Spire.Presentation for Java 10.8.0 enhances the conversion from PPTX to PDF
We’re glad to announce the release of Spire.Presentation for Java 10.8.0. This version optimizes the memory usage and processing time when converting PPTX to PDF, while also fixing several known issues. More details are provided below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Optimization | SPIREPPT-2896 | Optimized memory usage and processing time when converting PPTX to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2877 | Fixed the issue where adding a LaTeX formula resulted in incorrect rendering. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2890 | Fixed the issue where adding a blank paragraph caused incorrect shape height. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2907 | Fixed the issue where converting ODP to PDF caused the program to throw a "StackOverflowError". |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2910 | Fixed the issue where text was lost when converting PPTX to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2920 SPIREPPT-2923 | Fixed the issue where chart data was incorrect when converting slides to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2931 | Fixed the issue where adding the formula "\to" caused the program to throw a "NullPointerException". |
Spire.Doc 13.8.1 supports comparing whether two list levels are consistent
We're pleased to announce the release of Spire.Doc 13.8.1. This version supports comparing whether two list levels are consistent and setting or deleting the picture bullet. Besides, it has also made some adjustments to the properties and methods related to the lists in Word. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| New feature | - | Added 'ListLevel.Equals' to compare whether two ListLevels are consistent.
// Create a new Document object. Document document = new Document(); //Create list style 1 ListStyle listStyle_1 = document.Styles.Add(ListType.Bulleted, "bulletList"); ListLevelCollection Levels_1 = listStyle_1.ListRef.Levels; ListLevel L0 = Levels_1[0]; ListLevel L1 = Levels_1[1]; ListLevel L2 = Levels_1[2]; ListStyle listStyle_2 = document.Styles.Add(ListType.Bulleted, "bulletList"); ListLevelCollection Levels_2 = listStyle_2.ListRef.Levels; ListLevel l0 = Levels_2[0]; ListLevel l1 = Levels_2[1]; ListLevel l2 = Levels_2[2]; //Create list style 1 L0.ParagraphFormat.LineSpacing = 10 * 1.5f; L1.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 9; L1.IsLegalStyleNumbering = true; L1.PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic; L1.FollowCharacter = FollowCharacterType.Nothing; L1.BulletCharacter = "\x006e"; L1.NumberAlignment = ListNumberAlignment.Left; L1.NumberPosition = -10; L1.TabSpaceAfter = 0.5f; L1.TextPosition = 0.5f; L1.StartAt = 4; L1.NumberSufix = "Chapter"; L1.NumberPrefix = "No."; L1.NoRestartByHigher = false; L1.UsePrevLevelPattern = false; L2.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"; // Create list style 2 l0.ParagraphFormat.LineSpacing = 10 * 1.5f; l1.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 9; l1.IsLegalStyleNumbering = true; l1.PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic; l1.FollowCharacter = FollowCharacterType.Nothing; l1.BulletCharacter = "\x006e"; l1.NumberAlignment = ListNumberAlignment.Left; l1.NumberPosition = -10; l1.TabSpaceAfter = 0.5f; l1.TextPosition = 0.5f; l1.StartAt = 4; l1.NumberSufix = "Chapter"; l1.NumberPrefix = "No."; l1.NoRestartByHigher = false; l1.UsePrevLevelPattern = false; l1.CreatePictureBullet(); l2.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"; //Add 'ListLevel.Equals' to compare whether two ListLevels are consistent. bool r0 = L0.Equals(l0); bool r1 = L1.Equals(l1); bool r2 = L2.Equals(l2); |
| New feature | - | Supported setting or deleting the picture bullet.
// Create a new Document object.
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section sec = document.AddSection();
Spire.Doc.Documents.Paragraph paragraph = sec.AddParagraph();
//Create list style
ListStyle listStyle = document.Styles.Add(ListType.Bulleted, "bulletList");
ListLevelCollection Levels = listStyle.ListRef.Levels;
Levels[0].CreatePictureBullet();
Levels[0].PictureBullet.LoadImage(@"logo.jpg");
Levels[1].CreatePictureBullet();
Levels[1].PictureBullet.LoadImage(@"py.jpg");
//Add paragraph and apply the list style
paragraph = sec.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("List Item 1");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle(listStyle);
paragraph = sec.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("List Item 1.1");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle(listStyle);
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1;
//DeletePictureBullet
Levels[0].DeletePictureBullet();
//Save doc file.
document.SaveToFile(@"out.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
document.Close();
|
| Optimization | - | Deprecated the “Document.ListStyles” and replaced it with “Document.ListReferences”. Added new methods in “Document.ListReferences” to create ListDefinitionReference classes.
// Create a new Document object.
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section sec = document.AddSection();
Spire.Doc.Documents.Paragraph paragraph = sec.AddParagraph();
//Create listTemplate1
ListTemplate template = ListTemplate.BulletDefault;
ListDefinitionReference listRef = document.ListReferences.Add(template);
//Create listTemplate2
ListTemplate template1 = ListTemplate.NumberDefault;
ListDefinitionReference listRef1 = document.ListReferences.Add(template1);
listRef1.Levels[2].StartAt = 4;
int levelcount = listRef.Levels.Count;
//Add paragraph and apply the list style
paragraph = sec.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("List Item 1");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyListRef(listRef, 1);
paragraph = sec.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("List Item 2");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyListRef(listRef, 2);
//Add paragraph and apply the list style
paragraph = sec.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("List Item 3");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyListRef(listRef1, 1);
paragraph = sec.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("List Item 4");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyListRef(listRef1, 2);
//Save doc file.
document.SaveToFile("out.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
document.Close();
|
| Optimization | - | The public constructor for “ListStyle” has been removed. “ListStyle” objects are now managed within the “Document.Styles” collection and should be created using the “StyleCollection.Add(ListType listType, string name)” method.
ListStyle listStyle = document.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered, "levelstyle"); listStyle.IsCustomStyle = true; listStyle.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Trebuchet MS"; ListLevelCollection levels = listStyle.ListRef.Levels; levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic; levels[0].StartAt = 1; levels[0].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Trebuchet MS"; |
| Optimization | - | Changed to apply the list style using "ListFormat.AppleStyle" or "ListFormat.AppleListRef(ListDefinitionReference list, int leverNode)" method. |
| Optimization | - | Changed the property “ListFormat.CurrentListStyle” to “ListFormat.CurrentListRef”. |
| Optimization | - | Removed “ListFormat.IsRistNumbering” and “ListFormat.CustomStyleName”. |
| Optimization | - | Changed to set the List “starting number” using the following method.
ListStyle numberList2 = document.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered, "Numbered2"); ListLevelCollection Levels = numberList2.ListRef.Levels; Levels[0].StartAt = 10; |
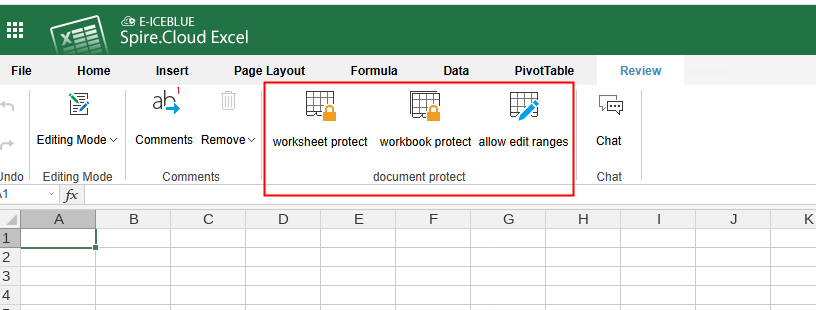
Spire.Cloud 10.7.10 supports the "document protect" function for Excel documents
We are excited to announce the release of Spire.Cloud 10.7.10. The latest version supports the "document protect" function for Excel documents. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | - | Support the "document protect" function for Excel documents. |
Spire.Office 10.7.0 is released
We are excited to announce the release of Spire.Office 10.7.0. In this version, Spire.Doc supports multiple new features, such as loading EPUB files for processing and creating combination charts; Spire.PDF supports extracting custom PDF data values and enhances the PDF-to-Excel conversion; Spire.XLS and Spire.Presentation support loading Markdown-format documents. Besides, a lot of known issues are fixed successfully in this version. More details are listed below.
In this version, the most recent versions of Spire.Doc, Spire.PDF, Spire.XLS, Spire.Presentation, Spire.Email, Spire.DocViewer, Spire.PDFViewer, Spire.Spreadsheet, Spire.OfficeViewer, Spire.DataExport, Spire.Barcode are included.
DLL Versions:
- Spire.Doc.dll v13.7.14
- Spire.Pdf.dll v11.7.14
- Spire.XLS.dll v15.7.8
- Spire.Presentation.dll v10.7.7
- Spire.Barcode.dll v7.3.7
- Spire.Email.dll v6.6.3
- Spire.DocViewer.Forms.dll v8.9.1
- Spire.PdfViewer.Asp.dll v8.1.3
- Spire.PdfViewer.Forms.dll v8.1.3
- Spire.Spreadsheet.dll v7.5.2
- Spire.OfficeViewer.Forms.dll v8.8.0
- Spire.DataExport.dll 4.9.0
- Spire.DataExport.ResourceMgr.dll v2.1.0
Here is a list of changes made in this release
Spire.Doc
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREDOC-3144 | Supports loading EPUB files for processing.
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("in.epub", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.EPub);
doc.SaveToFile(@"out.docx", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.Docx);
doc.SaveToFile(@"out.pdf", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.PDF);
|
| New feature | SPIREDOC-11179 | Supports converting Word to PDF/UA-1 format.
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("in.docx");
ToPdfParameterList list = new ToPdfParameterList();
list.PdfConformanceLevel = PdfConformanceLevel.Pdf_UA1;
doc.SaveToFile(@"out.pdf", list);
|
| New feature | SPIREDOC-11345 | Adds new configuration parameters to enhance the performance and output quality of Word-to-Markdown conversion. |
| New feature | SPIREDOC-9977 SPIREDOC-10012 | Supports creating combination charts.
Document doc = new Document();
Paragraph paragraph = doc.AddSection().AddParagraph();
Chart chart = paragraph.AppendChart(ChartType.Column, 450, 300).Chart;
//Modify 'Series 3' to a line chart and display it on the secondary axis
chart.ChangeSeriesType("Series 3", ChartSeriesType.Line, true);
Console.WriteLine(chart.Series[2].ChartType);
doc.SaveToFile("ComboChart.docx");
|
| New feature | - | Adds the ‘setDefaultSubstitutionFontName()’ method to specify default substitution fonts.
Document document = new Document();
//Set default replacement font
doc.DefaultSubstitutionFontName = "Arial";
Section sec = doc.AddSection();
Paragraph para = sec.AddParagraph();
TextRange tr = para.AppendText("test");
//The system does not have this font
tr.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Helvetica";
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PDF);
doc.Close();
|
| New feature | - | Adds the ‘StructureDocumentTag.RemoveSelfOnly()’ method to remove SDT tags while retaining their contents.
// Process inline structure tags
List tagInlines = structureTags.getM_tagInlines();
for (int i = 0; i < tagInlines.Count; i++)
{
tagInlines[i].RemoveSelfOnly();
}
// Process other structure tags
List tags = structureTags.getM_tags();
for (int i = 0; i < tags.Count; i++)
{
tags[i].RemoveSelfOnly();
}
// Process StructureDocumentTagRow
List rowtags = structureTags.getM_rowtags();
for (int i = 0; i < rowtags.Count; i++)
{
rowtags[i].RemoveSelfOnly();
}
// Process StructureDocumentTagCell
List celltags = structureTags.getM_celltags();
for (int i = 0; i < celltags.Count; i++)
{
celltags[i].RemoveSelfOnly();
}
|
| New feature | - | Supports setting image compression methods when converting Word to PDF.
Document document = new Document(); document.LoadFromFile(@"Sample.docx"); ToPdfParameterList para = new ToPdfParameterList(); para.PdfImageCompression = Spire.Doc.Export.PdfImageCompression.Jpeg; document.SaveToFile(outputFile,para); |
| New feature | - | Supports inserting formulas into Word documents using OMML code.
Document document = new Document();
Section section = doc.AddSection();
foreach (string ommlCode in OmmlCodes)
{
OfficeMath officeMath = new OfficeMath(doc);
officeMath.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 14f;
officeMath.FromOMMLCode(ommlCode);
section.AddParagraph().ChildObjects.Add(officeMath);
}
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2013);
doc.Dispose();
|
| New feature | - | Supports converting math formulas to LaTeX code.
Document document = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile);
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// Iterate through sections in the document
foreach (Section section in doc.Sections)
{
// Iterate through paragraphs in each section
foreach (Paragraph par in section.Body.Paragraphs)
{
// Iterate through child objects in each paragraph
foreach (DocumentObject obj in par.ChildObjects)
{
// Check if the object is an OfficeMath equation
OfficeMath omath = obj as OfficeMath;
if (omath == null) continue;
// Convert OfficeMath equation to LaTex code
string mathml = omath.ToLaTexMathCode();
// Append MathML code to the StringBuilder
stringBuilder.Append("LaTeX code" + mathml);
stringBuilder.Append("\r\n");
}
}
}
// Write the LaTex code to a text file
File.WriteAllText(outputFile, stringBuilder.ToString())
|
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11245 | Fixed an issue where header images were distorted When converting Doc to PDF. |
Spire.PDF
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREPDF-7505 | Adds GetCustomApplicationData() to support extracting custom PDF data values.
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument(inputFile); PdfApplicationData appplicationDataObject = doc.GetCustomApplicationData(); Dictionary privateDataObject = appplicationDataObject.Private as Dictionary; string privateData = privateDataObject["WinsertPrivateCatalogData"] as string; |
| New feature | SPIREPDF-7430 SPIREPDF-7427 | Supports integrating PaddleOCRSharp in XlsxLineLayoutOptions.TextRecognizer to enhance the PDF-to-Excel conversion.
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.LoadFromFile("in.pdf");
XlsxLineLayoutOptions options = new XlsxLineLayoutOptions(false, false, false, true);
options.TextRecognizer = new TextRecognizer();
doc.ConvertOptions.SetPdfToXlsxOptions(options);
doc.SaveToFile("out.xlsx", Spire.Pdf.FileFormat.XLSX);
// niget install PaddleOCRSharp lib
using PaddleOCRSharp;
using Spire.Pdf.Conversion;
public class TextRecognizer : ITextRecognizer
{
private static readonly PaddleOCREngine _engine;
static TextRecognizer()
{ _engine = new PaddleOCREngine(null, “”); }
public string RecognizeGlyph(Stream glyphImageStream)
{
var image = new System.Drawing.Bitmap(glyphImageStream);
// paint glyph in image center
var fixImage = new System.Drawing.Bitmap(160, 240);
using (Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(fixImage))
{ g.DrawImage(image, new RectangleF(20, 20, fixImage.Width - 40, fixImage.Height - 40), new RectangleF(0, 0, image.Width, image.Height), GraphicsUnit.Pixel); }
var unicodeResult = _engine.DetectText(fixImage).Text;
return unicodeResult;
}
}
|
| Bug | SPIREPDF-5089 | Optimizes the time consumption of converting PDF to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-6354 | Fixes the issue where Thai text displayed incorrectly when converting PDF to PDF/A-1A. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-6689 | Fixes the incorrect transparency effect when highlighting PDF text. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7359 | Fixes incorrect rendering when drawing images to PDF pages. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7459 | Fixes the incorrect Flatten effect for PDF form fields. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7486 | Fixes the "ArgumentException" thrown during PDF compression. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7495 SPIREPDF-7561 | Fixes the "NullReferenceException" thrown when converting PDF to TIFF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7529 | Fixes shadow issues in printed PDF content. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7570 | Fixes Adobe errors when converting OFD to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7571 | Fixes the "InvalidOperationException" thrown when defining fonts. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7579 | Fixes the "NullReferenceException" thrown when converting PDF to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7581 | Fixes the "System.Exception" thrown when canceling print operations in netstandard DLL. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7589 | Fixes the "Value cannot be null" error when merging PDF files. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-6991 | Fixed the issue where Arabic text did not display correctly when converting an EMF file to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-2800 | Fixes the issue that the content was incorrect when converting XPS to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-3727 SPIREPDF-3984 SPIREPDF-5085 | Optimizes performance for PDF-to-image conversion to reduce processing time. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-3818 | Improves PDF printing performance. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7004 | Fixes the issue where content was missing during PDF-to-image conversion. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7043 | Fixes the issue that the content was incorrect when converting PDF to PDF/A. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7399 | Fixes the issue where PDF content could not be extracted. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7574 SPIREPDF-7575 SPIREPDF-7576 SPIREPDF-7577 SPIREPDF-7578 | Fixes the issue that the content was incorrect when converting OFD to PDF or images. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7598 | Fixes the issue that duplicate "Indirect reference" entries were caused by Attachments.Add(). |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7609 | Fixes the issue where the program threw System.NullReferenceException error when releasing pdfTextFinder objects. |
Spire.XLS
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | — | Adds the LoadFromMarkdown() method to support for loading Markdown-format documents.
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromMarkdown("test.md");
wb.SaveToFile("out.pdf", FileFormat.PDF);
wb.SaveToFile("out.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
|
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5820 | Fixes the issue where checkboxes were displayed incorrectly after converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5833 | Fixes the issue where the AGGREGATE formula was calculated incorrectly. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5858 | Fixes the issue where content overlapped after converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5860 | Fixes the issue where text wrapping was incorrect after converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5832 | Fixed the issue where saving an Excel file to PDF/A3B was incorrect. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5862 | Fixes the issue where the Ungroup effect was incorrect. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5863 | Fixes the issue where page breaks were inconsistent after converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5868 | Fixes the issue where formula calculation returned "#VALUE!". |
Spire.Prensentation
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | — | Supports loading Markdown files.
Presentation pt = new Presentation(); pt.LoadFromFile(inputFilePath, FileFormat.Markdown); pt.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2013); |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2849 | Fixes the issue that files were corrupted when opening presentations containing copied slides. |
Spire.Doc for Java 13.7.6 supports the "Two Lines in One" function
We’re pleased to announce the release of Spire.Doc for Java 13.7.6. The latest version supports the "Two Lines in One" function, which enhances the conversion from Word to PDF. Furthermore, some known bugs are fixed successfully in the new version, such as the issue where accepting revisions did not affect the content in content controls. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| New feature | SPIREDOC-11113 SPIREDOC-11320 SPIREDOC-11338 | Supports the "Two Lines in One" function. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11276 | Fixes the issue where accepting revisions did not affect the content in content controls. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11314 | Fixes the issue where converting Word to PDF caused a "NullPointerException" to be thrown. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11325 | Fixes the issue where retrieving Word document properties was incorrect. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11333 | Fixes the issue where converting Word to Markdown resulted in disorganized bullet points. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11360 | Fixes the issue where converting Word to PDF caused vertically oriented text in tables to be incorrect. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11364 | Fixes the issue where replacing bookmark content caused an "IllegalArgumentException" to be thrown. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11389 | Fixes the issue where loading a Word document caused an "IllegalArgumentException: List level must be less than 8 and greater than 0" to be thrown. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11390 | Fixes the issue where accepting revisions did not produce the correct effect. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11398 | Fixes the issue where using "pictureWatermark.setPicture(bufferedImage)" caused a "java.lang.NullPointerException" to be thrown. |
Spire.OCR for Java 2.1.1 adds support for Linux-ARM platform
We’re excited to announce the release of Spire.OCR for Java 2.1.1. This version introduces support for Linux-ARM platform and enables text output that matches the original image layout. In addition, this update includes several bug fixes. More details are provided below.
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | - | Added support for Linux-ARM platform. |
| New feature | SPIREOCR-84 | Added support for automatically rotating images when necessary.
ConfigureOptions configureOptions = new ConfigureOptions(); configureOptions.setAutoRotate(true); |
| New feature | SPIREOCR-107 | Added support for preserving the original image layout in text output.
VisualTextAligner visualTextAligner = new VisualTextAligner(scanner.getText()); String scannedText = visualTextAligner.toString(); |
| Bug | SPIREOCR-103 | Fixed the issue where the cleanup of the temporary folder "temp" was not functioning correctly. |
| Bug | SPIREOCR-104 | Fixed the issue where an "Error occurred during ConfigureDependencies" message appeared when the path contained Chinese characters. |
| Bug | SPIREOCR-108 | Fixed the issue where the content extraction order was incorrect. |
How to Convert HTML to Word in Java (Complete Guide)

Converting HTML to Word in Java is essential for developers building reporting tools, content management systems, and enterprise applications. While HTML powers web content, Word documents offer professional formatting, offline accessibility, and easy editing, making them ideal for reports, invoices, contracts, and formal submissions.
This comprehensive guide demonstrates how to use Java and Spire.Doc for Java to convert HTML to Word. It covers everything from converting HTML files and strings, batch processing multiple files, and preserving formatting and images.
Table of Contents
- Why Convert HTML to Word in Java
- Set Up Spire.Doc for Java
- Convert HTML File to Word in Java
- Convert HTML String to Word in Java
- Batch Conversion of Multiple HTML Files to Word in Java
- Best Practices for HTML to Word Conversion
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Convert HTML to Word in Java?
Converting HTML to Word offers several advantages:
- Flexible editing – Add comments, track changes, and review content easily.
- Consistent formatting – Preserve layouts, fonts, and styles across documents.
- Professional appearance – DOCX files look polished and ready to share.
- Offline access – Word files can be opened without an internet connection.
- Integration – Word is widely supported across tools and industries.
Common use cases: exporting HTML reports from web apps, archiving dynamic content in editable formats, and generating formal reports, invoices, or contracts.
Set Up Spire.Doc for Java
Spire.Doc for Java is a robust library that enables developers to create Word documents, edit existing Word documents, and read and convert Word documents in Java without requiring Microsoft Word to be installed.
Before you can convert HTML content into Word documents, it’s essential to properly install and configure Spire.Doc for Java in your development environment.
1. Java Version Requirement
Ensure that your development environment is running Java 6 (JDK 1.6) or a higher version.
2. Installation
Option 1: Using Maven
For projects managed with Maven, you can add the repository and dependency to your pom.xml:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
For a step-by-step guide on Maven installation and configuration, refer to our article**:** How to Install Spire Series Products for Java from Maven Repository.
Option 2. Manual JAR Installation
For projects without Maven, you can manually add the library:
- Download Spire.Doc.jar from the official website.
- Add it to your project classpath.
Convert HTML File to Word in Java
If you already have an existing HTML file, converting it into a Word document is straightforward and efficient. This method is ideal for situations where HTML reports, templates, or web content need to be transformed into professionally formatted, editable Word files.
By using Spire.Doc for Java, you can preserve the original layout, text formatting, tables, lists, images, and hyperlinks, ensuring that the converted document remains faithful to the source. The process is simple, requiring only a few lines of code while giving you full control over page settings and document structure.
Conversion Steps:
- Create a new Document object.
- Load the HTML file with loadFromFile().
- Adjust settings like page margins.
- Save the output as a Word document with saveToFile().
Example:
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.XHTMLValidationType;
public class ConvertHtmlFileToWord {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load an HTML file
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.html",
FileFormat.Html,
XHTMLValidationType.None);
// Adjust margins
Section section = document.getSections().get(0);
section.getPageSetup().getMargins().setAll(2);
// Save as Word file
document.saveToFile("output/FromHtmlFile.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Release resources
document.dispose();
System.out.println("HTML file successfully converted to Word!");
}
}
You may also be interested in: Java: Convert Word to HTML
Convert HTML String to Word in Java
In many real-world applications, HTML content is generated dynamically - whether it comes from user input, database records, or template engines. Converting these HTML strings directly into Word documents allows developers to create professional, editable reports, invoices, or documents on the fly without relying on pre-existing HTML files.
Using Spire.Doc for Java, you can render rich HTML content, including headings, lists, tables, images, hyperlinks, and more, directly into a Word document while preserving formatting and layout.
Conversion Steps:
- Create a new Document object.
- Add a section and adjust settings like page margins.
- Add a paragraph.
- Add the HTML string to the paragraph using appendHTML().
- Save the output as a Word document with saveToFile().
Example:
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
public class ConvertHtmlStringToWord {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Sample HTML string
String htmlString = "<h1>Java HTML to Word Conversion</h1>" +
"<p><b>Spire.Doc</b> allows you to convert HTML content into Word documents seamlessly. " +
"This includes support for headings, paragraphs, lists, tables, links, and images.</p>" +
"<h2>Features</h2>" +
"<ul>" +
"<li>Preserve text formatting such as <i>italic</i>, <u>underline</u>, and <b>bold</b></li>" +
"<li>Support for ordered and unordered lists</li>" +
"<li>Insert tables with multiple rows and columns</li>" +
"<li>Add hyperlinks and bookmarks</li>" +
"<li>Embed images from URLs or base64 strings</li>" +
"</ul>" +
"<h2>Example Table</h2>" +
"<table border='1' style='border-collapse:collapse;'>" +
"<tr><th>Item</th><th>Description</th><th>Quantity</th></tr>" +
"<tr><td>Notebook</td><td>Spire.Doc Java Guide</td><td>10</td></tr>" +
"<tr><td>Pen</td><td>Blue Ink</td><td>20</td></tr>" +
"<tr><td>Marker</td><td>Permanent Marker</td><td>5</td></tr>" +
"</table>" +
"<h2>Links and Images</h2>" +
"<p>Visit <a href='https://www.e-iceblue.com/'>E-iceblue Official Site</a> for more resources.</p>" +
"<p>Sample Image:</p>" +
"<img src='https://www.e-iceblue.com/images/intro_pic/Product_Logo/doc-j.png' alt='Product Logo' width='150' height='150'/>" +
"<h2>Conclusion</h2>" +
"<p>Using Spire.Doc, Java developers can easily generate Word documents from rich HTML content while preserving formatting and layout.</p>";
// Create a Document
Document document = new Document();
// Add section and paragraph
Section section = document.addSection();
section.getPageSetup().getMargins().setAll(72);
Paragraph paragraph = section.addParagraph();
// Render HTML string
paragraph.appendHTML(htmlString);
// Save as Word
document.saveToFile("output/FromHtmlString.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
document.dispose();
System.out.println("HTML string successfully converted to Word!");
}
}

Batch Conversion of Multiple HTML Files to Word in Java
Sometimes you may need to convert hundreds of HTML files into Word documents. Here’s how to batch process them in Java.
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.documents.XHTMLValidationType;
import java.io.File;
public class BatchConvertHtmlToWord {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File folder = new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\HtmlFiles");
for (File file : folder.listFiles()) {
if (file.getName().endsWith(".html") || file.getName().endsWith(".htm")) {
Document document = new Document();
document.loadFromFile(file.getAbsolutePath(), FileFormat.Html, XHTMLValidationType.None);
String outputPath = "output/" + file.getName().replace(".html", ".docx");
document.saveToFile(outputPath, FileFormat.Docx);
document.dispose();
System.out.println(file.getName() + " converted to Word!");
}
}
}
}
This approach is great for reporting systems where multiple HTML reports are generated daily.
Best Practices for HTML to Word Conversion
- Use Inline CSS for Reliable Styling
Inline CSS ensures that fonts, colors, and spacing are preserved during conversion. External stylesheets may not always render correctly, especially if they are not accessible at runtime. - Validate HTML Structure
Well-formed HTML with proper nesting and closed tags helps render tables, lists, and headings accurately. - Optimize Images
Use absolute URLs or embed images as base64. Resize large images to fit Word layouts and reduce file size. - Manage Resources in Batch Conversion
When processing multiple files, convert them one by one and call dispose() after each document to prevent memory issues. - Preserve Page Layouts
Set page margins, orientation, and paper size to ensure the Word document looks professional, especially for reports and formal documents.
Conclusion
Converting HTML to Word in Java is an essential feature for many enterprise applications. Using Spire.Doc for Java, you can:
- Convert HTML files into Word documents.
- Render HTML strings directly into DOCX.
- Handle batch processing for multiple files.
- Preserve images, tables, and styles with ease.
By following the examples and best practices above, you can integrate HTML to Word conversion seamlessly into your Java applications.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1. Can Java convert multiple HTML files into one Word document?
A1: Yes. Instead of saving each file separately, you can load multiple HTML contents into the same Document and then save it once.
Q2. How to preserve CSS styles during HTML to Word conversion?
A2: Inline CSS will be preserved; external stylesheets can also be applied if they’re accessible at run time.
Q3. Can I generate a Word document directly from a web page?
A3: Yes. You can fetch the HTML using an HTTP client in Java, then pass it into the conversion method.
Q4. What Word formats are supported for saving the converted document?
A4: You can save as DOCX, DOC, or other Word-compatible formats supported by Spire.Doc. DOCX is recommended for modern applications due to its compatibility and smaller file size.
E-iceblue has an 8-Day Spring Festival Holiday during 28/01/2025-04/02/2025
As the Chinese New Year approaches, our office will be closed from 28/01/2025 to 04/02/2025 (GMT+8:00).
During the holiday, your emails will be received as usual and urgent issues will be handled as soon as possible by the staff on-duty. Please note that standard support may be limited during this time, so we kindly ask for your understanding and patience if you do not receive an immediate response.
Note: Our purchase system is available 24/7 and will automatically send out license files once you have completed the online order and payment.
To get a temporary license to evaluate our product, please click "Request a Temporary License" on the download page. If there are any problems with the request, we will make it available when we return to work on February 05, 2025.
We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause and really appreciate your understanding and support.
Pease feel free to contact us via the following emails
- Support Team: support@e-iceblue.com
- Sales Team: sales@e-iceblue.com
Spire.Office 10.1.0 is released
We are excited to announce the release of Spire.Office 10.1.0. In this version, Spire.Doc supports checking and modifying hyperlinks for images and shapes; Spire.XLS supports the CSCH, RANDARRAY, COTH, SEQUENCE, EXPAND functions; Spire.Presentation supports obtaining the file name of embedded OLE objects; Spire.PDF enhances the conversion from XPS to PDF and PDF to PNG, HTML, SVG, OFD, XPS, and Excel. More details are listed below.
In this version, the most recent versions of Spire.Doc, Spire.XLS, Spire.Presentation, and Spire.PDF are included.
DLL Versions:
- Spire.Doc 13.1.4
- Spire.XLS 15.1.3
- Spire.Presentation 10.1.1
- Spire.PDF 11.1.0
- Spire.PDF 11.1.5
Here is a list of changes made in this release
Spire.Doc
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREDOC-10532 SPIREDOC-11019 |
Support judging and modifying hyperlinks for images and shapes.
foreach (Section section in doc.Sections)
{
foreach (Paragraph paragraph in section.Paragraphs)
{
foreach (DocumentObject documentObject in paragraph.ChildObjects)
{
if (documentObject is DocPicture)
{
DocPicture pic=documentObject as DocPicture;
if (pic.HasHyperlink)
{
pic.HRef = "";
}
}
if (documentObject is ShapeObject)
{
ShapeObject shape = documentObject as ShapeObject;
if (shape.HasHyperlink)
{
shape.HRef = "";
}
}
}
}
}
|
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10551 | Fixes the issue that the program threw “The given key ‘5’ was not present in the dictionary” exception when converting HTML documents to Word documents. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11022 | Fixes the issue that the obtained ListText of paragraphs was incorrect. |
Spire.XLS
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5542 | Supports the CSCH function |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5548 | Supports the RANDARRAY function. |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5621 | Supports the COTH function. |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5622 | Supports the SEQUENCE function. |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5627 | Supports the EXPAND function. |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5638 | Supports the CHOOSECOLS function. |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5639 | Supports the CHOOSEROWS function. |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5642 | Supports the DROP function. |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5656 | Support setting HyLink for XlsPrstGeomShape.
PrstGeomShapeCollection prstGeomShapeType = worksheet.PrstGeomShapes;
for (int i = 0; i < prstGeomShapeType.Count; i++)
{
XlsPrstGeomShape shape = (XlsPrstGeomShape)prstGeomShapeType[i];
shape.HyLink.Address = "https://www.baidu.com/";
}
|
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5570 | Fixes the issue that the charts were lost when converting XLSM to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5608 | Fixes the issue that the content was lost when converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5611 | Fixes the issue that setting ShowLeaderLines did not take effect. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5612 | Fixes the issue that the data bar colors were incorrect when converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5625 SPIREXLS-5647 |
Fixes the issue that the values were incorrect after calling the CalculateAllValue() method to calculate formula values. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5635 | Fixes the issue that setting the worksheet tab color to Color.Empty resulted in black. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5640 | Fixes the issue that the images were extracted incorrectly. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5657 | Fixes the issue that it failed to delete pivot fields in pivot tables. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5659 | Fixes the issue that the text orientation in shapes was reversed when converting Excel to PDF. |
Spire.Presentation
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREPPT-2658 | Supports obtaining the file name of embedded OLE objects.
IOleObject oleObject = shape as IOleObject; oleObject.EmbeddedFileName |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2652 | Fixes the issue that the program threw an exception "object reference not set to object instance" when loading PPTX documents. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2657 | Fixes the issue that underlines were discontinuous when converting PPTX to SVG. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2690 | Fixes the issue that content was lost when converting PPTX to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2692 | Fixes the issue that checkboxes were missed when converting PPTX to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2702 | Fixes the issue that the program threw an "Object reference not set to an instance of an object" exception when obtaining font names. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2703 | Fixes the issue that setting ”Shrink text on overflow“ resulted in incorrect format. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2705 | Fixes the issue that setting "Resize shape to fit text" did not take effect. |
Spire.PDF
| Category | ID | Description |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7162 | Fixes the issue that multi-threaded PDF text extraction error happened. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7201 | Fixes the issue that there were incorrect links when converting XPS to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7235 | Fixes the issue that extracting incorrect content from PDF tables. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7246 | Fixes the issue that some content turned black when converting PDF to PNG. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7248 | Fixes the issue that HTML documents were too large when converting PDF to HTML. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7250 | Fixes the issue that annotation content wasn't displayed when converting PDF to XPS. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7264 | Fixes the issue that content was lost when converting PDF to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7279 SPIREPDF-7301 |
Fixes the issue that there were incorrect fonts when converting PDF to SVG. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7280 | Fixes the issue that character spaces were missed when converting XPS to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7286 | Fixes the issue that the program threw an "Object reference not set to an instance of an object." exception when loading PDF documents. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7288 | Fixes the issue that seal content was cut when converting PDF to OFD. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7289 | Fixes the issue that the program threw an "Object reference not set to an instance of an object." exception when converting PDF to grayscale PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7051 | Fixes the issue that the content was incorrect when printing PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7159 SPIREPDF-7294 |
Fixes the issue that replacing text caused some text to be lost. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7211 | Fixes the issue that the program suspended when saving PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7221 | Fixes the issue that modifying the value of text fields consumed a long time. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7249 | Fixes the issue that some Chinese characters were garbled after converting PDF to XPS. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7275 | Fixes the issue that converting PDF to grayscale PDF consumed a long time. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7278 | Fixes the issue that the result was incorrect when converting PDF to Excel. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7312 | Fixes the issue that the value of the field disappeared when the mouse entered the field after filling the text box field. |
Java: Extract Text from Images Using the New Model of Spire.OCR for Java
Spire.OCR for Java offers developers a new model for extracting text from images. In this article, we will demonstrate how to extract text from images in Java using the new model of Spire.OCR for Java.
The detailed steps are as follows.
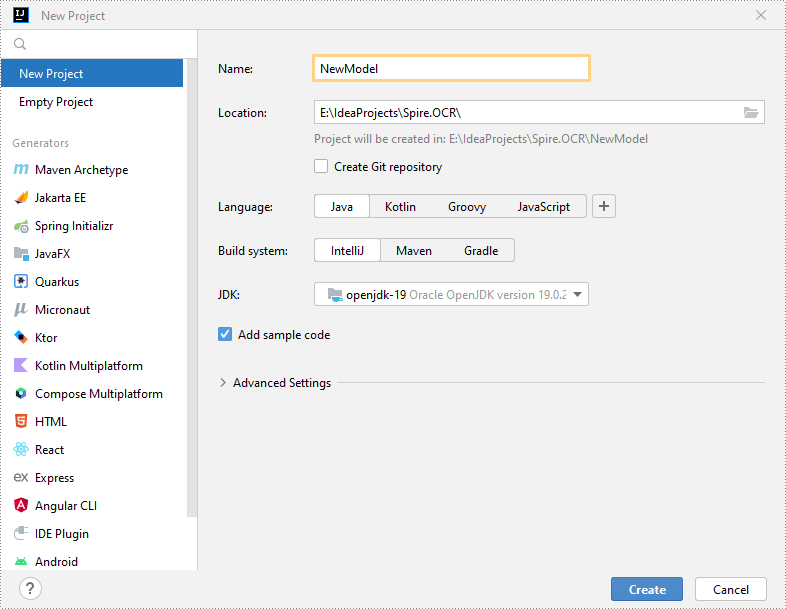
Step 1: Create a Java Project in IntelliJ IDEA.
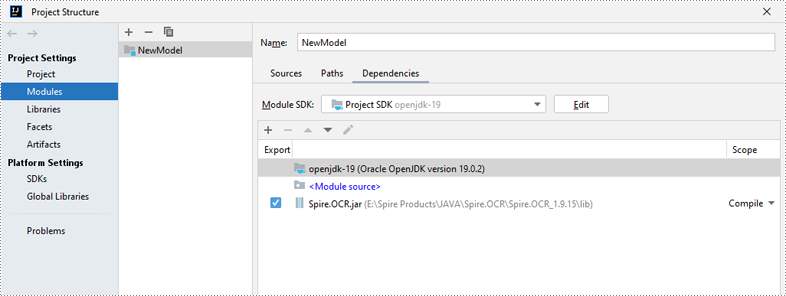
Step 2: Add Spire.OCR.jar to Your Project.
Option 1: Install Spire.OCR for Java via Maven.
If you're using Maven, you can install Spire.OCR for Java by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.ocr</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Option 2: Manually Import Spire.OCR.jar.
First, download Spire.OCR for Java from the following link and extract it to a specific directory:
https://www.e-iceblue.com/Download/ocr-for-java.html
Next, in IntelliJ IDEA, go to File > Project Structure > Modules > Dependencies. In the Dependencies pane, click the "+" button and select JARs or Directories. Navigate to the directory where Spire.OCR for Java is located, open the lib folder and select the Spire.OCR.jar file, then click OK to add it as the project’s dependency.
Step 3: Download the New Model of Spire.OCR for Java.
Download the model that fits in with your operating system from one of the following links.
Linux x64 (CentOS 8, Ubuntu 18 and above versions are required)
Then extract the package and save it to a specific directory on your computer. In this example, we saved the package to "D:\".
Step 4: Implement Text Extraction from Images Using the New Model of Spire.OCR for Java.
Use the following code to extract text from images with the new OCR model of Spire.OCR for Java:
- Java
import com.spire.ocr.*;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Create an instance of the OcrScanner class
OcrScanner scanner = new OcrScanner();
// Create an instance of the ConfigureOptions class to set up the scanner configurations
ConfigureOptions configureOptions = new ConfigureOptions();
// Set the path to the new model
configureOptions.setModelPath("D:\\win-x64");
// Set the language for text recognition. The default is English.
// Supported languages include English, Chinese, Chinesetraditional, French, German, Japanese, and Korean.
configureOptions.setLanguage("English");
// Apply the configuration options to the scanner
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(configureOptions);
// Extract text from an image
scanner.scan("Sample.png");
// Save the extracted text to a text file
saveTextToFile(scanner, "output.txt");
} catch (OcrException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void saveTextToFile(OcrScanner scanner, String filePath) {
try {
String text = scanner.getText().toString();
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath))) {
writer.write(text);
}
} catch (IOException | OcrException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.