Java: Convert Excel Charts to Images
Images are universally supported and can be seamlessly embedded and displayed in a variety of web platforms and documents. When you intend to publish Excel charts on websites or include them in videos or presentations, converting them to images is a practical option. By doing so, you can eliminate any potential compatibility issues and ensure that these charts are accessible to a wider audience. In this article, we will demonstrate how to convert Excel charts to images in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to an Image in Java
- Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Java
- Convert a Chart Sheet to an Image in Excel in Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
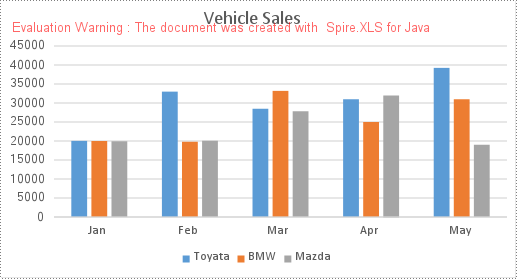
Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to an Image in Java
Spire.XLS for Java provides the Workbook.saveChartAsImage(Worksheet worksheet, int chartIndex) method to convert a specific chart in a worksheet as an image. The following are the detailed steps:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using Workbook.getWorksheets().get(int index) method.
- Save a specific chart in the worksheet as an image using Workbook.saveChartAsImage(Worksheet worksheet, int chartIndex) method.
- Save the image to a PNG file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConvertAExcelChartToImage {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Charts.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Save the first chart in the first worksheet as an image
BufferedImage image = workbook.saveChartAsImage(sheet, 0);
//Save the image to a .png file
ImageIO.write(image, "PNG", new File("output\\chart.png"));
workbook.dispose();
}
}
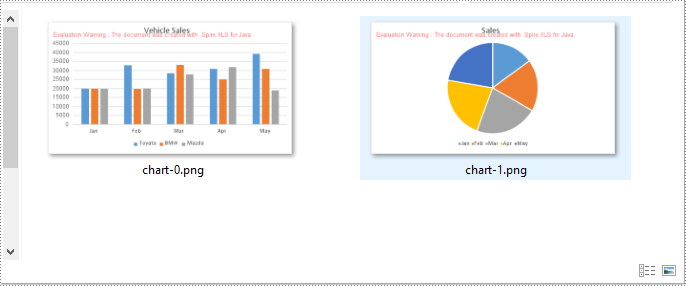
Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Java
To convert all charts in an Excel worksheet to images, you can use the Workbook.saveChartAsImage(Worksheet worksheet) method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using Workbook.getWorksheets().get(int index) method.
- Save all charts in the worksheet as images using Workbook.saveChartAsImage(Worksheet worksheet) method.
- Save the images to PNG files.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConvertAllExcelChartsToImage {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Charts.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Save all charts in the first worksheet as images
BufferedImage[] imgs = workbook.saveChartAsImage(sheet);
//Save the images to .png files
for (int i = 0; i < imgs.length; i++)
{
File file = new File("output\\" + String.format(("chart-%d.png"), i));
ImageIO.write(imgs[i], "PNG", file);
}
workbook.dispose();
}
}
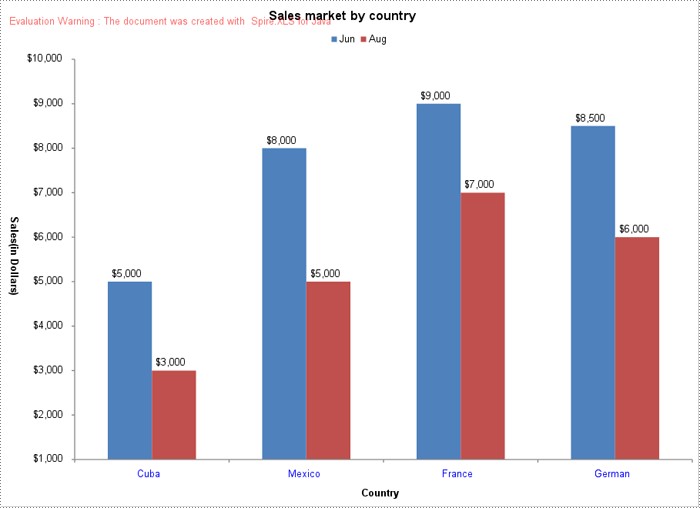
Convert a Chart Sheet to an Image in Excel in Java
A chart sheet in Excel is a separate sheet dedicated solely to displaying a chart. You can use the Workbook.saveChartAsImage(ChartSheet chartSheet) method to convert a chart sheet in an Excel workbook to an image. The following are the detailed steps:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific chart sheet by its index using Workbook.getChartsheets().get(int index) method.
- Save the chart sheet as an image using Workbook.saveChartAsImage(ChartSheet chartSheet) method.
- Save the image to a .png file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ChartSheet;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConvertExcelChartSheetToImage {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("ChartSheet.xlsx");
//Get the first chart sheet
ChartSheet chartSheet = workbook.getChartsheets().get(0);
//Save the first chart sheet as an image
BufferedImage image = workbook.saveChartAsImage(chartSheet);
//Save the image to a .png file
ImageIO.write(image, "PNG", new File("output\\chartSheet.png"));
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
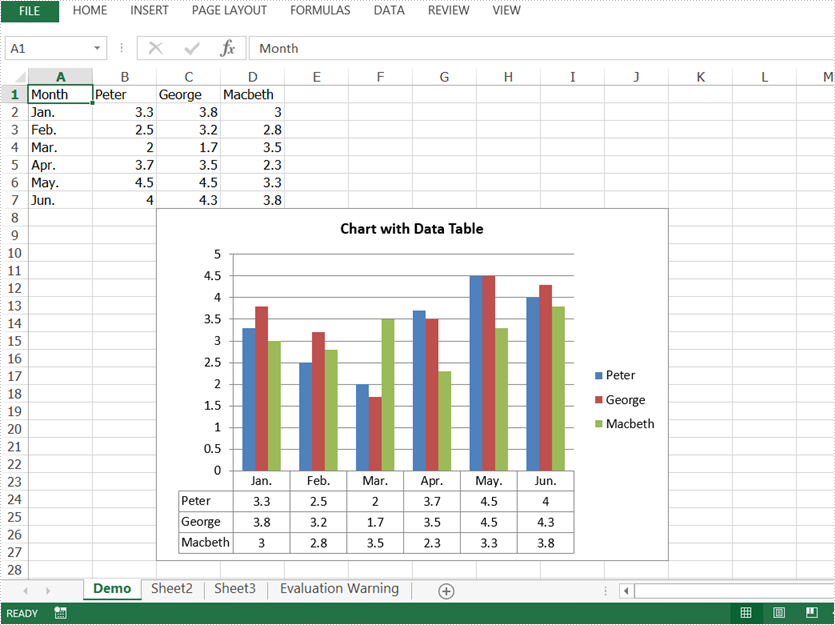
Add Data Table to Excel Chart in Java
In Excel, we could use charts to visualize and compare data. However, once the charts are created, it becomes much difficult for us to read the data precisely from charts, adding a data table below the chart is a good solution. This article is going to introduce how to add a data table to an Excel chart in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.charts.ChartSerie;
public class AddDataTableToChart {
public static void main(String[] args){
//Create a new workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Set sheet name
sheet.setName("Demo");
//Add Data to the sheet
sheet.getRange().get("A1").setValue("Month");
sheet.getRange().get("A2").setValue("Jan.");
sheet.getRange().get("A3").setValue("Feb.");
sheet.getRange().get("A4").setValue("Mar.");
sheet.getRange().get("A5").setValue("Apr.");
sheet.getRange().get("A6").setValue("May.");
sheet.getRange().get("A7").setValue("Jun.");
sheet.getRange().get("B1").setValue("Peter");
sheet.getRange().get("B2").setNumberValue(3.3);
sheet.getRange().get("B3").setNumberValue(2.5);
sheet.getRange().get("B4").setNumberValue(2.0);
sheet.getRange().get("B5").setNumberValue(3.7);
sheet.getRange().get("B6").setNumberValue(4.5);
sheet.getRange().get("B7").setNumberValue(4.0);
sheet.getRange().get("C1").setValue("George");
sheet.getRange().get("C2").setNumberValue(3.8);
sheet.getRange().get("C3").setNumberValue(3.2);
sheet.getRange().get("C4").setNumberValue(1.7);
sheet.getRange().get("C5").setNumberValue(3.5);
sheet.getRange().get("C6").setNumberValue(4.5);
sheet.getRange().get("C7").setNumberValue(4.3);
sheet.getRange().get("D1").setValue("Macbeth");
sheet.getRange().get("D2").setNumberValue(3.0);
sheet.getRange().get("D3").setNumberValue(2.8);
sheet.getRange().get("D4").setNumberValue(3.5);
sheet.getRange().get("D5").setNumberValue(2.3);
sheet.getRange().get("D6").setNumberValue(3.3);
sheet.getRange().get("D7").setNumberValue(3.8);
//Add a chart to the sheet
Chart chart = sheet.getCharts().add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
//Set chart data
chart.setDataRange(sheet.getRange().get("B1:D7"));
chart.setSeriesDataFromRange(false);
//Set chart position
chart.setTopRow(8);
chart.setBottomRow(28);
chart.setLeftColumn(3);
chart.setRightColumn(11);
//Set chart title
chart.setChartTitle("Chart with Data Table");
chart.getChartTitleArea().isBold(true);
chart.getChartTitleArea().setSize(12);
//Set category labels for the first series of the chart
ChartSerie cs1 = chart.getSeries().get(0);
cs1.setCategoryLabels(sheet.getRange().get("A2:A7"));
//Add data table to the chart
chart.hasDataTable(true);
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("AddDataTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
Output:
Java: Create a Pie Chart or a Doughnut Chart in Excel
A pie chart is a circular chart divided into sectors, and each sector represents a proportionate part of the whole. It presents data in the form of graphs, which makes it easy for users to analyze and compare data. As for the doughnut chart, it performs the same function as the pie chart, except that it has a "hole" in the center. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically create a pie chart or a doughnut chart in Excel using Spire.XLS for Java.
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
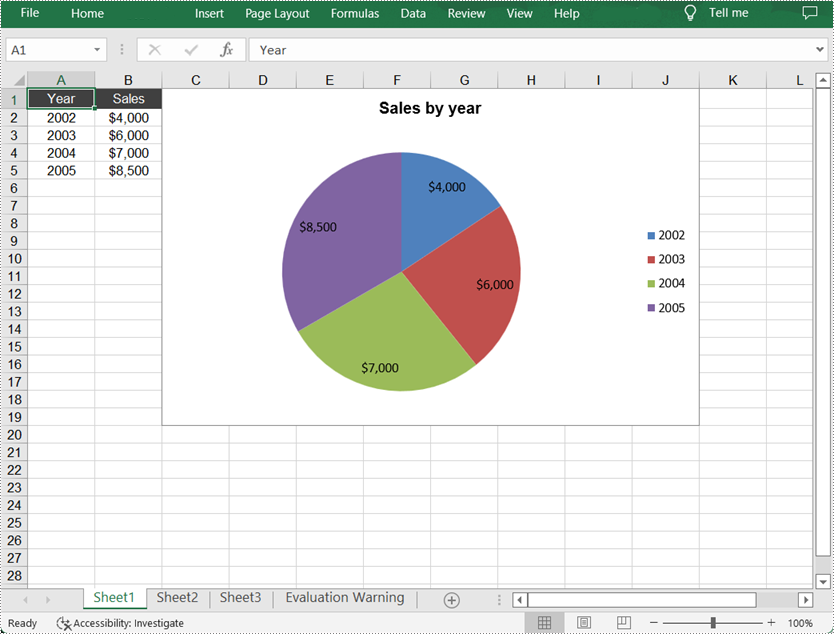
Create a Pie Chart in Excel
The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Add some data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a pie chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.getCharts().add(ExcelChartType.Pie) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.setDataRange() method.
- Set the position and title of the chart.
- Get a specified series in the chart and set category labels and values for the series using ChartSerie.setCategoryLabels() and ChartSerie.setValues() methods.
- Show data labels for data points.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.charts.ChartSerie;
import java.awt.*;
public class CreatePieChart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Insert data to specified cells
sheet.getCellRange("A1").setValue("Year");
sheet.getCellRange("A2").setValue("2002");
sheet.getCellRange("A3").setValue("2003");
sheet.getCellRange("A4").setValue("2004");
sheet.getCellRange("A5").setValue("2005");
sheet.getCellRange("B1").setValue("Sales");
sheet.getCellRange("B2").setNumberValue(4000);
sheet.getCellRange("B3").setNumberValue(6000);
sheet.getCellRange("B4").setNumberValue(7000);
sheet.getCellRange("B5").setNumberValue(8500);
//Set cell styles
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B1").setRowHeight(15);
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B1").getCellStyle().setColor(Color.darkGray);
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B1").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().setColor(Color.white);
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B5").getCellStyle().setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType.Center);
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B5").getCellStyle().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Center);
//Set number format
sheet.getCellRange("B2:C5").getCellStyle().setNumberFormat("\"$\"#,##0");
//Add a pie chart to the worksheet
Chart chart = sheet.getCharts().add(ExcelChartType.Pie);
//Set data range for the chart
chart.setDataRange(sheet.getCellRange("B2:B5"));
chart.setSeriesDataFromRange(false);
//Set position of the chart
chart.setLeftColumn(3);
chart.setTopRow(1);
chart.setRightColumn(11);
chart.setBottomRow(20);
//Set and format chart title
chart.setChartTitle("Sales by year");
chart.getChartTitleArea().isBold(true);
chart.getChartTitleArea().setSize(12);
//Get a specified series in the chart
ChartSerie cs = chart.getSeries().get(0);
//Set category labels for the series
cs.setCategoryLabels(sheet.getCellRange("A2:A5"));
//Set values for the series
cs.setValues(sheet.getCellRange("B2:B5"));
//Show data labels for data points
cs.getDataPoints().getDefaultDataPoint().getDataLabels().hasValue(true);
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("PieChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
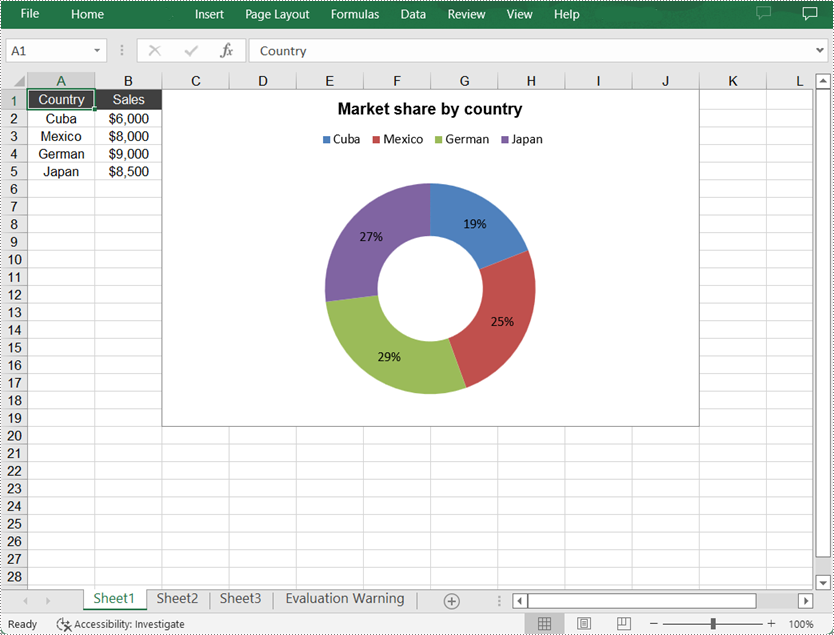
Create a Doughnut Chart in Excel
The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Add some data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a doughnut chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.getCharts().add(ExcelChartType.Doughnut) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.setDataRange() method.
- Set the position and title of the chart.
- Show data labels for data points.
- Set the legend position of the chart using Chart.getLegend().setPosition() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.charts.ChartSerie;
import com.spire.xls.charts.ChartSeries;
import java.awt.*;
public class CreateDoughnutChart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Insert data to specified cells
sheet.getCellRange("A1").setValue("Country");
sheet.getCellRange("A2").setValue("Cuba");
sheet.getCellRange("A3").setValue("Mexico");
sheet.getCellRange("A4").setValue("German");
sheet.getCellRange("A5").setValue("Japan");
sheet.getCellRange("B1").setValue("Sales");
sheet.getCellRange("B2").setNumberValue(6000);
sheet.getCellRange("B3").setNumberValue(8000);
sheet.getCellRange("B4").setNumberValue(9000);
sheet.getCellRange("B5").setNumberValue(8500);
//Set cell styles
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B1").setRowHeight(15);
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B1").getCellStyle().setColor(Color.darkGray);
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B1").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().setColor(Color.white);
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B5").getCellStyle().setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType.Center);
sheet.getCellRange("A1:B5").getCellStyle().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Center);
//Set number format
sheet.getCellRange("B2:C5").getCellStyle().setNumberFormat("\"$\"#,##0");
//Add a doughnut chart to the worksheet
Chart chart = sheet.getCharts().add(ExcelChartType.Doughnut);
//Set data range for chart
chart.setDataRange(sheet.getCellRange("A1:B5"));
chart.setSeriesDataFromRange(false);
//Set position of the chart
chart.setLeftColumn(3);
chart.setTopRow(1);
chart.setRightColumn(11);
chart.setBottomRow(20);
//Set chart title
chart.setChartTitle("Market share by country");
chart.getChartTitleArea().isBold(true);
chart.getChartTitleArea().setSize(12);
//Show data labels for data points
ChartSeries series = chart.getSeries();
for (int i = 0 ; i < series.size() ; i++) {
ChartSerie cs = series.get(i);
cs.getDataPoints().getDefaultDataPoint().getDataLabels().hasPercentage(true);
}
//Set the legend position of the chart
chart.getLegend().setPosition(LegendPositionType.Top);
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("DoughnutChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.