
Spire.PDF for Python (87)
 In daily work, extracting text from PDF files is a common task. For standard digital documents—such as those exported from Word to PDF—this process is usually straightforward. However, things get tricky when dealing with scanned PDFs, which are essentially images of printed documents. In such cases, traditional text extraction methods fail, and OCR (Optical Character Recognition) becomes necessary to recognize and convert the text within images into editable content.
In daily work, extracting text from PDF files is a common task. For standard digital documents—such as those exported from Word to PDF—this process is usually straightforward. However, things get tricky when dealing with scanned PDFs, which are essentially images of printed documents. In such cases, traditional text extraction methods fail, and OCR (Optical Character Recognition) becomes necessary to recognize and convert the text within images into editable content.
In this article, we’ll walk through how to perform PDF OCR using Python to automate this workflow and significantly reduce manual effort.
- Why OCR is Needed for PDF Text Extraction
- Best Python OCR Libraries for PDF Processing
- Convert PDF Pages to Images Using Python
- Scan and Extract Text from Images Using Spire.OCR
- Conclusion
Why OCR is Needed for PDF Text Extraction
When it comes to extracting text from PDF files, one important factor that determines your approach is the type of PDF. Generally, PDFs fall into two categories: scanned (image-based) PDFs and searchable PDFs. Each requires a different strategy for text extraction.
-
Scanned PDFs are typically created by digitizing physical documents such as books, invoices, contracts, or magazines. While the text appears readable to the human eye, it's actually embedded as an image—making it inaccessible to traditional text extraction tools. Older digital files or password-protected PDFs may also lack an actual text layer.
-
Searchable PDFs, on the other hand, contain a hidden text layer that allows computers to search, copy, or parse the content. These files are usually generated directly from applications like Microsoft Word or PDF editors and are much easier to process programmatically.
This distinction highlights the importance of OCR (Optical Character Recognition) when working with scanned PDFs. With tools like Python PDF OCR, we can convert these image-based PDFs into images, run OCR to recognize the text, and extract it for further use—all in an automated way.
Best Python OCR Libraries for PDF Processing
Before diving into the implementation, let’s take a quick look at the tools we’ll be using in this tutorial. To simplify the process, we’ll use Spire.PDF for Python and Spire.OCR for Python to perform PDF OCR in Python.
- Spire.PDF will handle the conversion from PDF to images.
- Spire.OCR, a powerful OCR tool for PDF files, will recognize the text in those images and extract it as editable content.
You can install Spire.PDF using the following pip command:
pip install spire.pdf
and install Spire.OCR with:
pip install spire.ocr
Alternatively, you can download and install them manually by visiting the official Spire.PDF and Spire.OCR pages.
Convert PDF Pages to Images Using Python
Before we dive into Python PDF OCR, it's crucial to understand a foundational step: OCR technology doesn't directly process PDF files. Especially with image-based PDFs (like those created from scanned documents), we first need to convert them into individual image files.
Converting PDFs to images using the Spire.PDF library is straightforward. You simply load your target PDF document and then iterate through each page. For every page, call the PdfDocument.SaveAsImage() method to save it as a separate image file. Once this step is complete, your images are ready for the subsequent OCR process.
Here's a code example showing how to convert PDF to PNG:
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("/AI-Generated Art.pdf")
# Loop through pages and save as images
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Convert each page to image
with pdf.SaveAsImage(i) as image:
# Save in different formats as needed
image.Save(f"/output/pdftoimage/ToImage_{i}.png")
# image.Save(f"Output/ToImage_{i}.jpg")
# image.Save(f"Output/ToImage_{i}.bmp")
# Close the PDF document
pdf.Close()
Conversion result preview: 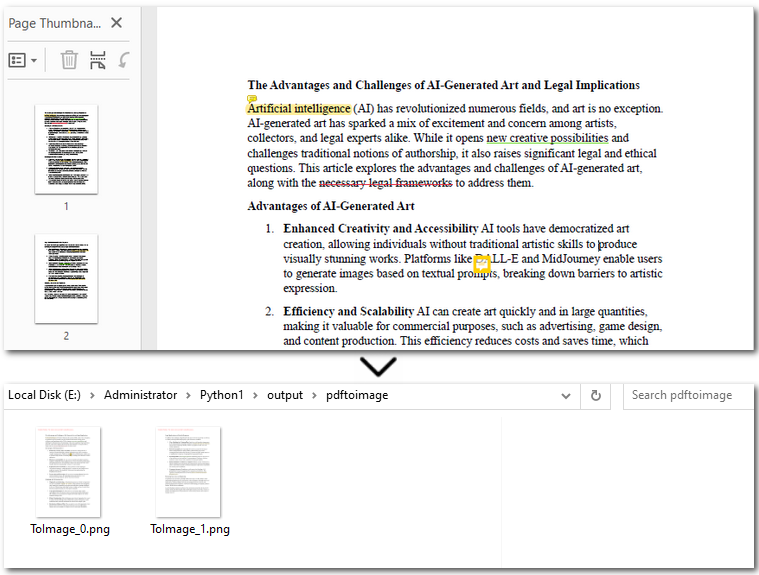
Scan and Extract Text from Images Using Spire.OCR
After converting the scanned PDF into images, we can now move on to OCR PDF with Python and to extract text from the PDF. With OcrScanner.Scan() from Spire.OCR, recognizing text in images becomes straightforward. It supports multiple languages such as English, Chinese, French, and German. Once the text is extracted, you can easily save it to a .txt file or generate a Word document.
The code example below shows how to OCR the first PDF page and export to text in Python:
from spire.ocr import *
# Create OCR scanner instance
scanner = OcrScanner()
# Configure OCR model path and language
configureOptions = ConfigureOptions()
configureOptions.ModelPath = r'E:/DownloadsNew/win-x64/'
configureOptions.Language = 'English'
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(configureOptions)
# Perform OCR on the image
scanner.Scan(r'/output/pdftoimage/ToImage_0.png')
# Save extracted text to file
text = scanner.Text.ToString()
with open('/output/scannedpdfoutput.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text + '\n')
Result preview: 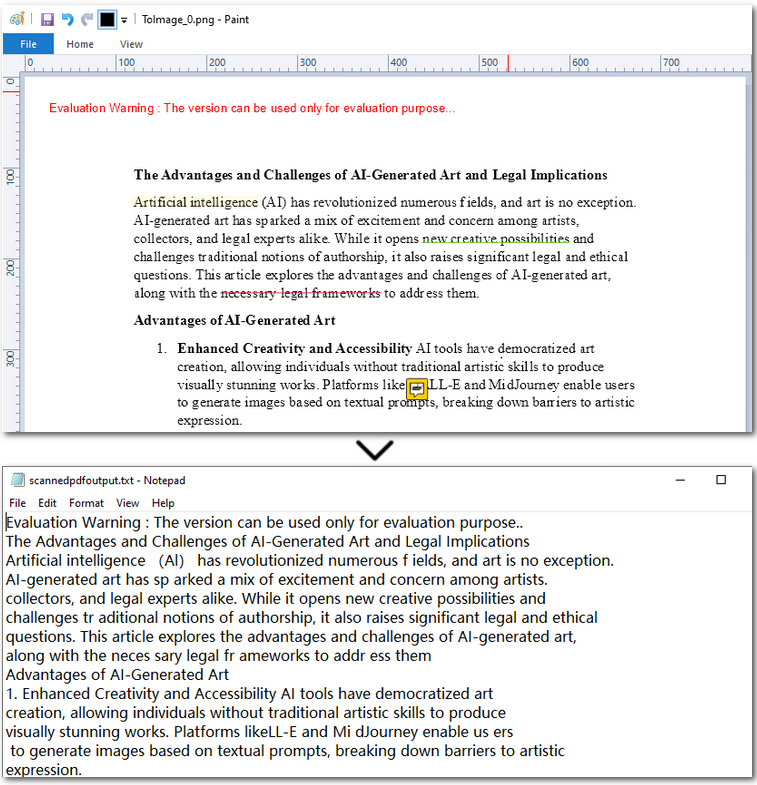
The Conclusion
In this article, we covered how to perform PDF OCR with Python—from converting PDFs to images, to recognizing text with OCR, and finally saving the extracted content as a plain text file. With this streamlined approach, extracting text from scanned PDFs becomes effortless. If you're looking to automate your PDF processing workflows, feel free to reach out and request a 30-day free trial. It’s time to simplify your document management.
Convert PDF to Markdown in Python – Single & Batch Conversion
2025-07-17 02:36:46 Written by zaki zou
PDFs are ubiquitous in digital document management, but their rigid formatting often makes them less than ideal for content that needs to be easily edited, updated, or integrated into modern workflows. Markdown (.md), on the other hand, offers a lightweight, human-readable syntax perfect for web publishing, documentation, and version control. In this guide, we'll explore how to leverage the Spire.PDF for Python library to perform single or batch conversions from PDF to Markdown in Python efficiently.
- Why Convert PDFs to Markdown?
- Python PDF Converter Library – Installation
- Convert PDF to Markdown in Python
- Batch Convert Multiple PDFs to Markdown in Python
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Why Convert PDFs to Markdown?
Markdown offers several advantages over PDF for content creation and management:
- Version control friendly: Easily track changes in Git
- Lightweight and readable: Plain text format with simple syntax
- Editability: Simple to modify without specialized software
- Web integration: Natively supported by platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and static site generators (e.g., Jekyll, Hugo).
Spire.PDF for Python provides a robust solution for extracting text and structure from PDFs while preserving essential formatting elements like tables, lists, and basic styling.
Python PDF Converter Library - Installation
To use Spire.PDF for Python in your projects, you need to install the library via PyPI (Python Package Index) using pip. Open your terminal/command prompt and run:
pip install Spire.PDF
To upgrade an existing installation to the latest version:
pip install --upgrade spire.pdf
Convert PDF to Markdown in Python
Here’s a basic example demonstrates how to use Python to convert a PDF file to a Markdown (.md) file.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an instance of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("TestFile.pdf")
# Convert the PDF to a Markdown file
pdf.SaveToFile("PDFToMarkdown.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
pdf.Close()
This Python script loads a PDF file and then uses the SaveToFile() method to convert it to Markdown format. The FileFormat.Markdown parameter specifies the output format.
How Conversion Works
The library extracts text, images, tables, and basic formatting from the PDF and converts them into Markdown syntax.
- Text: Preserved with paragraphs/line breaks.
- Images: Images in the PDF are converted to base64-encoded PNG format and embedded directly in the Markdown.
- Tables: Tabular data is converted to Markdown table syntax (rows/columns with pipes |).
- Styling: Basic formatting (bold, italic) is retained using Markdown syntax.
Output: 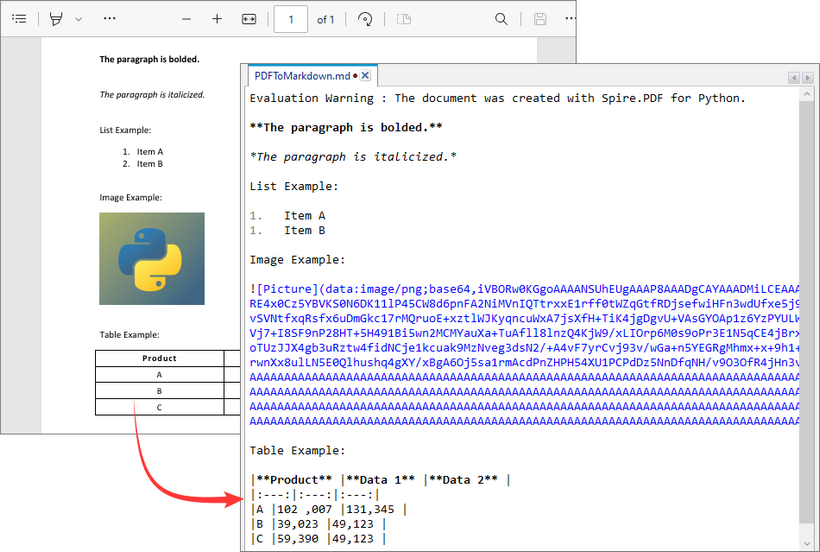
Batch Convert Multiple PDFs to Markdown in Python
This Python script uses a loop to convert all PDF files in a specified directory to Markdown format.
import os
from spire.pdf import *
# Configure paths
input_folder = "pdf_folder/"
output_folder = "markdown_output/"
# Create output directory
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# Process all PDFs in folder
for file_name in os.listdir(input_folder):
if file_name.endswith(".pdf"):
# Initialize document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile(os.path.join(input_folder, file_name))
# Generate output path
md_name = os.path.splitext(file_name)[0] + ".md"
output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, md_name)
# Convert to Markdown
pdf.SaveToFile(output_path, FileFormat.Markdown)
pdf.Close()
Key Characteristics
- Batch Processing: Automatically processes all PDFs in input folder, improving efficiency for bulk operations.
- 1:1 Conversion: Each PDF generates corresponding Markdown file.
- Sequential Execution: Files processed in alphabetical order.
- Resource Management: Each PDF is closed immediately after conversion.
Output:
Need to convert Markdown to PDF? Refer to: Convert Markdown to PDF in Python
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is Spire.PDF for Python free?
A: Spire.PDF offers a free version with limitations (e.g., maximum 3 pages per conversion). For unlimited use, request a 30-day free trial for evaluation.
Q2: Can I convert password-protected PDFs to Markdown?
A: Yes. Use the LoadFromFile method with the password as a second parameter:
pdf.LoadFromFile("ProtectedFile.pdf", "your_password")
Q3: Can Spire.PDF convert scanned/image-based PDFs to Markdown?
A: No. The library extracts text-based content only. For scanned PDFs, use OCR tools (like Spire.OCR for Python) to create searchable PDFs first.
Conclusion
Spire.PDF for Python simplifies PDF to Markdown conversion for both single file and batch processing.
Its advantages include:
- Simple API with minimal code
- Preservation of document structure
- Batch processing capabilities
- Cross-platform compatibility
Whether you're migrating documentation, processing research papers, or building content pipelines, by following the examples in this guide, you can efficiently transform static PDF documents into flexible, editable Markdown content, streamlining workflows and improving collaboration.
How to Add Text to PDF in Python (Create & Edit with Examples)
2025-07-10 08:51:40 Written by zaki zou
Adding text to a PDF is a common task in Python — whether you're generating reports, adding annotations, filling templates, or labeling documents. This guide will walk you through how to write text in a PDF file using Python, including both creating new PDF documents and updating existing ones.
We’ll be using a dedicated Python PDF library - Spire.PDF for Python, which allows precise control over text placement, font styling, and batch processing. The examples are concise, beginner-friendly, and ready for real-world projects.
Sections Covered
- Setup: Install the PDF Library in Python
- Add Text to a New PDF
- Add Text to an Existing PDF
- Control Text Style, Position, Transparency, and Rotation
- Common Pitfalls and Cross-Platform Tips
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Setup: Install the PDF Library in Python
To get started, install Spire.PDF for Python, a flexible and cross-platform PDF library.
pip install Spire.PDF
Or use Free Spire.PDF for Python:
pip install spire.pdf.free
Why use this library?
- Works without Adobe Acrobat or Microsoft Office
- Add and format text at exact positions
- Supports both new and existing PDF editing
- Runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux
Add Text to a New PDF Using Python
If you want to create a PDF from text using Python, the example below shows how to insert a line of text into a blank PDF page using custom font and position settings.
Example: Create and write text to a blank PDF
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTrueTypeFont, PdfFontStyle, PdfSolidBrush, PdfRGBColor, PointF, RectangleF, \
PdfStringFormat, PdfTextAlignment, PdfVerticalAlignment
# Create a new PDF document and add a new page
pdf = PdfDocument()
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
text = ("This report summarizes the sales performance of various products in the first quarter of 2025. " +
"Below is a breakdown of the total sales by product category, " +
"followed by a comparison of sales in different regions.")
# Set the font, brush, and point
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(0, 0, 0)) # black
point = PointF(50.0, 100.0)
# Set the layout area and string format
layoutArea = RectangleF(50.0, 50.0, page.GetClientSize().Width - 100.0, page.GetClientSize().Height)
stringFormat = PdfStringFormat(PdfTextAlignment.Left, PdfVerticalAlignment.Top)
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font, brush, layoutArea, stringFormat, False)
pdf.SaveToFile("output/new.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Technical Notes
- PdfTrueTypeFont() loads a TrueType font from the system with customizable size and style (e.g., regular, bold). It ensures consistent text rendering in the PDF.
- PdfSolidBrush() defines the fill color for text or shapes using RGB values. In this example, it's set to black ((0, 0, 0)).
- RectangleF(x, y, width, height) specifies a rectangular layout area for drawing text. It enables automatic line wrapping and precise control of text boundaries.
- PdfStringFormat() controls the alignment of the text inside the rectangle. Here, text is aligned to the top-left (Left and Top).
- DrawString() draws the specified text within the defined layout area without affecting existing content on the page.
Example output PDF showing wrapped black text starting at coordinates (50, 50).

Tip: To display multiple paragraphs or line breaks, consider adjusting the Y-coordinate dynamically or using multiple DrawString() calls with updated positions.
If you want to learn how to convert TXT files to PDF directly using Python, please check: How to Convert Text Files to PDF Using Python.
Add Text to an Existing PDF in Python
Need to add text to an existing PDF using Python? This method lets you load a PDF, access a page, and write new text anywhere on the canvas.
This is helpful for:
- Adding comments or annotations
- Labeling document versions
- Filling pre-designed templates
Example: Open an existing PDF and insert text
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfFontStyle, PdfSolidBrush, PdfRGBColor, PointF, PdfFont, PdfFontFamily
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("input.pdf")
page = pdf.Pages[0]
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold)
brush = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(255, 0, 0)) # red
location = PointF(150.0, 110.0)
page.Canvas.DrawString("This document is approved.", font, brush, location)
pdf.SaveToFile("output/modified.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Technical Notes
- LoadFromFile() loads an existing PDF into memory.
- You can access specific pages via pdf.Pages[index].
- New content is drawn on top of the existing layout, non-destructively.
- The text position is again controlled via PointF(x, y).
Modified PDF page with newly added red text annotation on the first page.
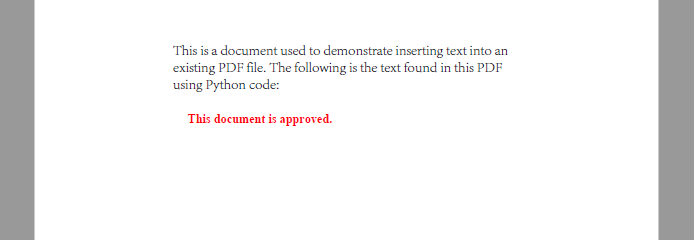
Use different x, y coordinates to insert content at custom positions.
Related article: Replace Text in PDF with Python
Control Text Style, Positioning, Transparency, and Rotation
When adding text to a PDF, you often need more than just plain content—you may want to customize the font, color, placement, rotation, and transparency, especially for annotations or watermarks.
Spire.PDF for Python offers fine-grained control for these visual elements, whether you’re building structured reports or stamping dynamic text overlays.
Set Font Style and Color
# Create PdfTrueTypeFont
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Calibri", 16.0, PdfFontStyle.Italic, True)
# Create PdfFont
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 16.0, PdfFontStyle.Italic)
# Create PdfBrush to specify text drawing color
brush = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(34, 139, 34)) # forest green
PdfTrueTypeFont will embed the font into the PDF file. To reduce file size, you may use PdfFont, which uses system fonts without embedding them.
Apply Transparency and Rotation
You can adjust transparency and rotation when drawing text to achieve effects like watermarks or angled labels.
# Save the current canvas state
state = page.Canvas.Save()
# Set semi-transparency (0.0 = fully transparent, 1.0 = fully opaque)
page.Canvas.SetTransparency(0.4)
# Move the origin to the center of the page
page.Canvas.TranslateTransform(page.Size.Width / 2, page.Size.Height / 2)
# Rotate the canvas -45 degrees (counterclockwise)
page.Canvas.RotateTransform(-45)
# Draw text at new origin
page.Canvas.DrawString("DRAFT", font, brush, PointF(-50, -20))
Example: Add a Diagonal Watermark to the Center of the Page
The following example demonstrates how to draw a centered, rotated, semi-transparent watermark using all the style controls above:
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTrueTypeFont, PdfFontStyle, PdfSolidBrush, PdfRGBColor, PointF
from spire.pdf.common import Color
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("input1.pdf")
page = pdf.Pages[0]
text = "Confidential"
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 40.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
brush = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(Color.get_DarkBlue())) # gray
# Measure text size to calculate center
size = font.MeasureString(text)
x = (page.Canvas.ClientSize.Width - size.Width) / 2
y = (page.Canvas.ClientSize.Height - size.Height) / 2
state = page.Canvas.Save()
page.Canvas.SetTransparency(0.3)
page.Canvas.TranslateTransform(x + size.Width / 2, y + size.Height / 2)
page.Canvas.RotateTransform(-45.0)
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font, brush, PointF(-size.Width / 2, -size.Height / 2))
page.Canvas.Restore(state)
pdf.SaveToFile("output/with_watermark.pdf")
pdf.Close()
PDF page displaying a centered, rotated, semi-transparent watermark text.
This approach works well for dynamic watermarking, diagonal stamps like "VOID", "COPY", or "ARCHIVED", and supports full automation.
Make sure all files are closed and not in use to avoid PermissionError.
For more details on inserting watermarks into PDF with Python, please refer to: How to Insert Text Watermarks into PDFs Using Python.
Common Pitfalls and Cross-Platform Considerations
Even with the right API, issues can arise when deploying PDF text operations across different environments or font configurations. Here are some common problems and how to resolve them:
| Issue | Cause | Recommended Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Text appears in wrong position | Hardcoded coordinates not accounting for page size | Use ClientSize and MeasureString() for dynamic layout |
| Font not rendered | Font lacks glyphs or isn't supported | Use PdfTrueTypeFont to embed supported fonts like Arial Unicode |
| Unicode text not displayed | Font does not support full Unicode range | Use universal fonts (e.g., Arial Unicode, Noto Sans) |
| Text overlaps existing content | Positioning too close to body text | Adjust Y-offsets or add padding with MeasureString() |
| Watermark text appears on output | You are using the paid version without a license | Use the free version or apply for a temporary license |
| Font file too large | Embedded font increases PDF size | Use PdfFont for system fonts (non-embedded), if portability is not a concern |
| Inconsistent results on macOS/Linux | Fonts not available or different metrics | Ship fonts with your application, or use built-in cross-platform fonts |
Conclusion
With Spire.PDF for Python, adding text to PDFs—whether creating new files, updating existing ones, or automating batch edits—can be done easily and precisely. From annotations to watermarks, the library gives you full control over layout and styling.
You can start with the free version right away, or apply for a temporary license to unlock full features.
FAQ
How to add text to a PDF using Python?
Use a PDF library such as Spire.PDF to insert text via the DrawString() method. You can define font, position, and styling.
Can I write text into an existing PDF file with Python?
Yes. Load the file with LoadFromFile(), then use DrawString() to add text at a specific location.
How do I generate a PDF from text using Python?
Create a new document and use drawing methods to write content line by line with precise positioning.
Can I add the same text to many PDFs automatically?
Yes. Use a loop to process multiple files and insert text programmatically using a template script.
How to Read PDF Files in Python – Text, Tables, Images, and More
2025-06-06 08:07:20 Written by zaki zou
Reading PDF files using Python is essential for tasks like document automation, content analysis, and data scraping. Whether you're working with contracts, reports, invoices, or scientific papers, being able to programmatically access PDF content saves time and enables powerful workflows.
To reliably read PDF content in Python — including text, tables, images, and metadata — you need a reliable Python PDF reader. In this guide, we’ll show you how to read PDFs in Python using Spire.PDF for Python, a professional and easy-to-use library that supports full-featured PDF reading without relying on any third-party tools.
Here's what's covered:
- Preparing Your Environment
- Load a PDF File in Python
- Read Text from PDF Pages in Python
- Read Table Data from PDFs in Python
- Read Images from PDFs in Python
- Read PDF Metadata (Title, Author, etc.)
- Common Questions on Reading PDFs
Environment Setup for Reading PDFs in Python
Spire.PDF for Python is a powerful Python PDF reader that allows users to read PDF content with simple Python code, including text, tables, images, and metadata. It offers a developer-friendly interface and supports a wide range of PDF reading operations:
- Read PDF files from disk or memory
- Access text, tables, metadata, and images
- No need for third-party tools
- High accuracy for structured data reading
- Free version available
It’s suitable for developers who want to read and process PDFs with minimal setup.
You can install Spire.PDF for Python via pip:
pip install spire.pdf
Or the free version Free Spire.PDF for Python for small tasks:
pip install spire.pdf.free
Load a PDF File in Python
Before accessing content, the first step is to load the PDF into memory. Spire.PDF lets you read PDF files from a path on disk or directly from in-memory byte streams — ideal for reading from web uploads or APIs.
Read PDF from File Path
To begin reading a PDF in Python, load the file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile(). This creates a document object you can use to access content.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
Read PDF from Bytes (In-Memory)
To read a PDF file from memory without saving it to disk, you can first load its byte content and then initialize a PdfDocument using a Stream object. This method is especially useful when handling PDF files received from web uploads, APIs, or temporary in-memory data.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, Stream
# Read the PDF file to a byte array
with open("sample.pdf", "rb") as f:
byte_data = f.read()
# Create a stream using the byte array
pdfStream = Stream(byte_data)
# Create a PdfDocument using the stream
pdf = PdfDocument(pdfStream)
To go further, check out this guide: Loading and Saving PDFs via Byte Streams in Python
Read Text from PDF Pages in Python
Reading text from a PDF file is one of the most common use cases in document automation. With Spire.PDF, you can easily retrieve all visible text from the entire PDF or from individual pages using simple methods.
Read All Text from PDF
To extract all text from a PDF, loop through each page and call PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() to collect visible text content.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextExtractor, PdfTextExtractOptions
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
all_text = ""
# Loop through each page
for pageIndex in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(pageIndex)
# Create a PdfTextExtract instance
text_extractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Configure extracting options
options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
options.IsExtractAllText = True
options.IsSimpleExtraction = True
# Extract text from the current page
all_text += text_extractor.ExtractText(options)
print(all_text)
Sample text content retrieved:

Read Text from Specific Area of a Page
You can also read text from a defined region of a page using a bounding box. This is useful when only a portion of the layout contains relevant information.
from spire.pdf import RectangleF, PdfDocument, PdfTextExtractor, PdfTextExtractOptions
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor instance
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Set the area to extract text by configuring the PdfTextExtractOptions
options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
area = RectangleF.FromLTRB(0, 200, page.Size.Width, 270) # x, y, width, height
options.ExtractArea = area
options.IsSimpleExtraction = True
# Extract text from the area
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(options)
print(text)
The text read from the PDF page area:
Read Table Data from PDFs in Python
PDF tables are often used in reports, invoices, and statements. With Spire.PDF, you can read PDF tables in Python by extracting structured tabular content using its layout-aware table extractor, making it ideal for financial and business documents. Use PdfTableExtractor.ExtractTable() to detect tables page by page and output each row and cell as structured text.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Create a PdfTableExtractor instance
table_extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
# Extract the table from the first page
tables = table_extractor.ExtractTable(0)
for table in tables:
# Get the number of rows and columns
row_count = table.GetRowCount()
column_count = table.GetColumnCount()
# Iterate all rows
for i in range(row_count):
table_row = []
# Iterate all columns
for j in range(column_count):
# Get the cell
cell_text = table.GetText(i, j)
table_row.append(cell_text)
print(table_row)
Table content extracted using the code above:
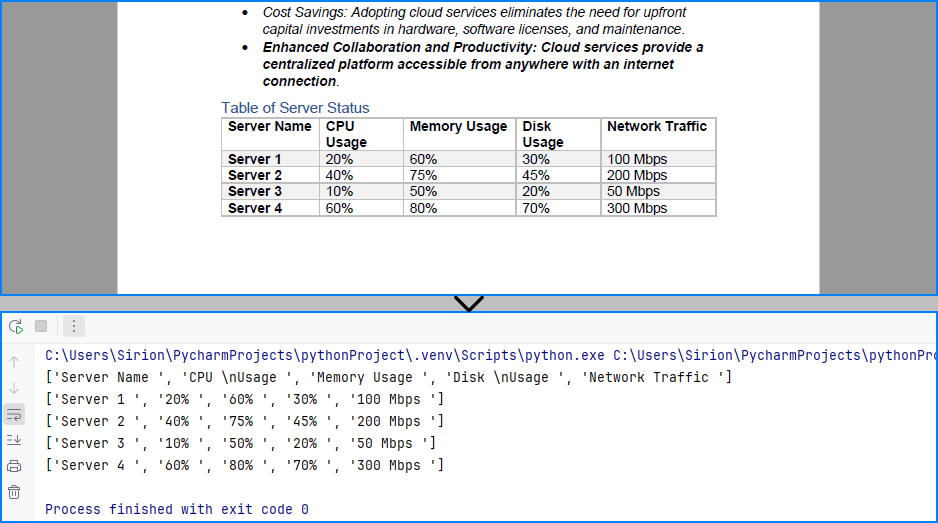
Want to extract text from scanned PDFs using OCR? Read this guide on OCR with Python
Read Images from PDF in Python
PDF files often contain logos, scanned pages, or embedded images. Spire.PDF allows you to read and export these images, which is helpful for working with digitized documents or preserving visual content. Use PdfImageHelper.GetImagesInfo() on each page to retrieve and save all embedded images.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfImageHelper
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper object
image_helper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image information from the page
images_info = image_helper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Save the images from the page as image files
for i in range(len(images_info)):
images_info[i].Image.Save("output/Images/image" + str(i) + ".png")
The image read from the PDF file:
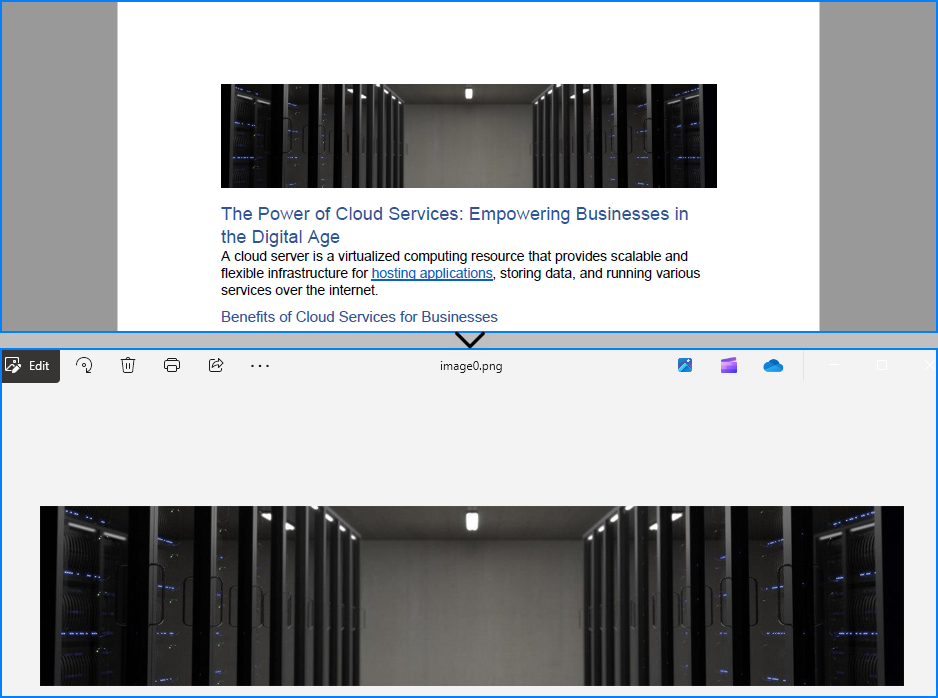
Read PDF Metadata (Title, Author, etc.)
Sometimes you may want to access document metadata like author, subject, and title. This can be helpful for indexing or organizing files. Use the ocumentInformation property to read metadata fields.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the document properties
properties = pdf.DocumentInformation
print("Title: " + properties.Title)
print("Author: " + properties.Author)
print("Subject: " + properties.Subject)
print("Keywords: " + properties.Keywords)
The metadata read from the PDF document:

Common Questions on Reading PDFs
Can Python parse a PDF file?
Yes. Libraries like Spire.PDF for Python allow you to read PDF text, extract tables, and access embedded images or metadata. It supports methods like PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() and PdfTableExtractor.ExtractTable() for structured content parsing.
How do I read a PDF in Jupyter?
Spire.PDF works seamlessly in Jupyter Notebooks. Just install it via pip and use its API to read PDF files, extract text, or parse tables and images directly in your notebook environment.
How to read text from a PDF file?
Use the PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() method on each page after loading the PDF with Spire.PDF. This lets you read PDF file to text in Python and retrieve visible content for processing or analysis.
Can I read a PDF file without saving it to disk?
Yes. You can use LoadFromStream() to read PDF content as bytes and load it directly from memory. This is useful for processing PDFs received from web APIs or file uploads.
Conclusion
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can easily read a PDF in Python — including reading PDF text, tables, images, and metadata — and even read a PDF file to text for further processing or automation. This makes it an ideal solution for document automation, data ingestion, and content parsing in Python.
Need to process large PDF files or unlock all features? Request a free license and take full advantage of Spire.PDF for Python today!
How to Convert PDF to CSV in Python (Fast & Accurate Table Extraction)
2025-05-19 03:43:16 Written by Administrator
Working with PDFs that contain tables, reports, or invoice data? Manually copying that information into spreadsheets is slow, error-prone, and just plain frustrating. Fortunately, there's a smarter way: you can convert PDF to CSV in Python automatically — making your data easy to analyze, import, or automate.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to use Python for PDF to CSV conversion by directly extracting tables with Spire.PDF for Python — a pure Python library that doesn’t require any external tools.
✅ No Adobe or third-party tools required
✅ High-accuracy table recognition
✅ Ideal for structured data workflows
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- Convert PDF to CSV in Python Using Table Extraction
- Related Use Cases
- Why Use Spire.PDF for PDF to CSV Conversion in Python?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Convert PDF to CSV in Python Using Table Extraction
The best way to convert PDF to CSV using Python is by extracting tables directly — no need for intermediate formats like Excel. This method is fast, clean, and highly effective for documents with structured data such as invoices, bank statements, or reports. It gives you usable CSV output with minimal code and high accuracy, making it ideal for automation and data analysis workflows.
Step 1: Install Spire.PDF for Python
Before writing code, make sure to install the required library. You can install Spire.PDF for Python via pip:
pip install spire.pdfYou can also install Free Spire.PDF for Python if you're working on smaller tasks:
pip install spire.pdf.freeStep 2: Python Code — Extract Table from PDF and Save as CSV
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
import csv
import os
# Load the PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a table extractor
extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
# Ensure output directory exists
os.makedirs("output/Tables", exist_ok=True)
# Loop through each page in the PDF
for page_index in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Extract tables on the current page
tables = extractor.ExtractTable(page_index)
for table_index, table in enumerate(tables):
table_data = []
# Extract all rows and columns
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
row_data = []
for col in range(table.GetColumnCount()):
# Get cleaned cell text
cell_text = table.GetText(row, col).replace("\n", "").strip()
row_data.append(cell_text)
table_data.append(row_data)
# Write the table to a CSV file
output_path = os.path.join("output", "Tables", f"Page{page_index + 1}-Table{table_index + 1}.csv")
with open(output_path, "w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
writer.writerows(table_data)
# Release PDF resources
pdf.Dispose()The conversion result:
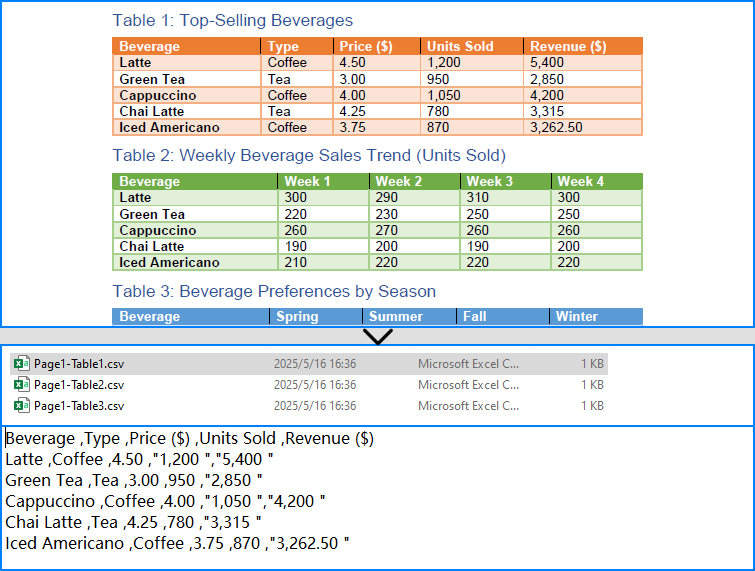
What is PdfTableExtractor?
PdfTableExtractor is a utility class provided by Spire.PDF for Python that detects and extracts table structures from PDF pages. Unlike plain text extraction, it maintains the row-column alignment of tabular data, making it ideal for converting PDF tables to CSV with clean structure.
Best for:
- PDFs with structured tabular data
- Automated Python PDF to CSV conversion
- Fast Python-based data workflows
Relate Article: How to Convert PDFs to Excel XLSX Files with Python
Related Use Cases
If your PDF doesn't contain traditional tables — such as when it's formatted as paragraphs, key-value pairs, or scanned as an image — the following approaches can help you convert such PDFs to CSV using Python effectively:
Useful when data is in paragraph or report form — format it into table-like CSV using Python logic.
Perfect for image-based PDFs — use OCR to detect and export tables to CSV.
Why Choose Spire.PDF for Python?
Spire.PDF for Python is a robust PDF SDK tailored for developers. Whether you're building automated reports, analytics tools, or ETL pipelines — it just works.
Key Benefits:
- Accurate Table Recognition
Smartly extracts structured data from tables
- Pure Python, No Adobe Needed
Lightweight and dependency-free
- Multi-Format Support
Also supports conversion to text, images, Excel, and more
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I convert PDF to CSV using Python?
Yes, you can convert PDF to CSV in Python using Spire.PDF. It supports both direct table extraction to CSV and an optional workflow that converts PDFs to Excel first. No Adobe Acrobat or third-party tools are required.
What's the best way to extract tables from PDFs in Python?
The most efficient way is using Spire.PDF’s PdfTableExtractor class. It automatically detects tables on each page and lets you export structured data to CSV with just a few lines of Python code — ideal for invoices, reports, and automated processing.
Why would I convert PDF to Excel before CSV?
You might convert PDF to Excel first if the layout is complex or needs manual review. This gives you more control over formatting and cleanup before saving as CSV, but it's slower than direct extraction and not recommended for automation workflows.
Does Spire.PDF work without Adobe Acrobat?
Yes. Spire.PDF for Python is a 100% standalone library that doesn’t rely on Adobe Acrobat or any external software. It's a pure Python solution for converting, extracting, and manipulating PDF content programmatically.
Conclusion
Converting PDF to CSV in Python doesn’t have to be a hassle. With Spire.PDF for Python, you can:
- Automatically extract structured tables to CSV
- Build seamless, automated workflows in Python
- Handle both native PDFs and scanned ones (with OCR)
Get a Free License
Spire.PDF for Python offers a free edition suitable for basic tasks. If you need access to more features, you can also apply for a free license for evaluation use. Simply submit a request, and a license key will be sent to your email after approval.
Edit PDF Using Python: A Practical Guide to PDF Modification
2025-05-06 03:42:04 Written by Administrator
PDFs are widely used in reports, invoices, and digital forms due to their consistent formatting across platforms. However, their fixed layout makes editing difficult without specialized tools. For developers looking to edit PDF using Python, Spire.PDF for Python provides a comprehensive and easy-to-use solution. This Python PDF editor enables you to modify PDF files programmatically—changing text, replacing images, adding annotations, handling forms, and securing files—without relying on Adobe Acrobat or any external software.
In this article, we will explore how to use Spire.PDF for Python to programmatically edit PDFs in Python applications.
- Why Use Python and Spire.PDF to Edit PDF Documents?
- Getting Started with Spire.PDF for Python
- How to Edit an Existing PDF Using Spire.PDF for Python
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Use Python and Spire.PDF to Edit PDF Documents?
Python is a highly versatile programming language that provides an excellent platform for automating and managing PDF documents. When it comes to edit PDF Python tasks, Spire.PDF for Python stands out as a comprehensive and easy-to-use solution for all your PDF manipulation needs.
Benefits of Using Python for PDF Editing
- Automation and Batch Processing: Streamline repetitive PDF editing tasks efficiently.
- Cost-Effective: Reduce manual work, saving time and resources when you Python-edit PDF files.
- Integration: Seamlessly incorporate PDF editing into existing Python-based systems and workflows.
Advantages of Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python is a standalone library that enables developers to create, read, edit, convert, and save PDF files without relying on external software. As a trusted Python PDF editor, it offers powerful features such as:
- Text and Image Editing
- Annotations and Bookmark Management
- Form Field Handling
- Security Settings (Encryption and Permissions)
- Conversion to Word, Excel, HTML, and Images
To learn more about these specific features, visit the Spire.PDF for Python tutorials.
With its intuitive API design, Spire.PDF makes it easier than ever to edit PDF files in Python quickly and effectively, ensuring a smooth development experience.
Getting Started with Spire.PDF for Python
Installation:
To install Spire.PDF for Python, simply run the following pip command:
pip install spire.pdf
Alternatively, you can install Free Spire.PDF for Python, a free version suitable for small projects, by running:
pip install spire.pdf.free
You can also download the library manually from the links.
Basic Setup Example:
The following example demonstrates how to create a simple PDF using Spire.PDF for Python:
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfFont, PdfBrushes, PdfFontFamily, PdfFontStyle
# Create a new PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a new page to the document
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create a font
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 28.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold)
# Create a brush
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Draw the string using the font and brush
page.Canvas.DrawString("Hello, World", font, brush, 100.0, 100.0)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/NewPDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result: The generated PDF displays the text "Hello, World" using Times Roman Bold.

With Spire.PDF installed, you're now ready to edit PDFs using Python. The sections below explain how to manipulate structure, content, security, and metadata.
How to Edit an Existing PDF Using Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides a simple yet powerful way to edit PDF using Python. With its intuitive API, developers can automate a wide range of PDF editing tasks including modifying document structure, page content, security settings, and properties. This section outlines the core categories of editing and their typical use cases.
Edit PDF Pages and Structure with Python
Structure editing lets you manipulate PDF page order, merge files, or insert/delete pages—ideal for document assembly workflows.
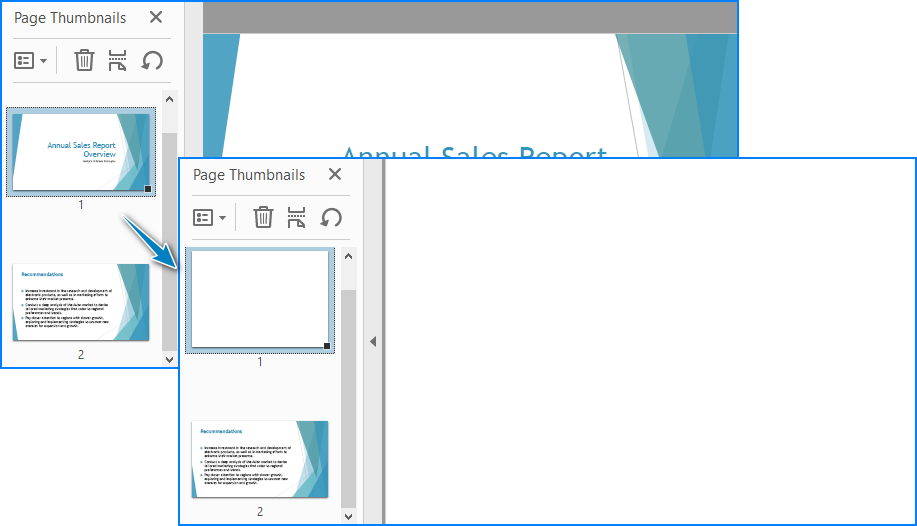
- Insert or Delete Pages
Use the Pages.Insert() and Pages.RemoveAt() methods of the PdfDocument class to insert or delete pages at specific positions.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfPageSize, PdfMargins, PdfPageRotateAngle
# Load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Insert and delete pages
# Insert at beginning
pdf.Pages.Insert(0, PdfPageSize.A4(), PdfMargins(50.0, 60.0), PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle90)
# Delete second page
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(1)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/InsertDeletePage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
- Merge Two PDF Files
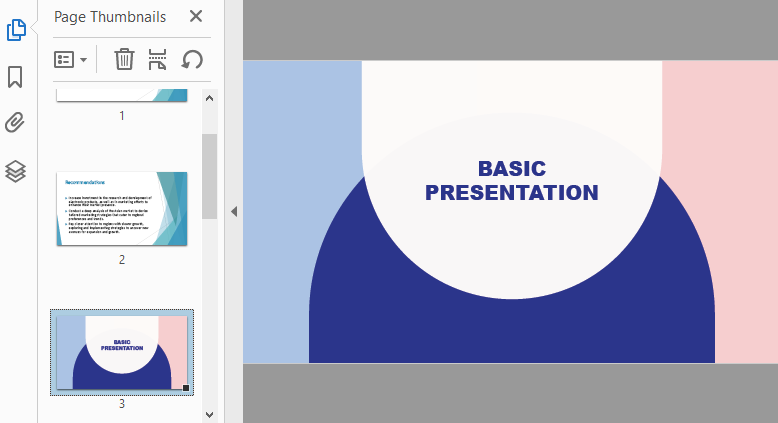
The AppendPage() method allows you to combine PDFs by inserting pages from one document into another.
Code Example
- Python
import os
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Specify the PDF file path
pdfPath = "PDFs/"
# Read the PDF file names from the path and add them to a list
files = [pdfPath + file for file in os.listdir(pdfPath) if file.endswith(".pdf")]
# Load the first PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile(files[0])
# Iterate through the other PDF files
for i in range(1, len(files)):
# Load the current PDF file
pdf2 = PdfDocument()
pdf2.LoadFromFile(files[i])
# Append the pages from the current PDF file to the first PDF file
pdf.AppendPage(pdf2)
# Save the merged PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/MergePDFs.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
You may also like: Splitting PDF Files with Python Code
Edit PDF Content with Python
As a Python PDF editor, Spire.PDF supports a variety of content-level operations, including modifying text, images, annotations, and interactive forms.
- Replace Text in a PDF
The PdfTextReplacer class can be used to find and replace text from a page. Note that precise replacement may require case and layout-aware handling.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextReplacer, ReplaceActionType, Color
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Iterate through the pages
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create a PdfTextReplacer object
replacer = PdfTextReplacer(page)
# Set the replacement options
replacer.Options.ReplaceType = ReplaceActionType.IgnoreCase
# Replace the text
replacer.ReplaceAllText("drones", "ROBOTS", Color.get_Aqua()) # Setting the color is optional
# Save the merged PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceText.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:

- Replace Images in a PDF
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfImageHelper class to help you replace images in a PDF file with ease. By retrieving image information from a specific page, you can use the ReplaceImage() method to directly substitute the original image with a new one.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfImageHelper, PdfImage
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image info of the first image on the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)[0]
# Load a new image
newImage = PdfImage.FromFile("Image.png")
# Replace the image
imageHelper.ReplaceImage(imageInfo, newImage)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceImage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:

- Add Comments or Notes
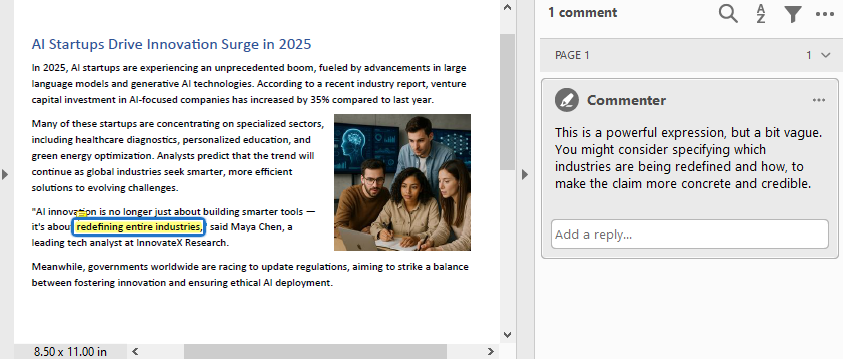
To add comments or notes with Python, use the PdfTextMarkupAnnotation class and add it to the page’s AnnotationsWidget collection.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextFinder, PdfTextMarkupAnnotation, PdfRGBColor, Color
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
#Create a PdfTextFinder instance and set the options
finder = PdfTextFinder(page)
finder.Options.Parameter.IgnoreCase = False
finder.Options.Parameter.WholeWord = True
# Find the text to comment
text = finder.Find("redefining entire industries")[0]
# Get the bound of the text
bound = text.Bounds[0]
# Add comment
commentText = ("This is a powerful expression, but a bit vague. "
"You might consider specifying which industries are "
"being redefined and how, to make the claim more "
"concrete and credible.")
comment = PdfTextMarkupAnnotation("Commenter", commentText, bound)
comment.TextMarkupColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Yellow())
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(comment)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CommentNote.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
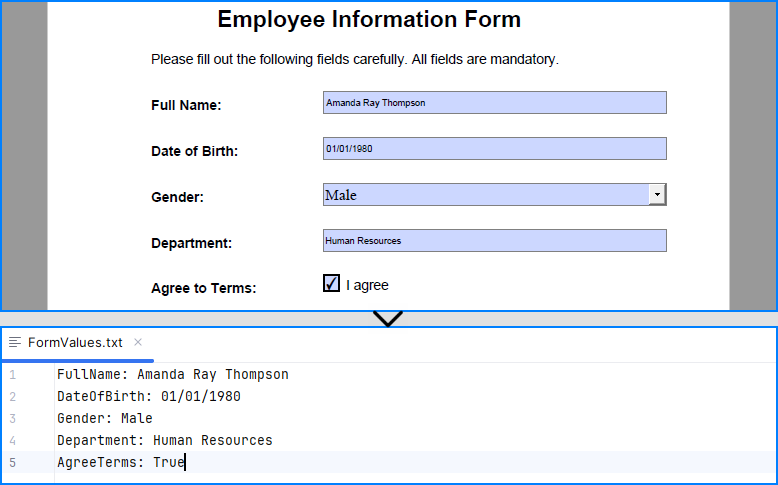
- Edit or Read Form Fields
Spire.PDF for Python allows you to programmatically fill out and read form fields in a PDF document. By accessing the FieldsWidget property of a PdfFormWidget object, you can iterate through all interactive form elements, such as text boxes, combo boxes, and checkboxes, and update or extract their values.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfFormWidget, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
forms = pdf.Form
formWidgets = PdfFormWidget(forms).FieldsWidget
# Fill the forms
for i in range(formWidgets.Count):
formField = formWidgets.get_Item(i)
if formField.Name == "FullName":
textBox = PdfTextBoxFieldWidget(formField)
textBox.Text = "Amanda Ray Thompson"
elif formField.Name == "DateOfBirth":
textBox = PdfTextBoxFieldWidget(formField)
textBox.Text = "01/01/1980"
elif formField.Name == "Gender":
comboBox = PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget(formField)
comboBox.SelectedIndex = [ 1 ]
elif formField.Name == "Department":
formField.Value = "Human Resources"
elif formField.Name == "AgreeTerms":
checkBox = PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget(formField)
checkBox.Checked = True
# Read the forms
formValues = []
for i in range(formWidgets.Count):
formField = formWidgets.get_Item(i)
if isinstance(formField, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + formField.Text)
elif isinstance(formField, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + formField.SelectedValue)
elif isinstance(formField, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + str(formField.Checked))
# Write the form values to a file
with open("output/FormValues.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("\n".join(formValues))
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/FilledForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
Explore more: How to Insert Page Numbers to PDF Using Python
Manage PDF Security with Python
PDF security editing is essential when dealing with sensitive documents. Spire.PDF supports encryption, password protection, digital signature handling, and permission settings.
- Add a Password and Set Permissions
The Encrypt() method lets you secure a PDF with user/owner passwords and define allowed actions like printing or copying.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfEncryptionAlgorithm, PdfDocumentPrivilege, PdfPasswordSecurityPolicy
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Create a PdfSecurityPolicy object and set the passwords and encryption algorithm
securityPolicy = PdfPasswordSecurityPolicy("userPSD", "ownerPSD")
securityPolicy.EncryptionAlgorithm = PdfEncryptionAlgorithm.AES_128
# Set the document privileges
pdfPrivileges = PdfDocumentPrivilege.ForbidAll()
pdfPrivileges.AllowPrint = True
pdfPrivileges.AllowFillFormFields = True
# Apply the document privileges
securityPolicy.DocumentPrivilege = pdfPrivileges
# Encrypt the PDF with the security policy
pdf.Encrypt(securityPolicy)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EncryptedForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result
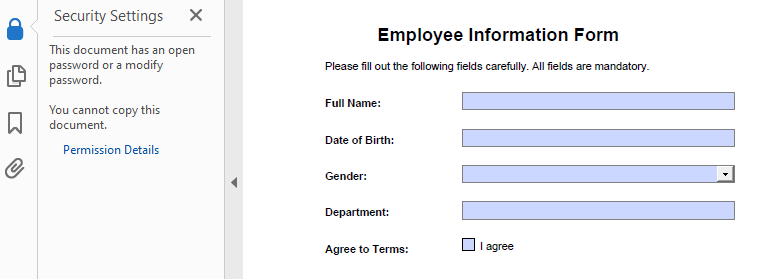
- Remove the Password from a PDF
To open a protected file, provide the user password when calling LoadFromFile(), use Decrypt() to decrypt the document, and save it again unprotected.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the encrypted PDF file with the owner password
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("output/EncryptedForm.pdf", "ownerPSD")
# Decrypt the PDF file
pdf.Decrypt()
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/DecryptedForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Recommended for you: Use Python to Add and Remove Digital Signature in PDF
Edit PDF Properties with Python
Use Spire.PDF to read and edit PDF metadata and viewer preferences—key features for document presentation and organization.
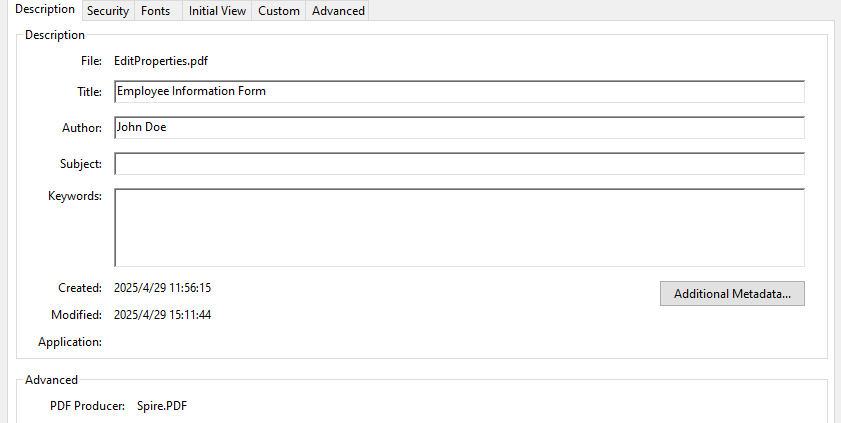
- Update Document Metadata
Update metadata such as title, author, or subject via the DocumentInformation property of the PDF document.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Set document metadata
pdf.DocumentInformation.Author = "John Doe"
pdf.DocumentInformation.Title = "Employee Information Form"
pdf.DocumentInformation.Producer = "Spire.PDF"
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EditProperties.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
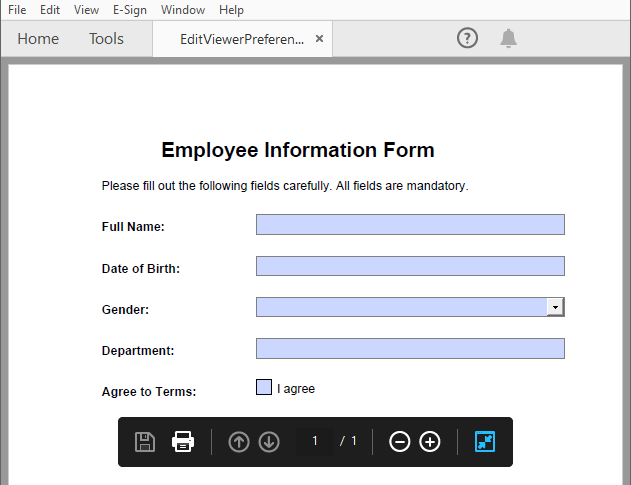
- Set View Preferences
The ViewerPreferences property allows you to customize the viewing mode of a PDF (e.g., two-column layout).
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfPageLayout, PrintScalingMode
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Set the viewer preferences
pdf.ViewerPreferences.DisplayTitle = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideToolbar = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideWindowUI = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.FitWindow = False
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideMenubar = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.PrintScaling = PrintScalingMode.AppDefault
pdf.ViewerPreferences.PageLayout = PdfPageLayout.OneColumn
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EditViewerPreference.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
Similar topic: Change PDF Version Easily with Python Code
Conclusion
Editing PDFs using Python is both practical and efficient with Spire.PDF for Python. Whether you're building automation tools, editing digital forms, or securing sensitive reports, Spire.PDF equips you with a comprehensive suite of editing features—all accessible via clean and simple Python code.
With capabilities that span content editing, form interaction, document structuring, and security control, this Python PDF editor is a go-to solution for developers and organizations aiming to streamline their PDF workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I edit a PDF using Python?
A: Yes, Python offers powerful libraries like Spire.PDF for Python that enable you to edit text, images, forms, annotations, and even security settings in a PDF file.
Q: How to edit a PDF using coding?
A: By using libraries such as Spire.PDF for Python, you can load an existing PDF, modify its content or structure programmatically, and save the changes with just a few lines of code.
Q: What is the Python library for PDF editor?
A: Spire.PDF for Python is a popular choice. It offers comprehensive functionalities for creating, reading, editing, converting, and securing PDF documents without the need for additional software.
Q: Can I modify a PDF for free?
A: Yes, you can use the free edition of Spire.PDF for Python to edit PDF files, although it comes with some limitations, such as processing up to 10 pages per document. Additionally, you can apply for a 30-day temporary license that removes all limitations and watermarks for full functionality testing.
PDF documents may occasionally include blank pages. These pages can affect the reading experience, increase the file size and lead to paper waste during printing. To improve the professionalism and usability of a PDF document, detecting and removing blank pages is an essential step.
This article shows how to accurately detect and remove blank pages—including those that appear empty but actually contain invisible elements—using Python, Spire.PDF for Python, and Pillow.
Install Required Libraries
This tutorial requires two Python libraries:
- Spire.PDF for Python: Used for loading PDFs and detecting/removing blank pages.
- Pillow: A library for image processing that helps detect visually blank pages, which may contain invisible content.
You can easily install both libraries using pip:
pip install Spire.PDF Pillow
Need help installing Spire.PDF? Refer to this guide:
How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
How to Effectively Detect and Remove Blank Pages from PDF Files in Python
Spire.PDF provides a method called PdfPageBase.IsBlank() to check if a page is completely empty. However, some pages may appear blank but actually contain hidden content like white text, watermarks, or background images. These cannot be reliably detected using the PdfPageBase.IsBlank() method alone.
To ensure accuracy, this tutorial adopts a two-step detection strategy:
- Use the PdfPageBase.IsBlank() method to identify and remove fully blank pages.
- Convert non-blank pages to images and analyze them using Pillow to determine if they are visually blank.
⚠️ Important:
If you don’t use a valid license during the PDF-to-image conversion, an evaluation watermark will appear on the image, potentially affecting the blank page detection.
Contact the E-iceblue sales team to request a temporary license for proper functionality.
Steps to Detect and Remove Blank Pages from PDF in Python
Follow these steps to implement blank page detection and removal in Python:
1. Define a custom is_blank_image() Method
This custom function uses Pillow to check whether the converted image of a PDF page is blank (i.e., if all pixels are white).
2. Load the PDF Document
Load the PDF using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
3. Iterate Through Pages
Loop through each page to check if it’s blank using two methods:
- If the PdfPageBase.IsBlank() method returns True, remove the page directly.
- If not, convert the page to an image using the PdfDocument.SaveAsImage() method and analyze it with the custom is_blank_image() method.
4. Save the Result PDF
Finally, save the PDF with blank pages removed using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Code Example
- Python
import io
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
from PIL import Image
# Apply the License Key
License.SetLicenseKey("License-Key")
# Custom function: Check if the image is blank (whether all pixels are white)
def is_blank_image(image):
# Convert to RGB mode and then get the pixels
img = image.convert("RGB")
# Get all pixel points and check if they are all white
white_pixel = (255, 255, 255)
return all(pixel == white_pixel for pixel in img.getdata())
# Load the PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample1111.pdf")
# Iterate through each page in reverse order to avoid index issues when deleting
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count - 1, -1, -1):
page = pdf.Pages[i]
# Check if the current page is completely blank
if page.IsBlank():
# If it's completely blank, remove it directly from the document
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(i)
else:
# Convert the current page to an image
with pdf.SaveAsImage(i) as image_data:
image_bytes = image_data.ToArray()
pil_image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_bytes))
# Check if the image is blank
if is_blank_image(pil_image):
# If it's a blank image, remove the corresponding page from the document
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the resulting PDF
pdf.SaveToFile("RemoveBlankPages.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is considered a blank page in a PDF file?
A: A blank page may be truly empty or contain hidden elements such as white text, watermarks, or transparent objects. This solution detects both types using a dual-check strategy.
Q2: Can I use this method without a Spire.PDF license?
A: Yes, you can run it without a license. However, during PDF-to-image conversion, an evaluation watermark will be added to the output images, which may affect the accuracy of blank page detection. It's best to request a free temporary license for testing.
Q3: What versions of Python are compatible with Spire.PDF?
A: Spire.PDF for Python supports Python 3.7 and above. Ensure that Pillow is also installed to perform image-based blank page detection.
Q4: Can I modify the script to only detect blank pages without deleting them?
A: Absolutely. Just remove or comment out the pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(i) line and use print() or logging to list detected blank pages for further review.
Conclusion
Removing unnecessary blank pages from PDF files is an important step in optimizing documents for readability, file size, and professional presentation. With the combined power of Spire.PDF for Python and Pillow, developers can precisely identify both completely blank pages and pages that appear empty but contain invisible content. Whether you're generating reports, cleaning scanned files, or preparing documents for print, this Python-based solution ensures clean and efficient PDFs.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Introduction
Digital signatures help verify the authenticity and integrity of PDF documents. However, if a signing certificate expires or is revoked, the signature alone may no longer be considered valid. To solve this, a timestamp can be added to the digital signature, proving that the document was signed at a specific point in time-validated by a trusted Time Stamp Authority (TSA).
In this tutorial, we will introduce how to use the Spire.PDF for Python library to digitally sign a PDF document with a timestamp in Python.
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, ensure you have the following:
- Spire.PDF for Python library
- A valid digital certificate (.pfx file)
- A sample PDF file
- An image to display as the signature appearance (optional)
- A reliable Time Stamp Authority (TSA) URL
pip install Spire.PDF
How to Digitally Sign a PDF with a Timestamp in Python
In Spire.PDF for Python, the Security_PdfSignature class is used to create a digital signature, and the ConfigureTimestamp(tsaUrl) method in this class is used to embed a timestamp into the signature. The tsaUrl parameter specifies the address of the TSA server.
Steps to Add a Timestamped Digital Signature
Follow these steps to add a timestamped digital signature to a PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python:
- Create a PdfDocument instance and use the LoadFromFile() method to load the PDF you want to sign.
- Create a Security_PdfSignature object, specifying the target page, certificate file path, certificate password, and signature name.
- Configure the signature's appearance, including its position, size, display labels, and signature image.
- Embed a timestamp by calling the ConfigureTimestamp(tsaUrl) method with a valid Time Stamp Authority (TSA) URL.
- Save the signed PDF using the SaveToFile() method.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import * inputFile = "Sample.pdf" inputFile_pfx = "gary.pfx" inputImage = "E-iceblueLogo.png" outputFile = "SignWithTimestamp.pdf" # Create a PdfDocument instance and load the PDF file to be signed doc = PdfDocument() doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Create a digital signature object by specifying the document, target page, certificate file path, certificate password, and signature name signature = Security_PdfSignature(doc, doc.Pages.get_Item(0), inputFile_pfx, "e-iceblue", "signature") # Define the position and size of the signature on the page (unit: point) signature.Bounds = RectangleF(PointF(90.0, 600.0), SizeF(180.0, 90.0)) # Set the labels and content for the signature details signature.NameLabel = "Digitally signed by: " signature.Name = "Gary" signature.LocationInfoLabel = "Location: " signature.LocationInfo = "CN" signature.ReasonLabel = "Reason: " signature.Reason = "Ensure authenticity" signature.ContactInfoLabel = "Contact Number: " signature.ContactInfo = "028-81705109" # Set document permissions: allow form filling, forbid further changes signature.DocumentPermissions = PdfCertificationFlags.AllowFormFill.value | PdfCertificationFlags.ForbidChanges.value # Set the graphic mode to include both image and signature details, # and set the signature image signature.GraphicsMode = Security_GraphicMode.SignImageAndSignDetail signature.SignImageSource = PdfImage.FromFile(inputImage) # Embed a timestamp into the signature using a Time Stamp Authority (TSA) server url = "http://tsa.cesnet.cz:3161/tsa" signature.ConfigureTimestamp(url) # Save the signed PDF and close the document doc.SaveToFile(outputFile) doc.Close()
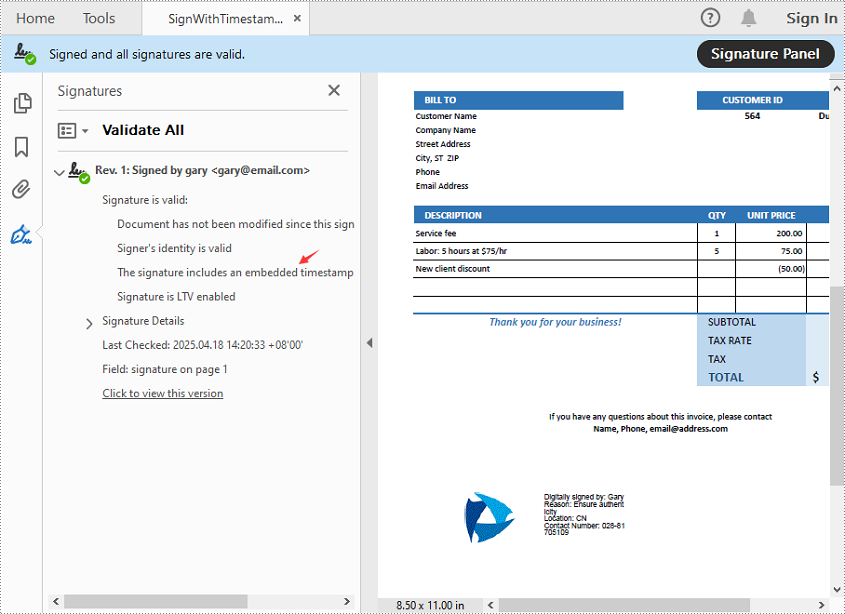
View the Timestamp in PDF
When you open the signed PDF in a viewer like Adobe Acrobat, you can click the Signature Panel to view both the digital signature and the timestamp, which confirm the document’s validity and the signing time:
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Conclusion
Timestamping enhances the reliability of digital signatures by proving when a PDF was signed-even after the certificate has expired. With Spire.PDF for Python, implementing a timestamped digital signature is a straightforward process. Whether you're handling contracts, invoices, or confidential records, this approach ensures long-term document validity and compliance.
PostScript, developed by Adobe, is a page description language known for its high-quality graphics and text rendering capabilities. By converting PDF to PostScript, you can have a precise control over complex graphics, fonts and colors when printing brochures, magazines, advertisements, or other materials.
PCL, on the other hand, is a printer control language developed by Hewlett-Packard. It is designed to be efficient and easy for the printers to interpret. Converting PDF to PCL ensures compatibility with a large number of printers and also optimizes the printing speed for text-heavy documents such as academic reports, letters, or contracts.
This article will demonstrate how to convert PDF to PS or PDF to PCL in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python. It can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert PDF to PostScript in Python
Converting PDF to PS can improve the quality of the printed output. Spire.PDF for .NET allows you to load a PDF file and then converting it to PS format using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename: string, FileFormat.POSTSCRIPT) method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the PDF file to PostScript format using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename: string, FileFormat.POSTSCRIPT) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "input1.pdf" outputFile = "PdfToPostScript.ps" # Create a PdfDocument instance pdf = PdfDocument() # Load a PDF document pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Convert the PDF to a PostScript file pdf.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.POSTSCRIPT) pdf.Close()

Convert PDF to PCL in Python
Converting PDF to PCL can ensure faster printing speed. By using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename: string, FileFormat.PCL) method, you can save a loaded PDF file as a PCL file. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the PDF file to PCL format using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename: string, FileFormat.PCL) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "input1.pdf" outputFile = "ToPCL\\PdfToPcl.pcl" # Create a PdfDocument instance pdf = PdfDocument() # Load a PDF document pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Convert the PDF to a PCL file pdf.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PCL) pdf.Close()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Python: Check if a PDF is Password Protected and Determine the Correct Password
2025-03-19 01:06:07 Written by KoohjiWhen working with PDF files, you may encounter documents that are password protected. This means that you cannot view or edit the content without entering the correct password. Understanding how to check if a PDF is password protected and determining the correct password is essential for accessing important information. In this guide, we will introduce how to check if a PDF is password protected and determine the correct password using Python and the Spire.PDF for Python library.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Check if a PDF is Password Protected
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected(fileName: str) method to check if a PDF file is password protected. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input and output file paths.
- Check if the PDF file is password protected or not using the PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected() method.
- Save the result to a text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Secured.pdf"
outputFile = "CheckPasswordProtection.txt"
# Check if the input PDF file is password protected
isProtected = PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected(inputFile)
# Write the result into a text file
with open(outputFile, "w") as fp:
fp.write("The PDF is " + ("password protected!" if isProtected else "not password protected!"))
Determine the Correct Password for a PDF
While Spire.PDF for Python does not provide a direct method to check if a password is correct, you can achieve this by attempting to load the PDF with the password and catching exceptions. If the password is incorrect, an exception will be thrown. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input and output file paths.
- Create a list of potential passwords to test.
- Iterate through the list and load the PDF with each password using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile(filename: str, password: str) method.
- If no exception is thrown, the password is correct. Otherwise, the password is incorrect.
- Save the results to a text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Secured.pdf"
outputFile = "DetermineCorrectPassword.txt"
# Create a list of potential passwords to test
passwords = ["password1", "password2", "password3", "test", "sample"]
# Create a text file to store the results
with open(outputFile, "w") as fp:
for value in passwords:
try:
# Load the PDF with the current password
doc = PdfDocument()
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile, value)
# If successful, write that the password is correct
fp.write(f'Password "{value}" is correct\n')
except SpireException:
# If an exception occurs, write that the password is not correct
fp.write(f'Password "{value}" is not correct\n')
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
