Table of Contents
- Method 1: Use Word’s Built-in Find and Replace Tool
- Method 2: Use Word’s Advanced Find & Replace
- Method 3: Find and Replace Formatting in Word
- Method 4: Batch Find and Replace Using Word Macros
- Method 5: Automate Find & Replace with Python
- Comparison: Which Method Should You Use?
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

Finding and replacing text is one of the most common tasks when working with Word documents. Whether you’re fixing typos, updating names, changing formatting, or processing documents in bulk, Word—and modern tools—offer several reliable ways to get the job done quickly and accurately.
This guide covers the five most practical ways to find and replace text in Word documents, from simple built-in features to full automation with Python.
Method Overview:
- Method 1: Use Word’s Built-in Find and Replace Tool
- Method 2: Use Word’s Advanced Find & Replace
- Method 3: Find and Replace Formatting in Word
- Method 4: Batch Find and Replace Using Word Macros
- Method 5: Automate Find & Replace with Python
Method 1: Use Word’s Built-in Find and Replace Tool
This is the fastest way to update words or phrases in a single document. It highlights each match and lets you replace items individually or all at once, making it ideal for simple, quick edits with no technical steps required.
How to do it
-
Open the Word document.
-
Press Ctrl + H (Windows) or Command + H (Mac).
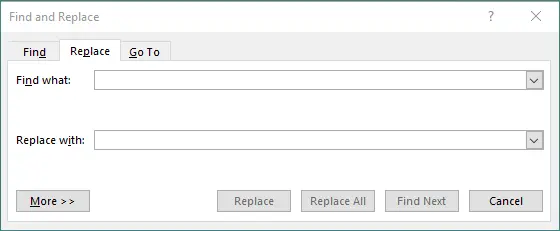
-
In the dialog box:
- Enter the text you want to find.
- Enter the text you want to replace it with.
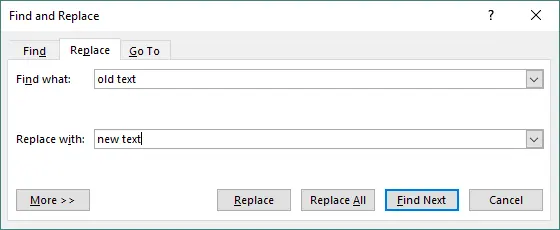
-
Click Find Next, Replace, or Replace All.
Example use cases
- Fixing spelling errors.
- Replacing outdated product names.
- Updating placeholders like [Name] or [Date].
- Changing repeated phrases throughout the document.
Method 2: Use Word’s Advanced Find & Replace (Patterns, Options, and Special Characters)
Advanced Find & Replace offers precise control with wildcards, case sensitivity, whole-word matching, and special character search. It’s great for refining complex documents, fixing layout inconsistencies, or applying structured changes.
How to do it
-
Open Find and Replace → click More >>.
-
Use options such as:
- Match case
- Find whole words only
- Use wildcards
- Special (tabs, line breaks, paragraph marks)
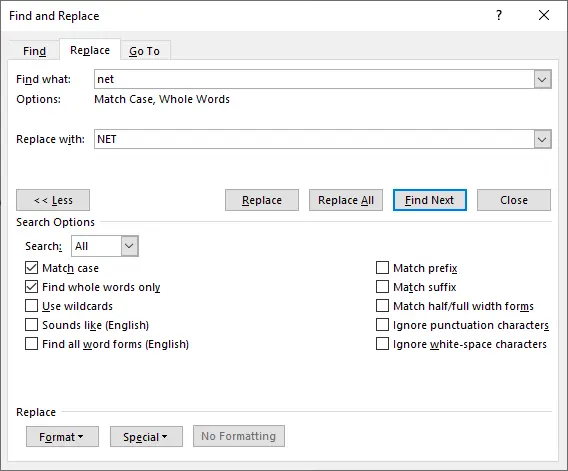
-
Click Find Next, Replace, or Replace All.
Example use cases
- Finding email addresses or dates using wildcard patterns.
- Replacing double spaces with single spaces.
- Removing extra paragraph breaks.
- Changing only capitalized or lowercase text.
Method 3: Find and Replace Formatting in Word
This method focuses on visual consistency. You can change font styles, colors, highlights, or even switch text from one style to another. It’s perfect for refreshing document formatting or aligning content with branding guidelines.
How to do it
-
Open Find and Replace → click More >>.

-
Click Format under the Find or Replace box.
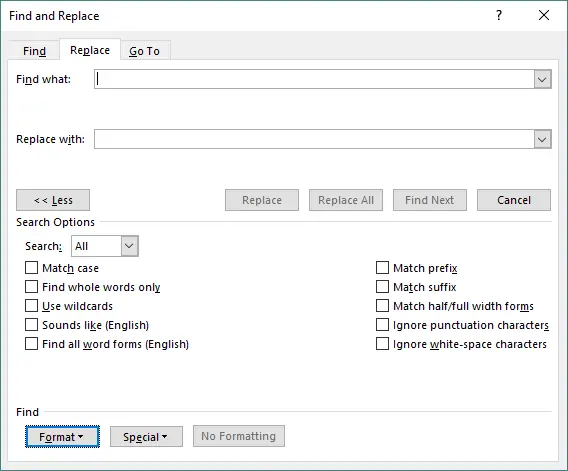
-
Select the formatting to find (e.g., bold, size, color).
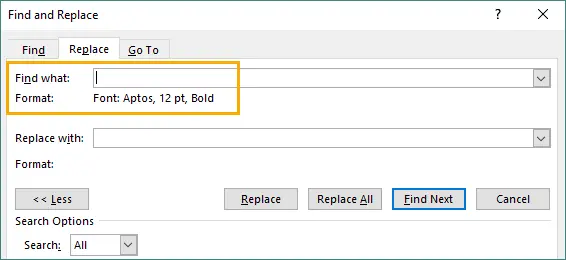
-
Choose formatting to apply OR leave Replace text blank to keep the same words.
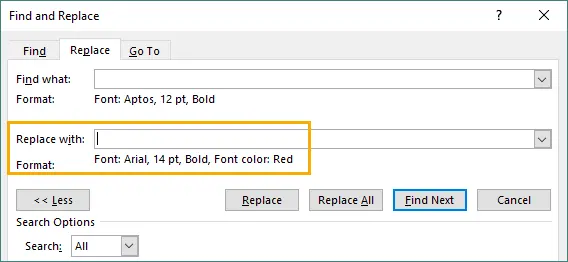
-
Click Replace All.
Example use cases
- Change all bold text to normal.
- Update all 11pt text to 12pt.
- Remove unwanted highlight colors.
- Switch old styles to a new branding style.
Method 4: Batch Find and Replace Using Word Macros (VBA)
VBA Macros allow you to automate repeated find-and-replace tasks across one or many documents. It’s efficient for recurring edits, template updates, or version migrations where manual work would be too slow.
How to do it
-
Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
-
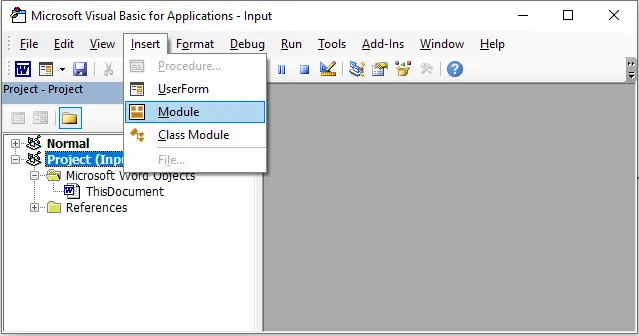
Go to Insert → Module.
-
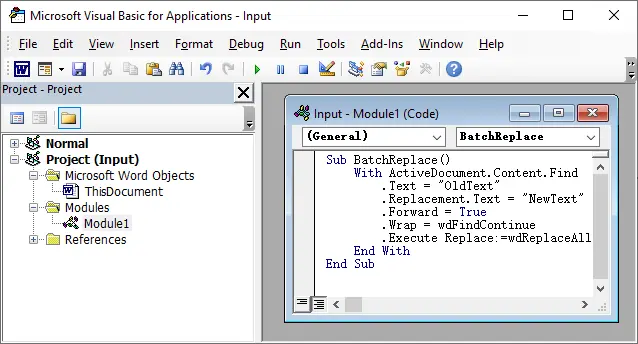
Paste your macro code.
-
Run the macro (Alt+F8) to perform replacements automatically.

Example VBA
Sub BatchReplace()
With ActiveDocument.Content.Find
.Text = "OldText"
.Replacement.Text = "NewText"
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
End With
End Sub
Example use cases
- Updating monthly report terminology.
- Replacing company names across templates.
- Fixing formatting issues in multiple files.
- Automating repeated editorial tasks.
Method 5: Automate Find & Replace with Python (Using Spire.Doc)
For large-scale or backend workflows, using Python provides high-speed, automated text replacement without opening Word. It’s ideal for processing hundreds of documents, generating reports, or integrating document edits into software systems. Among the many available libraries, Spire.Doc for Python is a powerful, full-featured API that works without Microsoft Word installed.
How to do it
-
Install Spire.Doc for Python.
pip install spire.doc -
Load the document in Python.
-
Call the Replace() method for text substitutions.
-
Save the updated document.
Python example
from spire.doc import *
# Load the Word file
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("input.docx")
# Replace simple text
doc.Replace("OldText", "NewText", True, True) # The two True parameters enable case-insensitive and whole-word matching.
# Save the updated file
doc.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Advanced replacement examples
-
Replace text using regex
regex = Regex("""\\#\\w+\\b""") document.Replace(regex, "NewText") -
Replace multiple keywords dynamically
replacements = { "CompanyName": "TechNova", "Year": "2025", "Product": "VisionX" } for key, value in replacements.items(): doc.Replace(key, value, True, True)
Read further: Find and Replace Text in Word Using Python
Why choose the Python/automation method?
- Extremely fast for large batches.
- No user interaction needed.
- Works on servers, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud environments.
- Supports advanced formatting and pattern-based replacement.
- Ideal for enterprise-scale document workflows.
Comparison: Which Method Should You Use?
| Method | Best For | Ease of Use | Automation | Flexibility | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Word’s Built-in Find & Replace | Quick edits; simple replacements | Very easy | None | Medium — supports wildcards & formatting | Not ideal for batch processing or complex logic |
| Advanced Find & Replace | Locating many occurrences visually | Easy | None | Low — mostly visual | Not suitable for mass replacements |
| Replace Formatting-Specific Content | Updating styles, fonts, formatting attributes | Medium | None | Medium — works well for style-driven changes | Still manual; limited logic |
| VBA Macro (Automated Find & Replace) | Repetitive replacements; batch changes; rule-based logic | Medium | Semi/full automation | High — supports loops, conditions, custom rules | Requires scripting; not beginner-friendly |
| Automate with Python (Spire.Doc) | Bulk processing; repetitive tasks; large-scale automation | Medium | Full automation | Very high — control over content, formatting, loops, logs | Requires Python; library installation needed |
Conclusion
Finding and replacing text in Word documents is a fundamental task, yet the method you choose greatly affects your speed and efficiency. For small, everyday edits, Word’s built-in tools are more than enough. For complex formatting adjustments, the advanced features give you fine control. And for enterprise or large-scale needs, automation with VBA or Python provides unmatched power and scalability.
By understanding the strengths of each approach, you can choose the method that best fits your workflow—whether you're editing a single page or generating thousands of documents automatically.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Can Word find and replace text inside headers, footers, or text boxes?
Yes, but text boxes are sometimes skipped. For full coverage, use VBA or Python automation.
Q2. How do I find and replace text with formatting in Word?
Use More > Format in Find & Replace to match or apply formatting such as bold, font, and color.
Q3. What’s the best way to replace text in multiple Word files at once?
Use VBA or Python automation, since Word’s built-in tool cannot process multiple files automatically.
Q4. Is Python or VBA better for automating find-and-replace?
VBA is faster for simple desktop tasks. Python is better for large-scale, batch, or server-side operations.