Markdown (.md) is widely used in web development, documentation, and technical writing. Its simple syntax makes content easy to write and read. However, web browsers do not render Markdown directly. Converting Markdown to HTML ensures your content is structured, readable, and compatible with web platforms.
In this step-by-step guide, you will learn how to efficiently convert Markdown (.md) files into HTML using Python and Spire.Doc for Python, complete with practical code examples, clear instructions, and best practices for both single-file and batch conversions.
Table of Contents
- What is Markdown
- Why Convert Markdown to HTML
- Introducing Spire.Doc for Python
- Step-by-Step Guide: Converting Markdown to HTML in Python
- Automating Batch Conversion
- Best Practices for Markdown to HTML Conversion
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Markdown?
Markdown is a lightweight markup language designed for readability and ease of writing. Unlike HTML, which can be verbose and harder to write by hand, Markdown uses simple syntax to indicate headings, lists, links, images, and more.
Example Markdown:
# This is a Heading
This is a paragraph with \*\*bold text\*\* and \*italic text\*.
- Item 1
- Item 2
Even in its raw form, Markdown is easy to read, which makes it popular for documentation, blogging, README files, and technical writing.
For more on Markdown syntax, see the Markdown Guide.
Why Convert Markdown to HTML?
While Markdown is excellent for authoring content, web browsers cannot render it natively. Converting Markdown to HTML allows you to:
- Publish content on websites – Most CMS platforms require HTML for web pages.
- Enhance styling – HTML supports CSS and JavaScript for advanced formatting and interactivity.
- Maintain compatibility – HTML is universally supported by browsers, ensuring content displays correctly everywhere.
- Integrate with web frameworks – Frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular require HTML as the base for rendering components.
Introducing Spire.Doc for Python
Spire.Doc for Python is a robust library for handling multiple document formats. It supports reading and writing Word documents, Markdown files, and exporting content to HTML. The library allows developers to convert Markdown directly to HTML with minimal code, preserving proper formatting and structure.
In addition to HTML, Spire.Doc for Python also allows you to convert Markdown to Word in Python or convert Markdown to PDF in Python, making it particularly useful for developers who want a unified tool for handling Markdown across different output formats.
Benefits of Using Spire.Doc for Python for Markdown to HTML Conversion
- Easy-to-use API – Simple, intuitive methods that reduce development effort.
- Accurate formatting – Preserves all Markdown elements such as headings, lists, links, and emphasis in HTML.
- No extra dependencies – Eliminates the need for manual parsing or third-party libraries.
- Flexible usage – Supports both single-file conversion and automated batch processing.
Step-by-Step Guide: Converting Markdown to HTML in Python
Now that you understand the purpose and benefits of converting Markdown to HTML, let’s walk through a clear, step-by-step process to transform your Markdown files into structured, web-ready HTML.
Step 1: Install Spire.Doc for Python
First, ensure that Spire.Doc for Python is installed in your environment. You can install it directly from PyPI using pip:
pip install spire.doc
Step 2: Prepare Your Markdown File
Next, create a sample Markdown file that you want to convert. For example, example.md:
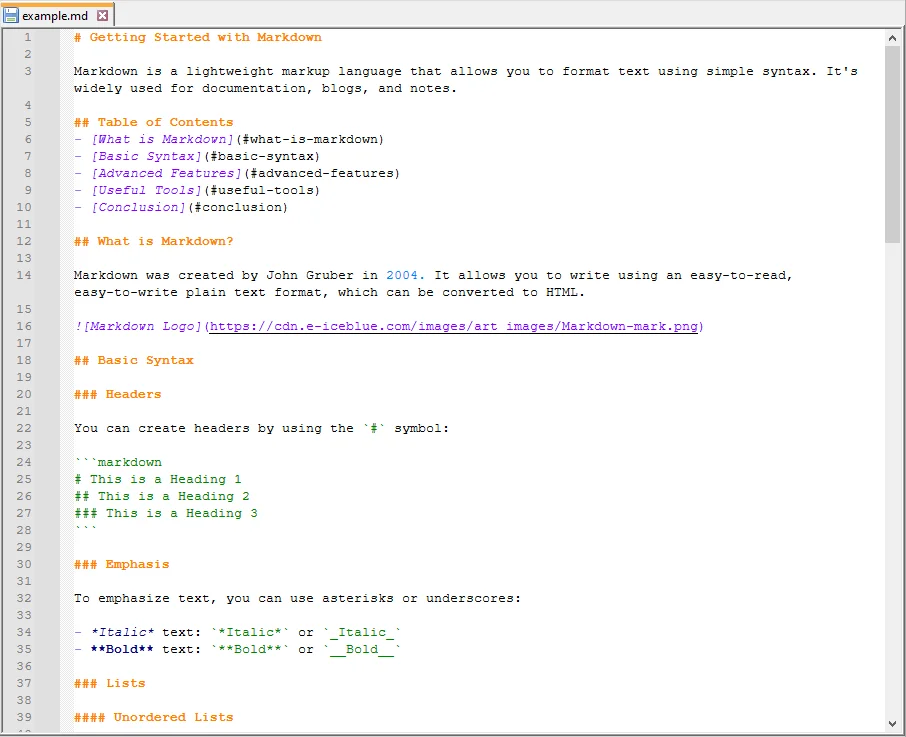
Step 3: Write the Python Script
Now, write a Python script that loads the Markdown file and converts it to HTML:
from spire.doc import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load the Markdown file
doc.LoadFromFile("example.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Save the document as HTML
doc.SaveToFile("example.html", FileFormat.Html)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
Explanation of the code:
- Document() initializes a new document object.
- LoadFromFile("example.md", FileFormat.Markdown) loads the Markdown file into memory.
- SaveToFile("example.html", FileFormat.Html) converts the loaded content into HTML and saves it to disk.
- doc.Close() ensures resources are released properly, which is particularly important when processing multiple files or running batch operations.
Step 4: Verify the HTML Output
Finally, open the generated example.html file in a web browser or HTML editor. Verify that the Markdown content has been correctly converted.

Automating Batch Conversion
You can convert multiple Markdown files in a folder automatically:
import os
from spire.doc import *
# Set the folder containing Markdown files
input_folder = "markdown_files"
# Set the folder where HTML files will be saved
output_folder = "html_files"
# Create the output folder if it doesn't exist
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# Loop through all files in the input folder
for filename in os.listdir(input_folder):
# Process only Markdown files
if filename.endswith(".md"):
# Create a new Document object for each file
doc = Document()
# Load the Markdown file into the Document object
doc.LoadFromFile(os.path.join(input_folder, filename), FileFormat.Markdown)
# Construct the output file path by replacing .md extension with .html
output_file = os.path.join(output_folder, filename.replace(".md", ".html"))
# Save the loaded Markdown content as HTML
doc.SaveToFile(output_file, FileFormat.Html)
# Close the document to release resources
doc.Close()
This approach allows you to process multiple Markdown files efficiently and generate corresponding HTML files automatically.
Best Practices for Markdown to HTML Conversion
While the basic steps are enough to complete a Markdown-to-HTML conversion, following a few best practices will help you avoid common pitfalls, improve compatibility, and ensure your output is both clean and professional:
- Use proper Markdown syntax – Ensure headings, lists, links, and emphasis are correctly written.
- Use UTF-8 Encoding: Always save your Markdown files in UTF-8 encoding to avoid issues with special characters or non-English text.
- Batch Processing: If you need to convert multiple files, wrap your script in a loop and process entire folders. This saves time and ensures consistent formatting across documents.
- Enhance Styling: Remember that HTML gives you the flexibility to add CSS and JavaScript for custom layouts, responsive design, and interactivity—something not possible in raw Markdown.
Conclusion
Converting Markdown to HTML using Python with Spire.Doc is simple, reliable, and efficient. It preserves formatting, supports automation, and produces clean HTML output ready for web use. By following this guide, you can implement a smooth Markdown to HTML workflow for both single documents and batch operations.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert multiple Markdown files to HTML in Python?
A1: Yes, you can automate batch conversions by iterating through Markdown files in a directory and applying the conversion logic to each file.
Q2: Will the HTML preserve all Markdown formatting?
A2: Yes, Spire.Doc effectively preserves all essential Markdown formatting, including headings, lists, bold and italic text, links, and more.
Q3: Is there a way to handle images in Markdown during conversion?
A3: Yes, Spire.Doc supports the conversion of images embedded in Markdown, ensuring they are included in the resulting HTML.
Q4: Do I need additional libraries besides Spire.Doc?
A4: No additional libraries are required. Spire.Doc for Python provides a comprehensive solution for converting Markdown to HTML without any external dependencies.
Q5: Can I use the generated HTML in web frameworks?
A5: Yes, the HTML produced is fully compatible with popular web frameworks such as React, Vue, and Angular, making integration seamless.