Making PDF content accessible on the web enhances usability, searchability, and compatibility across devices. Whether you're developing a PDF viewer, automating document workflows, or republishing content online, converting PDF to HTML using Python can significantly improve the user experience.
This comprehensive guide demonstrates how to convert PDF to HTML using Python. It covers everything from basic conversions and advanced customization to stream-based output—each section includes practical, easy-to-follow code snippets to help you get started quickly.
Table of Contents
- Why Export PDF as HTML
- Install Python PDF to HTML Converter Library
- Basic PDF to HTML Conversion in Python
- Customize the HTML Output
- Save PDF to HTML Stream
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Export PDF as HTML?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the foundation of web content. By exporting PDFs into HTML, you enable seamless viewing, editing, and indexing of document content online. Key advantages include:
- Improved Web Accessibility: HTML renders natively in all browsers.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Search engines can index content better than in PDFs.
- Responsive Layouts: HTML adjusts to different screen sizes.
- Interactive Enhancements: HTML allows for styling, scripts, and better user interaction.
- Plugin-Free Viewing: No need for third-party PDF viewers.
Install Python PDF to HTML Converter Library
To start exporting PDFs to HTML using Python, you’ll need a reliable library that supports PDF processing and HTML export. For this tutorial, we’re using Spire.PDF for Python, a high-performance PDF library that supports reading, editing, and converting PDF files in various formats, including HTML, with minimal effort.
Installation
The library can be installed easily via pip. Open your terminal and run the following command:
pip install Spire.PDF
This will download and install the latest version of the package along with its dependencies.
Need help with the installation? Follow this step-by-step guide: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Basic PDF to HTML Conversion in Python
Spire.PDF makes it easy to export an entire PDF document to HTML using the SaveToFile() method.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Initialize a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load your PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Convert and save it as HTML
doc.SaveToFile("PdfToHtml.html", FileFormat.HTML)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
This approach generates a single HTML file that preserves the layout and structure of the original PDF.
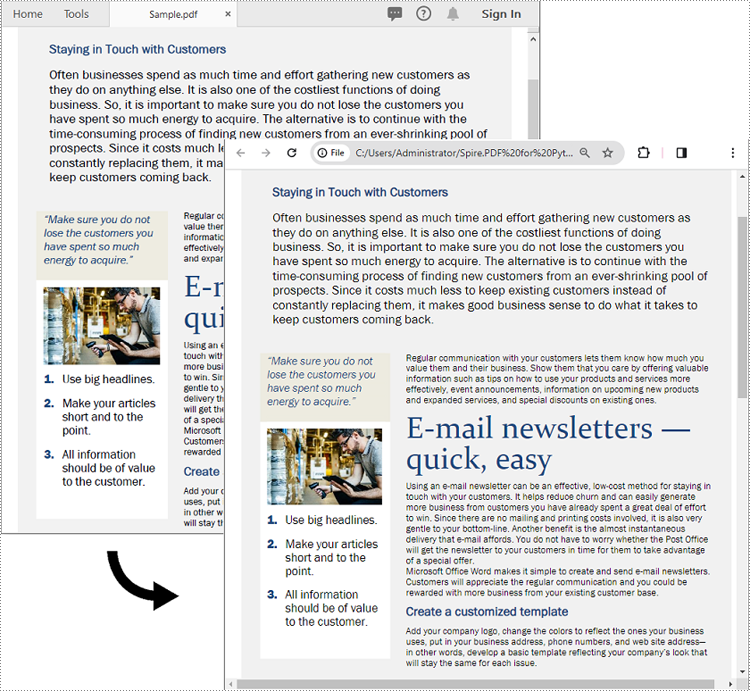
The screenshot below showcases the input PDF and the output HTML file:
Customize the HTML Output
If you need more control over the conversion process, the SetPdfToHtmlOptions() method lets you fine-tune the HTML output.
You can customize various aspects of the conversion—such as image embedding, page splitting, and SVG quality—using the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| useEmbeddedSvg | bool | If True, embeds SVG for vector content. |
| useEmbeddedImg | bool | If True, embeds images. Effective only if useEmbeddedSvg is False. |
| maxPageOneFile | bool | Limits HTML output to one page per file (if not using SVG). |
| useHighQualityEmbeddedSvg | bool | Enables high-resolution SVG (only when useEmbeddedSvg is True). |
Example Code
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Initialize a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load your PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Access conversion settings
options = doc.ConvertOptions
# Customize conversion: use image embedding, one page per file
options.SetPdfToHtmlOptions(False, True, 1, False)
# Save the PDF to HTML with the custom options
doc.SaveToFile("PdfToHtmlWithOptions.html", FileFormat.HTML)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
This configuration disables SVG and instead embeds images, outputting each page as a separate HTML file.
Save PDF to HTML Stream
In web or cloud-based applications, you might prefer to write the HTML output to a stream (e.g., for serving over HTTP) instead of saving directly to the file system. This can be achieved with the SaveToStream() method.
Example Code
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Initialize a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load your PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a stream to save the HTML output
fileStream = Stream("PdfToHtmlStream.html")
# Save the PDF to HTML stream
doc.SaveToStream(fileStream, FileFormat.HTML)
# Close the stream and the document
fileStream.Close()
doc.Close()
This approach is ideal for web servers, APIs, or any application that handles files dynamically in memory or over the network.
Conclusion
Converting PDF to HTML using Python is an effective way to make your documents web-compatible and more interactive. With Spire.PDF for Python, you get full control over the conversion process, from simple exports to advanced configurations like embedded images or SVGs and stream output.
Ready to transform your PDFs into interactive web content? Give Spire.PDF for Python a try and streamline your document-to-HTML workflow today.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert password-protected PDFs to HTML?
A1: Yes, Spire.PDF allows you to open encrypted PDFs using doc.LoadFromFile("file.pdf", "password").
Q2: Does this method support multi-page PDFs?
A2: Yes. By default, it converts all pages. You can control how many pages appear per HTML file using the maxPageOneFile parameter.
Q3: Are images and fonts preserved in HTML output?
A3: Yes, depending on the conversion settings (e.g., embedding images or SVGs), visual fidelity is preserved as closely as possible.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.