
Java (481)
Named ranges in Excel are valuable tools that empower you to assign meaningful names to specific cells or ranges within your spreadsheets. Instead of relying on traditional cell references like A1:B10, named ranges allow you to reference data by their logical names, making your formulas more intelligible and easier to understand and maintain. This article will demonstrate how to create, edit or delete named ranges in Excel in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Create a Named Range in Excel in Java
- Edit an Existing Named Range in Excel in Java
- Delete a Named Range from Excel in Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Create a Named Range in Excel in Java
You can use the Workbook.getNameRanges().add(String name) method provided by Spire.XLS for Java to add a named range to an Excel workbook. Once the named range is added, you can define the cell or range of cells it refers to using the INamedRange.setRefersToRange(IXLSRange range) method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Add a named range to the workbook using the Workbook.getNameRanges().add(String name) method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the workbook using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(int index) method.
- Set the cell range that the named range refers to using the INamedRange.setRefersToRange(IXLSRange range) method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import com.spire.xls.core.INamedRange;
public class CreateNamedRange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel workbook
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Add a named range to the workbook
INamedRange namedRange = workbook.getNameRanges().add("Amount");
//Get a specific worksheet in the workbook
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Set the cell range that the named range references
namedRange.setRefersToRange(sheet.getCellRange("D2:D5"));
//Save the result file to a specific location
String result = "CreateNamedRange.xlsx";
workbook.saveToFile(result, ExcelVersion.Version2013);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
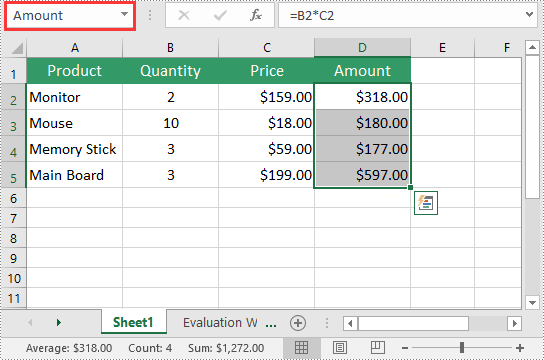
Edit an Existing Named Range in Excel in Java
After you've created a named range, you may want to modify its name or adjust the cells it refers to. The following are the detailed steps:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific named range in the workbook using the Workbook.getNameRanges().get(int index) method.
- Modify the name of the named range using the INamedRange.setName(String name) method.
- Modify the cells that the named range refers to using the INamedRange.setRefersToRange(IXLSRange range) method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.core.INamedRange;
public class ModifyNamedRange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel workbook
workbook.loadFromFile("CreateNamedRange.xlsx");
//Get a specific named range in the workbook
INamedRange namedRange = workbook.getNameRanges().get(0);
//Change the name of the named range
namedRange.setName("MonitorAmount");
//Set the cell range that the named range references
namedRange.setRefersToRange(workbook.getWorksheets().get(0).getCellRange("D2"));
//Save the result file to a specific location
String result = "ModifyNamedRange.xlsx";
workbook.saveToFile(result, ExcelVersion.Version2013);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
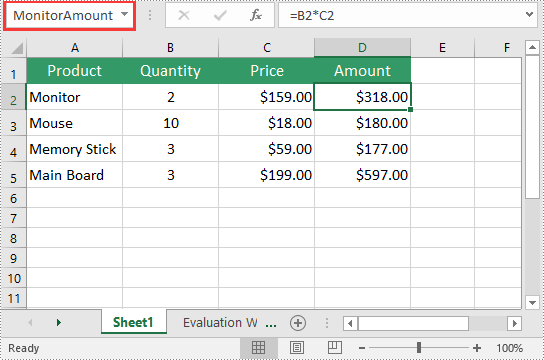
Delete a Named Range from Excel in Java
If you have made significant changes to the structure or layout of your spreadsheet, it might be necessary to delete a named range that is no longer relevant or accurate. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific named range by its index or name using the Workbook.getNameRanges().removeAt(int index) or Workbook.getNameRanges().remove(string name) method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
public class DeleteNamedRange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel workbook
workbook.loadFromFile("CreateNamedRange.xlsx");
//Remove a specific named range by its index
workbook.getNameRanges().removeAt(0);
//Remove a specific named range by its name
//workbook.getNameRanges().remove("Amount");
//Save the result file to a specific location
String result = "RemoveNamedRange.xlsx";
workbook.saveToFile(result, ExcelVersion.Version2013);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
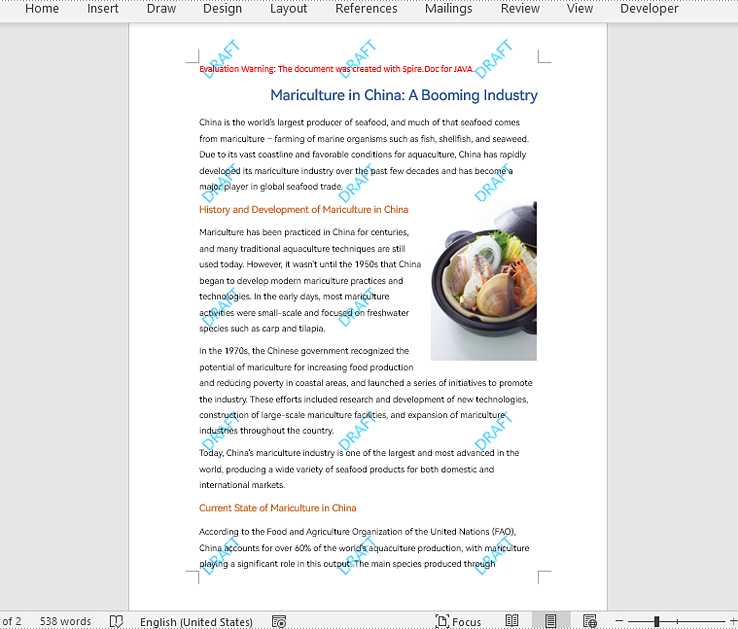
Repeating watermarks, also called multi-line watermarks, are a type of watermark that appears multiple times on a page of a Word document at regular intervals. Compared with single watermarks, repeating watermarks are more difficult to remove or obscure, thus offering a better deterrent to unauthorized copying and distribution. This article is going to show how to insert repeating text and image watermarks into Word documents programmatically using Spire.Doc for Java.
- Add Repeating Text Watermarks to Word Documents in Java
- Add Repeating Picture Watermarks to Word Documents in Java
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add Repeating Text Watermarks to Word Documents in Java
We can insert repeating text watermarks to Word documents by adding repeating WordArt to the headers of a document at specified intervals. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create an object of ShapeObject class and set the WordArt text using ShapeObject.getWordArt().setText() method.
- Specify the rotation angle and the number of vertical repetitions and horizontal repetitions.
- Set the format of the shape using methods under ShapeObject class.
- Loop through the sections in the document to insert repeating watermarks to each section by adding the WordArt shape to the header of each section multiple times at specified intervals using Paragraph.getChildObjects().add(ShapeObject) method.
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.HeaderFooter;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.documents.ShapeLineStyle;
import com.spire.doc.documents.ShapeType;
import com.spire.doc.fields.ShapeObject;
import java.awt.*;
public class insertRepeatingTextWatermark {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create an object of Document class
Document doc = new Document();
//Load a Word document
doc.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
//Create an object of ShapeObject class and set the WordArt text
ShapeObject shape = new ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.Text_Plain_Text);
shape.getWordArt().setText("DRAFT");
//Specify the watermark rotating angle and the number of vertical repetitions and horizontal repetitions
double rotation = 315;
int ver = 5;
int hor = 3;
//Set the format of the WordArt shape
shape.setWidth(60);
shape.setHeight(20);
shape.setVerticalPosition(30);
shape.setHorizontalPosition(20);
shape.setRotation(rotation);
shape.setFillColor(Color.BLUE);
shape.setLineStyle(ShapeLineStyle.Single);
shape.setStrokeColor(Color.CYAN);
shape.setStrokeWeight(1);
//Loop through the sections in the document
for (Section section : (Iterable<Section>) doc.getSections()) {
//Get the header of a section
HeaderFooter header = section.getHeadersFooters().getHeader();
//Add paragraphs to the header
Paragraph paragraph = header.addParagraph();
for (int i = 0; i < ver; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < hor; j++) {
//Add the WordArt shape to the header
shape = (ShapeObject) shape.deepClone();
shape.setVerticalPosition((float) (section.getPageSetup().getPageSize().getHeight()/ver * i + Math.sin(rotation) * shape.getWidth()/2));
shape.setHorizontalPosition((float) ((section.getPageSetup().getPageSize().getWidth()/hor - shape.getWidth()/2) * j));
paragraph.getChildObjects().add(shape);
}
}
}
//Save the document
doc.saveToFile("RepeatingTextWatermark.docx");
doc.dispose();
}
}
Add Repeating Picture Watermarks to Word Documents in Java
Similarly, we can insert repeating image watermarks into Word documents by adding repeating pictures to headers at regular intervals. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Load a picture using DocPicture.loadImage() method.
- Set the text wrapping style of the picture as Behind using DocPicture.setTextWrappingStyle(TextWrappingStyle.Behind) method.
- Specify the number of vertical repetitions and horizontal repetitions.
- Loop through the sections in the document to insert repeating picture watermarks to the document by adding a picture to the header of each section at specified intervals using Paragraph.getChildObjects().add(DocPicture) method.
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.HeaderFooter;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.documents.TextWrappingStyle;
import com.spire.doc.fields.DocPicture;
public class insertRepeatingPictureWatermark {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create an object of Document class
Document doc = new Document();
//Load a Word document
doc.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
//Load a picture
DocPicture pic = new DocPicture(doc);
pic.loadImage("watermark.png");
//Set the text wrapping style of the picture as Behind
pic.setTextWrappingStyle(TextWrappingStyle.Behind);
//Specify the number of vertical repetitions and horizontal repetitions
int ver = 4;
int hor = 3;
//Loop through the sections in the document
for (Section section : (Iterable<Section>) doc.getSections()) {
//Get the header of a section
HeaderFooter header = section.getHeadersFooters().getHeader();
//Add a paragraph to the section
Paragraph paragraph = header.addParagraph();
for (int i = 0; i < ver; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < hor; j++) {
//Add the picture to the header
pic = (DocPicture) pic.deepClone();
pic.setVerticalPosition((float) ((section.getPageSetup().getPageSize().getHeight()/ver) * i));
pic.setHorizontalPosition((float) (section.getPageSetup().getPageSize().getWidth()/hor - pic.getWidth()/2) * j);
paragraph.getChildObjects().add(pic);
}
}
}
//Save the document
doc.saveToFile("RepeatingPictureWatermark.docx", FileFormat.Auto);
doc.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Document properties in Excel are important pieces of metadata that provide additional information about a workbook. If you are managing multiple Excel workbooks and want to keep track of information like author, title, and other relevant metadata, you can read their document properties to quickly gather this information. Besides, in certain situations, you may need to delete document properties from Excel. For instance, if sensitive data is inadvertently stored in document properties, you may need to delete these document properties before sharing the workbook to ensure data security and confidentiality. This article will show you how to read or delete document properties from Excel in Java using Spire.XLS for Java library.
- Read Standard and Custom Document Properties from Excel in Java
- Delete Standard and Custom Document Properties from Excel in Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Read Standard and Custom Document Properties from Excel in Java
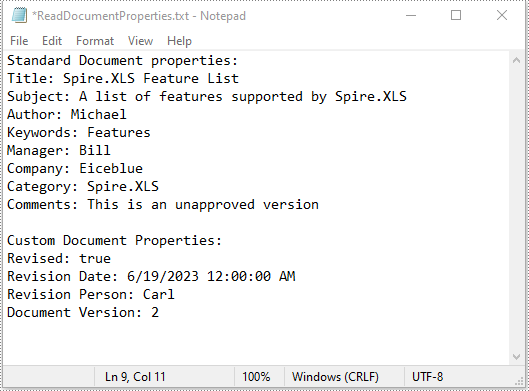
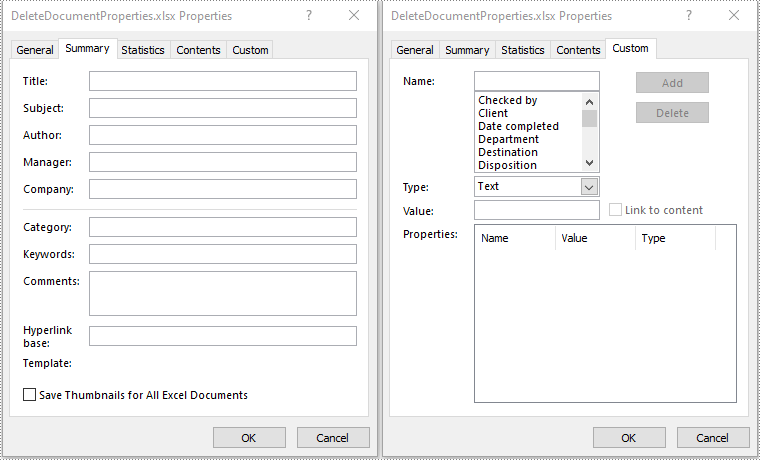
Standard document properties are pre-built properties included in every Excel file. These properties can include information such as the author, title, subject, keywords, and other details about the file. Custom document properties in Excel are user-defined, meaning that users can create them according to their specific needs. The value of custom document properties can be assigned as text, date time, numeric values, or simply a yes or no.
The following steps demonstrate how to read standard document properties and custom document properties of an Excel file using Spire.XLS for Java:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Initialize an instance of the StringBuilder class for storing the standard and custom document properties.
- Get the collection of all standard document properties of the file using the Workbook.getDocumentProperties() method.
- Get specific standard document properties using the corresponding methods under the BuiltInDocumentProperties class.
- Append the standard document properties to the StringBuilder instance.
- Get the collection of all custom document properties of the file using the Workbook.getCustomDocumentProperties() method.
- Iterate through the collection.
- Get the name and value of each custom document property using the IDocumentProperty.getName() and IDocumentProperty.getValue() methods and append them to the StringBuilder instance.
- Write the content of the StringBuilder instance into a text file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.collections.BuiltInDocumentProperties;
import com.spire.xls.core.ICustomDocumentProperties;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadStandardDocumentProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Initialize an instance of the StringBuilder instance
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//Get the collection of all standard document properties
BuiltInDocumentProperties standardProperties = workbook.getDocumentProperties();
//Get specific standard document properties
String title = standardProperties.getTitle();
String subject = standardProperties.getSubject();
String author = standardProperties.getAuthor();
String keywords = standardProperties.getKeywords();
String manager = standardProperties.getManager();
String company = standardProperties.getCompany();
String category = standardProperties.getCategory();
String comments = standardProperties.getComments();
//Append the standard document properties to the StringBuilder instance
sb.append("Standard Document properties:"
+"\r\nTitle: " + title
+ "\r\nSubject: " + subject
+ "\r\nAuthor: " + author
+ "\r\nKeywords: "+ keywords
+ "\r\nManager: " + manager.toString()
+ "\r\nCompany: " + company.toString()
+ "\r\nCategory: " + category.toString()
+ "\r\nComments: " + comments.toString()
);
sb.append("\r\n\nCustom Document Properties:");
//Get the collection of all custom document properties
ICustomDocumentProperties customProperties = workbook.getCustomDocumentProperties();
//Iterate through the collection
for(int i =0; i < customProperties.getCount(); i++)
{
//Append the name and value of each custom document property to the StringBuilder instance
sb.append("\r\n" + customProperties.get(i).getName() + ": " + customProperties.get(i).getValue());
}
//Write the content of the StringBuilder instance into a text file
String output = "ReadDocumentProperties.txt";
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(output, true);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
bw.append(sb);
bw.close();
fw.close();
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Delete Standard and Custom Document Properties from Excel in Java
You can easily delete standard document properties from an Excel file by setting their values as empty. For custom document properties, you can use the ICustomDocumentProperties.remove() method to delete them.
The following steps demonstrate how to delete standard and custom document properties from an Excel file using Spire.XLS for Java:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the collection of all standard document properties of the file using the Workbook.getDocumentProperties() method.
- Set the values of specific standard document properties as empty using the corresponding methods under the BuiltInDocumentProperties class.
- Get the collection of all custom document properties of the file using the Workbook.getCustomDocumentProperties() method.
- Iterate through the collection.
- Delete each custom document property from the collection using the ICustomDocumentProperties.remove() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.collections.BuiltInDocumentProperties;
import com.spire.xls.core.ICustomDocumentProperties;
public class DeleteDocumentProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Get the collection of all standard document properties
BuiltInDocumentProperties standardProperties = workbook.getDocumentProperties();
//Set the value of each standard document property as empty
standardProperties.setTitle("");
standardProperties.setSubject("");
standardProperties.setAuthor("");
standardProperties.setManager("");
standardProperties.setCompany("");
standardProperties.setCategory("");
standardProperties.setKeywords("");
standardProperties.setComments("");
//Get the collection of all custom document properties
ICustomDocumentProperties customProperties = workbook.getCustomDocumentProperties();
//Iterate through the collection
for(int i = customProperties.getCount() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
//Delete each custom document property from the collection by its name
customProperties.remove(customProperties.get(i).getName());
}
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("DeleteDocumentProperties.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
