Table of Contents
Install via NuGet
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Related Links
Efficiently writing Excel files is essential in Python-based workflows for data analysis, reporting, and automation. Among the many available libraries, Spire.XLS for Python stands out as a powerful, Excel-independent solution that supports complex features like charts, formulas, conditional formatting, encryption, and handling of large datasets.
This guide will show how to write XLSX files with Python using Spire.XLS for Python, covering details from basic writing to advanced formatting—all while using the reliable and enterprise-ready Excel library.

- How to Write XLSX Files with Spire.XLS for Python
- Write Different Types of Data into XLSX Files Using Python
- Applying Formatting and Styles to Excel Cells with Python
How to Write XLSX Files with Spire.XLS for Python
Why Use Spire.XLS for Python?
Spire.XLS for Python is a feature-rich library that allows developers to read, write, and manipulate Excel files without needing Microsoft Office. It's built for performance and flexibility, making it ideal for automation tasks and large-scale reporting.
Key benefits:
- All-in-One API: Read/write .xls and .xlsx, format cells, insert formulas, convert files, and more.
- Cross-Platform Support: Available for .NET, Java, Python, and compatible with cloud-based environments.
- Advanced Excel Features: Supports charts, pivot tables, conditional formatting, and protection.
- Reliable Documentation & Support: Extensive API reference, tutorials, developer forum, and support team.
- Free Edition Available: Ideal for lightweight Excel file processing without licensing costs.
Installation of Spire.XLS for Python
You can install either the full version or the free version of Spire.XLS depending on your requirements.
Full version:
pip install spire.xls
Free version (for smaller files and basic use cases):
pip install spire.xls.free
Basic XLSX File Writing Steps
To write to Excel files using Python, follow these fundamental steps:
- Create a new Excel workbook via the Workbook() constructor.
- Load an existing XLSX file (optional) with the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add or get a worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method or the get_Item() method.
- Access cells through the Worksheet.Range.get_Item() method.
- Write data using properties under the CellRange class, such as Value, Text, NumberValue, etc.
- Save the workbook using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
Basic XLSX File Writing Code Example
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, ExcelVersion
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first default worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Write a string to the cell B2
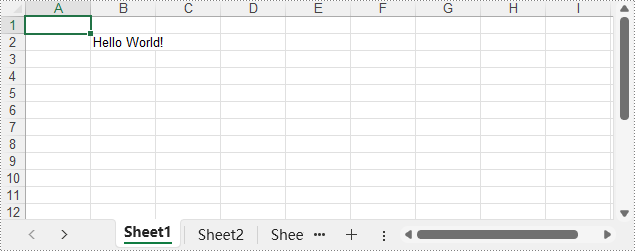
sheet.Range.get_Item(2, 2).Text = "Hello World!"
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/BasicWorkbook.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
The output XLSX file:
Write Different Types of Data into XLSX Files Using Python
Spire.XLS offers a series of properties in the CellRange class that support writing various data types directly into Excel cells, such as strings, date-time values, Boolean values, and numeric values. makes it easy for developers to write typed values directly into cells in an XLSX file.
Supported Data Types and Their Properties
| Property | Value Type | Function |
| NumberValue | float | Sets a number value |
| Text | str | Sets plain text |
| DateTimeValue | datetime | Sets a date and time |
| BooleanValue | bool | Sets a Boolean value |
| Formula | str | Inserts a formula |
| HtmlString | str | Inserts HTML-formatted text |
| Value | str | Sets a generic value |
Code Example – Writing Various Data Types
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, ExcelVersion, DateTime, HorizontalAlignType, Stream, ImageFormatType
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first default worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Write text to the cell B1
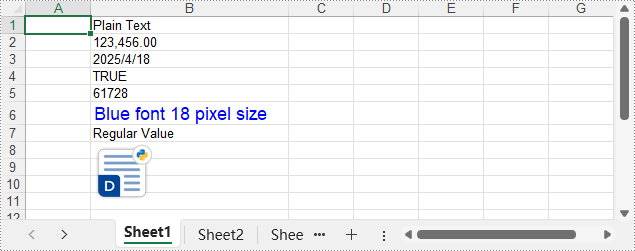
sheet.Range.get_Item(1, 2).Text = "Plain Text"
# Write a number to the cell B2
sheet.Range.get_Item(2, 2).NumberValue = 123456
sheet.Range.get_Item(2, 2).NumberFormat = "#,##0.00"
# Write a date to the cell B3
sheet.Range.get_Item(3, 2).DateTimeValue = DateTime.get_UtcNow()
# Write a boolean value to the cell B4
sheet.Range.get_Item(4, 2).BooleanValue = True
# Write a formula to the cell B5
sheet.Range.get_Item(5, 2).Formula = "B2/2"
# Write an HTML string to the cell B7
sheet.Range.get_Item(6, 2).HtmlString = "<p><span style='color: blue; font-size: 18px;'>Blue font 18 pixel size</span></p>"
# Write a regular value to the cell B7
sheet.Range.get_Item(7, 2).Value = "Regular Value"
# Insert a picture at the cell B8
with open("Logo.png", "rb") as f:
imageBytes = f.read()
stream = Stream(imageBytes)
sheet.Pictures.Add(8, 2, stream, ImageFormatType.Png)
# Set basic formatting
sheet.Range.get_Item(1, 2, 8, 2).HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
sheet.AutoFitColumn(2)
for i in range(sheet.Range.Columns.Count):
for j in range(sheet.Range.Rows.Count):
sheet.Range.get_Item(j + 1, i + 1).HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
# Save the workbook to an XLSX file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/WriteDataExcelCell.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
The output XLSX file:
Applying Formatting and Styles to Excel Cells with Python
Formatting plays a key role in making Excel reports clear and professional. With Spire.XLS for Python, you can customize cell appearance using fonts, colors, alignment, number formats, and built-in styles. These tools help enhance readability and present your data in a polished, consistent way—ideal for reporting and automation.
The following code example shows how to format worksheets using Python.
Format Cells with Font, Color, Border, and Alignment
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, Color, LineStyleType, BordersLineType, HorizontalAlignType
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the XLSX file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Set the font styles
# Header row
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).Style.Font.FontName = "Times New Roman"
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).Style.Font.Size = 14
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).Style.Font.IsBold = True
# Data rows
for i in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows.get_Item(i).Style.Font.FontName = "Arial"
sheet.Rows.get_Item(i).Style.Font.Size = 12
# Set the cell colors
# Header row
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(200, 245, 230)
# Data rows
for i in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows.get_Item(i).Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(240, 255, 250)
# Set the border styles
# Header row
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).Style.Borders.get_Item(BordersLineType.EdgeBottom).LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thick
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).Style.Borders.get_Item(BordersLineType.EdgeBottom).Color = Color.get_White()
# Data rows
for i in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows.get_Item(i).BorderInside(LineStyleType.Thin, Color.get_Black())
# Set the alignment
# Header row
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
# Data rows
for i in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows.get_Item(i).Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
# Auto-fit the column width
for i in range(sheet.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(i + 1)
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/FormatXLSXFile.xlsx")
workbook.Dispose()
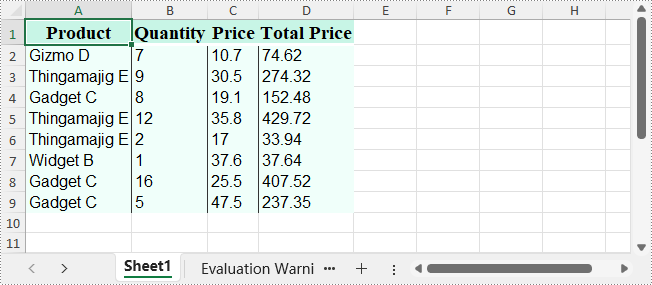
The output XLSX file:
Set Number Formats for Cells
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, ExcelVersion
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Format a cell as number
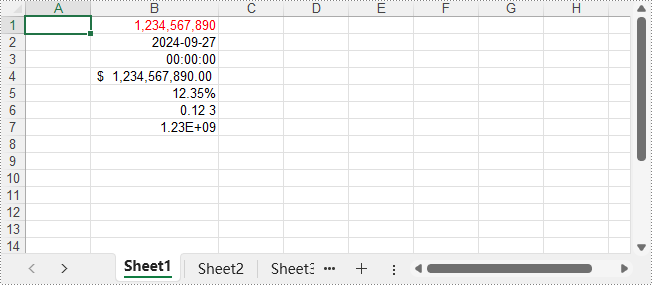
sheet.Range.get_Item(1, 2).NumberValue = 1234567890
sheet.Range.get_Item(1, 2).NumberFormat = "[Red]#,##0;[Green]#,##0"
# Format a cell as date
sheet.Range.get_Item(2, 2).NumberValue = 45562
sheet.Range.get_Item(2, 2).NumberFormat = "yyyy-mm-dd"
# Format a cell as time
sheet.Range.get_Item(3, 2).NumberValue = 45562
sheet.Range.get_Item(3, 2).NumberFormat = "hh:mm:ss"
# Format a cell as currency
sheet.Range.get_Item(4, 2).NumberValue = 1234567890
sheet.Range.get_Item(4, 2).NumberFormat = "_($* #,##0.00_);_($* (#,##0.00);_($* ""-""??_);_(@_)"
# Format a cell as percentage
sheet.Range.get_Item(5, 2).NumberValue = 0.1234567890
sheet.Range.get_Item(5, 2).NumberFormat = "0.00%"
# Format a cell as fraction
sheet.Range.get_Item(6, 2).NumberValue = 0.1234567890
sheet.Range.get_Item(6, 2).NumberFormat = "0.00_ ?"
# Format a cell as scientific number
sheet.Range.get_Item(7, 2).NumberValue = 1234567890
sheet.Range.get_Item(7, 2).NumberFormat = "0.00E+00"
# Auto-fit the column width
for i in range(sheet.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(i + 1)
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/SetNumberFormat.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
The output XLSX file:
Apply Built-in Styles to Cells
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, BuiltInStyles
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Apply built-in header style to the first row
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Heading2
# Apply built-in footer style to the data rows
for i in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows.get_Item(i).BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Accent2_20
# Auto-fit the column width
for i in range(sheet.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(i + 1)
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ApplyBuiltInStyle.xlsx")
workbook.Dispose()
The output XLSX file:
Conclusion
In this guide, we explored how to write XLSX files with Python using Spire.XLS—from basic writing to formatting. Whether it is generating reports, automating exports, or building data-driven applications, Spire.XLS for Python offers a reliable and efficient solution for Excel file generation.
Get a Free License
You can request a 30-day free trial license for the full version of Spire.XLS for Python. This lets you explore all advanced features without limitations during the trial period.