
Document Operation (13)
How to Read PDF Files in Python – Text, Tables, Images, and More
2025-06-06 08:07:20 Written by zaki zou
Reading PDF files using Python is essential for tasks like document automation, content analysis, and data scraping. Whether you're working with contracts, reports, invoices, or scientific papers, being able to programmatically access PDF content saves time and enables powerful workflows.
To reliably read PDF content in Python — including text, tables, images, and metadata — you need a reliable Python PDF reader. In this guide, we’ll show you how to read PDFs in Python using Spire.PDF for Python, a professional and easy-to-use library that supports full-featured PDF reading without relying on any third-party tools.
Here's what's covered:
- Preparing Your Environment
- Load a PDF File in Python
- Read Text from PDF Pages in Python
- Read Table Data from PDFs in Python
- Read Images from PDFs in Python
- Read PDF Metadata (Title, Author, etc.)
- Common Questions on Reading PDFs
Environment Setup for Reading PDFs in Python
Spire.PDF for Python is a powerful Python PDF reader that allows users to read PDF content with simple Python code, including text, tables, images, and metadata. It offers a developer-friendly interface and supports a wide range of PDF reading operations:
- Read PDF files from disk or memory
- Access text, tables, metadata, and images
- No need for third-party tools
- High accuracy for structured data reading
- Free version available
It’s suitable for developers who want to read and process PDFs with minimal setup.
You can install Spire.PDF for Python via pip:
pip install spire.pdf
Or the free version Free Spire.PDF for Python for small tasks:
pip install spire.pdf.free
Load a PDF File in Python
Before accessing content, the first step is to load the PDF into memory. Spire.PDF lets you read PDF files from a path on disk or directly from in-memory byte streams — ideal for reading from web uploads or APIs.
Read PDF from File Path
To begin reading a PDF in Python, load the file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile(). This creates a document object you can use to access content.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
Read PDF from Bytes (In-Memory)
To read a PDF file from memory without saving it to disk, you can first load its byte content and then initialize a PdfDocument using a Stream object. This method is especially useful when handling PDF files received from web uploads, APIs, or temporary in-memory data.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, Stream
# Read the PDF file to a byte array
with open("sample.pdf", "rb") as f:
byte_data = f.read()
# Create a stream using the byte array
pdfStream = Stream(byte_data)
# Create a PdfDocument using the stream
pdf = PdfDocument(pdfStream)
To go further, check out this guide: Loading and Saving PDFs via Byte Streams in Python
Read Text from PDF Pages in Python
Reading text from a PDF file is one of the most common use cases in document automation. With Spire.PDF, you can easily retrieve all visible text from the entire PDF or from individual pages using simple methods.
Read All Text from PDF
To extract all text from a PDF, loop through each page and call PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() to collect visible text content.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextExtractor, PdfTextExtractOptions
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
all_text = ""
# Loop through each page
for pageIndex in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(pageIndex)
# Create a PdfTextExtract instance
text_extractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Configure extracting options
options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
options.IsExtractAllText = True
options.IsSimpleExtraction = True
# Extract text from the current page
all_text += text_extractor.ExtractText(options)
print(all_text)
Sample text content retrieved:

Read Text from Specific Area of a Page
You can also read text from a defined region of a page using a bounding box. This is useful when only a portion of the layout contains relevant information.
from spire.pdf import RectangleF, PdfDocument, PdfTextExtractor, PdfTextExtractOptions
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor instance
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Set the area to extract text by configuring the PdfTextExtractOptions
options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
area = RectangleF.FromLTRB(0, 200, page.Size.Width, 270) # x, y, width, height
options.ExtractArea = area
options.IsSimpleExtraction = True
# Extract text from the area
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(options)
print(text)
The text read from the PDF page area:
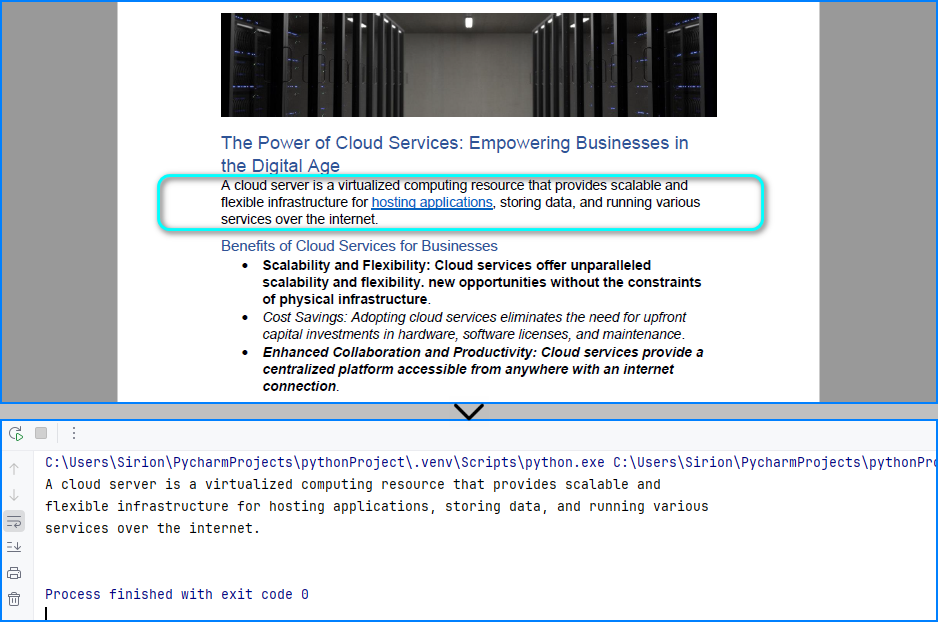
Read Table Data from PDFs in Python
PDF tables are often used in reports, invoices, and statements. With Spire.PDF, you can read PDF tables in Python by extracting structured tabular content using its layout-aware table extractor, making it ideal for financial and business documents. Use PdfTableExtractor.ExtractTable() to detect tables page by page and output each row and cell as structured text.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Create a PdfTableExtractor instance
table_extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
# Extract the table from the first page
tables = table_extractor.ExtractTable(0)
for table in tables:
# Get the number of rows and columns
row_count = table.GetRowCount()
column_count = table.GetColumnCount()
# Iterate all rows
for i in range(row_count):
table_row = []
# Iterate all columns
for j in range(column_count):
# Get the cell
cell_text = table.GetText(i, j)
table_row.append(cell_text)
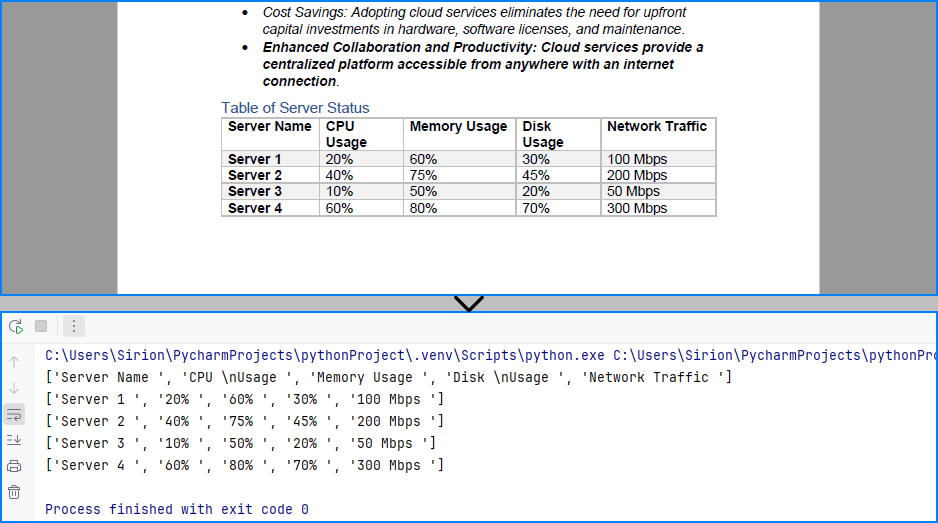
print(table_row)
Table content extracted using the code above:
Want to extract text from scanned PDFs using OCR? Read this guide on OCR with Python
Read Images from PDF in Python
PDF files often contain logos, scanned pages, or embedded images. Spire.PDF allows you to read and export these images, which is helpful for working with digitized documents or preserving visual content. Use PdfImageHelper.GetImagesInfo() on each page to retrieve and save all embedded images.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfImageHelper
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper object
image_helper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image information from the page
images_info = image_helper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Save the images from the page as image files
for i in range(len(images_info)):
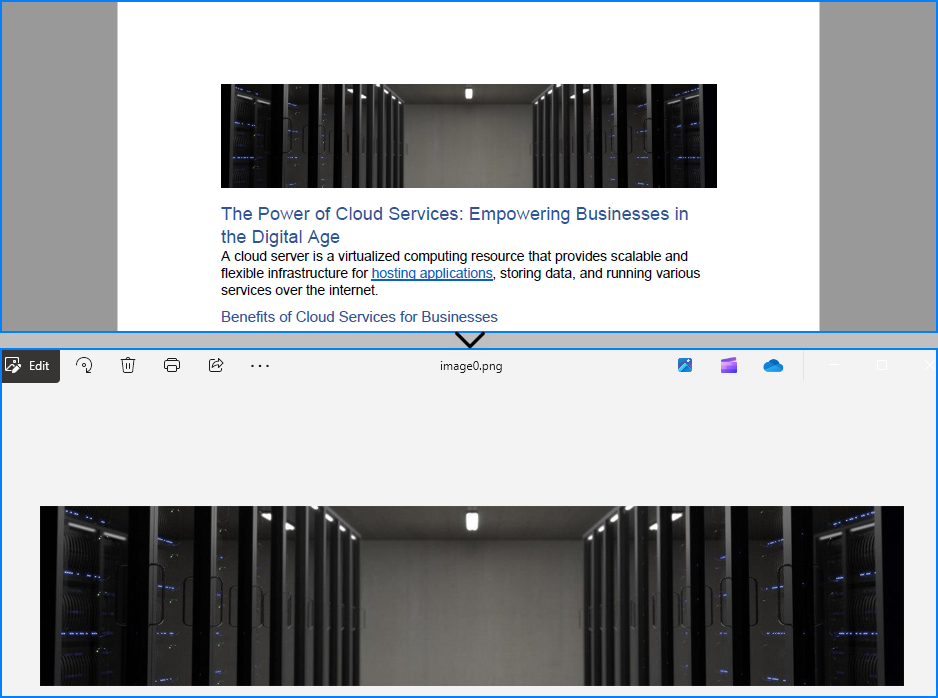
images_info[i].Image.Save("output/Images/image" + str(i) + ".png")
The image read from the PDF file:
Read PDF Metadata (Title, Author, etc.)
Sometimes you may want to access document metadata like author, subject, and title. This can be helpful for indexing or organizing files. Use the ocumentInformation property to read metadata fields.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the document properties
properties = pdf.DocumentInformation
print("Title: " + properties.Title)
print("Author: " + properties.Author)
print("Subject: " + properties.Subject)
print("Keywords: " + properties.Keywords)
The metadata read from the PDF document:

Common Questions on Reading PDFs
Can Python parse a PDF file?
Yes. Libraries like Spire.PDF for Python allow you to read PDF text, extract tables, and access embedded images or metadata. It supports methods like PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() and PdfTableExtractor.ExtractTable() for structured content parsing.
How do I read a PDF in Jupyter?
Spire.PDF works seamlessly in Jupyter Notebooks. Just install it via pip and use its API to read PDF files, extract text, or parse tables and images directly in your notebook environment.
How to read text from a PDF file?
Use the PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() method on each page after loading the PDF with Spire.PDF. This lets you read PDF file to text in Python and retrieve visible content for processing or analysis.
Can I read a PDF file without saving it to disk?
Yes. You can use LoadFromStream() to read PDF content as bytes and load it directly from memory. This is useful for processing PDFs received from web APIs or file uploads.
Conclusion
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can easily read a PDF in Python — including reading PDF text, tables, images, and metadata — and even read a PDF file to text for further processing or automation. This makes it an ideal solution for document automation, data ingestion, and content parsing in Python.
Need to process large PDF files or unlock all features? Request a free license and take full advantage of Spire.PDF for Python today!
Edit PDF Using Python: A Practical Guide to PDF Modification
2025-05-06 03:42:04 Written by Administrator
PDFs are widely used in reports, invoices, and digital forms due to their consistent formatting across platforms. However, their fixed layout makes editing difficult without specialized tools. For developers looking to edit PDF using Python, Spire.PDF for Python provides a comprehensive and easy-to-use solution. This Python PDF editor enables you to modify PDF files programmatically—changing text, replacing images, adding annotations, handling forms, and securing files—without relying on Adobe Acrobat or any external software.
In this article, we will explore how to use Spire.PDF for Python to programmatically edit PDFs in Python applications.
- Why Use Python and Spire.PDF to Edit PDF Documents?
- Getting Started with Spire.PDF for Python
- How to Edit an Existing PDF Using Spire.PDF for Python
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Use Python and Spire.PDF to Edit PDF Documents?
Python is a highly versatile programming language that provides an excellent platform for automating and managing PDF documents. When it comes to edit PDF Python tasks, Spire.PDF for Python stands out as a comprehensive and easy-to-use solution for all your PDF manipulation needs.
Benefits of Using Python for PDF Editing
- Automation and Batch Processing: Streamline repetitive PDF editing tasks efficiently.
- Cost-Effective: Reduce manual work, saving time and resources when you Python-edit PDF files.
- Integration: Seamlessly incorporate PDF editing into existing Python-based systems and workflows.
Advantages of Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python is a standalone library that enables developers to create, read, edit, convert, and save PDF files without relying on external software. As a trusted Python PDF editor, it offers powerful features such as:
- Text and Image Editing
- Annotations and Bookmark Management
- Form Field Handling
- Security Settings (Encryption and Permissions)
- Conversion to Word, Excel, HTML, and Images
To learn more about these specific features, visit the Spire.PDF for Python tutorials.
With its intuitive API design, Spire.PDF makes it easier than ever to edit PDF files in Python quickly and effectively, ensuring a smooth development experience.
Getting Started with Spire.PDF for Python
Installation:
To install Spire.PDF for Python, simply run the following pip command:
pip install spire.pdf
Alternatively, you can install Free Spire.PDF for Python, a free version suitable for small projects, by running:
pip install spire.pdf.free
You can also download the library manually from the links.
Basic Setup Example:
The following example demonstrates how to create a simple PDF using Spire.PDF for Python:
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfFont, PdfBrushes, PdfFontFamily, PdfFontStyle
# Create a new PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a new page to the document
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create a font
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 28.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold)
# Create a brush
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Draw the string using the font and brush
page.Canvas.DrawString("Hello, World", font, brush, 100.0, 100.0)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/NewPDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result: The generated PDF displays the text "Hello, World" using Times Roman Bold.

With Spire.PDF installed, you're now ready to edit PDFs using Python. The sections below explain how to manipulate structure, content, security, and metadata.
How to Edit an Existing PDF Using Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides a simple yet powerful way to edit PDF using Python. With its intuitive API, developers can automate a wide range of PDF editing tasks including modifying document structure, page content, security settings, and properties. This section outlines the core categories of editing and their typical use cases.
Edit PDF Pages and Structure with Python
Structure editing lets you manipulate PDF page order, merge files, or insert/delete pages—ideal for document assembly workflows.
- Insert or Delete Pages
Use the Pages.Insert() and Pages.RemoveAt() methods of the PdfDocument class to insert or delete pages at specific positions.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfPageSize, PdfMargins, PdfPageRotateAngle
# Load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Insert and delete pages
# Insert at beginning
pdf.Pages.Insert(0, PdfPageSize.A4(), PdfMargins(50.0, 60.0), PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle90)
# Delete second page
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(1)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/InsertDeletePage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
- Merge Two PDF Files
The AppendPage() method allows you to combine PDFs by inserting pages from one document into another.
Code Example
- Python
import os
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Specify the PDF file path
pdfPath = "PDFs/"
# Read the PDF file names from the path and add them to a list
files = [pdfPath + file for file in os.listdir(pdfPath) if file.endswith(".pdf")]
# Load the first PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile(files[0])
# Iterate through the other PDF files
for i in range(1, len(files)):
# Load the current PDF file
pdf2 = PdfDocument()
pdf2.LoadFromFile(files[i])
# Append the pages from the current PDF file to the first PDF file
pdf.AppendPage(pdf2)
# Save the merged PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/MergePDFs.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
You may also like: Splitting PDF Files with Python Code
Edit PDF Content with Python
As a Python PDF editor, Spire.PDF supports a variety of content-level operations, including modifying text, images, annotations, and interactive forms.
- Replace Text in a PDF
The PdfTextReplacer class can be used to find and replace text from a page. Note that precise replacement may require case and layout-aware handling.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextReplacer, ReplaceActionType, Color
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Iterate through the pages
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create a PdfTextReplacer object
replacer = PdfTextReplacer(page)
# Set the replacement options
replacer.Options.ReplaceType = ReplaceActionType.IgnoreCase
# Replace the text
replacer.ReplaceAllText("drones", "ROBOTS", Color.get_Aqua()) # Setting the color is optional
# Save the merged PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceText.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:

- Replace Images in a PDF
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfImageHelper class to help you replace images in a PDF file with ease. By retrieving image information from a specific page, you can use the ReplaceImage() method to directly substitute the original image with a new one.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfImageHelper, PdfImage
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image info of the first image on the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)[0]
# Load a new image
newImage = PdfImage.FromFile("Image.png")
# Replace the image
imageHelper.ReplaceImage(imageInfo, newImage)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceImage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:

- Add Comments or Notes
To add comments or notes with Python, use the PdfTextMarkupAnnotation class and add it to the page’s AnnotationsWidget collection.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextFinder, PdfTextMarkupAnnotation, PdfRGBColor, Color
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
#Create a PdfTextFinder instance and set the options
finder = PdfTextFinder(page)
finder.Options.Parameter.IgnoreCase = False
finder.Options.Parameter.WholeWord = True
# Find the text to comment
text = finder.Find("redefining entire industries")[0]
# Get the bound of the text
bound = text.Bounds[0]
# Add comment
commentText = ("This is a powerful expression, but a bit vague. "
"You might consider specifying which industries are "
"being redefined and how, to make the claim more "
"concrete and credible.")
comment = PdfTextMarkupAnnotation("Commenter", commentText, bound)
comment.TextMarkupColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Yellow())
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(comment)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CommentNote.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
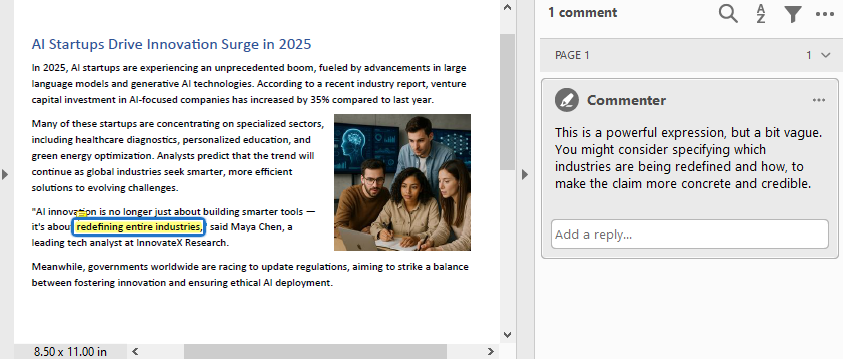
- Edit or Read Form Fields
Spire.PDF for Python allows you to programmatically fill out and read form fields in a PDF document. By accessing the FieldsWidget property of a PdfFormWidget object, you can iterate through all interactive form elements, such as text boxes, combo boxes, and checkboxes, and update or extract their values.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfFormWidget, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
forms = pdf.Form
formWidgets = PdfFormWidget(forms).FieldsWidget
# Fill the forms
for i in range(formWidgets.Count):
formField = formWidgets.get_Item(i)
if formField.Name == "FullName":
textBox = PdfTextBoxFieldWidget(formField)
textBox.Text = "Amanda Ray Thompson"
elif formField.Name == "DateOfBirth":
textBox = PdfTextBoxFieldWidget(formField)
textBox.Text = "01/01/1980"
elif formField.Name == "Gender":
comboBox = PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget(formField)
comboBox.SelectedIndex = [ 1 ]
elif formField.Name == "Department":
formField.Value = "Human Resources"
elif formField.Name == "AgreeTerms":
checkBox = PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget(formField)
checkBox.Checked = True
# Read the forms
formValues = []
for i in range(formWidgets.Count):
formField = formWidgets.get_Item(i)
if isinstance(formField, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + formField.Text)
elif isinstance(formField, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + formField.SelectedValue)
elif isinstance(formField, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + str(formField.Checked))
# Write the form values to a file
with open("output/FormValues.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("\n".join(formValues))
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/FilledForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
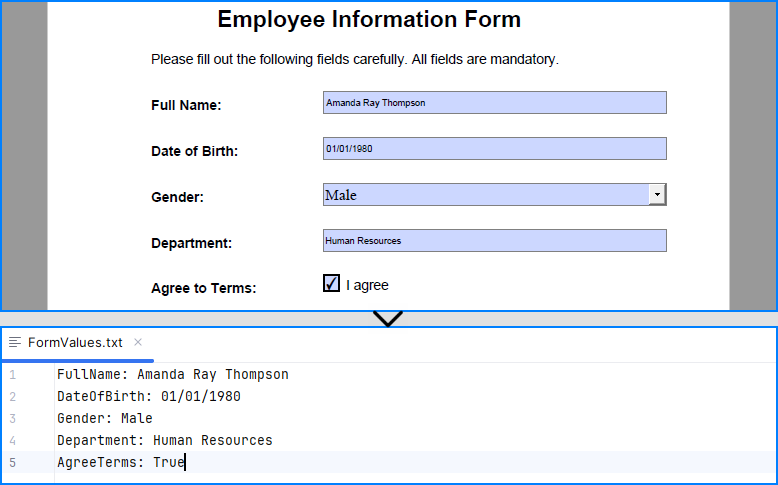
Explore more: How to Insert Page Numbers to PDF Using Python
Manage PDF Security with Python
PDF security editing is essential when dealing with sensitive documents. Spire.PDF supports encryption, password protection, digital signature handling, and permission settings.
- Add a Password and Set Permissions
The Encrypt() method lets you secure a PDF with user/owner passwords and define allowed actions like printing or copying.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfEncryptionAlgorithm, PdfDocumentPrivilege, PdfPasswordSecurityPolicy
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Create a PdfSecurityPolicy object and set the passwords and encryption algorithm
securityPolicy = PdfPasswordSecurityPolicy("userPSD", "ownerPSD")
securityPolicy.EncryptionAlgorithm = PdfEncryptionAlgorithm.AES_128
# Set the document privileges
pdfPrivileges = PdfDocumentPrivilege.ForbidAll()
pdfPrivileges.AllowPrint = True
pdfPrivileges.AllowFillFormFields = True
# Apply the document privileges
securityPolicy.DocumentPrivilege = pdfPrivileges
# Encrypt the PDF with the security policy
pdf.Encrypt(securityPolicy)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EncryptedForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result
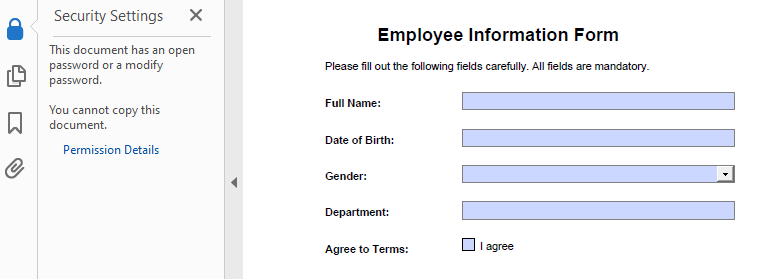
- Remove the Password from a PDF
To open a protected file, provide the user password when calling LoadFromFile(), use Decrypt() to decrypt the document, and save it again unprotected.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the encrypted PDF file with the owner password
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("output/EncryptedForm.pdf", "ownerPSD")
# Decrypt the PDF file
pdf.Decrypt()
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/DecryptedForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Recommended for you: Use Python to Add and Remove Digital Signature in PDF
Edit PDF Properties with Python
Use Spire.PDF to read and edit PDF metadata and viewer preferences—key features for document presentation and organization.
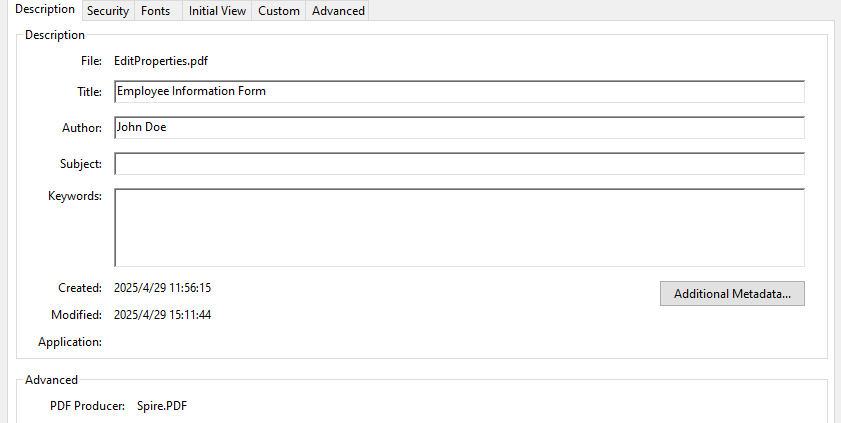
- Update Document Metadata
Update metadata such as title, author, or subject via the DocumentInformation property of the PDF document.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Set document metadata
pdf.DocumentInformation.Author = "John Doe"
pdf.DocumentInformation.Title = "Employee Information Form"
pdf.DocumentInformation.Producer = "Spire.PDF"
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EditProperties.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
- Set View Preferences
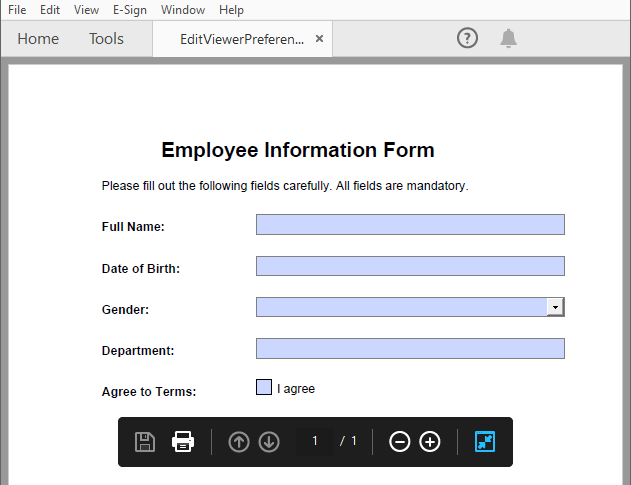
The ViewerPreferences property allows you to customize the viewing mode of a PDF (e.g., two-column layout).
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfPageLayout, PrintScalingMode
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Set the viewer preferences
pdf.ViewerPreferences.DisplayTitle = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideToolbar = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideWindowUI = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.FitWindow = False
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideMenubar = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.PrintScaling = PrintScalingMode.AppDefault
pdf.ViewerPreferences.PageLayout = PdfPageLayout.OneColumn
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EditViewerPreference.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
Similar topic: Change PDF Version Easily with Python Code
Conclusion
Editing PDFs using Python is both practical and efficient with Spire.PDF for Python. Whether you're building automation tools, editing digital forms, or securing sensitive reports, Spire.PDF equips you with a comprehensive suite of editing features—all accessible via clean and simple Python code.
With capabilities that span content editing, form interaction, document structuring, and security control, this Python PDF editor is a go-to solution for developers and organizations aiming to streamline their PDF workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I edit a PDF using Python?
A: Yes, Python offers powerful libraries like Spire.PDF for Python that enable you to edit text, images, forms, annotations, and even security settings in a PDF file.
Q: How to edit a PDF using coding?
A: By using libraries such as Spire.PDF for Python, you can load an existing PDF, modify its content or structure programmatically, and save the changes with just a few lines of code.
Q: What is the Python library for PDF editor?
A: Spire.PDF for Python is a popular choice. It offers comprehensive functionalities for creating, reading, editing, converting, and securing PDF documents without the need for additional software.
Q: Can I modify a PDF for free?
A: Yes, you can use the free edition of Spire.PDF for Python to edit PDF files, although it comes with some limitations, such as processing up to 10 pages per document. Additionally, you can apply for a 30-day temporary license that removes all limitations and watermarks for full functionality testing.
PDF files have different versions, each with unique features and compatibility standards. Changing the version of a PDF can be important when specific versions are required for compatibility with certain devices, software, or regulatory requirements. For instance, you may need to use an older PDF version when archiving or sharing files with users using older software. This article will introduce how to change the version of a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Change PDF Version in Python
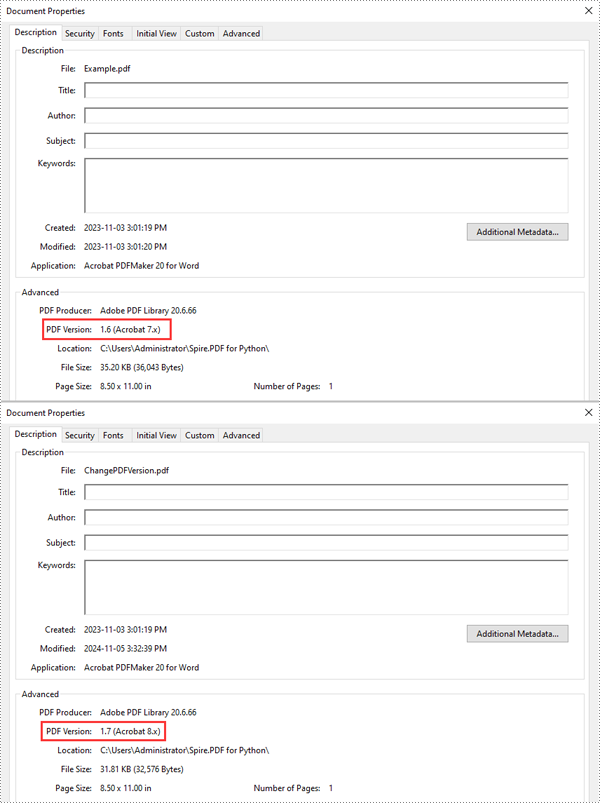
Spire.PDF for Python supports PDF versions ranging from 1.0 to 1.7. To convert a PDF file to a different version, simply set the desired version using the PdfDocument.FileInfo.Version property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a sample PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Change the version of the PDF document to a newer or older version using the PdfDocument.FileInfo.Version property.
- Save the resulting document using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Example.pdf")
# Change the version of the PDF to version 1.7
pdf.FileInfo.Version = PdfVersion.Version1_7
# Save the resulting document
pdf.SaveToFile("ChangePDFVersion.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Setting view preferences in PDF documents is a crucial feature that can significantly enhance user experience. By configuring options like page layout, display mode, and zoom level, you ensure recipients view the document as intended, without manual adjustments. This is especially useful for business reports, design plans, or educational materials, where consistent presentation is crucial for effectively delivering information and leaving a professional impression. This article will show how to set view preferences of PDF documents with Python code using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Set PDF Viewer Preferences with Python
Viewer preferences allow document creators to define how a PDF document is displayed when opened, including page layout, window layout, and display mode. Developers can use the properties under ViewerPreferences class to set those display options. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the ViewerPreferences through using PdfDocument.ViewerPreferences property.
- Set the viewer preferences using properties under ViewerPreferences class.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the viewer preferences
preferences = pdf.ViewerPreferences
# Set the viewer preferences
preferences.FitWindow = True
preferences.CenterWindow = True
preferences.HideMenubar = True
preferences.HideToolbar = True
preferences.DisplayTitle = True
preferences.HideWindowUI = True
preferences.PageLayout = PdfPageLayout.SinglePage
preferences.BookMarkExpandOrCollapse = True
preferences.PrintScaling = PrintScalingMode.AppDefault
preferences.PageMode = PdfPageMode.UseThumbs
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ViewerPreferences.pdf")
pdf.Close()
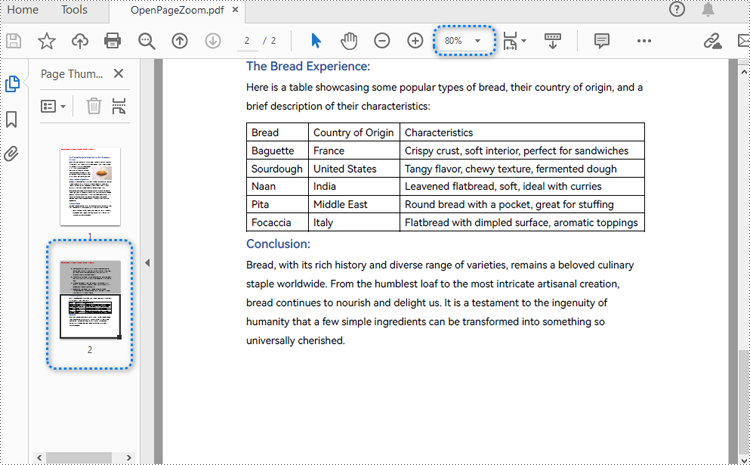
Set the Opening Page and Zoom Level with Python
By creating PDF actions and setting them to be executed when the document is opened, developers can configure additional viewer preferences, such as the initial page display and zoom level. Here are the steps to follow:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a page using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Create a PdfDestination object and set the location and zoom factor of the destination.
- Create a PdfGoToAction object using the destination.
- Set the action as the document open action through PdfDocument.AfterOpenAction property.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample1.pdf")
# Get the second page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Create a PdfDestination object
dest = PdfDestination(page)
# Set the location and zoom factor of the destination
dest.Mode = PdfDestinationMode.Location
dest.Location = PointF(0.0, page.Size.Height / 2)
dest.Zoom = 0.8
# Create a PdfGoToAction object
action = PdfGoToAction(dest)
# Set the action as the document open action
pdf.AfterOpenAction = action
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/OpenPageZoom.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Barcodes in PDFs can facilitate quicker data retrieval and processing. You can add barcodes to PDF files that contain detailed information such as the document's unique identifier, version number, creator, or even the entire document content. When scanned, all information is decoded immediately. This instant access is invaluable for businesses dealing with large volumes of documents, as it minimizes the time and effort required for manual searching and data entry. In this article, you will learn how to add barcodes to PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python and Spire.Barcode for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and Spire.Barcode for Python. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF pip install Spire.Barcode
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add Barcodes to PDF in Python
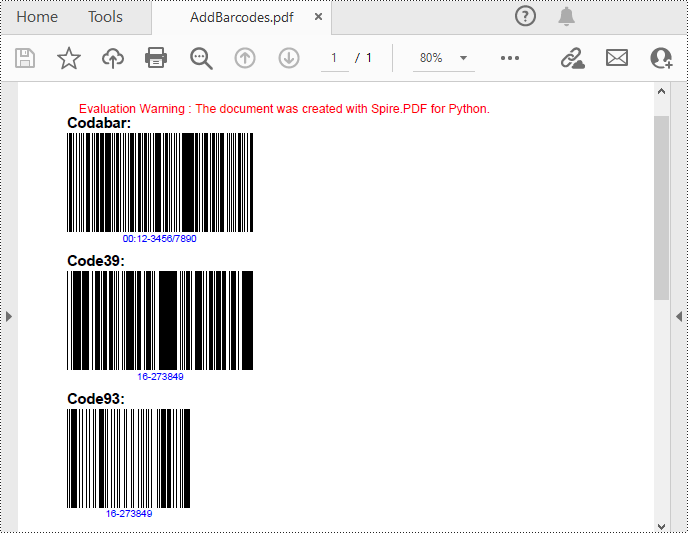
Spire.PDF for Python support several 1D barcode types represented by different classes, such as PdfCodabarBarcode, PdfCode11Barcode, PdfCode32Barcode, PdfCode39Barcode, PdfCode93Barcode.
Each class provides corresponding properties for setting the barcode text, size, color, etc. The following are the steps to draw the common Codabar, Code39 and Code93 barcodes at the specified locations on a PDF page.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a PDF page using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a PdfTextWidget object and draw text on the page using PdfTextWidget.Draw() method.
- Create PdfCodabarBarcode, PdfCode39Barcode, PdfCode93Barcode objects.
- Set the gap between the barcode and the displayed text through the BarcodeToTextGapHeight property of the corresponding classes.
- Sets the barcode text display location through the TextDisplayLocation property of the corresponding classes.
- Set the barcode text color through the TextColor property of the corresponding classes.
- Draw the barcodes at specified locations on the PDF page using the Draw(page: PdfPageBase, location: PointF) method of the corresponding classes.
- Save the result PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add(PdfPageSize.A4())
# Initialize y-coordinate
y = 20.0
# Create a true type font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
# Draw text on the page
text = PdfTextWidget()
text.Font = font
text.Text = "Codabar:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw Codabar barcode on the page
Codabar = PdfCodabarBarcode("00:12-3456/7890")
Codabar.BarcodeToTextGapHeight = 1.0
Codabar.EnableCheckDigit = True
Codabar.ShowCheckDigit = True
Codabar.TextDisplayLocation = TextLocation.Bottom
Codabar.TextColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
Codabar.Draw(page, PointF(0.0, y))
y = Codabar.Bounds.Bottom + 6
# Draw text on the page
text.Text = "Code39:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw Code39 barcode on the page
Code39 = PdfCode39Barcode("16-273849")
Code39.BarcodeToTextGapHeight = 1.0
Code39.TextDisplayLocation = TextLocation.Bottom
Code39.TextColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
Code39.Draw(page, PointF(0.0, y))
y = Code39.Bounds.Bottom + 6
# Draw text on the page
text.Text = "Code93:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw Code93 barcode on the page
Code93 = PdfCode93Barcode("16-273849")
Code93.BarcodeToTextGapHeight = 1.0
Code93.TextDisplayLocation = TextLocation.Bottom
Code93.TextColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
Code93.QuietZone.Bottom = 5.0
Code93.Draw(page, PointF(0.0, y))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("AddBarcodes.pdf")
pdf.Close()
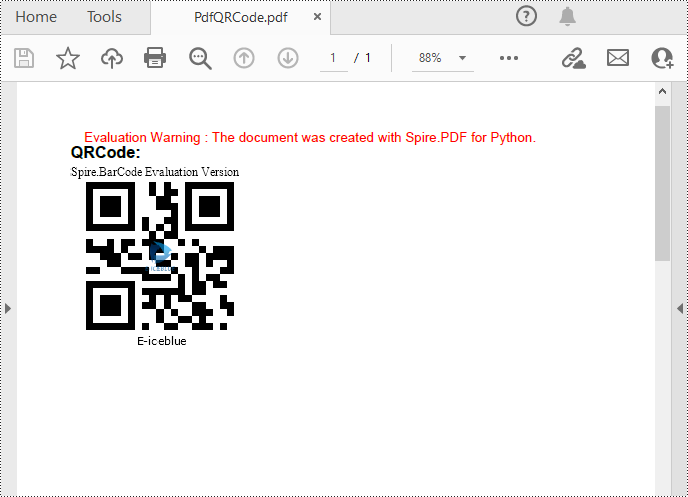
Add QR Codes to PDF in Python
To add 2D barcodes to a PDF file, the Spire.Barcode for Python library is required to generate QR code first, and then you can add the QR code image to the PDF file with the Spire.PDF for Python library. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a PDF page using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a BarcodeSettings object.
- Call the corresponding properties of the BarcodeSettings class to set the barcode type, data, error correction level and width, etc.
- Create a BarCodeGenerator object based on the settings.
- Generate QR code image using BarCodeGenerator.GenerateImage() method.
- Save the QR code image to a PNG file.
- Draw the QR code image at a specified location on the PDF page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawImage() method.
- Save the result PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.barcode import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
settings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type to QR code
settings.Type = BarCodeType.QRCode
# Set the data of the QR code
settings.Data = "E-iceblue"
settings.Data2D = "E-iceblue"
# Set the width of the QR code
settings.X = 2
# Set the error correction level of the QR code
settings.QRCodeECL = QRCodeECL.M
# Set to show QR code text at the bottom
settings.ShowTextOnBottom = True
# Generate QR code image based on the settings
barCodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(settings)
QRimage = barCodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
# Save the QR code image to a .png file
with open("QRCode.png", "wb") as file:
file.write(QRimage)
# Initialize y-coordinate
y = 20.0
# Create a true type font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
# Draw text on the PDF page
text = PdfTextWidget()
text.Font = font
text.Text = "QRCode:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw QR code image on the PDF page
pdfImage = PdfImage.FromFile("QRCode.png")
page.Canvas.DrawImage(pdfImage, 0.0, y)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("PdfQRCode.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Comparing PDF documents is a common task when collaborating on projects or tracking changes. This allows users to quickly review and understand what has been modified, added, or removed between revisions. Effective PDF comparison streamlines the review process and ensures all stakeholders are aligned on the latest document content.
In this article, you will learn how to compare two PDF documents using Python and the Spire.PDF for Python library.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Compare Two PDF Documents in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfComparer.Compare() method allowing developers to compare two PDF documents and save the comparison result to another PDF document. Here are the detailed steps.
- Load the first PDF document while initializing the PdfDocument object.
- Load the second PDF document while initializing another PdfDocument object.
- Initialize an instance of PdfComparer class, passing the two PdfDocument objects are the parameter.
- Call Compare() method of the PdfComparer object to compare the two PDF documents and save the result to a different PDF document.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the first document
doc_one = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_ONE.pdf")
# Load the section document
doc_two = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_TWO.pdf")
# Create a PdfComparer object
comparer = PdfComparer(doc_two, doc_one)
# Compare two documents and save the comparison result in a pdf document
comparer.Compare("output/CompareResult.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc_one.Dispose()
doc_two.Dispose()

Compare Selected Pages in PDF Documents in Python
Instead of comparing two entire documents, you can specify the pages to compare using the PdfComparer.PdfCompareOptions.SetPageRanges() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Load the first PDF document while initializing the PdfDocument object.
- Load the second PDF document while initializing another PdfDocument object.
- Initialize an instance of PdfComparer class, passing the two PdfDocument objects are the parameter.
- Specify the page range to compare using PdfComparer.PdfCompareOptions.SetPageRanges() method
- Call PdfComparer.Compare() method to compare the selected pages and save the result to a different PDF document.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the first document
doc_one = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_ONE.pdf")
# Load the section document
doc_two = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_TWO.pdf")
# Create a PdfComparer object
comparer = PdfComparer(doc_two, doc_one)
# Set page range for comparison
comparer.PdfCompareOptions.SetPageRanges(1, 3, 1, 3)
# Compare the selected pages and save the comparison result in a pdf document
comparer.Compare("output/CompareResult.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc_one.Dispose()
doc_two.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.

Large PDF files can slow down email delivery, break upload limits, and consume unnecessary storage. This is especially common in PDFs that include high-resolution scans, images, or embedded fonts. If you're working with Python and need to automate PDF compression without compromising quality, this guide will help you get started.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to compress PDF files in Python using the Spire.PDF for Python library. We'll cover several effective techniques, including image recompression, font optimization, metadata removal, and batch compression—perfect for web, backend, or desktop applications.
Table of Contents
- Common Scenarios Requiring PDF Compression
- Prerequisites
- Practical PDF Compression Techniques in Python
- Summary
Common Scenarios Requiring PDF Compression
Reducing the size of PDF documents is often essential in the following situations:
| Use Case | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Email Attachments | Avoid size limits and improve deliverability |
| Web Uploads | Reduce upload time and server storage |
| Mobile Access | Faster loading and less data consumption |
| Cloud Archiving | Lower storage cost for backups |
| App Submissions | Meet strict file size limits |
Prerequisites
Before you begin compressing PDFs with Python, make sure the following requirements are met:
- Python 3.7 or above
Ensure that Python (version 3.7 or later) is installed on your system. You can download it from the official Python website. - Spire.PDF for Python
This is a powerful PDF library that allows you to programmatically create, manipulate, and compress PDF documents—without relying on external software like Adobe Acrobat.
To install Spire.PDF for Python, run the following command in your terminal or command prompt:
pip install spire.pdf
Need help with the installation? See our step-by-step guide: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows_
Practical PDF Compression Techniques in Python
In this section, you'll explore five practical techniques for reducing PDF file size:
- Font compression and unembedding
- Image compression
- Full-document compression
- Metadata and attachment removal
- Batch compressing multiple PDFs
Font Compression and Unembedding
Fonts embedded in a PDF—especially those from large font libraries or multilingual character sets—can significantly increase the file size. Spire.PDF allows you to:
- Compress embedded fonts to minimize space usage
- Unembed fonts that are not essential for rendering
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfCompressor object and load the PDF file
compressor = PdfCompressor("C:/Users/Administrator/Documents/Example.pdf")
# Get the OptimizationOptions object
compression_options = compressor.OptimizationOptions
# Enable font compression
compression_options.SetIsCompressFonts(True)
# Optional: unembed fonts to further reduce size
# compression_options.SetIsUnembedFonts(True)
# Compress the PDF and save the result
compressor.CompressToFile("CompressFonts.pdf")
Image Compression
Spire.PDF lets you reduce the size of all images in a PDF by creating a PdfCompressor instance, enabling the image resizing and compression options, and specifying the image quality level. This approach applies compression uniformly across the entire document.
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfCompressor object and load the PDF file
compressor = PdfCompressor("C:/Users/Administrator/Documents/Example.pdf")
# Get the OptimizationOptions object
compression_options = compressor.OptimizationOptions
# Enable image resizing
compression_options.SetResizeImages(True)
# Enable image compression
compression_options.SetIsCompressImage(True)
# Set image quality (available options: Low, Medium, High)
compression_options.SetImageQuality(ImageQuality.Medium)
# Compress and save the PDF file
compressor.CompressToFile("Compressed.pdf")
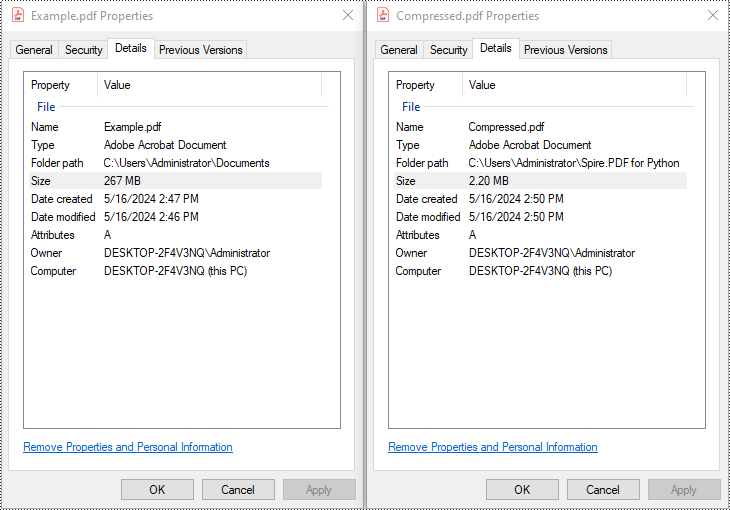
Full Document Compression
Beyond optimizing individual elements, Spire.PDF also supports full-document compression. By adjusting the document's CompressionLevel and disabling incremental updates, you can apply comprehensive optimization to reduce overall file size.
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Documents/Example.pdf")
# Disable incremental update
pdf.FileInfo.IncrementalUpdate = False
# Set the compression level to the highest
pdf.CompressionLevel = PdfCompressionLevel.Best
# Save the optimized PDF
pdf.SaveToFile("OptimizeDocumentContent.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Removing Metadata and Attachments
Cleaning up metadata and removing embedded attachments is a quick way to reduce PDF size. Spire.PDF lets you remove unnecessary information like author/title fields and attached files:
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the PDF
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Example.pdf")
# Disable the incremental update
pdf.FileInfo.IncrementalUpdate = False
# Remove metadata
pdf.DocumentInformation.Author = ""
pdf.DocumentInformation.Title = ""
# Remove attachments
pdf.Attachments.Clear()
# Save the optimized PDF
pdf.SaveToFile("Cleaned.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Batch Compressing Multiple PDFs
You can compress multiple PDFs at once by looping through files in a folder and applying the same optimization settings:
import os
from spire.pdf import *
# Folder containing the PDF files to compress
input_folder = "C:/PDFs/"
# Loop through all files in the input folder
for file in os.listdir(input_folder):
# Process only PDF files
if file.endswith(".pdf"):
# Create a PdfCompressor instance and load the file
compressor = PdfCompressor(os.path.join(input_folder, file))
# Access compression options
opt = compressor.OptimizationOptions
# Enable image resizing
opt.SetResizeImages(True)
# Enable image compression
opt.SetIsCompressImage(True)
# Set image quality to medium (options: Low, Medium, High)
opt.SetImageQuality(ImageQuality.Medium)
# Define output file path with "compressed_" prefix
output_path = os.path.join(input_folder, "compressed_" + file)
# Perform compression and save the result
compressor.CompressToFile(output_path)
Summary
Reducing the size of PDF files is a practical step toward faster workflows, especially when dealing with email sharing, web uploads, and large-scale archiving. With Spire.PDF for Python, developers can implement smart compression techniques—ranging from optimizing images and fonts to stripping unnecessary elements like metadata and attachments.
Whether you're building automation scripts, integrating PDF handling into backend services, or preparing documents for long-term storage, these tools give you the flexibility to control file size without losing visual quality. By combining multiple strategies—like full-document compression and batch processing—you can keep your PDFs lightweight, efficient, and ready for distribution across platforms.
Want to explore more ways to work with PDFs in Python? Explore the full range of Spire.PDF for Python tutorials to learn how to merge/split PDFs, convert PDF to PDF/A, add password protection, and more.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I use Spire.PDF for Python on Linux or macOS?
A1: Yes. Spire.PDF for Python is compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Q2: Is Spire.PDF for Python free?
A2: Spire.PDF for Python offers a free version suitable for small-scale and non-commercial use. For full functionality, including unrestricted use in commercial applications, a commercial version is available. You can request a free 30-day trial license to explore all its premium features.
Q3: Will compressing the PDF reduce the visual quality?
A3: Not necessarily. Spire.PDF’s compression methods are designed to preserve visual fidelity while optimizing file size. You can fine-tune image quality or leave it to the default settings.
Sometimes, when dealing with PDF documents, there is a need to split a page into different sections based on content or layout. For instance, splitting a mixed-layout page with both horizontal and vertical content into two separate parts. This type of splitting is not commonly available in basic PDF management functions but can be important for academic papers, magazine ads, or mixed-layout designs. This article explains how to use Spire.PDF for Python to perform horizontal or vertical PDF page splitting.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Split PDF Page Horizontally or Vertically with Python
Spire.PDF for Python not only supports splitting a PDF document into multiple PDF documents, but also allows splitting a specific page within a PDF into two or more pages. Here are the detailed steps to split a page:
- Create an instance of the PdfDocument class.
- Load the source PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the page(s) to be split using PdfDocument.Pages[].
- Create a new PDF document and set its page margins to 0.
- Set the width or height of the new document to half of the source document.
- Add a page to the new PDF document using the PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a template for the source document's page using the PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Draw the content of the source page onto the new page using the PdfTemplate.Draw() method.
- Save the split document using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Terms of service.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages[0]
# Create a new PDF document and remove the page margins
newpdf = PdfDocument()
newpdf.PageSettings.Margins.All=0
# Horizontal splitting: Set the width of the new document's page to be the same as the width of the first page of the original document, and the height to half of the first page's height
newpdf.PageSettings.Width=page.Size.Width
newpdf.PageSettings.Height=page.Size.Height/2
'''
# Vertical splitting: Set the width of the new document's page to be half of the width of the first page of the original document, and the height to the same as the first page's height
newpdf.PageSettings.Width=page.Size.Width/2
newpdf.PageSettings.Height=page.Size.Height
'''
# Add a new page to the new PDF document
newPage = newpdf.Pages.Add()
# Set the text layout format
format = PdfTextLayout()
format.Break=PdfLayoutBreakType.FitPage
format.Layout=PdfLayoutType.Paginate
# Create a template based on the first page of the original document and draw it onto the new page of the new document, automatically paginating when the page is filled
page.CreateTemplate().Draw(newPage, PointF(0.0, 0.0), format)
# Save the document
newpdf.SaveToFile("HorizontalSplitting.pdf")
# Close the objects
newpdf.Close()
pdf.Close()
The result of horizontal splitting is as follows:
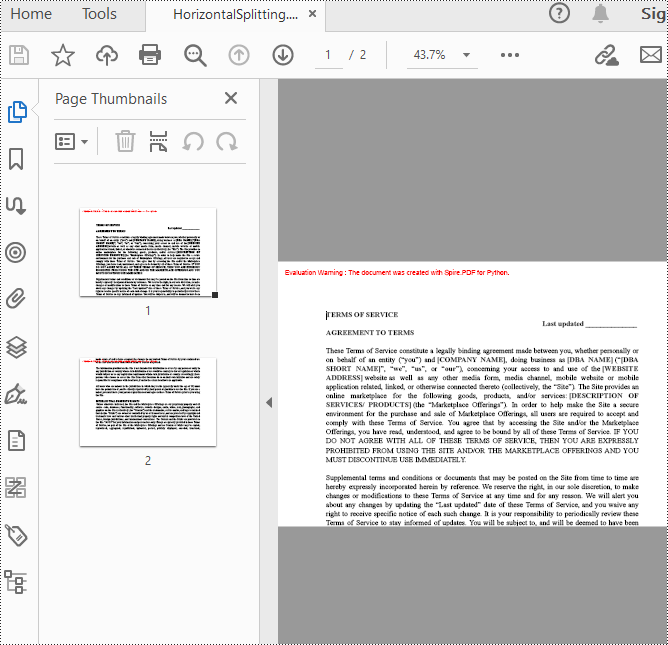
The result of vertical splitting is as follows:

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A PDF portfolio is a collection of files assembled into a single PDF document. It serves as a comprehensive and interactive showcase of various types of content, such as documents, images, presentations, videos, and more. Unlike a traditional PDF document, a PDF portfolio allows you to present multiple files in a cohesive and organized manner, providing a seamless browsing experience for the viewer. In this article, we will demonstrate how to create a PDF portfolio and how to identify if a PDF is a portfolio in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Create a PDF Portfolio with Python
Spire.PDF for Python allows you to generate a PDF portfolio by adding files to a PDF using the PdfDocument.Collection.AddFile() method. Furthermore, you can organize the files within the PDF portfolio by adding folders using the PdfDocument.Collection.Folders.CreateSubfolder() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the output file path and the folders where the files to be included in the PDF portfolio are located.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Iterate through the files in the first folder and add them to the PDF portfolio using the PdfDocument.Collection.AddFile() method.
- Iterate through the files in the second folder. For each file, create a separate folder within the PDF portfolio using the PdfDocument.Collection.Folders.CreateSubfolder() method, and then add the file to the corresponding folder using the PdfFolder.AddFile() method.
- Save the resulting PDF portfolio using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
import glob
# Specify the folders where the files to be included in the PDF portfolio are located
input_folder1 = "Folder1/*"
input_folder2 = "Folder2/*"
# Specify the output file path
output_file = "CreatePDFPortfolio.pdf"
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Get the list of file paths in the first folder
files1 = glob.glob(input_folder1)
# Loop through the files in the list
for i, file in enumerate(files1):
# Add each file to the PDF portfolio
doc.Collection.AddFile(file)
# Get the list of file paths in the second folder
files2 = glob.glob(input_folder2)
# Loop through the files in the list
for j, file in enumerate(files2):
# Create a separate folder for each file
folder = doc.Collection.Folders.CreateSubfolder(f"SubFolder{j + 1}")
# Add the file to the folder
folder.AddFile(file)
# Save the resulting PDF portfolio to the specified file path
doc.SaveToFile(output_file)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
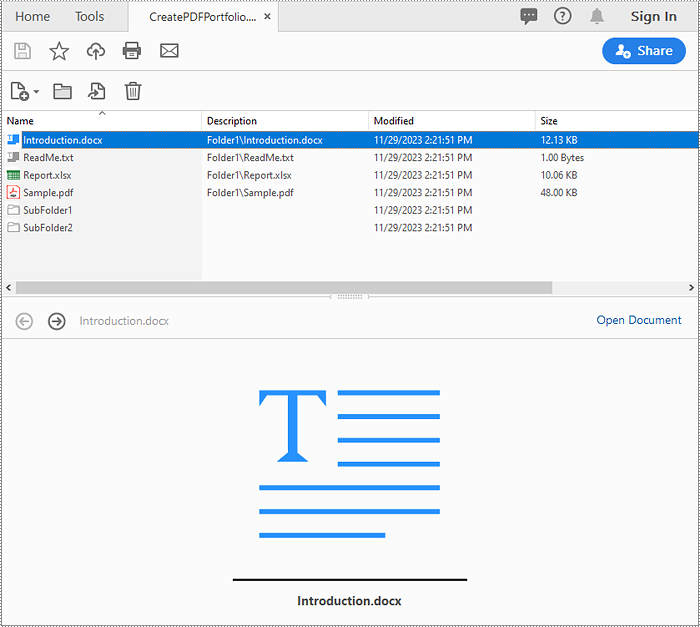
Identify if a PDF is a Portfolio with Python
You can use the PdfDocument.IsPortfolio property to easily identify whether a PDF document is a portfolio or not. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input and output file paths.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Identify whether the document is a portfolio or not using the PdfDocument.IsPortfolio property.
- Save the result to a text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
input_file = "CreatePDFPortfolio.pdf"
output_file = "IsPDFPortfolio.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile(input_file)
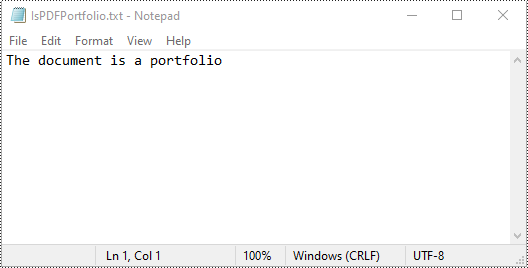
# Identify whether the document is a portfolio or not
if doc.IsPortfolio:
st = "The document is a portfolio"
else:
st = "The document is not a portfolio"
# Save the result to a text file
with open(output_file, "w") as text_file:
text_file.write(st)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Layers in PDF are similar to layers in image editing software, where different elements of a document can be organized and managed separately. Each layer can contain different content, such as text, images, graphics, or annotations, and can be shown or hidden independently. PDF layers are often used to control the visibility and positioning of specific elements within a document, making it easier to manage complex layouts, create dynamic designs, or control the display of information. In this article, you will learn how to add, hide, remove layers in a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add a Layer to PDF in Python
- Set Visibility of a Layer in PDF in Python
- Remove a Layer from PDF in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
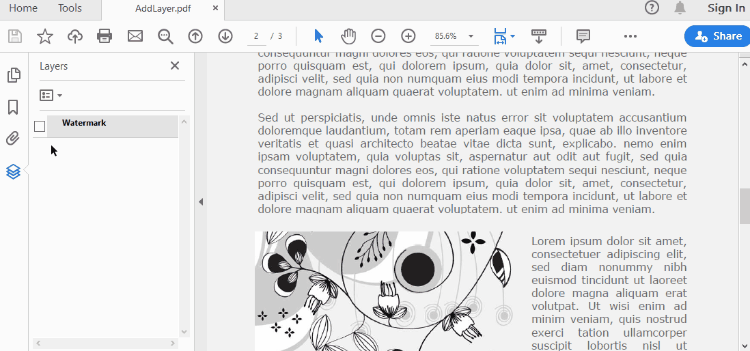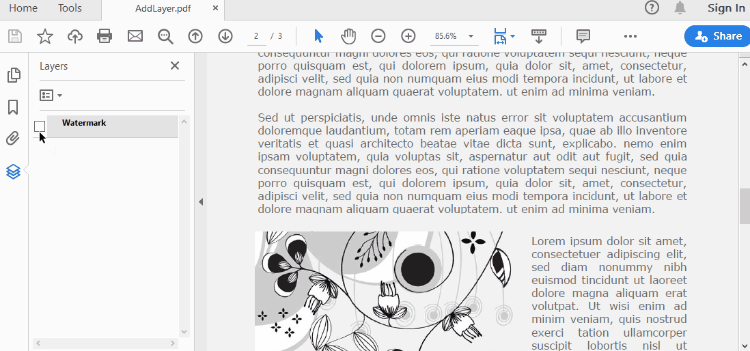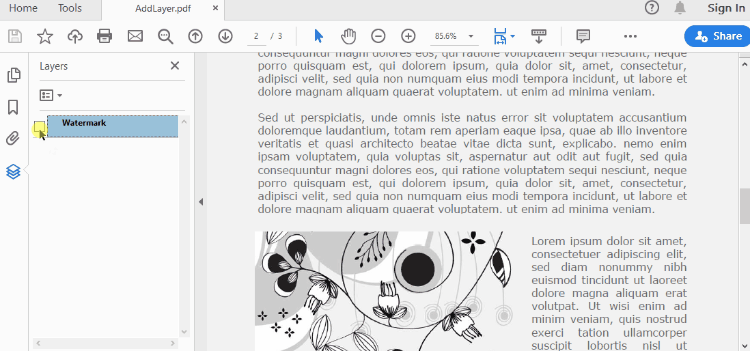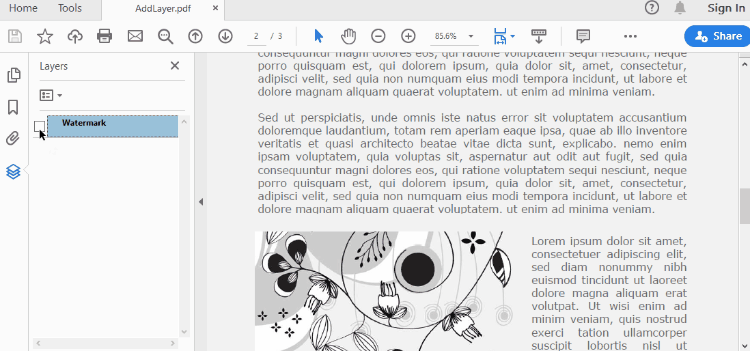
Add a Layer to PDF in Python
A layer can be added to a PDF document using the Document.Layers.AddLayer() method. After the layer object is created, you can draw text, images, fields, or other elements on it to form its appearance. The detailed steps to add a layer to PDF using Spire.PDF for Java are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a layer using Document.Layers.AddLayer() method.
- Get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Create a canvas for the layer based on the page using PdfLayer.CreateGraphics() method.
- Draw text on the canvas using PdfCanvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def AddLayerWatermark(doc):
# Create a layer named "Watermark"
layer = doc.Layers.AddLayer("Watermark")
# Create a font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Bodoni MT Black", 50.0, 1, True)
# Specify watermark text
watermarkText = "DO NOT COPY"
# Get text size
fontSize = font.MeasureString(watermarkText)
# Get page count
pageCount = doc.Pages.Count
# Loop through the pages
for i in range(0, pageCount):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages[i]
# Create canvas for layer
canvas = layer.CreateGraphics(page.Canvas)
# Draw sting on the graphics
canvas.DrawString(watermarkText, font, PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), (canvas.Size.Width - fontSize.Width)/2, (canvas.Size.Height - fontSize.Height)/2 )
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Invoke AddLayerWatermark method to add a layer
AddLayerWatermark(doc)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Set Visibility of a Layer in PDF in Python
To control the visibility of layers in a PDF document, you can use the PdfDocument.Layers[index].Visibility property. Set it to off to hide a layer, or set it to on to unhide a layer. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the visibility of a certain layer through Document.Layers[index].Visibility property.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Layer.pdf")
# Hide a layer by setting the visibility to off
doc.Layers[0].Visibility = PdfVisibility.Off
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/HideLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Remove a Layer from PDF in Python
If a layer is no more wanted, you can remove it using the PdfDocument.Layers.RmoveLayer() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific layer through PdfDocument.Layers[index] property.
- Remove the layer from the document using PdfDcument.Layers.RemoveLayer(PdfLayer.Name) method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Layer.pdf")
# Delete the specific layer
doc.Layers.RemoveLayer(doc.Layers[0].Name)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
