Table of Contents

Excel is one of the most powerful tools for organizing and analyzing structured data — from financial models to department reports. However, as a workbook grows to include multiple worksheets for different teams or purposes, it can become difficult to manage, share, or extract specific information. In such cases, it’s often more practical to split a workbook by worksheets , turning each sheet into its own file for easier distribution and collaboration.
For example, you might want to send the Sales worksheet to the sales team, the HR worksheet to the HR department, and the Finance worksheet to your accountant. The simplest way to achieve this is to split Excel sheets into separate files , so each recipient receives only the data relevant to them. In this article, we’ll explore three effective methods: a quick manual process, a VBA solution for Excel users, and a Python-based approach ideal for automation.
Methods Overview:
- Quick Manual Trick: Copy Sheets into New Workbooks
- Automate in Excel: VBA Macro to Split Sheets
- Automate with Python: Save Each Worksheet as a File
Why Split Excel Sheets into Separate Files?
There are several practical reasons why splitting a workbook into multiple files is helpful:
- Selective Sharing : Not every stakeholder needs access to all the data. Splitting sheets lets you distribute relevant files only.
- Improved Performance : Large workbooks with many sheets can become slow to open and process. Splitting them into smaller files improves performance.
- Better Organization : Separate files can make project management and reporting more structured.
- Automation and Reporting : Splitting is often part of automated workflows where different reports are generated for different departments.
- Version Control : Smaller files are easier to track and maintain in version control systems compared to one giant workbook.
Whether you’re an everyday Excel user or a developer building automated reporting pipelines, splitting sheets is a task worth mastering.
Quick Manual Trick: Copy Sheets into New Workbooks
If you only need to split a few sheets and don’t mind a bit of clicking, Excel’s built-in interface provides a straightforward way to do this.
How it works:
- Open your workbook using MS Excel.
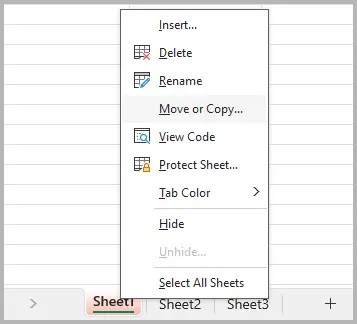
- Right-click on the sheet tab you want to separate and select Move or Copy... .
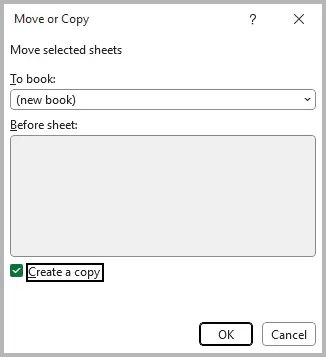
- In the To book: dropdown, select (new book) . Check the Create a copy box, then click OK .
- Repeat this process for every sheet you want to split into an individual file.
Pros:
- Requires no coding skills.
- Built directly into Excel — no installation needed.
- Simple and reliable for one-time tasks.
Cons:
- Time-consuming if you need to split many sheets.
- Prone to errors (forgetting to save or rename files properly).
- No automation — you must repeat the steps manually every time.
Best for:
- Users who rarely need to split sheets.
- Quick, one-off tasks where only a couple of sheets need separation.
Automate in Excel: VBA Macro to Split Sheets
For more frequent use, Excel’s built-in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) editor provides a way to automate splitting. With a small macro, Excel can loop through every worksheet and save it as a new workbook — saving hours of manual work.
How it works:
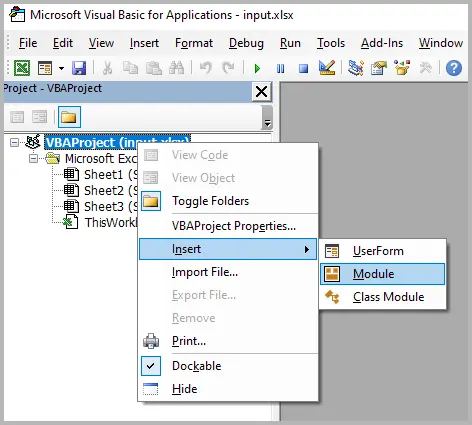
- Open Excel and press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
- Go to Insert > Module .
- Paste the following code into the module window:
- Press F5 (or go to Run > Run Sub/UserForm) to execute the macro.
- Excel will create separate files for each worksheet in the same folder as your original workbook.
Sub SplitSheetsIntoWorkbooks()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim newWorkbook As Workbook
Dim originalWorkbook As Workbook
Set originalWorkbook = ThisWorkbook
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
For Each ws In originalWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Copy
Set newWorkbook = ActiveWorkbook
newWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=originalWorkbook.Path & "\" & ws.Name & ".xlsx"
newWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False
Next ws
MsgBox "All sheets have been saved as separate files!"
End Sub
Pros:
- Fully automated— one click and every sheet is exported.
- Built into Excel — no extra software needed.
- Saves significant time compared to the manual approach.
Cons:
- Requires enabling macros, which some organizations restrict for security reasons.
- VBA is somewhat outdated, and debugging errors can be frustrating for beginners.
- Limited flexibility (e.g., handling very large workbooks or custom export rules requires editing the macro).
Best for:
- Intermediate to advanced Excel users.
- Scenarios where you frequently need to split sheets in workbooks.
Automate with Python: Save Each Worksheet as a File
If you’re a developer or need maximum flexibility, Python provides a modern approach. Using libraries like Spire.XLS for Python, you can process Excel files programmatically and split sheets in bulk. This is ideal for workflows involving large files, multiple workbooks, or integration with other systems.
How it works:
- Install Python (if you don’t already have it).
- Install the Spire.XLS for Python library:
- Use a script like the following:
pip install spire.xls
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Specify the folder path for the generated Excel files
folderPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Output\\"
# Iterate through all worksheets in the Excel file
for worksheet in workbook.Worksheets:
# For each worksheet, create a new Workbook object
newWorkbook = Workbook()
# Remove the worksheets from the new workbook
newWorkbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Copy the worksheet from the Excel file to the new workbook
newWorkbook.Worksheets.AddCopy(worksheet)
# Save the new workbook to the specified folder
newWorkbook.SaveToFile(folderPath + worksheet.Name + ".xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Here is the full guide on how to split Excel by sheets, rows, and columns in Python.
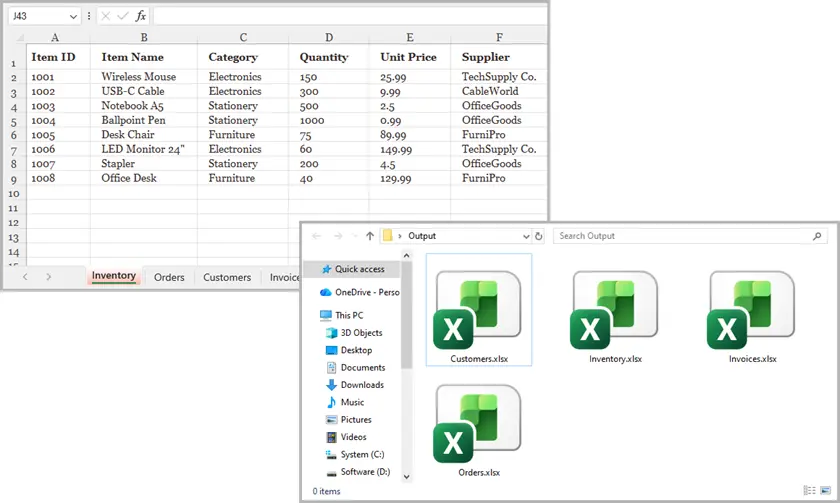
Output:
Pros:
- Highly flexible — you can extend the script to filter sheets, split by row/column, or export to CSV/PDF.
- Perfect for batch processing and large-scale automation.
- Integrates with other systems and workflows.
Cons:
- Requires some coding knowledge.- Initial setup (Python + libraries) takes longer than VBA.
Best for:
- Developers automating data pipelines.
- Businesses with large, repetitive splitting tasks.
- Advanced users who need more control than VBA offers.
Summary: Which Method Should You Choose?
Splitting Excel sheets into individual files is a common challenge, but the right method depends on your context:
- Quick Manual Trick : Perfect if you only need to separate a couple of sheets once in a while. It’s easy and doesn’t require any coding.
- VBA Macro : The go-to method for power Excel users. Once set up, it can save hours of manual work, especially if you frequently split workbooks.
- Python Script : The best option for developers or anyone building automated workflows. It provides full control, scalability, and the ability to extend the solution to fit complex business needs.
At the end of the day, the method you choose comes down to how often you need to split sheets and how comfortable you are with automation . Occasional users can rely on Excel’s interface, while professionals benefit more from VBA or Python automation.