CSV (Comma-Separated Values) is one of the most widely used formats for data exchange between applications, databases, and programming languages. For Python developers, the need to convert Python lists to CSV format arises constantly - whether exporting application data, generating reports, or preparing datasets for analysis. Spire.XLS for Python streamlines this critical process with an intuitive, reliable approach that eliminates common conversion pitfalls.
This comprehensive guide will explore how to write lists to CSV in Python. You'll discover how to handle everything from simple one-dimensional lists to complex nested dictionaries, while maintaining data integrity and achieving professional-grade output.
Table of Contents:
- Getting Started with Spire.XLS for Python
- Convert 1D List to CSV in Python
- Convert 2D List to CSV in Python
- Convert List of Dictionaries to CSV in Python
- Advanced: Custom Delimiters and Encoding
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Getting Started with Spire.XLS for Python
Why Use Spire.XLS for List-to-CSV Conversion?
While Python's built-in csv module is excellent for simple CSV operations, Spire.XLS offers additional benefits:
- Handles various data types seamlessly
- Lets you customize CSV output (e.g., semicolon delimiters for European locales).
- Can save in multiple file formats (CSV, XLSX, XLS, etc.)
- Works well with both simple and complex data structures
Install via pip
The Spire.XLS for Python lets you create, modify, and save Excel/CSV files programmatically. To use it, run this command in your terminal or command prompt:
pip install Spire.XLS
This command downloads and installs the latest version, enabling you to start coding immediately.
Convert 1D List to CSV in Python
A 1D (one-dimensional) list is a simple sequence of values (e.g., ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"]). The following are the steps to write these values to a single row or column in a CSV.
Step 1: Import Spire.XLS Modules
First, import the necessary classes from Spire.XLS:
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
Step 2: Create a Workbook and Worksheet
Spire.XLS uses workbooks and worksheets to organize data. We’ll create a new workbook and add a new worksheet:
# Create a workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Remove the default worksheet and add a new one
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add()
Step 3: Write 1D List Data to the Worksheet
Choose to write the list to a single row (horizontal) or a single column (vertical).
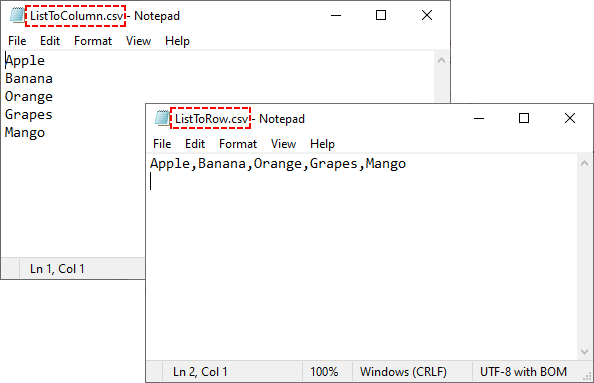
Example 1: Write 1D List to a Single Row
# Sample 1D list
data_list = ["Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Grapes", "Mango"]
# Write list to row 1
for i, item in enumerate(data_list):
worksheet.Range[1, i+1].Value = item
Example 2: Write 1D List to a Single Column
# Sample 1D list
data_list = ["Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Grapes", "Mango"]
# Write list to column 1
for i, item in enumerate(data_list):
worksheet.Range[i + 1, 1].Value = item
Step 4: Save the Worksheet as CSV
Use SaveToFile() to export the workbook to a CSV file. Specify FileFormat.CSV to ensure proper formatting:
# Save as CSV file
workbook.SaveToFile("ListToCSV.csv", FileFormat.CSV)
# Close the workbook to free resources
workbook.Dispose()
Output:
Convert 2D List to CSV in Python
A 2D (two-dimensional) list is a list of lists that represents tabular data. More commonly, you'll work with this type of list, where each inner list represents a row in the CSV file.
Python Code for 2D List to CSV:
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Remove the default worksheet and add a new one
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add()
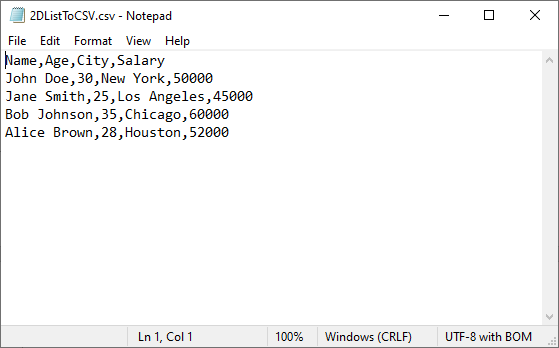
# Sample 2D list (headers + data)
data = [
["Name", "Age", "City", "Salary"],
["John Doe", 30, "New York", 50000],
["Jane Smith", 25, "Los Angeles", 45000],
["Bob Johnson", 35, "Chicago", 60000],
["Alice Brown", 28, "Houston", 52000]
]
# Write 2D list to worksheet
for row_index, row_data in enumerate(data):
for col_index, cell_data in enumerate(row_data):
worksheet.Range[row_index + 1, col_index + 1].Value = str(cell_data)
# Save as a CSV file
workbook.SaveToFile("2DListToCSV.csv", FileFormat.CSV)
workbook.Dispose()
Key points:
- Ideal for structured tabular data with headers
- Nested loops handle both rows and columns
- Converting all values to strings ensures compatibility
Output:
The generated CSV can be converted to PDF for secure presentation, or converted to JSON for web/API data exchange.
Convert List of Dictionaries to CSV in Python
Lists of dictionaries are ideal when data has named fields (e.g., [{"Name": "Alice", "Age": 30}, {"Name": "Bob", "Age": 25}]). The dictionary keys become CSV headers, and values become rows.
Python Code for List of Dictionaries to CSV
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Remove the default worksheet and add a new one
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add()
# Sample 2D list (headers + data)
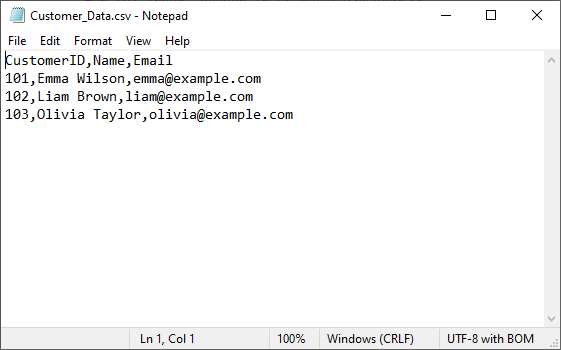
customer_list = [
{"CustomerID": 101, "Name": "Emma Wilson", "Email": "emma@example.com"},
{"CustomerID": 102, "Name": "Liam Brown", "Email": "liam@example.com"},
{"CustomerID": 103, "Name": "Olivia Taylor", "Email": "olivia@example.com"}
]
# Extract headers (dictionary keys) and write to row 1
if customer_list: # Ensure the list is not empty
headers = list(customer_list[0].keys())
# Write headers
for col_index, header in enumerate(headers):
worksheet.Range[1, col_index + 1].Value = str(header)
# Write dictionary values to rows 2 onwards
for row_index, record in enumerate(customer_list):
for col_index, header in enumerate(headers):
# Safely get value, use empty string if key doesn't exist
value = record.get(header, "")
worksheet.Range[row_index + 2, col_index + 1].Value = str(value)
# Save as CSV file
workbook.SaveToFile("Customer_Data.csv", FileFormat.CSV)
workbook.Dispose()
Key points:
- Extracts headers from the first dictionary's keys
- Uses .get() method to safely handle missing keys
- Maintains column order based on the header row
Output:
Advanced: Custom Delimiters and Encoding
One of the biggest advantages of using Spire.XLS for Python is its flexibility in saving CSV files with custom delimiters and encodings. This allows you to tailor your CSV output for different regions, applications, and data requirements.
To specify the delimiters and encoding, simply change the corresponding parameter in the SaveToFile() method of the Worksheet class. Example:
# Save with different delimiters and encodings
worksheet.SaveToFile("semicolon_delimited.csv", ";", Encoding.get_UTF8())
worksheet.SaveToFile("tab_delimited.csv", "\t", Encoding.get_UTF8())
worksheet.SaveToFile("unicode_encoded.csv", ",", Encoding.get_Unicode())
Conclusion
Converting Python lists to CSV is straightforward with the right approach. Whether you're working with simple 1D lists, structured 2D arrays, or more complex lists of dictionaries, Spire.XLS provides a robust solution. By choosing the appropriate method for your data structure, you can ensure efficient and accurate CSV generation in any application.
For more advanced features and detailed documentation, you can visit the official Spire.XLS for Python documentation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the best practices for list to CSV conversion?
- Validate input data before processing
- Handle exceptions with try-catch blocks
- Test with sample data before processing large datasets
- Clean up resources using Dispose()
Q2: Can I export multiple lists into separate CSV files in one go?
Yes. Loop through your lists and save each as a separate CSV:
lists = {
"fruits": ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"],
"scores": [85, 92, 78]
}
for name, data in lists.items():
wb = Workbook()
wb.Worksheets.Clear()
ws = wb.Worksheets.Add(name)
for i, val in enumerate(data):
ws.Range[i + 1, 1].Value = str(val)
wb.SaveToFile(f"{name}.csv", FileFormat.CSV)
wb.Dispose()
Q3: How to format numbers (e.g., currency, decimals) in CSV?
CSV stores numbers as plain text, so formatting must be applied before saving:
ws.Range["A1:A10"].NumberFormat = "$#,##0.00"
This ensures numbers appear as $1,234.56 in the CSV. For more number formatting options, refer to: Set the Number Format in Python
Q4: Does Spire.XLS for Python work on all operating systems?
Yes! Spire.XLS for Python is cross-platform and supports Windows, macOS, and Linux systems.