C++: Add Hyperlinks to Excel
Hyperlinks are a powerful tool in Excel that allows users to connect different parts of an Excel file or link to external sources such as websites, email addresses, or other files. They provide a quick and easy way for users to navigate within a worksheet or between different worksheets. In addition to facilitating navigation, hyperlinks can also provide additional context or resources related to the data in a file. For example, you can link to a website that provides more information about a specific product listed in your worksheet to help your readers gain a deeper understanding of the product. In this article, we will explore how to add hyperlinks to Excel, specifically, how to add text hyperlinks and image hyperlinks to Excel files in C++ using Spire.XLS for C++.
Install Spire.XLS for C++
There are two ways to integrate Spire.XLS for C++ into your application. One way is to install it through NuGet, and the other way is to download the package from our website and copy the libraries into your program. Installation via NuGet is simpler and more recommended. You can find more details by visiting the following link.
Integrate Spire.XLS for C++ in a C++ Application
Add Text Hyperlinks to Excel in C++
A text hyperlink in Excel is a word or phrase that you can click on to jump to a specific location, such as a different part of the Excel file, an email address, a webpage, or an external file. The following steps explain how to add a text hyperlink to an Excel file using Spire.XLS for C++:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(int index) method.
- Get the cell that you want to add a hyperlink to using the Worksheet->GetRange(LPCWSTR_S name) method.
- Add a hyperlink to the cell using the Worksheet->GetHyperLinks()->Add(intrusive_ptr<IXLSRange> range) method.
- Set the type, display text, and address for the hyperlink using the XlsHyperLink->SetType(HyperLinkType value), XlsHyperLink->SetTextToDisplay(LPCWSTR_S value) and XlsHyperLink->SetAddress(LPCWSTR_S value) methods.
- Autofit column width using the XlsWorksheet->AutoFitColumn(int columnIndex) method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook->SaveToFile(LPCWSTR_S fileName, ExcelVersion version) method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main()
{
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
intrusive_ptr<Workbook> workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
intrusive_ptr<Worksheet> sheet = dynamic_pointer_cast<Worksheet>(workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0));
//Add a text hyperlink that links to a webpage
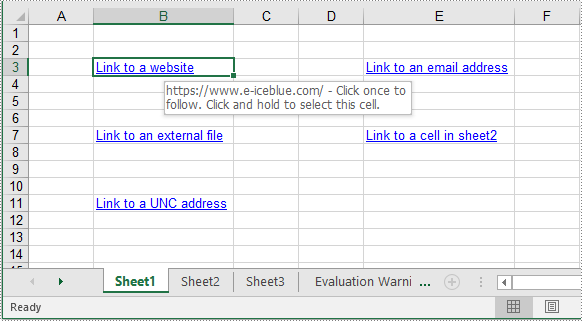
intrusive_ptr<CellRange> cell1 = dynamic_pointer_cast<CellRange>(sheet->GetRange(L"B3"));
intrusive_ptr<HyperLink> urlLink = sheet->GetHyperLinks()->Add(cell1);
urlLink->SetType(HyperLinkType::Url);
urlLink->SetTextToDisplay(L"Link to a website");
urlLink->SetAddress(L"https://www.e-iceblue.com/");
//Add a text hyperlink that links to an email address
intrusive_ptr<CellRange> cell2 = dynamic_pointer_cast<CellRange>(sheet->GetRange(L"E3"));
intrusive_ptr<HyperLink> mailLink = sheet->GetHyperLinks()->Add(cell2);
mailLink->SetType(HyperLinkType::Url);
mailLink->SetTextToDisplay(L"Link to an email address");
mailLink->SetAddress(L"mailto:support@e-iceblue.com");
//Add a text hyperlink that links to an external file
intrusive_ptr<CellRange> cell3 = dynamic_pointer_cast<CellRange>(sheet->GetRange(L"B7"));
intrusive_ptr<HyperLink> fileLink = sheet->GetHyperLinks()->Add(cell3);
fileLink->SetType(HyperLinkType::File);
fileLink->SetTextToDisplay(L"Link to an external file");
fileLink->SetAddress(L"C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Report.xlsx");
//Add a text hyperlink that links to a cell in another sheet
intrusive_ptr<CellRange> cell4 = dynamic_pointer_cast<CellRange>(sheet->GetRange(L"E7"));
intrusive_ptr<HyperLink> sheetLink = sheet->GetHyperLinks()->Add(cell4);
sheetLink->SetType(HyperLinkType::Workbook);
sheetLink->SetTextToDisplay(L"Link to a cell in sheet2");
sheetLink->SetAddress(L"Sheet2!B5");
//Add a text hyperlink that links to a UNC address
intrusive_ptr<CellRange> cell5 = dynamic_pointer_cast<CellRange>(sheet->GetRange(L"B11"));
intrusive_ptr<HyperLink> uncLink = sheet->GetHyperLinks()->Add(cell5);
uncLink->SetType(HyperLinkType::Unc);
uncLink->SetTextToDisplay(L"Link to a UNC address");
uncLink->SetAddress(L"\\192.168.0.121");
//Autofit column widths
sheet->AutoFitColumn(2);
sheet->AutoFitColumn(5);
//Save the result file
workbook->SaveToFile(L"AddTextHyperlinks.xlsx", ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
Add Image Hyperlinks to Excel in C++
Similar to a text hyperlink, an image hyperlink is an image that you can click on to navigate to a specific location. The following steps explain how to add an image hyperlink to an Excel file using Spire.XLS for C++:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(int index) method.
- Add text to a specific cell using the Worksheetsheet->GetRange(LPCWSTR_S name)->SetText(LPCWSTR_S value) method.
- Add an image to a specific cell using the Worksheet->GetPictures()->Add(int topRow,int leftColumn, LPCWSTR_S fileName) method.
- Set image width and height.
- Add a hyperlink to the image using the XlsBitmapShape->SetHyperLink(LPCWSTR_S linkString, bool isExternal) method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook->SaveToFile(LPCWSTR_S fileName, ExcelVersion version) method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main()
{
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
intrusive_ptr<Workbook> workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
intrusive_ptr<Worksheet> sheet = dynamic_pointer_cast<Worksheet>(workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0));
//Add text to a specific cell
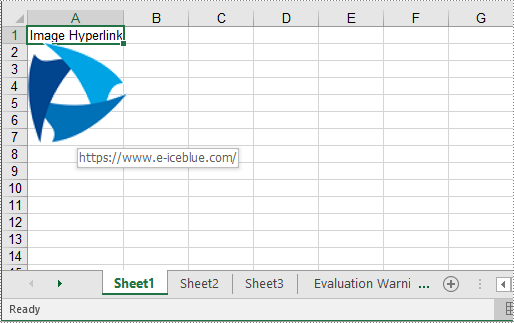
sheet->GetRange(L"A1")->SetText(L"Image Hyperlink");
//Add an image to a specific cell
intrusive_ptr<ExcelPicture> picture = ExcelPicture::Dynamic_cast<ExcelPicture>(sheet->GetPictures()->Add(2, 1, L"Logo.png"));
//Set image width and height
picture->SetWidth(100);
picture->SetHeight(100);
//Add a hyperlink to the image
picture->SetHyperLink(L"https://www.e-iceblue.com", true);
//Set column width
sheet->GetColumns()->GetItem(0)->SetColumnWidth(13);
//Save the result file
workbook->SaveToFile(L"AddImageHyperlink.xlsx", ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C++: Insert or Read Formulas and Functions in Excel
Formulas and functions are fundamental features of Microsoft Excel that allow users to perform a variety of mathematical, statistical, and logical operations on data. Formulas are expressions that can be entered into cells to automate calculations, usually consisting of cell references, constants, and operators that specify the calculation to be performed. Functions, on the other hand, are pre-built formulas that perform specific tasks, such as calculating the sum, average, maximum, or minimum value of a range of cells. Both formulas and functions are essential tools for anyone working with data in Excel. Whether you are analyzing financial data, experimental data, or any other dataset, using formulas and functions can help you quickly and accurately perform calculations on your data and gain insights from it. In this article, you will learn how to insert or Read formulas and functions in an Excel file in C++ using Spire.XLS for C++.
Install Spire.XLS for C++
There are two ways to integrate Spire.XLS for C++ into your application. One way is to install it through NuGet, and the other way is to download the package from our website and copy the libraries into your program. Installation via NuGet is simpler and more recommended. You can find more details by visiting the following link.
Integrate Spire.XLS for C++ in a C++ Application
Insert Formulas and Functions into Excel in C++
The Worksheet->GetRange(int row, int column)->SetFormula(LPCWSTR_S value) method in Spire.XLS for C++ is used to add formulas or functions to specific cells in an Excel worksheet. The main steps are as follows:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(int index) method.
- Add some text and numeric data to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet->GetRange(int row, int column)->SetText(LPCWSTR_S value) and Worksheet->GetRange(int row, int column)->SetNumberValue(double value) methods.
- Add text and formulas to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet->GetRange(int row, int column)->SetText(LPCWSTR_S value) and the Worksheet->GetRange(int row, int column)->SetFormula(LPCWSTR_S value) methods.
- Add text and functions to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet->GetRange(int row, int column)->SetText(LPCWSTR_S value) and the Worksheet->GetRange(int row, int column)->SetFormula(LPCWSTR_S value) methods.
- Save the result file using Workbook->SaveToFile(LPCWSTR_S fileName, ExcelVersion version) method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Declare two variables: currentRow, currentFormula
int currentRow = 1;
wstring currentFormula = L"";
//Add text to the worksheet and set cell style
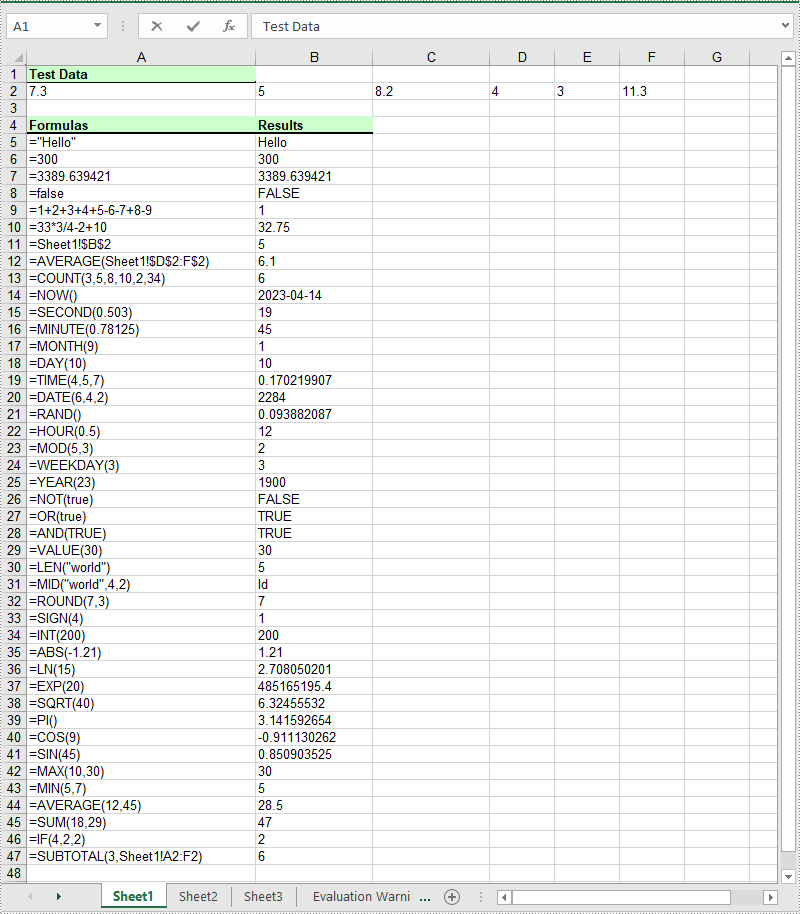
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText(L"Test Data:");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->GetStyle()->GetFont()->SetIsBold(true);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->GetStyle()->SetFillPattern(ExcelPatternType::Solid);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->GetStyle()->SetKnownColor(ExcelColors::LightGreen1);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->GetStyle()->GetBorders()->Get(BordersLineType::EdgeBottom)->SetLineStyle(LineStyleType::Medium);
//Add some numeric data to the worksheet
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetNumberValue(7.3);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetNumberValue(5);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 3)->SetNumberValue(8.2);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 4)->SetNumberValue(4);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 5)->SetNumberValue(3);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 6)->SetNumberValue(11.3);
currentRow++;
//Add text to the worksheet and set cell style
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText(L"Formulas");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetText(L"Results");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2)->GetStyle()->GetFont()->SetIsBold(true);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2)->GetStyle()->SetKnownColor(ExcelColors::LightGreen1);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2)->GetStyle()->SetFillPattern(ExcelPatternType::Solid);
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2)->GetStyle()->GetBorders()->Get(BordersLineType::EdgeBottom)->SetLineStyle(LineStyleType::Medium);
//Add text and formulas to the worksheet
currentFormula = (L"=\"Hello\"");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
currentFormula = (L"=300");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
currentFormula = (L"=3389.639421");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
currentFormula = (L"=false");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
currentFormula = (L"=1+2+3+4+5-6-7+8-9");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
currentFormula = (L"=33*3/4-2+10");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
currentFormula = (L"=Sheet1!$B$2");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//Add text and Functions to the worksheet
//AVERAGE
currentFormula = (L"=AVERAGE(Sheet1!$D$2:F$2)");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//COUNT
currentFormula = (L"=COUNT(3,5,8,10,2,34)");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//NOW
currentFormula = (L"=NOW()");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 2)->GetStyle()->SetNumberFormat(L"yyyy-MM-DD");
//SECOND
currentFormula = (L"=SECOND(0.503)");
sheet->GetRange(++currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//MINUTE
currentFormula = (L"=MINUTE(0.78125)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//MONTH
currentFormula = (L"=MONTH(9)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//DAY
currentFormula = (L"=DAY(10)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//TIME
currentFormula = (L"=TIME(4,5,7)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//DATE
currentFormula = (L"=DATE(6,4,2)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//RAND
currentFormula = (L"=RAND()");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//HOUR
currentFormula = (L"=HOUR(0.5)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//MOD
currentFormula = (L"=MOD(5,3)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//WEEKDAY
currentFormula = (L"=WEEKDAY(3)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//YEAR
currentFormula = (L"=YEAR(23)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//NOT
currentFormula = (L"=NOT(true)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//OR
currentFormula = (L"=OR(true)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//AND
currentFormula = (L"=AND(TRUE)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//VALUE
currentFormula = (L"=VALUE(30)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//LEN
currentFormula = (L"=LEN(\"world\")");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//MID
currentFormula = (L"=MID(\"world\",4,2)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//ROUND
currentFormula = (L"=ROUND(7,3)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//SIGN
currentFormula = (L"=SIGN(4)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//INT
currentFormula = (L"=INT(200)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//ABS
currentFormula = (L"=ABS(-1.21)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//LN
currentFormula = (L"=LN(15)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//EXP
currentFormula = (L"=EXP(20)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//SQRT
currentFormula = (L"=SQRT(40)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//PI
currentFormula = (L"=PI()");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//COS
currentFormula = (L"=COS(9)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//SIN
currentFormula = (L"=SIN(45)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//MAX
currentFormula = (L"=MAX(10,30)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//MIN
currentFormula = (L"=MIN(5,7)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//AVERAGE
currentFormula = (L"=AVERAGE(12,45)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//SUM
currentFormula = (L"=SUM(18,29)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//IF
currentFormula = (L"=IF(4,2,2)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//SUBTOTAL
currentFormula = (L"=SUBTOTAL(3,Sheet1!A2:F2)");
sheet->GetRange(currentRow, 1)->SetText((L"'" + currentFormula).c_str());
sheet->GetRange(currentRow++, 2)->SetFormula(currentFormula.c_str());
//Set width of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd columns
sheet->SetColumnWidth(1, 32);
sheet->SetColumnWidth(2, 16);
sheet->SetColumnWidth(3, 16);
//Create a cell style
CellStyle* style = workbook->GetStyles()->Add(L"Style");
//Set the horizontal alignment as left
style->SetHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType::Left);
//Apply the style to the worksheet
sheet->ApplyStyle(style);
//Save the result file
workbook->SaveToFile(L"InsertFormulasAndFunctions.xlsx", ExcelVersion::Version2016);
workbook->Dispose();
delete workbook;
}
Read Formulas and Functions in Excel in C++
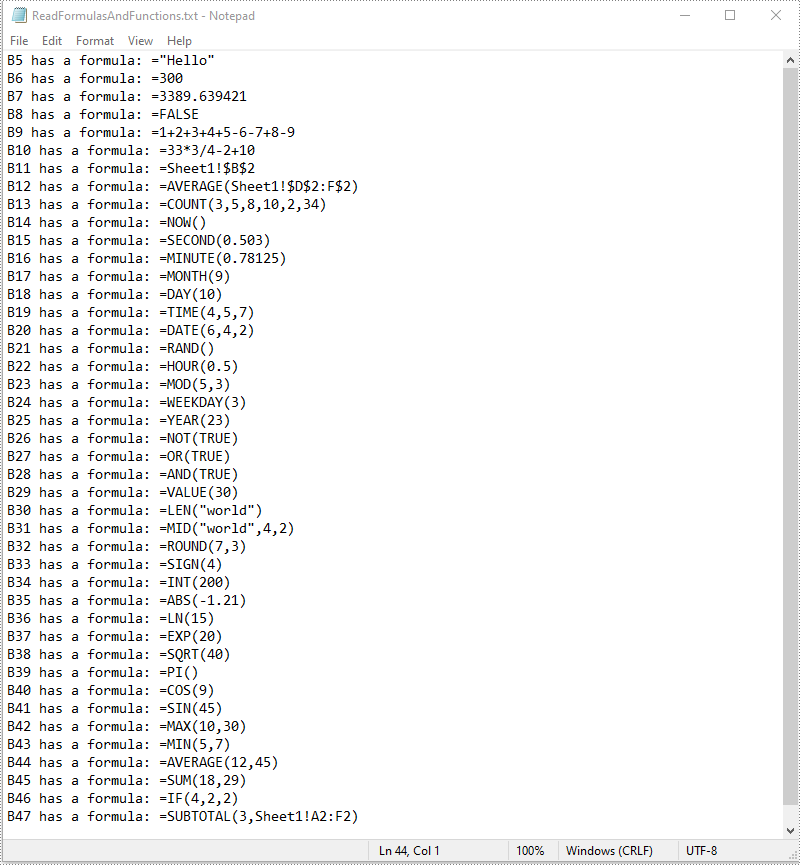
To read formulas and functions in an Excel worksheet, you need to iterate through all the cells in the worksheet, after that, find the cells containing formulas or functions using the Cell->GetHasFormula() method, then get the formulas or functions of the cells using the CellRange->GetFormula() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(int index) method.
- Access the used range of the worksheet using the Worksheet->GetAllocatedRange() method.
- Declare a wstring variable.
- Iterate through all the cells in the used range.
- Find the cells containing formulas/functions using the Cell->GetHasFormula() method.
- Get the names and the formulas/functions of the cells using the CellRange->GetRangeAddressLocal() and CellRange->GetFormula() methods.
- Append the cell names and formulas/functions to the wstring variable.
- Write the content of the wstring variable into a .txt file.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
#include <locale>
#include <codecvt>
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook->LoadFromFile(L"InsertFormulasAndFunctions.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Access the used range of the worksheet
CellRange* usedRange = sheet->GetAllocatedRange();
//Declare a wstring variable
wstring buffer = L"";
//Loop through all the cells in the used range
for(int i = 0; i < usedRange->GetCells()->GetCount(); i++)
{
CellRange* cell = usedRange->GetCells()->GetItem(i);
//Detect if the current cell has formula/function
if (cell->GetHasFormula())
{
//Get the cell name
wstring cellName = cell->GetRangeAddressLocal();
//Get the formula/function
wstring formula = cell->GetFormula();
//Append the cell name and formula/function to the wstring variable
buffer += ((cellName + L" has a formula: " + formula + L"\n").c_str());
}
}
//Write the content of the wstring variable into a .txt file
wofstream write(L"ReadFormulasAndFunctions.txt");
auto LocUtf8 = locale(locale(""), new std::codecvt_utf8<wchar_t>);
write.imbue(LocUtf8);
write << buffer;
write.close();
workbook->Dispose();
delete workbook;
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C++: Create a Pie Chart or a Doughnut Chart in Excel
Pie charts and donut charts are two similar types of charts used to show a percentage breakdown of data. Both charts are visually simple and provide an instant understanding of the part-to-whole relationship. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create a pie chart or a doughnut chart in Excel using Spire.XLS for C++.
Install Spire.XLS for C++
There are two ways to integrate Spire.XLS for C++ into your application. One way is to install it through NuGet, and the other way is to download the package from our website and copy the libraries into your program. Installation via NuGet is simpler and more recommended. You can find more details by visiting the following link.
Integrate Spire.XLS for C++ in a C++ Application
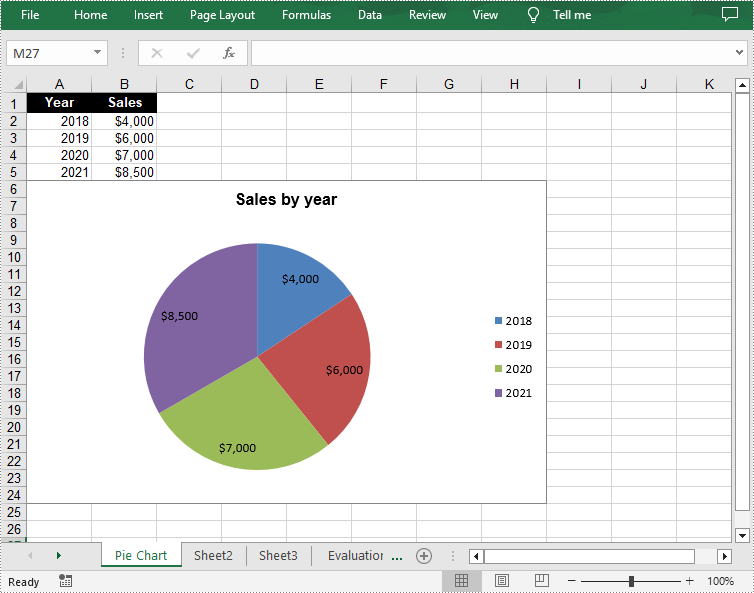
Create a Pie Chart in Excel in C++
A pie chart is a circular graph divided into several sectors. To add a pie chart in a worksheet, you can use the Worksheet->GetCharts()->Add(ExcelChartType::Pie) method provided by Spire.XLS for C++. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get() method.
- Add a pie chart to the worksheet using Worksheet->GetCharts()->Add(ExcelChartType::Pie) method.
- Add some data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart->SetDataRange() method.
- Set the position and title of the chart.
- Get a specified series in the chart and set category labels and values for the series using ChartSerie->SetCategoryLabels() and ChartSerie->SetValues() methods.
- Show data labels for data points.
- Save the result file using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main() {
//Specify the output file path
std::wstring outputFile = L"Output\\PieChart.xlsx";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet and set sheet name
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
sheet->SetName(L"Pie Chart");
//Add a pie chart to the worksheet
Chart* chart = nullptr;
chart = sheet->GetCharts()->Add(ExcelChartType::Pie);
//Set chart data
sheet->GetRange(L"A1")->SetValue(L"Year");
sheet->GetRange(L"A2")->SetValue(L"2018");
sheet->GetRange(L"A3")->SetValue(L"2019");
sheet->GetRange(L"A4")->SetValue(L"2020");
sheet->GetRange(L"A5")->SetValue(L"2021");
sheet->GetRange(L"B1")->SetValue(L"Sales");
sheet->GetRange(L"B2")->SetNumberValue(4000);
sheet->GetRange(L"B3")->SetNumberValue(6000);
sheet->GetRange(L"B4")->SetNumberValue(7000);
sheet->GetRange(L"B5")->SetNumberValue(8500);
//Set cell styles
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->SetRowHeight(15);
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->GetStyle()->SetColor(Spire::Common::Color::GetBlack());
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->GetStyle()->GetFont()->SetColor(Spire::Common::Color::GetWhite());
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->GetStyle()->SetVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType::Center);
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->GetStyle()->SetHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType::Center);
//Set number format
sheet->GetRange(L"B2:C5")->GetStyle()->SetNumberFormat(L"\"$\"#,##0");
//Set data range for the chart
chart->SetDataRange(sheet->GetRange(L"B2:B5"));
chart->SetSeriesDataFromRange(false);
//Set position of the chart
chart->SetLeftColumn(1);
chart->SetTopRow(6);
chart->SetRightColumn(9);
chart->SetBottomRow(25);
//Set and format chart title
chart->SetChartTitle(L"Sales by year");
chart->GetChartTitleArea()->SetIsBold(true);
chart->GetChartTitleArea()->SetSize(12);
//Get a specified series in the chart
ChartSerie* cs = chart->GetSeries()->Get(0);
//Set category labels for the series
cs->SetCategoryLabels(sheet->GetRange(L"A2:A5"));
//Set values for the series
cs->SetValues(sheet->GetRange(L"B2:B5"));
//Show data labels for data points
cs->GetDataPoints()->GetDefaultDataPoint()->GetDataLabels()->SetHasValue(true);
//Save the result file
workbook->SaveToFile(outputFile.c_str(), ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
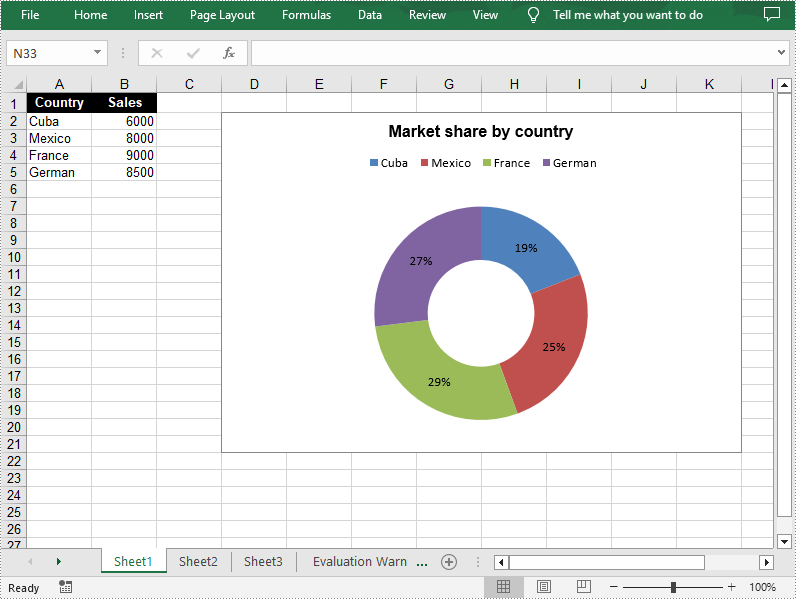
Create a Doughnut Chart in Excel in C++
The doughnut chart is a variant of the pie chart. It has a hole in the center which allows additional information to be displayed. The following are the steps to add a donut chart in an Excel worksheet.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get() method.
- Add some data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a chart to the worksheet using Worksheet->GetCharts()->Add() method and then set its type as doughnut chart using Chart->SetChartType(ExcelChartType::Doughnut) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart->SetDataRange() method.
- Set the position and title of the chart.
- Show data labels for data points.
- Set the legend position of the chart using Chart->GetLegend()->SetPosition() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main() {
//Specify the output file path
std::wstring outputFile = L"Output\\DoughnutChart.xlsx";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Insert data to specified cells
sheet->GetRange(L"A1")->SetValue(L"Country");
sheet->GetRange(L"A2")->SetValue(L"Cuba");
sheet->GetRange(L"A3")->SetValue(L"Mexico");
sheet->GetRange(L"A4")->SetValue(L"France");
sheet->GetRange(L"A5")->SetValue(L"German");
sheet->GetRange(L"B1")->SetValue(L"Sales");
sheet->GetRange(L"B2")->SetNumberValue(6000);
sheet->GetRange(L"B3")->SetNumberValue(8000);
sheet->GetRange(L"B4")->SetNumberValue(9000);
sheet->GetRange(L"B5")->SetNumberValue(8500);
//Set cell styles
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->SetRowHeight(15);
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->GetStyle()->SetColor(Spire::Common::Color::GetBlack());
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->GetStyle()->GetFont()->SetColor(Spire::Common::Color::GetWhite());
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->GetStyle()->GetFont()->SetIsBold(true);
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->GetStyle()->SetVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType::Center);
sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B1")->GetStyle()->SetHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType::Center);
//Add a doughnut chart to the worksheet
Chart* chart = sheet->GetCharts()->Add();
chart->SetChartType(ExcelChartType::Doughnut);
//Set data range for chart
chart->SetDataRange(sheet->GetRange(L"A1:B5"));
chart->SetSeriesDataFromRange(false);
//Set position of the chart
chart->SetLeftColumn(4);
chart->SetTopRow(2);
chart->SetRightColumn(12);
chart->SetBottomRow(22);
//Chart title
chart->SetChartTitle(L"Market share by country");
chart->GetChartTitleArea()->SetIsBold(true);
chart->GetChartTitleArea()->SetSize(12);
//Show data labels for data points
for (int i = 0; i < chart->GetSeries()->GetCount(); i++)
{
ChartSerie* cs = chart->GetSeries()->Get(i);
cs->GetDataPoints()->GetDefaultDataPoint()->GetDataLabels()->SetHasPercentage(true);
}
//Set the legend position of the chart
chart->GetLegend()->SetPosition(LegendPositionType::Top);
//Save the result file
workbook->SaveToFile(outputFile.c_str(), ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
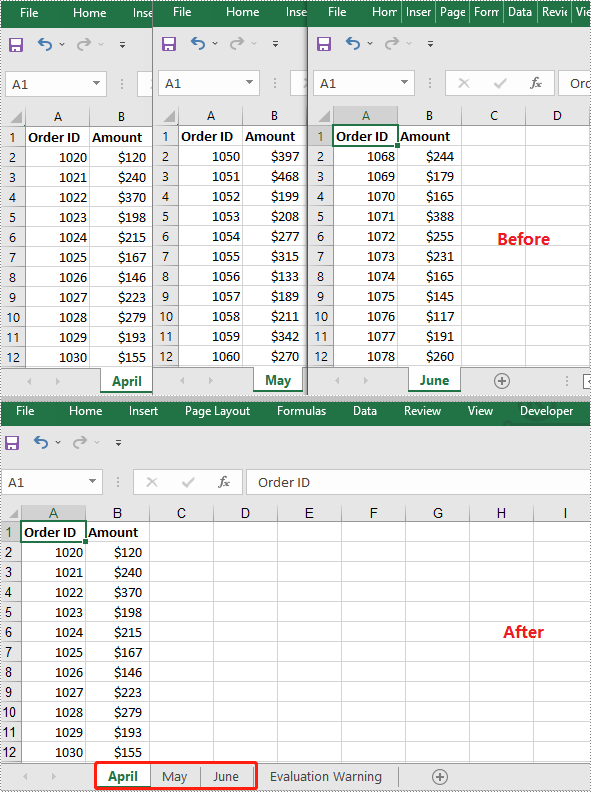
C++: Merge Excel files into One
Merging Excel files is an essential task when you need to summarize data stored in multiple Excel files. For instance, if you have sales reports for each quarter of the year, you might need to merge them into one file to get a more comprehensive view of the data for the entire year. By merging Excel files, you are able to concentrate on a single organized workbook instead of switching between multiple files. This streamlines your work process and improves efficiency. In this article, you will learn how to merge Excel files into one in C++ using Spire.XLS for C++ library.
Install Spire.XLS for C++
There are two ways to integrate Spire.XLS for C++ into your application. One way is to install it through NuGet, and the other way is to download the package from our website and copy the libraries into your program. Installation via NuGet is simpler and more recommended. You can find more details by visiting the following link.
Integrate Spire.XLS for C++ in a C++ Application
Merge Multiple Excel Workbooks into One in C++
You can merge multiple Excel workbooks into one by creating a new workbook, then copying worksheets in the original workbooks to the new workbook. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Put the paths of the original workbooks into a vector.
- Initialize a Workbook object to create a new workbook and clear the default worksheets in it.
- Initialize a temporary Workbook object.
- Iterate through the workbooks in the vector.
- Load the workbook into the temporary Workbook object using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the worksheets in the workbook, then copy each worksheet from the workbook to the new workbook using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->AddCopy() method.
- Save the result workbook to file using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Put the paths of the workbooks into a vector
std::vector<std::wstring> files = { L"File1.xlsx", L"File2.xlsx", L"File3.xlsx" };;
//Initialize a Workbook object to create a new workbook
Workbook* newWorkbook = new Workbook();
newWorkbook->SetVersion(ExcelVersion::Version2013);
//Clear the default worksheets
newWorkbook->GetWorksheets()->Clear();
//Initialize a temporary Workbook object
Workbook* tempWorkbook = new Workbook();
//Iterate through the workbooks in the vector
for (auto file : files)
{
//Load the current workbook
tempWorkbook->LoadFromFile(file.c_str());
//Iterate through all worksheets in the workbook
for (int i = 0; i < tempWorkbook->GetWorksheets()->GetCount(); i++)
{
Worksheet* sheet = tempWorkbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(i);
//Copy each worksheet from the workbook to the new workbook
(dynamic_cast<XlsWorksheetsCollection*>(newWorkbook->GetWorksheets()))->AddCopy(sheet, WorksheetCopyType::CopyAll);
}
}
//Save the result workbook to file
newWorkbook->SaveToFile(L"MergeExcelFiles.xlsx", ExcelVersion::Version2013);
newWorkbook->Dispose();
tempWorkbook->Dispose();
delete newWorkbook;
delete tempWorkbook;
}
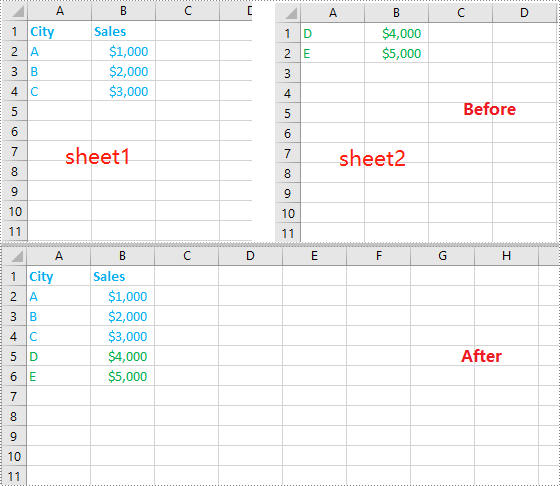
Merge Multiple Excel Worksheets into One in C++
You can merge multiple worksheets into one worksheet by copying the used data range in the original worksheets to the destination worksheet. The following steps show you how to merge two worksheets within the same workbook into one worksheet:
- Initialize a Workbook object and load an Excel workbook using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the two worksheets that need to be merged using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(int index) method (the sheet index here is zero-based).
- Get the used range of the second worksheet using Worksheet->GetAllocatedRange() method.
- Specify the destination range in the first worksheet using Worksheet->GetRange(int row, int column) method (the row and column indexes here are 1-based).
- Copy the used range of the second worksheet to the destination range in the first worksheet using CellRange->Copy(CellRange destRange) method.
- Remove the second worksheet from the workbook using XlsWorksheet->Remove() method.
- Save the result workbook to file using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Initialize a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel workbook
workbook->LoadFromFile(L"Sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet1 = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Get the second worksheet
Worksheet* sheet2 = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(1);
//Get the used range in the second worksheet
CellRange* sourceRange = sheet2->GetAllocatedRange();
//Specify the destination range in the first worksheet
CellRange* destRange = sheet1->GetRange(sheet1->GetLastRow() + 1, 1);
//Copy the used range of the second worksheet to the destination range in the first worksheet
sourceRange->Copy(destRange);
//Remove the second worksheet
sheet2->Remove();
//Save the result workbook to file
workbook->SaveToFile(L"MergeExcelWorksheets.xlsx", ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
delete workbook;
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C++: Protect or Unprotect Excel Documents
When an Excel document contains some sensitive financial or confidential data, it is essential to protect it during transmission. In MS Excel, you can encrypt an entire workbook with a password to prevent unauthorized access, or just lock selected Excel sheets or individual cells to avoid unwanted modifications. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically protect and unprotect a workbook or a worksheet using Spire.XLS for C++.
- Password Protect an Entire Workbook in C++
- Protect a Worksheet with a Specific Protection Type in C++
- Allow Users to Edit Ranges in a Protected Worksheet in C++
- Lock Specific Cells in a Worksheet in C++
- Unprotect a Password Protected Worksheet in C++
- Remove or Reset Password of an Encrypted Workbook in C++
Install Spire.XLS for C++
There are two ways to integrate Spire.XLS for C++ into your application. One way is to install it through NuGet, and the other way is to download the package from our website and copy the libraries into your program. Installation via NuGet is simpler and more recommended. You can find more details by visiting the following link.
Integrate Spire.XLS for C++ in a C++ Application
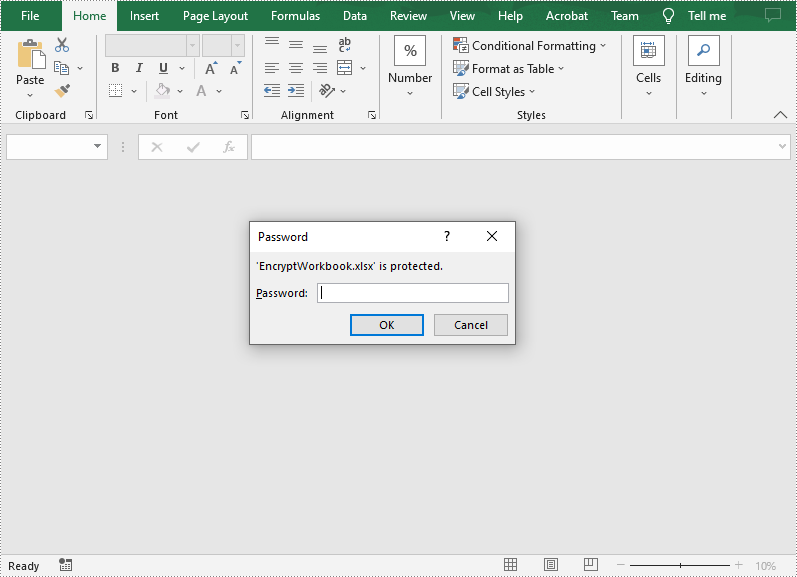
Password Protect an Entire Workbook in C++
By encrypting an Excel document with a password, you ensure that only you and authorized individuals can read or edit it. The following are the steps to password protect a workbook.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Protect the Excel workbook with a password using Workbook->Protect() method.
- Save the result document using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main() {
//Specify the input and output file paths
std::wstring inputFile = L"Data\\Budget.xlsx";
std::wstring outputFile = L"Output\\EncryptWorkbook.xlsx";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document from disk
workbook->LoadFromFile(inputFile.c_str());
//Protect workbook with a password
workbook->Protect(L"e-iceblue");
//Save the result document
workbook->SaveToFile(outputFile.c_str(), ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
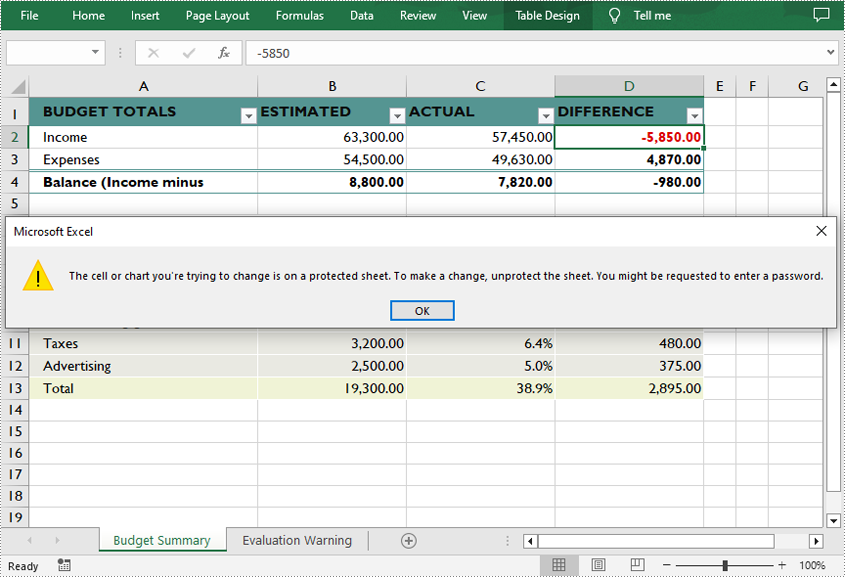
Protect a Worksheet with a Specific Protection Type in C++
If you wish to grant people permission to read your Excel document but restrict the types of modifications they are allowed to make on a worksheet, you can protect the worksheet with a specific protection type. The table below lists a variety of pre-defined protection types under the SheetProtectionType enumeration.
| Protection Type | Allow users to |
| Content | Modify or insert content. |
| DeletingColumns | Delete columns. |
| DeletingRows | Delete rows. |
| Filtering | Set filters. |
| FormattingCells | Format cells. |
| FormattingColumns | Format columns. |
| FormattingRows | Format rows. |
| InsertingColumns | Insert columns. |
| InsertingRows | Insert rows. |
| InsertingHyperlinks | Insert hyperlinks. |
| LockedCells | Select locked cells. |
| UnlockedCells | Select unlocked cells. |
| Objects | Modify drawing objects. |
| Scenarios | Modify saved scenarios. |
| Sorting | Sort data. |
| UsingPivotTables | Use pivot table and pivot chart. |
| All | Do any operations listed above on the protected worksheet. |
| None | Do nothing on the protected worksheet. |
The following are the steps to protect a worksheet with a specific protection type.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get() method.
- Protect the worksheet with a protection type using Worksheet->XlsWorksheetBase::Protect (LPCWSTR_S password, SheetProtectionType options) method.
- Save the result document using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main() {
//Specify the input and output file paths
std::wstring inputFile = L"Data\\Budget.xlsx";
std::wstring outputFile = L"Output\\ProtectWorksheet.xlsx";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document from disk
workbook->LoadFromFile(inputFile.c_str());
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Protect the worksheet with the permission password and the specific protect type
sheet->XlsWorksheetBase::Protect(L"e-iceblue", SheetProtectionType::None);
//Save the result document
workbook->SaveToFile(outputFile.c_str(), ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
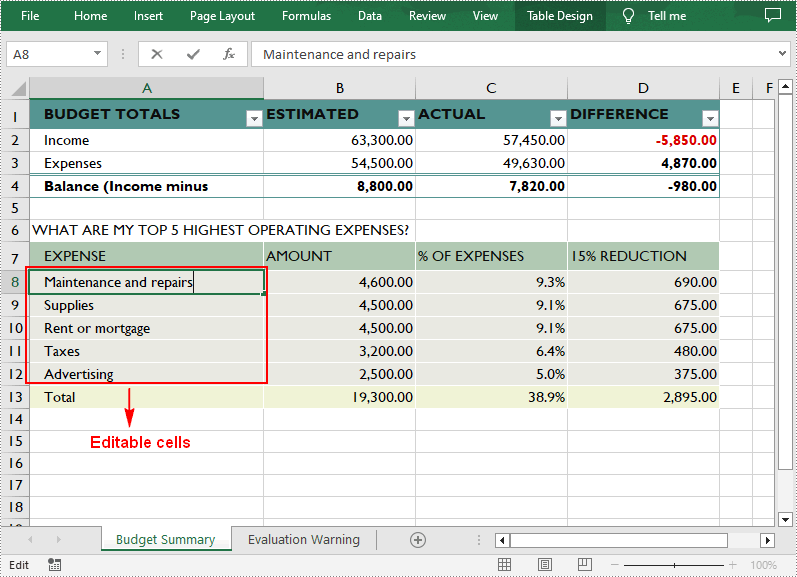
Allow Users to Edit Ranges in a Protected Worksheet in C++
In certain cases, you may need to allow users to be able to edit selected ranges in a protected worksheet. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get() method.
- Specify the editable cell ranges using Worksheet->AddAllowEditRange() method.
- Protect the worksheet with a password using Worksheet->XlsWorksheetBase::Protect() method.
- Save the result document using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main() {
//Specify the input and output file paths
std::wstring inputFile = L"Data\\Budget.xlsx";
std::wstring outputFile = L"Output\\AllowEditRange.xlsx";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document from disk
workbook->LoadFromFile(inputFile.c_str());
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Define a range that allow users to edit while sheet is protected
sheet->AddAllowEditRange(L"EditableRange", sheet->GetRange(L"A8:A12"));
//Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet->XlsWorksheetBase::Protect(L"TestPassword");
//Save the result document
workbook->SaveToFile(outputFile.c_str(), ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
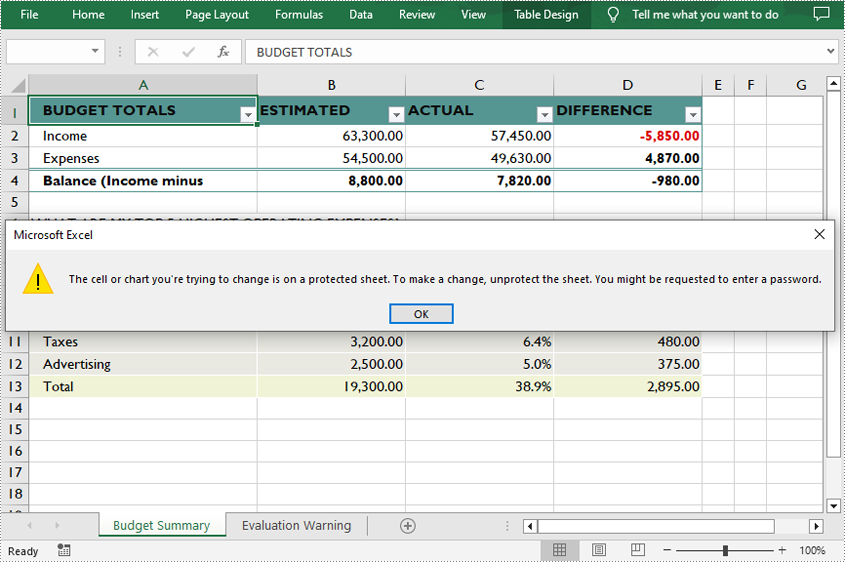
Lock Specific Cells in a Worksheet in C++
Normally, the locked option is enabled for all cells in a worksheet. Therefore, before locking a cell or range of cells, all cells must be unlocked. Keep in mind that locking cells doesn't take effect until the worksheet is protected. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get() method.
- Access the used range in the worksheet and then unlock all cells in the range.
- Access specific cells and then lock them by setting the parameter of XlsRange->GetStyle()->SetLocked() method to true.
- Protect the worksheet using Worksheet->XlsWorksheetBase::Protect() method.
- Save the result document using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main() {
//Specify the input and output file paths
std::wstring inputFile = L"Data\\Budget.xlsx";
std::wstring outputFile = L"Output\\LockCells.xlsx";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document from disk
workbook->LoadFromFile(inputFile.c_str());
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet->XlsWorksheet::GetRange()->GetStyle()->SetLocked(false);
//Lock specific cells
XlsRange* cells = sheet->GetRange(L"A1:D1");
cells->GetStyle()->SetLocked(true);
//Protect the worksheet with password
sheet->XlsWorksheetBase::Protect(L"TestPassword");
//Save the result document
workbook->SaveToFile(outputFile.c_str(), ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
Unprotect a Password Protected Worksheet in C++
To remove the protection of a password-protected worksheet, invoke the Worksheet->XlsWorksheetBase::Unprotect() method and pass in the original password as a parameter. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get() method.
- Unprotect the worksheet with the original password using Worksheet->XlsWorksheetBase::Unprotect(LPCWSTR_S password) method.
- Save the result document using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main() {
//Specify the input and output file paths
std::wstring inputFile = L"Data\\ProtectWorksheet.xlsx";
std::wstring outputFile = L"Output\\UnprotectWorksheet.xlsx";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document from disk
workbook->LoadFromFile(inputFile.c_str());
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Unprotect the worksheet using the specified password
sheet->XlsWorksheetBase::Unprotect(L"e-iceblue");
//Save the result document
workbook->SaveToFile(outputFile.c_str(), ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
Remove or Reset Password of an Encrypted Workbook in C++
To remove or reset password of an encrypted workbook, you can use the Workbook->UnProtect() method and the Workbook->Protect() method respectively. The following are the steps to load an encrypted Excel document and delete or change the password of it.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Specify the open password using Workbook->SetOpenPassword() method.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove the encryption using Workbook->UnProtect() method. Or change the password using Workbook->Protect() method.
- Save the result document using Workbook->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
int main() {
//Specify the input and output file paths
std::wstring inputFile = L"Output\\EncryptWorkbook.xlsx";
std::wstring outputFile = L"Output\\Unprotect.xlsx";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Specify the open password
workbook->SetOpenPassword(L"e-iceblue");
//Load an Excel document from disk
workbook->LoadFromFile(inputFile.c_str());
//Unprotect workbook
workbook->UnProtect();
//Reset password
//workbook->Protect(L"newpassword");
//Save the result document
workbook->SaveToFile(outputFile.c_str(), ExcelVersion::Version2013);
workbook->Dispose();
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.