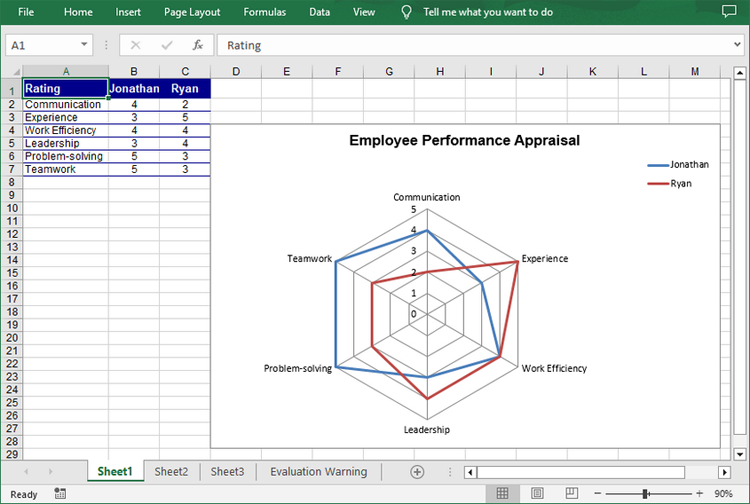
C#: Create a Radar Chart in Excel
Excel radar charts, also known as spider charts or web charts, are used to compare multiple data series in different categories. By plotting data points on a multi-axis chart, radar charts provide a clear and intuitive representation of data balance and skewness. This makes them particularly useful for visualizing performance metrics, market analysis, and other situations where multiple dimensions need to be compared. In this article, you will learn how to create a radar chart in Excel in C# using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Create a Simple Radar Chart in Excel in C#
Spire.XLS for .NET provides the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Radar) method to add a standard radar chart to an Excel worksheet. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add the chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a simple radar chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Radar) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, legend and title of the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ExcelRadarChart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Rating";
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Communication";
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Experience";
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Work Efficiency";
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Leadership";
sheet.Range["A6"].Value = "Problem-solving";
sheet.Range["A7"].Value = "Teamwork";
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jonathan";
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 4;
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 3;
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 4;
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 3;
sheet.Range["B6"].NumberValue = 5;
sheet.Range["B7"].NumberValue = 5;
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Ryan";
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 2;
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 5;
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 4;
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4;
sheet.Range["C6"].NumberValue = 3;
sheet.Range["C7"].NumberValue = 3;
//Set font styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Size = 11;
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.White;
//Set row height and column width
sheet.Rows[0].RowHeight = 20;
sheet.Range["A1:C7"].Columns[0].ColumnWidth = 15;
//Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.DarkBlue;
sheet.Range["A2:C7"].Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A2:C7"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.DarkBlue;
sheet.Range["B1:C7"].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
sheet.Range["A1:C7"].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
//Add a radar chart to the worksheet
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Radar);
//Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4;
chart.TopRow = 4;
chart.RightColumn = 14;
chart.BottomRow = 29;
//Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C7"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
//Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Employee Performance Appraisal";
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = true;
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 14;
//Set position of chart legend
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Corner;
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ExcelRadarChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
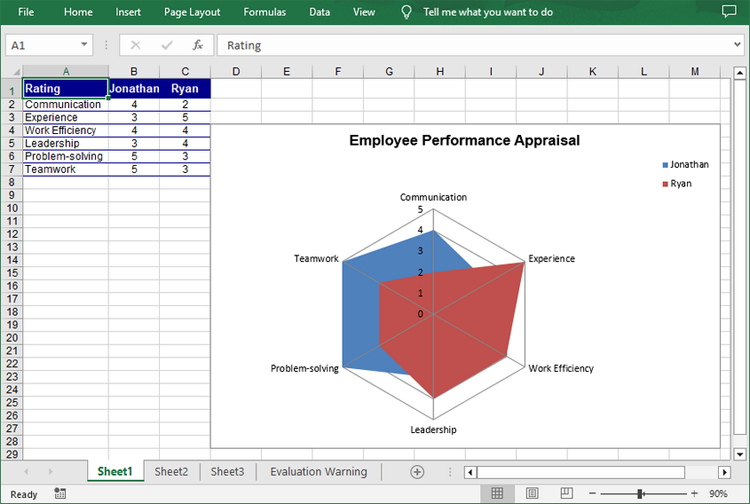
Create a Filled Radar Chart in Excel in C#
A filled radar chart is a variation of a standard radar chart, with the difference that the area between each data point is filled with color. The following are the steps to create a filled radar chart using C#:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add the chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a filled radar chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.RadarFilled) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, legend and title of the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ExcelRadarChart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Rating";
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Communication";
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Experience";
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Work Efficiency";
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Leadership";
sheet.Range["A6"].Value = "Problem-solving";
sheet.Range["A7"].Value = "Teamwork";
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jonathan";
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 4;
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 3;
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 4;
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 3;
sheet.Range["B6"].NumberValue = 5;
sheet.Range["B7"].NumberValue = 5;
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Ryan";
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 2;
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 5;
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 4;
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4;
sheet.Range["C6"].NumberValue = 3;
sheet.Range["C7"].NumberValue = 3;
//Set font styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Size = 11;
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.White;
//Set row height and column width
sheet.Rows[0].RowHeight = 20;
sheet.Range["A1:C7"].Columns[0].ColumnWidth = 15;
//Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.DarkBlue;
sheet.Range["A2:C7"].Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A2:C7"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.DarkBlue;
sheet.Range["B1:C7"].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
sheet.Range["A1:C7"].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
//Add a filled radar chart to the worksheet
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.RadarFilled);
//Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4;
chart.TopRow = 4;
chart.RightColumn = 14;
chart.BottomRow = 29;
//Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C7"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
//Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Employee Performance Appraisal";
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = true;
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 14;
//Set position of chart legend
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Corner;
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("FilledRadarChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
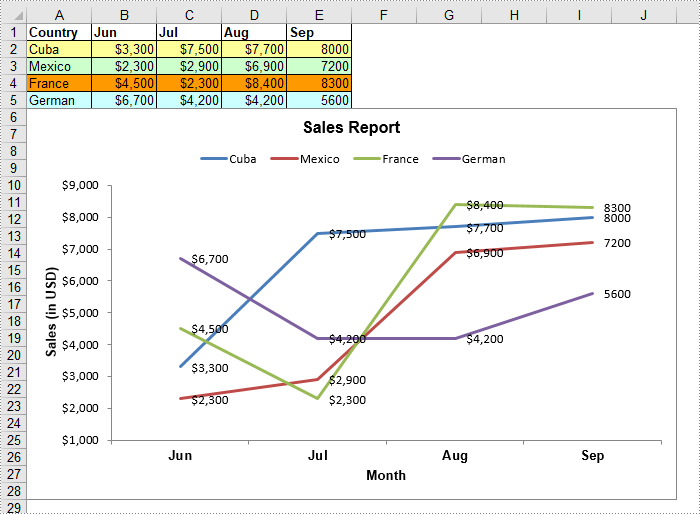
C#/VB.NET: Create a Line Chart in Excel
A line chart, also known as a line graph, is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points connected by straight line segments. It is generally used to show the changes of information over a period of time, such as years, months or days. In this article, you will learn how to create a line chart in Excel in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Create a Line Chart in Excel using C# and VB.NET
The following are the main steps to create a line chart:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet by its index (zero-based) though Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add some data to the worksheet.
- Add a line chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line) method.
- Set data range for the chart through Chart.DataRange property.
- Set position, title, category axis title and value axis title for the chart.
- Loop through the data series of the chart, show data labels for the data points of each data series by setting the ChartSerie.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue property as true.
- Set the position of chart legend through Chart.Legend.Position property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
using System.Drawing;
namespace CreateLineChart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Set sheet name
sheet.Name = "Line Chart";
//Hide gridlines
sheet.GridLinesVisible = false;
//Add some data to the the worksheet
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Country";
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Cuba";
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Mexico";
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "France";
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "German";
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jun";
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 3300;
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 2300;
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 4500;
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 6700;
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Jul";
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 7500;
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 2900;
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 2300;
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4200;
sheet.Range["D1"].Value = "Aug";
sheet.Range["D2"].NumberValue = 7700;
sheet.Range["D3"].NumberValue = 6900;
sheet.Range["D4"].NumberValue = 8400;
sheet.Range["D5"].NumberValue = 4200;
sheet.Range["E1"].Value = "Sep";
sheet.Range["E2"].NumberValue = 8000;
sheet.Range["E3"].NumberValue = 7200;
sheet.Range["E4"].NumberValue = 8300;
sheet.Range["E5"].NumberValue = 5600;
//Set font and fill color for specified cells
sheet.Range["A1:E1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A2:E2"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightYellow;
sheet.Range["A3:E3"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightGreen1;
sheet.Range["A4:E4"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightOrange;
sheet.Range["A5:E5"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightTurquoise;
//Set cell borders
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
//Set number format
sheet.Range["B2:D5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0";
//Add a line chart to the worksheet
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line);
//Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:E5"];
//Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1;
chart.TopRow = 6;
chart.RightColumn = 11;
chart.BottomRow = 29;
//Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales Report";
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = true;
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12;
//Set and format category axis title
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Month";
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = true;
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = true;
//Set and format value axis title
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales (in USD)";
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = -90;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 1000;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = true;
//Loop through the data series of the chart
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = true;
//Show data labels for data points
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = true;
}
//Set position of chart legend
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top;
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("LineChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
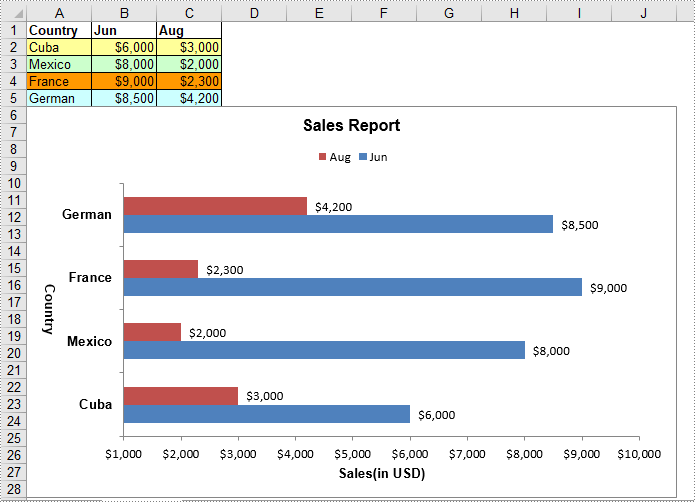
C#/VB.NET: Create Bar Chart in Excel
A bar chart in Excel is a data visualization tool that presents data using horizontal bars. The length of each bar in the chart is proportional to the value it represents. Using a bar chart, you can easily compare values across two or more categories. In this article, you will learn how to create bar chart in Excel in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Create Bar Chart in Excel in C# and VB.NET
The following are the main steps to create a bar chart:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet by its index (zero-based) though Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add some data to the worksheet.
- Add a clustered bar chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.BarClustered) method.
- Set data range for the chart through Chart.DataRange property.
- Set position, title, category axis title and value axis title for the chart.
- Loop through the data series of the chart, show data labels for the data points of each data series by setting the ChartSerie.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue property as true.
- Set the position of chart legend through Chart.Legend.Position property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
using System.Drawing;
namespace CreateBarChart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Set sheet name
sheet.Name = "Bar Chart";
//Hide gridlines
sheet.GridLinesVisible = false;
//Add data to the the worksheet
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Country";
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Cuba";
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Mexico";
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "France";
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "German";
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jun";
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 6000;
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 8000;
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 9000;
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500;
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Aug";
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 3000;
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 2000;
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 2300;
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4200;
//Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A2:C2"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightYellow;
sheet.Range["A3:C3"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightGreen1;
sheet.Range["A4:C4"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightOrange;
sheet.Range["A5:C5"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightTurquoise;
//Set cell borders
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
//Set number format
sheet.Range["B2:C5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0";
//Add a clustered bar chart to the worksheet
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.BarClustered);
//Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
//Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1;
chart.TopRow = 6;
chart.RightColumn = 11;
chart.BottomRow = 29;
//Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales Report";
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = true;
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12;
//Set and format category axis title
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Country";
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = true;
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = true;
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90;
//Set and format value axis title
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales(in USD)";
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 1000;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = true;
//Show data labels for data points
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = true;
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = true;
}
//Set position of chart legend
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top;
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("CreateBarChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Create a Column Chart in Excel
A column chart is a chart that visualizes data as a set of rectangular columns, and the height of the column indicates the value of the data point. Creating column charts in Excel is a great way to compare data and show data change over time. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create a column chart in Excel using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Create a Column Chart in Excel
The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a clustered column chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set position, title, category axis and value axis for the chart.
- Loop through the data series of the chart, and show data labels for data points by setting the ChartSerie.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue property as true.
- Set the position of chart legend using Chart.Legend.Position property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using System.Drawing;
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
namespace ColumnChart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Add data to specified cells
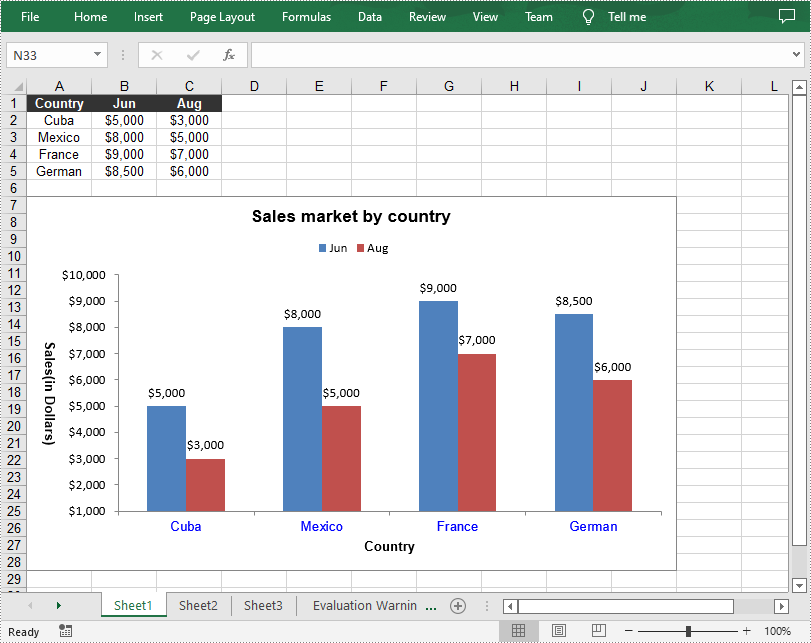
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Country";
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Cuba";
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Mexico";
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "France";
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "German";
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jun";
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 5000;
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 8000;
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 9000;
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500;
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Aug";
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 3000;
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 5000;
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 7000;
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 6000;
//Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Black;
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.White;
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
sheet.Range["A1:C5"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
//Set number format
sheet.Range["B2:C5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0";
//Add a column chart to the worksheet
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
//Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
//Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1;
chart.TopRow = 7;
chart.RightColumn = 11;
chart.BottomRow = 29;
//Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales market by country";
chart.ChartTitleArea.Font.Size = 13;
chart.ChartTitleArea.Font.IsBold = true;
//Set and format category axis
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Country";
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.Color = Color.Blue;
//Set and format value axis
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales(in Dollars)";
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 1000;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90;
//Show data labels for data points
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = true;
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = true;
}
//Set position of chart legend
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top;
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ExcelColumnChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Create a Pie Chart in Excel
A pie chart is a circular chart for visually representation of data. It divides a circular statistical graph into sectors or slices and each sector represents a specific portion of the total percentage. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create a pie chart in Excel using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Create a Pie Chart in Excel
The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add some data to specified cells and set the cell styles and borders.
- Add a pie chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Pie) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position and title of the chart.
- Get a specified series in the chart and set category labels and values for the series using ChartSerie.CategoryLabels and ChartSerie.Values properties.
- Show data labels for data points by setting the ChartSerie.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue property as true.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
using System.Drawing;
namespace CreatePieChart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Set sheet name
sheet.Name = "Chart data";
//Add data to specified cells
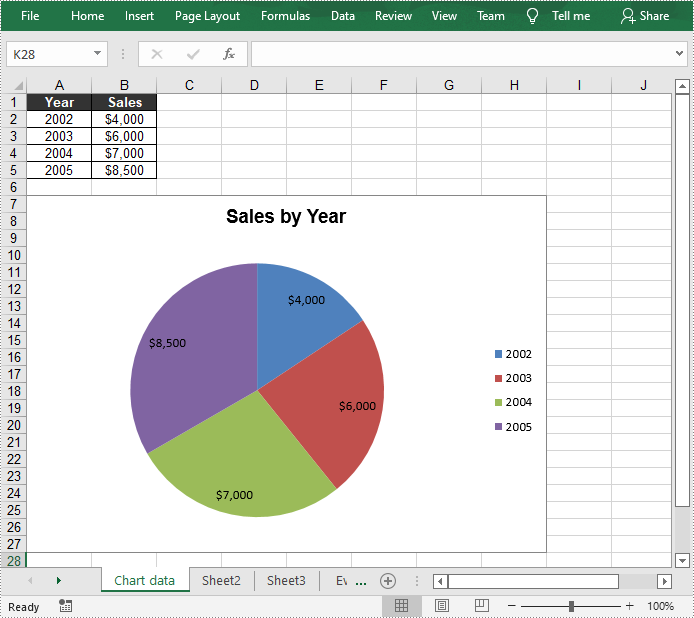
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Year";
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "2002";
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "2003";
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "2004";
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "2005";
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Sales";
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 4000;
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 6000;
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 7000;
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500;
//Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Black;
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.White;
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
//Set number format
sheet.Range["B2:C5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0";
//Set cell borders
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:B5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
//Add a pie chart to the worksheet
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Pie);
//Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["B2:B5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
//Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1;
chart.TopRow = 7;
chart.RightColumn = 9;
chart.BottomRow = 28;
//Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales by Year";
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = true;
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 14;
// Get a specified series in the chart
ChartSerie cs = chart.Series[0];
//Set category labels for the series
cs.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A5"];
//Set values for the series
cs.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B5"];
// Show data labels for data points
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = true;
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("PieChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.