Table of Contents
Install with pip
pip install Spire.XLS
Related Links

Excel files (*.xlsx, *.xls) are ubiquitous in data-driven workflows. Python developers need robust tools to parse, analyze, and manipulate Excel data programmatically. Spire.XLS for Python stands out as a powerful, dependency-free library that simplifies Excel reading operations without requiring Microsoft Office.
This guide explores how to read Excel file in Python, covering everything from installation to advanced data extraction techniques.
- Python Excel Reader Library
- Step-by-Step: Read Excel File in Python
- Full Example: Read Cell Range or Worksheet
- Advanced Python Excel Reading Techniques
- How Does Spire.XLS Compare to Pandas read_excel()
- Conclusion & Resources
Python Excel Reader Library
Why Choose Spire.XLS?
Choosing Spire.XLS for Python to read Excel file offers unique advantages:
- Zero Dependencies: Works without MS Excel installations.
- Cross-Platform: Compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- Rich Features:
- Read/write XLS, XLSX, XLSB, CSV, etc.
- Extract text, formulas, images, comments.
- Handle tables, hyperlinks, and data validation.
Install via pip
Before using Python to read XLSX file (or XLS file), ensure you have installed the Spire.XLS for Python library. The easiest way to install it is through pip, the Python package installer.
Open your terminal or command prompt and run:
pip install Spire.XLS
Step-by-Step: Read Excel File in Python
Let's start with the fundamentals of reading data from Excel cells using Spire.XLS for Python. The following example demonstrates how to open an Excel file, access a worksheet, and read cell data.
1. Import the Necessary Libraries:
First, import the spire.xls library and its common components, which are essential for working with Excel files in Python.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *2. Load the Excel File:
Next, load a XLS or XLSX file using the Workbook class.
- Python
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data.xlsx")3. Access a Worksheet:
After loading the file, access a specific worksheet by index. In Spire.XLS for Python, worksheet indexing is zero-based.
- Python
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]4. Read Cell Data:
Now, read data from a specific cell in the worksheet.
- Python
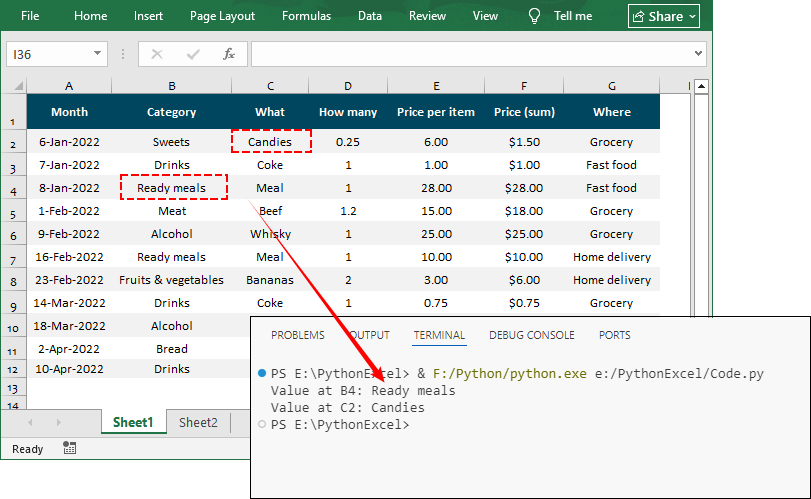
# Read cell B4
cell_value = sheet.Range["B4"].Value
print(f"Value at B4: {cell_value}")
# Using row/column indices # (row 2, column 3 → C2)
cell = sheet.Range[2, 3]
print(f"Value at C2: {cell.Value}")Output:
Full Example: Read Cell Range or Worksheet
Once you've mastered the above skills of reading Excel cell data, you can write Python code to read data from a cell area or a worksheet.
The following example demonstrates how to access a specified cell range or the used cell range in a worksheet, then iterate through each cell within to retrieve the cell value.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an existing Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the used range in the sheet
cellRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# or get a specified range
# cellRange = sheet.Range["A2:H5"]
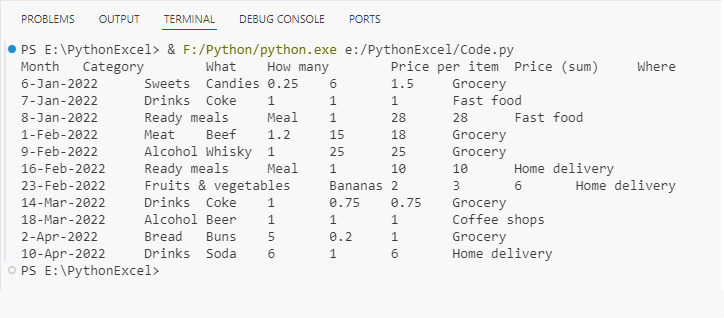
# Iterate through each cell in the range
for row in cellRange.Rows:
for cell in row.Cells:
# Retrieve cell data and print out
print(cell.Value, end="\t")
print()Output:
Advanced Python Excel Reading Techniques
Spire.XLS for Python offers advanced features for reading complex Excel files that contain formulas, images and charts.
Read Formulas & Calculated Results
Excel files often contain formulas that calculate values based on other cells. Spire.XLS for Python can read both the formula and the calculated result.
- Python
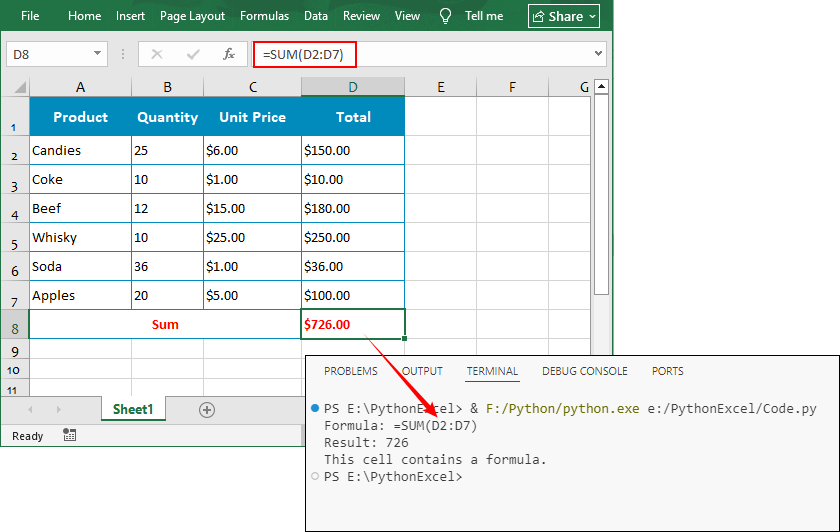
# Get a cell with a formula (e.g., "=SUM(D2:D7)")
formula_cell = sheet.Range["D8"]
print(f"Formula: {formula_cell.Formula}")
# Calculate the formula
calculated_value = formula_cell.FormulaValue
print(f"Result: {calculated_value}")
# Check if a cell contains a formula
if formula_cell.HasFormula:
print("This cell contains a formula.")Output:
Read Charts in Excel
The following Python code reads the critical chart elements and exports the chart as an image:
- Python
# Read chart title and type
for chart in sheet.Charts:
print(f"Chart Title: {chart.ChartTitle}")
print(f"Chart Type: {chart.ChartType}")
# Export chart to a PNG image
chartImage = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet, 0)
chartImage.Save("chart.png")Output:

Read Images in Excel
The following Python code reads the image location and size and extract them to the specified file path:
- Python
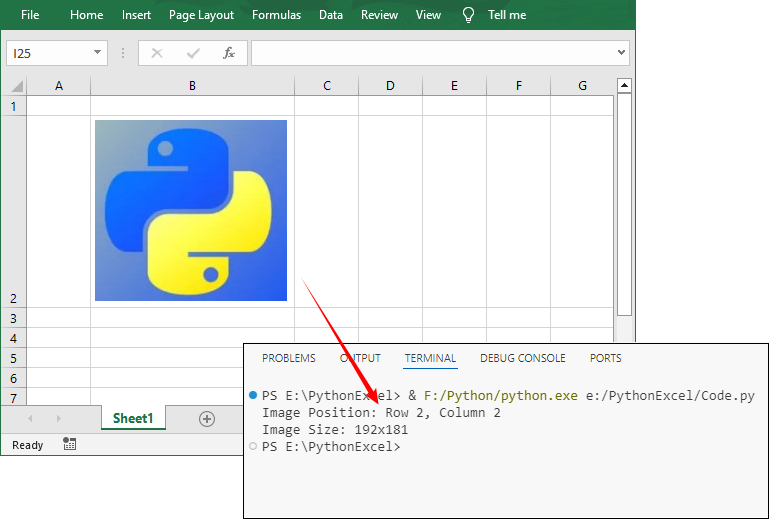
# Read image position and size
for image in sheet.Pictures:
print(f"Image Position: Row {image.TopRow}, Column {image.LeftColumn}")
print(f"Image Size: {image.Width}x{image.Height}")
# Extract image and save
image.Picture.Save(f"image_{image.TopRow}.png")Output:
How Does Spire.XLS Compare to Pandas read_excel()
Pandas and Spire.XLS for Python are both tools for working with Excel files, but their design goals and feature focuses differ:
- Pandas: A general-purpose tool for data extraction and analysis. It provides the pandas.read_excel() method to read data from Excel files into a DataFrame.
- Spire.XLS for Python: A standalone library dedicated to comprehensive Excel operations. It provides the CellRange.Value property to read Excel cell data.
Key Function Comparison
| Feature | Pandas | Spire.XLS |
| Feature | Pandas | Spire.XLS |
| Data Structure | Returns DataFrame objects | Returns custom object model (workbook/worksheet/cell) |
| Data Reading | ✅ Excellent | ✅ Excellent |
| Formatting | Limited (only data) | ✅ Full (fonts, colors, borders) |
| Formulas | Limited (Reads results only) | ✅ Reads formulas + calculations |
| Charts/Images | ❌ No | ✅ Full support |
| License | ✅ Open-source | Paid license (there’s also a Free Version) |
Pandas has no native support for non-data elements. Spire.XLS for Python, on the other hand, is optimized for complex Excel operations. Therefore, except for reading Excel data, Spire.XLS also enables:
- Read formulas, images & charts in Excel
- Retrieve Excel worksheet names
- Read document properties in Excel
- Extract comments and hyperlinks from Excel
Conclusion & Resources
Spire.XLS for Python provides an enterprise-grade solution for reading Excel files in Python without external dependencies. Its intuitive API supports everything from basic Excel data extraction to advanced formula handling, making it ideal for automation, data migration, and reporting.
Next Steps: