Python: Get Revisions of Word Document
With the increasing popularity of team collaboration, the track changes function in Word documents has become the cornerstone of version control and content review. However, for developers who pursue automation and efficiency, how to flexibly extract these revision information from Word documents remains a significant challenge. This article will introduce you to how to use Spire.Doc for Python to obtain revision information in Word documents.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Get Revisions of Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the IsInsertRevision and DeleteRevision properties to support determining whether an element in a Word document is an insertion revision or a deletion revision. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create an instance of the Document class and load the Word document that contains revisions.
- Initialize lists to collect insertion and deletion revision information.
- Iterate through the sections of the document and their body elements.
- Obtain the paragraphs in the body and use the IsInsertRevision property to determine if the paragraph is an insertion revision.
- Get the type, author, and associated text of the insertion revision.
- Use the IsDeleteRevision property to determine if the paragraph is a deletion revision, and obtain its revision type, author, and associated text.
- Iterate through the child elements of the paragraph, similarly checking if the TextRange is an insertion or deletion revision, and retrieve the revision type, author, and associated text.
- Define a WriteAllText function to save the insertion and deletion revision information to TXT documents.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
# Function to write text to a file
def WriteAllText(fname: str, text: str):
with open(fname, "w", encoding='utf-8') as fp:
fp.write(text)
# Input and output file names
inputFile = "sample.docx"
outputFile1 = "InsertRevision.txt"
outputFile2 = "DeleteRevision.txt"
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load the Word document
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Initialize lists to store insert and delete revisions
insert_revisions = []
delete_revisions = []
# Iterate through sections in the document
for k in range(document.Sections.Count):
sec = document.Sections.get_Item(k)
# Iterate through body elements in the section
for m in range(sec.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
# Check if the item is a Paragraph
docItem = sec.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(m)
if isinstance(docItem, Paragraph):
para = docItem
para.AppendField("",FieldType.FieldDocVariable)
# Check if the paragraph is an insertion revision
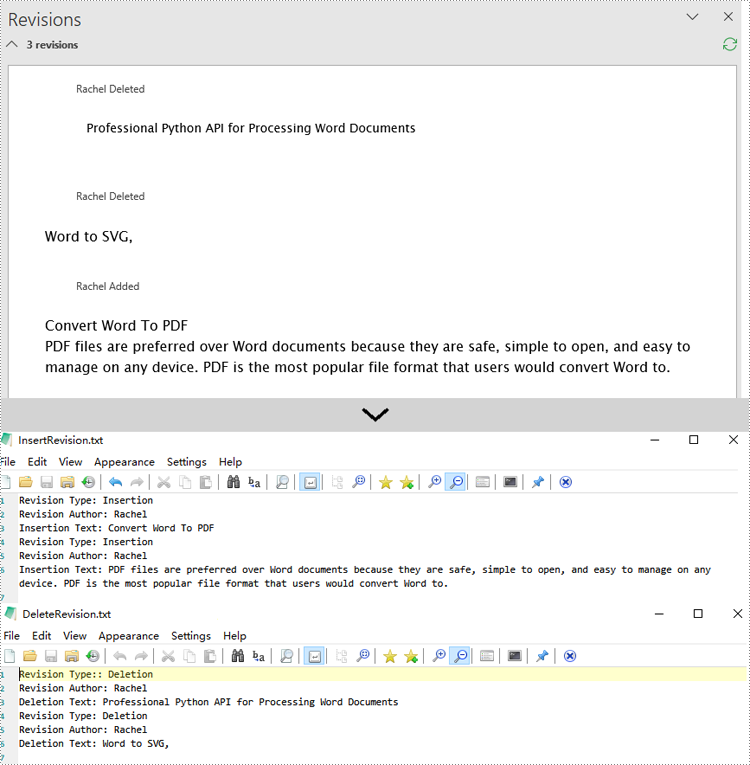
if para.IsInsertRevision:
insRevison = para.InsertRevision
insType = insRevison.Type
insAuthor = insRevison.Author
# Add insertion revision details to the list
insert_revisions.append(f"Revision Type: {insType.name}\n")
insert_revisions.append(f"Revision Author: {insAuthor}\n")
insert_revisions.append(f"Insertion Text: {para.Text}\n")
# Check if the paragraph is a deletion revision
elif para.IsDeleteRevision:
delRevison = para.DeleteRevision
delType = delRevison.Type
delAuthor = delRevison.Author
# Add deletion revision details to the list
delete_revisions.append(f"Revision Type:: {delType.name}\n")
delete_revisions.append(f"Revision Author: {delAuthor}\n")
delete_revisions.append(f"Deletion Text: {para.Text}\n")
else:
# Iterate through all child objects of Paragraph
for j in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
# Check if the current object is an instance of TextRange
if isinstance(obj, TextRange):
textRange = obj
# Check if the textrange is an insertion revision
if textRange.IsInsertRevision:
insRevison = textRange.InsertRevision
insType = insRevison.Type
insAuthor = insRevison.Author
# Add insertion revision details to the list
insert_revisions.append(f"Revision Type: {insType.name}\n")
insert_revisions.append(f"Revision Author: {insAuthor}\n")
insert_revisions.append(f"Insertion Text: {textRange.Text}\n")
# Check if the textrange is a deletion revision
elif textRange.IsDeleteRevision:
delRevison = textRange.DeleteRevision
delType = delRevison.Type
delAuthor = delRevison.Author
# Add deletion revision details to the list
delete_revisions.append(f"Revision Type: {delType.name}\n")
delete_revisions.append(f"Revision Author: {delAuthor}\n")
delete_revisions.append(f"Deletion Text: {textRange.Text}\n")
# Write all the insertion revision details to the 'outputFile1' file
WriteAllText(outputFile1, ''.join(insert_revisions))
# Write all the deletion revision details to the 'outputFile2' file
WriteAllText(outputFile2, ''.join(delete_revisions))
# Dispose the document
document.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Create a Table Of Contents for a Newly Created Word Document
Creating a table of contents in a Word document significantly enhances its navigability and readability. It serves as a road map for the document, enabling readers to quickly overview the structure and grasp the content framework. This feature facilitates easy navigation for users to jump to any section within the document, which is particularly valuable for lengthy reports, papers, or manuals. It not only saves readers time in locating information but also augments the professionalism of the document and enhances the user experience. Moreover, a table of contents is easy to maintain and update; following any restructuring of the document, it can be swiftly revised to reflect the latest content organization, ensuring coherence and accuracy throughout the document. This article will demonstrate how to use Spire.Doc for Python to create a table of contents in a newly created Word document within a Python project.
- Python Create a Table Of Contents Using Heading Styles
- Python Create a Table Of Contents Using Outline Level Styles
- Python Create a Table Of Contents Using Image Captions
- Python Create a Table Of Contents Using Table Captions
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Python Create a Table Of Contents Using Heading Styles
Creating a table of contents using heading styles is a default method in Word documents to automatically generate a table of contents by utilizing different levels of heading styles to mark titles and sub-titles within the document, followed by leveraging Word's table of contents feature to automatically populate the contents. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using the Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a paragraph using the Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Create a table of contents object using the Paragraph.AppendTOC(int lowerLevel, int upperLevel) method.
- Create a CharacterFormat object and set the font.
- Apply a heading style to the paragraph using the Paragraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading1) method.
- Add text content using the Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Apply character formatting to the text using the TextRange.ApplyCharacterFormat() method.
- Update the table of contents using the Document.UpdateTableOfContents() method.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a new document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document
section = doc.AddSection()
# Append a Table of Contents (TOC) paragraph
TOC_paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
TOC_paragraph.AppendTOC(1, 3)
# Create and set character format objects for font
character_format1 = CharacterFormat(doc)
character_format1.FontName = "Microsoft YaHei"
character_format2 = CharacterFormat(doc)
character_format2.FontName = "Microsoft YaHei"
character_format2.FontSize = 12
# Add a paragraph with Heading 1 style
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading1)
# Add text and apply character formatting
text_range1 = paragraph.AppendText("Overview")
text_range1.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format1)
# Insert normal content
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
text_range2 = paragraph.AppendText("Spire.Doc for Python is a professional Python Word development component that enables developers to easily integrate Word document creation, reading, editing, and conversion functionalities into their own Python applications. As a completely standalone component, Spire.Doc for Python does not require the installation of Microsoft Word on the runtime environment.")
# Add a paragraph with Heading 1 style
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading1)
text_range1 = paragraph.AppendText("Main Functions")
text_range1.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format1)
# Add a paragraph with Heading 2 style
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading2)
textRange1 = paragraph.AppendText("Only Spire.Doc, No Microsoft Office Automation")
textRange1.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format1)
# Add regular content
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
textRange2 = paragraph.AppendText("Spire.Doc for Python is a totally independent Python Word class library which doesn't require Microsoft Office installed on system. Microsoft Office Automation is proved to be unstable, slow and not scalable to produce MS Word documents. Spire.Doc for Python is many times faster than Microsoft Word Automation and with much better stability and scalability.")
textRange2.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format2)
# Add a paragraph with Heading 3 style
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading3)
textRange1 = paragraph.AppendText("Word Versions")
textRange1.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format1)
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
textRange2 = paragraph.AppendText("Word97-03 Word2007 Word2010 Word2013 Word2016 Word2019")
textRange2.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format2)
# Add a paragraph with Heading 2 style
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading2)
textRange1 = paragraph.AppendText("Convert File Documents with High Quality")
textRange1.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format1)
# Add regular content
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
textRange2 = paragraph.AppendText("By using Spire.Doc for Python, users can save Word Doc/Docx to stream, save as web response and convert Word Doc/Docx to XML, Markdown, RTF, EMF, TXT, XPS, EPUB, HTML, SVG, ODT and vice versa. Spire.Doc for Python also supports to convert Word Doc/Docx to PDF and HTML to image.")
textRange2.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format2)
# Add a paragraph with Heading 2 style
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading2)
extRange1 = paragraph.AppendText("Other Technical Features")
textRange1.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format1)
# Add regular content
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
textRange2 = paragraph.AppendText("By using Spire.Doc for Python, developers can build any type of a 64-bit Python application to create and handle Word documents.")
textRange2.ApplyCharacterFormat(character_format2)
# Update the table of contents
doc.UpdateTableOfContents()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("CreateTOCUsingHeadingStyles.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Release resources
doc.Dispose()

Python Create a Table Of Contents Using Outline Level Styles
In a Word document, you can create a table of contents using outline level styles. You can assign an outline level to a paragraph using the ParagraphFormat.OutlineLevel property. Afterwards, you apply these outline levels to the rules for generating the table of contents using the TableOfContent.SetTOCLevelStyle() method. Here's a detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using the Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a ParagraphStyle object and set the outline level using ParagraphStyle.ParagraphFormat.OutlineLevel = OutlineLevel.Level1.
- Add the created ParagraphStyle object to the document using the Document.Styles.Add() method.
- Add a paragraph using the Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Create a table of contents object using the Paragraph.AppendTOC(int lowerLevel, int upperLevel) method.
- Set the default setting for creating the table of contents with heading styles to False, TableOfContent.UseHeadingStyles = false.
- Apply the outline level style to the table of contents rules using the TableOfContent.SetTOCLevelStyle(int levelNumber, string styleName) method.
- Create a CharacterFormat object and set the font.
- Apply the style to the paragraph using the Paragraph.ApplyStyle(ParagraphStyle.Name) method.
- Add text content using the Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Apply character formatting to the text using the TextRange.ApplyCharacterFormat() method.
- Update the table of contents using the Document.UpdateTableOfContents() method.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document
section = doc.AddSection()
# Define Outline Level 1
titleStyle1 = ParagraphStyle(doc)
titleStyle1.Name = "T1S"
titleStyle1.ParagraphFormat.OutlineLevel = OutlineLevel.Level1
titleStyle1.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
titleStyle1.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Microsoft YaHei"
titleStyle1.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 18
titleStyle1.ParagraphFormat.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
doc.Styles.Add(titleStyle1)
# Define Outline Level 2
titleStyle2 = ParagraphStyle(doc)
titleStyle2.Name = "T2S"
titleStyle2.ParagraphFormat.OutlineLevel = OutlineLevel.Level2
titleStyle2.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
titleStyle2.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Microsoft YaHei"
titleStyle2.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 16
titleStyle2.ParagraphFormat.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
doc.Styles.Add(titleStyle2)
# Define Outline Level 3
titleStyle3 = ParagraphStyle(doc)
titleStyle3.Name = "T3S"
titleStyle3.ParagraphFormat.OutlineLevel = OutlineLevel.Level3
titleStyle3.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
titleStyle3.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Microsoft YaHei"
titleStyle3.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 14
titleStyle3.ParagraphFormat.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
doc.Styles.Add(titleStyle3)
# Add a paragraph
TOCparagraph = section.AddParagraph()
toc = TOCparagraph.AppendTOC(1, 3)
toc.UseHeadingStyles = False
toc.UseHyperlinks = True
toc.UseTableEntryFields = False
toc.RightAlignPageNumbers = True
toc.SetTOCLevelStyle(1, titleStyle1.Name)
toc.SetTOCLevelStyle(2, titleStyle2.Name)
toc.SetTOCLevelStyle(3, titleStyle3.Name)
# Define character format
characterFormat = CharacterFormat(doc)
characterFormat.FontName = "Microsoft YaHei"
characterFormat.FontSize = 12
# Add a paragraph and apply outline level style 1
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(titleStyle1.Name)
paragraph.AppendText("Overview")
# Add a paragraph and set the text content
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
textRange = paragraph.AppendText("Spire.Doc for Python is a professional Word Python API specifically designed for developers to create, read, write, convert, and compare Word documents with fast and high-quality performance.")
textRange.ApplyCharacterFormat(characterFormat)
# Add a paragraph and apply outline level style 1
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(titleStyle1.Name)
paragraph.AppendText("Main Functions")
# Add a paragraph and apply outline level style 2
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(titleStyle2.Name)
paragraph.AppendText("Only Spire.Doc, No Microsoft Office Automation")
# Add a paragraph and set the text content
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
textRange = paragraph.AppendText("Spire.Doc for Python is a totally independent Python Word class library which doesn't require Microsoft Office installed on system. Microsoft Office Automation is proved to be unstable, slow and not scalable to produce MS Word documents. Spire.Doc for Python is many times faster than Microsoft Word Automation and with much better stability and scalability.")
textRange.ApplyCharacterFormat(characterFormat)
# Add a paragraph and apply outline level style 3
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(titleStyle3.Name)
paragraph.AppendText("Word Versions")
# Add a paragraph and set the text content
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
textRange = paragraph.AppendText("Word97-03 Word2007 Word2010 Word2013 Word2016 Word2019")
textRange.ApplyCharacterFormat(characterFormat)
# Add a paragraph and apply outline level style 2
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(titleStyle2.Name)
paragraph.AppendText("Convert File Documents with High Quality")
# Add a paragraph and set the text content
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
textRange = paragraph.AppendText("By using Spire.Doc for Python, users can save Word Doc/Docx to stream, save as web response and convert Word Doc/Docx to XML, RTF, EMF, TXT, XPS, EPUB, HTML, SVG, ODT and vice versa. Spire.Doc for Python also supports to convert Word Doc/Docx to PDF and HTML to image.")
textRange.ApplyCharacterFormat(characterFormat)
# Add a paragraph and apply outline level style 2
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.ApplyStyle(titleStyle2.Name)
paragraph.AppendText("Other Technical Features")
# Add a paragraph and set the text content
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
textRange = paragraph.AppendText("By using Spire.Doc for Python, developers can build any type of a 64-bit Python application to create and handle Word documents.")
textRange.ApplyCharacterFormat(characterFormat)
# Update the table of contents
doc.UpdateTableOfContents()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("CreateTOCUsingOutlineStyles.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Release resources
doc.Dispose()

Python Create a Table Of Contents Using Image Captions
Using the Spire.Doc library, you can create a table of contents based on image captions by employing the TableOfContent(Document, "\\h \\z \\c \"Picture\"") method. Below are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using the Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a table of content object with tocForImage = new TableOfContent(Document, " \\h \\z \\c \"Picture\"") and specify the style of the table of contents.
- Add a paragraph using the Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add the table of content object to the paragraph using the Paragraph.Items.Add(tocForImage) method.
- Add a field separator using the Paragraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldSeparator) method.
- Add the text content "TOC" using the Paragraph.AppendText("TOC") method.
- Add a field end mark using the Paragraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldEnd) method.
- Add an image using the Paragraph.AppendPicture() method.
- Add a caption paragraph for the image using the DocPicture.AddCaption() method, including product information and formatting.
- Update the table of contents to reflect changes in the document using the Document.UpdateTableOfContents(tocForImage) method.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a new document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a table of content object for images
tocForImage = TableOfContent(doc, " \\h \\z \\c \"Picture\"")
# Add a paragraph to the section
tocParagraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
# Add the TOC object to the paragraph
tocParagraph.Items.Add(tocForImage)
# Add a field separator
tocParagraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldSeparator)
# Add text content
tocParagraph.AppendText("TOC")
# Add a field end mark
tocParagraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldEnd)
# Add a blank paragraph to the section
section.Body.AddParagraph()
# Add a paragraph to the section
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
# Add an image
docPicture = paragraph.AppendPicture("images/DOC-Python.png")
docPicture.Width = 100
docPicture.Height = 100
# Add a caption paragraph for the image
obj = docPicture.AddCaption("Picture",CaptionNumberingFormat.Number,CaptionPosition.BelowItem)
paragraph = (Paragraph)(obj)
paragraph.AppendText(" Spire.Doc for Python product")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 20
# Continue adding paragraphs to the section
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
docPicture = paragraph.AppendPicture("images/PDF-Python.png")
docPicture.Width = 100
docPicture.Height = 100
obj = docPicture.AddCaption("Picture",CaptionNumberingFormat.Number,CaptionPosition.BelowItem)
paragraph = (Paragraph)(obj)
paragraph.AppendText(" Spire.PDF for Python product")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 20
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
docPicture = paragraph.AppendPicture("images/XLS-Python.png")
docPicture.Width = 100
docPicture.Height = 100
obj = docPicture.AddCaption("Picture",CaptionNumberingFormat.Number,CaptionPosition.BelowItem)
paragraph = (Paragraph)(obj)
paragraph.AppendText(" Spire.XLS for Python product")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 20
paragraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
docPicture = paragraph.AppendPicture("images/PPT-Python.png")
docPicture.Width = 100
docPicture.Height = 100
obj = docPicture.AddCaption("Picture",CaptionNumberingFormat.Number,CaptionPosition.BelowItem)
paragraph = (Paragraph)(obj)
paragraph.AppendText(" Spire.Presentation for Python product")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 20
# Update the table of contents
doc.UpdateTableOfContents(tocForImage)
# Save the document to a file
doc.SaveToFile("CreateTOCWithImageCaptions.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Dispose of the document object
doc.Dispose()

Python Create a Table Of Contents Using Table Captions
Similarly, you can create a table of contents based on table captions by employing the TableOfContent(Document, " \\h \\z \\c \"Table\"") method. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using the Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a table of content object tocForTable = new TableOfContent(Document, " \\h \\z \\c \"Table\"") and specify the style of the table of contents.
- Add a paragraph using the Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add the table of content object to the paragraph using the Paragraph.Items.Add(tocForTable) method.
- Add a field separator using the Paragraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldSeparator) method.
- Add the text content "TOC" using the Paragraph.AppendText("TOC") method.
- Add a field end mark using the Paragraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldEnd) method.
- Add a table using the Section.AddTable() method and set the number of rows and columns using the Table.ResetCells(int rowsNum, int columnsNum) method.
- Add a table caption paragraph using the Table.AddCaption() method, including product information and formatting.
- Update the table of contents to reflect changes in the document using the Document.UpdateTableOfContents(tocForTable) method.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a new document
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a TableOfContent object
tocForTable = TableOfContent(doc, " \\h \\z \\c \"Table\"")
# Add a paragraph in the section to place the TableOfContent object
tocParagraph = section.Body.AddParagraph()
tocParagraph.Items.Add(tocForTable)
tocParagraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldSeparator)
tocParagraph.AppendText("TOC")
tocParagraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldEnd)
# Add two empty paragraphs in the section
section.Body.AddParagraph()
section.Body.AddParagraph()
# Add a table in the section
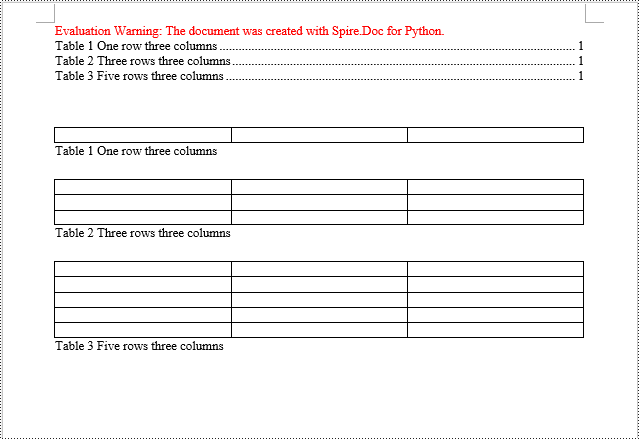
table = section.Body.AddTable(True)
table.ResetCells(1, 3)
# Add a caption paragraph for the table
obj = table.AddCaption("Table", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.BelowItem)
paragraph = (Paragraph)(obj)
paragraph.AppendText(" One row three columns")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 20
# Add a new table in the section
table = section.Body.AddTable(True)
table.ResetCells(3, 3)
# Add a caption paragraph for the second table
obj = table.AddCaption("Table", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.BelowItem)
paragraph = (Paragraph)(obj)
paragraph.AppendText(" Three rows three columns")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 20
# Add another new table in the section
table = section.Body.AddTable(True)
table.ResetCells(5, 3)
# Add a caption paragraph for the third table
obj = table.AddCaption("Table", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.BelowItem)
paragraph = (Paragraph)(obj)
paragraph.AppendText(" Five rows three columns")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 20
# Update the table of contents
doc.UpdateTableOfContents(tocForTable)
# Save the document to a specified file
doc.SaveToFile("CreateTOCUsingTableCaptions.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add, Read, and Remove Built-in Document Properties in Word Documents
Word documents often contain metadata known as document properties, which include information like title, author, subject, and keywords. Manipulating these properties is invaluable for maintaining organized documentation, enhancing searchability, and ensuring proper attribution in collaborative environments. With Spire.Doc for Python, developers can automate the tasks of adding, reading, and removing document properties in Word documents to streamline document management workflows and enable the integration of these processes into larger automated systems. This article provides detailed steps and code examples that demonstrate how to utilize Spire.Doc for Python to effectively manage document properties within Word files.
- Add Built-in Document Properties to Word Documents with Python
- Read Built-in Document Properties from Word Documents with Python
- Remove Built-in Document Properties from Word Documents with Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
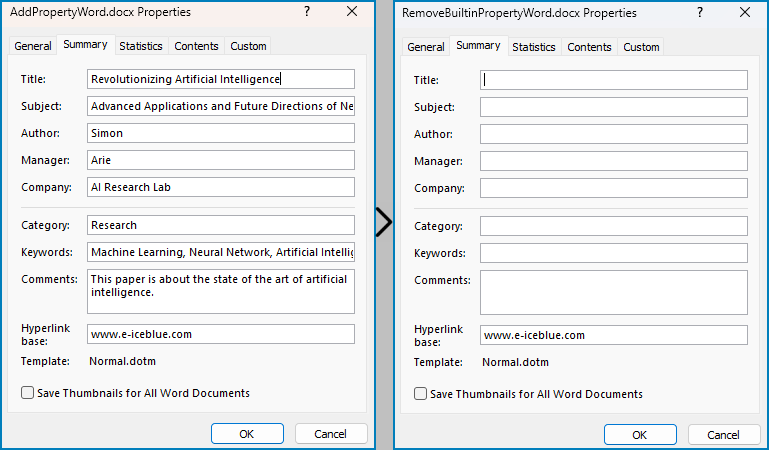
Add Built-in Document Properties to Word Documents with Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides developers with the Document.BuiltinDocumentProperties property to access the built-in properties of Word documents. The value of these properties can be set using the corresponding properties under the BuiltinDocumentProperties class.
The following steps show how to add the main built-in properties in Word documents:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the built-in properties through Document.BuiltinDocumentProperties property.
- Add values to the properties with properties under BuiltinDocumentProperties property.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
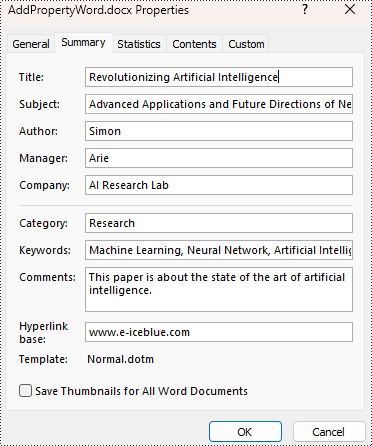
# Set the built-in property
builtinProperty = doc.BuiltinDocumentProperties
builtinProperty.Title = "Revolutionizing Artificial Intelligence"
builtinProperty.Subject = "Advanced Applications and Future Directions of Neural Networks in Artificial Intelligence"
builtinProperty.Author = "Simon"
builtinProperty.Manager = "Arie"
builtinProperty.Company = "AI Research Lab"
builtinProperty.Category = "Research"
builtinProperty.Keywords = "Machine Learning, Neural Network, Artificial Intelligence"
builtinProperty.Comments = "This paper is about the state of the art of artificial intelligence."
builtinProperty.HyperLinkBase = "www.e-iceblue.com"
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddPropertyWord.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
doc.Close()
Read Built-in Document Properties from Word Documents with Python
Besides adding values, the properties under the BuiltinDocumentProperties class also empower developers to read existing built-in properties of Word documents. This enables various functionalities like document search, information extraction, and document analysis.
The detailed steps for reading document built-in properties using Spire.Doc for Python are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the built-in properties of Document using Document.BuiltinDocumentProperties property.
- Get the value of the properties using properties under BuiltinDocumentProperties class.
- Output the built-in properties of the document.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("output/AddPropertyWord.docx")
# Get the built-in properties of the document
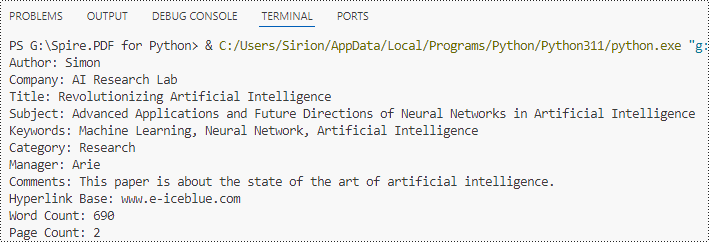
builtinProperties = doc.BuiltinDocumentProperties
# Get the value of the built-in properties
properties = [
"Author: " + builtinProperties.Author,
"Company: " + builtinProperties.Company,
"Title: " + builtinProperties.Title,
"Subject: " + builtinProperties.Subject,
"Keywords: " + builtinProperties.Keywords,
"Category: " + builtinProperties.Category,
"Manager: " + builtinProperties.Manager,
"Comments: " + builtinProperties.Comments,
"Hyperlink Base: " + builtinProperties.HyperLinkBase,
"Word Count: " + str(builtinProperties.WordCount),
"Page Count: " + str(builtinProperties.PageCount),
]
# Output the built-in properties
for i in range(0, len(properties)):
print(properties[i])
doc.Close()
Remove Built-in Document Properties from Word Documents with Python
The built-in document properties of a Word document that contain specific content can be removed by setting them to null values. This protects private information while retaining necessary details.
The detailed steps for removing specific built-in document properties from Word documents are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the built-in properties of the document through Document.BuiltinDocumentProperties property.
- Set the value of some properties to none to remove the properties with properties under BuiltinDocumentProperties class.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load the Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("output/AddPropertyWord.docx")
# Get the document's built-in properties
builtinProperties = doc.BuiltinDocumentProperties
# Remove the built-in properties by setting them to None
builtinProperties.Author = None
builtinProperties.Company = None
builtinProperties.Title = None
builtinProperties.Subject = None
builtinProperties.Keywords = None
builtinProperties.Comments = None
builtinProperties.Category = None
builtinProperties.Manager = None
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemovePropertyWord.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add Page Numbers to a Word Document
Adding page numbers to a Word document is a fundamental feature that enhances readability and navigation, especially in lengthy documents. It allows readers to find specific content more easily and helps authors organize their work. Word offers flexible options for adding page numbers, including choosing the location (header, footer, or body) and customizing the format and appearance to match your document's design needs.
In this article, you will learn how to add pager numbers to a Word document, as well as customizing their appearance using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Add Page Numbers to a Word Document
- Add Page Numbers to a Specific Section
- Add Discontinuous Page Numbers to Different Sections
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
Add Page Numbers to a Word Document in Python
To dynamically add page numbers to a Word document using Spire.Doc, you can leverage various fields such as FieldPage, FieldNumPages, and FieldSection. These fields serve as placeholders for the current page number, total page count, and section number, enabling you to customize and automate the pagination process.
You can embed these placeholders in the header or footer of your document by calling the Paragraph.AppendField() method.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to insert a FieldPage and FieldNumPages field in the footer, which will display the page number in the format "X / Y":
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document from a specified file path.
- Get the first section using Document.Sections[index] property
- Get the footer of the first section using Section.HeadersFooters.Footer property.
- Add a paragraph to the footer using HeaderFooter.AddParagraph() method.
- Insert a FieldPage field, and a FieldNumPages field to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendField() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Get the first section
section = document.Sections[0]
# Get the footer of the section
footer = section.HeadersFooters.Footer
# Add "page number / page count" to the footer
footerParagraph = footer.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.AppendField("page number", FieldType.FieldPage)
footerParagraph.AppendText(" / ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("page count", FieldType.FieldNumPages)
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Apply formatting to the page number
style = ParagraphStyle(document)
style.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 18
style.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
document.Styles.Add(style)
footerParagraph.ApplyStyle(style)
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("Output/AddPageNumbersToDocument.docx")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()

Add Page Numbers to a Specific Section in Python
By default, when you add page numbers to the footer of a section, they are automatically linked to the preceding section, maintaining a continuous sequence of page numbers. This behavior is convenient for most documents but may not be ideal when you want to start numbering from a certain section without affecting the numbering in other parts of the document.
If you need to add page numbers to a specific section without them being linked to the previous section, you must unlink the subsequent sections and clear the contents of their footers. Here's how you can do it using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document from a specified file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property
- Get the footer of the section using Section.HeadersFooters.Footer property.
- Restart page numbering from 1 by setting Section.PageSetup.RestartPageNumbering property to true and Section.PageSetup.PageStartingNumber property to 1.
- Insert a FieldPage field and a FieldSection field to the footer using Paragraph.AppendField() method.
- Disable "Link to previous" by setting HeadersFooters.Footer.LinkToPrevious propety to false.
- Delete the content of the footers in the subsequent sections
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Get a specific section
sectionIndex = 1
section = document.Sections[sectionIndex]
# Restart page numbering from 1
section.PageSetup.RestartPageNumbering = True
section.PageSetup.PageStartingNumber = 1
# Get the footer of the section
footer = section.HeadersFooters.Footer
# Add "Page X, Section Y" to the footer
footerParagraph = footer.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.AppendText("Page ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("page number", FieldType.FieldPage)
footerParagraph.AppendText(", Section ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("section number", FieldType.FieldSection)
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Apply formatting to the page number
style = ParagraphStyle(document);
style.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 18
style.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
document.Styles.Add(style)
footerParagraph.ApplyStyle(style)
# Disable "Link to previous" in the subsequent section
document.Sections[sectionIndex + 1].HeadersFooters.Footer.LinkToPrevious = False
# Delete the content of the footers in the subsequent sections
for i in range(sectionIndex +1, document.Sections.Count, 1):
document.Sections[i].HeadersFooters.Footer.ChildObjects.Clear()
document.Sections[i].HeadersFooters.Footer.AddParagraph()
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("Output/AddPageNumbersToSection.docx")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()

Add Discontinuous Page Numbers to Different Sections in Python
When working with documents that contain multiple sections, you might want to start page numbering anew for each section to clearly distinguish between them. To achieve this, you must go through each section individually, add page numbers, and then reset the page numbering for the next section.
The following are the steps to add discontinuous page numbers to different sections using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document from a specified file path.
- Iterate through the sections in the document.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property
- Get the footer of the section using Section.HeadersFooters.Footer property.
- Restart page numbering from 1 by setting Section.PageSetup.RestartPageNumbering property to true and Section.PageSetup.PageStartingNumber property to 1.
- Insert a FieldPage field and a FieldSection field to the footer using Paragraph.AppendField() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Iterate through the sections in the document
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections[i]
# Restart page numbering from 1
section.PageSetup.RestartPageNumbering = True
section.PageSetup.PageStartingNumber = 1
# Get the footer of the section
footer = section.HeadersFooters.Footer
# Add "Page X, Section Y" to the footer
footerParagraph = footer.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.AppendText("Page ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("page number", FieldType.FieldPage)
footerParagraph.AppendText(", Section ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("section number", FieldType.FieldSection)
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Apply formatting to the page number
style = ParagraphStyle(document)
style.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman";
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 18;
style.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
document.Styles.Add(style)
footerParagraph.ApplyStyle(style)
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("Output/AddDifferentPageNumbersToSections.docx")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Enable Track Changes, Accept or Reject Tracked Changes in Word
Track changes in Microsoft Word is a powerful feature that facilitates document collaboration and review processes. When track changes is enabled, any modifications made to the document, such as text additions or deletions, formatting changes, and comments, are visually highlighted. This makes it easier for document editors or collaborators to identify and review the changes made by themselves or others. In this article, we will explain how to enable track changes, as well as accept or reject the tracked changes in Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Enable Track Changes in Word in Python
- Accept Tracked Changes in Word in Python
- Reject Tracked Changes in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Enable Track Changes in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Document.TrackChanges property to enable the track changes mode for a Word document. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Enable the track changes mode for the document by setting the Document.TrackChanges property to True.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Enable the track changes mode for the document
doc.TrackChanges = True
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("EnableTrackChanges.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
doc.Close()
Accept Tracked Changes in Word in Python
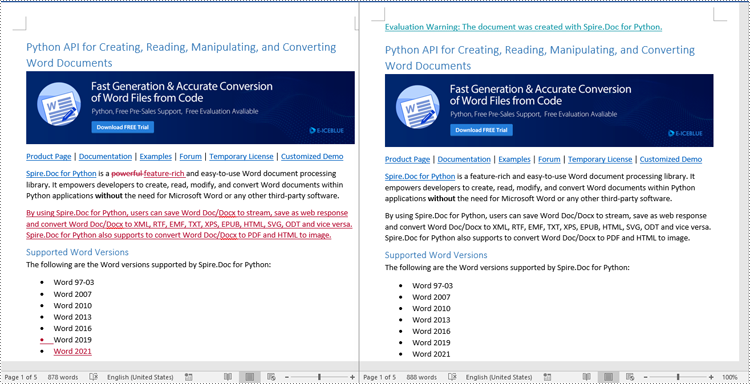
Accepting tracked changes allows you to incorporate the suggested modifications permanently into the document. By using the Document.AcceptChanges() method provided by Spire.Doc for Python, you can easily accept all tracked changes in a Word document. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Check if the document has tracked changes using Document.HasChanges property.
- Accept the tracked changes in the document using Document.AcceptChanges() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Check if the document has tracked changes
if(doc.HasChanges):
# Accept the tracked changes in the document
doc.AcceptChanges()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("AcceptChanges.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
doc.Close()
Reject Tracked Changes in Word in Python
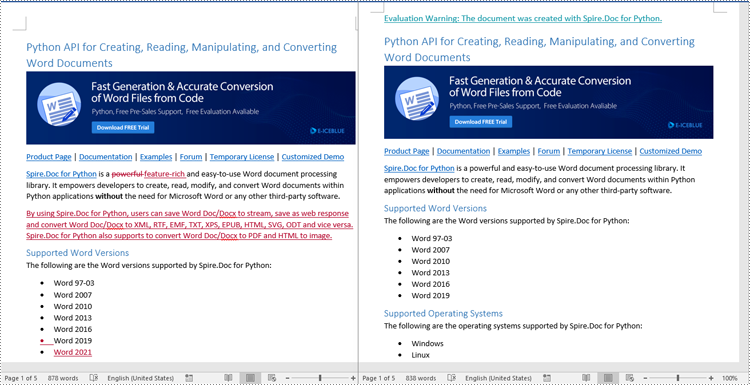
Sometimes, suggested modifications may not align with your vision or requirements for the document. In such cases, rejecting these changes becomes essential to ensure that the document accurately reflects your intended content and formatting choices.
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Document.RejectChanges() method to reject the tracked changes in a Word document. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Check if the document has tracked changes using Document.HasChanges property.
- Reject the tracked changes in the document using Document.RejectChanges() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Check if the document has tracked changes
if(doc.HasChanges):
# Reject the tracked changes in the document
doc.RejectChanges()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("RejectChanges.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Split Word Documents
Efficiently managing Word documents often requires the task of splitting them into smaller sections. However, manually performing this task can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Fortunately, Spire.Doc for Python provides a convenient and efficient way to programmatically segment Word documents, helping users to extract specific parts of a document, split lengthy documents into smaller chunks, and streamline data extraction. This article demonstrates how to use Spire.Doc for Python to split a Word document into multiple documents in Python.
The splitting of a Word document is typically done by page breaks and section breaks due to the dynamic nature of document content. Therefore, this article focuses on the following two parts:
- Split a Word Document by Page Breaks with Python
- Split a Word Document by Section Breaks with Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Split a Word Document by Page Breaks with Python
Page breaks allow for the forced pagination of a document, thereby achieving a fixed division of content. By using page breaks as divisions, we can split a Word document into smaller content-related documents. The detailed steps for splitting a Word document by page breaks are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a new document, add a section to it using Document.AddSection() method.
- Iterate through all body child objects in each section in the original document and check if the child object is a paragraph or a table.
- If the child object is a table, add it to the section in the new document using Section.Body.ChildObjects.Add() method.
- If the child object is a paragraph, add the paragraph object to the section in the new document. Then, iterate through all child objects of the paragraph and check if a child object is a page break.
- If the child object in the paragraph is a page break, get its index using Paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf() method and remove it from the paragraph by its index.
- Save the new document using Document.SaveToFile() method and repeat the above process.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "Sample.docx"
outputFolder = "output/SplitDocument/"
# Create an instance of Document
original = Document()
# Load a Word document
original.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a new word document and add a section to it
newWord = Document()
section = newWord.AddSection()
original.CloneDefaultStyleTo(newWord)
original.CloneThemesTo(newWord)
original.CloneCompatibilityTo(newWord)
index = 0
# Iterate through all sections of original document
for m in range(original.Sections.Count):
sec = original.Sections.get_Item(m)
# Iterate through all body child objects of each section
for k in range(sec.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = sec.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
if isinstance(obj, Paragraph):
para = obj if isinstance(obj, Paragraph) else None
sec.CloneSectionPropertiesTo(section)
# Add paragraph object in original section into section of new document
section.Body.ChildObjects.Add(para.Clone())
for j in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
parobj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
if isinstance(parobj, Break) and ( parobj if isinstance(parobj, Break) else None).BreakType == BreakType.PageBreak:
# Get the index of page break in paragraph
i = para.ChildObjects.IndexOf(parobj)
# Remove the page break from its paragraph
section.Body.LastParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the new document
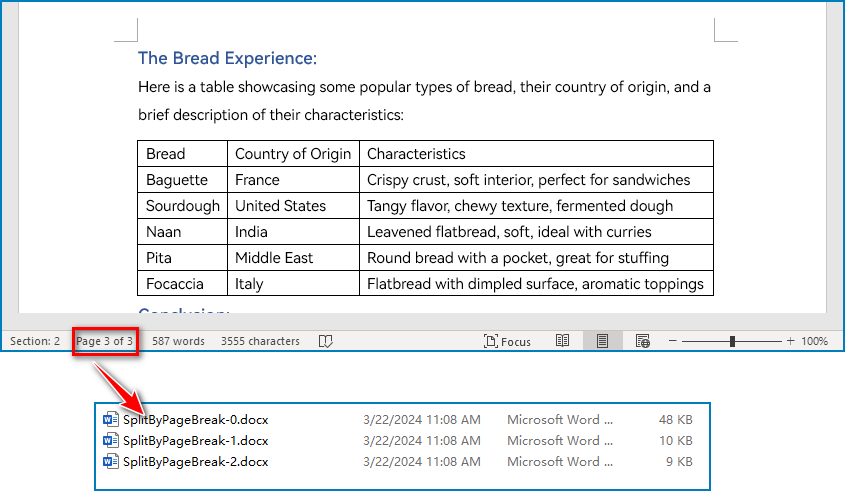
resultF = outputFolder
resultF += "SplitByPageBreak-{0}.docx".format(index)
newWord.SaveToFile(resultF, FileFormat.Docx)
index += 1
# Create a new document and add a section
newWord = Document()
section = newWord.AddSection()
original.CloneDefaultStyleTo(newWord)
original.CloneThemesTo(newWord)
original.CloneCompatibilityTo(newWord)
sec.CloneSectionPropertiesTo(section)
# Add paragraph object in original section into section of new document
section.Body.ChildObjects.Add(para.Clone())
if section.Paragraphs[0].ChildObjects.Count == 0:
# Remove the first blank paragraph
section.Body.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(0)
else:
# Remove the child objects before the page break
while i >= 0:
section.Paragraphs[0].ChildObjects.RemoveAt(i)
i -= 1
if isinstance(obj, Table):
# Add table object in original section into section of new document
section.Body.ChildObjects.Add(obj.Clone())
# Save the document
result = outputFolder+"SplitByPageBreak-{0}.docx".format(index)
newWord.SaveToFile(result, FileFormat.Docx2013)
newWord.Close()
Split a Word Document by Section Breaks with Python
Sections divide a Word document into different logical parts and allow for independent formatting for each section. By splitting a Word document into sections, we can obtain multiple documents with relatively independent content and formatting. The detailed steps for splitting a Word document by section breaks are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each section in the document.
- Get a section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Create a new Word document and copy the section in the original document to the new document using Document.Sections.Add() method.
- Save the new document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Iterate through all sections
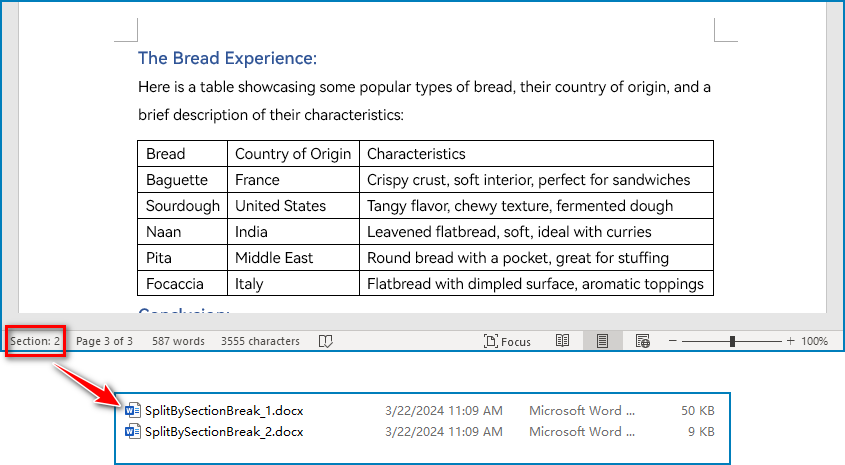
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
section = document.Sections.get_Item(i)
result = "output/SplitDocument/" + "SplitBySectionBreak_{0}.docx".format(i+1)
# Create a new Word document
newWord = Document()
# Add the section to the new document
newWord.Sections.Add(section.Clone())
#Save the new document
newWord.SaveToFile(result)
newWord.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Compare Two Versions of a Word Document
Comparing two Word documents for differences is a crucial task when reviewing changes, ensuring accuracy, and collaborating on content. This process allows you to identify additions, deletions, and modifications made between different document iterations. By comparing versions, you can efficiently track alterations, verify updates, and maintain document integrity. In this article, you will learn how to compare two versions of a Word document in Python using the Spire.Doc for Python library.
- Compare Two Versions of a Word Document in Python
- Compare Two Versions of a Word Document While Ignoring Formatting in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Compare Two Versions of a Word Document in Python
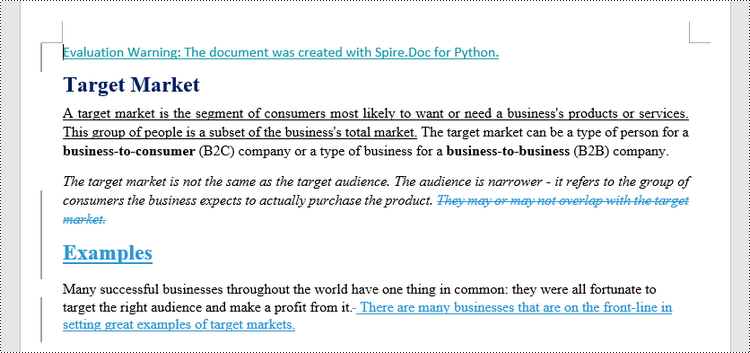
MS Word also offers a "Compare" feature that allows you to directly compare two versions of a document. This feature generates a new document that highlights the differences between the two versions.
To achieve similar results using Spire.Doc for Python, load the original and revised versions into two separate Document objects. Then, use the Compare() method to compare the revised version against the original. Finally, save the comparative document, which highlights the alterations, using the SaveToFile() method.
The steps to compare two version of a Word document using Python are as follows.
- Load the first document (original version) while initializing the Document object.
- Load the second document (revised version) while initializing the Document object.
- Call Compare() method of the first Document object to compare the revised version against the original version.
- Save the comparison results in a new Word document.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Load the first document while initializing the Document object
firstDoc = Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Original.docx")
# Load the second document while initializing the Document object
secondDoc = Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Revised.docx")
# Compare two documents
firstDoc.Compare(secondDoc, "E-ICEBLUE")
# Save the comparison results in a new document
firstDoc.SaveToFile("Output/Differences.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Dispose resources
firstDoc.Dispose()
secondDoc.Dispose()

Compare Two Versions of a Word Document While Ignoring Formatting in Python
Comparing two versions of a Word document while ignoring formatting can be useful when you want to focus solely on the textual changes and disregard any formatting modifications.
To customize the comparison options in Spire.Doc for Python, use the CompareOptions class. If you want to exclude formatting from the comparison process, you can set the IgnoreFormatting property of the CompareOptions object to True. When you call the Compare() method, simply pass the CompareOptions object as an argument to achieve the desired comparison behavior.
The following are the steps to compare two versions of a Word document while ignoring formatting using Python.
- Load the first document (original version) while initializing the Document object.
- Load the second document (revised version) while initializing the Document object.
- Create a CompareOptions object and set its IgnoreFormatting property to True.
- Call Compare() method of the first Document object, passing the CompareOptions object as a parameter, to compare the revision against the original while ignoring formatting.
- Save the comparison results in a new Word document.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Load the first document while initializing the Document object
firstDoc = Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Original.docx")
# Load the second document while initializing the Document object
secondDoc = Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Revised.docx")
# Set compare option to ignore formatting changes
compareOptions = CompareOptions()
compareOptions.IgnoreFormatting = True
# Compare the two Word documents with options
firstDoc.Compare(secondDoc, "E-ICEBLUE", compareOptions)
# Save the comparison results in a new document
firstDoc.SaveToFile("Output/DifferencesWithoutFormattingChanges.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Dispose resources
firstDoc.Dispose()
secondDoc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Insert a Table of Contents into a Word Document
Efficient document organization and navigability are crucial for lengthy Word documents. One powerful way to streamline document readability and accessibility is by incorporating a table of contents (TOC) into a Word document, which allows readers to quickly locate specific sections and jump to relevant content. By harnessing the capabilities of Python, users can effortlessly generate a table of contents that dynamically updates as the document evolves. This article provides a step-by-step guide and code examples for inserting a table of contents into a Word document in Python programs using Spire.Doc for Python, empowering users to create professional-looking documents with ease.
- Insert the Default Table of Contents into a Word Document
- Insert a Custom Table of Contents into a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert the Default Table of Contents into a Word Document
Spire.Doc for Python supports inserting a table of contents in a Word document based on the headings of different levels. If the document does not have heading levels set, developers can set the heading levels using the Paragraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle) method before inserting a table of contents.
By using the Paragraph.AppendTOC(lowerLevel: int, upperLevel: int) method, developers can insert a table of contents at any paragraph and specify the titles to be displayed. It is important to note that after inserting the table of contents, developers need to use the Document.UpdateTableOfContents() method to update the table of contents so that its contents are displayed correctly.
- Create an object of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method, add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method, and insert the new section after the cover section using Document.Sections.Insert(index: int, entity: Section) method.
- Update the table of contents using Document.UpdateTableOfContents() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Create a section for the table of contents
section = doc.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph in the section
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Append a table of contents in the paragraph
paragraph.AppendTOC(1, 2)
# Insert the section after the cover section
doc.Sections.Insert(1, section)
# Update the table of contents
doc.UpdateTableOfContents()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/DefaultTOC.docx")
doc.Close()
Insert a Custom Table of Contents into a Word Document
Developers can also create a table of contents by initializing a TableOfContent object, and customize it through switches. For example, the switch "{\\o \"1-2\" \\n 1-1}" indicates showing headings from level one to level three in the table of contents and omitting the page numbers of level one headings. The detailed steps for inserting a customized table of contents into a Word document are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a section to the document using Document.AddSecction() method, add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method, and insert the section after the cover section using Document.Sections.Insert() method.
- Create an object of TableOfContents class and insert it into the added paragraph using Paragraph.Items.Add() method.
- Append field separator and field end mark to end the TOC filed using Paragraph.AppendFieldMark() method.
- Set the created table of contents as the table of contents of the document through Document.TOC property.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Add a section and a paragraph and insert the section after the cover section
section = doc.AddSection()
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
doc.Sections.Insert(1, section)
# Customize a table of contents with switches
toc = TableOfContent(doc, "{\\o \"1-2\" \\n 1-1}")
# Insert the TOC to the paragraph
paragraph.Items.Add(toc)
# Insert field separator and filed end mark to end the TOC field
paragraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldSeparator)
paragraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldEnd)
# Set the TOC field as the table of contents of the document
doc.TOC = toc
# Update the TOC
doc.UpdateTableOfContents()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/CustomizedTOC.docx")
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Insert or Remove Footnotes in Word
Footnotes are a valuable tool in Microsoft Word that allows you to enhance the content of your documents by providing additional information, references, or citations at the bottom of a page. For example, you can use footnotes to provide in-depth explanations of complex concepts, cite sources to support your arguments, or offer tangential information that might be interesting to your readers. Whether you're working on an academic paper, a book, or any document that requires citations or explanations, footnotes offer a convenient way to maintain a clean and organized layout while presenting supplementary details. In this article, we will explain how to insert or remove footnotes in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Insert a Footnote for a Specific Paragraph in Word in Python
- Insert a Footnote for a Specific Text in Word in Python
- Remove Footnotes in a Word Document in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert a Footnote for a Specific Paragraph in Word in Python
You can use the Paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python to easily add a footnote for a specific paragraph. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section in the document using Document.Section[int] property and then get a specific paragraph of the section using Section.Paragraphs[int] property.
- Add a footnote at the end of the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote) method.
- Set the text content of the footnote, and then set the font and color for the footnote text and the footnote reference mark.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(3)
# Add a footnote at the end of the paragraph
footnote = paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote)
# Set the text content of the footnote
text = footnote.TextBody.AddParagraph().AppendText("The industry code list is available online.")
# Set the text font and color
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
text.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkBlue()
# Set the font and color of the footnote reference mark
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri"
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontSize = 15
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.Bold = True
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkCyan()
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AddFootnoteForParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Insert a Footnote for a Specific Text in Word in Python
To add a footnote for a specific text, you need to find the text in the document, get the location of the text in its owner paragraph, and then insert the footnote after the text. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find a specific text using Document.FindString() method.
- Get the found text as a single text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method.
- Get the paragraph where the text range is located using TextRange.OwnerParagraph property.
- Get the index position of the text range in the paragraph using Paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf() method.
- Add a footnote to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote) method, and then insert the footnote after the specific text using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method.
- Set the text content of the footnote, and then set the font and color for the footnote text and the footnote reference mark.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Find a specific text
selection = document.FindString("major players", False, True)
# Get the found text as a single text range
textRange = selection.GetAsOneRange()
# Get the paragraph where the text range is located
paragraph = textRange.OwnerParagraph
# Get the index position of the text range in the paragraph
index = paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(textRange)
# Add a footnote to the paragraph
footnote = paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote)
# Insert the footnote after the text range
paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(index + 1, footnote)
# Set the text content of the footnote
text = footnote.TextBody.AddParagraph().AppendText("Including suppliers, competitors, and customers")
# Set the text font and color
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
text.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkBlue()
# Set the font and color of the footnote reference mark
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri"
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontSize = 15
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.Bold = True
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkGreen()
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AddFootnoteForText.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Remove Footnotes in a Word Document in Python
When the footnotes of a Word document are no longer needed, you can remove them to make the document neater. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[int] property.
- Loop through each paragraph in the section to find the footnotes.
- Remove the footnotes using Paragraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("AddFootnoteForParagraph.docx")
# Get the first section of the document
section = document.Sections[0]
# Loop through the paragraphs in the section
for y in range(section.Paragraphs.Count):
para = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(y)
index = -1
i = 0
cnt = para.ChildObjects.Count
while i < cnt:
pBase = para.ChildObjects[i] if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[i], ParagraphBase) else None
if isinstance(pBase, Footnote):
index = i
break
i += 1
if index > -1:
# Remove the footnotes from the paragraph
para.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(index)
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveFootnotes.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
document.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Merge Word Documents
Dealing with a large number of Word documents can be very challenging. Whether it's editing or reviewing a large number of documents, there's a lot of time wasted on opening and closing documents. What's more, sharing and receiving a large number of separate Word documents can be annoying, as it may require a lot of repeated sending and receiving operations by both the sharer and the receiver. Therefore, in order to enhance efficiency and save time, it is advisable to merge related Word documents into a single file. From this article, you will know how to use Spire.Doc for Python to easily merge Word documents through Python programs.
- Merge Word Documents by Inserting Files with Python
- Merge Word Documents by Cloning Contents with Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Merge Word Documents by Inserting Files with Python
The method Document.insertTextFromFile() is used to insert other Word documents to the current one, and the inserted content will start from a new page. The detailed steps for merging Word documents by inserting are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Insert the content from another document to it using Document.InsertTextFromFile() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
# Insert the content from another Word document to this one
doc.InsertTextFromFile("Sample2.docx", FileFormat.Auto)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/InsertDocuments.docx")
doc.Close()

Merge Word Documents by Cloning Contents with Python
Merging Word documents can also be achieved by cloning contents from one Word document to another. This method maintains the formatting of the original document, and content cloned from another document continues at the end of the current document without starting a new Page. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create two objects of Document class and load two Word documents using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the last section of the destination document using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Loop through the sections in the document to be cloned and then loop through the child objects of the sections.
- Get a section child object using Section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item() method.
- Add the child object to the last section of the destination document using Section.Body.ChildObjects.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create two objects of Document class and load two Word documents
doc1 = Document()
doc1.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
doc2 = Document()
doc2.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx")
# Get the last section of the first document
lastSection = doc1.Sections.get_Item(doc1.Sections.Count - 1)
# Loop through the sections in the second document
for i in range(doc2.Sections.Count):
section = doc2.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Loop through the child objects in the sections
for j in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
# Add the child objects from the second document to the last section of the first document
lastSection.Body.ChildObjects.Add(obj.Clone())
# Save the result document
doc1.SaveToFile("output/MergeByCloning.docx")
doc1.Close()
doc2.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.