Parse Excel Files in Java Easily – Read .XLS and .XLSX Files

Excel files are widely used to store and exchange structured data, such as reports, user-submitted forms, and exported records from other systems. In many Java applications, developers need to open these Excel files and extract the data for further processing.
In Java, parsing an Excel file usually means loading an .xls or .xlsx file, reading worksheets, and converting cell values into Java-friendly formats such as strings, numbers, or dates. This article shows how to parse Excel files in Java step by step using Spire.XLS for Java, with practical examples ranging from basic text reading to data type–aware parsing.
Table of Contents
- Prepare the Environment
- Load and Parse an Excel File in Java
- Read Excel Data as Text (Basic Parsing)
- Parse Excel Cells into Different Data Types
- Common Parsing Scenarios in Real Applications
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Prepare the Environment
Before parsing Excel files, you need to add Spire.XLS for Java to your project. The library supports both .xls and .xlsx formats and does not require Microsoft Excel to be installed.
Add the Dependency
If you are using Maven, add the following dependency to your pom.xml:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>16.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Once the dependency is added, you are ready to load and parse Excel files in Java.
If you are not using Maven, you can also download Spire.XLS for Java and add it to your project manually.
Load and Parse an Excel File in Java
The first step when parsing an Excel file is to load it into a Workbook object and access the worksheet you want to read.
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class ParseExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.loadFromFile("data.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
System.out.println("Worksheet loaded: " + sheet.getName());
}
}
Preview of the reading result:
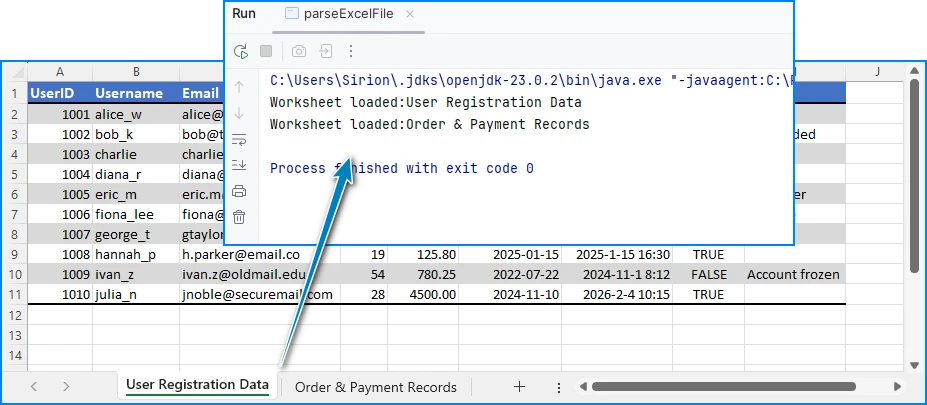
This code works for both .xls and .xlsx files. After loading the worksheet, you can start reading rows and cells.
Read Excel Data as Text (Basic Parsing)
In many cases, developers only need to read Excel data as text, without worrying about specific data types. This approach is simple and suitable for logging, displaying data, or quick imports.
Read All Cells as Strings
for (int i = 1; i <= sheet.getLastRow(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sheet.getLastColumn(); j++) {
String cellText = sheet.getCellRange(i, j).getValue();
System.out.print(cellText + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
Preview of the text reading result:
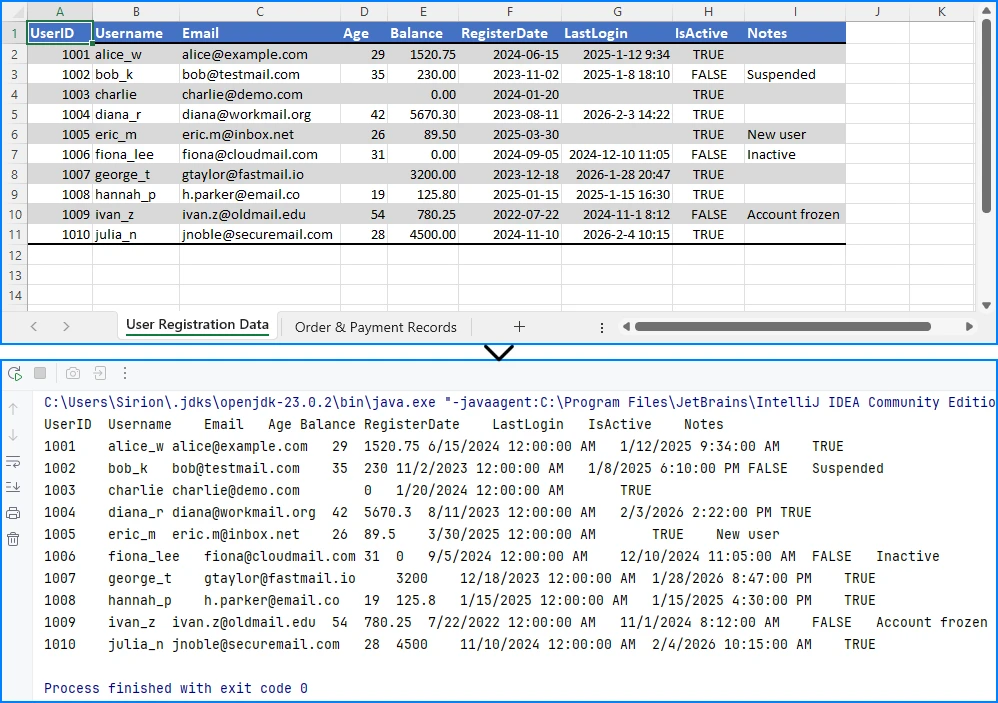
Using getValue() returns the formatted value shown in Excel. This is often the easiest way to read data when precision or data type conversion is not critical.
If your requirement goes beyond reading and involves modifying or editing Excel files, you can refer to a separate guide that demonstrates how to edit Excel documents in Java using Spire.XLS.
Parse Excel Cells into Different Data Types
For data processing, validation, or calculations, reading everything as text is usually not enough. In these cases, you need to parse Excel cell values into proper Java data types.
Parse Numeric Values (int / double / float)
In Excel, many cells are stored internally as numeric values, even if they are displayed as dates, currencies, or percentages. Spire.XLS for Java allows you to read these cells directly using getNumberValue().
CellRange usedRange = sheet.getAllocatedRange();
System.out.println("Raw number values:");
for (int i = usedRange.getRow(); i <= usedRange.getLastRow(); i++) {
for (int j = usedRange.getColumn(); j <= usedRange.getLastColumn(); j++) {
CellRange cell = sheet.getRange().get(i, j);
if (!(Double.isNaN(cell.getNumberValue())))
{
System.out.print(cell.getNumberValue() + "\t");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
Below is a preview of the numeric reading result:
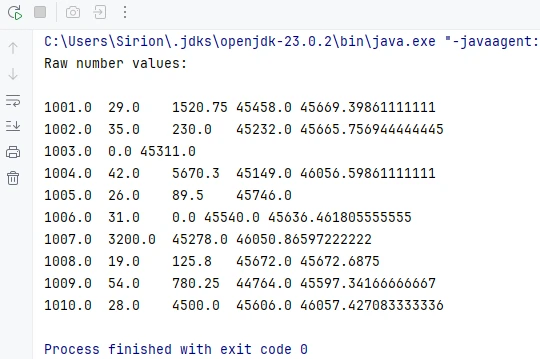
This method returns the underlying numeric value stored in the cell, regardless of the display format applied in Excel.
Convert Numeric Values Based on Application Logic
Once you have the numeric value, you can convert it to the appropriate Java type according to your application requirements.
double numberValue = cell.getNumberValue();
// Convert to int
int intValue = (int) numberValue;
// Convert to float
float floatValue = (float) numberValue;
// Keep as double
double doubleValue = numberValue;
For example, IDs, counters, or quantities are often converted to int, while prices, balances, or measurements are better handled as double or float.
Note: Excel dates are also stored as numeric values. If a cell represents a date or time, it is recommended to read it using date-related APIs instead of treating it as a plain number. This is covered in the next section.
Parse Date and Time Values
In Excel, date and time values are internally stored as numbers, while the display format determines how they appear in the worksheet. Spire.XLS for Java provides the getDateTimeValue() method to read these values directly as Date objects, allowing you to handle date and time data more conveniently in Java.
For example, if a column is designed to store date values, you can read all cells in that range as Date objects:
CellRange usedRange = sheet.getAllocatedRange();
System.out.println("Date values:");
for (int i = 0; i < usedRange.getRowCount(); i++) {
// Read values from column F (for example, a date column)
CellRange cell = usedRange.get(String.format("G%d", i + 1));
java.util.Date date = cell.getDateTimeValue();
System.out.println(date);
}
Preview of the date reading result from the seventh column:
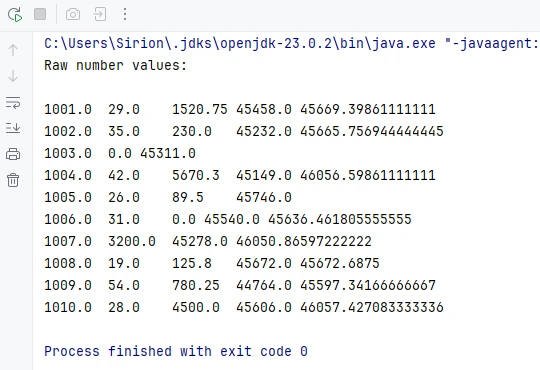
This approach is widely used in real-world applications such as reports, data imports, or spreadsheets with predefined columns.
Because Excel dates are stored as numeric values, getDateTimeValue() converts the numeric value into a Date object and is typically applied to columns that represent date or time information.
Parse Mixed Cell Values in a Practical Way
In real-world Excel files, a single column may contain different kinds of values, such as text, numbers, dates, booleans, or empty cells. When parsing such data in Java, a practical approach is to read cell values using different APIs and select the most appropriate representation based on your business logic.
CellRange cell = sheet.getRange().get(2, 1); // B2
// Formatted text (what is displayed in Excel)
String text = cell.getText();
// Raw string value
String value = cell.getValue();
// Generic underlying value (number, boolean, date, etc.)
Object rawValue = cell.getValue2();
// Formula, if the cell contains one
String formula = cell.getFormula();
// Evaluated result of the formula
String evaluated = cell.getEnvalutedValue();
// Numeric value
double numberValue = cell.getNumberValue();
// Date value (commonly used for columns representing dates or times)
java.util.Date dateValue = cell.getDateTimeValue();
// Boolean value
boolean booleanValue = cell.getBooleanValue();
In practice, many applications use getText() as a safe fallback for display, logging, or export scenarios. For data processing, methods like getNumberValue(), getDateTimeValue(), or getBooleanValue() are typically applied based on the known meaning of each column.
This flexible approach works well for user-generated or loosely structured Excel files and helps avoid incorrect assumptions while keeping the parsing logic simple and robust.
If your primary goal is reading Excel files in Java—for example, extracting cell values for display or reporting—you may also want to refer to a separate guide that focuses specifically on Excel data reading scenarios in Java.
Common Parsing Scenarios in Real Applications
Parse Excel Rows into Java Objects
A common use case is mapping each row in an Excel sheet to a Java object, such as a DTO or entity class.
For example, one row can represent a product or a record, and each column maps to a field in the object. After parsing, you can store the objects in a list for further processing or database insertion.
Read Excel Data into Collections
Another typical scenario is reading Excel data into a List<List
Read CSV Files in Java Efficiently: Step-by-Step Examples
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) remains a universal format for data exchange due to its simplicity, readability, and wide compatibility across platforms. If you're looking for a robust and efficient method to read CSV in Java, the Spire.XLS for Java library offers a powerful and straightforward solution.
This guide will walk you through how to use Java to load and read CSV files, as well as convert them into structured DataTables for seamless data manipulation and analysis in your applications.
- Why Choose Spire.XLS for Java to Parse CSV Files?
- Step-by-Step: Read a CSV File in Java
- Advanced: Read CSV into DataTable in Java
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Why Choose Spire.XLS for Java to Parse CSV Files?
Compared with other CSV parser in Java, Spire.XLS offers several advantages for CSV processing:
- Simplified API for reading CSV files
- Support for custom delimiters (not just commas)
- Built-in range detection to avoid empty rows/columns
- Natively converts CSV data to DataTable
- Seamlessly switch between CSV, XLS, and XLSX formats
Step-by-Step: Read a CSV File in Java
Spire.XLS for Java provides the Workbook class to load CSV files and the Worksheet class to access data. Below are the steps to read CSV files line by line with automatic delimiter detection:
1. Setup and Dependencies
First, ensure you have Spire.XLS for Java included in your project. You can add it via Maven by including the following dependency:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>16.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2. Load the CSV File
Spire.XLS for Java loads CSV files into a Workbook object, where each CSV row becomes a worksheet row.
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class ReadCSV {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load CSV file (specify delimiter)
workbook.loadFromFile("sample.csv", ",", 1, 1);
}
}
Parameters:
The loadFromFile() method accepts four parameters:
- "sample.csv": The input CSV file path.
- ", ": Custom delimiter (e.g."," ";" or "\t").
- 1: Start row index.
- 1: Start column index.
3. Access Worksheet & Read CSV Data
Spire.XLS treats CSV files as single-worksheet workbooks, so we access the first worksheet and then iterate through rows/columns:
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the used range (avoids iterating over empty rows/columns)
CellRange dataRange = sheet.getAllocatedRange();
//Iterate through the rows
for (int i = 0; i < dataRange.getRowCount(); i++) {
//Iterate through the columns
for (int j = 0; j < dataRange.getColumnCount(); j++) {
// Get cell text
CellRange cell = dataRange.get(i+1,j+1);
System.out.print(cell.getText() + "\t"); // Use tab to separate columns
}
System.out.println(); // New line per row
Output: Read data from a CSV file and print out with tab separation for readability.

Advanced: Read CSV into DataTable in Java
For structured data manipulation, converting CSV to a DataTable is invaluable. A DataTable organizes data into rows and columns, making it easy to query, filter, or integrate with databases.
Java code to read a CSV file and export to a DataTable:
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.data.table.DataTable;
public class CSVtoDataTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a workbook and load a csv file
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.loadFromFile("sample.csv", ",", 1, 1);
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Export to DataTable
DataTable dataTable = sheet.exportDataTable();
// Get row and column count
System.out.println("Total columns: " + dataTable.getColumns().size());
System.out.println("Total rows: " + dataTable.getRows().size());
System.out.println();
// Print column names
for (int i = 0; i < dataTable.getColumns().size(); i++) {
System.out.print(dataTable.getColumns().get(i).getColumnName() + " | ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------");
// Print rows
for (int i = 0; i < dataTable.getRows().size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < dataTable.getColumns().size(); j++) {
System.out.print(dataTable.getRows().get(i).getString(j) + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Key Explanations:
- exportDataTable(): convert CSV data into a DataTable directly, no manual row/column mapping required.
- DataTable Benefits: Easily access basic information such as column count, row count, column names, and row data etc.
Output:
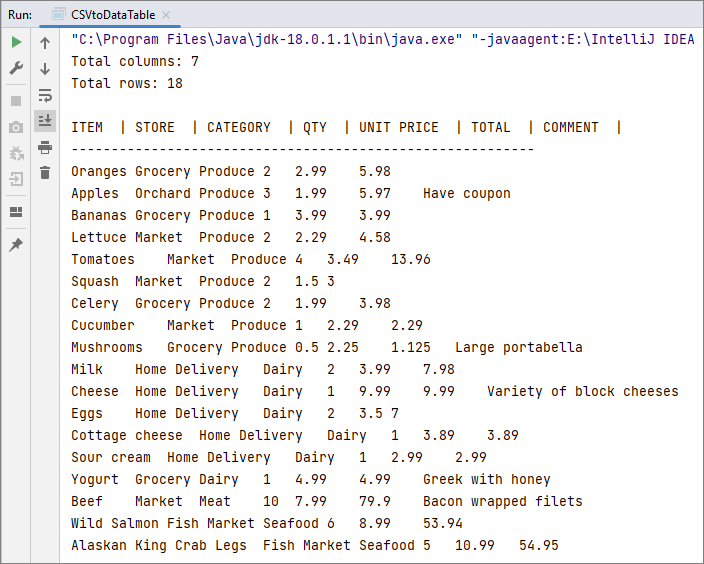
You may also read: Convert CSV to Excel in Java
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How do I handle CSV files with different delimiters (semicolon, tab, etc.)?
A: Specify the delimiter in the loadFromFile() method:
// For semicolon-delimited files
workbook.loadFromFile("sample.csv", ";", 0, 0);
// For tab-delimited files
workbook.loadFromFile("sample.csv", "\t", 0, 0);
// For pipe-delimited files
workbook.loadFromFile("sample.csv", "|", 0, 0);
Q2: How do I skip header rows in a CSV file?
A: You can skip header rows by iterating from the second row. For example, if your CSV has 2 header rows (rows 1 and 2) and data starts at row 3:
// Start reading from the third row
for (int i = 2; i < dataRange.getRowCount(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < dataRange.getColumnCount(); j++) {
// Convert 0-based loop index to Spire.XLS's 1-based cell index
CellRange cell = dataRange.get(i + 1, j + 1);
System.out.print(cell.getText() + "\t");
Q3. Can I export a specific range of a CSV to a DataTable?
A: Yes. Spire.XLS lets you define a precise cell range and export it to a DataTable with the exportDataTable(CellRange range, boolean exportColumnNames) method.
Conclusion
Spire.XLS for Java simplifies CSV file reading in Java, offering a robust alternative to manual parsing or basic libraries. Whether you need to read a simple CSV, or convert it to a structured DataTable, this guide provides the corresponding examples to help you implement CSV parsing efficiently.
For more advanced features (e.g., exporting to PDF), check the Spire.XLS for Java Documentation.
How to Read Excel Files in Java (XLS/XLSX) – Complete Guide

Reading Excel files using Java is a common requirement in enterprise applications, especially when dealing with reports, financial data, user records, or third-party integrations. Whether you're building a data import feature, performing spreadsheet analysis, or integrating Excel parsing into a web application, learning how to read Excel files in Java efficiently is essential.
In this tutorial, you’ll discover how to read .xls and .xlsx Excel files using Java. We’ll use practical Java code examples which also cover how to handle large files, read Excel files from InputStream, and extract specific content line by line.
Table of Contents
- 1. Set Up Your Java Project
- 2. How to Read XLSX and XLS Files in Java
- 3. Best Practices for Large Excel Files
- 4. Full Example: Java Program to Read Excel File
- 5. Summary
- 6. FAQ
1. Set Up Your Java Project
To read Excel files using Java, you need a library that supports spreadsheet file formats. Spire.XLS for Java offers support for both .xls (legacy) and .xlsx (modern XML-based) files and provides a high-level API that makes Excel file reading straightforward.
Add Spire.XLS to Your Project
If you're using Maven, add the following to your pom.xml:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>16.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
If you're not using Maven, you can manually download the JAR from the official Spire.XLS website and add it to your classpath.
For smaller Excel processing tasks, you can also choose Free Spire.XLS for Java.
2. How to Read XLSX and XLS Files in Java
Java programs can easily read Excel files by loading the workbook and iterating through worksheets, rows, and cells. The .xlsx format is commonly used in modern Excel, while .xls is its older binary counterpart. Fortunately, Spire.XLS supports both formats seamlessly with the same code.
Load and Read Excel File (XLSX or XLS)
Here’s a basic example that loads an Excel file and prints its content:
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class ReadExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a workbook object and load the Excel file
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.loadFromFile("data.xlsx"); // or "data.xls"
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Loop through each used row and column
for (int i = 1; i <= sheet.getLastRow(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= sheet.getLastColumn(); j++) {
// Get cell text of a cell range
String cellText = sheet.getCellRange(i, j).getValue();
System.out.print(cellText + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
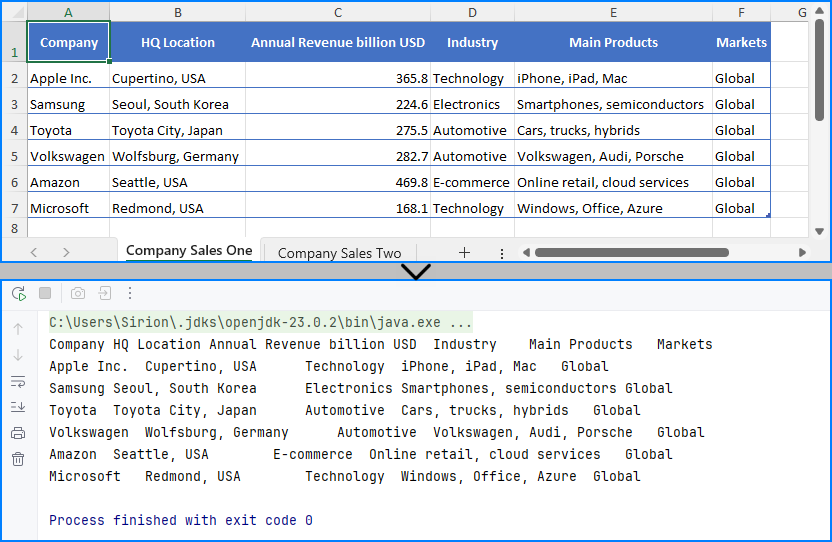
You can replace the file path with an .xls file and the code remains unchanged. This makes it simple to read Excel files using Java regardless of format.
The Excel file being read and the output result shown in the console.
Read Excel File Line by Line with Row Objects
In scenarios like user input validation or applying business rules, processing each row as a data record is often more intuitive. In such cases, you can read the Excel file line by line using row objects via the getRows() method.
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.getRows().length; i++) {
// Get a row
CellRange row = sheet.getRows()[i];
if (row != null && !row.isBlank()) {
for (int j = 0; j < row.getColumns().length; j++) {
String text = row.getColumns()[j].getText();
System.out.print((text != null ? text : "") + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
This technique works particularly well when reading Excel files in Java for batch operations or when you only need to process rows individually.
Read Excel File from InputStream
In web applications or cloud services, Excel files are often received as streams. Here’s how to read Excel files from an InputStream in Java:
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class ReadExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// Create a InputStream
InputStream stream = new FileInputStream("data.xlsx");
// Load the Excel file from the stream
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.loadFromStream(stream);
System.out.println("Load Excel file successfully.");
}
}
This is useful when handling file uploads, email attachments, or reading Excel files stored in remote storage.
Read Excel Cell Values in Different Formats
Once you load an Excel file and get access to individual cells, Spire.XLS allows you to read the contents in various formats—formatted text, raw values, formulas, and more.
Here's a breakdown of what each method does:
CellRange cell = sheet.getRange().get(2, 1); // B2
// Formatted text (what user sees in Excel)
String text = cell.getText();
// Raw string value
String value = cell.getValue();
// Generic object (number, boolean, date, etc.)
Object rawValue = cell.getValue2();
// Formula (if exists)
String formula = cell.getFormula();
// Evaluated result of the formula
String result = cell.getEnvalutedValue();
// If it's a number cell
double number = cell.getNumberValue();
// If it's a date cell
java.util.Date date = cell.getDateTimeValue();
// If it's a boolean cell
boolean bool = cell.getBooleanValue();
Tip: Use getValue2() for flexible handling, as it returns the actual underlying object. Use getText() when you want to match Excel's visible content.
You May Also Like: How to Write Data into Excel Files in Java
3. Best Practices for Reading Large Excel Files in Java
When your Excel file contains tens of thousands of rows or multiple sheets, performance can become a concern. To ensure your Java application reads large Excel files efficiently:
- Load only required sheets
- Access only relevant columns or rows
- Avoid storing entire worksheets in memory
- Use row-by-row reading patterns
Here’s an efficient pattern for reading only non-empty rows:
for (int i = 1; i <= sheet.getRows().length; i++) {
Row row = sheet.getRows()[i];
if (row != null && !row.isBlank()) {
// Process only rows with data
}
}
Even though Spire.XLS handles memory efficiently, following these practices helps scale your Java Excel reading logic smoothly.
See also: Delete Blank Rows and Columns in Excel Using Java
4. Full Example: Java Program to Read Excel File
Here’s a full working Java example that reads an Excel file (users.xlsx) with extended columns such as name, email, age, department, and status. The code extracts only the original three columns (name, email, and age) and filters the output for users aged 30 or older.
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class ExcelReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.loadFromFile("users.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
System.out.println("Name\tEmail\tAge");
for (int i = 2; i <= sheet.getLastRow(); i++) {
String name = sheet.getCellRange(i, 1).getValue();
String email = sheet.getCellRange(i, 2).getValue();
String ageText = sheet.getCellRange(i, 3).getValue();
int age = 0;
try {
age = Integer.parseInt(ageText);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
continue; // Skip rows with invalid age data
}
if (age >= 30) {
System.out.println(name + "\t" + email + "\t" + age);
}
}
}
}
Result of Java program reading the Excel file and printing its contents. 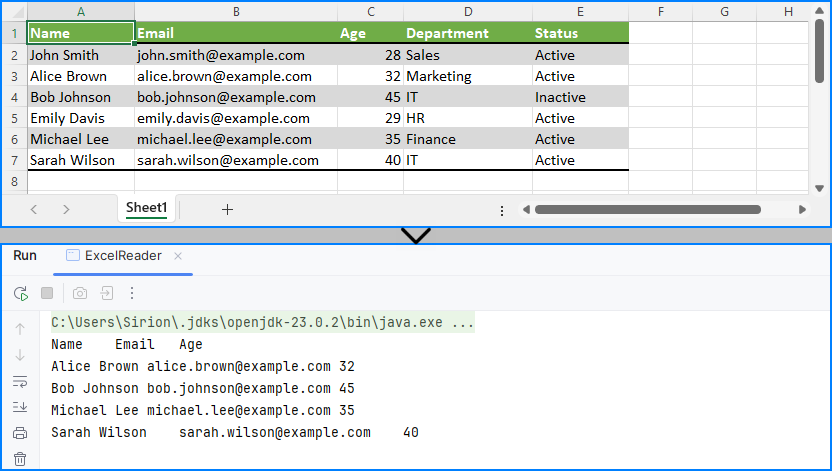
This code demonstrates how to read specific cells from an Excel file in Java and output meaningful tabular data, including applying filters on data such as age.
5. Summary
To summarize, this article showed you how to read Excel files in Java using Spire.XLS, including both .xls and .xlsx formats. You learned how to:
- Set up your Java project with Excel-reading capabilities
- Read Excel files using Java in row-by-row or stream-based fashion
- Handle legacy and modern Excel formats with the same API
- Apply best practices when working with large Excel files
Whether you're reading from an uploaded spreadsheet, a static report, or a stream-based file, the examples provided here will help you build robust Excel processing features in your Java applications.
If you want to unlock all limitations and experience the full power of Excel processing, you can apply for a free temporary license.
6. FAQ
Q1: How to read an Excel file dynamically in Java?
To read an Excel file dynamically in Java—especially when the number of rows or columns is unknown—you can use getLastRow() and getLastColumn() methods to determine the data range at runtime. This ensures that your program can adapt to various spreadsheet sizes without hardcoded limits.
Q2: How to extract data from Excel file in Java?
To extract data from Excel files in Java, load the workbook and iterate through the cells using nested loops. You can retrieve values with getCellRange(row, column).getValue(). Libraries like Spire.XLS simplify this process and support both .xls and .xlsx formats.
Q3: How to read a CSV Excel file in Java?
If your Excel data is saved as a CSV file, you can read it using Java’s BufferedReader or file streams. Alternatively, Spire.XLS supports CSV parsing directly—you can load a CSV file by specifying the separator, such as Workbook.loadFromFile("data.csv", ","). This lets you handle CSV files along with Excel formats using the same API.
Q4: How to read Excel file in Java using InputStream?
Reading Excel files from InputStream in Java is useful in server-side applications, such as handling file uploads. With Spire.XLS, simply call workbook.loadFromStream(inputStream) and process it as you would with any file-based Excel workbook.
Java: Edit Excel Documents
In today's digital age, Excel documents have become essential tools for businesses, individuals, and organizations to manage data, analyze information, and share reports. However, manually editing Excel documents is not only time-consuming but also prone to errors. Fortunately, with the Spire.XLS library in Java, you can easily automate these tasks, improving efficiency and reducing mistakes.
This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to use Spire.XLS for Java to edit Excel documents in Java, helping you master this powerful skill.
- Read and Write Excel Files in Java
- Apply Formatting to Excel Cells in Java
- Find and Replace Text in Excel in Java
- Add Formulas and Charts to Excel in Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>16.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Read and Write Excel Files in Java
One of the most common tasks when working with Excel files in Java is reading and writing data. Spire.XLS for Java simplifies this process with the CellRange.getValue() and CellRange.setValue() methods, allowing developers to easily retrieve and assign values to individual cells.
To read and write an Excel file using Java, follow these steps:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from the specified file path.
- Access a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Retrieve a specific cell using the Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Get the cell value with CellRange.getValue() and update it using CellRange.setValue().
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.CellRange;
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class ReadAndWriteExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get a specific cell
CellRange cell = worksheet.getCellRange("A1");
// Read the cell value
String text = cell.getValue();
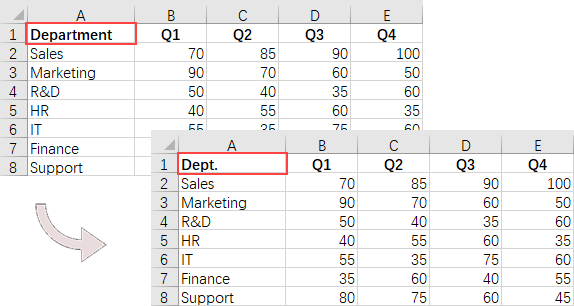
// Determine if the cell value is "Department"
if (text.equals("Department"))
{
// Update the cell value
cell.setValue ("Dept.");
}
// Save the workbook to a different
workbook.saveToFile("ModifyExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply Formatting to Excel Cells in Java
Formatting Excel documents is essential for creating professional-looking reports. Spire.XLS for Java provides a range of APIs within the CellRange class to manage font styles, colors, cell backgrounds, and alignments, as well as to adjust row heights and column widths.
To apply styles and formats to Excel cells, follow these steps:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from the specified file path.
- Access a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Retrieve the allocated range of cells using the Worksheet.getAllocatedRange() method.
- Select a specific row using CellRange.getRows()[rowIndex], and customize the cell background color, text color, text alignment, and row height using methods from the CellRange object.
- Choose a specific column with CellRange.getColumns()[columnIndex], and set the column width using the setColumnWidth() method from the CellRange object.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ApplyFormatting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get all located range from the worksheet
CellRange allocatedRange = worksheet.getAllocatedRange();
// Iterate through the rows
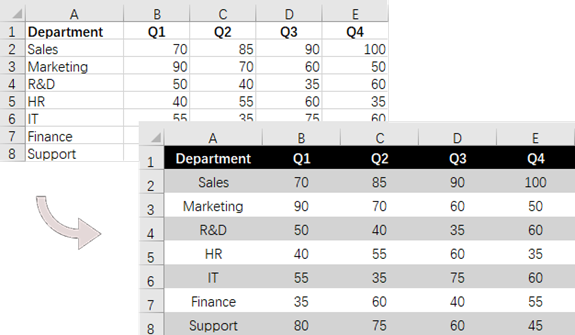
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < allocatedRange.getRowCount(); rowNum++) {
if (rowNum == 0) {
// Apply cell color to the header row
allocatedRange.getRows()[rowNum].getStyle().setColor(Color.black);
// Change the font color of the header row
allocatedRange.getRows()[rowNum].getStyle().getFont().setColor(Color.white);
}
// Apply alternate colors to other rows
else if (rowNum % 2 == 1) {
allocatedRange.getRows()[rowNum].getStyle().setColor(Color.lightGray);
} else if (rowNum % 2 == 0) {
allocatedRange.getRows()[rowNum].getStyle().setColor(Color.white);
}
// Align text to center
allocatedRange.getRows()[rowNum].setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Center);
allocatedRange.getRows()[rowNum].setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType.Center);
// Set the row height
allocatedRange.getRows()[rowNum].setRowHeight(20);
}
// Iterate through the columns
for (int columnNum = 0; columnNum < allocatedRange.getColumnCount(); columnNum++) {
// Set the column width
if (columnNum > 0) {
allocatedRange.getColumns()[columnNum].setColumnWidth(10);
}
}
// Save the workbook to a different
workbook.saveToFile("FormatExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Find and Replace Text in Excel in Java
The find and replace feature streamlines data management and enhances productivity by simplifying updates and corrections. With Spire.XLS for Java, you can quickly locate a cell containing a specific string using the Worksheet.findString() method and replace its value with the CellRange.setValue() method.
To find and replace text in Excel using Java, follow these steps:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from the specified file path.
- Access a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Locate the cell containing the specified string with Worksheet.findString().
- Update the cell's value using the CellRange.setValue() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.CellRange;
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class FindAndReplace {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input4.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Define an array of department names for replacement
String[] departments = new String[] { "Sales", "Marketing", "R&D", "HR", "IT", "Finance", "Support" };
// Define an array of placeholders that will be replaced in the Excel sheet
String[] placeholders = new String[] { "#dept_one", "#dept_two", "#dept_three", "#dept_four", "#dept_five", "#dept_six", "#dept_seven" };
// Iterate through the placeholder strings
for (int i = 0; i < placeholders.length; i++)
{
// Find the cell containing the current placeholder string
CellRange cell = worksheet.findString(placeholders[i], false, false);
// Replace the text in the found cell with the corresponding department name
cell.setValue(departments[i]);
}
// Save the workbook to a different
workbook.saveToFile("ReplaceText.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}

Add Formulas and Charts to Excel in Java
Besides basic file operations, Spire.XLS for Java offers a range of advanced techniques for working with Excel files. These methods allow you to automate complex tasks, perform calculations, and create dynamic reports.
To add formulas and create a chart in Excel using Java, follow these steps:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from the specified file path.
- Access a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Select a specific cell with the Worksheet.getRange().get() method.
- Insert a formula into the cell using the CellRange.setFormula() method.
- Add a column chart to the worksheet with the Worksheet.getCharts().add() method.
- Configure the chart's data range, position, title, and other attributes using methods from the Chart object.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class AddFormulaAndChart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get all located range
CellRange allocatedRange = worksheet.getAllocatedRange();
// Iterate through the rows
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < allocatedRange.getRowCount(); rowNum++) {
if (rowNum == 0) {
// Write text in cell G1
worksheet.getRange().get(rowNum + 1, 6).setText("Total");
// Apply style to the cell
worksheet.getRange().get(rowNum + 1, 6).getStyle().getFont().isBold(true);
worksheet.getRange().get(rowNum + 1, 6).getStyle().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Right);
} else {
// Add formulas to the cells from G2 to G8
worksheet.getRange().get(rowNum + 1, 6).setFormula("=SUM(B" + (rowNum + 1) + ":E" + (rowNum + 1) + ")");
}
}
// Add a clustered column chart
Chart chart = worksheet.getCharts().add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
// Set data range for the chart
chart.setDataRange(worksheet.getCellRange("A1:E8"));
chart.setSeriesDataFromRange(false);
// Set position of the chart
chart.setLeftColumn(1);
chart.setTopRow(10);
chart.setRightColumn(8);
chart.setBottomRow(23);
// Set and format chart title
chart.setChartTitle("Sales by Department per Quarter");
chart.getChartTitleArea().setSize(13);
chart.getChartTitleArea().isBold(true);
// Save the workbook to a different
workbook.saveToFile("AddFormulaAndChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Set Page Setup Options in Excel
Setting up the page layout in Excel is an important step to make your worksheets look polished and professional. Whether you’re printing a report or sharing it digitally, customizing options like margins, orientation, paper size, and scaling helps ensure your data is presented clearly and effectively. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically set page setup options in Excel in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Set Page Margins in Excel in Java
- Set Page Orientation in Excel in Java
- Set Paper Size in Excel in Java
- Set Print Area in Excel in Java
- Set Scaling Factor in Excel in Java
- Set FitToPages Options in Excel in Java
- Set Headers and Footers in Excel in Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>16.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
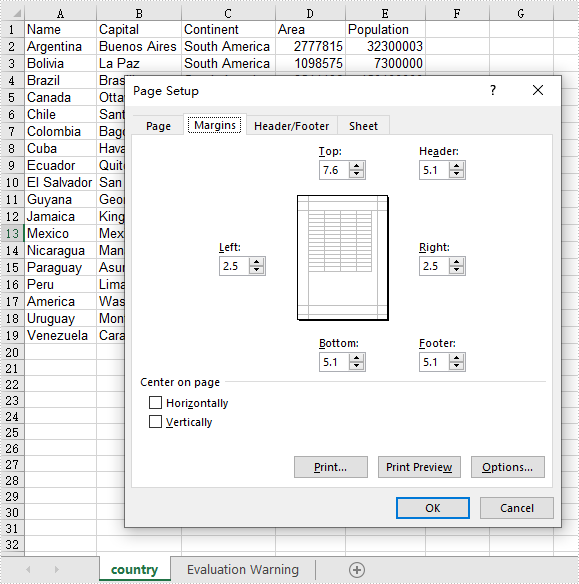
Set Page Margins in Excel in Java
The PageSetup class in Spire.XLS for Java allows you to customize page setup options for Excel worksheets. It provides methods like setTopMargin(), setBottomMargin(), setLeftMargin(), setRightMargin(), setHeaderMarginInch(), and setFooterMarginInch(), enabling you to adjust the top, bottom, left, right, header, and footer margins of a worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(index) method.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using the Worksheet.getPageSetup() method.
- Set the top, bottom, left, right, header, and footer margins using the PageSetup.setTopMargin(), PageSetup.setBottomMargin(), PageSetup.setLeftMargin(), PageSetup.setRightMargin(), PageSetup.setHeaderMarginInch(), and PageSetup.setFooterMarginInch() methods.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.PageSetup;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class PageMargins {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.getPageSetup();
// Set top, bottom, left, and right margins for the worksheet
// The measure of the unit is Inch (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
pageSetup.setTopMargin(1);
pageSetup.setBottomMargin(1);
pageSetup.setLeftMargin(1);
pageSetup.setRightMargin(1);
pageSetup.setHeaderMarginInch(1);
pageSetup.setFooterMarginInch(1);
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.saveToFile("SetPageMargins.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}

Set Page Orientation in Excel in Java
The PageSetup.setOrientation() method allows you to specify the page orientation for printing. You can choose between two options: portrait mode or landscape mode. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(index) method.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using the Worksheet.getPageSetup() method.
- Set the page orientation using the PageSetup.setOrientation() method.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class PageOrientation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.getPageSetup();
pageSetup.setOrientation(PageOrientationType.Landscape);
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.saveToFile("SetPageOrientation.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}

Set Paper Size in Excel in Java
The PageSetup.setPaperSize() method enables you to select from a variety of paper sizes for printing your worksheet. These options include A3, A4, A5, B4, B5, letter, legal, tabloid, and more. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(index) method.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using the Worksheet.getPageSetup() method.
- Set the paper size using the PageSetup.setPaperSize() method.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class PaperSize {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.getPageSetup();
// Set the paper size to A4
pageSetup.setPaperSize(PaperSizeType.PaperA4);
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.saveToFile("SetPaperSize.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
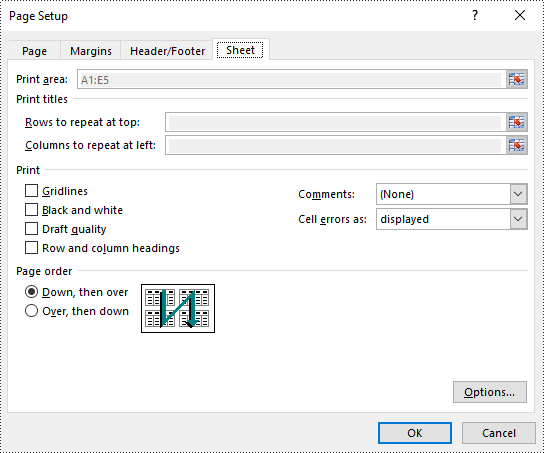
Set Print Area in Excel in Java
You can define the specific area to be printed by using the PageSetup.setPrintArea() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(index) method.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using the Worksheet.getPageSetup() method.
- Set the print area using the PageSetup.setPringArea() method.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.PageSetup;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class PrintArea {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.getPageSetup();
// Set the print area of the worksheet to "A1:E5"
pageSetup.setPrintArea("A1:E5");
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.saveToFile("SetPrintArea.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
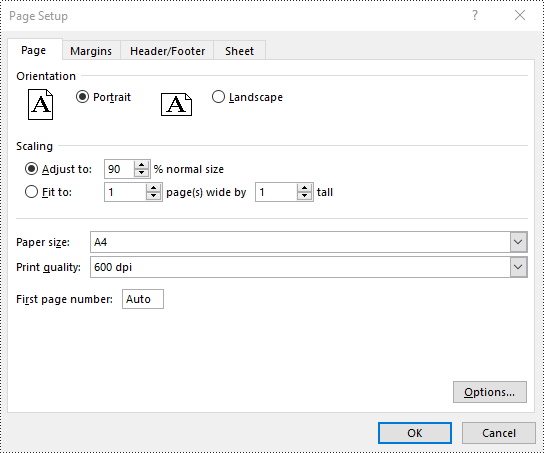
Set Scaling Factor in Excel in Java
To scale the content of your worksheet to a specific percentage of its original size, you can use the PageSetup.setZoom() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(index) method.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using the Worksheet.getPageSetup() method.
- Set the scaling factor using the PageSetup.setZoom() method.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.PageSetup;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class ScalingFactor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.getPageSetup();
// Set the scaling factor of the worksheet to 90%
pageSetup.setZoom(90);
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.saveToFile("SetScalingFactor.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
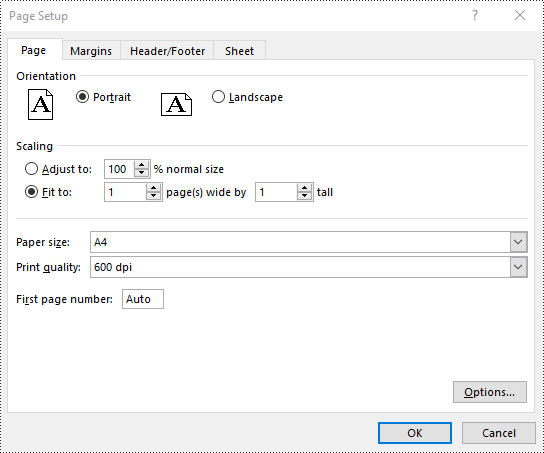
Set FitToPages Options in Excel in Java
Spire.XLS also provides the ability to adjust your worksheet content to fit a specific number of pages by using the PageSetup.setFitToPagesTall() and PageSetup.setFitToPagesWide() methods. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(index) method.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using the Worksheet.getPageSetup() method.
- Fit the content of the worksheet to one page using the PageSetup.setFitToPagesTall() and PageSetup.setFitToPagesWide() methods.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.PageSetup;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class FitToPages {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.getPageSetup();
// Fit the content of the worksheet within one page vertically (i.e., all rows will fit on a single page)
pageSetup.setFitToPagesTall(1);
// Fit the content of the worksheet within one page horizontally (i.e., all columns will fit on a single page)
pageSetup.setFitToPagesWide(1);
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.saveToFile("FitToPages.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Set Headers and Footers in Excel in Java
For instructions on setting headers and footers in Excel, please refer to this article: Java: Add Headers and Footers to Excel.
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Read or Delete Document Properties from Excel
Document properties in Excel are important pieces of metadata that provide additional information about a workbook. If you are managing multiple Excel workbooks and want to keep track of information like author, title, and other relevant metadata, you can read their document properties to quickly gather this information. Besides, in certain situations, you may need to delete document properties from Excel. For instance, if sensitive data is inadvertently stored in document properties, you may need to delete these document properties before sharing the workbook to ensure data security and confidentiality. This article will show you how to read or delete document properties from Excel in Java using Spire.XLS for Java library.
- Read Standard and Custom Document Properties from Excel in Java
- Delete Standard and Custom Document Properties from Excel in Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>16.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
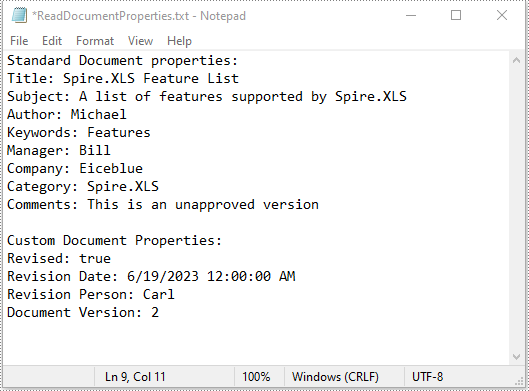
Read Standard and Custom Document Properties from Excel in Java
Standard document properties are pre-built properties included in every Excel file. These properties can include information such as the author, title, subject, keywords, and other details about the file. Custom document properties in Excel are user-defined, meaning that users can create them according to their specific needs. The value of custom document properties can be assigned as text, date time, numeric values, or simply a yes or no.
The following steps demonstrate how to read standard document properties and custom document properties of an Excel file using Spire.XLS for Java:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Initialize an instance of the StringBuilder class for storing the standard and custom document properties.
- Get the collection of all standard document properties of the file using the Workbook.getDocumentProperties() method.
- Get specific standard document properties using the corresponding methods under the BuiltInDocumentProperties class.
- Append the standard document properties to the StringBuilder instance.
- Get the collection of all custom document properties of the file using the Workbook.getCustomDocumentProperties() method.
- Iterate through the collection.
- Get the name and value of each custom document property using the IDocumentProperty.getName() and IDocumentProperty.getValue() methods and append them to the StringBuilder instance.
- Write the content of the StringBuilder instance into a text file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.collections.BuiltInDocumentProperties;
import com.spire.xls.core.ICustomDocumentProperties;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadStandardDocumentProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Initialize an instance of the StringBuilder instance
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//Get the collection of all standard document properties
BuiltInDocumentProperties standardProperties = workbook.getDocumentProperties();
//Get specific standard document properties
String title = standardProperties.getTitle();
String subject = standardProperties.getSubject();
String author = standardProperties.getAuthor();
String keywords = standardProperties.getKeywords();
String manager = standardProperties.getManager();
String company = standardProperties.getCompany();
String category = standardProperties.getCategory();
String comments = standardProperties.getComments();
//Append the standard document properties to the StringBuilder instance
sb.append("Standard Document properties:"
+"\r\nTitle: " + title
+ "\r\nSubject: " + subject
+ "\r\nAuthor: " + author
+ "\r\nKeywords: "+ keywords
+ "\r\nManager: " + manager.toString()
+ "\r\nCompany: " + company.toString()
+ "\r\nCategory: " + category.toString()
+ "\r\nComments: " + comments.toString()
);
sb.append("\r\n\nCustom Document Properties:");
//Get the collection of all custom document properties
ICustomDocumentProperties customProperties = workbook.getCustomDocumentProperties();
//Iterate through the collection
for(int i =0; i < customProperties.getCount(); i++)
{
//Append the name and value of each custom document property to the StringBuilder instance
sb.append("\r\n" + customProperties.get(i).getName() + ": " + customProperties.get(i).getValue());
}
//Write the content of the StringBuilder instance into a text file
String output = "ReadDocumentProperties.txt";
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(output, true);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
bw.append(sb);
bw.close();
fw.close();
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Delete Standard and Custom Document Properties from Excel in Java
You can easily delete standard document properties from an Excel file by setting their values as empty. For custom document properties, you can use the ICustomDocumentProperties.remove() method to delete them.
The following steps demonstrate how to delete standard and custom document properties from an Excel file using Spire.XLS for Java:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the collection of all standard document properties of the file using the Workbook.getDocumentProperties() method.
- Set the values of specific standard document properties as empty using the corresponding methods under the BuiltInDocumentProperties class.
- Get the collection of all custom document properties of the file using the Workbook.getCustomDocumentProperties() method.
- Iterate through the collection.
- Delete each custom document property from the collection using the ICustomDocumentProperties.remove() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.collections.BuiltInDocumentProperties;
import com.spire.xls.core.ICustomDocumentProperties;
public class DeleteDocumentProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Get the collection of all standard document properties
BuiltInDocumentProperties standardProperties = workbook.getDocumentProperties();
//Set the value of each standard document property as empty
standardProperties.setTitle("");
standardProperties.setSubject("");
standardProperties.setAuthor("");
standardProperties.setManager("");
standardProperties.setCompany("");
standardProperties.setCategory("");
standardProperties.setKeywords("");
standardProperties.setComments("");
//Get the collection of all custom document properties
ICustomDocumentProperties customProperties = workbook.getCustomDocumentProperties();
//Iterate through the collection
for(int i = customProperties.getCount() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
//Delete each custom document property from the collection by its name
customProperties.remove(customProperties.get(i).getName());
}
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("DeleteDocumentProperties.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
3 Efficient Methods to Write Data to Excel in Java

Looking to automate Excel data entry in Java? Manually inputting data into Excel worksheets is time-consuming and error-prone, especially when dealing with large datasets. The good news is that with the right Java Excel library, you can streamline this process. This comprehensive guide explores three efficient methods to write data to Excel in Java using the powerful Spire.XLS for Java library, covering basic cell-by-cell entries, bulk array inserts, and DataTable exports.
- Prerequisites: Setup & Installation
- 3 Ways to Write Data to Excel using Java
- Performance Tips for Large Datasets
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
Prerequisites: Setup & Installation
Before you start, you’ll need to add Spire.XLS for Java to your project. Here’s how to do it quickly:
Option 1: Download the JAR File
- Visit the Spire.XLS for Java download page.
- Download the latest JAR file.
- Add the JAR to your project’s build path.
Option 2: Use Maven
If you’re using Maven, add the following repository and dependency to your pom.xml file. This automatically downloads and integrates the library:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.7.7</version>
</dependency>
3 Ways to Write Data to Excel using Java
Spire.XLS for Java offers flexible methods to write data, tailored to different scenarios. Let’s explore each with complete code samples, explanations, and use cases.
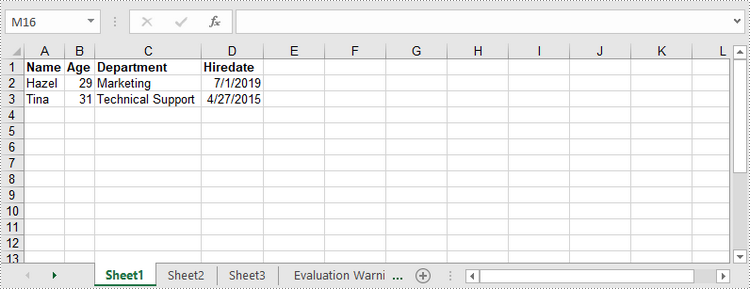
1. Write Text or Numbers to Excel Cells
Need to populate individual cells with text or numbers? Spire.XLS lets you directly target a specific cell using row/column indices (e.g., (2,1) for row 2, column 1) or Excel-style references (e.g., "A1", "B3"):
How It Works:
- Use the Worksheet.get(int row, int column) or Worksheet.get(String name) method to access a specific Excel cell.
- Use the setValue() method to write a text value to the cell.
- Use the setNumberValue() method to write a numeric value to the cell.
**Java code to write data to Excel: **
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class WriteToCells {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Write data to specific cells
worksheet.get("A1").setValue("Name");
worksheet.get("B1").setValue("Age");
worksheet.get("C1").setValue("Department");
worksheet.get("D1").setValue("Hiredate");
worksheet.get(2,1).setValue("Hazel");
worksheet.get(2,2).setNumberValue(29);
worksheet.get(2,3).setValue("Marketing");
worksheet.get(2,4).setValue("2019-07-01");
worksheet.get(3,1).setValue("Tina");
worksheet.get(3,2).setNumberValue(31);
worksheet.get(3,3).setValue("Technical Support");
worksheet.get(3,4).setValue("2015-04-27");
// Autofit column widths
worksheet.getAllocatedRange().autoFitColumns();
// Apply a style to the first row
CellStyle style = workbook.getStyles().addStyle("newStyle");
style.getFont().isBold(true);
worksheet.getRange().get(1,1,1,4).setStyle(style);
// Save to an Excel file
workbook.saveToFile("output/WriteToCells.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
When to use this: Small datasets where you need precise control over cell placement (e.g., adding a title, single-row entries).
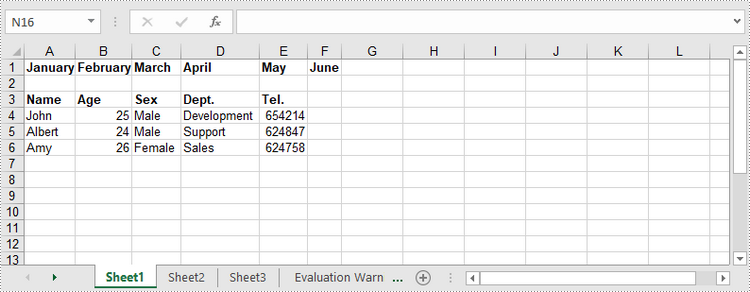
2. Write Arrays to Excel Worksheets
For bulk data, writing arrays (1D or 2D) is far more efficient than updating cells one by one. Spire.XLS for Java allows inserting arrays into a contiguous cell range.
insertArray() Method Explained:
The insertArray() method handles 1D arrays (single rows) and 2D arrays (multiple rows/columns) effortlessly. Its parameters are:
- Object[] array/ Object[][] array: The 1D or 2D array containing data to insert.
- int firstRow: The starting row index (1-based).
- int firstColumn: The starting column index (1-based).
- boolean isVertical: A boolean indicating the insertion direction:
- false: Insert horizontally (left to right).
- true: Insert vertically (top to bottom).
**Java code to insert arrays into Excel: **
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class WriteArrayToWorksheet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Create a one-dimensional array
Object[] oneDimensionalArray = {"January", "February", "March", "April","May", "June"};
// Write the array to the first row of the worksheet
worksheet.insertArray(oneDimensionalArray, 1, 1, false);
// Create a two-dimensional array
Object[][] twoDimensionalArray = {
{"Name", "Age", "Sex", "Dept.", "Tel."},
{"John", "25", "Male", "Development","654214"},
{"Albert", "24", "Male", "Support","624847"},
{"Amy", "26", "Female", "Sales","624758"}
};
// Write the array to the worksheet starting from the cell A3
worksheet.insertArray(twoDimensionalArray, 3, 1);
// Autofit column width in the located range
worksheet.getAllocatedRange().autoFitColumns();
// Apply a style to the first and the third row
CellStyle style = workbook.getStyles().addStyle("newStyle");
style.getFont().isBold(true);
worksheet.getRange().get(1,1,1,6).setStyle(style);
worksheet.getRange().get(3,1,3,6).setStyle(style);
// Save to an Excel file
workbook.saveToFile("WriteArrays.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
When to use this: Sequential data (e.g., inventory logs, user lists) that needs bulk insertion.
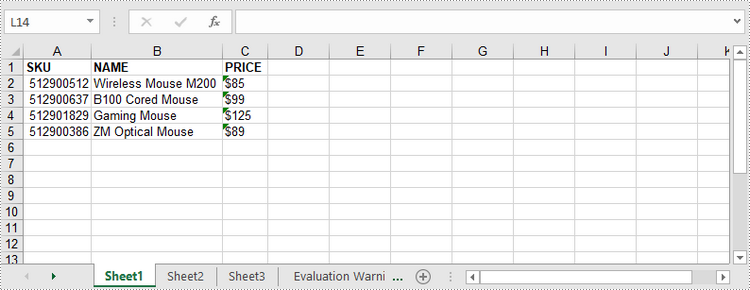
3. Write DataTable to Excel
If your data is stored in a DataTable (e.g., from a database), Spire.XLS lets you directly export it to Excel with insertDataTable(), preserving structure and column headers.
insertDataTable() Method Explained:
The insertDataTable() method is a sophisticated bulk-insert operation designed specifically for transferring structured data collections into Excel. Its parameters are:
- DataTable dataTable: The DataTable object containing the data to insert.
- boolean columnHeaders: A boolean indicating whether to include column names from the DataTable as headers in Excel.
- true: Inserts column names as the first row.
- false: Skips column names; data starts from the first row.
- int firstRow: The starting row index (1-based).
- int firstColumn: The starting column index (1-based).
- boolean transTypes: A boolean indicating whether to preserve data types.
Java code to export DataTable to Excel:
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.data.table.DataRow;
import com.spire.xls.data.table.DataTable;
public class WriteDataTableToWorksheet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Create a DataTable object
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataTable.getColumns().add("SKU", Integer.class);
dataTable.getColumns().add("NAME", String.class);
dataTable.getColumns().add("PRICE", String.class);
// Create rows and add data
DataRow dr = dataTable.newRow();
dr.setInt(0, 512900512);
dr.setString(1,"Wireless Mouse M200");
dr.setString(2,"$85");
dataTable.getRows().add(dr);
dr = dataTable.newRow();
dr.setInt(0,512900637);
dr.setString(1,"B100 Cored Mouse ");
dr.setString(2,"$99");
dataTable.getRows().add(dr);
dr = dataTable.newRow();
dr.setInt(0,512901829);
dr.setString(1,"Gaming Mouse");
dr.setString(2,"$125");
dataTable.getRows().add(dr);
dr = dataTable.newRow();
dr.setInt(0,512900386);
dr.setString(1,"ZM Optical Mouse");
dr.setString(2,"$89");
dataTable.getRows().add(dr);
// Write datatable to the worksheet
worksheet.insertDataTable(dataTable,true,1,1,true);
// Autofit column width in the located range
worksheet.getAllocatedRange().autoFitColumns();
// Apply a style to the first row
CellStyle style = workbook.getStyles().addStyle("newStyle");
style.getFont().isBold(true);
worksheet.getRange().get(1,1,1,3).setStyle(style);
// Save to an Excel file
workbook.saveToFile("output/WriteDataTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
When to use this: Database exports, CRM data, or any structured data stored in a DataTable (e.g., SQL query results, CSV imports).
Performance Tips for Large Datasets
- Use bulk operations (insertArray()/insertDataTable()) instead of writing cells one by one.
- Disable auto-fit columns or styling during data insertion, then apply them once after all data is written.
- For datasets with 100,000+ rows, consider streaming mode to reduce memory usage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What Excel formats does Spire.XLS support for writing data?
A: Spire.XLS for Java supports all major Excel formats, including:
- Legacy formats: XLS (Excel 97-2003)
- Modern formats: XLSX, XLSM (macro-enabled), XLSB, and more.
You can specify the output format when saving Excel with the saveToFile() method.
Q2: How do I format cells (colors, fonts, borders) when writing data?
A: Spire.XLS offers robust styling options. Check these guides:
- Set Background Color for Excel Cells in Java
- Apply Different Fonts to Excel Cells in Java
- Add Cell Borders in Excel in Java
Q3: How do I avoid the "Evaluation Warning" in output files?
A: To remove the evaluation sheets, get a 30-day free trial license here and then apply the license key in your code before creating the Workbook object:
com.spire.xls.license.LicenseProvider.setLicenseKey("Key");
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Final Thoughts
Mastering Excel export functionality is crucial for Java developers in data-driven applications. The Spire.XLS for Java library provides three efficient approaches to write data to Excel in Java:
- Precision control with cell-by-cell writing
- High-performance bulk inserts using arrays
- Database-style exporting with DataTables
Each method serves distinct use cases - from simple reports to complex enterprise data exports. By following the examples in the article, developers can easily create and write to Excel files in Java applications.
Java: Accept or Reject Tracked Changes in Excel
An Excel document with Track Changes turned on will let you know what changes have been made to the document since the author has saved it. If you have the full authority over the document, you can accept or reject each revision. This article covers how to accept or reject all tracked changes at once using Spire.XLS for Java.
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>16.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Accept Tracked Changes in a Workbook
To determine whether a workbook has tracked changes, use Workbook.hasTrackedChanegs() method. If yes, you can accept all changes at once using Workbook.acceptAllTrackedchanges() method. The following are the steps to accept tracked changes in an Excel workbook.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load the sample Excel document using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Determine if the workbook has tracked changes by Workbook.hasTrackedChanegs() method.
- Accept tracked changes using Workbook.acceptAllTrackedChanges() method.
- Save the document to another file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.FileFormat;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
public class AcceptTrackedChanges {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Load the sample Excel file
wb.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Employees.xlsx");
//Determine if the workbook has tracked changes
if (wb.hasTrackedChanges())
{
//Accept tracked changes in the workbook
wb.acceptAllTrackedChanges();
}
//Save to file
wb.saveToFile("output/AcceptChanges.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
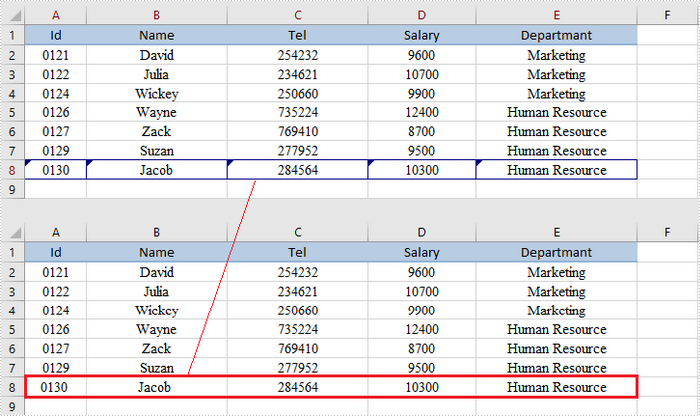
Reject Tracked Changes in a Workbook
If the tracked changes have been proven to exist in a workbook, you can reject them using Workbook.rejectAllTrackedChanges() method. The following are the steps to achieve this.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load the sample Excel document using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Determine if the workbook has tracked changes by Workbook.hasTrackedChanegs() method.
- Reject all tracked changes using Workbook.rejectAllTrackedChanges() method.
- Save the document to another file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.FileFormat;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
public class RejectTrackedChanges {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Load the sample Excel file
wb.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Employees.xlsx");
//Determine if the workbook has tracked changes
if (wb.hasTrackedChanges())
{
//Reject tracked changes in the workbook
wb.rejectAllTrackedChanges();
}
//Save to file
wb.saveToFile("output/RejectChanges.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
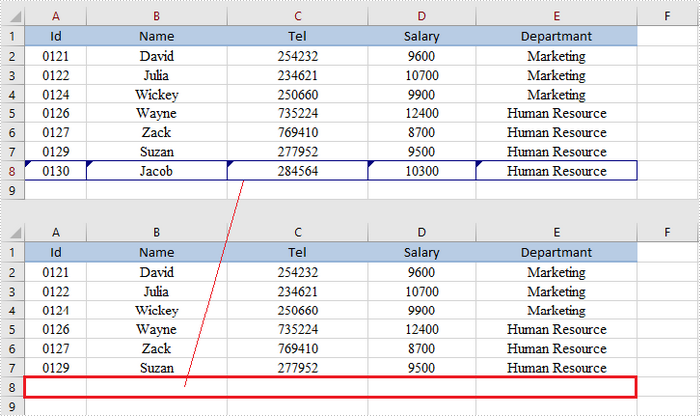
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Split a Worksheet into Several Excel Files
Splitting a worksheet can be beneficial when you have a large amount of data and want to organize it into separate files for easier management and sharing. By using this approach, you can organize and distribute your data in a more organized and structured manner. In this tutorial, we will demonstrate how to split a worksheet into multiple Excel documents by using Spire.XLS for Java.
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>16.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Split a Worksheet into Several Excel Files
Spire.XLS for Java provides powerful features that enable us to achieve this task efficiently. The specific steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the specific sheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get the header row and cell ranges using Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Create a new workbook and copy the header row and range 1 to the new workbook using Worksheet.copy(CellRange sourceRange, Worksheet worksheet, int destRow, int destColumn, boolean copyStyle, boolean updateRerence) method.
- Copy the column width from the original workbook to the new workbook using Workbook.getWorksheets().get(0).setColumnWidth() method.
- Save the new workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Repeat the above operation to copy the header row and range 2 to another new workbook, and save it to another Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.CellRange;
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class SplitWorksheet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook object to load the original Excel document
Workbook bookOriginal = new Workbook();
bookOriginal.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Emplyees.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = bookOriginal.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Get the header row
CellRange headerRow = sheet.getCellRange(1, 1, 1, 5);
//Get two cell ranges
CellRange range1 = sheet.getCellRange(2, 1, 6, 5);
CellRange range2 = sheet.getCellRange(7, 1, 11, 5);
//Create a new workbook
Workbook newBook1 = new Workbook();
//Copy the header row and range 1 to the new workbook
sheet.copy(headerRow, newBook1.getWorksheets().get(0), 1, 1, true, false);
sheet.copy(range1, newBook1.getWorksheets().get(0), 2, 1, true, false);
//Copy the column width from the original workbook to the new workbook
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.getLastColumn(); i++) {
newBook1.getWorksheets().get(0).setColumnWidth(i + 1, sheet.getColumnWidth(i + 1));
}
//Save the new workbook to an Excel file
newBook1.saveToFile("Sales.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
//Create another new workbook
Workbook newBook2 = new Workbook();
//Copy the header row and range 2 to the new workbook
sheet.copy(headerRow, newBook2.getWorksheets().get(0), 1, 1, true, false);
sheet.copy(range2, newBook2.getWorksheets().get(0), 2, 1, true, false);
//Copy the column width from the original workbook to another new workbook
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.getLastColumn(); i++) {
newBook2.getWorksheets().get(0).setColumnWidth(i + 1, sheet.getColumnWidth(i + 1));
}
//Save it to another new Excel file
newBook2.saveToFile("Technicians.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
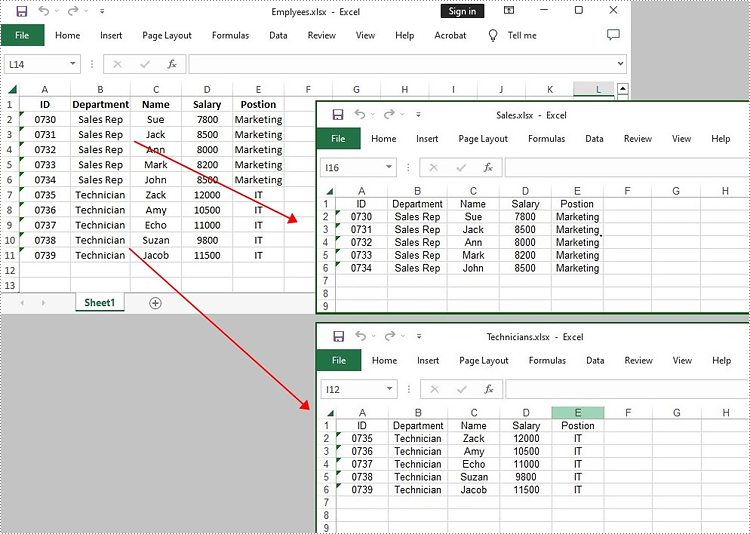
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java set Excel print page margins
This article demonstrates how to set Excel page margins before printing the Excel worksheets in Java applications. By using Spire.XLS for Java, we could set top margin, bottom margin, left margin, right margin, header margin, and footer margin. Please note that the unit for margin is inch on Spire.XLS for Java while On Microsoft Excel, it is cm (1 inch=2.54 cm).
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class setMargins {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String outputFile="output/setMarginsOfExcel.xlsx";
//Load the sample document from file
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Get the PageSetup object of the first worksheet.
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.getPageSetup();
//Set the page margins of bottom, left, right and top.
pageSetup.setBottomMargin(2);
pageSetup.setLeftMargin(1);
pageSetup.setRightMargin(1);
pageSetup.setTopMargin(3);
//Set the margins of header and footer.
pageSetup.setHeaderMarginInch(2);
pageSetup.setFooterMarginInch(2);
//Save to file.
workbook.saveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
Output: