Table of Contents

Python scripts are commonly shared in development workflows, documentation pipelines, training courses, and academic environments. Converting Python (.py) files to PDF ensures consistent formatting, improves readability during distribution, and provides a non-editable version of your code suitable for archiving, printing, or publishing.
This guide explains every practical method to convert Python code to PDF, including online tools, IDE print-to-PDF workflows, Python-automated conversions with or without syntax highlighting, and batch-processing solutions. Each method includes detailed steps, technical notes, and installation guidance where required.
Overview:
- Online Python-to-PDF Converters
- IDE Print-to-PDF Workflows
- Python Automated Python-to-PDF Conversion
- Methods Comparison
- Frequently Asked Questions
1. Online Python-to-PDF Converters
Online tools offer the quickest way to convert a .py file into PDF without configuring software. They are convenient for users who simply need a readable PDF version of their code.
How Online Converters Work
After uploading a .py file, the service processes the content and outputs a PDF that preserves code indentation and basic formatting. Some platforms provide optional settings such as font size, page margins, and line numbering.
Example: Convert Python Code to PDF with CodeConvert AI
Steps
-
Navigate to CodeConvert AI (a browser-based code conversion platform).
-
Upload your .py file or paste the code into the editor.
-
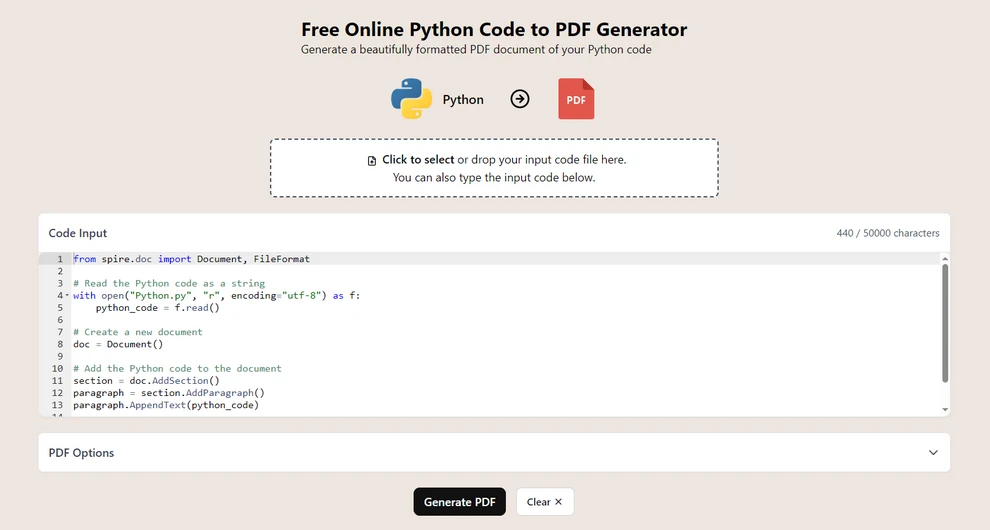
Choose Generate PDF to generate the PDF document.
-
Print the document as a PDF file in the pop-up menu.
Advantages
- No installation or setup required.
- Works across operating systems and devices.
- Suitable for quick conversions and lightweight needs.
Limitations
- Avoid uploading confidential or proprietary scripts.
- Formatting options depend on the service.
- Syntax highlighting quality varies across platforms.
2. Convert Python to PDF via IDE “Print to PDF”
Most development editors—including VS Code, PyCharm, Sublime Text, and Notepad++—support exporting files to PDF through the operating system’s print subsystem.
How It Works
When printing, the IDE renders the code using its internal syntax highlighting engine and passes the styled output to the OS, which then generates a PDF.
Steps (PyCharm Example)
-
Open your Python file.
-
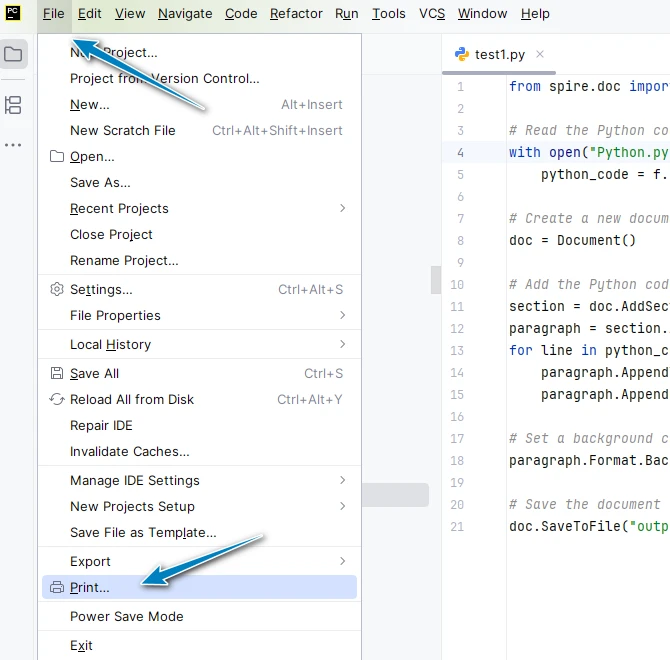
Go to File → Print.
-
Optionally adjust page setup (margins, orientation, scaling).
-
Choose Microsoft Print to PDF as the printer and save the PDF document.
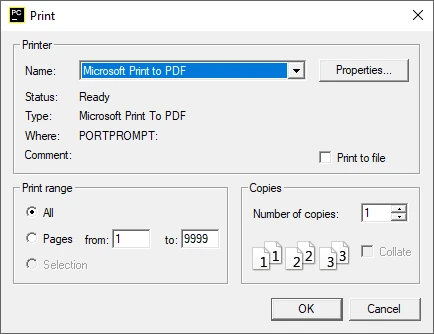
Advantages
- Clean, readable formatting.
- Syntax highlighting usually preserved.
- No additional libraries required.
Limitations
- Minimal control over line wrapping or layout.
- Not designed for batch workflows.
- Output quality varies by IDE theme.
3. Python Script–Based PY to PDF Conversion (Automated and Customizable)
Python-based tools provide flexible ways to convert .py files to PDF, supporting automated pipelines, consistent formatting, and optional syntax highlighting.
Before using the following methods, install the required components.
Required Packages
Free Spire.Doc for Python – handles PDF export
pip install spire.doc.free
Pygments – generates syntax-highlighted HTML
pip install pygments
3.1 Method A: Direct Text-to-PDF (No Syntax Highlighting)
This method reads the .py file as plain text and writes it into a PDF. It is suitable for simple exports, documentation snapshots, and internal archiving, which may not require syntax highlighting.
Example Code
from spire.doc import Document, FileFormat, BreakType, Color, LineSpacingRule, LineNumberingRestartMode, TextRange
# Read the Python code as a string
with open("Python.py", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
python_code = f.read()
# Create a new document
doc = Document()
# Add the Python code to the document
section = doc.AddSection()
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
for line_number, line in enumerate(python_code.split("\n")):
tr = paragraph.AppendText(line)
# Set the character format
tr.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Consolas"
tr.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 10.0
if line_number < len(python_code.split("\n")) - 1:
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Optional settings
# Set the background color and line spacing
paragraph.Format.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
paragraph.Format.LineSpacingRule = LineSpacingRule.Multiple
paragraph.Format.LineSpacing = 12.0 # 12pt meaning single spacing
# Set the line numbering
section.PageSetup.LineNumberingStartValue = 1
section.PageSetup.LineNumberingStep = 1
section.PageSetup.LineNumberingRestartMode = LineNumberingRestartMode.RestartPage
section.PageSetup.LineNumberingDistanceFromText = 10.0
# Save the document to a PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Python-PDF.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.SaveToFile("output/Python-PDF.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
How It Works
This method inserts the Python code line by line using AppendText(), adds line breaks with AppendBreak(), and exports the final document through SaveToFile().
Below is the output effect after applying this method:
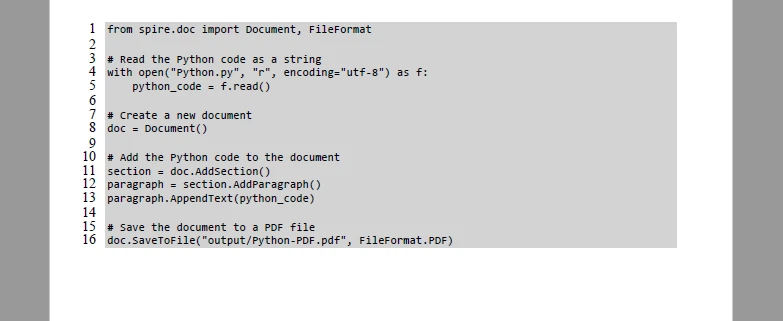
For more details on customizing and inserting text into a PDF document, see our guide on Appending Text to PDF Documents with Python.
3.2 Method B: Syntax-Highlighted PDF (HTML → PDF)
When producing tutorials or readable documentation, syntax highlighting helps distinguish keywords and improves overall clarity. This method uses Pygments to generate inline-styled HTML, then inserts the HTML into a document.
Example Code
from spire.doc import Document, FileFormat, ParagraphStyle, IParagraphStyle
from pygments import highlight
from pygments.lexers import PythonLexer
from pygments.formatters import HtmlFormatter
def py_to_inline_html(py_file_path):
with open(py_file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
code = f.read()
formatter = HtmlFormatter(noclasses=True, linenostart=1, linenos='inline') # Line numbers are optional
inline_html = highlight(code, PythonLexer(), formatter)
return inline_html
html_result = py_to_inline_html("Python.py")
doc = Document()
section = doc.AddSection()
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Insert formatted HTML
paragraph.AppendHTML(html_result)
doc.SaveToFile("output/Python-PDF-Highlighted.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
How It Works
Pygments first formats the code as inline CSS-based HTML. The HTML is added through AppendHTML(), and the completed document is exported using SaveToFile().
Below is the visual result generated by this styled HTML method:
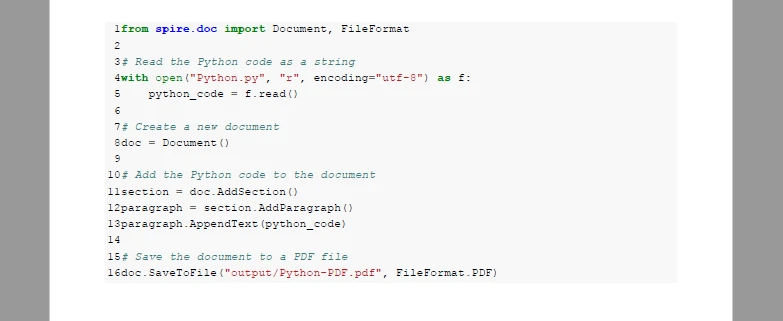
3.3 Batch Conversion (Folder-to-PDF Workflows)
For converting multiple .py files at once, you only need a short loop to process all files in a directory and save them as PDFs.
Example Code (Minimal Batch Processing)
import os
input_folder = "scripts"
output_folder = "pdf-output"
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
for file in os.listdir(input_folder):
if file.endswith(".py"):
py_path = os.path.join(input_folder, file)
pdf_path = os.path.join(output_folder, file.replace(".py", ".pdf"))
# Call your chosen conversion function here
convert_py_to_pdf(py_path, pdf_path)
Notes
- Reuses the conversion function defined earlier.
- Automatically saves each .py file as a PDF with the same filename.
- Works for both plain-text and syntax-highlighted methods.
You can also refer to our guide "Directly Convert HTML to PDF in Python" to learn more.
4. Comparison Table: Choosing the Right Conversion Method
| Method | Advantages | Drawbacks | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Converters | Fast, no installation | Privacy concerns, limited formatting | Small, non-sensitive files |
| IDE Print-to-PDF | Easy, preserves syntax (often) | No automation | Single-file conversion |
| Python Script (Direct/HTML) | Automation, batch processing, customization | Requires scripting knowledge | Documentation, tutorials, pipelines |
5. Best Practices for Generating Clear and Readable PDF Code
Follow these practices to ensure your Python code PDFs are easy to read, well-formatted, and professional-looking.
Use a Monospace Font
Monospace fonts preserve indentation and alignment, making code easier to read and debug.
Manage Long Lines and Wrapping
Enable line wrapping or adjust page margins to prevent horizontal scrolling and clipped code lines.
Maintain Consistent Formatting
Keep font sizes, colors, spacing, and page layout consistent across multiple PDFs, especially in batch processing.
Preserve Logical Code Blocks
Avoid splitting functions, loops, or multi-line statements across pages to maintain readability and structure.
Organize File Naming and Folder Structure
Use systematic file names and folder organization for batch exports, automated documentation, or project archives.
6. Conclusion
Converting Python (.py) files to PDF provides a reliable way to preserve code formatting, improve readability, and create shareable or archival documents. Whether for documentation, tutorials, educational purposes, or personal use, these methods allow developers, teams, and individual users to generate consistent and professional-looking PDF files from their Python source code.
7. Frequently Asked Questions About Converting Python Files to PDF
Below are some common questions developers, educators, and students ask about converting Python files to PDF. These answers are based on the methods covered in this guide.
How do I turn a Python code file (.py) into a PDF?
You can convert a Python .py file into a PDF using online converters like CodeConvert AI, IDE print-to-PDF functions, or Python-based scripts with Spire.Doc for automated and batch processing. Choose the method based on your workflow, formatting needs, and whether syntax highlighting is required.
How can I convert a Python Jupyter notebook to PDF?
For Jupyter notebooks (.ipynb), you can use the built-in File → Download As → PDF option if LaTeX is installed, or first export the notebook to .py script and then apply the Python-to-PDF methods described in this guide.
How do I ensure syntax highlighting is preserved in the PDF?
To retain syntax colors and formatting, convert the code to HTML with inline CSS styles using Pygments, then append it to a PDF document using AppendHTML(). This preserves keywords, comments, and indentation for clearer, professional-looking output.
How do I convert a text file to a PDF using Python on Windows?
On Windows, you can use free Python libraries like Spire.Doc to read the .txt or .py file, write it to a PDF, and optionally style it. IDE print-to-PDF is another option for single-file conversion without coding. Batch scripts can automate multiple files while maintaining consistent formatting.