Converting Image to PDF with Python: 4 Code Examples
Table of Contents
Install with Pip
pip install Spire.PDF
Related Links
Converting an image to PDF is a convenient and efficient way to transform a visual file into a portable, universally readable format. Whether you're working with a scanned document, a photo, or a digital image, converting it to PDF provides numerous benefits. It maintains the image's original quality and guarantees compatibility across diverse devices and operating systems. Moreover, converting images to PDF allows for easy sharing, printing, and archiving, making it a versatile solution for various professional, educational, and personal purposes. This article provides several examples showing you how to convert images to PDF using Python.
- Convert an Image to a PDF Document in Python
- Convert Multiple Images to a PDF Document in python
- Create a PDF from Multiple Images Customizing Page Margins in Python
- Create a PDF with Several Images per Page in Python
PDF Converter API for Python
If you want to turn image files into PDF format in a Python application, Spire.PDF for Python can help with this. It enables you to build a PDF document with custom page settings (size and margins), add one or more images to every single page, and save the final document as a PDF file. Various image forms are supported which include PNG, JPEG, BMP, and GIF images.
In addition to the conversion from images to PDF, this library supports converting PDF to Word, PDF to Excel, PDF to HTML, PDF to PDF/A with high quality and precision. As an advanced Python PDF library, it also provides a rich API for developers to customize the conversion options to meet a variety of conversion requirements.
The library can be installed by running the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
Steps to Convert an Image to PDF in Python
- Initialize PdfDocument class.
- Load an image file from path using FromFile method.
- Add a page with the specified size to the document.
- Draw the image on the page at the specified location using DrawImage method.
- Save the document to a PDF file using SaveToFile method.
Convert an Image to a PDF Document in Python
This code example converts an image file to a PDF document using the Spire.PDF for Python library by creating a blank document, adding a page with the same dimensions as the image, and drawing the image onto the page.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the page margins to 0
doc.PageSettings.SetMargins(0.0)
# Load a particular image
image = PdfImage.FromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Images\\img-1.jpg")
# Get the image width and height
width = image.PhysicalDimension.Width
height = image.PhysicalDimension.Height
# Add a page that has the same size as the image
page = doc.Pages.Add(SizeF(width, height))
# Draw image at (0, 0) of the page
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0, width, height)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/ImageToPdf.pdf")
doc.Dispose()

Convert Multiple Images to a PDF Document in python
This example illustrates how to convert a collection of images into a PDF document using Spire.PDF for Python. The following code snippet reads images from a specified folder, creates a PDF document, adds each image to a separate page in the PDF, and saves the resulting PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
import os
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the page margins to 0
doc.PageSettings.SetMargins(0.0)
# Get the folder where the images are stored
path = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Images\\"
files = os.listdir(path)
# Iterate through the files in the folder
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for file in files:
# Load a particular image
image = PdfImage.FromFile(os.path.join(root, file))
# Get the image width and height
width = image.PhysicalDimension.Width
height = image.PhysicalDimension.Height
# Add a page that has the same size as the image
page = doc.Pages.Add(SizeF(width, height))
# Draw image at (0, 0) of the page
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0, width, height)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile('output/ImagesToPdf.pdf')
doc.Dispose()

Create a PDF from Multiple Images Customizing Page Margins in Python
This code example creates a PDF document and populates it with images from a specified folder, adjusts the page margins and saves the resulting document to a file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
import os
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the left, top, right, bottom page margin
doc.PageSettings.SetMargins(30.0, 30.0, 30.0, 30.0)
# Get the folder where the images are stored
path = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Images\\"
files = os.listdir(path)
# Iterate through the files in the folder
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for file in files:
# Load a particular image
image = PdfImage.FromFile(os.path.join(root, file))
# Get the image width and height
width = image.PhysicalDimension.Width
height = image.PhysicalDimension.Height
# Specify page size
size = SizeF(width + doc.PageSettings.Margins.Left + doc.PageSettings.Margins.Right, height + doc.PageSettings.Margins.Top+ doc.PageSettings.Margins.Bottom)
# Add a page with the specified size
page = doc.Pages.Add(size)
# Draw image on the page at (0, 0)
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0, width, height)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile('output/CustomizeMargins.pdf')
doc.Dispose()

Create a PDF with Several Images per Page in Python
This code demonstrates how to use the Spire.PDF library in Python to create a PDF document with two images per page. The images in this example are the same size, if your image size is not consistent, then you need to adjust the code to achieve a desired result.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
import os
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the left, top, right, bottom page margins
doc.PageSettings.SetMargins(15.0, 15.0, 15.0, 15.0)
# Get the folder where the images are stored
path = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Images\\"
files = os.listdir(path)
# Iterate through the files in the folder
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for i in range(len(files)):
# Load a particular image
image = PdfImage.FromFile(os.path.join(root, files[i]))
# Get the image width and height
width = image.PhysicalDimension.Width
height = image.PhysicalDimension.Height
# Specify page size
size = SizeF(width + doc.PageSettings.Margins.Left + doc.PageSettings.Margins.Right, height*2 + doc.PageSettings.Margins.Top+ doc.PageSettings.Margins.Bottom + 15.0)
if i % 2 == 0:
# Add a page with the specified size
page = doc.Pages.Add(size)
# Draw first image on the page at (0, 0)
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0, width, height)
else :
# Draw second image on the page at (0, height + 15)
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, 0.0, height + 15.0, width, height)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile('output/SeveralImagesPerPage.pdf')
doc.Dispose()
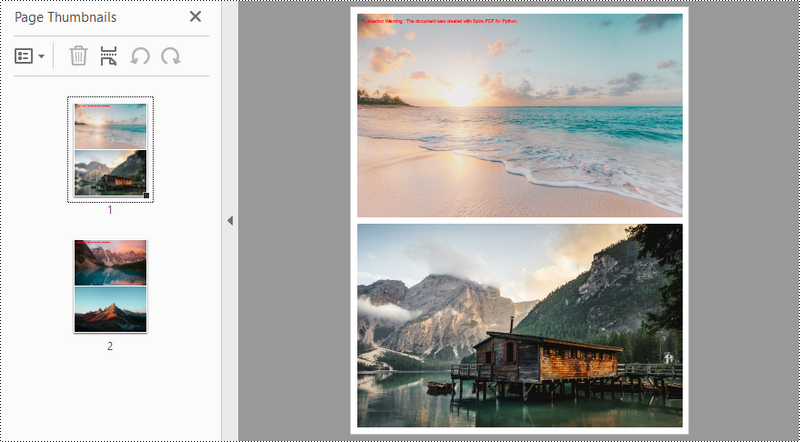
Conclusion
In this blog post, we explored how to use Spire.PDF for python to create PDF documents from images, containing one or more images per page. Additionally, we demonstrated how to customize the PDF page size and the margins around the images. For more tutorials, please check out our online documentation. If you have any questions, feel free to contact us by email or on the forum.
How to Convert PDF to Text in Python (Free & Easy Guide)
Table of Contents
Install with Pip
pip install Spire.PDF
Related Links
Converting PDF files to editable text is a common need for researchers, analysts, and professionals who deal with large volumes of documents. Manual copying wastes time—Python offers a faster, more flexible solution. In this guide, you’ll learn how to convert PDF to text in Python efficiently, whether you want to keep the layout or extract specific content.

- Why Choose Spire.PDF for PDF to Text
- General Workflow for PDF to Text in Python
- Convert PDF to Text in Python Without Layout
- Convert PDF to Text in Python With Layout
- Convert a Specific PDF Page to Text
- To Wrap Up
- FAQs
Getting Started: Why Choose Spire.PDF for PDF to Text in Python
To convert PDF files to text using Python, you’ll need a reliable PDF processing library. Spire.PDF for Python is a powerful and developer-friendly API that allows you to read, edit, and convert PDF documents in Python applications — no need for Adobe Acrobat or other third-party software.
This library is ideal for automating PDF workflows such as extracting text, adding annotations, or merging and splitting files. It supports a wide range of PDF features and works seamlessly in both desktop and server environments. You can donwload it to install mannually or quickly install Spire.PDF via PyPI using the following command:
pip install Spire.PDFFor smaller or personal projects, a free version is available with basic functionality. If you need advanced features such as PDF signing or form filling, you can upgrade to the commercial edition at any time.
General Workflow for PDF to Text in Python
Converting a PDF to text becomes simple and efficient with the help of Spire.PDF for Python. You can easily complete the task by reusing the sample code provided in the following sections and customizing it to fit your needs. But before diving into the code, let’s take a quick look at the general workflow behind this process.
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF file using LoadFromFile() method.
- Create an object of PdfTextExtractOptions class and set the text extracting options, including extracting all text, showing hidden text, only extracting text in a specified area, and simple extraction.
- Get a page in the document using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method and create PdfTextExtractor objects based on each page to extract the text from the page using Extract() method with specified options.
- Save the extracted text as a text file and close the object.
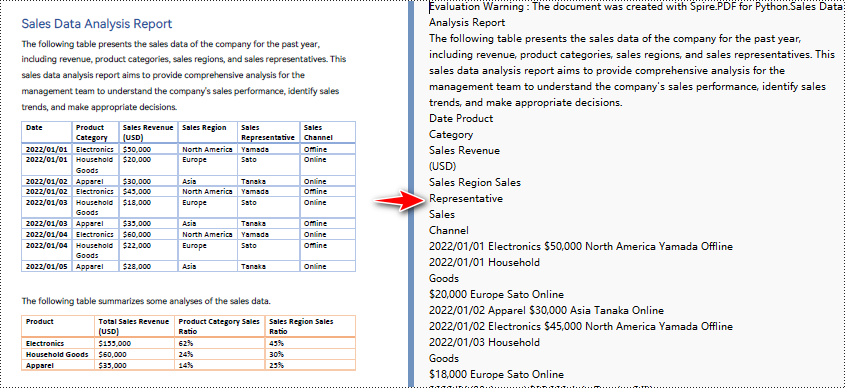
How to Convert PDF to Text in Python Without Layout
If you only need the plain text content from a PDF and don’t care about preserving the original layout, you can use a simple method to extract text. This approach is faster and easier, especially when working with scanned documents or large batches of files. In this section, we’ll show you how to convert PDF to text in Python without preserving the layout.
To extract text without preserving layout, follow these simplified steps:
- Create an instance of PdfDocument and load the PDF file.
- Create a PdfTextExtractOptions object and configure the text extraction options.
- Set IsSimpleExtraction = True to ignore the layout and extract raw text.
- Loop through all pages of the PDF.
- Extract text from each page and write it to a .txt file.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
from spire.pdf import PdfTextExtractOptions
from spire.pdf import PdfTextExtractor
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a string object to store the text
extracted_text = ""
# Create an object of PdfExtractor
extract_options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Set to use simple extraction method
extract_options.IsSimpleExtraction = True
# Loop through the pages in the document
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create an object of PdfTextExtractor passing the page as paramter
text_extractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Extract the text from the page
text = text_extractor.ExtractText(extract_options)
# Add the extracted text to the string object
extracted_text += text
# Write the extracted text to a text file
with open("output/ExtractedText.txt", "w") as file:
file.write(extracted_text)
pdf.Close()
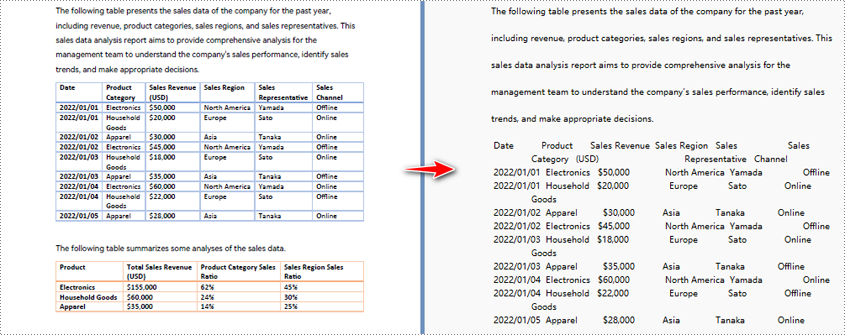
How to Convert PDF to Text in Python With Layout
To convert PDF to text in Python with layout, Spire.PDF preserves formatting like tables and paragraphs by default. The steps are similar to the general overview, but you still need to loop through each page for full-text extraction.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
from spire.pdf import PdfTextExtractOptions
from spire.pdf import PdfTextExtractor
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a string object to store the text
extracted_text = ""
# Create an object of PdfExtractor
extract_options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Loop through the pages in the document
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create an object of PdfTextExtractor passing the page as paramter
text_extractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Extract the text from the page
text = text_extractor.ExtractText(extract_options)
# Add the extracted text to the string object
extracted_text += text
# Write the extracted text to a text file
with open("output/ExtractedText.txt", "w") as file:
file.write(extracted_text)
pdf.Close()
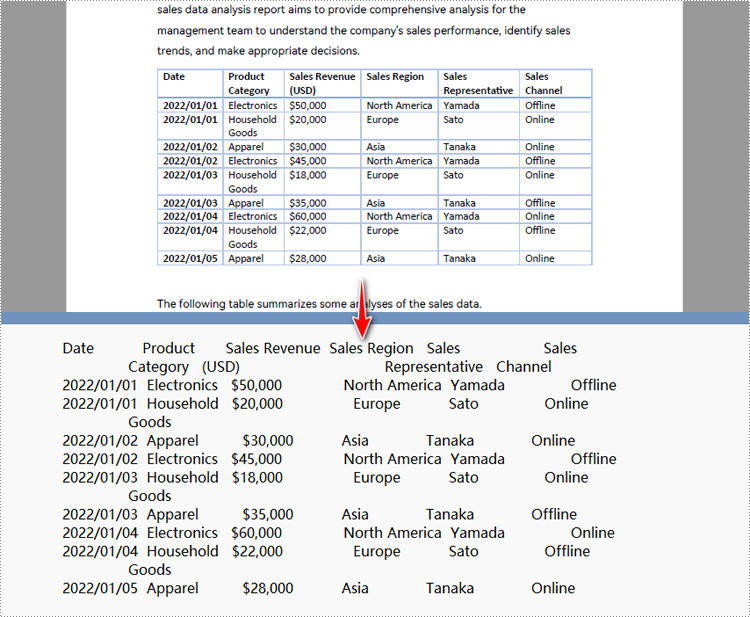
Convert a Specific PDF Page to Text in Python
Need to extract text from only one page of a PDF instead of the entire document? With Spire.PDF, the PDF to Text converter in Python, you can easily target and convert a specific PDF page to text. The steps are the same as shown in the general overview. If you're already familiar with them, just copy the code below into any Python editor and automate your PDF to text conversion!
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
from spire.pdf import PdfTextExtractOptions
from spire.pdf import PdfTextExtractor
from spire.pdf import RectangleF
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create an object of PdfExtractor
extract_options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Set to extract specific page area
extract_options.ExtractArea = RectangleF(50.0, 220.0, 700.0, 230.0)
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create an object of PdfTextExtractor passing the page as paramter
text_extractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Extract the text from the page
extracted_text = text_extractor.ExtractText(extract_options)
# Write the extracted text to a text file
with open("output/ExtractedText.txt", "w") as file:
file.write(extracted_text)
pdf.Close()
To Wrap Up
In this post, we covered how to convert PDF to text using Python and Spire.PDF, with clear steps and code examples for fast, efficient conversion. We also highlighted the benefits and pointed to OCR tools for image-based PDFs. For any issues or support, feel free to contact us.
FAQs about Converting PDF to Text
Q1: How do I convert a PDF to readable and editable text in Python?
A: You can convert a PDF to text in Python using the Spire.PDF library. It allows you to extract text from PDF files while optionally keeping the original layout. You don’t need Adobe Acrobat, and both visible and image-based PDFs are supported.
Q2: Is there a free tool to convert PDF to text?
A: Yes. Spire.PDF for Python provides a free edition that allows you to convert PDF to text without relying on Adobe Acrobat or other software. Online tools are also available, but they’re more suitable for occasional use or small files.
Q3: Can Python extract data from PDF? A: Yes, Python can extract data from PDF files. Using Spire.PDF, you can easily extract not only text but also other elements such as images, annotations, bookmarks, and even attachments. This makes it a versatile tool for working with PDF content in Python.
SEE ALSO:
Read Excel Files in Python: Data, Formulas, Images & Charts
Table of Contents
Install with pip
pip install Spire.XLS
Related Links

Excel files (*.xlsx, *.xls) are ubiquitous in data-driven workflows. Python developers need robust tools to parse, analyze, and manipulate Excel data programmatically. Spire.XLS for Python stands out as a powerful, dependency-free library that simplifies Excel reading operations without requiring Microsoft Office.
This guide explores how to read Excel file in Python, covering everything from installation to advanced data extraction techniques.
- Python Excel Reader Library
- Step-by-Step: Read Excel File in Python
- Full Example: Read Cell Range or Worksheet
- Advanced Python Excel Reading Techniques
- How Does Spire.XLS Compare to Pandas read_excel()
- Conclusion & Resources
Python Excel Reader Library
Why Choose Spire.XLS?
Choosing Spire.XLS for Python to read Excel file offers unique advantages:
- Zero Dependencies: Works without MS Excel installations.
- Cross-Platform: Compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- Rich Features:
- Read/write XLS, XLSX, XLSB, CSV, etc.
- Extract text, formulas, images, comments.
- Handle tables, hyperlinks, and data validation.
Install via pip
Before using Python to read XLSX file (or XLS file), ensure you have installed the Spire.XLS for Python library. The easiest way to install it is through pip, the Python package installer.
Open your terminal or command prompt and run:
pip install Spire.XLS
Step-by-Step: Read Excel File in Python
Let's start with the fundamentals of reading data from Excel cells using Spire.XLS for Python. The following example demonstrates how to open an Excel file, access a worksheet, and read cell data.
1. Import the Necessary Libraries:
First, import the spire.xls library and its common components, which are essential for working with Excel files in Python.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *2. Load the Excel File:
Next, load a XLS or XLSX file using the Workbook class.
- Python
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data.xlsx")3. Access a Worksheet:
After loading the file, access a specific worksheet by index. In Spire.XLS for Python, worksheet indexing is zero-based.
- Python
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]4. Read Cell Data:
Now, read data from a specific cell in the worksheet.
- Python
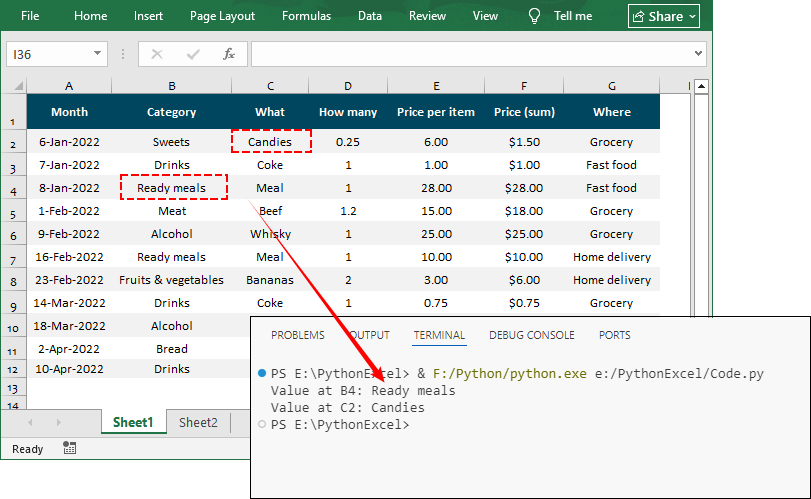
# Read cell B4
cell_value = sheet.Range["B4"].Value
print(f"Value at B4: {cell_value}")
# Using row/column indices # (row 2, column 3 → C2)
cell = sheet.Range[2, 3]
print(f"Value at C2: {cell.Value}")Output:
Full Example: Read Cell Range or Worksheet
Once you've mastered the above skills of reading Excel cell data, you can write Python code to read data from a cell area or a worksheet.
The following example demonstrates how to access a specified cell range or the used cell range in a worksheet, then iterate through each cell within to retrieve the cell value.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an existing Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the used range in the sheet
cellRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# or get a specified range
# cellRange = sheet.Range["A2:H5"]
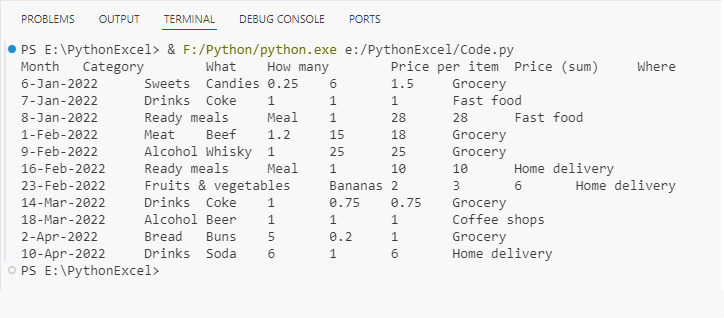
# Iterate through each cell in the range
for row in cellRange.Rows:
for cell in row.Cells:
# Retrieve cell data and print out
print(cell.Value, end="\t")
print()Output:
Advanced Python Excel Reading Techniques
Spire.XLS for Python offers advanced features for reading complex Excel files that contain formulas, images and charts.
Read Formulas & Calculated Results
Excel files often contain formulas that calculate values based on other cells. Spire.XLS for Python can read both the formula and the calculated result.
- Python
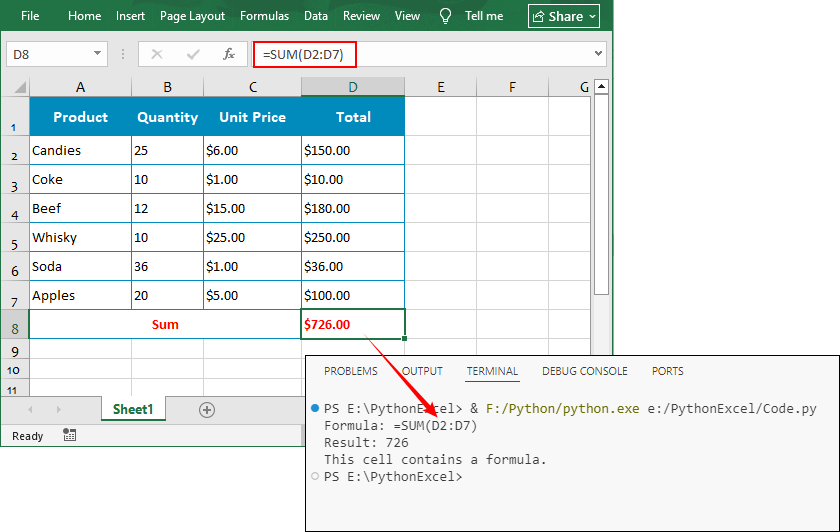
# Get a cell with a formula (e.g., "=SUM(D2:D7)")
formula_cell = sheet.Range["D8"]
print(f"Formula: {formula_cell.Formula}")
# Calculate the formula
calculated_value = formula_cell.FormulaValue
print(f"Result: {calculated_value}")
# Check if a cell contains a formula
if formula_cell.HasFormula:
print("This cell contains a formula.")Output:
Read Charts in Excel
The following Python code reads the critical chart elements and exports the chart as an image:
- Python
# Read chart title and type
for chart in sheet.Charts:
print(f"Chart Title: {chart.ChartTitle}")
print(f"Chart Type: {chart.ChartType}")
# Export chart to a PNG image
chartImage = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet, 0)
chartImage.Save("chart.png")Output:

Read Images in Excel
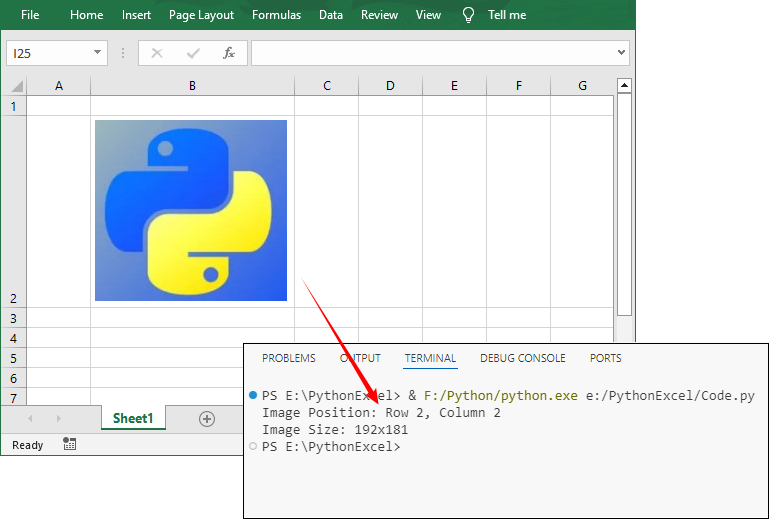
The following Python code reads the image location and size and extract them to the specified file path:
- Python
# Read image position and size
for image in sheet.Pictures:
print(f"Image Position: Row {image.TopRow}, Column {image.LeftColumn}")
print(f"Image Size: {image.Width}x{image.Height}")
# Extract image and save
image.Picture.Save(f"image_{image.TopRow}.png")Output:
How Does Spire.XLS Compare to Pandas read_excel()
Pandas and Spire.XLS for Python are both tools for working with Excel files, but their design goals and feature focuses differ:
- Pandas: A general-purpose tool for data extraction and analysis. It provides the pandas.read_excel() method to read data from Excel files into a DataFrame.
- Spire.XLS for Python: A standalone library dedicated to comprehensive Excel operations. It provides the CellRange.Value property to read Excel cell data.
Key Function Comparison
| Feature | Pandas | Spire.XLS |
| Feature | Pandas | Spire.XLS |
| Data Structure | Returns DataFrame objects | Returns custom object model (workbook/worksheet/cell) |
| Data Reading | ✅ Excellent | ✅ Excellent |
| Formatting | Limited (only data) | ✅ Full (fonts, colors, borders) |
| Formulas | Limited (Reads results only) | ✅ Reads formulas + calculations |
| Charts/Images | ❌ No | ✅ Full support |
| License | ✅ Open-source | Paid license (there’s also a Free Version) |
Pandas has no native support for non-data elements. Spire.XLS for Python, on the other hand, is optimized for complex Excel operations. Therefore, except for reading Excel data, Spire.XLS also enables:
- Read formulas, images & charts in Excel
- Retrieve Excel worksheet names
- Read document properties in Excel
- Extract comments and hyperlinks from Excel
Conclusion & Resources
Spire.XLS for Python provides an enterprise-grade solution for reading Excel files in Python without external dependencies. Its intuitive API supports everything from basic Excel data extraction to advanced formula handling, making it ideal for automation, data migration, and reporting.
Next Steps:
Python: Merge Word Documents
Table of Contents
Install with Pip
pip install Spire.Doc
Related Links
Dealing with a large number of Word documents can be very challenging. Whether it's editing or reviewing a large number of documents, there's a lot of time wasted on opening and closing documents. What's more, sharing and receiving a large number of separate Word documents can be annoying, as it may require a lot of repeated sending and receiving operations by both the sharer and the receiver. Therefore, in order to enhance efficiency and save time, it is advisable to merge related Word documents into a single file. From this article, you will know how to use Spire.Doc for Python to easily merge Word documents through Python programs.
- Merge Word Documents by Inserting Files with Python
- Merge Word Documents by Cloning Contents with Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your VS Code through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python in VS Code
Merge Word Documents by Inserting Files with Python
The method Document.insertTextFromFile() is used to insert other Word documents to the current one, and the inserted content will start from a new page. The detailed steps for merging Word documents by inserting are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Insert the content from another document to it using Document.InsertTextFromFile() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
# Insert the content from another Word document to this one
doc.InsertTextFromFile("Sample2.docx", FileFormat.Auto)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/InsertDocuments.docx")
doc.Close()

Merge Word Documents by Cloning Contents with Python
Merging Word documents can also be achieved by cloning contents from one Word document to another. This method maintains the formatting of the original document, and content cloned from another document continues at the end of the current document without starting a new Page. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create two objects of Document class and load two Word documents using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the last section of the destination document using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Loop through the sections in the document to be cloned and then loop through the child objects of the sections.
- Get a section child object using Section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item() method.
- Add the child object to the last section of the destination document using Section.Body.ChildObjects.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create two objects of Document class and load two Word documents
doc1 = Document()
doc1.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
doc2 = Document()
doc2.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx")
# Get the last section of the first document
lastSection = doc1.Sections.get_Item(doc1.Sections.Count - 1)
# Loop through the sections in the second document
for i in range(doc2.Sections.Count):
section = doc2.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Loop through the child objects in the sections
for j in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
# Add the child objects from the second document to the last section of the first document
lastSection.Body.ChildObjects.Add(obj.Clone())
# Save the result document
doc1.SaveToFile("output/MergeByCloning.docx")
doc1.Close()
doc2.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.