dependency. There are two common ways to import:
Method 1: Install via Maven
If you are using Maven, add the following to your pom.xml file:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Method 2: Manual Installation
- Download Spire.XLS for Java package through the official website.
- Unzip it to get the Spire.Xls.jar file and then add the JAR file to your project.
Step-by-Step Guide to Splitting Excel Text to Columns
- Load Excel File and Access a Worksheet
Use the Workbook.loadFromFile() method to load the input Excel file, and then access the specific worksheet in it.
- Access Cells and Get Cell Data
Iterate through each row in the sheet. Access a specified cell and then get its text through the CellRange.getText() method.
- Split Text in Excel Cells
Use the String.split(String regex) method to split the cell text based on the specified delimiter (e.g., ",").
- Write the Split Text to Columns
Iterate through each split data and then write it into different columns.
- Save the Modified Excel File
Use the Workbook.saveToFile() method to save the modified Excel file.
Sample Java Code:
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class splitDataIntoMultipleColumns {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Data.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Iterate through each row in the worksheet
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.getLastRow(); i++)
{
// Get the text of the first cell in the current row
String text = sheet.getRange().get(i + 1, 1).getText();
// Split the text by comma
String[] splitText = text.split(",");
// Iterate through each split data
for (int j = 0; j < splitText.length; j++)
{
// Write the split data to different columns
sheet.getRange().get(i + 1, j + 3).setText(splitText[j]);
}
}
// Autofit column widths
sheet.getAllocatedRange().autoFitColumns();
// Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("SplitExcelData.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Result File:
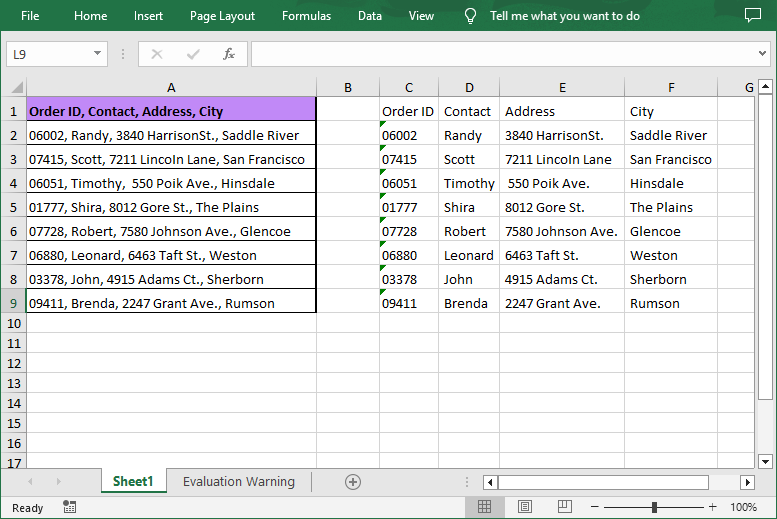
Handling Different Delimiters
To split text by other delimiters such as spaces, semicolons, or tabs, modify the regex in the split() method. Examples:
- Spaces: String.split(" ")
- Semicolons: String.split(";")
- Tabs: String.split("\t")
Conclusion
Splitting text into columns in Excel using Java is effortless with Spire.XLS for Java API. By automating this task, you can enhance productivity and ensure data consistency. Whether you’re processing user inputs, logs, or reports, this approach adapts to various delimiters and use cases.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Java without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
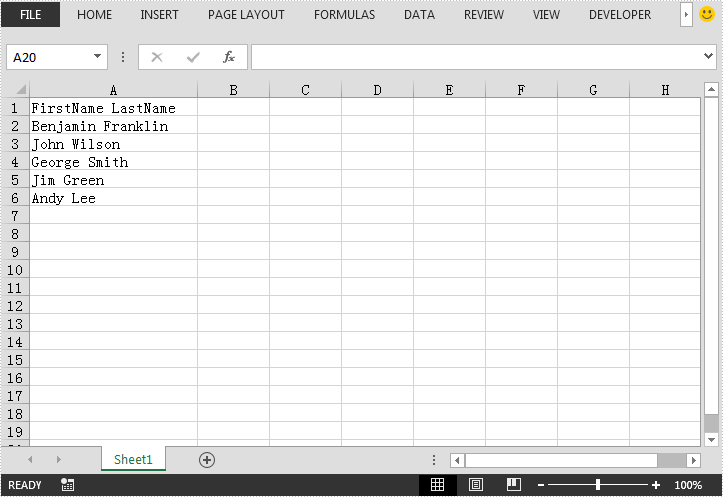
This article demonstrates how to convert text to columns in Excel using Spire.XLS for Java. The following screenshot shows the sample Excel file before converting:
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class ConvertTextToColumns {
public static void main(String[] args){
//Create a workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load the Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Template.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Convert text into columns by the delimited characters of space
String[] splitText = null;
String text = null;
for (int i = 1; i < sheet.getLastRow()+1; i++)
{
text = sheet.getRange().get(i, 1).getText();
splitText = text.split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < splitText.length; j++)
{
sheet.getRange().get(i, 1 + j + 1).setText(splitText[j]);
}
}
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("ConvertTextToColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
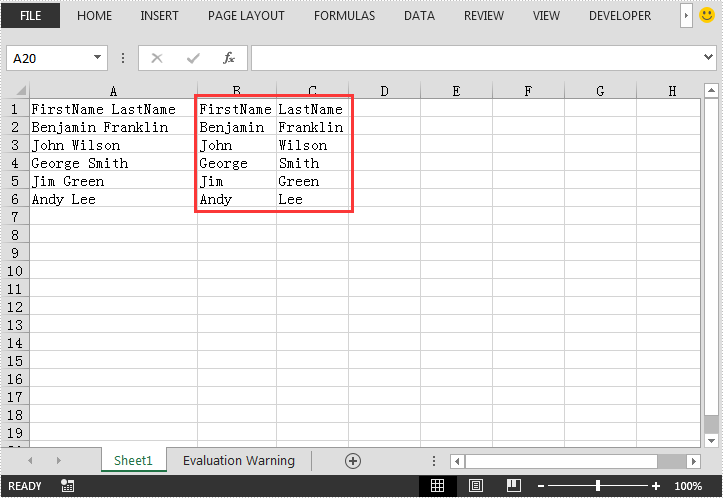
The following screenshot shows the output Excel file after converting:
Sorting data in Excel is a key task for improving data analysis and presentation. By organizing rows based on criteria such as alphabetical order, numerical values, or dates, users can easily identify trends, patterns, and outliers, making data more actionable. This article explores how to sort Excel data programmatically using Java with the Spire.XLS for Java library.
- Sort Data by a Single Column in Excel
- Sort Data by Multiple Columns in Excel
- Sort by a Custom List in Excel
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
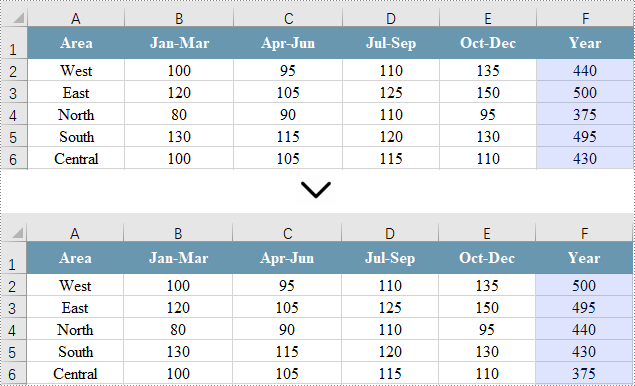
Sort Data by a Single Column in Excel
Sorting a single column in Excel allows for quick organization of your data in either ascending or descending order, facilitating easier analysis. However, this approach leaves other columns unchanged, which can lead to misalignment of related data.
Spire.XLS for Java offers the Workbook.getDataSorter().getSortColumns().add(int key, SortComparisonType sortComparisonType, OrderBy orderBy) method. This allows developers to establish sorting criteria by selecting a specific column, defining the comparison type, and specifying the sort order. To apply the sorting to the chosen column, you can use the Workbook.getDataSorter().sort(CellRange range) method.
Here are the steps to sort a single column in Excel using Spire.XLS for Java:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet with the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Access the column you want to sort using the Worksheet.getRange().get() method.
- Create sorting criteria for the selected column using the Workbook.getDataSorter().getSortColumns().add() method.
- Perform the sorting on the column using the Workbook.getDataSorter().sort() method.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class SortSingleColumn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the cell range (a single column) where you want to sort data
CellRange cellRange = sheet.getRange().get("F1:F6");
// Create sorting criteria for the selected column
workbook.getDataSorter().getSortColumns().add(5, SortComparsionType.Values, OrderBy.Descending);
// Sort in the specified cell range
workbook.getDataSorter().sort(cellRange);
// Save the workbook
workbook.saveToFile("SortSingleColumn.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Sort Data by Multiple Columns in Excel
To ensure that all related data across multiple columns stays aligned and meaningful, sorting across these columns is essential. This is particularly valuable for complex datasets where maintaining the relationships between data points is critical.
While sorting multiple columns is similar to sorting a single column, the key distinction is in the CellRange parameter used in the Workbook.getDataSorter().sort(CellRange range) method. Instead of specifying a single column, this parameter defines a range that includes multiple columns.
Here are the steps to sort multiple columns in Excel using Spire.XLS for Java:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet with the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get the cell range (columns) you want to sort using the Worksheet.getRange().get() method.
- Create sorting criteria for the selected column using the Workbook.getDataSorter().getSortColumns().add() method.
- Perform the sorting on the cell range using the Workbook.getDataSorter().sort() method.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class SortMultipleColumns {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the cell range (multiple columns) where you want to sort data
CellRange cellRange = sheet.getRange().get("A1:F6");
// Create sorting criteria for the selected column
workbook.getDataSorter().getSortColumns().add(5, SortComparsionType.Values, OrderBy.Descending);
// Sort in the specified cell range
workbook.getDataSorter().sort(cellRange);
// Save the workbook
workbook.saveToFile("SortMultipleColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}
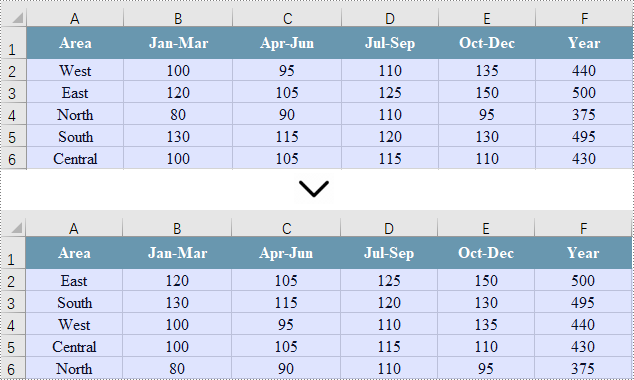
Sort by a Custom List in Excel
In Excel, you can sort data using a custom list, which allows for arrangement based on specific criteria that may not follow alphabetical order. This approach ensures that the order of data is relevant to your analysis or reporting needs.
To achieve this, start by creating an array of strings that outlines the desired custom sorting order. Then, use the Workbook.getDataSorter().getSortColumns().add(int key, OrderBy orderBy) method to set your sorting criteria. Finally, call the Workbook.getDataSorter().sort(CellRange range) method to sort the designated cell range.
Here are the steps for sorting data by a custom list in Excel using Spire.XLS for Java:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet with the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get the cell range you want to sort using the Worksheet.getRange().get() method.
- Define the custom sorting order with an array of strings.
- Create sorting criteria for the selected column using the Workbook.getDataSorter().getSortColumns().add() method.
- Perform the sorting on the cell range using the Workbook.getDataSorter().sort() method.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.CellRange;
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class SortByCustomList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the cell range where you want to sort data
CellRange cellRange = sheet.getRange().get("A1:F6");
// Create an array of strings to define the sorting order
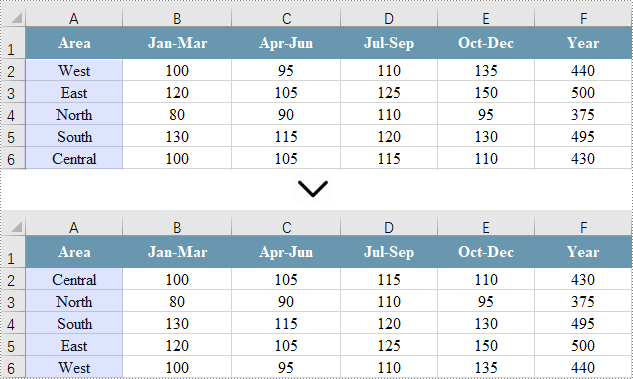
String[] customList = { "Central", "North", "South", "East", "West" };
// Create sorting criteria for the selected column
workbook.getDataSorter().getSortColumns().add(0, customList);
// Sort data in the specified cell range
workbook.getDataSorter().sort(cellRange);
// Save the workbook
workbook.saveToFile("SortByCustomList.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When working with a large workbook containing dozens of columns and rows, it may often be necessary to use the "Find" function to quickly locate specific values. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically find all cells with a specific value and highlight them with a background color using Spire.XLS for Java.
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Find and Highlight Data in Excel
The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Find all cells with matching text using Worksheet.findAllString(java.lang.String stringValue, boolean formula, boolean formulaValue) method.
- Set color to highlight the cells using CellRange.getCellStyle().setColor() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class FindandHighlight {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load the sample document
workbook.loadFromFile("Test.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
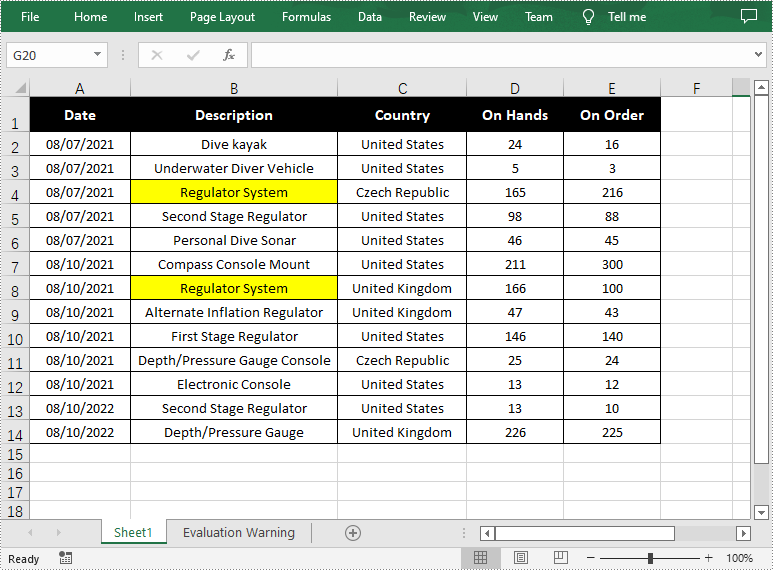
//Find all cells with the text "Regulator System"
CellRange[] ranges = worksheet.findAllString("Regulator System", true, true);
for (CellRange range : ranges)
{
//Set color to highlight the cells
range.getCellStyle().setColor(Color.yellow);
}
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("FindandHighlight.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Formatting numbers in Excel cells is a critical step when working with spreadsheets, especially in professional or data-driven environments. Proper number formatting ensures that data is presented clearly, consistently, and in a way that aligns with its purpose—whether it's financial data, percentages, dates, or scientific values. When automating Excel tasks using Java, applying the correct number format programmatically can save time, reduce errors, and enhance the readability of reports or dashboards. This article explores how to use Spire.XLS for Java to set number formats in Excel cells, enabling you to create polished and well-structured spreadsheets with ease.
- How to Set Number Formats in Excel with Java
- Add Values in Specified Number Formats to Excel Cells with Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
How to Set Number Formats in Excel with Java
Spire.XLS for Java provides the CellRange.setNumberFormat() method, enabling developers to set number formats for cells using Excel's number format codes. The table below highlights commonly used symbols in Excel number format codes and their functions:
| Symbols | Description |
| 0 and # | 0 forces display of digit places, padding with zeros if necessary; # shows digits only when needed. |
| ? | Placeholder for aligning numbers, leaves space but does not display anything if not used. |
| , and . | , serves as a thousands separator and can also indicate division by 1000; . is the decimal point. |
| % | Multiplies the number by 100 and adds a percent sign. |
| E+ / E- | Scientific notation, for positive and negative exponents respectively. |
| Currency ($, €, ¥, etc.) | Displays the respective currency symbol. |
| [Color] | Sets text color (e.g., [Red], [Blue]). |
| @ | Text placeholder, used to represent text in custom formats. |
| Date/Time (yyyy, mmmm, mm, dd, hh, ss, AM/PM) | Represent year, full month name, month, day, hour, minute, second, and 12-hour clock markers respectively. |
The detailed steps for setting number formats of Excel cells with Java are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object to create a new Excel workbook.
- Get the first default worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Add values using the CellRange.setValue() method or add numeric values using the CellRange.setNumberValue() method.
- Set the number formats using the CellRange.setNumberFormat() method.
- Save the workbook using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class SetNumberFormat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Add a title
sheet.getCellRange("B1").setText("NUMBER FORMATTING");
sheet.getCellRange("B1").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().isBold(true);
sheet.getCellRange("B1:C1").merge(); // Merge cells B1 and C1
sheet.getCellRange("B1:C1").setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Center); // Center align the text
// Add number format examples and corresponding values
// Add positive number formats
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B3", "C3", "0", "1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B4", "C4", "0.00", "1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B5", "C5", "#,##0.00", "1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B6", "C6", "$#,##0.00", "1234.5678");
// Add negative number formats
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B7", "C7", "0;[Red]-0", "-1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B8", "C8", "0.00;[Red]-0.00", "-1234.5678");
// Add scientific notation and percentage formats
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B9", "C9", "0.00E+00", "1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B10", "C10", "0.00%", "0.5678");
// Add date and time formats
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B11", "C11", "yyyy-MM-dd", "44930.0"); // Excel date value for 2023-01-01
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B12", "C12", "HH:mm:ss", "0.75"); // Excel time value for 18:00:00
// Add text format
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B13", "C13", "@", "Text Example");
// Set the formatting
sheet.getCellRange("B3:B13").getCellStyle().setKnownColor(ExcelColors.Gray25Percent);
sheet.getCellRange("C3:C13").getCellStyle().setKnownColor(ExcelColors.Gray50Percent);
sheet.setColumnWidth(2, 24); // Column B
sheet.setColumnWidth(3, 24); // Column C
// Save the workbook to a file
workbook.saveToFile("output/SetExcelNumberFormat.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
/**
* Adds a number format example to the specified cells in the worksheet.
*
* @param sheet The worksheet to modify.
* @param textCell The cell for displaying the number format string.
* @param valueCell The cell for displaying the formatted value.
* @param format The number format code.
* @param value The numeric value to format.
*/
private static void addNumberFormatExample(Worksheet sheet, String textCell, String valueCell, String format, String value) {
sheet.getCellRange(textCell).setText(format); // Display the number format code
sheet.getCellRange(valueCell).setValue(value); // Add the value
// sheet.getCellRange(valueCell).setNumberValue(Double); // Or set numeric value with setNumberValue() method
sheet.getCellRange(valueCell).setNumberFormat(format); // Apply the number format
}
}

Add Values in Specified Number Formats to Excel Cells with Java
Spire.XLS for Java also supports directly adding data with specific number formats to Excel cells with methods under the CellRange class. The following table outlines the methods for adding data with common number formats to cells and their corresponding data types:
| Method | Description |
| setText(String text) | Sets a text value in a cell or range of cells. |
| setNumberValue(double numberValue) | Sets a numeric value in a cell or range of cells. |
| setBooleanValue(boolean booleanValue) | Sets a boolean value (true/false) in a cell or range of cells. |
| setDateTimeValue(java.util.Date dateTime) | Sets a date and time value in a cell or range of cells. |
| setHtmlString(String htmlCode) | Sets an HTML-formatted string in a cell or range of cells. |
The detailed steps for adding values with number formats to Excel cells are as follows:
- Create an instance of the Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get a cell or cell range using the Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Add values in specific number formats using the methods under the CellRange class.
- Set the cell styles as needed.
- Save the workbook using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class AddFormattedDataExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Add a text value
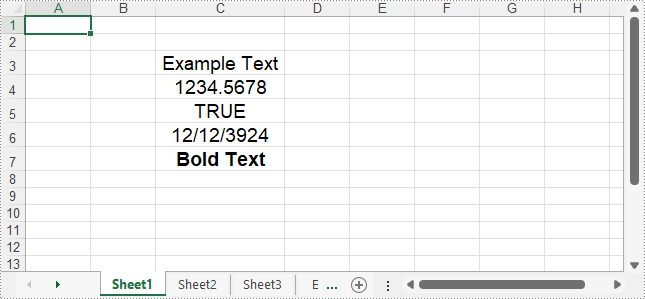
sheet.getCellRange("C3").setText("Example Text");
// Add number value
sheet.getCellRange("C4").setNumberValue(1234.5678);
// Add boolean value
sheet.getCellRange("C5").setBooleanValue(true);
// Add date time value
sheet.getCellRange("C6").setDateTimeValue(new Date(2024, Calendar.DECEMBER, 12));
// Add HTML string
sheet.getCellRange("C7").setHtmlString("Bold Text");
// Format the cells
sheet.getCellRange("C3:C7").setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Center);
sheet.getCellRange("C3:C7").setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType.Center);
sheet.getCellRange("C3:C7").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().setSize(14);
for (int i = 3; i <= 7; i++) {
sheet.autoFitColumn(i);
}
// Save the workbook
workbook.saveToFile("output/AddFormattedDataExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When working with large datasets, finding information that matches certain criteria in seconds can be quite challenging. Fortunately, MS Excel provides the AutoFilter tool to help you narrow down the search by displaying only the relevant information and hiding all other data from view. In this article, you will learn how to add or remove AutoFilter in Excel with Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Add AutoFilter to Excel Cells in Java
- Apply Date AutoFilter in Excel in Java
- Apply Custom AutoFilter in Excel in Java
- Remove AutoFilter in Excel in Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add AutoFilter to Excel Cells in Java
Spire.XLS for Java allows you to apply AutoFilter on a specific cell range through the Worksheet.getAutoFilters().setRange() method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Add an AutoFilter to a specified cell range using Worksheet.getAutoFilters().setRange() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class createFilter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Create an AutoFilter in the sheet and specify the range to be filtered
sheet.getAutoFilters().setRange(sheet.getCellRange("A1:C1"));
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("CreateFilter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Apply Date AutoFilter in Excel in Java
If you need to explore information related to specific dates or time, you can apply a date filter to the selected range using the Workbook.getAutoFilters().addDateFilter(IAutoFilter column, DateTimeGroupingType dateTimeGroupingType, int year, int month, int day, int hour, int minute, int second) method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Add an AutoFilter to a specified range using Workbook.getAutoFilters().setRange() method.
- Get the column to be filtered.
- Call the Workbook.getAutoFilters().addDateFilter() method to add a date filter to the column to filter data related to a specified year/month/date, etc.
- Apply the filter using Workbook.getAutoFilters().filter() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.core.IAutoFilter;
import com.spire.xls.core.spreadsheet.autofilter.DateTimeGroupingType;
public class ApplyDateFilter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Create an auto filter in the sheet and specify the range to be filtered
sheet.getAutoFilters().setRange(sheet.getCellRange("A1:A12"));
//Get the column to be filtered
IAutoFilter filterColumn = sheet.getAutoFilters().get(0);
//Add a date filter to filter data related to February 2022
sheet.getAutoFilters().addDateFilter(filterColumn, DateTimeGroupingType.Month, 2022, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0);
//Apply the filter
sheet.getAutoFilters().filter();
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("ApplyDateFilter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
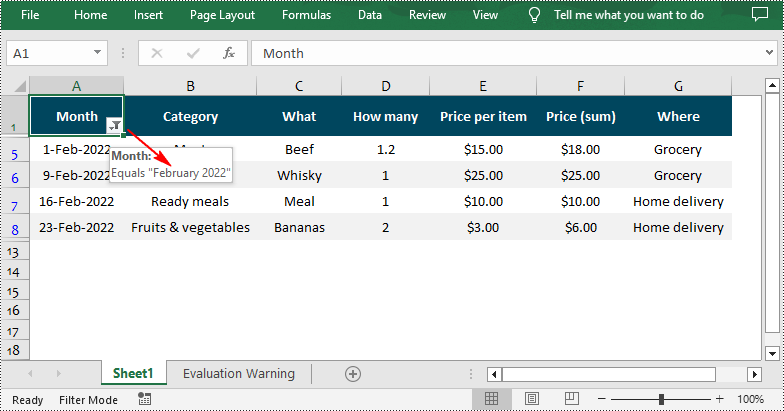
Apply Custom AutoFilter in Excel in Java
The Workbook.getAutoFilters().customFilter(FilterColumn column, FilterOperatorType operatorType, java.lang.Object criteria) method allows you to create custom filters based on certain criteria. For example, you can filter data that contains specific text. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Add an AutoFilter to a specified range using Workbook.getAutoFilters().setRange() method.
- Get the column to be filtered.
- Add a custom filter to the column to filter data containing the specified string using Workbook.getAutoFilters().customFilter() method.
- Apply the filter using Workbook.getAutoFilters().filter() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.core.spreadsheet.autofilter.FilterColumn;
import com.spire.xls.core.spreadsheet.autofilter.FilterOperatorType;
public class CustomFilter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Create an auto filter in the sheet and specify the range to be filtered
sheet.getAutoFilters().setRange(sheet.getCellRange("G1:G12"));
//Get the column to be filtered
FilterColumn filterColumn = sheet.getAutoFilters().get(0);
//Add a custom filter to filter data containing the string "Grocery"
String strCrt = "Grocery";
sheet.getAutoFilters().customFilter(filterColumn, FilterOperatorType.Equal, strCrt);
//Apply the filter
sheet.getAutoFilters().filter();
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("ApplyCustomFilter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
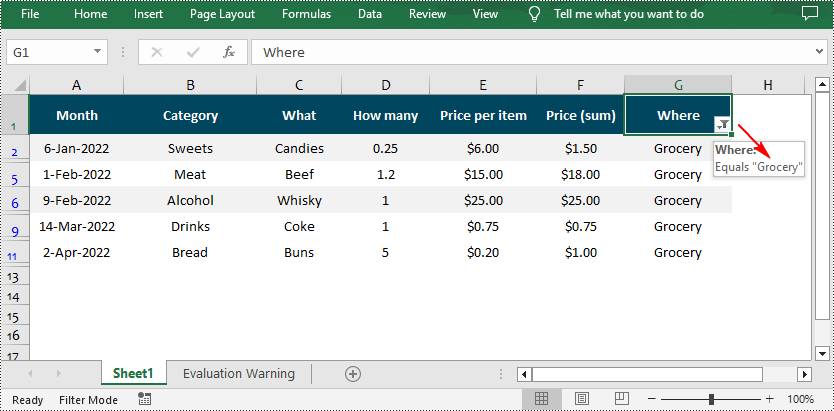
Remove AutoFilter in Excel in Java
In addition to adding AutoFilters in Excel files, Spire.XLS for Java also support removing or deleting the AutoFilters from Excel through the Worksheet.getAutoFilters().clear() method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Remove AutoFilter from the worksheet using Worksheet.getAutoFilters().clear() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class removeAutoFilters {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("CustomAutoFilter.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Remove the auto filters
sheet.getAutoFilters().clear();
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("RemoveFilter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Excel is a versatile tool extensively utilized for data management and analysis. There are occasions when you may require locating specific data within an Excel file and replacing it with updated values. In this article, we will explore how to find and replace data in Excel in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Find and Replace Data in a Worksheet in Excel
- Find and Replace Data in a Specific Cell Range in Excel
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Find and Replace Data in a Worksheet in Excel
The Worksheet.findAllString() method provided by Spire.XLS for Java can help you find the cells containing specific text in Excel documents. Once found, you can conveniently replace these values with new ones using the CellRange.setText() method. The steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Find the specific value in the worksheet using Worksheet.findAllString() method and replace the value of the cell with another value using CellRange.setText() method.
- Set a background for the cell so you can easily find the updated cells using CellRange. getStyle().setColor() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.CellRange;
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import java.awt.Color;
public class ReplaceData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Test.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Find the cells with the specific string value "Total" in the worksheet
CellRange[] cells = worksheet.findAllString("Total", true, true);
// Iterate through the found cells
for (CellRange cell : cells) {
// Replace the value of the cell with another value
cell.setText("Sum");
// Set a background color for the cell
cell.getStyle().setColor(Color.YELLOW);
}
// Save the result file to a specific location
workbook.saveToFile("ReplaceDataInWorksheet.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
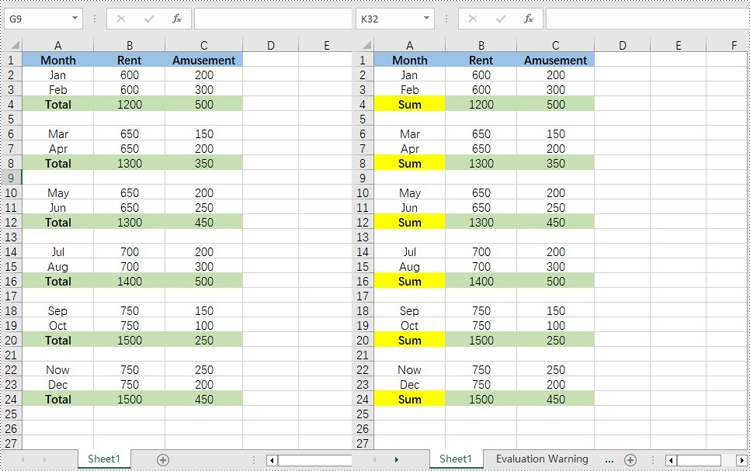
Find and Replace Data in a Specific Cell Range in Excel
To replace data within a specific range of cells, you can utilize the CellRange.findAllString() method to locate cells within the range that contain the desired values. Then, use the CellRange.setText() method to replace the cell value with a new value. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get a specific cell range using Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Find the cells with the specific value in the cell range using CellRange.findAllString() method.
- Iterate through the found cells
- Replace the value of the cell with another value using CellRange setText() method.
- Set a background for the cell so you can easily find the updated cells using the CellRange. getStyle().setColor() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.CellRange;
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import java.awt.Color;
public class ReplaceDataInCellRange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Test.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get a specific cell range
CellRange range = worksheet.getCellRange("A1:C12");
// Find the cells with the specific value "Total" in the cell range
CellRange[] cells = range.findAllString("Total", true, true);
// Iterate through the found cells
for (CellRange cell : cells) {
// Replace the value of the cell with another value
cell.setText("Sum");
// Set a background color for the cell
cell.getStyle().setColor(Color.YELLOW);
}
// Save the result file to a specific location
workbook.saveToFile("ReplaceDataInCellRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
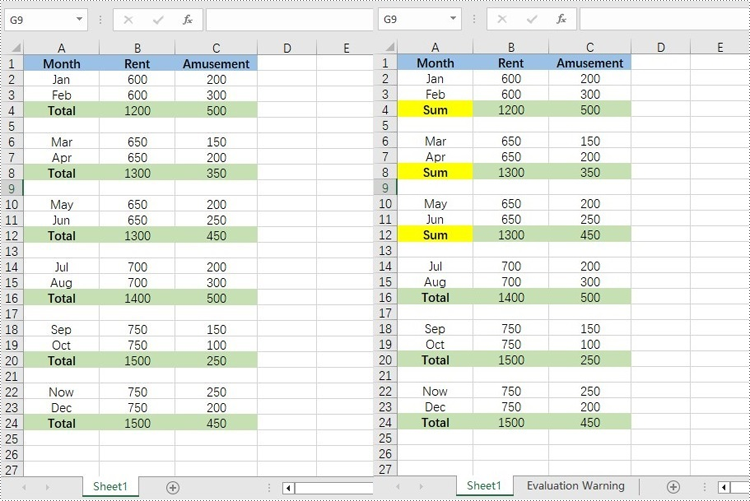
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In Excel worksheets, a table is a specially designated area within a worksheet that comes with headers, optional total rows, and built-in features such as filtering, sorting, data inserting and deleting, and calculated columns, which greatly facilitate data handling and analysis. For developers looking to automate or integrate Excel data operations within their Java applications, the ability to create, modify, or remove tables within these worksheets becomes an essential skill. This article explores how to create, modify, and remove tables in Excel worksheets with Java using Spire.XLS for Java to manage data in Excel files effectively.
- Create Tables in Excel Worksheets with Java
- Modify Tables in Excel Worksheets with Java
- Remove Tables from Excel Worksheets with Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Create Tables in Excel Worksheets with Java
To create a table in an Excel worksheet using Java, you can use the Worksheet.getListObjects().create(String tableName, IXLSRange cellRange) method. Follow these steps to create and customize a table:
- Create an instance of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.loadFromFile() method to load an existing Excel file.
- Retrieve the desired worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Obtain the table’s cell range using the Worksheet.getRange().get() method.
- Use the Worksheet.getListObjects().create(String tableName, IXLSRange cellRange) method to create the table with a name and range.
- Format the table as needed.
- Save the changes using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.CellRange;
import com.spire.xls.TableBuiltInStyles;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import com.spire.xls.core.IListObject;
public class CreateTableExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of Workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the cell range of the table
CellRange range = sheet.getCellRange("A1:I11");
// Create a table
IListObject table1 = sheet.getListObjects().create("Table1", range);
// Apply a built-in style to the table
table1.setBuiltInTableStyle(TableBuiltInStyles.TableStyleLight16);
// Save the workbook
workbook.saveToFile("output/CreateTableExcel.xlsx");
workbook.dispose();
}
}
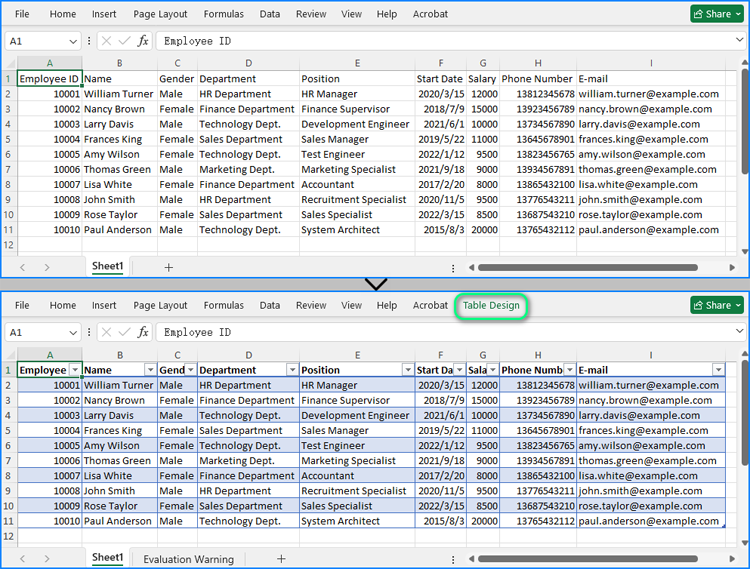
Modify Tables in Excel Worksheets with Java
Spire.XLS for Java provides methods in the IListObject class to modify worksheet table properties, such as the table name, cell range, style, and header visibility. Follow these steps to modify tables in Excel worksheets:
- Create an instance of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.loadFromFile() method to open an existing Excel file.
- Retrieve the worksheet containing the table using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Access the table using the Worksheet.getListObjects().get() method.
- Use the methods in the IListObject class to update the table's properties, such as its name, style, or headers.
- Save the updated workbook using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.TableBuiltInStyles;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import com.spire.xls.core.IListObject;
public class ModifyTableExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of Workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("output/CreateTableExcel.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the table
IListObject table = sheet.getListObjects().get(0);
// Modify the table
table.setName("NewTable"); // Change the name
table.setLocation(sheet.getRange().get("A1:D11")); // Change the location
table.setBuiltInTableStyle(TableBuiltInStyles.TableStyleDark5); // Change the style
table.setDisplayHeaderRow(false); // Hide the header row
// Save the workbook
workbook.saveToFile("output/ModifyTableExcel.xlsx");
workbook.dispose();
}
}

Remove Tables from Excel Worksheets with Java
You can remove tables from Excel worksheets using the Worksheet.getListObjects().removeAt(int index) method. This action converts the table area back to a normal cell range and removes any associated formatting. Follow these steps to remove tables:
- Create an instance of the Workbook class.
- Open an existing Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the worksheet containing the table using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Use the Worksheet.getListObjects().removeAt() method to delete the table by its index.
- Save the changes using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class RemoveTableExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of Workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("output/CreateTableExcel.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Remove the table
sheet.getListObjects().removeAt(0);
// Save the workbook
workbook.saveToFile("output/RemoveTableExcel.xlsx");
workbook.dispose();
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
