
Spire.XLS for Python (110)
Merging cells means combining multiple adjacent cells into a larger one. The merged cell will inherit all the properties and contents of the original cells. This feature is particularly useful when you need to create a larger cell to accommodate more content or create a header row. Unmerging cells, on the other hand, involves reverting the merged cells back to the original multiple cells. The unmerged cells will revert back to their original independent state, and you can input different content into each individual cell. Merging and unmerging cells are common operations in spreadsheet software, allowing you to adjust the layout and structure of a table as needed, making the data clearer and easier to understand. In this article, you will learn how to merge or unmerge cells in Excel in Python by using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Merge the Cells of the Specified Row or Column
- Merge Ranges of Cells
- Unmerge the Cells of the Specified Row or Column
- Unmerge Ranges of Cells
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Merge the Cells of the Specified Row or Column
With Spire.XLS for Python, users are able to effortlessly merge the cells of the specific column or row in Excel, thereby enhancing their data manipulation capabilities. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet by using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Access the cells of the specific column or row and merge them by calling Worksheet.Columns[].Merge() or Worksheet.Rows[].Merge() methods.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "Sample.xlsx" outputFile = "MergeRowColumn.xlsx" #Create an object of Workbook class workbook = Workbook() #Load a sample Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Merge the first column in Excel #sheet.Columns[0].Merge() #Merge the first row in Excel sheet.Rows[0].Merge() #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
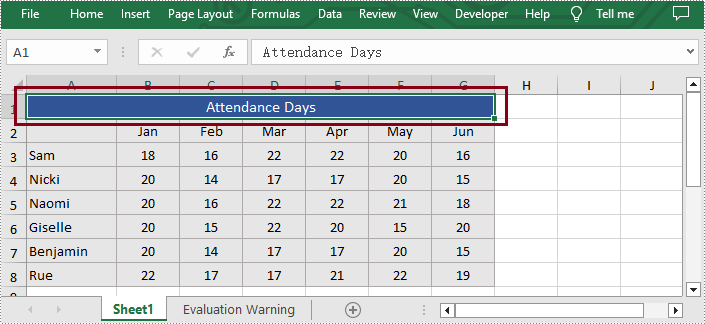
Merge Ranges of Cells
In addition to merging the specific column or row, Spire.XLS for Python also supports users to merge the specified cell ranges. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet by using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Access the specific range of cells and merge them together by calling Worksheet.Range[].Merge() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "Sample.xlsx" outputFile = "MergeCellRange.xlsx" #Create an object of Workbook class workbook = Workbook() #Load a sample Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Merge the particular cell range in Excel sheet.Range["B6:G6"].Merge() #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
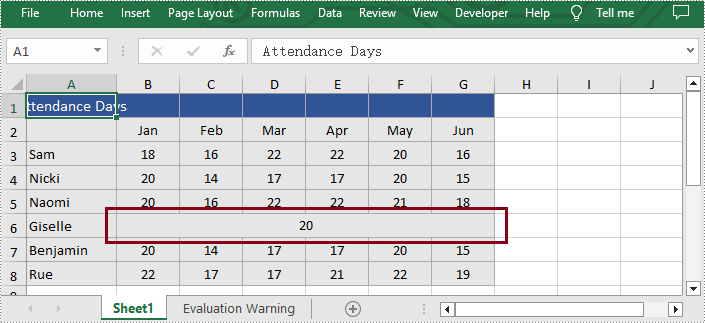
Unmerge the Cells of the Specified Row or Column
Additionally, users are also allowed to unmerge the merged cells of the specific column or row at any time with Spire.XLS for Python. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet by using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Access the merged cells of the specific column or row and unmerge them by calling Worksheet.Columns[].UnMerge() and Worksheet.Rows[].UnMerge() methods.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "MergeRowColumn.xlsx" outputFile = "UnmergeRowColumn.xlsx" #Create an object of Workbook class workbook = Workbook() #Load a sample file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Unmerge the first column in Excel #sheet.Columns[0].UnMerge() #Unmerge the first column in Excel sheet.Rows[0].UnMerge() #Save to file. workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
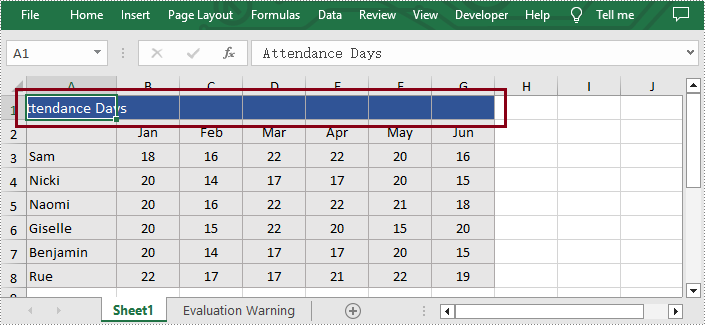
Unmerge Ranges of Cells
What's more, users are also able to unmerge the specified cell ranges using Spire.XLS for Python. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet by using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Access the specific cell ranges and unmerge them by calling Worksheet.Range[].UnMerge() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "MergeCellRange.xlsx" outputFile = "UnmergeCellRange.xlsx" #Create an object of Workbook class workbook = Workbook() #Load a sample file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Unmerge the particular cell range in Excel sheet.Range["B6:G6"].UnMerge() #Save to file. workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
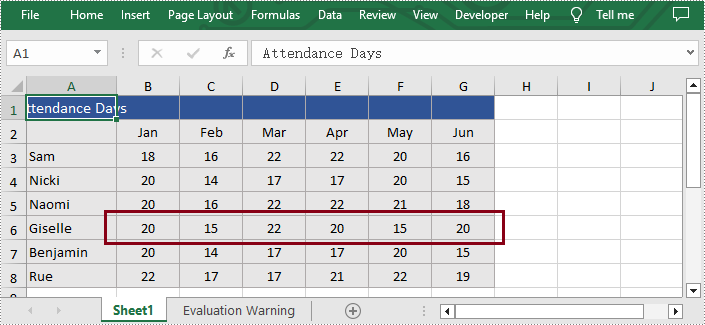
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Hyperlinks are a useful tool in Microsoft Excel that allows users to create clickable links within their spreadsheets. By adding hyperlinks, you can conveniently navigate between different sheets, workbooks, websites, or even specific cells within the same workbook. Whether you need to reference external resources, connect related data, or create interactive reports, hyperlinks can help you achieve your purpose with ease. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add hyperlinks to Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Text Hyperlinks to Excel in Python
Text hyperlinks in Excel are clickable words or phrases that can direct users to different parts of the Excel file, external resources, or email addresses. The following steps explain how to add a text hyperlink to an Excel file using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Access the specific cell that you want to add a hyperlink to using Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Add a hyperlink to the cell using Worksheet.HyperLinks.Add() method.
- Set the type, display text and address of the hyperlink using XlsHyperLink.Type, XlsHyperLink.TextToDisplay and XlsHyperLink.Address properties.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a text hyperlink that leads to a webpage
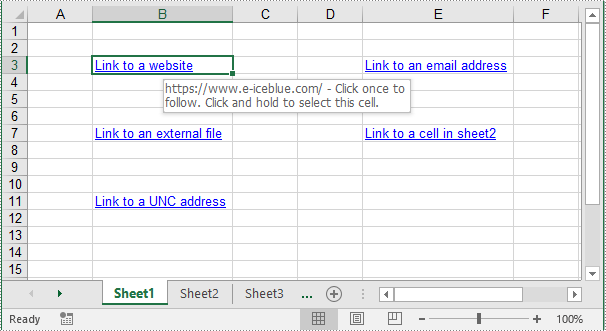
cell1 = sheet.Range["B3"]
urlLink = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell1)
urlLink.Type = HyperLinkType.Url
urlLink.TextToDisplay = "Link to a website"
urlLink.Address = "https://www.e-iceblue.com/"
# Add a text hyperlink that leads to an email address
cell2 = sheet.Range["E3"]
mailLink = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell2)
mailLink.Type = HyperLinkType.Url
mailLink.TextToDisplay = "Link to an email address"
mailLink.Address = "mailto:example@outlook.com"
# Add a text hyperlink that leads to an external file
cell3 = sheet.Range["B7"]
fileLink = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell3)
fileLink.Type = HyperLinkType.File
fileLink.TextToDisplay = "Link to an external file"
fileLink.Address = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Report.xlsx"
# Add a text hyperlink that leads to a cell in another sheet
cell4 = sheet.Range["E7"]
linkToSheet = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell4)
linkToSheet.Type = HyperLinkType.Workbook
linkToSheet.TextToDisplay = "Link to a cell in sheet2"
linkToSheet.Address = "Sheet2!B5"
# Add a text hyperlink that leads to a UNC address
cell5 = sheet.Range["B11"]
uncLink = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell5)
uncLink.Type = HyperLinkType.Unc
uncLink.TextToDisplay = "Link to a UNC address"
uncLink.Address = "\\\\192.168.0.121"
# Autofit column widths
sheet.AutoFitColumn(2)
sheet.AutoFitColumn(5)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddTextHyperlinks.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Add Image Hyperlinks to Excel in Python
Image hyperlinks in Excel work similarly to text hyperlinks but use images as clickable elements instead of words or phrases. They provide a visually appealing and intuitive way to navigate within the spreadsheet or to external resources. The following steps explain how to add an image hyperlink to an Excel file using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Insert an image into the worksheet using Worksheet.Pictures.Add() method.
- Add a hyperlink to the image using XlsBitmapShape.SetHyperLink() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add text to the worksheet
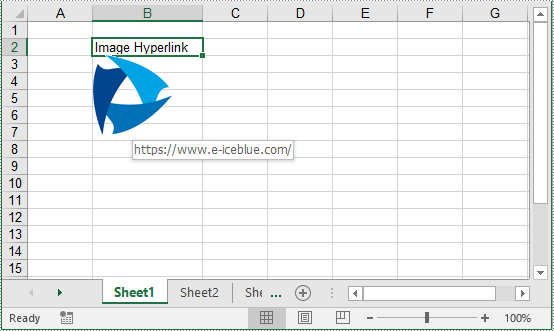
sheet.Range["B2"].Text = "Image Hyperlink"
# Set the width of the second column
sheet.Columns[1].ColumnWidth = 15
# Insert an image into the worksheet
picture = sheet.Pictures.Add(3, 2, "logo2.png")
# Add a hyperlink to the image
picture.SetHyperLink("https://www.e-iceblue.com", True)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddImageHyperlink.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Fonts play a crucial role in enhancing the visual appeal and readability of data in Microsoft Excel. Whether you're creating a spreadsheet, designing a report, or simply organizing information, the ability to set or change fonts can greatly impact the overall presentation. Excel offers a wide range of font options, allowing you to customize the style, size, and formatting to suit your specific needs. In this article, you will learn how to set or change fonts in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Set Different Fonts for Different Cells in Python
- Apply Multiple Fonts in a Single Cell in Python
- Change the Font Style of a Cell Range in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set Different Fonts for Different Cells in Python
With Spire.XLS for Python, customizing fonts in specific cells becomes a breeze. By utilizing the CellRange.Style.Font property, you gain control over font name, color, size, and style effortlessly. Follow these steps to apply a font style to a particular cell using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell through Worksheet.Range[int Row, int Column] property.
- Set the value of the cell through CellRange.Value property.
- Set the font name, color, size and style of the cell value through the properties under the CellRange.Style.Font object.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set font name
row = 1
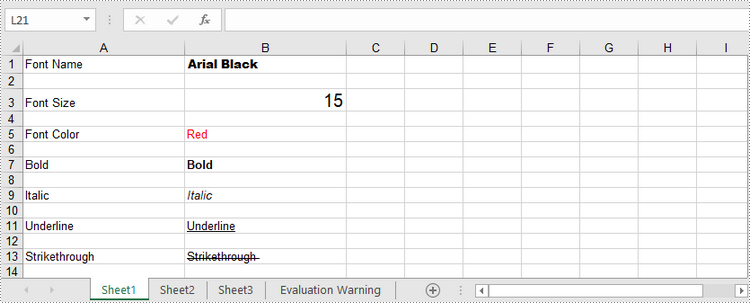
sheet.Range[row, 1].Value = "Font Name"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Arial Black"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.FontName = "Arial Black"
# Set font size
row += 2
sheet.Range[row, 1].Value = "Font Size"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "15"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.Size = 15
# Set font color
row += 2
sheet.Range[row, 1].Value = "Font Color"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Red"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_Red()
# Make text bold
row += 2
sheet.Range[row, 1].Value = "Bold"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Bold"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.IsBold = True;
# Make text italic
row += 2
sheet.Range[row, 1].Value = "Italic"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Italic"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.IsItalic = True
# Underline text
row += 2
sheet.Range[row, 1].Value = "Underline"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Underline"
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.Underline = FontUnderlineType.Single
# Strikethrough text
row += 2
sheet.Range[row, 1].Value = "Strikethrough "
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Strikethrough "
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.IsStrikethrough = True
# Set column width
sheet.Columns[0].ColumnWidth = 25
sheet.Columns[1].ColumnWidth = 25
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ApplyFontInCell.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Apply Multiple Fonts in a Single Cell in Python
To emphasize specific characters within a cell, you can mix fonts. Here are the steps to apply multiple fonts in a single cell using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Create two ExcelFont objects using Workbook.CreateFont() method.
- Get a specific cell through Worksheet.Range[int Row, int Column] property, and set the rich text content of the cell through CellRange.RichText.Text property.
- Apply the two ExcelFont objects to the rich text using RichText.SetFont() method.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create a font
font1 = workbook.CreateFont()
font1.FontName = "Arial Black"
font1.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightBlue
font1.IsBold = True
font1.Size = 13
# Create another font
font2 = workbook.CreateFont()
font2.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Red
font2.IsBold = True
font2.IsItalic = True
font2.FontName = "Algerian"
font2.Size = 15;
# Returns a RichText object from a specified cell
richText = sheet.Range["A1"].RichText
# Set the text of RichText object
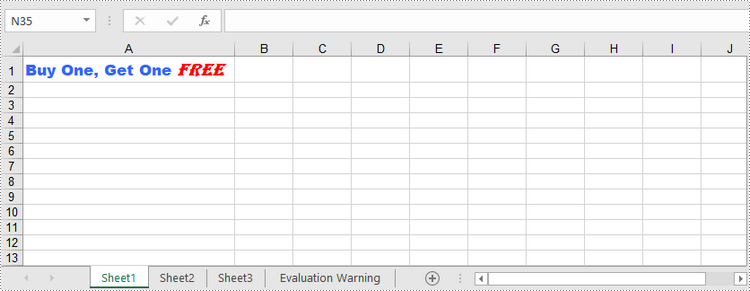
richText.Text = "Buy One, Get One Free"
# Apply the first font to specified range of characters
richText.SetFont(0, 16, font1)
# Apply the second font to specified range of characters
richText.SetFont(17, 21, font2)
# Set column width
sheet.Columns[0].ColumnWidth = 33
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ApplyMultipleFontsInSingleCell.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Change the Font Style of a Cell Range in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the CellStyle class, enabling users to handle cell formatting like fill color, text alignment, and font style. By creating a cell style, you can apply it to a specific range of cells using the CellRange.ApplyStyle() method or to an entire worksheet using the Worksheet.ApplyStyle() method. To change the font style of a cell range using Spire.XLS for Python, follow these steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Create a CellStyle object using Workbook.Styles.Add() method, and set the font style through the CellStyle.Font property.
- Apply the cell style to a cell range using CellRange.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create a CellStyle object
fontStyle = workbook.Styles.Add("headerFontStyle")
# Set the font color, size and style
fontStyle.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
fontStyle.Font.IsBold = True
fontStyle.Font.Size = 12
# Create a CellStyleFlag object, setting the FontColor, FontBold, ad FontSize properties to true
flag = CellStyleFlag()
flag.FontColor = True
flag.FontBold = True
flag.FontSize = True
# Apply the cell style to header row
sheet.Range[1, 1, 1, 8].ApplyStyle(fontStyle, flag)
# Apply the cell style to the whole worksheet
# sheet.ApplyStyle(fontStyle)
# Save the workbook to another Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ApplyFontToCellRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Converting Excel spreadsheets to image formats can be extremely valuable and versatile in a wide range of situations. Whether you need to share data with others who don’t have Excel installed on their devices, present information in a document or presentation, or publish content online, converting Excel to image format offers a convenient solution. In this article, we will introduce how to programmatically convert Excel to images in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Convert an Excel Worksheet to an Image in Python
- Convert an Excel Worksheet to an Image without White Margins in Python
- Convert a Specific Cell Range to an Image in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
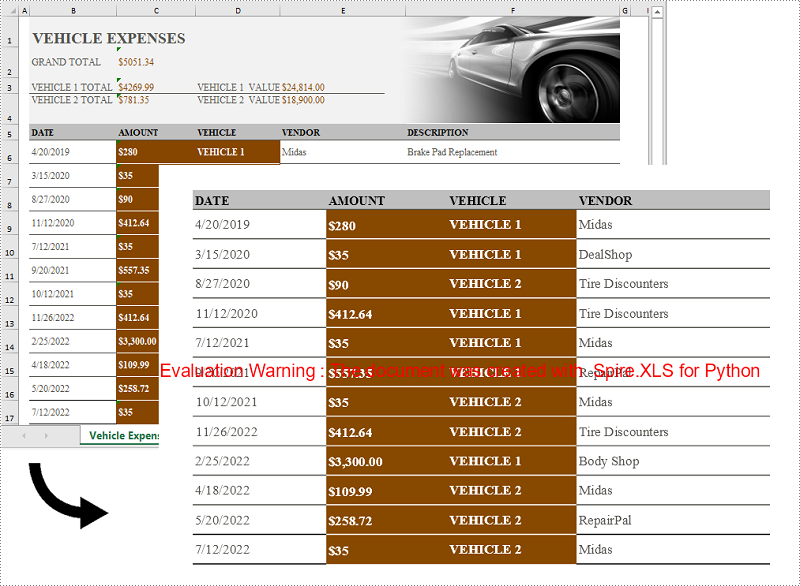
Convert an Excel Worksheet to an Image in Python
You can easily convert a whole Excel worksheet to an image by using the Worksheet.SaveToImage() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using Workbook.Worksheets[int index] property.
- Convert the worksheet to an image using Worksheet.ToImage() method.
- Save the image to a PNG file (you can also save the image as other image formats such as JPG and BMP).
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Save the worksheet to an image
image = sheet.ToImage(sheet.FirstRow, sheet.FirstColumn, sheet.LastRow, sheet.LastColumn)
# Save the image to a PNG file
image.Save("SheetToImage.png")
workbook.Dispose()
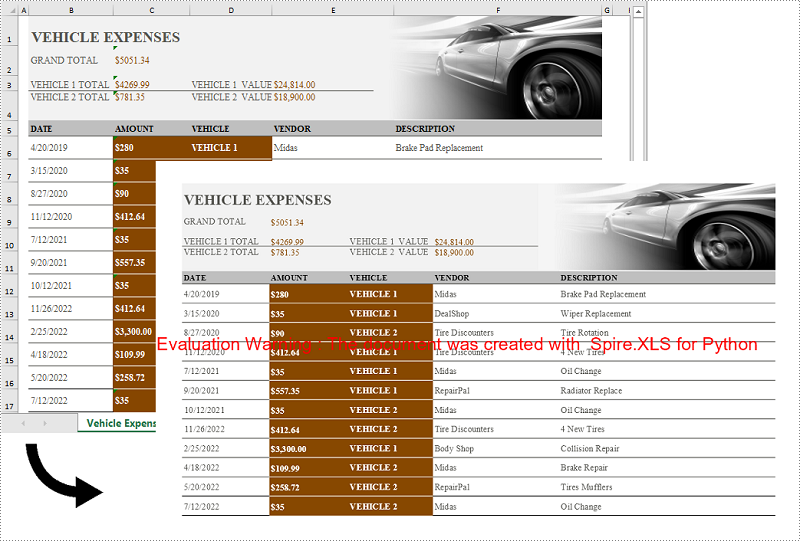
Convert an Excel Worksheet to an Image without White Margins in Python
When converting an Excel worksheet to an image, you may find the resulting image has unwanted white margins surrounding the cells. If you want to convert the worksheet to an image without any extraneous margins, you can remove the page margins set in the original worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using Workbook.Worksheets[int index] property.
- Remove all margins from the worksheet by setting its left, right, top, and bottom margin values to zero.
- Convert the worksheet to an image using Worksheet.ToImage() method.
- Save the image to a PNG file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set all margins of the worksheet to zero
sheet.PageSetup.LeftMargin = 0
sheet.PageSetup.BottomMargin = 0
sheet.PageSetup.TopMargin = 0
sheet.PageSetup.RightMargin = 0
# Convert the worksheet to an image
image = sheet.ToImage(sheet.FirstRow, sheet.FirstColumn, sheet.LastRow, sheet.LastColumn)
# Save the image to a PNG file
image.Save("SheetToImageWithoutMargins.png")
workbook.Dispose()
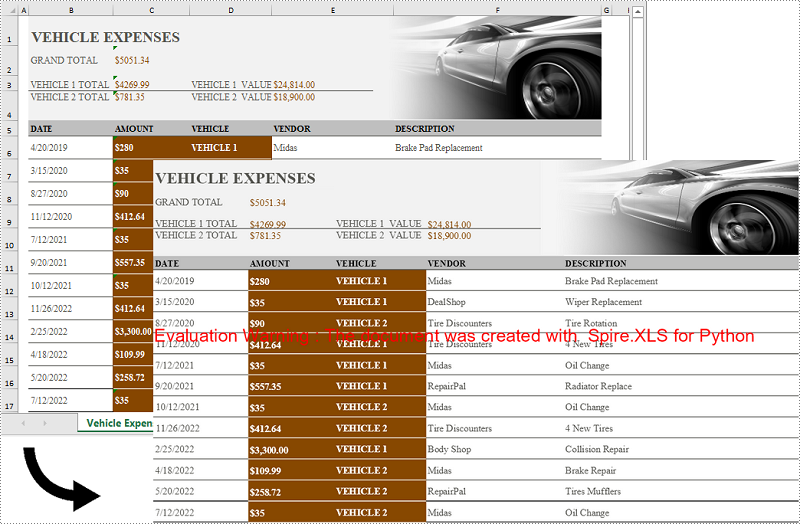
Convert a Specific Cell Range to an Image in Python
In addition to converting a whole worksheet to an image, Spire.XLS for Python also supports converting a specific cell range of a worksheet to an image. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using Workbook.Worksheets[int index] property.
- Convert a specific cell range of the worksheet to an image using Worksheet.ToImage() method and pass the index of the start row, start column, end row, and end column of the cell range to the method as parameters.
- Save the image to a PNG file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Convert a specific cell range of the worksheet to an image
image = sheet.ToImage(5, 2, 17, 5)
# Save the image to a PNG file
image.Save("CellRangeToImage.png")
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Inserting or deleting images in Excel can be a powerful way to enhance your spreadsheets and make them visually appealing. Whether you want to include logos, charts, diagrams, or any other graphical elements, Excel provides the functionality to seamlessly integrate images into your worksheets. Additionally, Excel offers the options to manipulate and organize images, allowing you to resize, move, or delete them as needed. In this article, we will explore how to programmatically insert or delete pictures in Excel in Python by using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Insert a Picture to a Specific Cell in Python
To add a picture to a certain cell, you use Worksheet.Pictures.Add(int topRow, int leftColumn, Image image) method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Initialize a Workbook instance.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Insert a picture into a specific cell using Worksheet.Pictures.Add() method and return an object of ExcelPicture.
- Set the width and height of the picture, as well as the distance between the picture and the cell border through the properties under the ExcelPicture object.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet.
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a picture to a specific cell
imgPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png"
picture = sheet.Pictures.Add(1, 3, imgPath)
# Set the picture width and height
picture.Width = 150
picture.Height = 150
# Adjust the column width and row height so that the cell can accommodate the picture
sheet.Columns[2].ColumnWidth = 25
sheet.Rows[0].RowHeight = 135
# Set the distance between cell border and image
picture.LeftColumnOffset = 90
picture.TopRowOffset = 20
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/InsertImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Delete Pictures in a Worksheet in Python
A picture in a worksheet can be removed using Worksheet.Pictures[imgIndex].Remove() method. To delete all pictures, you can use a for loop to iterate through the pictures in the worksheet. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Delete images in the worksheet using Worksheet.Pictures[imgIndex].Remove() method.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\InsertImage.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Delete all pictures from the worksheet
for i in range(sheet.Pictures.Count - 1, -1, -1):
sheet.Pictures[i].Remove()
# Delete a specific picture
# sheet.Pictures[imgIndex].Remove()
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/DeleteImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A clustered column chart and a stacked column chart are two variants of column chart. The clustered column chart enables straightforward comparison of values across different categories, while the stacked column chart displays both the total for each category and the proportion of its individual components. In this article, you will learn how to create clustered or stacked column charts in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Clustered Column Chart in Excel in Python
To add a chart to a worksheet, use Worksheet.Chart.Add(ExcelChartType chartType) method. The ExcelChartType enumeration includes various chart types predefined in MS Excel. The following are the steps to add a clustered column chart in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Write data into the specified cells.
- Add a clustered column char to the worksheet using Worksheet.Chart.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered) method.
- Set the chart data through Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, title, and other attributes of the chart through the properties under the Chart object.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set chart data
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Product"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Diet Coke"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Mountain Dew"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Diet Pesi"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Cherry Coke"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Store A"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 35000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 46000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 28000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 51000
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Store B"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 41000
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 32000
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 38000
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 40000
# Set cell style
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].RowHeight = 15
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.AutoFitColumn(1)
# Add a chart to the sheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered)
# Set data range of chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 5
chart.TopRow = 1
chart.RightColumn = 14
chart.BottomRow = 21
# Set chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Store Wise Soda Soft Drink Sales"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set axis title
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Product"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
# Set series color, overlap, gap width and data labels
series = chart.Series
for i in range(len(series)):
cs = series[i]
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.Format.Options.Overlap = -50
cs.Format.Options.GapWidth = 350
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("ClusteredColumnChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
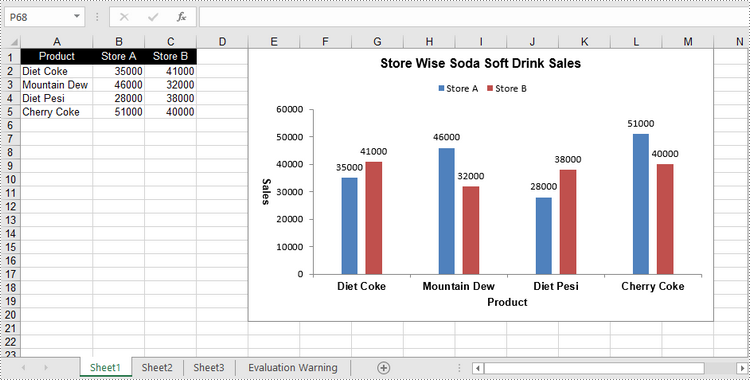
Create a Stacked Column Chart in Excel in Python
The process of creating a stacked column chart is similar to that of creating a clustered column chart. The only difference is that you must change the Excel chart type from ColumnClustered to ColumnStacked.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Write data into the specified cells.
- Add a clustered column char to the worksheet using Worksheet.Chart.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnStacked) method.
- Set the chart data through Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, title, and other attributes of the chart through the properties under the Chart object.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set chart data
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Product"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Diet Coke"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Mountain Dew"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Diet Pesi"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Cherry Coke"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Store A"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 35000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 46000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 28000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 51000
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Store B"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 41000
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 32000
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 38000
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 40000
# Set cell style
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].RowHeight = 15
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.AutoFitColumn(1)
# Add a chart to the sheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnStacked)
# Set data range of chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 5
chart.TopRow = 1
chart.RightColumn = 14
chart.BottomRow = 21
# Set chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Store Wise Soda Soft Drink Sales"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set axis title
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Product"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
# Set series color, gap width and data labels
series = chart.Series
for i in range(len(series)):
cs = series[i]
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.Format.Options.GapWidth = 270
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.Position = DataLabelPositionType.Inside
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("StackedColumnChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
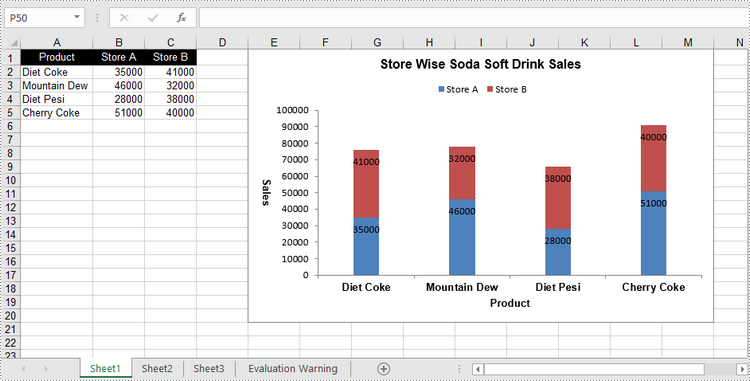
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Copying worksheets in Excel is a critical skill to have, especially when you need to create new worksheets based on existing ones. By utilizing the copy function, you can avoid potential errors that may arise from manually recreating the same content. This not only saves time and effort but also ensures that your data remains accurate and reliable. In this article, we will demonstrate how to copy worksheets in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Copy a Worksheet in the Same Excel Workbook
- Copy a Worksheet to Another Excel Workbook
- Copy Visible Worksheets to a New Excel Workbook
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
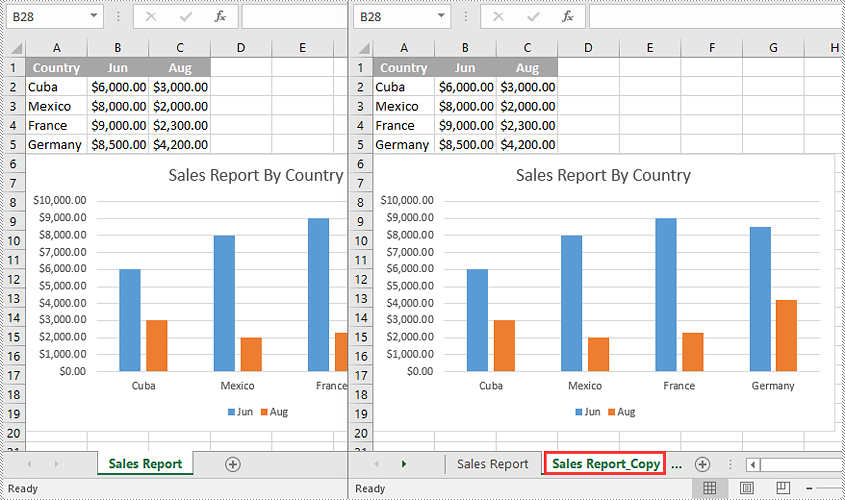
Copy a Worksheet in the Same Excel Workbook in Python
You can copy a worksheet within the same workbook by adding a new worksheet to the workbook and then copying the data from the original worksheet to the new one.
The following steps demonstrate how to copy a worksheet within the same workbook:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[int index] property.
- Add a new worksheet to the workbook using the Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Copy the data from the specific worksheet to the new worksheet using the Worksheet.CopyFrom(Worksheet worksheet) method.
- Save the resulting workbook to another file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
#Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input.xlsx")
#Get the first worksheet
sourceSheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheetName = sourceSheet.Name + "_Copy"
#Add a new worksheet with a specific name to the workbook
destSheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName)
#Copy the first worksheet to the newly added worksheet
destSheet.CopyFrom(sourceSheet)
#Save the result workbook to another file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyInSameWorkbook.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
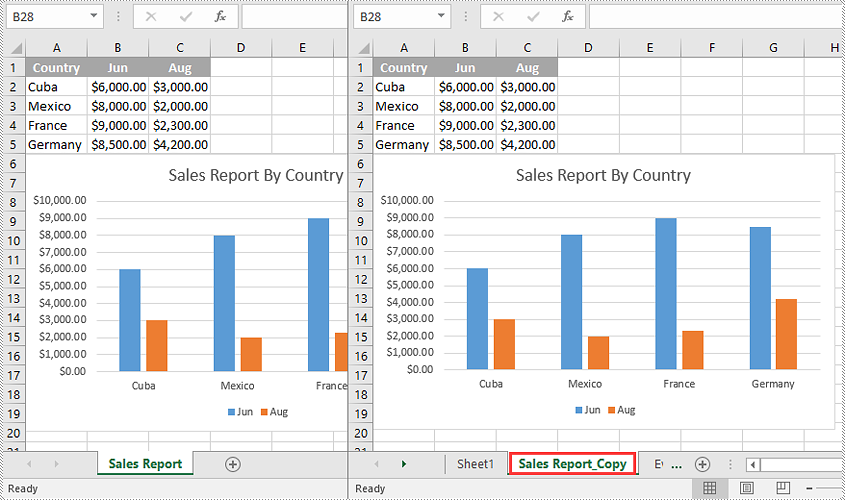
Copy a Worksheet to Another Excel Workbook in Python
To copy a worksheet from one workbook to another, you need to add a new worksheet to the destination workbook and then copy the data of the worksheet from the source workbook to the new worksheet of the destination workbook. If you want to maintain the source formatting, you can copy the theme of the source workbook to the destination workbook.
The following steps demonstrate how to copy a worksheet from one workbook to another:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load the source workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[int index] property.
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load the destination workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a new worksheet to the destination workbook using the Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Copy the specific worksheet of the source workbook to the new worksheet of the destination workbook using the Worksheet.CopyFrom(Worksheet worksheet) method.
- Copy the theme from the source workbook to the destination workbook using the Workbook.CopyTheme (Workbook srcWorkbook) method.
- Save the resulting workbook to another file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
#Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
sourceWorkbook = Workbook()
#Load the source Excel workbook
sourceWorkbook.LoadFromFile("CopyWorksheets-Input.xlsx")
#Get the first worksheet of the source workbook
sourceSheet = sourceWorkbook.Worksheets[0]
#Get the name of the first worksheet
sheetName = sourceSheet.Name + "_Copy"
#Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
destWorkbook = Workbook()
#Load the destination Excel workbook
destWorkbook.LoadFromFile("CopyWorksheets-Sample.xlsx")
#Add a new worksheet with a specific name to the destination workbook
destSheet = destWorkbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName)
#Copy the first worksheet of the source workbook to the new worksheet of the destination workbook
destSheet.CopyFrom(sourceSheet)
#Copy the theme from the source workbook to the destination workbook
destWorkbook.CopyTheme(sourceWorkbook)
#Save the destination workbook to another file
destWorkbook.SaveToFile("CopyToAnotherWorkbook.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
sourceWorkbook.Dispose()
destWorkbook.Dispose()
Copy Visible Worksheets to a New Excel Workbook in Python
If you only want to share visible worksheets rather than the entire workbook with others, you can copy the visible worksheets to a new workbook.
The following steps demonstrate how to copy visible worksheets from a workbook to a new workbook:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load the source workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class to create a new workbook, then clear the default worksheets in the new workbook using the Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Iterate through all the worksheets in the source workbook.
- Check if the current worksheet is visible using the Worksheet.Visibility property.
- If the result is true, add a new worksheet to the new workbook using the Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Copy the worksheet from the source workbook to the new worksheet of the new workbook using the Worksheet.CopyFrom(Worksheet worksheet) method.
- Copy the theme from the source workbook to the new workbook using the Workbook.CopyTheme(Workbook srcWorkbook) method.
- Save the resulting workbook to another file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
#Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
sourceWorkbook = Workbook()
#Load the source Excel workbook
sourceWorkbook.LoadFromFile("CopyWorksheets-Input.xlsx")
#Initialize an instance of the Workbook class to create a new workbook
newWorkbook = Workbook()
newWorkbook.Version = ExcelVersion.Version2013
#Clear the default worksheets in the new workbook
newWorkbook.Worksheets.Clear()
#Iterate through all the worksheets in the source workbook
for sourceSheet in sourceWorkbook.Worksheets:
#Check if the current worksheet is visible
if sourceSheet.Visibility == WorksheetVisibility.Visible:
sheetName = sourceSheet.Name + "_Copy"
#Add a new worksheet with a specific name to the new workbook
destSheet = newWorkbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName)
#Copy the worksheet from the source workbook to the new worksheet of the new workbook
destSheet.CopyFrom(sourceSheet)
#Copy the theme from the source workbook to the new workbook
newWorkbook.CopyTheme(sourceWorkbook)
#Save the new workbook to another file
newWorkbook.SaveToFile("CopyVisibleSheetsToNewWorkbook.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
sourceWorkbook.Dispose()
newWorkbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Convert Excel (XLSX/XLS) to CSV in Python – Batch & Multi-Sheet
2023-08-11 00:58:16 Written by Koohji
If you’re looking to convert xlsx to csv in Python, or even handle .xls files, this guide is for you. CSV files are lightweight, easy to parse, and widely supported across databases and data tools—making them ideal for automation and data exchange.
In this article, we’ll show you how to convert Excel to CSV in Python using Spire.XLS for Python. The library supports .xlsx, .xls, and other common Excel spreadsheet formats, and doesn’t rely on any third-party components. You’ll learn how to export the entire workbook, handle multiple worksheets, and ensure encoding—all with clean and efficient Python code.
What’s Covered:
- Convert XLSX to CSV in Python
- Convert Excel (XLS/XLSX) to CSV: All Sheets, Old Files & Batch
- Advanced Conversion: Customize CSV Output in Python
- Bonus Tip: Convert CSV Back to Excel (XLSX)
- Frequently Asked Questions
Convert XLSX to CSV in Python
To follow along, install Spire.XLS for Python (pip install spire.xls) or Free Spire.XLS for Python (pip install spire.xls.free) for lightweight tasks.
The most common use case is converting .xlsx files to .csv. Here’s a simple script using Spire.XLS:
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat
# Initialize a workbook and load the xlsx file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Save the workbook as a csv file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/XLSXToCSV.csv", FileFormat.CSV)
workbook.Dispose()
Result:
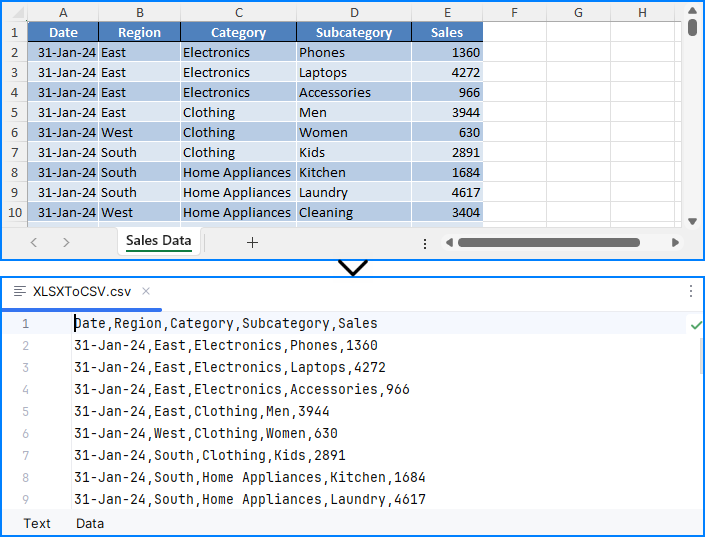
⚠️ Note: The SaveToFile() method saves only the first worksheet. If you need to convert all sheets, see the next section.
This method is perfect for simple, single-sheet Excel-to-CSV conversions in Python.
Convert Excel (XLS/XLSX) to CSV: All Sheets, Old Files & Batch
Whether you're working with modern .xlsx, older .xls, or multi-sheet Excel files, Spire.XLS offers multiple ways to export everything to CSV in Python.
Export All Worksheets to Separate CSV Files
To export every worksheet into its own CSV file—for example, monthly tabs or department data:
from spire.xls import Workbook, Encoding
# Initialize a workbook and load the Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Iterate through each sheet
for i in range(workbook.Worksheets.Count):
# Save the current sheet to CSV format
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(i)
sheet.SaveToFile(f"output/Sheets/Sheet{i}.csv", ",", Encoding.get_UTF8())
workbook.Dispose()
Result:
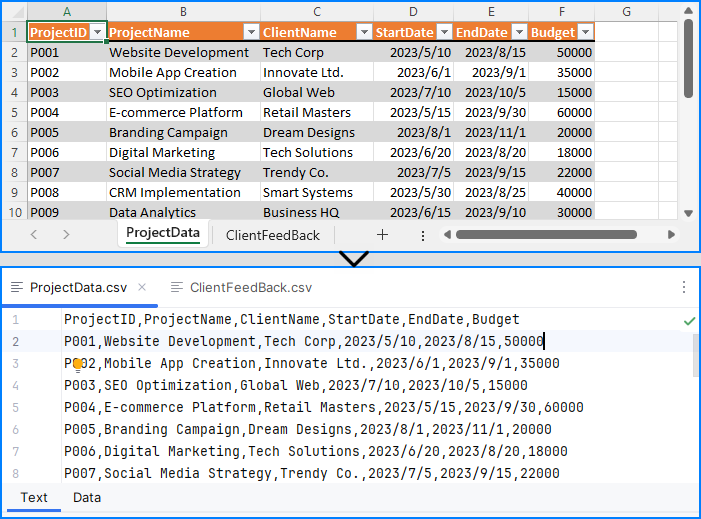
Each worksheet becomes an individual CSV, ideal for segmented data processing and distribution.
Convert XLS to CSV in Python
Legacy Excel files (.xls) are still common in many industries. Fortunately, Spire.XLS fully supports them:
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("legacy.xls")
workbook.SaveToFile("legacy_output.csv", FileFormat.CSV)
This converts the first worksheet by default. To convert all .xls sheets, apply the loop method shown above.
You may also like: Convert XLS Files to XLSX Files with Python
Batch Convert Excel Files to CSV
To automate conversion of multiple .xlsx and .xls files stored in a folder:
import os
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat
excel_dir = "./excels"
output_dir = "./csvs"
for file in os.listdir(excel_dir):
if file.endswith(".xlsx") or file.endswith(".xls"):
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(os.path.join(excel_dir, file))
base_name = os.path.splitext(file)
workbook.SaveToFile(os.path.join(output_dir, base_name + ".csv"), FileFormat.CSV)
Note: This script saves only the first worksheet. Use sheet.SaveToFile() in a loop if you want all sheets.
Advanced Conversion: Customize CSV Output in Python
Need to export only specific cells, rows, or columns from Excel to CSV? You can read worksheet content manually and write customized CSV output:
import csv
from itertools import chain
from spire.xls import Workbook
# Initialize a Workbook object and load the Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Export data to CSV
with open("output/FilteredOutput.csv", "w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
for row in range(sheet.AllocatedRange.RowCount): # Export rows 1 to 5
row_data = []
for col in chain(range(0, 2), range(3, sheet.AllocatedRange.ColumnCount)): # Export columns A to C
row_data.append(sheet.Range.get_Item(row + 1, col + 1).Value)
writer.writerow(row_data)
Result:
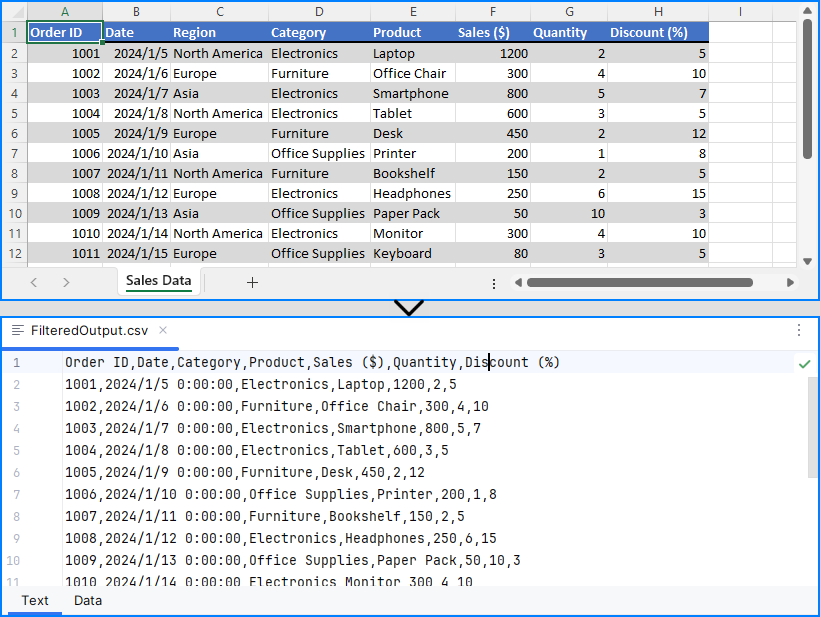
This provides full control for custom Excel to CSV conversion in Python, such as skipping headers or exporting limited ranges.
Explore More: Export & Import Data Between Excel Files and Databases | Python
Bonus Tip: Convert CSV Back to Excel (XLSX)
While this guide focuses on Excel to CSV, you can also convert CSV files back to Excel using Spire.XLS:
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("output.csv", ",")
workbook.SaveToFile("restored.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
This is useful for restoring structured Excel files after processing raw CSV data.
Want to explore more? Check out our dedicated guide on how to convert CSV to Excel using Python for more advanced methods, formatting options, and batch conversion tips.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How to convert an XLSX file to CSV in Python?
A: You can use Python libraries like Spire.XLS to load the XLSX file and save it as CSV. See the detailed steps in Convert XLSX to CSV in Python.
Q2: How to convert xlsx into csv?
A: Convert XLSX to CSV by loading the file and exporting to CSV format, either saving the first sheet or iterating through all sheets to save separately. Check Convert Excel (XLS/XLSX) to CSV: All Sheets, Old Files & Batch for multi-sheet and batch examples.
Q3: How to convert xlsx to csv from the command line?
A: While this article focuses on Python, you can create Python scripts using Spire.XLS or other libraries and run them from the command line to batch convert XLSX to CSV files. See the Batch Convert Excel Files to CSV section for related code.
Q4: How to convert Excel to text in Python?
A: Converting Excel to text typically means extracting cell values and saving them as CSV or TXT. Using libraries like Spire.XLS or pandas in Python, you can export Excel data into plain text formats easily. For more advanced output, check Advanced Conversion: Customize CSV Output in Python.
Conclusion
In this guide, you’ve learned effective ways to convert XLSX and XLS files to CSV using Python, including exporting entire workbooks or specific sheets, handling batch conversions, and restoring Excel files from CSV. You also gained insights on customizing CSV outputs by selecting precise cell ranges.
Whether you want to automate your Excel to CSV conversion in Python, process legacy Excel files, or streamline data workflows, Spire.XLS provides a robust, code-friendly solution without requiring Microsoft Excel.
Get a Free License for the Full Version
While the free version of Spire.XLS for Python covers basic Python Excel to CSV tasks, if you need the full features and enhanced performance, you can apply for a temporary free license of the full version. This lets you unlock all capabilities and simplify your Python Excel to CSV processing even further.
The Excel spreadsheet is extensively utilized for organizing, analyzing, and presenting data in a tabular format. The capacity to programmatically interact with Excel files holds great value as it facilitates automation and integration of Excel functionality within software applications. Specifically, knowing how to create new Excel documents, retrieve information from existing ones, and update or modify them as needed through code would be very helpful. This article will demonstrate how to create, read, or update Excel documents in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create an Excel Document in Python
- Read Data from a Worksheet in Python
- Update an Excel Document in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create an Excel Document in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers a variety of classes and interfaces that you can use to create and edit Excel documents. Here is a list of important classes, properties and methods involved in this article.
| Member | Description |
| Workbook class | Represents an Excel workbook model. |
| Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method | Adds a worksheet to workbook. |
| Workbook.SaveToFile() method | Saves the workbook to an Excel document. |
| Worksheet class | Represents a worksheet in a workbook. |
| Worksheet.Range property | Gets a specific cell or cell range from worksheet. |
| Worksheet.Range.Text property | Gets or sets the text value of a cell. |
| Worksheet.Rows property | Gets a collection of rows in worksheet. |
| CellRange class | Represents a cell or cell range in worksheet. |
The following are the steps to create an Excel document from scratch using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Add a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Write data to specific cells through Worksheet.Range.Text property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook()
# Remove default worksheets
wb.Worksheets.Clear()
# Add a worksheet and name it "Employee"
sheet = wb.Worksheets.Add("Employee")
# Merge the cells between A1 and G1
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Merge()
# Write data to A1 and apply formatting to it
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Basic Information of Employees of Huanyu Automobile Company"
sheet.Range["A1"].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1"].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Font.Size = 13
# Set row height of the first row
sheet.Rows[0].RowHeight = 30
# Write data to specific cells
sheet.Range["A2"].Text = "Name"
sheet.Range["B2"].Text = "Gender"
sheet.Range["C2"].Text = "Birth Date"
sheet.Range["D2"].Text = "Educational Background"
sheet.Range["E2"].Text = "Contact Number"
sheet.Range["F2"].Text = "Position"
sheet.Range["G2"].Text = "ID"
sheet.Range["A3"].Text = "Allen"
sheet.Range["B3"].Text = "Male"
sheet.Range["C3"].Text = "1990-02-10"
sheet.Range["D3"].Text = "Bachelor"
sheet.Range["E3"].Text = "24756854"
sheet.Range["F3"].Text = "Mechanic"
sheet.Range["G3"].Text = "0021"
sheet.Range["A4"].Text = "Patrick"
sheet.Range["B4"].Text = "Male"
sheet.Range["C4"].Text = "1985-06-08"
sheet.Range["D4"].Text = "Master"
sheet.Range["E4"].Text = "59863247"
sheet.Range["F4"].Text = "Mechanic"
sheet.Range["G4"].Text = "0022"
sheet.Range["A5"].Text = "Jenna"
sheet.Range["B5"].Text = "Female"
sheet.Range["C5"].Text = "1989-11-25"
sheet.Range["D5"].Text = "Bachelor"
sheet.Range["E5"].Text = "79540352"
sheet.Range["F5"].Text = "Sales"
sheet.Range["G5"].Text = "0023"
sheet.Range["A6"].Text = "Tommy"
sheet.Range["B6"].Text = "Male"
sheet.Range["C6"].Text = "1988-04-16"
sheet.Range["D6"].Text = "Master"
sheet.Range["E6"].Text = "52014060"
sheet.Range["F6"].Text = "Mechanic"
sheet.Range["G6"].Text = "0024"
sheet.Range["A7"].Text = "Christina"
sheet.Range["B7"].Text = "Female"
sheet.Range["C7"].Text = "1998-01-21"
sheet.Range["D7"].Text = "Bachelor"
sheet.Range["E7"].Text = "35401489"
sheet.Range["F7"].Text = "HR"
sheet.Range["G7"].Text = "0025"
# Set row height of a range
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].RowHeight = 15
# Set column width
sheet.SetColumnWidth(3, 15)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(4, 21)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(5, 15)
# Set border style of a range
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium)
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].BorderInside(LineStyleType.Thin)
sheet.Range["A2:G2"].BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium)
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].Borders.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Black
# Save to a .xlsx file
wb.SaveToFile("output/NewSpreadsheet.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
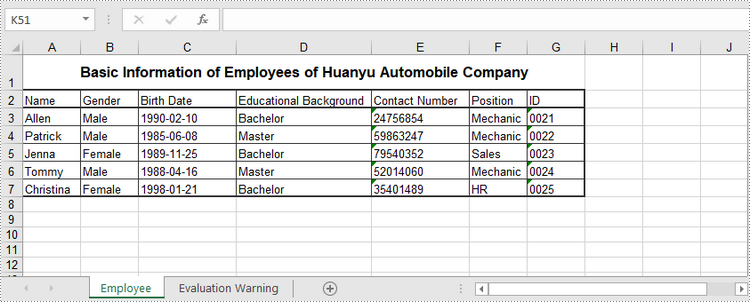
Read Data from a Worksheet in Python
The Worksheet.Range.Value property returns number value or text value of a cell as a string. To get data of a whole worksheet or a cell range, loop through the cells within it. The following are the steps to get data of a worksheet using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the cell range contain data though Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Iterate through the rows and columns to get cells within the range, and return the value of each cell through CellRange.Value property.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook()
# Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\NewSpreadsheet.xlsx");
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]
# Get the cell range containing data
locatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Iterate through the rows
for i in range(len(sheet.Rows)):
# Iterate through the columns
for j in range(len(locatedRange.Rows[i].Columns)):
# Get data of a specific cell
print(locatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value + " ", end='')
print("")

Update an Excel Document in Python
To change the value of a certain cell, just re-assign a value to it through Worksheet.Range.Value property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Change the value of a particular cell though Worksheet.Range.Value property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook();
# Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\NewSpreadsheet.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]
# Change the value of a specific cell
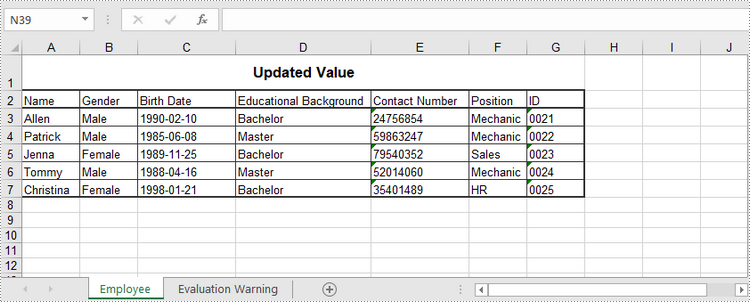
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Updated Value"
# Save to file
wb.SaveToFile("output/Updated.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Converting Excel files to PDF format can be a useful way to share and distribute spreadsheets, especially if you want to ensure that the formatting and layout of the file remains consistent across different devices and software. In addition, PDFs often appear more polished and professional than Excel files, making them a popular choice for official reports, presentations, and other business documents. In this article, you will learn how to convert Excel to PDF in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
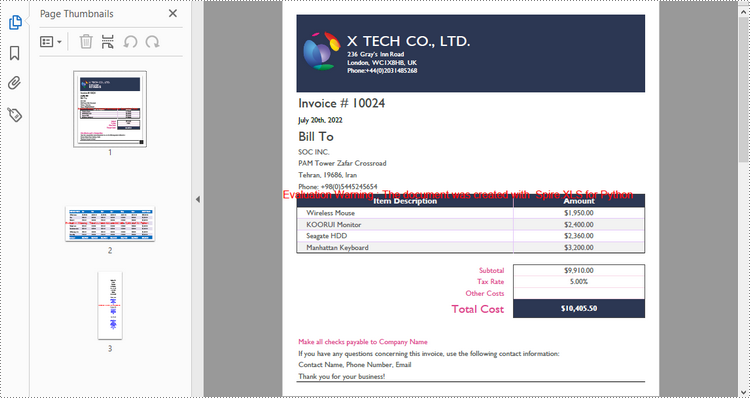
Convert a Whole Excel Document to PDF in Python
The Workbook.SaveToFile() method is used to convert a complete Excel document into a single PDF file. Once the conversion is done, each worksheet will appear as a separate page in the resultant PDF file. To control the conversion settings, use the Workbook.ConverterSetting property.
The following are the detailed steps to convert an Excel document to a PDF file in Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the margins of every worksheet through Worksheet.PageSetup property, which will later become the blank edges of the generated PDF.
- Set the Excel to PDF conversion options through the properties under Workbook.ConverterSetting object.
- Convert the whole Excel document to PDF using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx")
# Iterate through the worksheets in the workbook
for sheet in workbook.Worksheets:
# Get the PageSetup object
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set page margins
pageSetup.TopMargin = 0.3
pageSetup.BottomMargin = 0.3
pageSetup.LeftMargin = 0.3
pageSetup.RightMargin = 0.3
# Set worksheet to fit to page when converting
workbook.ConverterSetting.SheetFitToPage = True
# Convert to PDF file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ToPdf.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
workbook.Dispose()
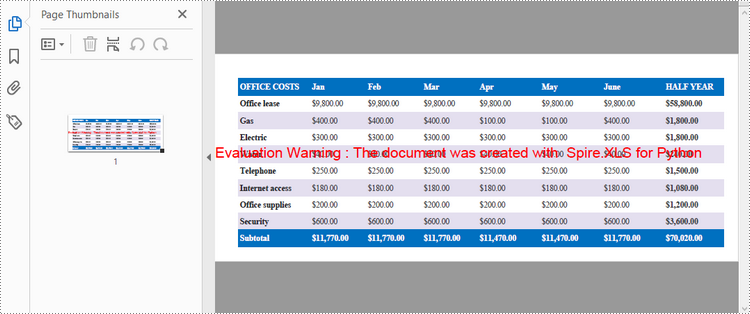
Convert a Particular Worksheet to PDF in Python
The Worksheet.SaveToPdf() method is used to convert a specific worksheet into a PDF document. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a particular worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set the margins of the worksheet through Worksheet.PageSetup property, which will later become the blank edges of the generated PDF.
- Set the Excel to PDF conversion options through the properties under Workbook.ConverterSetting object.
- Convert the worksheet to PDF using Worksheet.SaveToPdf() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.xlsx")
# Get a particular worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the PageSetup object
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set page margins
pageSetup.TopMargin = 0.3
pageSetup.BottomMargin = 0.3
pageSetup.LeftMargin = 0.3
pageSetup.RightMargin = 0.3
# Set worksheet to fit to page when converting
workbook.ConverterSetting.SheetFitToPage = True
# Convert the worksheet to PDF file
sheet.SaveToPdf("output/WorksheetToPdf.pdf")
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
