Converting between Excel and JSON formats is a valuable skill for developers dealing with data exchange, API integration, and modern web applications.
Excel files (.xls, .xlsx) are excellent for organizing and analyzing tabular data, while JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is lightweight, human-readable, and ideal for transmitting data across platforms.
In this step-by-step tutorial, you’ll learn how to seamlessly convert Excel to JSON and JSON to Excel in C# using the Spire.XLS for .NET library. Whether you’re exporting Excel data for frontend apps, feeding structured datasets into APIs, or importing JSON into spreadsheets, this guide provides clear explanations, complete code samples, and tips to help you get started quickly.
What You Will Learn
- Why Convert Between Excel and JSON Formats
- Prerequisites
- Installing Required Packages
- How to Convert Excel to JSON in C# .NET (Step-by-Step)
- How to Convert JSON to Excel in C# .NET (Step-by-Step)
- Tips and Best Practices
- Conclusion
- Further Reading
- FAQs
Why Convert Between Excel and JSON Formats?
Converting between Excel and JSON can be beneficial for several reasons:
- Data Exchange: JSON is a standard format for data interchange in web applications, making it easier to share data across platforms.
- Integration with APIs: Many web APIs require data in JSON format, necessitating conversion from Excel for seamless integration.
- Lightweight and Compact: JSON files are generally smaller in size compared to Excel files, leading to faster data transfer and reduced storage needs.
- Readability: JSON is human-readable and easier to understand, which can simplify data analysis and troubleshooting.
- Compatibility with NoSQL Databases: JSON format is commonly used in NoSQL databases, facilitating easy data migration and storage.
Prerequisites
Before we start, ensure you have the following:
- Visual Studio or any C# development IDE installed.
- .NET Framework or .NET Core installed.
- Spire.XLS package installed for handling Excel files.
- Newtonsoft.Json package installed for handling JSON serialization and deserialization.
Installing Required Packages
You can install the required packages using NuGet Package Manager in Visual Studio:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Install-Package Newtonsoft.Json
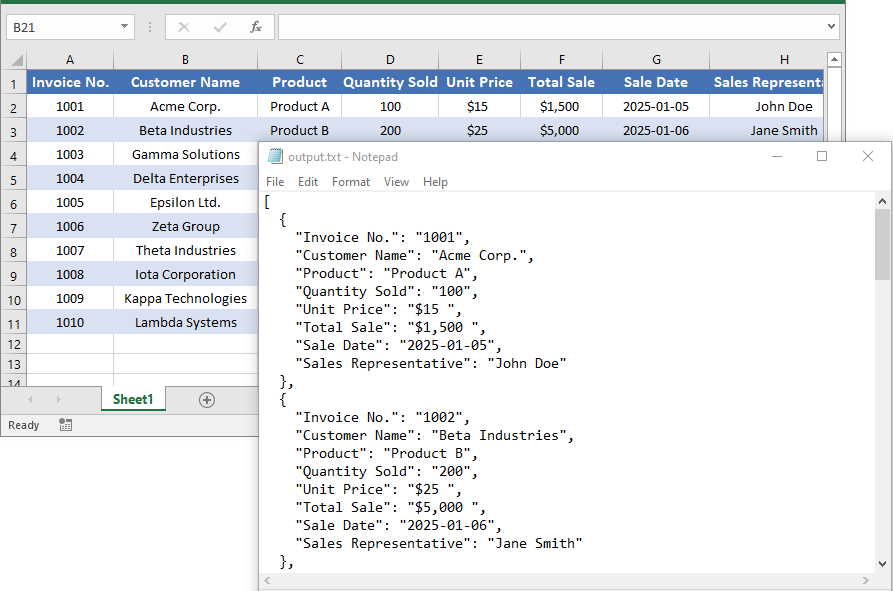
How to Convert Excel to JSON in C# .NET (Step-by-Step)
Exporting Excel files to JSON format in C# involves extracting data from Excel spreadsheets and transforming it into a structured JSON string. This process is particularly useful for applications that require data interchange between web services or databases. Below are detailed steps to guide you through the conversion process.
Steps to Export Excel to JSON
- Load the Excel File:
- Begin by creating a Workbook object that will hold the Excel file's content using the Spire.XLS library. Load the Excel file into this object.
- Access the Desired Worksheet:
- Identify and access the specific worksheet from which you want to extract data. This is done by referencing the appropriate index of the Worksheets collection.
- Export to DataTable:
- Utilize the ExportDataTable() method to convert the worksheet's content into a DataTable. This provides a structured representation of the data, making it easier to manipulate.
- Serialize to JSON:
- Use the Newtonsoft.Json library to serialize the DataTable into a JSON string. This step involves converting the structured data into a JSON format, which is human-readable and suitable for web applications.
- Save the JSON to a File:
- Finally, write the generated JSON string to a file. This allows for easy access and reuse of the data in future applications or processes.
Complete Code Example: Excel to JSON
Here’s a complete code example demonstrating the process:
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
using System.IO;
namespace ConvertExcelToJSON
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Path to the Excel file
string excelFilePath = @"Sample.xlsx";
// Create a new Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(excelFilePath);
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Export the worksheet content to a DataTable
DataTable dataTable = worksheet.ExportDataTable();
// Convert the DataTable to a JSON string
string jsonResult = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(dataTable, Formatting.Indented);
// Save JSON string to a text file
File.WriteAllText("output.txt", jsonResult);
}
}
}
How to Convert JSON to Excel in C# .NET (Step-by-Step)
Importing JSON data into an Excel file is a valuable process, especially when you need to analyze or present data in a more user-friendly format. JSON is easy for humans to read and write, and easy for machines to parse and generate. However, for many users, Excel remains the preferred tool for data analysis, reporting, and visualization.
In the following steps, we will outline the process of importing JSON into Excel, enabling you to effectively utilize your JSON data within Excel for further analysis and reporting.
Steps to Import JSON into Excel
- Read the JSON String:
- Start by reading the JSON data from a file or other sources. This could include API responses, local files, or even hardcoded strings for testing purposes.
- Deserialize to DataTable:
- Use the Newtonsoft.Json library to deserialize the JSON string into a DataTable. This structured format makes it easy to manipulate data before inserting it into Excel.
- Create a New Excel Workbook:
- Initialize a new Workbook instance using the Spire.XLS library. This workbook will serve as the container for your Excel data.
- Insert the DataTable into the Worksheet:
- Use the InsertDataTable() method to transfer the contents of the DataTable into the first worksheet of the workbook. This method allows you to include column headers and organize the data neatly.
- Apply Optional Formatting:
- Enhance the visual appeal of your Excel file by applying formatting to headers and data cells. This step involves defining styles for fonts, background colors, and borders, making the data easier to read.
- Save the Workbook:
- Finally, save the populated workbook as an Excel file. Choose an appropriate file format (e.g., .xlsx) to ensure compatibility with modern Excel versions.
Complete Code Example: JSON to Excel
Here’s a complete code snippet demonstrating the conversion process:
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ConvertJSONToExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
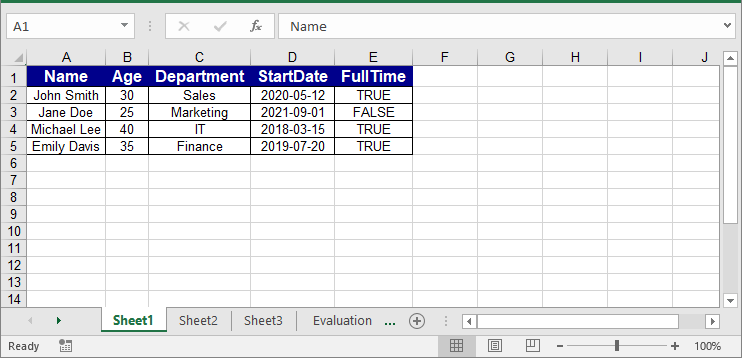
// Sample JSON data
string json = @"
[
{""Name"":""John Smith"",""Age"":30,""Department"":""Sales"",""StartDate"":""2020-05-12"",""FullTime"":true},
{""Name"":""Jane Doe"",""Age"":25,""Department"":""Marketing"",""StartDate"":""2021-09-01"",""FullTime"":false},
{""Name"":""Michael Lee"",""Age"":40,""Department"":""IT"",""StartDate"":""2018-03-15"",""FullTime"":true},
{""Name"":""Emily Davis"",""Age"":35,""Department"":""Finance"",""StartDate"":""2019-07-20"",""FullTime"":true}
]";
// Deserialize JSON into DataTable
DataTable dataTable = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<DataTable>(json);
// Create a new Excel workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Insert DataTable into worksheet with column headers
worksheet.InsertDataTable(dataTable, true, 1, 1);
// (Optional) Applying formatting to Excel data
// Set style for heading row
CellStyle headerStyle = workbook.Styles.Add("HeaderStyle");
headerStyle.Font.IsBold = true;
headerStyle.Font.Size = 12;
headerStyle.Font.Color = Color.White;
headerStyle.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
headerStyle.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
headerStyle.Color = Color.DarkBlue;
int colCount = dataTable.Columns.Count;
for (int c = 1; c <= colCount; c++)
{
worksheet.Range[1, c].CellStyleName = "HeaderStyle";
}
// Set style for data cells
CellStyle dataStyle = workbook.Styles.Add("DataStyle");
dataStyle.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
dataStyle.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
dataStyle.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
dataStyle.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
dataStyle.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
dataStyle.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
int rowCount = dataTable.Rows.Count;
worksheet.Range[2, 1, rowCount + 1, colCount].CellStyleName = "DataStyle";
// Auto-fit column widths
worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
// Save Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
// Release resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Tips and Best Practices
When converting between Excel and JSON, following best practices can help ensure data integrity and usability. Here are some key tips to keep in mind:
- Validate Data Types: Ensure that data types (e.g., dates, numbers) are correctly formatted to avoid issues during conversion.
- Handle Empty Cells: Decide how to treat empty cells (e.g., convert to null or omit) to maintain data integrity.
- Use Consistent Naming Conventions: Standardize column names in Excel for clear and consistent JSON keys.
- Test Thoroughly: Always test the conversion processes to ensure valid JSON output and accurate Excel representation.
- Include Headers: When converting JSON to Excel, always insert headers for improved readability and usability.
Conclusion
Converting Excel to JSON and JSON to Excel is a common but critical operation in modern C# development, especially for applications involving data exchange and API integration. Using Spire.XLS together with Newtonsoft.Json simplifies this process with intuitive APIs and robust functionality.
This guide has walked you through every step—from installing necessary packages to implementing complete converters—with clear explanations and sample code. With these tools and knowledge, you can confidently integrate Excel-JSON conversion into your applications, improving flexibility and interoperability.
Further Reading
FAQs
Q1: How to convert multiple worksheets to JSON at once?
You can iterate through the Workbook.Worksheets collection and export each worksheet’s data individually, supporting batch Excel to JSON conversion.
Q2: How to customize JSON output formatting?
JsonConvert.SerializeObject allows you to set indentation, camelCase naming, or ignore null values. You can also use custom converters for more control.
Q3: How to improve readability when converting JSON to Excel?
Keep column headers, set alignment, apply borders and styles to generate a clear and easy-to-read Excel report.
Q4: Is this method compatible with .NET Core?
Yes, it is fully compatible. Both Spire.XLS and Newtonsoft.Json support .NET Core and .NET Framework, making it usable in various C# projects.


