In development, reading CSV files in Python is a common task in data processing, analytics, and backend integration. While Python offers built-in modules like csv and pandas for handling CSV files, Spire.XLS for Python provides a powerful, feature-rich alternative for working with CSV and Excel files programmatically.
In this article, you’ll learn how to use Python to read CSV files, from basic CSV parsing to advanced techniques.
- Getting Started with Spire.XLS for Python
- Basic Example: Read a CSV in Python
- Advanced CSV Reading Techniques
- Conclusion
Getting Started with Spire.XLS for Python
Spire.XLS for Python is a feature-rich library for processing Excel and CSV files. Unlike basic CSV parsers in Python, it offers advanced capabilities such as:
- Simple API to load, read, and manipulate CSV data.
- Reading/writing CSV files with support for custom delimiters.
- Converting CSV files to Excel formats (XLSX, XLS) and vice versa.
These features make Spire.XLS ideal for data analysts, developers, and anyone working with structured data in CSV format.
Install via pip
Before getting started, install the library via pip. It works with Python 3.6+ on Windows, macOS, and Linux:
pip install Spire.XLS
Basic Example: Read a CSV in Python
Let’s start with a simple example: parsing a CSV file and extracting its data. Suppose we have a CSV file named “input.csv” with the following content:
Name,Age,City,Salary
Alice,30,New York,75000
Bob,28,Los Angeles,68000
Charlie,35,San Francisco,90000
Python Code to Read the CSV File
Here’s how to load and get data from the CSV file with Python:
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a CSV file
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.csv", ",", 1, 1)
# Get the first worksheet (CSV files are loaded as a single sheet)
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the number of rows and columns with data
row_count = worksheet.LastRow
col_count = worksheet.LastColumn
# Iterate through rows and columns to print data
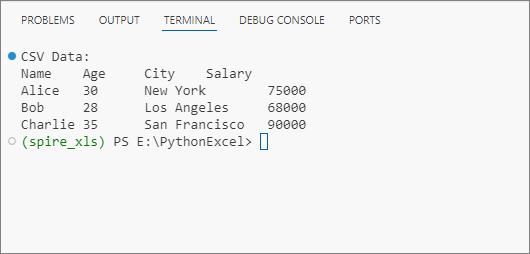
print("CSV Data:")
for row in range(row_count):
for col in range(col_count):
# Get cell value
cell_value = worksheet.Range[row+1, col+1].Value
print(cell_value, end="\t")
print() # New line after each row
# Close the workbook
workbook.Dispose()
Explanation:
-
Workbook Initialization: The Workbook class is the core object for handling Excel files.
-
Load CSV File: LoadFromFile() imports the CSV data. Its parameters are:
- fileName: The CSV file to read.
- separator: Specified delimiter (e.g., “,”).
- row/column: The starting row/column index.
-
Access Worksheet: The CSV data is loaded into the first worksheet.
-
Read Data: Iterate through rows and columns to extract cell values via worksheet.Range[].Value.
Output: Get data from a CSV file and print in a tabular format.
Advanced CSV Reading Techniques
1. Read CSV with Custom Delimiters
Not all CSVs use commas. If your CSV file uses a different delimiter (e.g., ;), specify it during loading:
# Load a CSV file
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.csv", ";", 1, 1)
2. Skip Header Rows
If your CSV has headers, skip them by adjusting the row iteration to start from the second row instead of the first.
for row in range(1, row_count):
for col in range(col_count):
# Get cell value (row+1 because Spire.XLS uses 1-based indexing)
cell_value = worksheet.Range[row+1, col+1].Value
print(cell_value, end="\t")
3. Convert CSV to Excel in Python
One of the most powerful features of Spire.XLS is the ability to convert a CSV file into a native Excel format effortlessly. For example, you can read a CSV and then:
- Apply Excel formatting (e.g., set cell colors, borders).
- Create charts (e.g., a bar chart for sales by region).
- Save the data as an Excel file (.xlsx) for sharing.
Code Example: Convert CSV to Excel (XLSX) in Python – Single & Batch
Conclusion
Reading CSV files in Python with Spire.XLS simplifies both basic and advanced data processing tasks. Whether you need to extract CSV data, convert it to Excel, or handle advanced scenarios like custom delimiters, the examples outlined in this guide enables you to implement robust CSV reading capabilities in your projects with minimal effort.
Try the examples above, and explore the online documentation for more advanced features!