Convert Python Code to Word (Plain or Syntax-Highlighted)

Developers often need to include Python code inside Word documents for technical documentation, tutorials, code reviews, internal reports, or client deliverables. While copying and pasting code manually works for small snippets, automated solutions provide better consistency, formatting control, and scalability — especially when working with long scripts or multiple files.
This tutorial demonstrates multiple practical methods to export Python code into Word documents using Python. Each method has its own strengths depending on whether you prioritize formatting, automation, syntax highlighting, or readability.
On This Page:
- Install Required Libraries
- Export Python Code to Word as Plain Text
- Add Syntax-Highlighted Python Code to Word
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Install Required Libraries
Install the necessary dependencies before running the examples:
pip install spire.doc pygments
Library Overview:
- Spire.Doc for Python — used to create and manipulate Word documents programmatically
- Pygments — used to generate syntax-highlighted code in RTF, HTML, or image formats
- Pathlib (built-in) — used for reading Python files from disk
- textwrap (built-in) — used to wrap long code lines before generating images formatting
Export Python Code to Word as Plain Text
Plain text insertion is the most straightforward method for embedding code in Word. It keeps scripts fully editable and preserves formatting such as indentation and line breaks.
Method 1. Insert Raw Python Code into a Word Document
This method reads a .py file and inserts the code directly into Word while applying a monospace font style.
from pathlib import Path
from spire.doc import *
# Read Python file
code_string = Path("demo.py").read_text(encoding="utf-8")
# Create a Word document
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 60
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Insert code string to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText(code_string)
# Create a paragraph style
style = ParagraphStyle(doc)
style.Name = "code"
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Consolas"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
style.ParagraphFormat.LineSpacing = 12
doc.Styles.Add(style)
# Apply the style to the paragraph
paragraph.ApplyStyle("code")
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("Output.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
doc.Dispose()
How It Works:
This technique treats Python code as plain text and inserts it directly into a Word paragraph. The script reads the .py file using Path.read_text(), preserving indentation, blank lines, and overall structure.
After inserting the text, a custom paragraph style is created and applied. The use of a monospace font such as Consolas ensures alignment and readability, while fixed line spacing maintains consistent formatting across lines.
Because no intermediate format is used, this is the simplest and fastest approach. However, it does not provide syntax highlighting or semantic styling—Word only displays the code as formatted text.
Output:
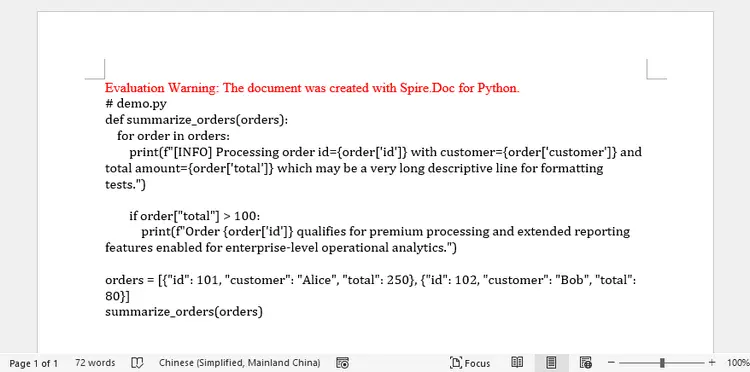
You May Also Like: Generate Word Documents Using Python
Method 2. Generate a Word File from Markdown-Wrapped Code
If your workflow already uses Markdown, wrapping Python code inside fenced blocks provides a structured way to convert scripts into Word documents.
from pathlib import Path
from spire.doc import *
# Read Python file
code = Path("demo.py").read_text(encoding="utf-8")
# Convert to Markdown
md_content = f"```python\n{code}\n```"
Path("temp.md").write_text(md_content, encoding="utf-8")
# Load Markdown into Word
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("temp.md")
# Update page settings
doc.Sections[0].PageSetup.Margins.All = 60
# Save as a DOCX file
doc.SaveToFile("Output.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Dispose()
How It Works:
Instead of inserting text directly, this method wraps Python code inside Markdown fenced code blocks. The generated Markdown file is then loaded into Word using Spire.Doc’s Markdown parsing capability.
When Word imports Markdown, it automatically preserves code formatting such as indentation and line breaks. This approach is useful when your documentation workflow already uses Markdown or when code needs to coexist with headings, lists, and descriptive text.
Since Markdown itself does not inherently apply syntax coloring inside Word, the result is still plain code formatting—but the structure is cleaner and easier to manage within technical documentation pipelines.
Output:
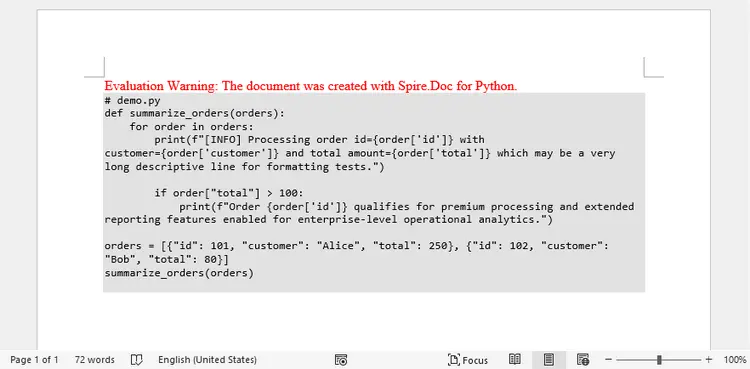
Add Syntax-Highlighted Python Code to Word
Syntax highlighting makes code easier to read and understand. By integrating Pygments, Python scripts can be converted into stylized formats before being embedded into Word.
This section explores three approaches — RTF, HTML, and image rendering — each with different strengths depending on your formatting goals.
Method 1. Use RTF for Preformatted Code Blocks
RTF allows syntax-highlighted code to remain fully editable within Word.
from pathlib import Path
from pygments import highlight
from pygments.lexers import PythonLexer
from pygments.formatters import RtfFormatter
from spire.doc import *
# Read Python file
code = Path("demo.py").read_text(encoding="utf-8")
# Set font
formatter = RtfFormatter(fontface ="Consolas")
# Specify the lexer
rtf_text = highlight(code, PythonLexer(), formatter)
rtf_text = rtf_text.replace(r"\f0", r"\f0\fs24") # font size (24 for 12-point font)
# Create a Word document
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 60
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Insert the syntax-highlighted code as RTF
paragraph.AppendRTF(rtf_text)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("Output.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
doc.Dispose()
How It Works:
Pygments analyzes Python syntax using a lexer, identifying tokens such as keywords, strings, and comments. The RTF formatter applies styling rules that represent colors and fonts using RTF control words.
The resulting RTF string is inserted directly into Word using AppendRTF(). Because RTF is a native Word-compatible format, the document preserves fonts, colors, and spacing without requiring additional rendering steps.
Font size is controlled by modifying RTF control words (e.g., \fs24), allowing precise control over appearance. This method produces editable, selectable code with syntax highlighting inside Word.
Output:
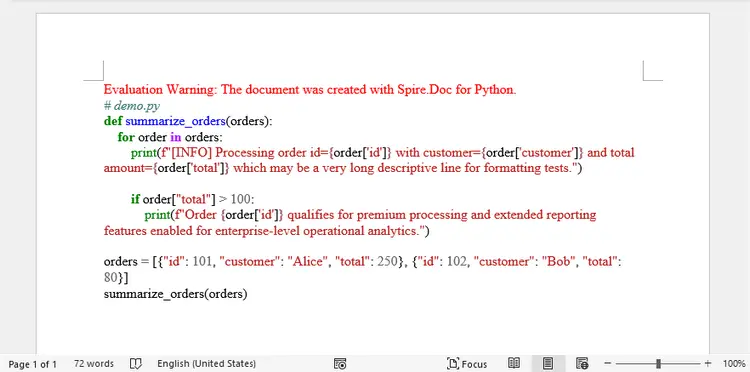
Method 2. Render Highlighted Code via HTML Formatting
HTML rendering provides visually rich syntax highlighting and automatic text wrapping.
from pathlib import Path
from pygments import highlight
from pygments.lexers import PythonLexer
from pygments.formatters import HtmlFormatter
from spire.doc import *
# Read Python file
code = Path("demo.py").read_text(encoding="utf-8")
# Generate HTML from the Python code with syntax highlighting
html_text = highlight(code, PythonLexer(), HtmlFormatter(full=True))
# Create a Word document
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 60
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Add the HTML string to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendHTML(html_text)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("Output.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
doc.Dispose()
How It Works:
Here, Pygments converts Python code into styled HTML using the HtmlFormatter. The HTML output includes inline styles or CSS rules that represent syntax colors and formatting.
Spire.Doc then interprets the HTML content and renders it into Word. During this process, HTML elements are translated into Word formatting structures, allowing the highlighted code to appear visually similar to web-based code blocks.
This approach is ideal when code originates from web content, static documentation sites, or Markdown-to-HTML workflows.
Output:
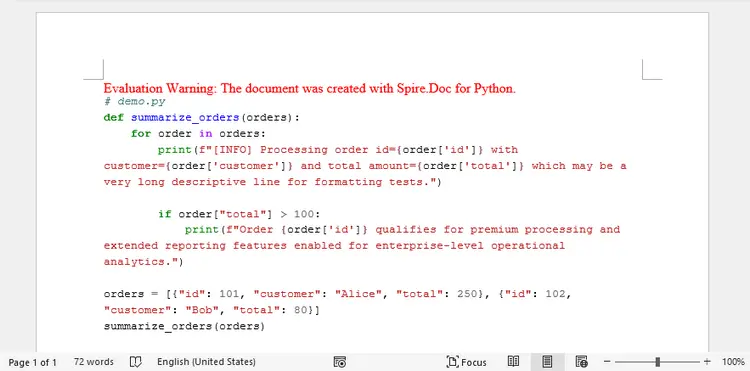
You May Also Like: Convert HTML to Word DOC or DOCX in Python
Method 3. Insert Syntax-Highlighted Code as Images
For scenarios where visual consistency matters more than editability, code can be rendered as an image before insertion.
from pathlib import Path
import textwrap
from pygments import highlight
from pygments.lexers import PythonLexer
from pygments.formatters import ImageFormatter
from spire.doc import *
# Read Python file
code = Path("demo.py").read_text(encoding="utf-8")
# Wrap long lines manually
def wrap_code_lines(code_text, max_width=75):
wrapped_lines = []
for line in code_text.splitlines():
if len(line) > max_width:
wrapped_lines.extend(textwrap.wrap(
line,
width=max_width,
replace_whitespace=False,
drop_whitespace=False
))
else:
wrapped_lines.append(line)
return "\n".join(wrapped_lines)
code = wrap_code_lines(code, max_width=75)
# Step 3: Generate image
formatter = ImageFormatter(
font_name="Consolas",
font_size=18,
scale=2,
image_pad=10,
line_pad=2,
background_color="#ffffff"
)
img_bytes = highlight(code, PythonLexer(), formatter)
with open("code.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(img_bytes)
# Create a Word document
doc = Document()
section = doc.AddSection()
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 60
# Insert into Word
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
picture = paragraph.AppendPicture("code.png")
# Ensure image fits page width
page_width = (
section.PageSetup.PageSize.Width
- section.PageSetup.Margins.Left
- section.PageSetup.Margins.Right
)
picture.Width = page_width
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("Output.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
doc.Dispose()
How It Works:
This method renders Python code as an image instead of editable text. Pygments generates a syntax-highlighted bitmap using the ImageFormatter, allowing full visual control over fonts, colors, padding, and DPI.
Since image rendering does not automatically wrap long lines, the script manually wraps lengthy code lines using Python’s textwrap module before generating the image. This prevents oversized images that exceed page width.
After inserting the image into Word, its width is dynamically resized to fit the printable page area. Because the code is embedded as a graphic, it preserves exact visual appearance across platforms and prevents formatting inconsistencies—but the text is no longer editable.
Output:
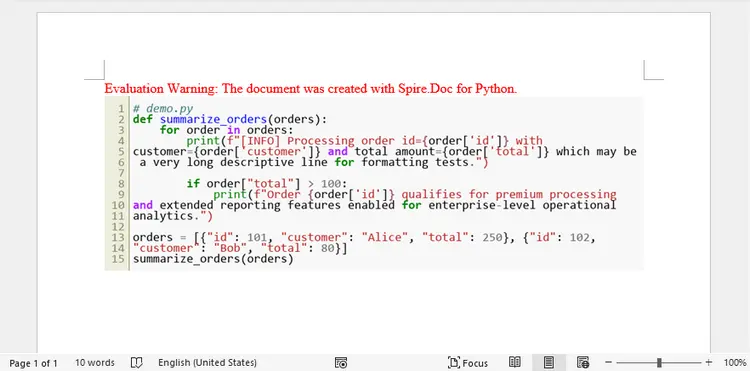
Conclusion
Converting Python code to Word documents can be achieved through several approaches depending on your goals. Plain text methods provide simplicity and flexibility, while RTF and HTML techniques offer powerful syntax highlighting with selectable text. Image-based code blocks deliver consistent visual formatting but require careful line wrapping and scaling.
For most documentation workflows:
- Use plain text for editable technical content
- Use HTML or RTF for syntax-highlighted documentation
- Use images when formatting consistency is critical
FAQs
Which method is best for tutorials?
HTML or RTF methods provide clear syntax highlighting with selectable text.
How can I preserve indentation and blank lines?
Read the .py file using .read_text() without stripping or modifying lines.
Why do image-based code blocks become too small?
Word scales images to fit page width. Increasing the image formatter’s scale or adjusting the wrapping width can improve readability.
Can readers copy code from Word?
Yes — except when code is inserted as an image.
Do I need Markdown for conversion?
No. Markdown is optional but useful when working with documentation pipelines.
Can I export the generated document as a PDF file?
Yes. When saving the document, simply specify PDF as the output format in the Document.SaveToFile() method.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a 30-day trial license.
How to Convert HTML to Markdown in Python: Step-by-Step Guide

Converting HTML to Markdown using Python is a common task for developers managing web content, documentation, or API data. While HTML provides powerful formatting and structure, it can be verbose and harder to maintain for tasks like technical writing or static site generation. Markdown, by contrast, is lightweight, human-readable, and compatible with platforms such as GitHub, GitLab, Jekyll, and Hugo.
Automating HTML to Markdown conversion with Python streamlines workflows, reduces errors, and ensures consistent output. This guide covers everything from converting HTML files and strings to batch processing multiple files, along with best practices to ensure accurate Markdown results.
What You Will Learn
- Why Convert HTML to Markdown
- Install HTML to Markdown Library for Python
- Convert an HTML File to Markdown in Python
- Convert an HTML String to Markdown in Python
- Batch Conversion of Multiple HTML Files
- Best Practices for HTML to Markdown Conversion
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Convert HTML to Markdown?
Before diving into the code, let’s look at why developers often prefer Markdown over raw HTML in many workflows:
- Simplicity and Readability
Markdown is easier to read and edit than verbose HTML tags. - Portability Across Tools
Markdown is supported by GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Obsidian, Notion, and static site generators like Hugo and Jekyll. - Better for Version Control
Being plain text, Markdown makes it easier to track changes with Git, review diffs, and collaborate. - Faster Content Creation
Writing Markdown is quicker than remembering HTML tag structures. - Integration with Static Site Generators
Popular frameworks rely on Markdown as the main content format. Converting from HTML ensures smooth migration. - Cleaner Documentation Workflows
Many documentation systems and wikis use Markdown as their primary format.
In short, converting HTML to Markdown improves maintainability, reduces clutter, and fits seamlessly into modern developer workflows.
Install HTML to Markdown Library for Python
Before converting HTML content to Markdown in Python, you’ll need a library that can handle both formats effectively. Spire.Doc for Python is a reliable choice that allows you to transform HTML files or HTML strings into Markdown while keeping headings, lists, images, and links intact.
You can install it from PyPI using pip:
pip install spire.doc
Once installed, you can automate the HTML to Markdown conversion in your Python scripts. The same library also supports broader scenarios. For example, when you need editable documents, you can rely on its HTML to Word conversion feature to transform web pages into Word files. And for distribution or archiving, HTML to PDF conversion is especially useful for generating standardized, platform-independent documents.
Convert an HTML File to Markdown in Python
One of the most common use cases is converting an existing .html file into a .md file. This is especially useful when migrating old websites, technical documentation, or blog posts into Markdown-based workflows, such as static site generators (Jekyll, Hugo) or Git-based documentation platforms (GitHub, GitLab, Read the Docs).
Steps
- Create a new Document instance.
- Load the .html file into the document using LoadFromFile().
- Save the document as a .md file using SaveToFile() with FileFormat.Markdown.
- Close the document to release resources.
Code Example
from spire.doc import *
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load an existing HTML file
doc.LoadFromFile("input.html", FileFormat.Html)
# Save as Markdown file
doc.SaveToFile("output.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
This converts input.html into output.md, preserving structural elements such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, and images.
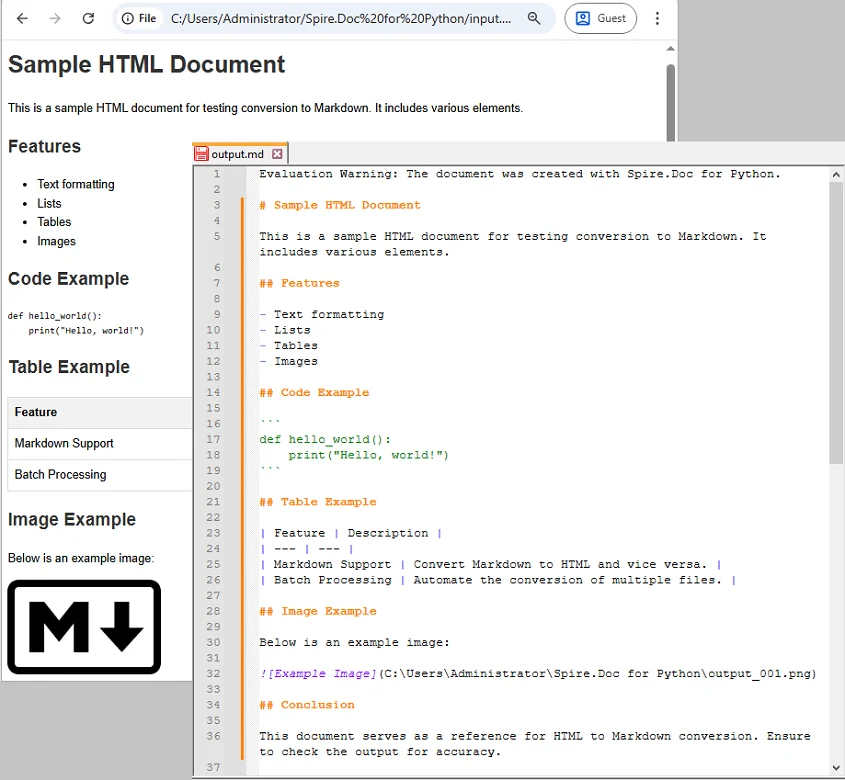
If you’re also interested in the reverse process, check out our guide on converting Markdown to HTML in Python.
Convert an HTML String to Markdown in Python
Sometimes, HTML content is not stored in a file but is dynamically generated—for example, when retrieving web content from an API or scraping. In these scenarios, you can convert directly from a string without needing to create a temporary HTML file.
Steps
- Create a new Document instance.
- Add a Section to the document.
- Add a Paragraph to the section.
- Append the HTML string to the paragraph using AppendHTML().
- Save the document as a Markdown file using SaveToFile().
- Close the document to release resources.
Code Example
from spire.doc import *
# Sample HTML string
html_content = """
<h1>Welcome</h1>
<p>This is a <strong>sample</strong> paragraph with <em>emphasis</em>.</p>
<ul>
<li>First item</li>
<li>Second item</li>
</ul>
"""
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph and append the HTML string
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendHTML(html_content)
# Save the document as Markdown
doc.SaveToFile("string_output.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# close the document to release resources
doc.Close()
The resulting Markdown will look like this:
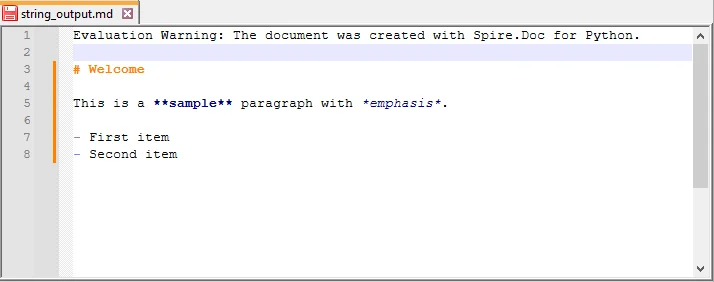
Batch Conversion of Multiple HTML Files
For larger projects, you may need to convert multiple .html files in bulk. A simple loop can automate the process.
import os
from spire.doc import *
# Define the folder containing HTML files to convert
input_folder = "html_files"
# Define the folder where converted Markdown files will be saved
output_folder = "markdown_files"
# Create the output folder if it doesn't exist
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# Loop through all files in the input folder
for filename in os.listdir(input_folder):
# Process only files with .html extension
if filename.endswith(".html"):
# Create a new Document object
doc = Document()
# Load the HTML file into the Document object
doc.LoadFromFile(os.path.join(input_folder, filename), FileFormat.Html)
# Generate the output file path by replacing .html with .md
output_file = os.path.join(output_folder, filename.replace(".html", ".md"))
# Save the Document as a Markdown file
doc.SaveToFile(output_file, FileFormat.Markdown)
# Close the Document to release resources
doc.Close()
This script processes all .html files inside html_files/ and saves the Markdown results into markdown_files/.
Best Practices for HTML to Markdown Conversion
Turning HTML to Markdown makes content easier to read, manage, and version-control. To ensure accurate and clean conversion, follow these best practices:
- Validate HTML Before Conversion
Ensure your HTML is properly structured. Invalid tags can cause incomplete or broken Markdown output. - Understand Markdown Limitations
Markdown does not support advanced CSS styling or custom HTML tags. Some formatting might get lost. - Choose File Encoding Carefully
Always be aware of character encoding. Open and save your files with a specific encoding (like UTF-8) to prevent issues with special characters. - Batch Processing
If converting multiple files, create a robust script that includes error handling (try-except blocks), logging, and skips problematic files instead of halting the entire process.
Conclusion
Converting HTML to Markdown in Python is a valuable skill for developers handling documentation pipelines, migrating web content, or processing data from APIs. With Spire.Doc for Python, you can:
- Convert individual HTML files into Markdown with ease.
- Transform HTML strings directly into .md files.
- Automate batch conversions to efficiently manage large projects.
By applying these methods, you can streamline your workflows and ensure your content remains clean, maintainable, and ready for modern publishing platforms.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert Markdown back to HTML in Python?
A1: Yes, Spire.Doc supports the conversion of Markdown to HTML, allowing for seamless transitions between these formats.
Q2: Will the conversion preserve complex HTML elements like tables?
A2: While Spire.Doc effectively handles standard HTML elements, it's advisable to review complex layouts, such as tables and nested elements, to ensure accurate conversion results.
Q3: Can I automate batch conversion for multiple HTML files?
A3: Absolutely! You can automate batch conversion using scripts in Python, enabling efficient processing of multiple HTML files at once.
Q4: Is Spire.Doc free to use?
A4: Spire.Doc provides both free and commercial versions, giving developers the flexibility to access essential features at no cost or unlock advanced functionality with a license.
How to Convert Markdown to HTML in Python: Step-by-Step Guide

Markdown (.md) is widely used in web development, documentation, and technical writing. Its simple syntax makes content easy to write and read. However, web browsers do not render Markdown directly. Converting Markdown to HTML ensures your content is structured, readable, and compatible with web platforms.
In this step-by-step guide, you will learn how to efficiently convert Markdown (.md) files into HTML using Python and Spire.Doc for Python, complete with practical code examples, clear instructions, and best practices for both single-file and batch conversions.
Table of Contents
- What is Markdown
- Why Convert Markdown to HTML
- Introducing Spire.Doc for Python
- Step-by-Step Guide: Converting Markdown to HTML in Python
- Automating Batch Conversion
- Best Practices for Markdown to HTML Conversion
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Markdown?
Markdown is a lightweight markup language designed for readability and ease of writing. Unlike HTML, which can be verbose and harder to write by hand, Markdown uses simple syntax to indicate headings, lists, links, images, and more.
Example Markdown:
# This is a Heading
This is a paragraph with \*\*bold text\*\* and \*italic text\*.
- Item 1
- Item 2
Even in its raw form, Markdown is easy to read, which makes it popular for documentation, blogging, README files, and technical writing.
For more on Markdown syntax, see the Markdown Guide.
Why Convert Markdown to HTML?
While Markdown is excellent for authoring content, web browsers cannot render it natively. Converting Markdown to HTML allows you to:
- Publish content on websites – Most CMS platforms require HTML for web pages.
- Enhance styling – HTML supports CSS and JavaScript for advanced formatting and interactivity.
- Maintain compatibility – HTML is universally supported by browsers, ensuring content displays correctly everywhere.
- Integrate with web frameworks – Frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular require HTML as the base for rendering components.
Introducing Spire.Doc for Python
Spire.Doc for Python is a robust library for handling multiple document formats. It supports reading and writing Word documents, Markdown files, and exporting content to HTML. The library allows developers to convert Markdown directly to HTML with minimal code, preserving proper formatting and structure.
In addition to HTML, Spire.Doc for Python also allows you to convert Markdown to Word in Python or convert Markdown to PDF in Python, making it particularly useful for developers who want a unified tool for handling Markdown across different output formats.
Benefits of Using Spire.Doc for Python for Markdown to HTML Conversion
- Easy-to-use API – Simple, intuitive methods that reduce development effort.
- Accurate formatting – Preserves all Markdown elements such as headings, lists, links, and emphasis in HTML.
- No extra dependencies – Eliminates the need for manual parsing or third-party libraries.
- Flexible usage – Supports both single-file conversion and automated batch processing.
Step-by-Step Guide: Converting Markdown to HTML in Python
Now that you understand the purpose and benefits of converting Markdown to HTML, let’s walk through a clear, step-by-step process to transform your Markdown files into structured, web-ready HTML.
Step 1: Install Spire.Doc for Python
First, ensure that Spire.Doc for Python is installed in your environment. You can install it directly from PyPI using pip:
pip install spire.doc
Step 2: Prepare Your Markdown File
Next, create a sample Markdown file that you want to convert. For example, example.md:
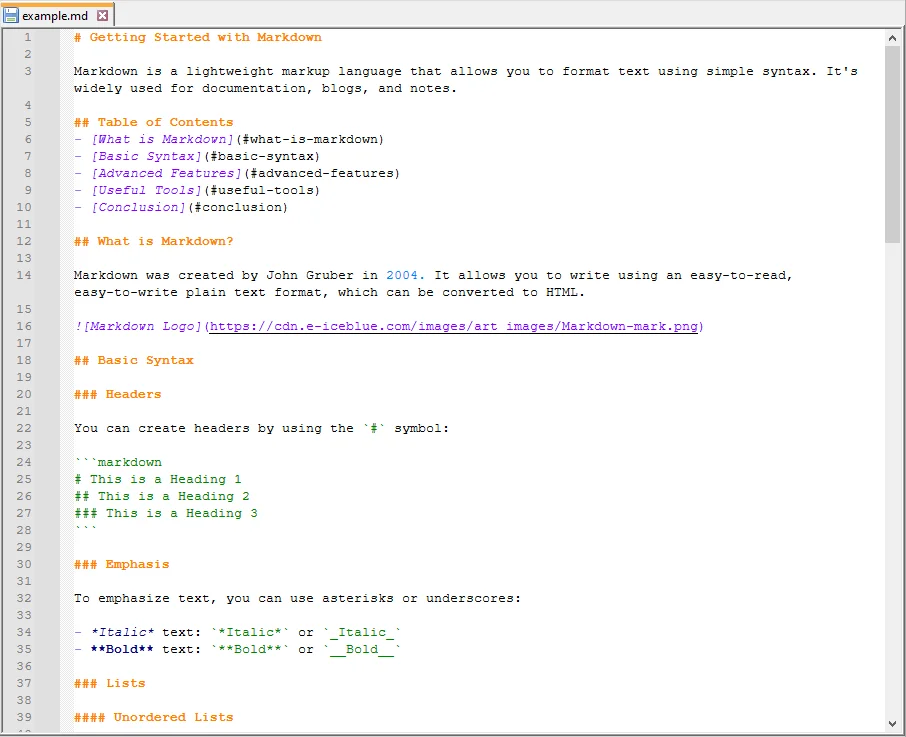
Step 3: Write the Python Script
Now, write a Python script that loads the Markdown file and converts it to HTML:
from spire.doc import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load the Markdown file
doc.LoadFromFile("example.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Save the document as HTML
doc.SaveToFile("example.html", FileFormat.Html)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
Explanation of the code:
- Document() initializes a new document object.
- LoadFromFile("example.md", FileFormat.Markdown) loads the Markdown file into memory.
- SaveToFile("example.html", FileFormat.Html) converts the loaded content into HTML and saves it to disk.
- doc.Close() ensures resources are released properly, which is particularly important when processing multiple files or running batch operations.
Step 4: Verify the HTML Output
Finally, open the generated example.html file in a web browser or HTML editor. Verify that the Markdown content has been correctly converted.

Automating Batch Conversion
You can convert multiple Markdown files in a folder automatically:
import os
from spire.doc import *
# Set the folder containing Markdown files
input_folder = "markdown_files"
# Set the folder where HTML files will be saved
output_folder = "html_files"
# Create the output folder if it doesn't exist
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# Loop through all files in the input folder
for filename in os.listdir(input_folder):
# Process only Markdown files
if filename.endswith(".md"):
# Create a new Document object for each file
doc = Document()
# Load the Markdown file into the Document object
doc.LoadFromFile(os.path.join(input_folder, filename), FileFormat.Markdown)
# Construct the output file path by replacing .md extension with .html
output_file = os.path.join(output_folder, filename.replace(".md", ".html"))
# Save the loaded Markdown content as HTML
doc.SaveToFile(output_file, FileFormat.Html)
# Close the document to release resources
doc.Close()
This approach allows you to process multiple Markdown files efficiently and generate corresponding HTML files automatically.
Best Practices for Markdown to HTML Conversion
While the basic steps are enough to complete a Markdown-to-HTML conversion, following a few best practices will help you avoid common pitfalls, improve compatibility, and ensure your output is both clean and professional:
- Use proper Markdown syntax – Ensure headings, lists, links, and emphasis are correctly written.
- Use UTF-8 Encoding: Always save your Markdown files in UTF-8 encoding to avoid issues with special characters or non-English text.
- Batch Processing: If you need to convert multiple files, wrap your script in a loop and process entire folders. This saves time and ensures consistent formatting across documents.
- Enhance Styling: Remember that HTML gives you the flexibility to add CSS and JavaScript for custom layouts, responsive design, and interactivity—something not possible in raw Markdown.
Conclusion
Converting Markdown to HTML using Python with Spire.Doc is simple, reliable, and efficient. It preserves formatting, supports automation, and produces clean HTML output ready for web use. By following this guide, you can implement a smooth Markdown to HTML workflow for both single documents and batch operations.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert multiple Markdown files to HTML in Python?
A1: Yes, you can automate batch conversions by iterating through Markdown files in a directory and applying the conversion logic to each file.
Q2: Will the HTML preserve all Markdown formatting?
A2: Yes, Spire.Doc effectively preserves all essential Markdown formatting, including headings, lists, bold and italic text, links, and more.
Q3: Is there a way to handle images in Markdown during conversion?
A3: Yes, Spire.Doc supports the conversion of images embedded in Markdown, ensuring they are included in the resulting HTML.
Q4: Do I need additional libraries besides Spire.Doc?
A4: No additional libraries are required. Spire.Doc for Python provides a comprehensive solution for converting Markdown to HTML without any external dependencies.
Q5: Can I use the generated HTML in web frameworks?
A5: Yes, the HTML produced is fully compatible with popular web frameworks such as React, Vue, and Angular, making integration seamless.
Convert HTML to Text in Python | Simple Plain Text Output

HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to create web pages, allowing developers to build rich and visually appealing layouts. However, HTML files often contain a large number of tags, which makes them difficult to read if you only need the main content. By using Python to convert HTML to text, this problem can be easily solved. Unlike raw HTML, the converted text file strips away all unnecessary markup, leaving only clean and readable content that is easier to store, analyze, or process further.
- Install HTML to Text Converter in Python
- Python Convert HTML File to Text
- Python Convert HTML String to Text
- The Conclusion
- FAQs
Install HTML to Text Converter in Python
To simplify the task, we recommend using Spire.Doc for Python. This Python Word library allows you to quickly remove HTML markup and extract clean plain text with ease. It not only works as an HTML-to-text converter, but also offers a wide range of features—covering almost everything you can do in Microsoft Word.
To install it, you can run the following pip command:
pip install spire.doc
Alternatively, you can download the Spire.Doc package and install it manually.
Python Convert HTML Files to Text in 3 Steps
After preparing the necessary tools, let's dive into today's main topic: how to convert HTML to plain text using Python. With the help of Spire.Doc, this task can be accomplished in just three simple steps: create a new document object, load the HTML file, and save it as a text file. It’s straightforward and efficient, even for beginners. Let’s take a closer look at how this process can be implemented in code!
Code Example – Converting an HTML File to a Text File:
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Open an html file
document = Document()
document.LoadFromFile("/input/htmlsample.html", FileFormat.Html, XHTMLValidationType.none)
# Save it as a Text document.
document.SaveToFile("/output/HtmlFileTotext.txt", FileFormat.Txt)
document.Close()
The following is a preview comparison between the source document (.html) and the output document (.txt):
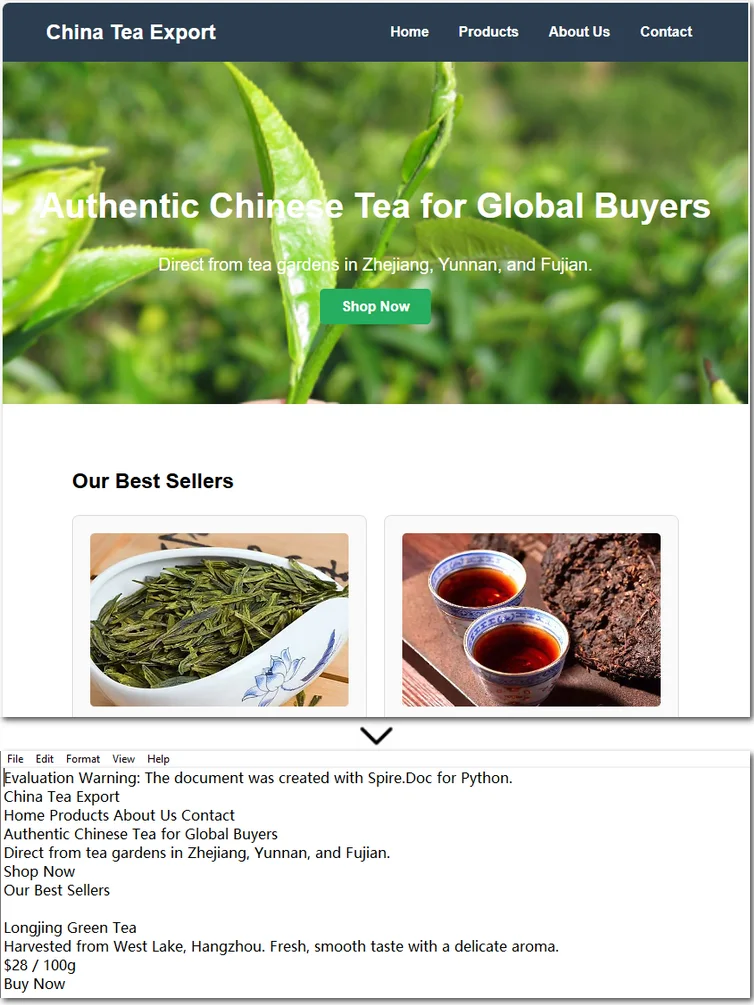
Note that if the HTML file contains tables, the output text file will only retain the values within the tables and cannot preserve the original table formatting. If you want to keep certain styles while removing markup, it is recommended to convert HTML to a Word document . This way, you can retain headings, tables, and other formatting, making the content easier to edit and use.
How to Convert an HTML String to Text in Python
Sometimes, we don’t need the entire content of a web page and only want to extract specific parts. In such cases, you can convert an HTML string directly to text. This approach allows you to precisely control the information you need without further editing. Using Python to convert an HTML string to a text file is also straightforward. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide:
Steps to convert an HTML string to a text document using Spire.Doc:
- Input the HTML string directly or read it from a local file.
- Create a Document object and add sections and paragraphs.
- Use Paragraph.AppendHTML() method to insert the HTML string into a paragraph.
- Save the document as a .txt file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
The following code demonstrates how to convert an HTML string to a text file using Python:
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
#Get html string.
#with open(inputFile) as fp:
#HTML = fp.read()
# Load HTML from string
html = """<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>HTML to Text Example</title>
<style>
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; margin: 20px; }
header { background: #f4f4f4; padding: 10px; }
nav a { margin: 0 10px; text-decoration: none; color: #333; }
main { margin-top: 20px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>My Demo Page</h1>
<nav>
<a href="#">Home</a>
<a href="#">About</a>
<a href="#">Contact</a>
</nav>
</header>
<main>
<h2>Convert HTML to Text</h2>
<p>This is a simple demo showing how HTML content can be displayed before converting it to plain text.</p>
</main>
</body>
</html>
"""
# Create a new document
document = Document()
section = document.AddSection()
section.AddParagraph().AppendHTML(html)
# Save directly as TXT
document.SaveToFile("/output/HtmlStringTotext.txt", FileFormat.Txt)
document.Close()
Here's the preview of the converted .txt file: 
The Conclusion
In today’s tutorial, we focused on how to use Python to convert HTML to a text file. With the help of Spire.Doc, you can handle both HTML files and HTML strings in just a few lines of code, easily generating clean plain text files. If you’re interested in the other powerful features of the Python Word library, you can request a 30-day free trial license and explore its full capabilities for yourself.
FAQs about Converting HTML to Text in Python
Q1: How can I convert HTML to plain text using Python?
A: Use Spire.Doc to load an HTML file or string, insert it into a Document object with AppendHTML(), and save it as a .txt file.
Q2: Can I keep some formatting when converting HTML to text?
A: To retain styles like headings or tables, convert HTML to a Word document first, then export to text if needed.
Q3: Is it possible to convert only part of an HTML page to text?
A: Yes, extract the specific HTML segment as a string and convert it to text using Python for precise control.
Python: Convert Word to Excel
While Word is a powerful tool for creating and formatting documents, it is not optimized for advanced data management and analysis. In contrast, Excel excels at handling data in tabular form, allowing users to perform calculations, create charts, and conduct thorough data analysis.
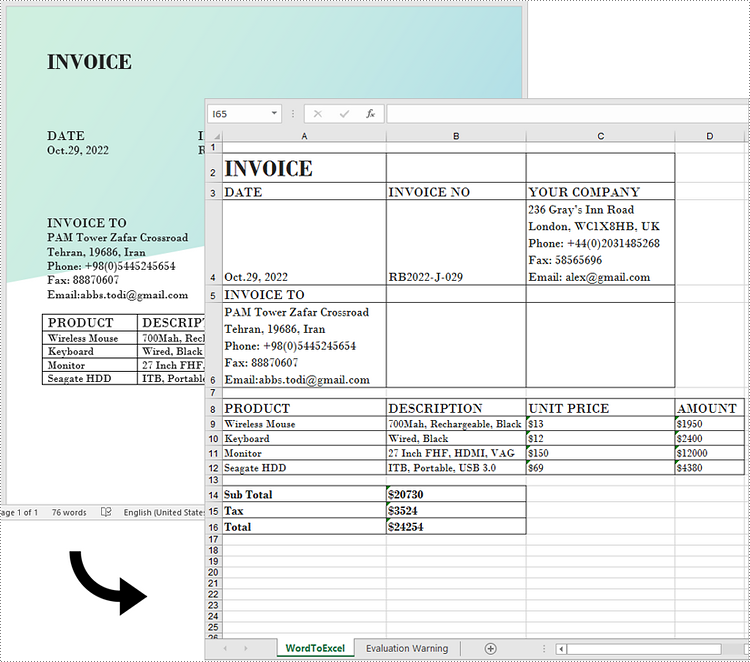
Generally, converting complex Word documents into Excel spreadsheets is not advisable, as Excel may struggle to preserve the original layout. However, if your Word document primarily consists of tables, converting it to Excel can be highly beneficial. This transformation unlocks Excel's advanced functions, formulas, and visualization tools, enabling you to organize your data more effectively and improve your reporting and decision-making capabilities. In this article, we will focus specifically on how to convert this kind of Word documents to Excel in Python using Spire.Office for Python.
Install Spire.Office for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Office for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Office
Convert Word to Excel in Python
This process uses two libraries in the Spire.Office for Python package. They're Spire.XLS for Python and Spire.Doc for Python. The former is used to read and extract content from a Word document, and the latter is used to create an Excel document and write data in specific cells. To make this code example easy to understand, we have defined the following three custom methods that handle specific tasks:
- ExportTableInExcel() - Export data from a Word table to specified Excel cells.
- CopyContentInTable() - Copy content from a table cell in Word to an Excel cell.
- CopyTextAndStyle() - Copy text with formatting from a Word paragraph to an Excel cell.
The following steps demonstrate how to export data from an entire Word document to an Excel worksheet using Spire.Office for Python.
- Create a Document object to load a Word file.
- Create a Worbbook object and add a worksheet named "WordToExcel" to it.
- Traverse through all the sections in the Word document and all the document objects under a certain section, and then determine if a document object is a paragraph or a table.
- If the document object is a paragraph, write the paragraph in a specified cell in Excel using CoypTextAndStyle() method.
- If the document object is a table, export the table data from Word to Excel cells using ExportTableInExcel() method.
- Auto fit the row height and column width in Excel so that the data within a cell will not exceed the bound of the cell.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.doc import *
# Export data from Word table to Excel cells
def ExportTableInExcel(worksheet, row, table):
for rowIndex in range(len(table.Rows)):
tbRow = table.Rows[rowIndex]
column = 1
for cellIndex in range(len(tbRow.Cells)):
tbCell = tbRow.Cells[cellIndex]
cell = worksheet.Range[row, column]
cell.BorderAround()
CopyContentInTable(worksheet, tbCell, cell)
column += 1
row += 1
return row
# Copy content from a Word table cell to an Excel cell
def CopyContentInTable(worksheet, tbCell, cell):
newPara = Paragraph(tbCell.Document)
for i in range(len(tbCell.ChildObjects)):
documentObject = tbCell.ChildObjects[i]
if isinstance(documentObject, Paragraph):
paragraph = documentObject
for cObj in range(len(paragraph.ChildObjects)):
newPara.ChildObjects.Add(paragraph.ChildObjects[cObj].Clone())
if i < len(tbCell.ChildObjects) - 1:
newPara.AppendText("\n")
CopyTextAndStyle(worksheet, cell, newPara)
# Copy text and style of a paragraph to a cell
def CopyTextAndStyle(worksheet, cell, paragraph):
richText = cell.RichText
richText.Text = paragraph.Text
startIndex = 0
for documentObject in range(len(paragraph.ChildObjects)):
documentObject = paragraph.ChildObjects[documentObject]
if isinstance(documentObject, TextRange):
textRange = documentObject
fontName = textRange.CharacterFormat.FontName
isBold = textRange.CharacterFormat.Bold
textColor = textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor
fontSize = textRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize
textRangeText = textRange.Text
strLength = len(textRangeText)
font = worksheet.Workbook.CreateFont()
font.Color = textColor
font.IsBold = isBold
font.Size = fontSize
font.FontName = fontName
endIndex = startIndex + strLength
richText.SetFont(startIndex, endIndex, font)
startIndex += strLength
if isinstance(documentObject, DocPicture):
picture = documentObject
worksheet.Pictures.Add(cell.Row, cell.Column, picture.Image)
worksheet.SetRowHeightInPixels(cell.Row, 1, picture.Image.Height)
if paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment == HorizontalAlignment.Left:
cell.Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
elif paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment == HorizontalAlignment.Center:
cell.Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
elif paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment == HorizontalAlignment.Right:
cell.Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Right
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Invoice.docx")
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook()
# Remove the default worksheets
wb.Worksheets.Clear()
# Create a worksheet named "WordToExcel"
worksheet = wb.CreateEmptySheet("WordToExcel")
row = 1
column = 1
# Loop through the sections in the Word document
for sec_index in range(doc.Sections.Count):
section = doc.Sections[sec_index]
# Loop through the document object under a certain section
for obj_index in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
documentObject = section.Body.ChildObjects[obj_index]
# Determine if the object is a paragraph
if isinstance(documentObject, Paragraph):
cell = worksheet.Range[row, column]
paragraph = documentObject
# Copy paragraph from Word to a specific cell
CopyTextAndStyle(worksheet, cell, paragraph)
row += 1
# Determine if the object is a table
if isinstance(documentObject, Table):
table = documentObject
# Export table data from Word to Excel
currentRow = ExportTableInExcel(worksheet, row, table)
row = currentRow
# Auto fit row height and column width
worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitRows()
worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Wrap text in cells
worksheet.AllocatedRange.IsWrapText = True
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
wb.SaveToFile("WordToExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
wb.Dispose()
doc.Dispose()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Python: Convert Word to XML, Word XML
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is widely used for its structured format and readability on different platforms and systems. Its self-descriptive tags enable you to process data more easily. Meanwhile, Word XML focuses specifically on storing and exchanging Microsoft Word documents. It allows Word documents to transfer without loss. They both show flexibility under various scenarios that Word documents cannot achieve.
On the page, you will learn how to convert Word to XML and Word XML formats using Python with Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows.
Convert Word to XML in Python with Spire.Doc for Python
This part will explain how to convert Word documents to XML in Python with step-by-step instructions and a code example. Spire.Doc for Python provides the Document.SaveToFile() method to make it easy to save Word as XML. Check out the steps below and start processing your Word documents without effort!
Steps to Convert Word to XML:
- Create a new Document object.
- Load the Word document that you wish to be operated using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Covert it to XML by calling Document.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Word document object
document = Document()
# Load the file from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx")
# Save the document to an XML file
document.SaveToFile("WordtoXML.xml", FileFormat.Xml)
document.Close()

Convert Word to Word XML in Python
To convert Word to Word XML, you can utilize the Document.SaveToFile() method provided by Spire.Doc for Python. It not only helps to convert Word documents to Word XML but also to many other formats, such as PDF, XPS, HTML, RTF, etc.
Steps to Convert Word to Word XML:
- Create a new Document object.
- Load the Word document by Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert it to Word XML using Document.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example for you:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Word document object
document = Document()
# Load the file from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx")
# For Word 2003
document.SaveToFile("WordtoWordML.wordml", FileFormat.WordML)
# For Word 2007-2013
document.SaveToFile("WordtoWordXML.wordxml", FileFormat.WordXml)
document.Close()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Python: Convert Markdown to PDF
Markdown has become a popular choice for writing structured text due to its simplicity and readability, making it widely used for documentation, README files, and note-taking. However, sometimes there arises a need to present this content in a more universal and polished format, such as PDF, which is compatible across various devices and platforms without formatting inconsistencies. Converting Markdown files to PDF documents not only enhances portability but also adds a professional touch, enabling easier distribution for reports, manuals, or sharing content with non-technical audiences who may not be familiar with Markdown syntax.
This article will demonstrate how to convert Markdown files to PDF documents using Spire.Doc for Python to automate the conversion process.
- Convert Markdown Files to PDF Documents with Python
- Convert Markdown to PDF and Customize Page Settings
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
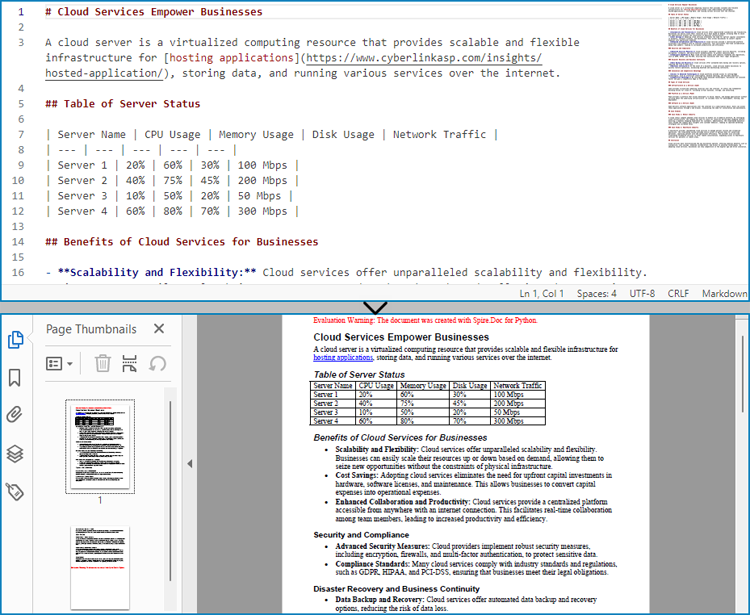
Convert Markdown Files to PDF Documents with Python
With Spire.Doc for Python, developers can load Markdown files using Document.LoadFromFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method, and then save the files to PDF documents using Document.SaveToFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method. Besides, developers can also convert Markdown files to HTML, XPS, and SVG formats by specifying enumeration items of the FileFormat enumeration class.
The detailed steps for converting a Markdown file to a PDF document are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Markdown file using Document.LoadFromFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Convert the Markdown file to a PDF document and save it using Document.SaveToFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Markdown file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Save the file to a PDF document
doc.SaveToFile("output/MarkdownToPDF.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Dispose()
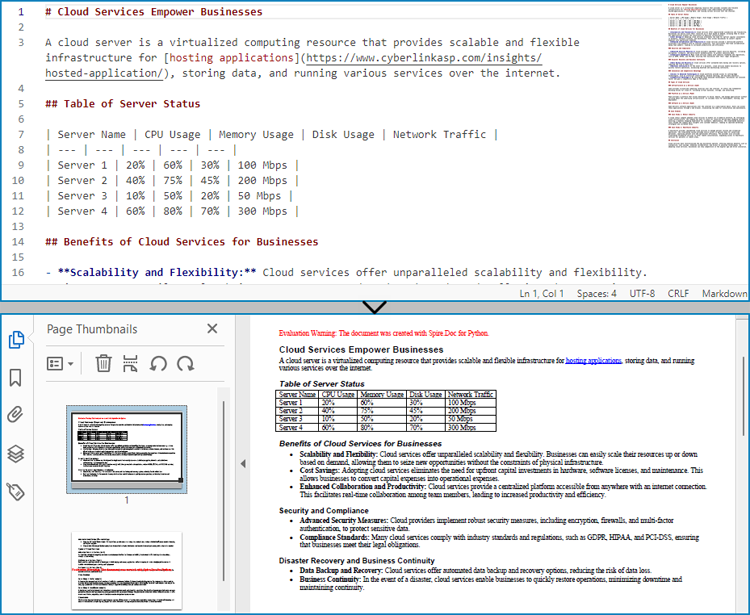
Convert Markdown to PDF and Customize Page Settings
Spire.Doc for Python supports performing basic page setup before converting Markdown files to formats like PDF, allowing for control over the appearance of the converted document.
The detailed steps to convert a Markdown file to a PDF document and customize the page settings are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Markdown file using Document.LoadFromFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Get the default section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Get the page settings through Section.PageSetup property and set the page size, orientation, and margins through properties under PageSetup class.
- Convert the Markdown file to a PDF document and save it using Document.SaveToFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Get the default section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the page settings
pageSetup = section.PageSetup
# Customize the page settings
pageSetup.PageSize = PageSize.A4()
pageSetup.Orientation = PageOrientation.Landscape
pageSetup.Margins.All = 50
# Save the Markdown document to a PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("output/MarkdownToPDFPageSetup.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Dispose()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Python: Convert Markdown to Word or Word to Markdown
Markdown is a lightweight markup language that is becoming increasingly popular for writing content on the web. It offers a simple and human-readable syntax for formatting text, adding links, images, lists, and more. Many websites and content management systems support Markdown, as it can be easily converted to HTML. On the other hand, Microsoft Word is a widely used word-processing software that utilizes its own proprietary file format. While Word offers robust formatting options, its files are not always compatible with other platforms or content management systems.
In certain scenarios, it is useful to convert between Word and Markdown file formats. It allows you to take advantage of Word's advanced editing tools while also being able to publish your content in a web-friendly Markdown format. In this article, we will demonstrate how to convert Markdown to Word DOC or DOCX and convert Word DOC or DOCX to Markdown in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Convert Markdown to Word in Python
You can load a Markdown file using the Document.LoadFromFile(fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method and then convert it to Word DOC or DOCX format using the Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Doc) or Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Docx) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Markdown file using the Document.LoadFromFile(fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Save the Markdown file to a Word DOC or DOCX file using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Doc) or Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Docx) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Markdown file
document.LoadFromFile("input.md")
# Save the Markdown file to a Word DOCX file
document.SaveToFile("MdToDocx.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Save the Markdown file to a Word DOC file
document.SaveToFile("MdToDoc.doc", FileFormat.Doc)
document.Close()

Convert Word to Markdown in Python
You are also able to convert a Word DOC or DOCX file to Markdown format using the Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word DOC or DOCX file using the Document.LoadFromFile(fileName) method.
- Save the Word DOC or DOCX file to a Markdown file using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word DOCX file
document.LoadFromFile("input.docx")
# Or load a Word DOC file
#document.LoadFromFile("input.doc")
# Save the Word file to a Markdown file
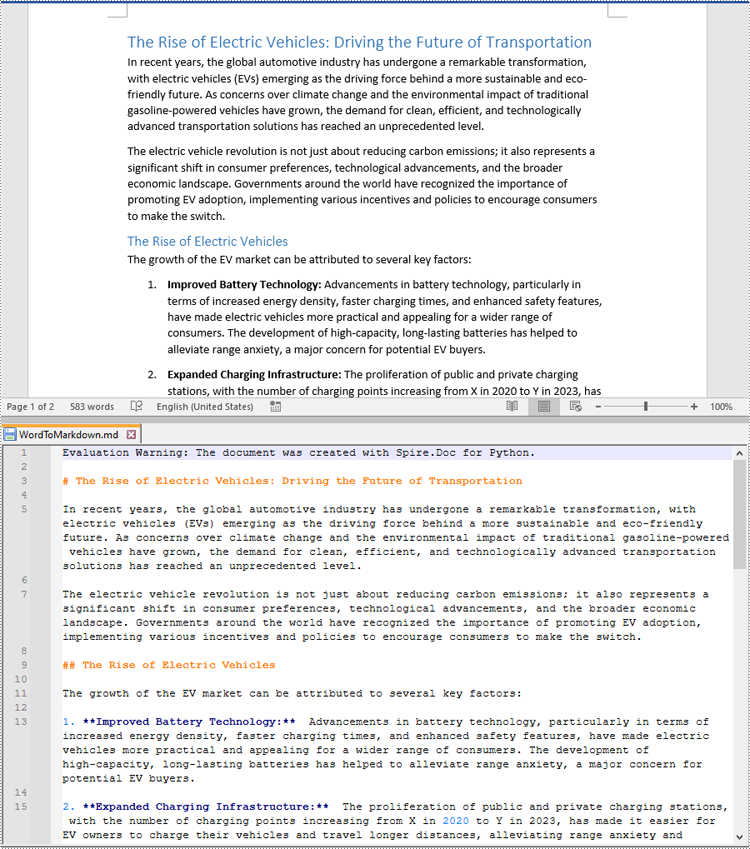
document.SaveToFile("WordToMarkdown.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
document.Close()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Python: Convert Word to TIFF and TIFF to Word
Converting a document from Word to TIFF can be useful when you need to share the content as an image file, such as for electronic forms, presentations, or publishing. The TIFF format preserves the visual layout and appearance of the document. Conversely, converting a TIFF image to a Word document can be helpful when you want to present information in the Word format.
This article demonstrates how to convert Word to TIFF and TIFF to Word (non-editable) using Python and the Spire.Doc for Python library.
Install the Required Libraries
This situation relies on the combination of Spire.Doc for Python and Pillow (PIL). Spire.Doc is used to read, create and convert Word documents, while the PIL library is used for handling TIFF files and accessing their frames.
The libraries can be easily installed on your device through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc pip install pillow
Convert Word to TIFF in Python
To convert a Word document into a TIFF image, the initial step is to use the Spire.Doc library to load the Word document and transform the individual pages into image data streams. Then, you can leverage the functionality provided by the PIL to merge these separate image streams into a unified TIFF image.
The following are the steps to convert Word to TIFF using Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document from a specified file path.
- Iterate through the pages in the document.
- Convert each page into an image stream using Document.SaveImageToSteams() method.
- Convert the image stream into a PIL image.
- Combine these PIL images into a single TIFF image.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
from PIL import Image
from io import BytesIO
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Create an empty list to store PIL Images
images = []
# Iterate through pages in the document
for i in range(doc.GetPageCount()):
# Convert a specific page to image stream
with doc.SaveImageToStreams(i, ImageType.Bitmap) as imageData:
# Open a specific image stream as a PIL image
img = Image.open(BytesIO(imageData.ToArray()))
# Append the PIL image to list
images.append(img)
# Save the PIL Images as a multi-page TIFF file
images[0].save("Output/ToTIFF.tiff", save_all=True, append_images=images[1:])
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()

Convert TIFF to Word in Python
By utilizing PIL library, you can load a TIFF file and break it down into separate PNG images for each frame. You can then utilize the Spire.Doc library to incorporate these separate PNG files as distinct pages within a Microsoft Word document.
To convert a TIFF image to a Word document using Python, follow these steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section to it and set the page margins to zero.
- Load a TIFF image.
- Iterate though the frames in the TIFF image.
- Get a specific frame, and save it as a PNG file.
- Add a paragraph to the section.
- Append the image file to the paragraph.
- Set the page size to be the same as the image size.
- Save the document to a Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
from PIL import Image
import io
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Set margins to 0
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 0.0
# Load a TIFF image
tiff_image = Image.open("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\TIFF.tiff")
# Iterate through the frames in it
for i in range(tiff_image.n_frames):
# Go to the current frame
tiff_image.seek(i)
# Extract the image of the current frame
frame_image = tiff_image.copy()
# Save the image to a PNG file
frame_image.save(f"temp/output_frame_{i}.png")
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Append image to the paragraph
image = paragraph.AppendPicture(f"temp/output_frame_{i}.png")
# Get image width and height
width = image.Width
height = image.Height
# Set the page size to be the same as the image size
section.PageSetup.PageSize = SizeF(width, height)
# Save the document to a Word file
doc.SaveToFile("Output/ToWord.docx",FileFormat.Docx2019)
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Python: Convert Word to XPS, PostScript, or OFD
Converting Word documents to XPS, PostScript, and OFD documents is of significant importance. Firstly, this conversion makes it easier to share and display documents across different platforms and applications, as these formats typically have broader compatibility.
Secondly, converting to these formats can preserve the document's formatting, layout, and content, ensuring consistent display across different systems.
Additionally, XPS and OFD formats support high-quality printing, helping to maintain the visual appearance and print quality of the document. The PostScript format is commonly used for printing and graphic processing, converting to PostScript can ensure that the document maintains high quality when printed.
In this article, you will learn how to convert Word to XPS, PostScript, or OFD with Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Convert Word to XPS in Python
The Document.SaveToFile(filename:str, FileFormat.XPS) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python can convert a Word document to XPS format. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Use the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load the Word document.
- Use the Document.SaveToFile(filename:str, FileFormat.XPS) method to convert the Word document to an XPS document.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Save the loaded document as an XPS document
doc.SaveToFile("Result.xps", FileFormat.XPS)
# Close the document object and release the resources occupied by the document object
doc.Close()
doc.Dispose()

Convert Word to PostScript in Python
With Document.SaveToFile(filename:str, FileFormat.PostScript) method in Spire.Doc for Python, you can convert a Word document to PostScript format. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Use the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load the Word document.
- Use the Document.SaveToFile(filename:str, FileFormat.PostScript) method to convert the Word document to a PostScript document.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# # Save the loaded document as a PostScript document
doc.SaveToFile("Result.ps", FileFormat.PostScript)
# Close the document object and release the resources occupied by the document object
doc.Close()
doc.Dispose()
Convert Word to OFD in Python
By utilizing the Document.SaveToFile() method in the Spire.Doc for Python library and specifying the file format as FileFormat.OFD, you can save a Word document as an OFD file format. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Use the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load the Word document.
- Use the Document.SaveToFile(filename:str, FileFormat.OFD) method to convert the Word document to an OFD document.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Save the loaded document as an OFD document
doc.SaveToFile("Result.ofd", FileFormat.OFD)
# Close the document object and release the resources occupied by the document object
doc.Close()
doc.Dispose()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.