
Java (481)
Comments in Word documents often hold valuable information, such as feedback, suggestions, and notes. Unfortunately, editors like Microsoft Word lack a built-in feature for batch-extracting comments, leaving users to rely on cumbersome methods like copying and pasting or using VBA macros. To simplify this process, this article demonstrates how to use Java to extract comments from Word documents with Spire.Doc for Java. With a streamlined approach, you can easily retrieve all comment text and images in a single operation—quickly, efficiently, and error-free. Let's explore how it’s done.
- Extract Comments Text from Word Documents in Java
- Extract Comment Images from Word Documents in Java
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Extract Comments Text from Word Documents in Java
Using Java to extract all comment text is easy and quick. Firstly, loop through all comments in the Word file and get the current comment using the Document.getComments().get() method offered by Spire.Doc for Java. Then iterate through all paragraphs in the comment body and get the current paragraph. Finally, text from comment paragraphs will be extracted using the Paragraph.getText() method. Let's dive into the detailed steps.
Steps to extract comment text from Word files:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document from files using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through all comments in the Word file.
- Get the current comment with Document.getComments().get() method.
- Loop through paragraphs in the comment and access the current paragraph through Comment.getBody().getParagraphs().get() method.
- Extract the text of the paragraphs in comments by calling Paragraph.getText() method.
- Get the current comment with Document.getComments().get() method.
- Save the extracted comments.
The code example below demonstrates how to extract all comment text from a Word document:
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
import java.io.*;
public class ExtractComments {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Create a new Document instance
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from the specified input file
doc.loadFromFile("/comments.docx");
// Iterate over each comment in the document
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getComments().getCount(); i++) {
// Get the comment at the current index
Comment comment = doc.getComments().get(i);
// Iterate over each paragraph in the comment's body
for (int j = 0; j < comment.getBody().getParagraphs().getCount(); j++) {
// Get the paragraph at the current index
Paragraph para = comment.getBody().getParagraphs().get(j);
// Get the text of the paragraph and append a line break
String result = para.getText() + "\r\n";
// Write the extracted comment a text file
writeStringToTxt(result, "/commenttext.txt");
}
}
// Dispose of the document resources
doc.dispose();
}
// Custom method to write a string to a text file
public static void writeStringToTxt(String content, String txtFileName) throws IOException {
FileWriter fWriter = new FileWriter(txtFileName, true);
try {
// Write the content to the text file
fWriter.write(content);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// Flush and close the FileWriter
fWriter.flush();
fWriter.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
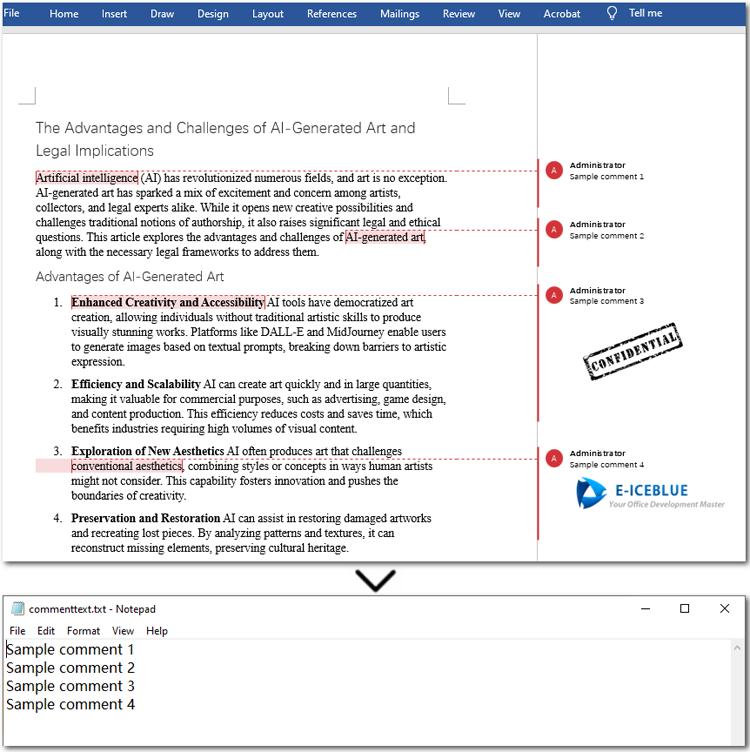
Extract Comments Images from Word Documents with Java
Sometimes, comments in a document may contain not only text but also images. With the methods provided by Spire.Doc for Java, you can easily extract all images from comments in bulk. The process is similar to extracting text: you need to iterate through each comment, the paragraphs in the comment body, and the child objects of each paragraph. Then, check if the object is a DocPicture. If it is, use the DocPicture.getImageBytes() method to extract the image.
Steps to extract comment images from Word documents:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Specify the file path to load a source Word file through Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store extracted data.
- Loop through comments in the Word file and get the current comment using Document.getComments().get() method.
- Loop through all paragraphs in a comment, and get the current paragraph with Comment.getBody().getParagraphs().get() method.
- Iterate through each child object of a paragraph, and access a child object through Paragraph.getChildObjects().get() method.
- Check if the child object is DocPicture, if it is, get the image data using DocPicture.getImageBytes() method.
- Loop through all paragraphs in a comment, and get the current paragraph with Comment.getBody().getParagraphs().get() method.
- Add the image data to the list and save it as image files.
Here is the code example of extracting all comment images from a Word file:
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ExtractCommentImages {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an object of the Document class
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document with comments
document.loadFromFile("/comments.docx");
// Create a list to store the extracted image data
List<byte[]> images = new ArrayList<>();
// Loop through the comments in the document
for (int i = 0; i < document.getComments().getCount(); i++) {
Comment comment = document.getComments().get(i);
// Iterate through the paragraphs in the comment body
for (int j = 0; j < comment.getBody().getParagraphs().getCount(); j++) {
Paragraph paragraph = comment.getBody().getParagraphs().get(j);
// Loop through the child objects in the paragraph
for (int k = 0; k < paragraph.getChildObjects().getCount(); k++) {
DocumentObject obj = paragraph.getChildObjects().get(k);
// Check if it is a picture
if (obj instanceof DocPicture) {
DocPicture picture = (DocPicture) obj;
// Get the image date and add it to the list
images.add(picture.getImageBytes());
}
}
}
}
// Specify the output file path
String outputDir = "/comment_images/";
new File(outputDir).mkdirs();
// Save the image data as image files
for (int i = 0; i < images.size(); i++) {
String fileName = String.format("comment-image-%d.png", i);
Path filePath = Paths.get(outputDir, fileName);
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filePath.toFile())) {
fos.write(images.get(i));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Retrieving and replacing fonts in Word documents is a key aspect of document design. This process enables users to refresh their text with modern typography, improving both appearance and readability. Mastering font adjustments can enhance the overall impact of your documents, making them more engaging and accessible.
In this article, you will learn how to retrieve and replace fonts in a Word document using Spire.Doc for Java.
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Retrieve Fonts Used in a Word Document
To retrieve font information from a Word document, you'll need to navigate through the document's sections, paragraphs, and their child objects. For each child object, check if it is an instance of TextRange. If a TextRange is detected, you can extract the font details, including the font name and size, using the methods under the TextRange class.
Here are the steps to retrieve font information from a Word document using Java:
- Create a Document object.
- Load the Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each section, paragraph, and child object.
- For each child object, check if it is an instance of TextRange class.
- If it is, retrieve the font name and size using the TextRange.getCharacterFormat().getFontName() and TextRange.getCharacterFormat().getFontSize() methods.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.TextRange;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
// Customize a FontInfo class to help store font information
class FontInfo {
private String name;
private Float size;
public FontInfo() {
this.name = "";
this.size = null;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Float getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(Float size) {
this.size = size;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) return true;
if (!(obj instanceof FontInfo)) return false;
FontInfo other = (FontInfo) obj;
return name.equals(other.getName()) && size.equals(other.getSize());
}
}
public class RetrieveFonts {
// Function to write string to a txt file
public static void writeAllText(String filename, List<String> text) {
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filename))) {
for (String s : text) {
writer.write(s);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<FontInfo> fontInfos = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder fontInformations = new StringBuilder();
// Create a Document instance
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Iterate through the sections
for (int i = 0; i < document.getSections().getCount(); i++) {
Section section = document.getSections().get(i);
// Iterate through the paragraphs
for (int j = 0; j < section.getBody().getParagraphs().getCount(); j++) {
Paragraph paragraph = section.getBody().getParagraphs().get(j);
// Iterate through the child objects
for (int k = 0; k < paragraph.getChildObjects().getCount(); k++) {
DocumentObject obj = paragraph.getChildObjects().get(k);
if (obj instanceof TextRange) {
TextRange txtRange = (TextRange) obj;
// Get the font name and size
String fontName = txtRange.getCharacterFormat().getFontName();
Float fontSize = txtRange.getCharacterFormat().getFontSize();
String textColor = txtRange.getCharacterFormat().getTextColor().toString();
// Store the font information
FontInfo fontInfo = new FontInfo();
fontInfo.setName(fontName);
fontInfo.setSize(fontSize);
if (!fontInfos.contains(fontInfo)) {
fontInfos.add(fontInfo);
String str = String.format("Font Name: %s, Size: %.2f, Color: %s%n", fontInfo.getName(), fontInfo.getSize(), textColor);
fontInformations.append(str);
}
}
}
}
}
// Write font information to a txt file
writeAllText("output/GetFonts.txt", Arrays.asList(fontInformations.toString().split("\n")));
// Dispose resources
document.dispose();
}
}

Replace a Specific Font with Another in Word
Once you obtain the font name of a specific text range, you can easily replace it with a different font, by using the TextRange.getCharacterFormat().setFontName() method. Additionally, you can adjust the font size and text color using the appropriate methods in the TextRange class.
Here are the steps to replace a specific font in a Word document using Java:
- Create a Document object.
- Load the Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each section, paragraph, and child object.
- For each child object, check if it is an instance of TextRange class.
- If it is, get the font name using the TextRange.getCharacterFormat().getFontName() method.
- Check if the font name is the specified font.
- If it is, set a new font name for the text range using the TextRange.getCharacterFormat().setFontName() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.TextRange;
public class ReplaceFont {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document instance
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Iterate through the sections
for (int i = 0; i < document.getSections().getCount(); i++) {
// Get a specific section
Section section = document.getSections().get(i);
// Iterate through the paragraphs
for (int j = 0; j < section.getBody().getParagraphs().getCount(); j++) {
// Get a specific paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.getBody().getParagraphs().get(j);
// Iterate through the child objects
for (int k = 0; k < paragraph.getChildObjects().getCount(); k++) {
// Get a specific child object
DocumentObject obj = paragraph.getChildObjects().get(k);
// Determine if a child object is a TextRange
if (obj instanceof TextRange) {
// Get a specific text range
TextRange txtRange = (TextRange) obj;
// Get the font name
String fontName = txtRange.getCharacterFormat().getFontName();
// Determine if the font name is Microsoft JhengHei
if ("Microsoft JhengHei".equals(fontName)) {
// Replace the font with another font
txtRange.getCharacterFormat().setFontName("Segoe Print");
}
}
}
}
}
// Save the document to a different file
document.saveToFile("output/ReplaceFonts.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resources
document.dispose();
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Extracting tables from Word documents is essential for many applications, as they often contain critical data for analysis, reporting, or system integration. By automating this process with Java, developers can create robust applications that seamlessly access this structured data, enabling efficient conversion into alternative formats suitable for databases, spreadsheets, or web-based visualizations. This article will demonstrate how to use Spire.Doc for Java to efficiently extract tables from Word documents in Java programs.
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Extract Tables from Word Documents with Java
With Spire.Doc for Java, developers can extract tables from Word documents using the Section.getTables() method. Table data can be accessed by iterating through rows and cells. The process for extracting tables is detailed below:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Access the sections in the document using the Document.getSections() method and iterate through them.
- Access the tables in each section using the Section.getTables() method and iterate through them.
- Access the rows in each table using the Table.getRows() method and iterate through them.
- Access the cells in each row using the TableRow.getCells() method and iterate through them.
- Retrieve text from each cell by iterating through its paragraphs using the TableCell.getParagraphs() and Paragraph.getText() methods.
- Add the extracted table data to a StringBuilder object.
- Write the StringBuilder object to a text file or use it as needed.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExtractWordTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document doc = new Document();
try {
// Load a Word document
doc.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Iterate the sections in the document
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getSections().getCount(); i++) {
// Get a section
Section section = doc.getSections().get(i);
// Iterate the tables in the section
for (int j = 0; j < section.getTables().getCount(); j++) {
// Get a table
Table table = section.getTables().get(j);
// Collect all table content
StringBuilder tableText = new StringBuilder();
for (int k = 0; k < table.getRows().getCount(); k++) {
// Get a row
TableRow row = table.getRows().get(k);
// Iterate the cells in the row
StringBuilder rowText = new StringBuilder();
for (int l = 0; l < row.getCells().getCount(); l++) {
// Get a cell
TableCell cell = row.getCells().get(l);
// Iterate the paragraphs to get the text in the cell
String cellText = "";
for (int m = 0; m < cell.getParagraphs().getCount(); m++) {
Paragraph paragraph = cell.getParagraphs().get(m);
cellText += paragraph.getText() + " ";
}
if (l < row.getCells().getCount() - 1) {
rowText.append(cellText).append("\t");
} else {
rowText.append(cellText).append("\n");
}
}
tableText.append(rowText);
}
// Write the table text to a file using try-with-resources
try (FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("output/Tables/Section-" + (i + 1) + "-Table-" + (j + 1) + ".txt")) {
writer.write(tableText.toString());
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
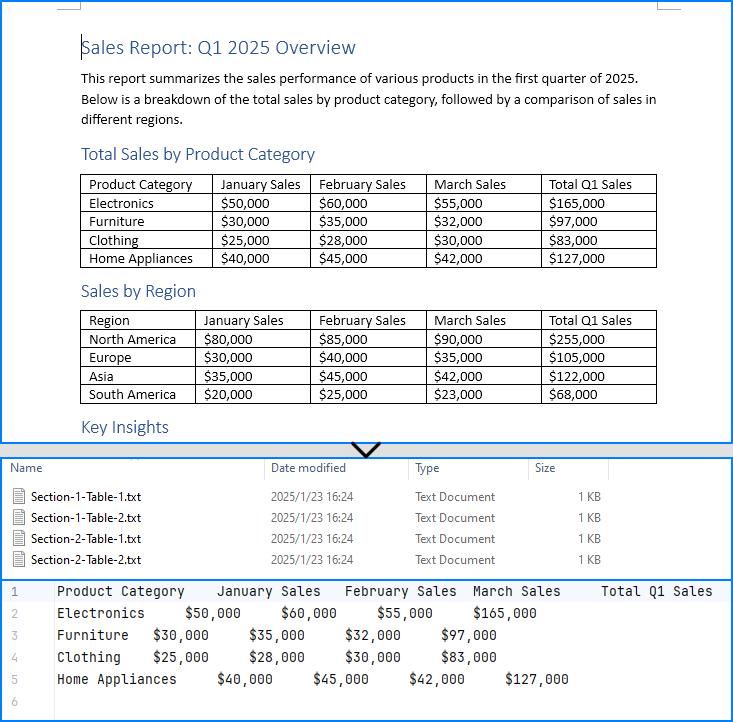
Extract Tables from Word Documents to Excel Worksheets
Developers can use Spire.Doc for Java with Spire.XLS for Java to extract table data from Word documents and write it to Excel worksheets. To get started, download Spire.XLS for Java or add the following Maven configuration:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
The detailed steps for extracting tables from Word documents to Excel workbooks are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Create a Workbook object and remove the default worksheets using the Workbook.getWorksheets().clear() method.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Access the sections in the document using the Document.getSections() method and iterate through them.
- Access the tables in each section using the Section.getTables() method and iterate through them.
- Create a worksheet for each table using the Workbook.getWorksheets().add() method.
- Access the rows in each table using the Table.getRows() method and iterate through them.
- Access the cells in each row using the TableRow.getCells() method and iterate through them.
- Retrieve text from each cell by iterating through its paragraphs using the TableCell.getParagraphs() and Paragraph.getText() methods.
- Write the extracted cell text to the corresponding cell in the worksheet using the Worksheet.getRange().get(row, column).setValue() method.
- Format the worksheet as needed.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.xls.FileFormat;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class ExtractWordTableToExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Remove the default worksheets
workbook.getWorksheets().clear();
try {
// Load a Word document
doc.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Iterate the sections in the document
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getSections().getCount(); i++) {
// Get a section
Section section = doc.getSections().get(i);
// Iterate the tables in the section
for (int j = 0; j < section.getTables().getCount(); j++) {
// Get a table
Table table = section.getTables().get(j);
// Create a worksheet for each table
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().add("Section-" + (i + 1) + "-Table-" + (j + 1));
for (int k = 0; k < table.getRows().getCount(); k++) {
// Get a row
TableRow row = table.getRows().get(k);
for (int l = 0; l < row.getCells().getCount(); l++) {
// Get a cell
TableCell cell = row.getCells().get(l);
// Iterate the paragraphs to get the text in the cell
String cellText = "";
for (int m = 0; m < cell.getParagraphs().getCount(); m++) {
Paragraph paragraph = cell.getParagraphs().get(m);
if (m > 0 && m < cell.getParagraphs().getCount() - 1) {
cellText += paragraph.getText() + "\n";
}
else {
cellText += paragraph.getText();
}
// Write the cell text to the corresponding cell in the worksheet
sheet.getRange().get(k + 1, l + 1).setValue(cellText);
}
// Auto-fit columns
sheet.autoFitColumn(l + 1);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
workbook.saveToFile("output/WordTableToExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016);
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
