CSV (Comma-Separated Values) is a universal file format for storing tabular data, while lists are Python’s fundamental data structure for easy data manipulation. Converting CSV to lists in Python enables seamless data processing, analysis, and integration with other workflows. While Python’s built-in csv module works for basic cases, Spire.XLS for Python simplifies handling structured CSV data with its intuitive spreadsheet-like interface.
This article will guide you through how to use Python to read CSV into lists (and lists of dictionaries), covering basic to advanced scenarios with practical code examples.
Table of Contents:
- Why Choose Spire.XLS for CSV to List Conversion?
- Basic Conversion: CSV to Python List
- Advanced: Convert CSV to List of Dictionaries
- Handle Special Scenarios
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Choose Spire.XLS for CSV to List Conversion?
Spire.XLS is a powerful library designed for spreadsheet processing, and it excels at CSV handling for several reasons:
- Simplified Indexing: Uses intuitive 1-based row/column indexing (matching spreadsheet logic).
- Flexible Delimiters: Easily specify custom separators (commas, tabs, semicolons, etc.).
- Structured Access: Treats CSV data as a worksheet, making row/column traversal straightforward.
- Robust Data Handling: Automatically parses numbers, dates, and strings without extra code.
Installation
Before starting, install Spire.XLS for Python using pip:
pip install Spire.XLS
This command installs the latest stable version, enabling immediate use in your projects.
Basic Conversion: CSV to Python List
If your CSV file has no headers (pure data rows), Spire.XLS can directly read rows and convert them to a list of lists (each sublist represents a CSV row).
Step-by-Step Process:
- Import the Spire.XLS module.
- Create a Workbook object and load the CSV file.
- Access the first worksheet (Spire.XLS parses CSV into a worksheet).
- Traverse rows and cells, extracting values into a Python list.
CSV to List Python Code Example:
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Initialize Workbook and load CSV
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Employee.csv",",")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Convert sheet data to a list of lists
data_list = []
for i in range(sheet.Rows.Length):
row = []
for j in range(sheet.Columns.Length):
cell_value = sheet.Range[i + 1, j + 1].Value
row.append(cell_value)
data_list.append(row)
# Display the result
for row in data_list:
print(row)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Output:
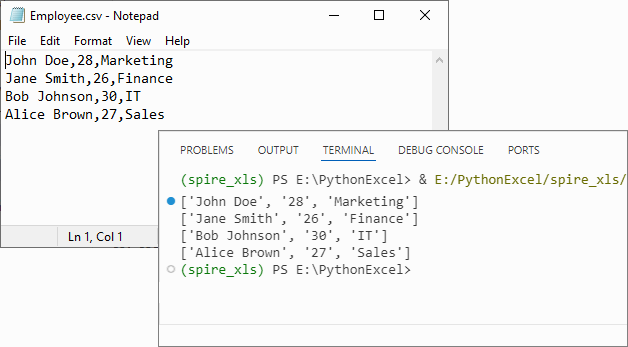
If you need to convert the list back to CSV, refer to: Python List to CSV: 1D/2D/Dicts – Easy Tutorial
Advanced: Convert CSV to List of Dictionaries
For CSV files with headers (e.g., name,age,city), converting to a list of dictionaries (where keys are headers and values are row data) is more intuitive for data manipulation.
CSV to Dictionary Python Code Example:
from spire.xls import *
# Initialize Workbook and load CSV
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Customer_Data.csv", ",")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Extract headers (first row)
headers = []
for j in range(sheet.Columns.Length):
headers.append(sheet.Range[1, j + 1].Value)
# Convert data rows to list of dictionaries
dict_list = []
for i in range(1, sheet.Rows.Length): # Skip header row
row_dict = {}
for j in range(sheet.Columns.Length):
key = headers[j]
value = sheet.Range[i + 1, j + 1].Value
row_dict[key] = value
dict_list.append(row_dict)
# Output the result
for record in dict_list:
print(record)
workbook.Dispose()
Explanation
- Load the CSV: Use LoadFromFile() method of Workbook class.
- Extracting Headers: Pull the first row of the worksheet to use as dictionary keys.
- Map Rows to Dictionaries: For each data row (skipping the header row), create a dictionary where keys are headers and values are cell contents.
Output:
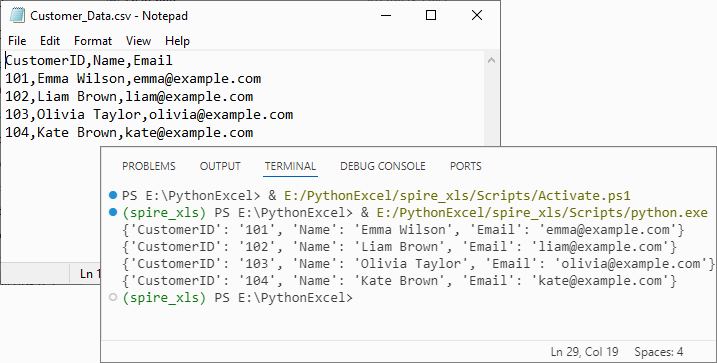
Handle Special Scenarios
CSV with Custom Delimiters (e.g., Tabs, Semicolons)
To process CSV files with delimiters other than commas (e.g., tab-separated TSV files), specify the delimiter in LoadFromFile:
# Load a tab-separated file
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.tsv", "\t")
# Load a semicolon-separated file
workbook.LoadFromFile("data_eu.csv", ";")
Clean Empty Values
Empty cells in the CSV are preserved as empty strings ('') in the list. To replace empty strings with a custom value (e.g., "N/A"), modify the cell value extraction:
cell_value = sheet.Range[i + 1, j + 1].Value or "N/A"
Conclusion
Converting CSV to lists in Python using Spire.XLS is efficient, flexible, and beginner-friendly. Whether you need a list of lists for raw data or a list of dictionaries for structured analysis, this library handles parsing, indexing, and resource management efficiently. By following the examples above, you can integrate this conversion into data pipelines, analysis scripts, or applications with minimal effort.
For more advanced features (e.g., CSV to Excel conversion, batch processing), you can visit the Spire.XLS for Python documentation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is Spire.XLS suitable for large CSV files?
A: Spire.XLS handles large files efficiently, but for very large datasets (millions of rows), consider processing in chunks or using specialized big data tools. For typical business datasets, it performs excellently.
Q2: How does this compare to using pandas for CSV to list conversion?
A: Spire.XLS offers more control over the parsing process and doesn't require additional data science dependencies. While pandas is great for analysis, Spire.XLS is ideal when you need precise control over CSV parsing or are working in environments without pandas.
Q3: How do I handle CSV files with headers when converting to lists?
A: For headers, use the dictionary conversion method. Extract the first row as headers, then map subsequent rows to dictionaries where keys are header values. This preserves column meaning and enables easy data access by column name.
Q4: How do I convert only specific columns from my CSV to a list?
A: Modify the inner loop to target specific columns:
# Convert only columns 1 and 3 (index 0 and 2)
target_columns = [0, 2]
for i in range(sheet.Rows.Length):
row = []
for j in target_columns:
cell_value = sheet.Range[i + 1, j + 1].Value
row.append(cell_value)
data_list.append(row)