Create and Scan Barcode (4)
How to Generate QR Codes in Python (Full Tutorial with Examples)
2025-07-15 02:49:34 Written by zaki zou
QR codes have transformed how we bridge physical and digital experiences—from marketing campaigns to secure data sharing. For developers looking to generate QR codes in Python , Spire.Barcode for Python provides a complete toolkit for seamless QR code generation, offering both simplicity for basic needs and advanced customization for professional applications.
This step-by-step guide walks you through the entire QR code generation process in Python. You'll learn to programmatically create scannable codes, customize their appearance, embed logos, and optimize error correction - everything needed to implement robust QR code generation solutions for any business or technical requirement.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Spire.Barcode for Python
- Setting Up the Environment
- Basic Example: Generating QR Codes in Python
- Customizing QR Code Appearance
- Generating QR Code with Logo
- Wrapping up
- FAQs
1. Introduction to Spire.Barcode for Python
Spire.Barcode for Python is a powerful library that enables developers to generate and read various barcode types, including QR codes, in Python applications. This robust solution supports multiple barcode symbologies while offering extensive customization options for appearance and functionality.
Key features of Spire.Barcode include:
- Support for QR Code generation with customizable error correction levels
- Flexible data encoding options (numeric, alphanumber, byte/binary)
- Comprehensive appearance customization (colors, sizes, fonts)
- High-resolution output capabilities
- Logo integration within QR codes
2. Setting Up the Environment
Before we dive into generating QR codes, you need to set up your Python environment. Ensure you have Python installed, and then install the Spire.Barcode library using pip:
pip install spire.barcode
For the best results, obtain a free temporary license from our website. This will allow you to create professional QR code images without evaluation messages, enhancing both user experience and quality of the generated codes.
3. Basic Example: Generating QR Codes in Python
Now that we have everything set up, let's generate our first QR code. Below is the step-by-step process:
-
Initial Setup :
- Import the Spire.Barcode library.
- Activate the library with a valid license key to remove the
-
Configure Barcode Settings :
- Create a BarcodeSettings object to control QR code properties.
- Set barcode type to QR code.
- Configure settings such as data mode and error correction level.
- Define the content to encode.
- Configure visual aspects like module width and text display options.
-
Generate Barcode Image :
- Create a BarCodeGenerator object with the configured settings.
- Convert the configured QR code into an image object in memory.
-
Save Image to File :
- Write the generated QR code image to a specified file path in PNG format.
The following code snippet demonstrates how to generate QR codes in Python:
from spire.barcode import *
# Function to write all bytes to a file
def WriteAllBytes(fname: str, data):
with open(fname, "wb") as fp:
fp.write(data)
fp.close()
# Apply license key for the barcode generation library
License.SetLicenseKey("your license key")
# Create a BarcodeSettings object to configure barcode properties
barcodeSettings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the type of barcode to QR code
barcodeSettings.Type = BarCodeType.QRCode
# Set the data mode for QR code (automatic detection of data type)
barcodeSettings.QRCodeDataMode = QRCodeDataMode.Auto
# Set the error correction level (M means medium level of error correction)
barcodeSettings.QRCodeECL = QRCodeECL.M
# Set the data that will be encoded in the QR code
barcodeSettings.Data2D = "visit us at www.e-iceblue.com"
# Set the width of each module (the square bars) in the barcode
barcodeSettings.X = 3
# Hide the text that typically accompanies the barcode
barcodeSettings.ShowText = False
# Create a BarCodeGenerator object with the specified settings
barCodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(barcodeSettings)
# Generate the image for the barcode based on the settings
image = barCodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
# Write the generated PNG image to disk at the specified path
WriteAllBytes("output/QRCode.png", image)
Key Concepts:
A. QRCodeDataMode (Data Encoding Scheme)
Controls how the input data is encoded in the QR code:
| Mode | Best For | Example Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Auto | Let library detect automatically | General purpose (default choice) |
| Numeric | Numbers only (0-9) | Product codes, phone numbers |
| AlphaNumber | A-Z, 0-9, and some symbols | URLs, simple messages |
| Byte | Binary/Unicode data | Complex text, special characters |
Why it matters:
- Different modes have different storage capacities.
- Numeric mode can store more digits than other modes.
- Auto mode is safest for mixed content.
B. QRCodeECL (Error Correction Level)
Determines how much redundancy is built into the QR code:
| Level | Recovery Capacity | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| L (Low) | 7% damage recovery | Small codes, short URLs |
| M (Medium) | 15% damage recovery | General purpose (recommended) |
| Q (Quartile) | 25% damage recovery | Codes with logos or decorations |
| H (High) | 30% damage recovery | Critical applications |
Visual Impact:
Higher ECLs:
- Increase QR code complexity (more modules/squares).
- Make the code more scannable when damaged.
- Are essential when adding logos (use at least Q or H).
Output:
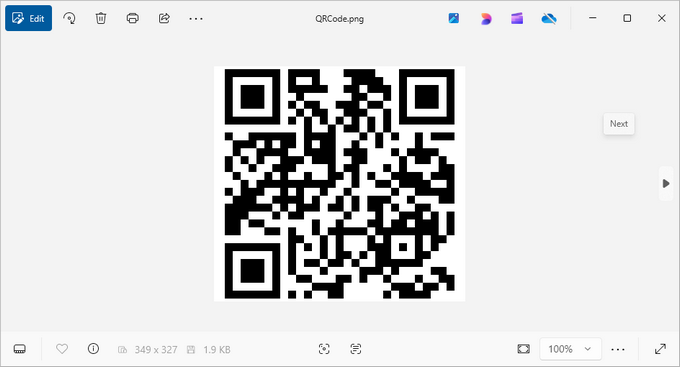
4. Customizing QR Code Appearance
Once you've generated a basic QR code, you can further customize its appearance to make it more visually appealing or to fit your brand. Here are some customization options:
4.1 Adjusting DPI Settings
The DPI (dots per inch) settings control the image quality of the QR code. Higher DPI values result in sharper images suitable for printing, while lower values (72-150) are typically sufficient for digital use.
barcodeSettings.DpiX = 150
barcodeSettings.DpiY = 150
4.2 Changing Foreground and Background Colors
You can customize your QR code’s color scheme. The ForeColor determines the color of the QR code modules (squares), while BackColor sets the background color. Ensure sufficient contrast for reliable scanning.
barcodeSettings.BackColor = Color.get_GhostWhite()
barcodeSettings.ForeColor = Color.get_Purple()
4.3 Displaying the Encoded Data
If you want users to see the encoded information without scanning, set the following properties:
barcodeSettings.ShowTextOnBottom = True
barcodeSettings.TextColor = Color.get_Purple()
barcodeSettings.SetTextFont("Arial", 13, FontStyle.Bold)
4.4 Adding Text Under QR Code
You can also add custom text under the QR code, which could be a call-to-action or instructions.
barcodeSettings.ShowBottomText = True
barcodeSettings.BottomText = "Scan Me"
barcodeSettings.SetBottomTextFont("Arial", 13, FontStyle.Bold)
barcodeSettings.BottomTextColor = Color.get_Black()
4.5 Setting Margins and Border
Defining margins and border styles enhances the presentation of the QR code. Here’s how to do it:
barcodeSettings.LeftMargin = 2
barcodeSettings.RightMargin = 2
barcodeSettings.TopMargin = 2
barcodeSettings.BottomMargin = 2
barcodeSettings.HasBorder = True
barcodeSettings.BorderWidth = 0.5
barcodeSettings.BorderColor = Color.get_Black()
5. Generating QR Code with Logo
For branding purposes, you might want to add a logo to your QR code. Spire.Barcode makes this process seamless while maintaining scannability. Here’s how:
barcodeSettings.SetQRCodeLogoImage("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png")
When adding a logo:
- Use a simple, high-contrast logo for best results.
- Test the scannability after adding the logo.
- The QR code's error correction (set earlier) helps compensate for the obscured area.
The logo will be centered within the QR code, and Spire.Barcode will automatically resize it to ensure the QR code remains scannable.
Output:
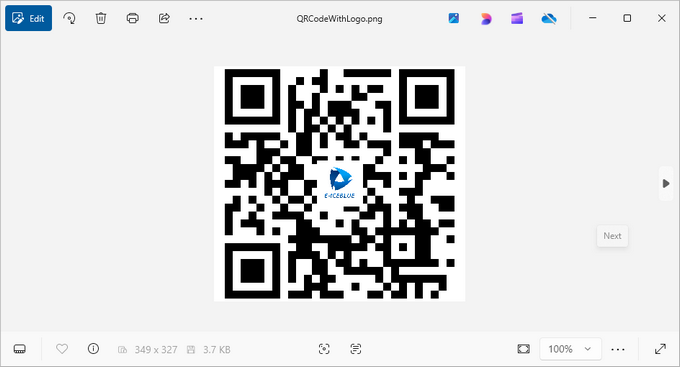
6. Wrapping up
Generating QR codes in Python using Spire.Barcode is a straightforward process that offers extensive customization options. From basic QR codes to branded versions with logos and custom styling, the library provides all the tools needed for professional barcode generation.
Key Benefits:
- Spire.Barcode simplifies QR code generation with a clean API.
- Extensive customization options allow for branded, visually appealing QR codes.
- Error correction ensures reliability even with added logos.
- High-resolution output supports both digital and print use cases.
Whether you're building an inventory system, creating marketing materials, or developing a mobile app integration, Spire.Barcode provides a robust solution for all your QR code generation needs in Python.
7. FAQs
Q1: What is a QR code?
A QR code (Quick Response code) is a type of matrix barcode that can store URLs and other information. It is widely used for quickly linking users to websites, apps, and digital content through mobile devices.
Q2: Can I generate QR codes without a license key?
Yes, you can generate QR codes without a license key; however, the generated barcode will display an evaluation message along with our company logo, which may detract from the user experience.
Q3: Can I generate different types of barcodes with Spire.Barcode?
Yes, Spire.Barcode supports various barcode types, not just QR codes. Detailed documentation can be found here: How to Generate Barcode in Python
Q4: How can I implement a QR code generator in Python using Spire.Barcode?
To implement a QR code generator in Python with Spire.Barcode, create a BarcodeSettings object to configure the QR code properties. Then, use the BarCodeGenerator class to generate the QR code image by calling the GenerateImage() method.
Q5: Can I scan or read QR code using Spire.Barcode?
Yes, you can scan and read QR codes using Spire.Barcode for Python. The library provides functionality for both generating and decoding QR codes. Follow this guide: How to Read Barcode Using Python
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Barcode for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Modern business systems, from retail checkout lanes to warehouse inventory tracking, rely heavily on barcode scanning, and Python-based solutions have become a popular choice due to their versatility and ease of use. In this article, we’ll explore how to read barcodes in Python using the Spire.Barcode for Python library, covering setup, scanning from image files or bytes, and customization options for improved accuracy.
Table of Contents:
- Python Library for Reading Barcodes
- Integrate Spire.Barcode into Your Python Application
- Read a Barcode from an Image File
- Read Multiple Barcodes from an Image File
- Read Barcodes from Image Bytes
- Adjust Barcode Recognition Settings
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Python Library for Reading Barcodes
Spire.Barcode for Python is a powerful library specifically crafted for creating and reading barcodes in Python applications. The library supports a variety of barcode formats, including:
- 1D Barcodes : Such as Code 128, Code 39, EAN-13, and UPC-A.
- 2D Barcodes : Including QR Code, DataMatrix, and PDF417.
Notable Features of Spire.Barcode
- Format Support : Capable of reading barcodes from various image formats, including PNG, JPG, BMP, GIF, and TIFF.
- Batch Scanning : Enables the detection of multiple barcodes within a single image file.
- Recognition Accuracy : Utilizes advanced algorithms to deliver reliable barcode detection.
- Customization : Allows users to specify barcode types and enable checksum verification for enhanced recognition efficiency.
This library provides the capability to read barcodes from both image files and bytes, along with extensive customization options to meet diverse requirements.
Integrate Spire.Barcode into Your Python Application
To get started with Spire.Barcode, you first need to install the library. You can do this via pip. Open your terminal and run:
pip install spire.barcode
Once you have installed the library, you will need a license key to unlock its full capabilities. You can obtain a trial license from our website. and set up the library in your Python script:
from spire.barcode import *
License.SetLicenseKey("your license key")
Now that you have the library in place, you can begin reading barcodes using Python.
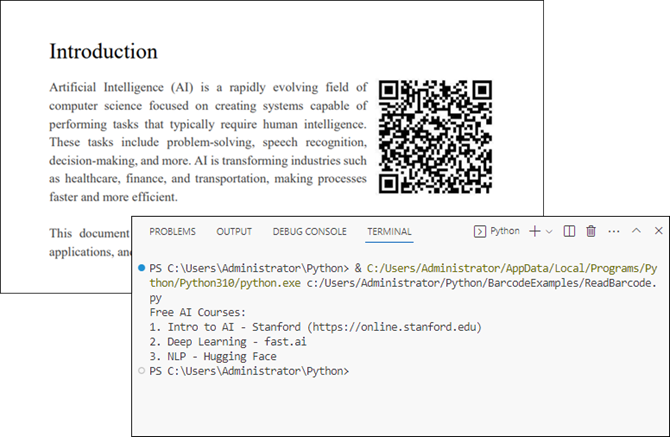
Read a Barcode from an Image File in Python
Reading a single barcode from an image file is straightforward with Spire.Barcode. Here's how you can do it:
from spire.barcode import *
# Apply license key to unlock full capabilities
License.SetLicenseKey("your license key")
# Read barcode from an image file
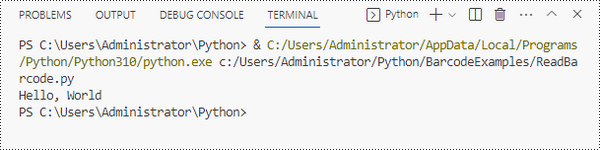
result = BarcodeScanner.ScanOneFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/qr_code.png")
# Print the result
print(result)
Explanation
- License.SetLicenseKey() : Initializes the library with your license key.
- BarcodeScanner.ScanOneFile() : Reads a single barcode from the specified image file.
- The result is printed to the console, displaying the barcode's data.
Output:
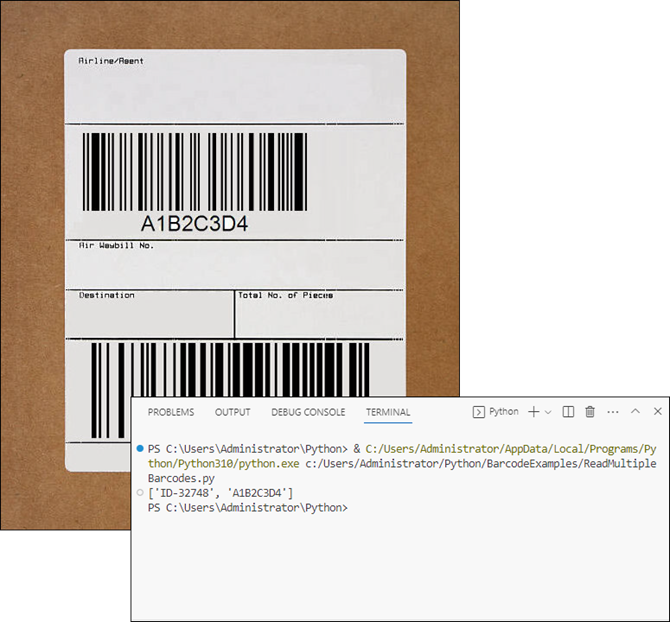
Read Multiple Barcodes from an Image File in Python
If you need to read multiple barcodes from a single image file, Spire.Barcode makes this easy as well. Here’s an example:
from spire.barcode import *
# Apply license key to unlock full capabilities
License.SetLicenseKey("your license key")
# Read multiple barcodes from stream
results = BarcodeScanner.ScanFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/barcodes.jpg")
# Print results
print(results)
Explanation
- BarcodeScanner.ScanFile() : Scans the entire image for multiple barcodes.
- The results are stored as a list. Each element in the list contains the data from a detected barcode.
Output:
Read Barcodes from Image Bytes in Python
In addition to reading barcodes directly from files, Spire.Barcode for Python supports decoding barcodes from in-memory image bytes . This approach is useful when working with dynamically loaded images (e.g., from APIs, databases, or user uploads).
Here’s how to do it:
from spire.barcode import *
# Apply license key to unlock full capabilities
License.SetLicenseKey("your license key")
# Read an image file into bytes
image_path = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/barcodes.jpg"
with open(image_path, "rb") as file:
image_bytes = file.read()
# Wrap bytes in Spire.Barcode's Stream object
stream = Stream(image_bytes)
# Read one barcode from stream
# result = BarcodeScanner.ScanOneStream(stream)
# Read multiple barcodes from stream
results = BarcodeScanner.ScanStream(stream)
# Print results
print(results)
Explanation
- image_bytes: Raw binary data read from an image file (e.g., PNG, JPG) or other sources like APIs or databases.
- Stream (Spire.Barcode class): Converts image_bytes into an in-memory stream compatible with Spire.Barcode’s scanner.
- BarcodeScanner.ScanStream() : Scans the stream for barcodes and returns a list of detected barcodes.
Adjust Barcode Recognition Settings
The BarcodeScanner class provides various methods to customize barcode recognition settings. This can help improve detection accuracy and efficiency. Some of the key methods include:
- ScanOneFileBarCodeTypeIncludeCheckSum(fileName: str, barcodeType: BarCodeType, IncludeCheckSum: bool)
- ScanFileBarCodeTypeIncludeCheckSum(fileName: str, barcodeType: BarCodeType, IncludeCheckSum: bool)
- ScanOneStreamBarCodeTypeIncludeCheckSum(stream: Stream, barcodeType: BarCodeType, IncludeCheckSum: bool)
- ScanStreamBarCodeTypeIncludeCheckSum(stream: Stream, barcodeType: BarCodeType, IncludeCheckSum: bool)
Here’s an example of how to specify a barcode type and include checksum verification:
from spire.barcode import *
# Apply license key to unlock full capabilities
License.SetLicenseKey("your license key")
# Specify the barcode type (e.g., EAN13)
barcode_type = BarCodeType.EAN13
# Read a barcode from an image file with checksum included
result = BarcodeScanner.ScanOneFileBarCodeTypeIncludeCheckSum("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/EAN_13.png", barcode_type, True)
# Print the result
print(result)
Explanation
- BarcodeType : Specifies the type of barcode you want to scan.
- IncludeCheckSum (bool): Determines whether to verify the checksum during scanning. Setting it to True can help catch errors in data.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to read barcodes in Python using the Spire.Barcode library. We covered the setup process, reading single and multiple barcodes from image files, and reading from image bytes. Additionally, we discussed how to customize barcode detection settings for improved accuracy. With these tools at your disposal, you can easily integrate barcode scanning capabilities into your Python applications.
FAQs
Q1: What types of barcodes can I read with Spire.Barcode?
Spire.Barcode supports a wide range of barcode formats, including QR codes, UPC, EAN, Code 128, Code 39, and many others.
Q2: Do I need a license to use Spire.Barcode?
Yes, a license key is required to unlock the full functionality of the library. You can obtain a free 30-day trial license from our website.
Q3: Can I read barcodes from a webcam using Spire.Barcode?
While Spire.Barcode does not directly support webcam input, you can capture images from a webcam and then read barcodes from those images using the library.
Q4: How can I improve barcode scanning accuracy?
You can improve accuracy by specifying the barcode type and enabling checksum verification during scanning. Additionally, ensure that the images are clear and well-lit.
Q5. Can I generate barcodes using Spire.Barcode for Python?
Yes, Spire.Barcode supports both barcode recognition and generation. For detailed instructions, check out this tutorial: How to Generate Barcodes in Python: A Step-by-Step Guide.

Barcodes are essential in inventory management, retail systems, logistics, and many other data-driven fields. For Python developers, generating barcodes in Python can be complex—especially when working with multiple formats or large-scale automation. That’s why a reliable Python barcode generator library is necessary to ensure flexible and efficient barcode creation, with support for various barcode types and batch processing.
This article provides an accurate and efficient approach to generating barcodes in Python using Spire.Barcode for Python.
- Get Started with Spire.Barcode for Python
- How to Generate Barcode in Python
- Supported Barcode Types
- Frequently Asked Questions
Get Started with Spire.Barcode for Python
Why Choose Spire.Barcode?
Spire.Barcode for Python is a professional and user-friendly Python Barcode API designed for developers who want to add barcode generation or reading features to their Python applications. Here’s why it stands out:
- Supports multiple barcode symbologies including Code 128, QR Code, EAN-13, UPC, and more
- High-quality image output with complete customization settings
- Comprehensive and easy-to-integrate API
- No need for third-party dependencies
- One library to generate and scan barcodes
Installation and Importing
To install Spire.Barcode for Python, simply run:
pip install spire.barcodeYou can also install Free Spire.Barcode for Python for simple barcode generating tasks:
pip install spire.barcode.freeHow to Generate Barcode in Python
To generate a barcode in Python, you typically need to define the barcode type (such as Code 128 or QR Code) and the content to encode. Using a library like Spire.Barcode, you can configure them in just a few lines of code.
Key Classes and Methods:
- BarcodeSettings: Defines properties such as type, data, color, text, etc.
- BarCodeGenerator: Generates barcode images based on settings.
- GenerateImage(): Outputs barcode as an image stream.
Step 1: Import the Required Modules
To start coding your Python barcode generator, import the necessary classes.
- Python
from spire.barcode import BarcodeSettings, BarCodeType, BarCodeGenerator, Code128SetMode, FontStyle, ColorStep2: Configure Barcode Settings
Create a BarcodeSettings object and define barcode properties:
- Python
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
barcodeSettings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type
barcodeSettings.Type = BarCodeType.Code128
# Set the barcode data
barcodeSettings.Data = "ABC123456789"
# Set the barcode code128 set mode
barcodeSettings.Code128SetMode = Code128SetMode.Auto
# Choose the data display position
barcodeSettings.ShowTextOnBottom = True
# Set the bottom text and style
barcodeSettings.BottomText = "Code 128 Example"
barcodeSettings.SetTextFont("Arial", 12.0, FontStyle.Regular)
barcodeSettings.ShowBottomText = True
# Set the background color
barcodeSettings.BackColor = Color.get_Beige()Step 3: Generate the Barcode Image
Create a BarCodeGenerator object using the configured BarcodeSettings, then generate the barcode image as a stream and save it to a local file:
- Python
# Create a BarCodeGenerator object
barcodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(barcodeSettings)
# Generate the barcode image
barcodeImage = barcodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
# Save the image
with open("output/Code 128.png", "wb") as fp:
fp.write(barcodeImage)The generated barcode:

This script allows you to generate a Code 128 barcode and save it as an image. Just replace the BarCodeType and Data value to customize.
Generating Other Barcode Types
Spire.Barcode for Python supports a wide range of barcode symbologies, including the most commonly used types such as Code 39, UPC, QR Code, and EAN-13. This ensures developers can generate barcodes for various applications with compatibility and ease.
Barcode Type Support Overview
| Barcode Category | Barcode Types (Examples) | Free Version | Paid Version |
| 1D Linear Barcodes | Codabar, Code11, Code25, Interleaved25, Code39, Code39Extended, Code93, Code93Extended, Code128, EAN8, EAN13, EAN128, EAN14, UPCA, UPCE, MSI, PostNet, Planet, SCC14, SSCC18, ITF14, ITF6, PZN, OPC | ✅ (Partial) | ✅ (All) |
| 2D Barcodes | QRCode, DataMatrix, Pdf417, Pdf417Macro, Aztec, MicroQR | ✅ (QRCode only) | ✅ (All) |
| Stacked/Composite Codes | RSS14, RSS14Truncated, RSSLimited, RSSExpanded | ❌ | ✅ |
| Postal Barcodes | USPS, SwissPostParcel, DeutschePostIdentcode, DeutschePostLeitcode, RoyalMail4State, SingaporePost4State | ❌ | ✅ |
Advanced: Generate Barcodes in Bulk
You can easily generate multiple barcodes in bulk using Spire.Barcode for Python. This is especially useful for inventory management, batch labeling, or automated systems where each item requires a unique barcode.
Code Example
- Python
# Create a list of barcode data
data = ["Barcode 1", "Barcode 2", "Barcode 3"]
# Loop through the data to generate barcodes
for barcode_data in data:
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
settings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type and data
settings.Type = BarCodeType.Code39
settings.Data = barcode_data
# Create a BarCodeGenerator object
generator = BarCodeGenerator(settings)
# Save the barcode image
barcode_stream = generator.GenerateImage()
with open(f"output/{barcode_data}.png", "wb") as file:
file.write(barcode_stream)This Python script generates and saves a barcode image for each entry in the list, streamlining barcode creation workflow.
Conclusion
Generating barcodes in Python is simple and efficient with Spire.Barcode for Python. Whether you’re creating a single Code 128 barcode or automating batch QR code generation, this robust and flexible library gives you the control and quality needed for professional barcode integration. From supporting various symbologies to delivering high-quality output with minimal code, this Python barcode generator is an excellent tool for developers across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How to create a barcode in Python?
You can create a barcode using libraries like Spire.Barcode for Python, which supports a variety of symbologies like Code 128, QR Code, and more. Just install the package, configure barcode settings, and save the output image.
Q: How is barcode generated?
Barcodes are generated by encoding data into a visual pattern of bars or modules. With Python, this is done through barcode libraries like Spire.Barcode, which translate string input into a corresponding image.
Q: How to create a code generator in Python?
If you're referring to a barcode generator, define the barcode type (e.g., Code 128), provide the data, and use a library like Spire.Barcode to generate and save the image. You can automate this process using loops and functions.
Q: How to generate QR code by Python?
You can use Spire.Barcode for Python to generate QR codes quickly and efficiently. Here's a full example that creates a QR code with embedded data:
- Python
from spire.barcode import BarcodeSettings, BarCodeGenerator, BarCodeType
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
barcodeSettings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type to QRCode
barcodeSettings.Type = BarCodeType.QRCode
# Set the barcode data
barcodeSettings.Data = "ABC123456"
# Generate the barcode
barcodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(barcodeSettings)
barcodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
with open("output/QRCode.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(barcodeGenerator.GenerateImage())Result:

This enables you to embed URLs, text, or IDs into scannable QR images.
See Also: How to Generate and Scan QR Codes with Python
Get a Free License
Spire.Barcode for Python offers a free trial license that removes limitations and watermarking. Get a free license today and explore the full capabilities of this powerful Python barcode library.
QR codes are a type of two-dimensional barcode that can store a variety of information, including URLs, contact details, and even payment information. QR codes have become increasingly popular, allowing for quick and convenient access to digital content, making them a useful tool in our modern, technology-driven world.
In this article, you will learn how to create and scan QR codes in Python using Spire.Barcode for Python.
Get a Free Trial License
The trial version of Spire.Barcode for Python does not support scanning QR code images without a valid license being applied. Additionally, it displays an evaluation message on any QR code images that are generated.
To remove these limitations, you can get a 30-day trial license for free.
Create a QR Code in Python
Spire.Barcode for Python offers the BarcodeSettings class, which enables you to configure the settings for generating a barcode. These settings encompass the barcode type, the data to be encoded, the color, the margins, and the horizontal and vertical resolution.
After you have set up the desired settings, you can create a BarcodeGenerator instance using those configurations. Subsequently, you can invoke the GenerateImage() method of the generator to produce the barcode image.
The following are the steps to create a QR code in Python.
- Create a BarcodeSettings object.
- Set the barcode type to QR code using BarcodeSettings.Type property.
- Set the data of the 2D barcode using BarcodeSettings.Data2D property.
- Set other attributes of the barcode using the properties under the BarcodeSettings object.
- Create a BarCodeGenerator object based on the settings.
- Create a QR code image using BarCodeGenerator.GenerateImage() method.
- Python
from spire.barcode import *
# Write all bytes to a file
def WriteAllBytes(fname: str, data):
with open(fname, "wb") as fp:
fp.write(data)
fp.close()
# Apply license key
License.SetLicenseKey("license key")
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
barcodeSettings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the type of barcode to QR code
barcodeSettings.Type = BarCodeType.QRCode
# Set the data for the 2D barcode
barcodeSettings.Data2D = "Hello, World"
# Set margins
barcodeSettings.LeftMargin = 0.2
barcodeSettings.RightMargin = 0.2
barcodeSettings.TopMargin = 0.2
barcodeSettings.BottomMargin = 0.2
# Set the horizontal resolution
barcodeSettings.DpiX = 500
# Set the vertical resolution
barcodeSettings.DpiY = 500
# Set error correction level
barcodeSettings.QRCodeECL = QRCodeECL.M
# Do not display text on barcode
barcodeSettings.ShowText = False
# Add a logo at the center of the QR code
barcodeSettings.SetQRCodeLogoImage("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png")
# Create an instance of BarCodeGenerator with the specified settings
barCodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(barcodeSettings)
# Generate the image for the barcode
image = barCodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
# Write the PNG image to disk
WriteAllBytes("output/QRCode.png", image)

Scan a QR Code Image in Python
Spire.Barcode provides the BarcodeScanner class, which is responsible for barcode image recognition. This class offers several methods to extract data from barcodes, including:
- ScanOneFile(): Scans a single barcode image file and returns the extracted data.
- ScanFile(): Scans all barcodes present in a specified image file and returns the extracted data.
- ScanStream(): Scans barcodes from a stream of image data and returns the extracted information.
The following code demonstrates how to scan a QR code image using it.
- Python
from spire.barcode import *
# Apply license key
License.SetLicenseKey("license key")
# Scan an image file that contains one barcode
result = BarcodeScanner.ScanOneFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\QRCode.png")
# Scan an image file that contains multiple barcodes
# results = BarcodeScanner.ScanFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Image.png")
# Print the result
print(result)