
Data Import/Export (8)

Exporting list data to Excel with C# is a common requirement in modern .NET applications. Whether you are building a desktop application, a web system, or a background service, developers often need to convert in-memory collections—especially List<T>—into well-structured Excel files that users can download, analyze, or share.
This tutorial demonstrates how to export a list of objects to Excel in C# without using Excel Interop, using Spire.XLS for .NET. The solution is fully compatible with .NET Core and modern .NET versions, works with typical business data models, and does not require Microsoft Excel to be installed.
Table of Contents
- Why Export a List to Excel in C# Without Interop?
- Export a List of Objects to Excel in C#
- Formatting the Exported Excel Worksheet
- .NET Core and Server-Side Compatibility
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Export a List to Excel in C# Without Interop?
Exporting list data to Excel is a practical way to present structured information in a familiar and widely accepted format. In real-world applications, this requirement commonly appears in scenarios such as:
- Generating operational or financial reports
- Allowing users to download query results from web applications
- Sharing structured data with non-technical stakeholders
- Performing offline analysis or audits using Excel
Traditionally, many developers rely on Excel Interop to generate Excel files. While Interop can work in certain desktop environments, it also introduces several limitations:
- Microsoft Excel must be installed on the machine
- It is not recommended for server-side or ASP.NET Core applications
- It adds unnecessary dependencies for simple export tasks
As a result, exporting Excel files without Interop has become the preferred approach for modern .NET applications. Libraries such as Spire.XLS for .NET provide a clean, reliable, and server-friendly way to export a List<T> directly to Excel—without requiring Microsoft Office.
Export a List of Objects to Excel in C#
In most real-world applications, data is stored as a list of business objects rather than simple values. This section focuses on exporting a List<T> that represents a realistic reporting scenario, using a reusable and Interop-free approach.
Prerequisites
Before exporting a list to Excel, make sure Spire.XLS for .NET is installed in your project.
You can install it via NuGet:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Once installed, you can start exporting List<T> data to Excel without any additional configuration.
Core Export Workflow
The overall process of exporting a list of objects to Excel can be summarized as follows:
- Prepare business-ready data in a
List<T> - Create an Excel workbook and worksheet
- Generate column headers dynamically from object properties
- Write list data into worksheet rows
- Save the Excel file
The following example demonstrates the complete implementation.
Complete Example: Export List to Excel
using Spire.Xls;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Reflection;
public class OrderReport
{
public int OrderId { get; set; }
public string CustomerName { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
public decimal TotalAmount { get; set; }
public string Status { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Prepare sample business data
List<OrderReport> orders = new List<OrderReport>
{
new OrderReport { OrderId = 1001, CustomerName = "Alice", OrderDate = DateTime.Today.AddDays(-2), TotalAmount = 1200.50m, Status = "Completed" },
new OrderReport { OrderId = 1002, CustomerName = "Bob", OrderDate = DateTime.Today.AddDays(-1), TotalAmount = 850.00m, Status = "Pending" },
new OrderReport { OrderId = 1003, CustomerName = "Charlie", OrderDate = DateTime.Today, TotalAmount = 430.75m, Status = "Cancelled" }
};
// Create workbook and worksheet
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Read object properties dynamically
PropertyInfo[] properties = typeof(OrderReport).GetProperties();
// Write column headers
for (int i = 0; i < properties.Length; i++)
{
sheet.Range[1, i + 1].Text = properties[i].Name;
}
// Write data rows
for (int row = 0; row < orders.Count; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < properties.Length; col++)
{
object value = properties[col].GetValue(orders[row]);
sheet.Range[row + 2, col + 1].Value2 = value;
}
}
// Save Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("OrderReport.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Below is a preview of the generated Excel file:
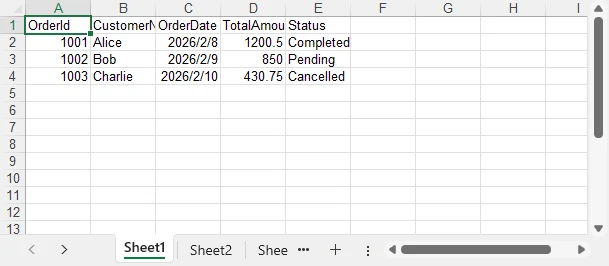
Technical Notes and Implementation Details
- An Excel file is created by instantiating
Workbook, with the first worksheet accessed viaworkbook.Worksheets[0] - Column headers are generated dynamically using reflection (
Type.GetProperties) to avoid hardcoded mappings - Header cells are written using
Range.Text, ensuring clear string output in the first row - Object values are written row by row using
Range.Value2to preserve native Excel data types - The final Excel document is generated with
Workbook.SaveToFile, without requiring Microsoft Excel or Interop
This pattern is ideal for building reusable export utilities and report-generation modules.
In scenarios where data is retrieved as a DataTable instead of a List, Spire.XLS also provides an efficient export approach. Refer to How to Export a DataTable to Excel in C# for detailed instructions.
Formatting the Exported Excel Worksheet
Beyond basic data export, Spire.XLS for .NET allows you to apply formatting to improve readability and usability of the generated Excel file.
Common formatting tasks include:
- Styling header rows
- Formatting dates and numeric values
- Adjusting column widths automatically
- Highlighting key fields
Example: Apply Basic Formatting
using System.Drawing;
// Format header row
CellStyle headerStyle = workbook.Styles.Add("HeaderStyle");
headerStyle.Font.FontName = "Arial";
headerStyle.Font.Size = 12f;
headerStyle.Font.IsBold = true;
headerStyle.Color = Color.LightGray; // Set cell background color
headerStyle.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
sheet.Range[1, 1, 1, sheet.LastColumn].Style = headerStyle;
// Format date and amount columns
sheet.Range[2, 3, orders.Count + 1, 3].NumberFormat = "yyyy-mm-dd";
sheet.Range[2, 4, orders.Count + 1, 4].NumberFormat = "#,##0.00";
// Auto-fit row height and column width
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitRows();
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
Below is a preview of the formatted Excel sheet:
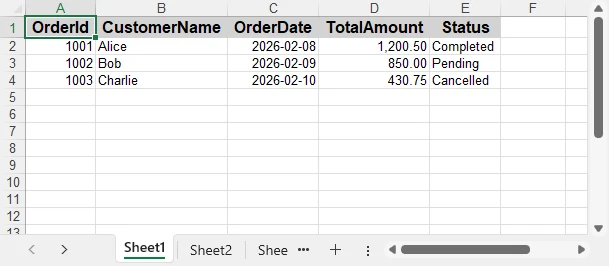
Applying formatting makes the exported Excel file more professional and suitable for direct business use.
For more advanced worksheet formatting—such as styles, merged cells, conditional formatting, and formulas—see How to Create and Format Excel Worksheets in C#.
.NET Core and Server-Side Compatibility
Spire.XLS for .NET is fully compatible with .NET Core and modern .NET versions, making it suitable for:
- ASP.NET Core web applications
- Web APIs
- Cloud and containerized environments
- Background services and scheduled jobs
Because it does not rely on Excel Interop, the export logic is safe to use in server-side and production environments.
If you are working in an ASP.NET Core or Web API project, this guide shows how to generate and format Excel files and return them to the client: Export Excel Files in ASP.NET Core Using C#.
Conclusion
Exporting a list to Excel in C# does not have to rely on Excel Interop. With Spire.XLS for .NET, you can efficiently convert a List<T> into a well-structured and formatted Excel file that works seamlessly across .NET Framework and .NET Core environments.
By adopting an Interop-free approach, you reduce deployment complexity, improve application stability, and gain greater flexibility when exporting business data.
Whether you need to export complex reports or simple lists, Spire.XLS provides a reliable and scalable solution for modern C# applications. For evaluation purposes or to remove trial limitations, a 30-day temporary license is available.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Can this approach export large lists efficiently?
Yes. Spire.XLS for .NET is designed for server-side usage and can handle large List datasets efficiently. For very large exports, batching or streaming strategies can further improve performance.
Q2. Does this solution require Microsoft Excel to be installed?
No. Spire.XLS for .NET works independently of Microsoft Excel and does not rely on Excel Interop, making it suitable for server and cloud environments.
Q3. Can I customize column headers or formats?
Yes. Column headers can be customized manually, and cell formats such as dates, numbers, and styles can be applied programmatically. For advanced formatting scenarios, refer to the C# Excel formatting guide.
Q4. Is this compatible with ASP.NET Core and Web APIs?
Yes. The export logic works seamlessly in ASP.NET Core applications, Web APIs, background services, and other server-side .NET environments.
Export DataGrid and GridView to Excel in C# (Without Interop)
2026-02-03 08:05:39 Written by zaki zou
Exporting tabular data from UI controls to Excel is a common requirement in C# applications. In both WinForms and ASP.NET projects, users often need to take the data currently displayed in a DataGrid, DataGridView, or GridView and export it to an Excel file for reporting, sharing, or further processing.
In real-world scenarios, exported Excel files are rarely used as raw data only. Readable layouts, header styles, column widths, and number formats are usually expected as part of the export result.
This article demonstrates how to export DataGridView and GridView/DataGrid data to Excel in C# using Spire.XLS for .NET, without relying on Microsoft Office Interop. The solution focuses on exporting displayed data accurately, keeping the implementation clean, and applying Excel formatting in a consistent and reusable way.
Table of Contents
- Advantages of Programmatic Excel Export in C#
- Core Concept: Export Displayed Data via a DataTable
- Step 1: Extract Displayed Data into a DataTable
- Step 2: Export DataTable to Excel in C#
- Step 3: Apply Formatting to the Exported Excel File
- Performance and Practical Considerations
- Summary
- FAQ
Advantages of Programmatic Excel Export in C#
While Microsoft Office Interop can generate Excel files, using a programmatic approach in C# provides clear benefits for exporting data from DataGrid, DataGridView, or GridView:
- Does not require Microsoft Excel to be installed on the machine
- Suitable for server-side or cloud environments
- Maintains high performance even with large datasets
- Simplifies automation and background export scenarios
By exporting data directly via code, developers can create reliable, maintainable, and scalable Excel exports that work consistently across different application types.
Core Concept: Export Displayed Data via a DataTable
Although DataGrid, DataGridView, and GridView are UI controls, they serve the same fundamental purpose: displaying structured data in rows and columns. Attempting to export these controls directly often leads to UI-dependent logic and maintenance challenges.
A more reliable and reusable workflow is:
Displayed UI data → DataTable → Excel file
In this design:
- The DataTable represents exactly what the user sees
- The Excel export logic remains independent of the UI layer
- The same approach works for WinForms and ASP.NET applications
- Formatting and layout can be applied at the Excel level
The DataTable acts as a clean intermediate structure rather than the final export target, and using Spire.XLS for .NET, DataTable can be easily exported to a well-formatted Excel file.
Step 1: Extract Displayed Data into a DataTable
The first step is to extract the currently displayed data from the UI control into a DataTable. This step focuses on capturing visible rows and columns, not on reconstructing the original data source.
Export Displayed Data from DataGridView (WinForms)
In WinForms applications, users typically expect the DataGridView content to be exported as it appears on screen. The following method converts the displayed DataGridView data into a DataTable:
DataTable ConvertDataGridViewToDataTable(DataGridView dgv)
{
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
foreach (DataGridViewColumn column in dgv.Columns)
{
dt.Columns.Add(column.HeaderText, column.ValueType ?? typeof(string));
}
foreach (DataGridViewRow row in dgv.Rows)
{
if (row.IsNewRow) continue;
DataRow dr = dt.NewRow();
for (int i = 0; i < dgv.Columns.Count; i++)
{
dr[i] = row.Cells[i].Value ?? DBNull.Value;
}
dt.Rows.Add(dr);
}
return dt;
}
This approach preserves column headers, column order, and displayed values when exporting DataGridView data to Excel in C#.
Export Displayed Data from GridView (ASP.NET)
In ASP.NET applications, GridView controls render tabular data for users to view and interact with. To export the displayed GridView data, the rendered rows can be converted into a DataTable as shown below:
DataTable ConvertGridViewToDataTable(GridView gv)
{
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
foreach (TableCell cell in gv.HeaderRow.Cells)
{
dt.Columns.Add(cell.Text);
}
foreach (GridViewRow row in gv.Rows)
{
DataRow dr = dt.NewRow();
for (int i = 0; i < row.Cells.Count; i++)
{
dr[i] = row.Cells[i].Text;
}
dt.Rows.Add(dr);
}
return dt;
}
This method provides a consistent data structure that can be reused for exporting GridView data to Excel in C#, without introducing UI-specific export logic.
If you need to export data directly from a database to an Excel file, you can refer to this guide: Export Database to Excel in C#.
Step 2: Export DataTable to Excel in C#
Once the displayed data has been extracted into a DataTable, exporting it to Excel becomes a UI-independent operation.
In this example, Spire.XLS for .NET is used to generate Excel files programmatically, without requiring Microsoft Excel to be installed.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
Spire.XLS for .NET can be installed via NuGet:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
You can also download Spire.XLS for .NET and add it to your project manually.
Basic Excel Export Example
using Spire.Xls;
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Import DataTable into Excel, including column headers
worksheet.InsertDataTable(exportTable, true, 1, 1);
// Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("ExportedData.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
Below is a preview of the exported Excel file:
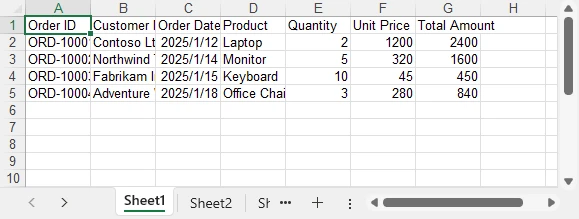
This export logic can be reused for DataGrid, DataGridView, and GridView scenarios without modification.
Step 3: Apply Formatting to the Exported Excel File
Formatting is a common requirement for Excel exports, regardless of how the data was sourced. Applying styles, adjusting column widths, and setting number formats significantly improves the usability of the exported file.
The following example demonstrates common formatting operations that can be applied to any exported Excel worksheet:
CellStyle headerStyle = workbook.Styles.Add("HeaderStyle");
headerStyle.Font.IsBold = true;
headerStyle.Font.Size = 13;
headerStyle.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
headerStyle.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
headerStyle.Color = Color.LightGray;
// Apply header style
CellRange headerRange = worksheet.Range[1, 1, 1, worksheet.AllocatedRange.Rows[0].CellsCount];
headerRange.Style = headerStyle;
// Auto-fit columns
worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
// Format date and currency columns
worksheet.Range[$"C2:C{worksheet.AllocatedRange.RowCount}"].NumberFormat = "yyyy-mm-dd";
worksheet.Range[$"F2:G{worksheet.AllocatedRange.RowCount}"].NumberFormat = "$#,##0.00";Below is a preview of the Excel file after applying formatting:
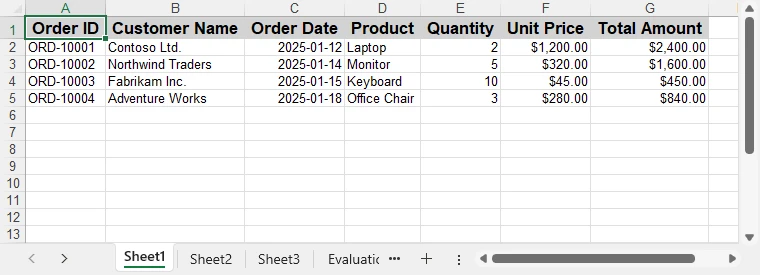
These formatting steps can be combined or extended based on reporting requirements, without changing the data extraction logic.
Spire.XLS for .NET also supports more Excel formatting features, such as conditional formatting, charts, and more. You can check How to Create Excel Files in C# for more formating options.
Performance and Practical Considerations
When exporting large DataGrid or GridView datasets:
- Run export operations asynchronously in desktop applications
- Avoid blocking the UI thread during Excel generation
- Export only necessary or visible columns
- Generate Excel files server-side in ASP.NET applications
Because the export process operates on a DataTable rather than UI elements, it remains maintainable and scalable as data volume increases.
Summary
Exporting DataGrid, DataGridView, or GridView data to Excel in C# does not require Microsoft Office Interop. By extracting the displayed data into a DataTable and generating Excel files programmatically, developers can implement reliable and reusable Excel export functionality.
With consistent formatting support and a clear separation between UI and export logic, this approach works well for real-world reporting scenarios in both desktop and web applications. For evaluating the library or testing export functionality, you can apply for a temporary license.
FAQ
Q1: How can I export DataGridView data to Excel in C#?
A1: You can extract the displayed data from a DataGridView into a DataTable and then use Spire.XLS for .NET to generate an Excel file programmatically, without relying on Microsoft Excel.
Q2: Can I apply formatting when exporting GridView to Excel in C#?
A2: Yes, Spire.XLS allows you to apply styles, adjust column widths, and set number formats to any exported Excel worksheet, ensuring readable and professional-looking reports.
Q3: Do I need Microsoft Excel installed to export DataGrid or GridView data in C#?
A3: No. By using a programmatic library like Spire.XLS, Excel files can be generated directly from DataTable objects without requiring Excel on the machine, making it suitable for server-side and cloud applications.
Working with Data in C#: Exporting DataSet to Excel Made Easy
2025-09-05 09:30:38 Written by zaki zou
In C# development, DataSet is widely used to manage in-memory data, often as a result of database queries or integration processes. There are many scenarios where you may need to create Excel files from DataSet in C# — for example, generating reports, sharing structured data with non-developers, or archiving records for future reference.
In this guide, we’ll walk through different approaches to export DataSet to Excel in C# using Spire.XLS for .NET, including creating an Excel file, writing multiple DataTables into separate sheets, applying formatting, and handling large data volumes.
Here's what's covered in this guide:
- DataSet Basics and Environment Setup
- Creating an Excel File from DataSet in C#
- Adding Formatting to Excel Sheets Using C#
- Handling Large DataSet Exports
- Read Excel into DataSet in C#
- Conclusion
- FAQ
1. DataSet Basics and Environment Setup for Excel Export
What is a DataSet?
A DataSet in C# is an in-memory representation of structured data. It can hold multiple DataTables, including their rows, columns, and relationships, making it useful for working with relational-style data without direct database connections.
Why Export DataSet to Excel?
- Data exchange – Excel is widely supported and easy to share across teams.
- Data analysis – Analysts can manipulate Excel data directly using formulas, pivot tables, and charts.
- Archiving – Storing query results or processed data in a readable, portable format.
Compared to raw text or CSV, Excel supports rich formatting, multiple sheets, and better readability.
Environment Setup
To export a DataSet to an Excel file in C#, we will use Spire.XLS for .NET, which provides APIs for handling Excel files. Install Spire.XLS via NuGet:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Add the required namespaces:
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing; // for Color
2. Creating an Excel File from DataSet in C#
Exporting a DataSet to Excel involves two key steps: preparing the data and writing it into a workbook. In practice, the DataSet may come from queries or APIs, but for clarity, we’ll demonstrate with a simple example. First, we’ll build a DataSet in memory, then show how to export it into an Excel file where each DataTable becomes its own worksheet.
2.1 Initialize a DataSet with Sample Data
First, we’ll build a DataSet using C#. The following sample DataSet contains multiple business-style tables and a variety of column types (int, string, DateTime, decimal).
using System;
using System.Data;
class Program
{
static DataSet CreateSampleDataSet()
{
DataSet ds = new DataSet("CompanyData");
// Employees
DataTable employees = new DataTable("Employees");
employees.Columns.Add("ID", typeof(int));
employees.Columns.Add("Name", typeof(string));
employees.Columns.Add("DepartmentID", typeof(int));
employees.Columns.Add("HireDate", typeof(DateTime));
employees.Columns.Add("Salary", typeof(decimal));
employees.Rows.Add(1, "Alice", 101, new DateTime(2020, 5, 12), 5500.00m);
employees.Rows.Add(2, "Bob", 102, new DateTime(2019, 3, 8), 7200.50m);
employees.Rows.Add(3, "Charlie", 103, new DateTime(2021, 11, 20), 4800.75m);
// Departments
DataTable departments = new DataTable("Departments");
departments.Columns.Add("DepartmentID", typeof(int));
departments.Columns.Add("DepartmentName", typeof(string));
departments.Rows.Add(101, "HR");
departments.Rows.Add(102, "IT");
departments.Rows.Add(103, "Finance");
// Projects
DataTable projects = new DataTable("Projects");
projects.Columns.Add("ProjectID", typeof(int));
projects.Columns.Add("ProjectName", typeof(string));
projects.Columns.Add("OwnerID", typeof(int));
projects.Columns.Add("StartDate", typeof(DateTime));
projects.Rows.Add(1001, "Recruitment System", 1, new DateTime(2023, 1, 15));
projects.Rows.Add(1002, "ERP Upgrade", 2, new DateTime(2023, 4, 10));
projects.Rows.Add(1003, "Budget Planning", 3, new DateTime(2023, 7, 5));
ds.Tables.Add(employees);
ds.Tables.Add(departments);
ds.Tables.Add(projects);
return ds;
}
}
2.2 Export DataSet to Excel File
With the DataSet prepared, the next step is generating the Excel file. This involves creating a Workbook, iterating through the DataTables, inserting them into worksheets, and saving the workbook to an Excel file.
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
DataSet ds = CreateSampleDataSet();
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Export each DataTable as a separate worksheet
for (int i = 0; i < ds.Tables.Count; i++)
{
Worksheet sheet = (i == 0)
? workbook.Worksheets[0]
: workbook.Worksheets.Add(ds.Tables[i].TableName);
sheet.InsertDataTable(ds.Tables[i], true, 1, 1);
sheet.Name = ds.Tables[i].TableName; // ensure sheet is named after the table
}
workbook.SaveToFile("DatasetToExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
About the Exporting Process
- Each DataTable is written into a separate worksheet.
- InsertDataTable(DataTable table, bool columnHeaders, int row, int column) inserts data starting from a specific cell.
- SaveToFile() writes the workbook to disk in the specified format.
In addition to creating separate worksheets for each DataTable, you can also insert multiple DataTables into the same worksheet by adjusting the starting row and column parameters of the InsertDataTable method.
Result preview
Below is a quick preview of the output workbook showing three sheets populated from the DataSet.
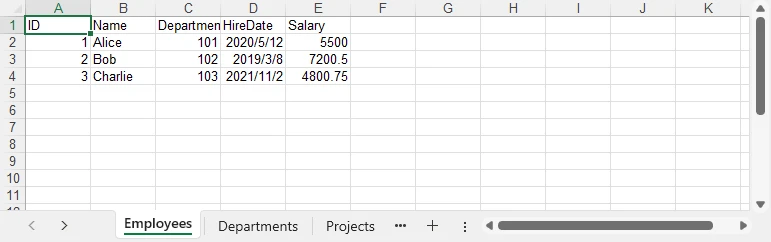
For a practical example of exporting data directly from a database to Excel, see our guide on Export Database to Excel in C#.
3. Adding Formatting to Excel Sheets Using C#
Raw data often isn’t enough for reporting. Formatting improves readability and makes the Excel file more professional. With Spire.XLS, you can style fonts, apply background colors, add borders, and format numbers and dates.
using System.Drawing;
using Spire.Xls;
// Get the first sheet
Worksheet sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets["Employees"];
// 1) Header styling (A1:E1)
CellRange header = sheet1.AllocatedRange.Rows[0];
header.Style.Font.IsBold = true;
header.Style.Font.Size = 12;
header.Style.Font.Color = Color.White;
header.Style.Color = Color.SteelBlue;
// Borders around the header row
header.BorderAround(LineStyleType.Thin);
// 2) Number formats for entire columns (D: HireDate, E: Salary)
sheet1.AllocatedRange.Columns[3].Style.NumberFormat = "yyyy-mm-dd";
sheet1.AllocatedRange.Columns[4].Style.NumberFormat = "$#,##0.00";
// 3) Optional: zebra stripes for data area (A2:E4 here as example)
CellRange data = sheet1.Range["A2:E4"];
// CellRange data = sheet1.Range[2, 1, 4, 5];
data.Style.Color = Color.FromArgb(245, 247, 250);
data.BorderAround(LineStyleType.Thin);
// Auto-fit after formatting
sheet1.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
sheet1.AllocatedRange.AutoFitRows();
How Formatting Works
- Style.Font — font properties such as IsBold, Size, Color.
- Style.Color — background fill color for the selected range.
- Borders / BorderAround — draw borders on edges/around ranges with LineStyleType.
- NumberFormat — Excel-native formats (e.g., dates, currency, percentages).
- AutoFitColumns() / AutoFitRows() — adjust column widths / row heights to fit content.
For more formatting options, refer to the API reference for CellRange and CellStyle.
Formatting preview
The following image shows styled headers, borders, and proper date/currency formats applied.
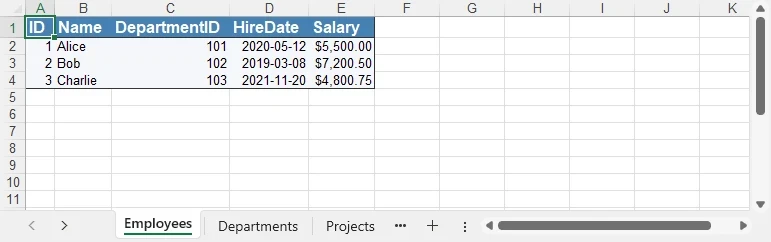
4. Handling Large DataSet Exports
When exporting large datasets, performance and memory become critical. Consider:
- Split across sheets — When rows approach Excel/version limits or for logical separation.
- Batch writing — Insert data in segments (e.g., table-by-table or range-by-range).
- Lightweight formatting — Minimize heavy styling to reduce file size and processing time.
- Streaming (where applicable) — Prefer APIs that avoid loading everything into memory at once.
5. Bonus: Read Excel into DataSet in C#
In addition to exporting, the reverse workflow is equally important: reading Excel data back into a DataSet for processing or migration. This is useful when importing data from external reports, integrating spreadsheets with applications, or performing preprocessing before database insertion.
using System.Data;
using Spire.Xls;
class Program
{
static DataSet ReadExcelIntoDataSet(string filePath)
{
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile(filePath);
foreach (Worksheet sheet in workbook.Worksheets)
{
DataTable dt = sheet.ExportDataTable();
dt.TableName = sheet.Name;
ds.Tables.Add(dt);
}
return ds;
}
}
The ExportDataTable method allows each worksheet to be converted into a DataTable object, preserving both the structure and the cell values. By assigning the sheet name to TableName and adding it into a DataSet, you can combine multiple sheets into a single in-memory data container that is ready for further processing.
For a complete workflow on persisting Excel data into a database, see our guide on Import Excel into Database in C#.
Conclusion
Exporting a DataSet to Excel in C# allows you to generate reports, share data, and make information easier to analyze or present. With Spire.XLS for .NET, you can create Excel files directly from DataSet objects, apply formatting, manage multiple sheets, and handle large datasets efficiently. You can also import Excel data back into a DataSet for integration with applications or databases.
To explore more advanced features, you may request a free temporary license or use Free Spire.XLS for .NET for smaller projects.
FAQ: C# DataSet and Excel Integration
Q1: How can I export multiple DataTables from a DataSet into different Excel sheets?
Loop through ds.Tables and call InsertDataTable for each one, creating a new worksheet per DataTable.
Q2: Can I export a DataSet to a specific worksheet in an existing Excel file?
Yes. Load the file using Workbook.LoadFromFile(), then choose the worksheet and use InsertDataTable.
Q3: Does exporting DataSet to Excel preserve column formatting and data types?
Values are exported with the same data types as in the DataSet. You can also apply formatting (date, currency, alignment, etc.) after inserting.
Q4: How do I handle very large DataSet exports (over 100,000 rows)?
Split into multiple sheets, use batch inserts, and reduce complex formatting to improve performance.
Export Database to Excel in C#: Practical Guide with SQL Example
2025-08-06 01:59:33 Written by zaki zou
Exporting data from a database to Excel using C# is a frequent requirement in business applications—be it for internal reporting, audit logs, data migration, or ad-hoc analysis. Excel's portability and familiarity make it a go-to format for sharing structured data with both technical and non-technical users.
In this guide, you'll learn how to export database records to Excel using C# and Spire.XLS for .NET. We’ll walk through retrieving data from a SQL Server database and writing it into a well-formatted Excel file. The same workflow applies to other relational databases such as SQLite, MySQL, or Oracle with only minimal adjustments.
Table of Contents:
- Prerequisites and Environment Setup
- Exporting Data from SQL Database to Excel in C#
- Format the Excel Output
- Alternative Approaches to Read Data
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Prerequisites and Environment Setup
Before we dive into code, ensure your development environment is ready:
-
.NET Version: .NET Framework or .NET Core / .NET 6 / .NET 8
-
IDE: Visual Studio (Community or higher)
-
Database: A relational database (e.g., SQL Server, SQLite, MySQL, Oracle). This tutorial uses SQL Server Express as the example. By default, the connection uses Windows Authentication, but you can switch to SQL Authentication if needed.
-
Libraries:
- Spire.XLS for .NET (Install via NuGet: Install-Package Spire.XLS)
- Microsoft.Data.SqlClient (Install via NuGet if using SQL Server)
Sample Data
In the following examples, we'll use a simple Employees table stored in SQL Server Express. Here's the SQL script to create and populate it:
CREATE TABLE Employees (
Id INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY,
Name NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
Department NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
Position NVARCHAR(50),
HireDate DATE NOT NULL,
Salary DECIMAL(10, 2) NOT NULL,
IsFullTime BIT NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO Employees (Name, Department, Position, HireDate, Salary, IsFullTime) VALUES
('Alice Johnson', 'Human Resources', 'HR Manager', '2018-05-01', 5500.00, 1),
('Bob Smith', 'IT', 'Software Engineer', '2020-09-15', 7200.50, 1),
('Charlie Lee', 'Finance', 'Accountant', '2019-11-20', 6300.75, 0),
('Diana Chen', 'Marketing', 'Content Specialist', '2021-02-10', 4800.00, 1);
If you're using another database system like MySQL or SQLite, just adjust the SQL syntax and connection string accordingly. The export logic remains the same.
Exporting Data from SQL Database to Excel in C#
Let’s walk through how to retrieve data from a database and export it to an Excel file using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Step 1: Connect to the SQL Server Database
We start by establishing a connection to the database using SqlConnection. Here's an example connection string targeting SQL Server Express:
string connectionString = @"Data Source=YourServer\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=YourDatabaseName;Integrated Security=True;";
The above connection string uses Windows Authentication (Integrated Security=True). If you prefer SQL Server Authentication, replace it with: User ID=yourUsername;Password=yourPassword;Encrypt=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;
Make sure that your SQL Server Express instance is running, and that the specified database and table exist.
Step 2: Retrieve Data into a DataTable
To make the data ready for export, we use SqlDataAdapter to fill a DataTable with the results of a SQL query:
using System.Data;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
conn.Open();
string query = "SELECT * FROM Employees";
using (SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter(query, conn))
{
adapter.Fill(dataTable);
}
}
Spire.XLS can directly import data from a DataTable using InsertDataTable, which makes it ideal for structured exports from relational databases.
Step 3: Export the DataTable to Excel Using Spire.XLS
Once the DataTable is populated, we can use Spire.XLS to write its contents into a new Excel worksheet:
using Spire.Xls;
// Create a new workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Clear the default sheets and create a new one
workbook.Worksheets.Clear();
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Employees");
// Insert data starting from row 1, column 1, and include column headers
sheet.InsertDataTable(dataTable, true, 1, 1);
// Save the workbook as an Excel xlsx file
workbook.SaveToFile("Employees.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
Key classes and methods used:
- Workbook: The main entry point for creating or loading Excel files.
- Worksheet: Represents a single sheet in the workbook. Use workbook.Worksheets[] to access a sheet, or Worksheets.Add() to add more.
- InsertDataTable(DataTable dataTable, bool columnHeaders, int firstRow, int firstColumn):
- columnHeaders = true tells Spire.XLS to write column names as the first row.
- firstRow, firstColumn specify where the data begins (1-based index).
- Workbook.SaveToFile(string fileName, ExcelVersion version): Saves the workbook to a file. Spire.XLS supports saving Excel workbooks to various formats, including .xlsx, .xls, and .csv. You can also save to a stream using SaveToStream().
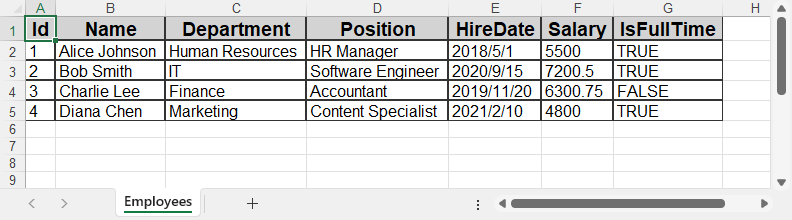
Here’s what the resulting Excel file looks like with the raw data exported from the database.
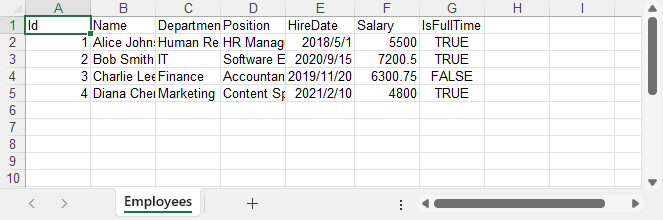
Step 4: Format the Excel Output (Optional but Recommended)
While the data is already exported, applying some formatting can significantly improve readability for end users:
// Write data to Excel, including column names, starting at row 1, column 1
sheet.InsertDataTable(dataTable, true, 1, 1);
// Make header row bold and highlight with background color
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Font.Size = 14;
sheet.Rows[0].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Color = System.Drawing.Color.LightGray;
// Format data rows
for (int i = 1; i < sheet.Rows.Count(); i++)
{
CellRange dataRow = sheet.Rows[i];
dataRow.Style.Font.Size = 12;
dataRow.Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left;
}
// Set font name
sheet.AllocatedRange.Style.Font.FontName = "Arial";
// Set borders
sheet.AllocatedRange.BorderAround(LineStyleType.Thin, System.Drawing.Color.Black);
sheet.AllocatedRange.BorderInside(LineStyleType.Medium, System.Drawing.Color.Black);
// Auto-fit columns
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
Here's what the Excel file looks like after formatting.
Spire.XLS provides full access to cell styles, fonts, colors, borders, alignment, and more—making it suitable for generating production-quality Excel reports.
If you need advanced number formatting, learn how to set number formats for Excel cells using C#.
Alternative Approaches to Read Data
The export process relies on having a DataTable, but how you populate it can vary based on your application architecture:
A. Using Entity Framework (ORM)
If you use EF Core or EF6, you can load data via LINQ and manually insert it into Excel:
var employees = dbContext.Employees.ToList();
To export, either convert this list into a DataTable, or use a loop to write rows manually using sheet.Range[row, col].Value = value.
B. Using Stored Procedures
Stored procedures allow encapsulating SQL logic. You can execute them using SqlCommand and fill the result into a DataTable:
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("GetEmployees", conn);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
C. Reading from SQLite
For lightweight scenarios, replace the connection string and class:
using (SQLiteConnection conn = new SQLiteConnection("Data Source=mydb.db"))
Export logic remains identical—fill a DataTable and use InsertDataTable.
D. Reading from MySQL or Oracle
Same pattern applies—just change the connection class:
using (MySqlConnection conn = new MySqlConnection("server=localhost;uid=root;pwd=123;database=test"))
Make sure to install the appropriate ADO.NET data provider (e.g., Microsoft.Data.SqlClient, Microsoft.Data.Sqlite, or MySql.Data) via NuGet when connecting to different databases.
As long as you populate a DataTable, Spire.XLS handles the Excel generation the same way.
You may also like: How to Import Data from Excel to Database – learn how to complete the full data exchange cycle using Spire.XLS.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Excel file opens empty | Ensure the DataTable has data before calling InsertDataTable() |
| Access denied on save | Check folder permissions or file path conflicts |
| Connection fails | Verify your database server, credentials, and connection string |
| Special characters not displaying | Use NVARCHAR in SQL and Unicode-compatible fonts in Excel |
| Login failed or authentication error | Check authentication method: use Integrated Security=True for Windows, or provide User ID and Password for SQL Authentication. |
Conclusion
Exporting a database to Excel in C# can be done efficiently using Spire.XLS for .NET. By retrieving data into a DataTable and exporting it with InsertDataTable(), you can automate reporting and data extraction without needing Microsoft Office installed.
This solution can also be integrated into scheduled tasks, background services, or web applications for automated report generation.
To unlock all features during development or testing, you can apply for a free 30-day temporary license. For smaller projects, Free Spire.XLS for .NET may also be sufficient.
FAQ
How do I export SQL to Excel in C#?
Use SqlConnection to retrieve data into a DataTable, and export it using Spire.XLS’s InsertDataTable() method.
Can I use this method with SQLite or MySQL?
Yes. Just change the connection type and query, then pass the resulting DataTable to Spire.XLS.
Do I need Excel installed to use Spire.XLS?
No. Spire.XLS is a standalone library and does not require Microsoft Excel on the machine.
Can I export multiple tables to Excel?
Yes. Use Workbook.Worksheets.Add() to create additional worksheets, and export each DataTable separately.
Exporting a DataTable to Excel in C# is a common task in .NET development, such as generating reports, exporting logs, or preparing data for sharing across systems. By using a standalone component, developers can quickly export data and apply formatting to create professional, ready-to-use Excel files from DataTables without relying on complex setup or external dependencies.
To streamline this process, Spire.XLS for .NET offers a lightweight and fully independent library. In this article, you'll learn how to export a DataTable to Excel (.xlsx or .xls) in C#, apply formatting to improve readability, and address common export scenarios effectively.
Quick Navigation
- Install and Configure Spire.XLS
- Step-by-Step: Export DataTable to Excel
- Format and Style the Exported Excel File
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Install and Configure Spire.XLS
Before you start, make sure your project includes Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS via NuGet
Run this command in the NuGet Package Manager Console:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Spire.XLS works with .NET Framework, .NET Core, .NET 6/7+, and ASP.NET projects — no Microsoft Office installation required.
Step-by-Step: Export DataTable to Excel in C#
The following steps demonstrate how to export a DataTable to an Excel file using Spire.XLS, including data preparation, file generation, optional streaming, and output formatting.
1. Create a Sample DataTable
First, create a DataTable and add some sample rows:
DataTable dt = new DataTable("Employees");
// Insert columns
dt.Columns.Add("ID", typeof(int));
dt.Columns.Add("Name", typeof(string));
dt.Columns.Add("Department", typeof(string));
dt.Columns.Add("Join Date", typeof(DateTime));
dt.Columns.Add("Salary", typeof(double));
dt.Columns.Add("Full-Time", typeof(bool));
dt.Columns.Add("Bonus Rate", typeof(decimal));
// Insert rows
dt.Rows.Add(1001, "Alice", "HR", new DateTime(2021, 5, 10), 55000.5, true, 0.05m);
dt.Rows.Add(1002, "Bob", "IT", new DateTime(2020, 11, 23), 72000.0, false, 0.03m);
dt.Rows.Add(1003, "Carol", "Finance", new DateTime(2019, 8, 15), 63000.75, true, 0.07m);
dt.Rows.Add(1004, "David", "Marketing", new DateTime(2022, 3, 8), 48800.0, true, 0.06m);
Tip: This is just sample data — you can bind any DataTable your app generates.
2. Import DataTable and Save to Excel File
Next, initialize the Excel workbook, import the DataTable into a worksheet, and save the file:
// Create a new workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Clear the default worksheets and add a new one
workbook.Worksheets.Clear();
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(dt.TableName);
// Import the DataTable starting at cell A1
sheet.InsertDataTable(dt, true, 1, 1);
// Save as XLSX (recommended)
workbook.SaveToFile("EmployeeData.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016);
// Or save as XLS (older format)
workbook.SaveToFile("EmployeeData.xls", FileFormat.Version97to2003);
Explanation:
- Workbook is the container for your Excel file.
- InsertDataTable(dataTable, includeColumnHeaders, startRow, startColumn) maps the entire table to the Excel grid.
- SaveToFile() writes the file to disk in your chosen format.
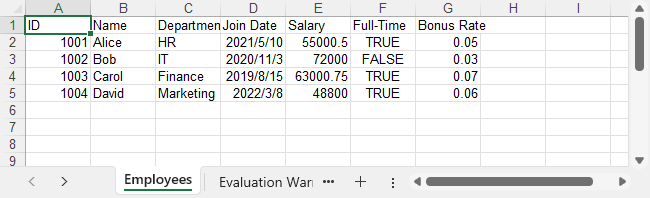
Output Preview
Example of the exported Excel file:
3. Export Excel File as Stream in ASP.NET
When building a web app, you might want to export the file directly as a stream instead of saving to disk:
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
workbook.SaveToStream(stream, FileFormat.Version2013);
stream.Position = 0;
Return this MemoryStream in your ASP.NET controller to trigger a file download in the browser.
For additional tips on managing Excel files in C#, check out How to Create and Manipulate Excel Files in C#.
Format and Style the Exported Excel File
Formatting is optional but recommended for creating professional Excel files. Below is how you can format the exported content using Spire.XLS.
// Style the header row
CellRange header = sheet.Rows[0];
header.Style.Font.IsBold = true;
header.Style.Font.FontName = "Arial";
header.Style.Font.Size = 13;
header.Style.Color = Color.LightGray;
header.Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thick;
// Style the data rows
for (int i = 1; i < sheet.Rows.Length; i++)
{
CellRange dataRow = sheet.Rows[i];
dataRow.Style.Font.FontName = "Times New Roman";
dataRow.Style.Font.Size = 11;
dataRow.BorderInside();
}
// Format date column to display as date
CellRange dateColumn = sheet.Range[2, 4, sheet.Rows.Length + 1, 4];
dateColumn.Style.NumberFormat = "yyyy-mm-dd";
// Auto-fit columns
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
Key Properties and Methods:
- Style: Applies font, color, border, number formatting, etc. to cells.
- AutoFitColumns(): Automatically adjusts column width to fit content.
- NumberFormat: Sets how dates or numbers are displayed in Excel, e.g., "yyyy-mm-dd".
- BorderInside(): Adds internal borders to improve table readability.
Formatted Output Preview
Excel file with formatted header and date column:
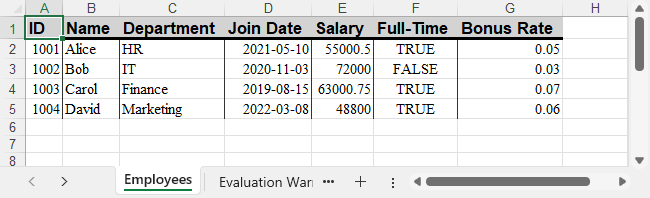
For more advanced number formatting options, see how to set number format in Excel using C#.
Common Issues and Solutions
- File won’t open or shows corruption error
Ensure streams are closed properly and file extensions match the format.
- Special characters or non-English text look garbled
Confirm strings are UTF-8 encoded and use appropriate fonts.
- Columns too narrow
Use AutoFitColumns() to adjust widths automatically or use CellRange.ColumnWidth to set a fixed column width.
Conclusion
Exporting a DataTable to Excel in C# is straightforward with Spire.XLS. This approach lets you create .xlsx or .xls files easily without relying on Office, while giving you full control over the output layout for both desktop and web applications.
If needed, you can also request a free temporary license to unlock the full feature set for evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How to convert DataTable to Excel in C#?
You can use sheet.InsertDataTable() from Spire.XLS to load a DataTable into a worksheet, then save it as an Excel file using workbook.SaveToFile().
Q2: Is there a free library to export a DataTable to Excel in C#?
Yes — Free Spire.XLS for .NET is a standalone library that lets you create and export Excel files directly in C# without needing to install Microsoft Office.
Q3: Can I export DataTable to Excel in ASP.NET?
Yes, the same logic can be applied in ASP.NET by generating the workbook in a controller and streaming it back as a downloadable file.
Q4: What's the difference between .xlsx and .xls export?
.xlsx is the newer Office Open XML format, compatible with Excel 2007 and later. .xls supports legacy Excel 97–2003 but is limited to 65,536 rows.
Efficiently integrating data between systems is vital for boosting productivity and informed decision-making. A common task in this area is transferring data between Excel and databases. Importing Excel files into a database enables businesses to utilize powerful features like efficient queries, transaction support, and concurrency control, which Excel lacks. Conversely, exporting database data to Excel allows for detailed analysis, reporting, and sharing in a widely used and familiar format. In this article, we will explore how to import Excel data into databases and export data from databases into Excel files using Spire.XLS for .NET with C#.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Import Excel Data into Databases with C#
With the help of Spire.XLS for .NET, we can use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel file and then access the cell data using CellRange.Value property. Subsequently, we can utilize the relevant database operation modules, such as the System.Data.SQLite module for SQLite, to write the data into the database. This approach enables the seamless import of data from an Excel file into a database.
The following steps and code use SQLite as an example to demonstrate how to import Excel data into a database using C#:
- Define the path for the Excel file and the output database.
- Create an instance of Workbook class and load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a new SQLite database or connect to an existing database.
- Iterate through each worksheet in the workbook and create a table in the database for each worksheet.
- Get the cells in the first row through Worksheet.Rows.CellList property.
- Iterate through the cells to get their values through CellRange.Value property, and use these values as the column names of the database table.
- Iterate through the rest rows and cells, and insert them as values into the database.
- Close the database connection and release resources.
- C#
using System.Data.SQLite;
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ExcelToSQLite
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Excel file path
string excelFilePath = "Sample.xlsx";
// SQLite database path
string sqliteFilePath = "output/Database.db";
// Open the Excel file
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile(excelFilePath);
// If the database file doesn't exist, create it
if (!File.Exists(sqliteFilePath))
{
SQLiteConnection.CreateFile(sqliteFilePath);
Console.WriteLine("A new SQLite database file has been created: output.db");
}
// Create SQLite connection
using (SQLiteConnection connection = new SQLiteConnection($"Data Source={sqliteFilePath};Version=3;"))
{
connection.Open();
// Iterate through each worksheet
foreach (Worksheet sheet in workbook.Worksheets)
{
string tableName = sheet.Name;
// Get the first row as column names
var columns = sheet.Rows[0].CellList;
string createTableQuery = $"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS [{tableName}] (";
foreach (var column in columns)
{
createTableQuery += $"[{column.Value}] TEXT,";
}
createTableQuery = createTableQuery.TrimEnd(',') + ");";
// Create table
using (SQLiteCommand createTableCommand = new SQLiteCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createTableCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
// Insert data
for (int i = 1; i < sheet.Rows.Length; i++) // Skip the first row
{
var row = sheet.Rows[i];
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO [{tableName}] VALUES (";
foreach (var cell in row.CellList)
{
insertQuery += $"'{cell.Value?.Replace("'", "''")}',"; // Prevent SQL injection
}
insertQuery = insertQuery.TrimEnd(',') + ");";
using (SQLiteCommand insertCommand = new SQLiteCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
connection.Close();
workbook.Dispose();
}
Console.WriteLine("Excel data has been successfully written to the new SQLite database!");
}
}
}
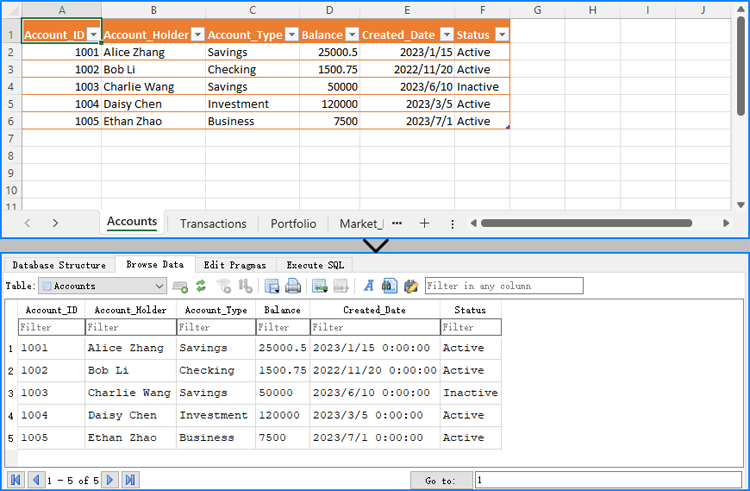
Export Data from Databases into Excel Files with C#
Similarly, we can use the database handling module to read data from the database. Then, by creating a Workbook object, we can generate an Excel file and use the CellRange.Value property to write the data into the Excel file. This allows us to export data from the database to an Excel file.
The following steps and code use an SQLite database as an example to demonstrate how to export data from a database to an Excel file.
- Define the path for the database and the output Excel file.
- Create a Workbook instance to create a new Excel workbook and clear the default worksheets using Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Connect to the database and get all the table names.
- Create a worksheet for each table with the table names as sheet names using Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Get the column names in the tables and write them to the first row of the worksheet through Worksheet.Range[].Value property.
- Get the data in the table and write it to the worksheet sequentially through Worksheet.Range[].Value property.
- Format the worksheet through CellRange.Style property if needed.
- Close the database connection and save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SQLite;
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SQLiteToExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// SQLite database path
string sqliteFilePath = "Sample.db";
// Excel file path
string excelFilePath = "output/DatabaseToExcel.xlsx";
// Create a new Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Clear the default worksheet
workbook.Worksheets.Clear();
// Create SQLite connection
using (SQLiteConnection connection = new SQLiteConnection($"Data Source={sqliteFilePath};Version=3;"))
{
connection.Open();
// Get all table names
DataTable tables = connection.GetSchema("Tables");
// Iterate through each table
foreach (DataRow tableRow in tables.Rows)
{
string tableName = tableRow["TABLE_NAME"].ToString();
// Create a new worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(tableName);
// Get table data
string selectQuery = $"SELECT * FROM [{tableName}]";
using (SQLiteCommand command = new SQLiteCommand(selectQuery, connection))
{
using (SQLiteDataReader reader = command.ExecuteReader())
{
// Get column names and write them in the first row
for (int col = 0; col < reader.FieldCount; col++)
{
sheet.Range[1, col + 1].Value = reader.GetName(col);
}
// Set the font style for the header
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Font.Size = 12;
// Write data rows
int rowIndex = 2;
while (reader.Read())
{
for (int col = 0; col < reader.FieldCount; col++)
{
sheet.Range[rowIndex, col + 1].Value = reader.GetValue(col).ToString();
// Auto-fit column width
sheet.AutoFitColumn(col + 1);
}
// Set the font style for data rows
sheet.Rows[rowIndex - 1].Style.Font.Size = 11;
rowIndex++;
}
}
}
}
connection.Close();
}
// Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile(excelFilePath);
workbook.Dispose();
Console.WriteLine("Data has been successfully exported to the Excel file!");
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
This section will show you an easy solution to quickly export datatable from database to Excel via an Excel .NET component in C#, VB.NET.
Spire.XLS for .NET enables you to both export datatable to excel and import excel to datatable. This solution shows you two lines of key souce code for exporting data from datatable to Excel. One is XlsWorksheet.InsertDataTable(System.Data.DataTable dataTable, bool columnHeaders, int firstRow, int firstColumn) which is responsible for importing the data into worksheet. The other is Workbook.SaveToFile(string fileName) that is called to save the workbook to Excel file.
Here you can download Spire.XLS for .NET and start to perform the datatable to Excel task by below code.
Sample code:
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//connect database
OleDbConnection connection = new OleDbConnection();
connection.ConnectionString @"Provider=""Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0"";Data Source=""demo.mdb"";User Id=;Password="
OleDbCommand command = new OleDbCommand();
command.CommandText = "select * from parts";
DataSet dataSet = new System.Data.DataSet();
OleDbDataAdapter dataAdapter = new OleDbDataAdapter(command.CommandText,connection);
dataAdapter.Fill(dataSet);
DataTable t = dataSet.Tables[0];
//export datatable to excel
Workbook book = new Workbook();
Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
sheet.InsertDataTable(t, true, 1, 1);
book.SaveToFile("insertTableToExcel.xls",ExcelVersion.Version97to2003);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("insertTableToExcel.xls");
}
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As System.Object, e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
//connect database
Dim connection As OleDbConnection = New OleDbConnection
connection.ConnectionString = “Provider=””Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0””;
Data Source=""demo.mdb""; User Id=;Password="
Dim command As OleDbCommand = New OleDbCommand
command.CommandText = "select * from parts"
Dim dataSet As DataSet = New System.Data.DataSet
Dim dataAdapter As OleDbDataAdapter = New OleDbDataAdapter(command.CommandText, connection)
dataAdapter.Fill(dataSet)
Dim t As DataTable = dataSet.Tables(0)
//export datatable to excel
Dim book As Workbook = New Workbook
Dim sheet As Worksheet = book.Worksheets(0)
sheet.InsertDataTable(t, True, 1, 1)
book.SaveToFile("insertTableToExcel.xls",ExcelVersion.Version97to2003)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("insertTableToExcel.xls")
End Sub
End Class
Convert Excel to DataTable in C#: Worksheets, Ranges & Beyond
2024-11-14 03:59:00 Written by hayes Liu
Working with Excel data is a common requirement in .NET development. Developers often need to convert Excel files into a DataTable, which provides a structured way to manipulate data, perform LINQ queries, bind to UI controls, or import into a database.
Although this task is common, the implementation details are not always straightforward. Converting Excel data into a DataTable in C# can be achieved in several ways, but traditional approaches often depend on OLEDB drivers or involve lengthy OpenXML programming, both of which add unnecessary complexity and external dependencies. In this guide, we’ll use Spire.XLS for .NET to simplify the process of importing Excel data into a DataTable with C# code. The library provides built-in methods to load Excel files, export worksheets or specific ranges, and work with the data directly in a DataTable.
Quick Navigation
- What is a DataTable and Why Use It?
- Preparing the Environment
- Converting Excel to DataTable in C#
- Bonus: Exporting DataTable Back to Excel
- Handling Large Excel Files and Performance Tips
- Best Practices
- Conclusion
- FAQ
What is a DataTable and Why Use It?
A DataTable in C# is a memory-resident representation of structured data. It allows developers to:
- Store Excel data in tabular form.
- Perform filtering, sorting, and LINQ queries.
- Bind to UI components like DataGridView.
- Bulk insert into relational databases.
Compared with DataSet, a DataTable is lightweight and especially well-suited for working with a single worksheet or range of data.
Preparing the Environment
Before starting, install Spire.XLS for .NET in your project. The easiest way is through NuGet:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Then, import the required namespaces in your C# code:
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
Converting Excel to DataTable in C#
The following sections demonstrate how to load an Excel file and convert its contents into a DataTable using Spire.XLS. Unlike older methods that depend on OLEDB, this library works without Microsoft Office installation, making it reliable for both desktop and server-side applications.
Load an Excel File
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
This creates a Workbook object from the specified Excel file, which you can then use to access individual worksheets.
Convert a Worksheet to DataTable
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
DataTable dataTable = sheet.ExportDataTable(sheet.AllocatedRange, true);
Here, the entire first worksheet is exported to a DataTable.
- sheet.AllocatedRange retrieves the used range of the worksheet.
- The true parameter means the first row will be treated as column headers.
This approach is useful when you want to import all data from a sheet directly into a DataTable, for example when binding to a DataGridView or performing bulk inserts into a database.
Convert a Specific Range to DataTable
DataTable partialTable = sheet.ExportDataTable(sheet.Range["A1:C10"], true);
This snippet converts only the range A1:C10 into a DataTable. It’s a practical choice when dealing with large Excel files, where only part of the sheet is needed for processing, or when extracting a specific report section.
Complete Example: Excel Worksheet to DataTable with C#
The following example demonstrates the entire workflow of loading an Excel file and converting it into a DataTable. After running this code, you can process the table further, such as querying, filtering, or inserting into a database.
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Load Excel file
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Convert first worksheet to DataTable
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
DataTable dataTable = sheet.ExportDataTable(sheet.AllocatedRange, true);
// Print row count
Console.WriteLine("Rows imported: " + dataTable.Rows.Count);
// Print column names
foreach (DataColumn col in dataTable.Columns)
{
Console.Write(col.ColumnName + "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// Print all rows
foreach (DataRow row in dataTable.Rows)
{
foreach (var item in row.ItemArray)
{
Console.Write(item + "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
This code loads the first worksheet from an Excel file, exports its content into a DataTable, and prints the table to the console. The following screenshot shows an example of the output:
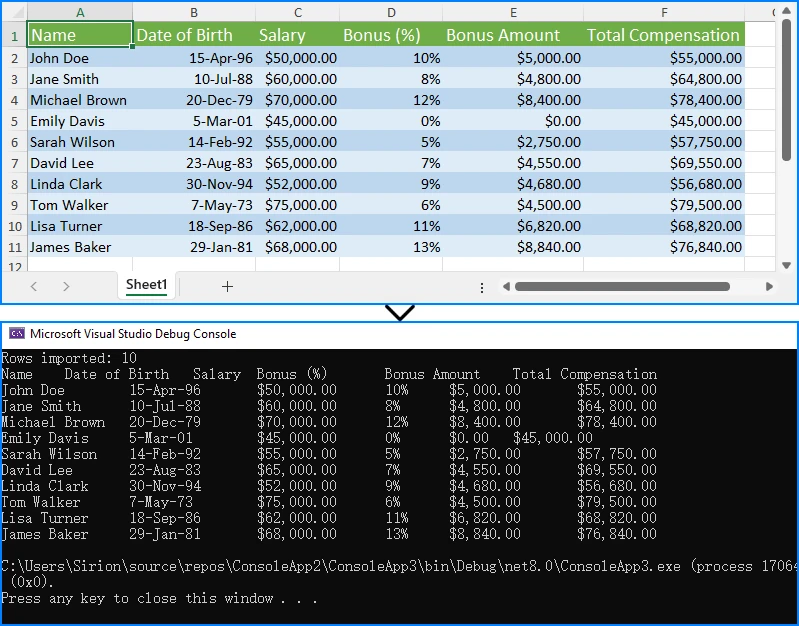
For scenarios where you need to read Excel data cell by cell, see our guide on reading Excel files in C#.
Bonus: Exporting DataTable Back to Excel in C#
In some cases, you may also need to write modified data from a DataTable back to Excel. This can be done easily:
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Assume dataTable is already populated
ws.InsertDataTable(dataTable, true, 1, 1);
wb.SaveToFile("Output.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
This code inserts the DataTable starting at cell A1 and saves the file. It demonstrates the reverse workflow, ensuring smooth two-way data exchange between Excel and C#. For more details, you can check How to Export DataTable into Excel in C#.
Handling Large Excel Files and Performance Tips
When working with large Excel files, performance optimization is key. Here are a few best practices:
- Read only the required worksheets instead of loading all.
- Export specific ranges rather than entire sheets if possible.
- Use stream-based methods (LoadFromStream) to avoid file locks.
- Minimize memory usage by processing rows iteratively when handling very large DataTables.
Spire.XLS supports .xls, .xlsx, and .csv formats consistently, making it suitable across different scenarios.
Best Practices
When converting Excel to DataTable, keep in mind:
- Data type handling: Excel stores values as text by default. Convert them to int, decimal, or DateTime as needed.
- Null or empty cells: Always check for missing values to prevent runtime errors.
- Database integration: Before bulk inserting into SQL Server or another database, validate and sanitize the DataTable.
Conclusion
Converting Excel data into a DataTable is a common but critical task in .NET development. With Spire.XLS for .NET, you can achieve this efficiently without relying on OLEDB drivers or complex OpenXML parsing.
Whether you need to convert an entire worksheet, extract a specific range, or write data back to Excel, the process remains straightforward and reliable. Mastering this workflow ensures smoother integration between Excel data and your C# applications.
If you want to unlock the full feature set of Spire.XLS, you can apply for a free temporary license. For smaller projects, you can also use Free Spire.XLS for .NET.
FAQ
Q: How do I import data from Excel to DataTable in C#?
Use Worksheet.ExportDataTable() to directly convert worksheet data into a DataTable.
Q: Can I read Excel into DataTable without OLEDB?
Yes. Spire.XLS does not require OLEDB or Microsoft Office installation.
Q: How to read only a specific worksheet or range into a DataTable?
Pass the target Worksheet or Range to ExportDataTable().
Q: Can I export a DataTable back to Excel in C#?
Yes. Use Worksheet.InsertDataTable() and then save the file with SaveToFile().
