
Program Guide (86)
Children categories
Barcodes in PDFs can facilitate quicker data retrieval and processing. You can add barcodes to PDF files that contain detailed information such as the document's unique identifier, version number, creator, or even the entire document content. When scanned, all information is decoded immediately. This instant access is invaluable for businesses dealing with large volumes of documents, as it minimizes the time and effort required for manual searching and data entry. In this article, you will learn how to add barcodes to PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python and Spire.Barcode for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and Spire.Barcode for Python. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF pip install Spire.Barcode
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
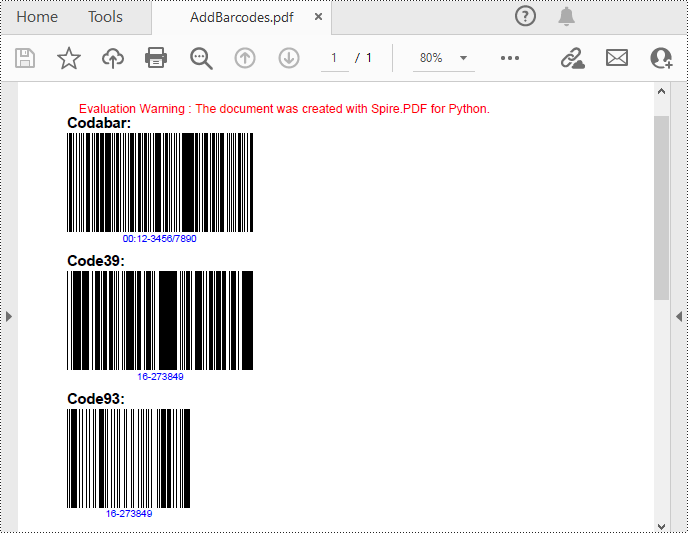
Add Barcodes to PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python support several 1D barcode types represented by different classes, such as PdfCodabarBarcode, PdfCode11Barcode, PdfCode32Barcode, PdfCode39Barcode, PdfCode93Barcode.
Each class provides corresponding properties for setting the barcode text, size, color, etc. The following are the steps to draw the common Codabar, Code39 and Code93 barcodes at the specified locations on a PDF page.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a PDF page using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a PdfTextWidget object and draw text on the page using PdfTextWidget.Draw() method.
- Create PdfCodabarBarcode, PdfCode39Barcode, PdfCode93Barcode objects.
- Set the gap between the barcode and the displayed text through the BarcodeToTextGapHeight property of the corresponding classes.
- Sets the barcode text display location through the TextDisplayLocation property of the corresponding classes.
- Set the barcode text color through the TextColor property of the corresponding classes.
- Draw the barcodes at specified locations on the PDF page using the Draw(page: PdfPageBase, location: PointF) method of the corresponding classes.
- Save the result PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add(PdfPageSize.A4())
# Initialize y-coordinate
y = 20.0
# Create a true type font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
# Draw text on the page
text = PdfTextWidget()
text.Font = font
text.Text = "Codabar:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw Codabar barcode on the page
Codabar = PdfCodabarBarcode("00:12-3456/7890")
Codabar.BarcodeToTextGapHeight = 1.0
Codabar.EnableCheckDigit = True
Codabar.ShowCheckDigit = True
Codabar.TextDisplayLocation = TextLocation.Bottom
Codabar.TextColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
Codabar.Draw(page, PointF(0.0, y))
y = Codabar.Bounds.Bottom + 6
# Draw text on the page
text.Text = "Code39:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw Code39 barcode on the page
Code39 = PdfCode39Barcode("16-273849")
Code39.BarcodeToTextGapHeight = 1.0
Code39.TextDisplayLocation = TextLocation.Bottom
Code39.TextColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
Code39.Draw(page, PointF(0.0, y))
y = Code39.Bounds.Bottom + 6
# Draw text on the page
text.Text = "Code93:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw Code93 barcode on the page
Code93 = PdfCode93Barcode("16-273849")
Code93.BarcodeToTextGapHeight = 1.0
Code93.TextDisplayLocation = TextLocation.Bottom
Code93.TextColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
Code93.QuietZone.Bottom = 5.0
Code93.Draw(page, PointF(0.0, y))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("AddBarcodes.pdf")
pdf.Close()
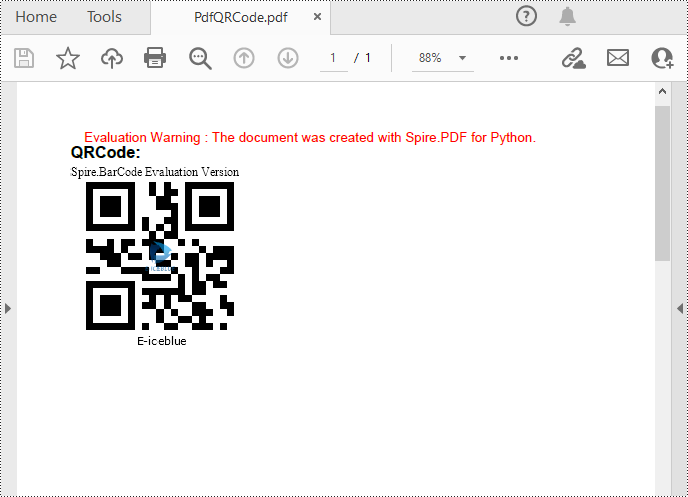
Add QR Codes to PDF in Python
To add 2D barcodes to a PDF file, the Spire.Barcode for Python library is required to generate QR code first, and then you can add the QR code image to the PDF file with the Spire.PDF for Python library. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a PDF page using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a BarcodeSettings object.
- Call the corresponding properties of the BarcodeSettings class to set the barcode type, data, error correction level and width, etc.
- Create a BarCodeGenerator object based on the settings.
- Generate QR code image using BarCodeGenerator.GenerateImage() method.
- Save the QR code image to a PNG file.
- Draw the QR code image at a specified location on the PDF page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawImage() method.
- Save the result PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.barcode import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
settings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type to QR code
settings.Type = BarCodeType.QRCode
# Set the data of the QR code
settings.Data = "E-iceblue"
settings.Data2D = "E-iceblue"
# Set the width of the QR code
settings.X = 2
# Set the error correction level of the QR code
settings.QRCodeECL = QRCodeECL.M
# Set to show QR code text at the bottom
settings.ShowTextOnBottom = True
# Generate QR code image based on the settings
barCodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(settings)
QRimage = barCodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
# Save the QR code image to a .png file
with open("QRCode.png", "wb") as file:
file.write(QRimage)
# Initialize y-coordinate
y = 20.0
# Create a true type font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
# Draw text on the PDF page
text = PdfTextWidget()
text.Font = font
text.Text = "QRCode:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw QR code image on the PDF page
pdfImage = PdfImage.FromFile("QRCode.png")
page.Canvas.DrawImage(pdfImage, 0.0, y)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("PdfQRCode.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Managing PDF documents often involves removing annotations. Whether you're preparing documents for a presentation, sharing the final files with clients when questions are settled down, or archiving important records, deleting annotations can be essential.
Spire.PDF for Python allows users to delete annotations from PDFs in Python efficiently. Follow the instructions below to clean up your PDF files seamlessly.
- Delete Specified Annotations
- Delete All Annotations from a Page
- Delete All Annotations from the PDF Document
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install it, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows.
Delete Specified Annotations from PDF in Python
To delete a specified annotation from PDF documents, you need to target the annotation to be removed at first. Then you can remove it by calling the Page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method offered by Spire.PDF for Python. This section will guide you through the whole process step by step.
Steps to remove an annotation from a page:
- Create a new PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document from files using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specific page of the PDF with PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Delete the annotation from the page by calling Page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the resulting document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example for you to refer to:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a new PDF document
doc = PdfDocument()
# Open the PDF document to be modified from the disk
doc.LoadFromFile("sample1.pdf")
# Get the first page of the document
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Remove the 2nd annotation from the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt(1)
# Save the PDF document
doc.SaveToFile("output/delete_2nd_annotation.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Delete All Annotations from a PDF Page in Python
The Pages.AnnotationsWidget.Clear() method provided by Spire.PDF for Python helps you to complete the task of removing each annotation from a page. This part will demonstrate how to delete all annotations from a page in Python with a detailed guide and a code example.
Steps to delete all annotations from a page:
- Create an instance of the PdfDocument class.
- Read the PDF document from the disk by PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove annotations on the page using Pages.AnnotationsWidget.Clear() method.
- Write the document to disk with PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Below is the code example of deleting annotations from the first page:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a new PDF document
document = PdfDocument()
# Load the file from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample1.pdf")
# Remove all annotations from the first page
document.Pages[0].AnnotationsWidget.Clear()
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("output/delete_annotations_page.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
document.Close()
Delete All Annotations of PDF Documents in Python
Removing all annotations from a PDF document involves retrieving the annotations first, which means you need to loop through each page to ensure that every annotation is deleted. The section will introduce how to accomplish the task in Python, providing detailed steps and an example to assist in cleaning up PDF documents.
Steps to remove all annotations of the whole PDF document:
- Instantiate a PdfDocument object.
- Open the document from files using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through pages of the PDF document.
- Get each page of the PDF document with PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Remove all annotations from each page using Page.AnnotationsWidget.Clear() method.
- Save the document to your local file with PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Here is the example for reference:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of PDF class
document = PdfDocument()
# Load the file to be operated from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample1.pdf")
# Loop through all pages in the PDF document
for i in range(document.Pages.Count):
# Get a specific page
page = document.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Remove all annotations from the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.Clear()
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("output/delete_all_annotations.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
document.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When creating a new PDF document, you can add information about the company, icons, and page numbers as the header and footer to enhance the appearance and professionalism of PDF documents.
This detailed guide will introduce how to add a header and footer when creating a new PDF Document in Python with Spire.PDF for Python effortlessly. Read on.
- Add Header with Python When Creating a PDF Document
- Add Footer with Python When Creating a PDF Document
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows.
Background Knowledge
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfPageTemplateElement class for defining page template elements. It provides users with PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawString(), PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawLine(), PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawImage(), and more to draw text, lines, and images. Furthermore, Spire.PDF for Python supports drawing automatic fields like PdfPageCountField and PdfPageNumberField to the template element by PdfGraphicsWidget.Draw() method.
To draw content on the PdfPageTemplateElement template element, the coordinate system settings are as follows:
- The coordinates system's origin is positioned at the top left corner of the template.
- The x-axis extends to the right, and the y-axis extends downward.
Spire.PDF for Python provides PdfDocumentTemplate class to design the entire page templates of a PDF. The defined PdfPageTemplateElement page template elements above can be applied to the PdfDocumentTemplate page template directly.
PdfDocumentTemplate can apply one or more PdfPageTemplateElement page template elements. For example, apply them to PdfDocumentTemplate.Top and PdfDocumentTemplate.Bottom page templates to create a header and footer in the PDF.
The new page generated by Spire.PDF contains margins by default. The initialization coordinates for the PdfDocumentTemplate page template are set as follows:
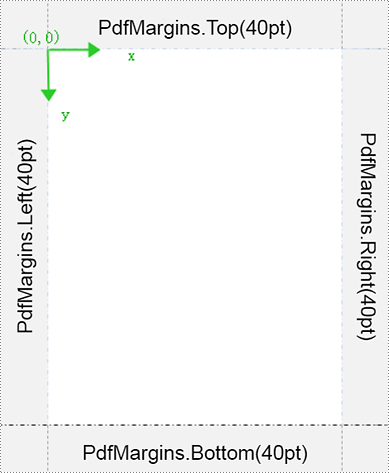
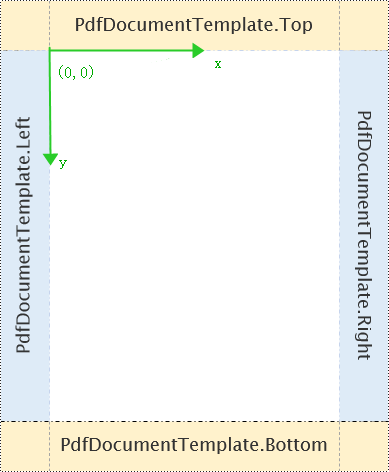
Content cannot be drawn in the margins. To apply PdfPageTemplateElement to PdfDocumentTemplate for the header and footer, you can reset the PDF margins to 0. This way, the coordinate system of the PdfDocumentTemplate page template on the new page will adjust based on the size set by the PdfPageTemplateElement. For example:
Add a Header with Python When Creating a PDF Document
The following explains how to add text, images, and lines to the header using Spire.PDF for Python when creating a new PDF.
Part 1: Design the header template elements by customizing the CreateHeaderTemplate() method.
- Create PdfPageTemplateElement objects.
- Set the font, brush, pen, and text alignment format for drawing the content of the header by defining PdfTrueTypeFont, PdfBrushes, PdfPen, and PdfTextAlignment.
- Load images to be drawn in the header with PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Draw text, lines, and images at specified positions in the header template elements using PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawString(), PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawLine(), and PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawImage() methods.
Part 2: Create PDF document objects and call the custom method above to add the header
- Create a new PdfDocument object.
- Set page size by PdfDocoment.PageSettings.Size. Reset the top, bottom, left, and right margins to 0 using PageSettings.Margins.
- Create a new PdfMargins object to set the sizes of the header, the footer, and the left and right templates.
- Call the custom method CreateHeaderTemplate() to add a header.
- Add pages using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Define PdfTrueTypeFont and PdfBrushes to set font and brushes for drawing the main content.
- Draw content in the specified area on the newly created page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the resulting file with PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Define CreateHeaderTemplate()
def CreateHeaderTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins):
#Create a header template with a specified size
headerSpace = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Top)
headerSpace.Foreground = True
doc.Template.Top = headerSpace
# Initialize the x and y coordinate points
x = margins.Left
y = 0.0
# Set font, brush, pen, and ext alignment format
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 10.0, PdfFontStyle.Italic, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Gray()
pen = PdfPen(PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), 1.0)
leftAlign = PdfTextAlignment.Left
# Load the header image and get its height and width values
headerImage = PdfImage.FromFile("E:\Administrator\Python1\header.png")
width = headerImage.Width
height = headerImage.Height
unitCvtr = PdfUnitConvertor()
pointWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(width, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
pointFeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(height, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
# Draw a header image at the specified position
headerSpace.Graphics.DrawImage(headerImage, headerSpace.Width-x-pointWidth, headerSpace.Height-pointFeight)
# Draw the header text at the specified place
headerSpace.Graphics.DrawString("E-iceblue Co. Ltd.\nwww.e-iceblue.com", font, brush, x, headerSpace.Height-font.Height*2, PdfStringFormat(leftAlign))
# Draw the header line at the specified position
headerSpace.Graphics.DrawLine(pen, x, margins.Top, pageSize.Width - x, margins.Top)
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the page size and margins
pageSize =PdfPageSize.A4()
doc.PageSettings.Size = pageSize
doc.PageSettings.Margins = PdfMargins(0.0)
# Create a new PdfMargins object to set the size of the header, footer, and left and right templates
margins = PdfMargins(50.0, 50.0, 50.0, 50.0)
doc.Template.Left = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Left, pageSize.Height-margins.Bottom-margins.Top)
doc.Template.Right = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Right, pageSize.Height-margins.Bottom-margins.Top)
doc.Template.Bottom = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Bottom)
# Call CreateHeaderTemplate() to add a header
CreateHeaderTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins)
# Add pages according to the settings above
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Define the font and brush to be used for the page content
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
# Draw text on the page
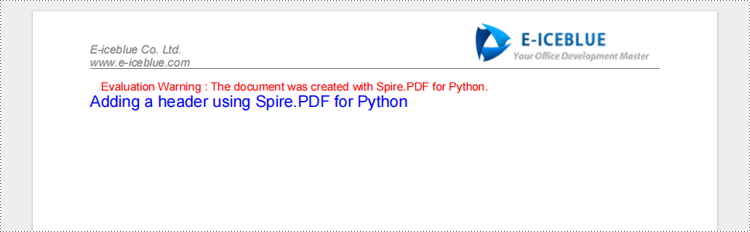
text = "Adding a header using Spire.PDF for Python"
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font, brush, 0.0, 20.0)
# Save the document as PDF
doc.SaveToFile("output/result.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose document objects
doc.Close()
Adding A Footer When Creating A New PDF Document with Python
The following is about how to add text, lines, and page content to the footer by Spire.PDF for Python when creating a new PDF:
Part 1: Customize CreateFooterTemplate() to design footer template elements
- Create a PdfPageTemplateElement object.
- Define PdfTrueTypeFont, PdfBrushes, PdfPen, and PdfTextAlignment to set font, brush, pen, and the text alignment format for drawing the content of footers.
- Draw lines and text in the footer template element using PdfPageTemplateElement Graphics.DrawString() and PdfPageTemplateElement Graphics.DrawLine() methods.
- Create PdfPageNumberField () and PdfPageCountField() objects.
- Create a PdfCompositeField() object to set the composite format and convert it to a PdfGraphicsWidget type. Use PdfGraphicsWidget.Draw() method to draw the page number field content.
Part 2: Create PDF document objects and call the custom method above to add the footer
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Set page size using PdfDocoment.PageSettings.Size. Reset the top, bottom, left, and right margins to 0 by PageSettings.Margins.
- Create a new PdfMargins object to set the sizes of the header, footer, and left and right templates.
- Call the custom method CreateFooterTemplate() to add a Footer.
- Add pages using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Define PdfTrueTypeFont and PdfBrushes to set font and brushes for drawing the main content.
- Draw content in the specified area on the newly created page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the resulting file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Define CreateFooterTemplate()
def CreateFooterTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins):
# Create a footer template with specified sizes
footerSpace = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Bottom)
footerSpace.Foreground = True
doc.Template.Bottom = footerSpace
# Initialize the x and y coordinate points
x = margins.Left
y = 0.0
# Set font, brush, pen, and ext alignment format
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Italic, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Gray()
pen = PdfPen(PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), 1.0)
leftAlign = PdfTextAlignment.Left
# Draw footer lines at the specified place
footerSpace.Graphics.DrawLine(pen, x, y, pageSize.Width - x, y)
# Draw footer text at the specified position
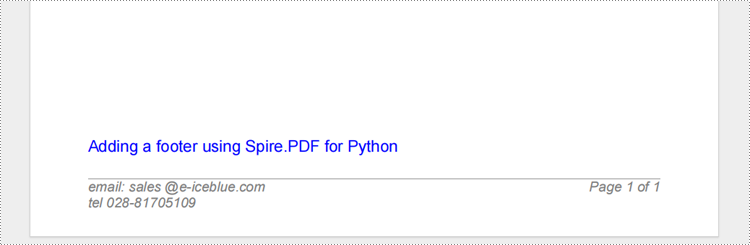
footerSpace.Graphics.DrawString("email: sales @e-iceblue.com\ntel:028-81705109 ", font, brush, x, y, PdfStringFormat(leftAlign))
# Create fields for page number and total page count
number = PdfPageNumberField()
count = PdfPageCountField()
listAutomaticField = [number, count]
# Create a composite field and set string formatting for drawing
compositeField = PdfCompositeField(font, PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), "Page {0} of {1}", listAutomaticField)
compositeField.StringFormat = PdfStringFormat(PdfTextAlignment.Right, PdfVerticalAlignment.Top)
size = font.MeasureString(compositeField.Text)
compositeField.Bounds = RectangleF(pageSize.Width -x-size.Width, y, size.Width, size.Height)
newTemplate = compositeField
templateGraphicsWidget = PdfGraphicsWidget(newTemplate.Ptr)
templateGraphicsWidget.Draw(footerSpace.Graphics)
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set page sizes and the margin
pageSize =PdfPageSize.A4()
doc.PageSettings.Size = pageSize
doc.PageSettings.Margins = PdfMargins(0.0)
# Create a new PdfMargins object for setting sizes of the header, footer, and left and right templates
margins = PdfMargins(50.0, 50.0, 50.0, 50.0)
doc.Template.Left = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Left, pageSize.Height-margins.Top-margins.Bottom)
doc.Template.Right = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Right, pageSize.Height-margins.Top-margins.Bottom)
doc.Template.Top = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Top)
# Call CreateFooterTemplate() to add a footer
CreateFooterTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins)
# Add pages according to the settings above
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Create font and brush for page content
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
# Draw text on the page
text = "Adding a footer using Spire.PDF for Python"
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font, brush, 0.0, pageSize.Height-margins.Bottom-margins.Top-font.Height-20)
# Save the document as PDF
doc.SaveToFile("output/result.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose document object
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PDF (Portable Document Format) files are widely used for sharing and distributing documents due to their consistent formatting and broad compatibility. However, when it comes to presentations, PowerPoint remains the preferred format for many users. PowerPoint offers a wide range of features and tools that enable the creation of dynamic, interactive, and visually appealing slideshows. Unlike static PDF documents, PowerPoint presentations allow for the incorporation of animations, transitions, multimedia elements, and other interactive components, making them more engaging and effective for delivering information to the audience.
By converting PDF to PowerPoint, you can transform a static document into a captivating and impactful presentation that resonates with your audience and helps to achieve your communication goals. In this article, we will explain how to convert PDF files to PowerPoint format in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert PDF to PowerPoint in Python
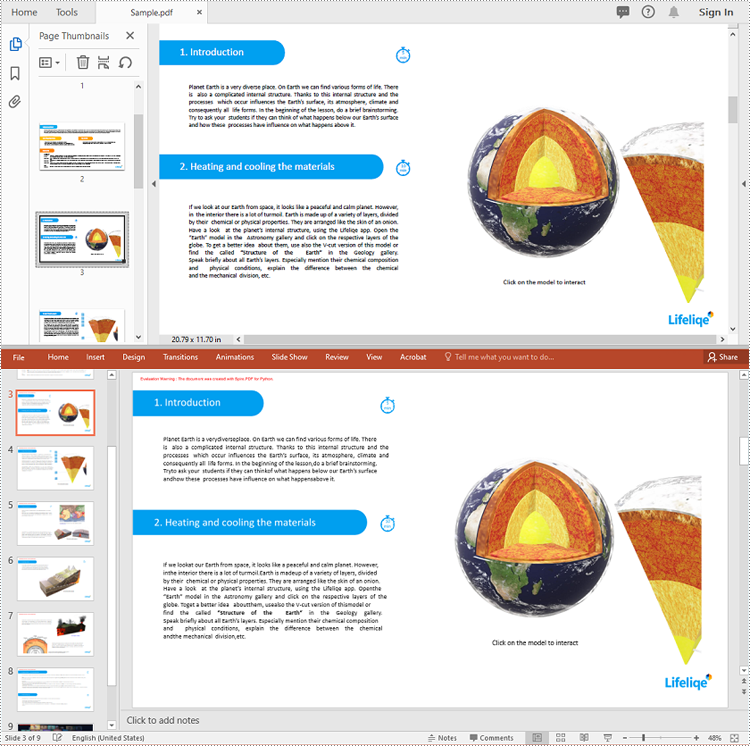
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, FileFormat.PPTX) method to convert a PDF document into a PowerPoint presentation. With this method, each page of the original PDF document will be converted into a single slide in the output PPTX presentation.
The detailed steps to convert a PDF document to PowerPoint format are as follows:
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a sample PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the PDF document as a PowerPoint PPTX file using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, FileFormat.PPTX) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Save the PDF document as a PowerPoint PPTX file
pdf.SaveToFile("PdfToPowerPoint.pptx", FileFormat.PPTX)
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Comparing PDF documents is a common task when collaborating on projects or tracking changes. This allows users to quickly review and understand what has been modified, added, or removed between revisions. Effective PDF comparison streamlines the review process and ensures all stakeholders are aligned on the latest document content.
In this article, you will learn how to compare two PDF documents using Python and the Spire.PDF for Python library.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Compare Two PDF Documents in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfComparer.Compare() method allowing developers to compare two PDF documents and save the comparison result to another PDF document. Here are the detailed steps.
- Load the first PDF document while initializing the PdfDocument object.
- Load the second PDF document while initializing another PdfDocument object.
- Initialize an instance of PdfComparer class, passing the two PdfDocument objects are the parameter.
- Call Compare() method of the PdfComparer object to compare the two PDF documents and save the result to a different PDF document.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the first document
doc_one = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_ONE.pdf")
# Load the section document
doc_two = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_TWO.pdf")
# Create a PdfComparer object
comparer = PdfComparer(doc_two, doc_one)
# Compare two documents and save the comparison result in a pdf document
comparer.Compare("output/CompareResult.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc_one.Dispose()
doc_two.Dispose()

Compare Selected Pages in PDF Documents in Python
Instead of comparing two entire documents, you can specify the pages to compare using the PdfComparer.PdfCompareOptions.SetPageRanges() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Load the first PDF document while initializing the PdfDocument object.
- Load the second PDF document while initializing another PdfDocument object.
- Initialize an instance of PdfComparer class, passing the two PdfDocument objects are the parameter.
- Specify the page range to compare using PdfComparer.PdfCompareOptions.SetPageRanges() method
- Call PdfComparer.Compare() method to compare the selected pages and save the result to a different PDF document.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the first document
doc_one = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_ONE.pdf")
# Load the section document
doc_two = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_TWO.pdf")
# Create a PdfComparer object
comparer = PdfComparer(doc_two, doc_one)
# Set page range for comparison
comparer.PdfCompareOptions.SetPageRanges(1, 3, 1, 3)
# Compare the selected pages and save the comparison result in a pdf document
comparer.Compare("output/CompareResult.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc_one.Dispose()
doc_two.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Retrieving the coordinates of text or images within a PDF document can quickly locate specific elements, which is valuable for extracting content from PDFs. This capability also enables adding annotations, marks, or stamps to the desired locations in a PDF, allowing for more advanced document processing and manipulation.
In this article, you will learn how to get coordinates of the specified text or image in a PDF document using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Get Coordinates of the Specified Text in PDF in Python
- Get Coordinates of the Specified Image in PDF in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Coordinate System in Spire.PDF
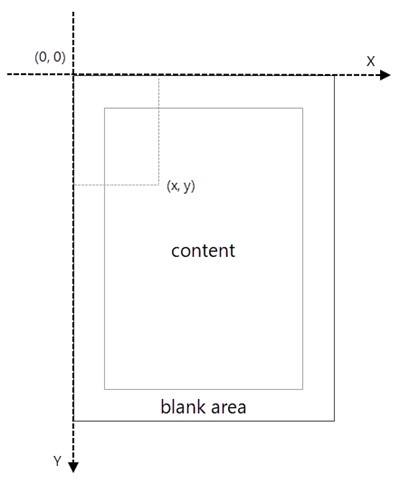
When using Spire.PDF to process an existing PDF document, the origin of the coordinate system is located at the top left corner of the page. The X-axis extends horizontally from the origin to the right, and the Y-axis extends vertically downward from the origin (shown as below).
Get Coordinates of the Specified Text in PDF in Python
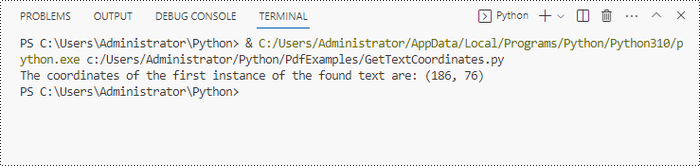
To find the coordinates of a specific piece of text within a PDF document, you must first use the PdfTextFinder.Find() method to locate all instances of the target text on a particular page. Once you have found these instances, you can then access the PdfTextFragment.Positions property to retrieve the precise (X, Y) coordinates for each instance of the text.
The steps to get coordinates of the specified text in PDF are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document from a specified path.
- Get a specific page from the document.
- Create a PdfTextFinder object.
- Specify find options through PdfTextFinder.Options property.
- Search for a string within the page using PdfTextFinder.Find() method.
- Get a specific instance of the search results.
- Get X and Y coordinates of the text through PdfTextFragment.Positions[0].X and PdfTextFragment.Positions[0].Y properties.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
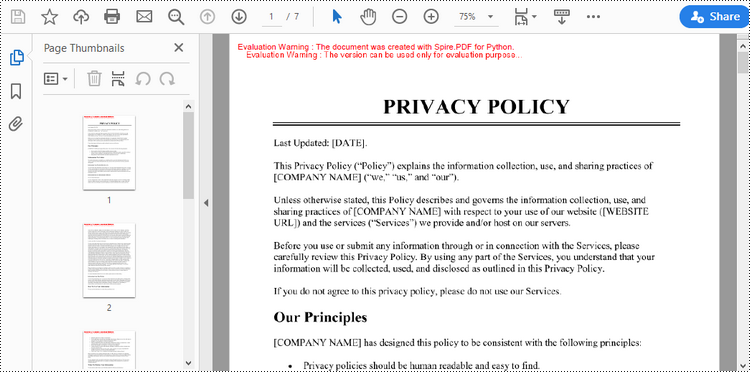
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Privacy Policy.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages[0]
# Create a PdfTextFinder object
textFinder = PdfTextFinder(page)
# Specify find options
findOptions = PdfTextFindOptions()
findOptions.Parameter = TextFindParameter.IgnoreCase
findOptions.Parameter = TextFindParameter.WholeWord
textFinder.Options = findOptions
# Search for the string "PRIVACY POLICY" within the page
findResults = textFinder.Find("PRIVACY POLICY")
# Get the first instance of the results
result = findResults[0]
# Get X/Y coordinates of the found text
x = int(result.Positions[0].X)
y = int(result.Positions[0].Y)
print("The coordinates of the first instance of the found text are:", (x, y))
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Get Coordinates of the Specified Image in PDF in Python
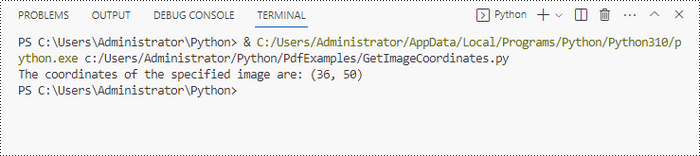
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfImageHelper class, which allows users to extract image details from a specific page within a PDF file. By doing so, you can leverage the PdfImageInfo.Bounds property to retrieve the (X, Y) coordinates of an individual image.
The steps to get coordinates of the specified image in PDF are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document from a specified path.
- Get a specific page from the document.
- Create a PdfImageHelper object.
- Get the image information from the page using PdfImageHelper.GetImagesInfo() method.
- Get X and Y coordinates of a specific image through PdfImageInfo.Bounds property.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Privacy Policy.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages[0]
# Create a PdfImageHelper object
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get image information from the page
imageInformation = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Get X/Y coordinates of a specific image
x = int(imageInformation[0].Bounds.X)
y = int(imageInformation[0].Bounds.Y)
print("The coordinates of the specified image are:", (x, y))
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.

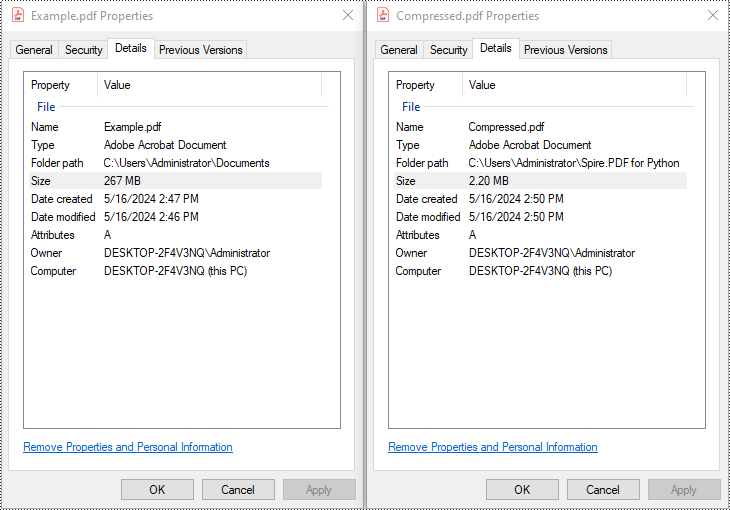
Large PDF files can slow down email delivery, break upload limits, and consume unnecessary storage. This is especially common in PDFs that include high-resolution scans, images, or embedded fonts. If you're working with Python and need to automate PDF compression without compromising quality, this guide will help you get started.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to compress PDF files in Python using the Spire.PDF for Python library. We'll cover several effective techniques, including image recompression, font optimization, metadata removal, and batch compression—perfect for web, backend, or desktop applications.
Table of Contents
- Common Scenarios Requiring PDF Compression
- Prerequisites
- Practical PDF Compression Techniques in Python
- Summary
Common Scenarios Requiring PDF Compression
Reducing the size of PDF documents is often essential in the following situations:
| Use Case | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Email Attachments | Avoid size limits and improve deliverability |
| Web Uploads | Reduce upload time and server storage |
| Mobile Access | Faster loading and less data consumption |
| Cloud Archiving | Lower storage cost for backups |
| App Submissions | Meet strict file size limits |
Prerequisites
Before you begin compressing PDFs with Python, make sure the following requirements are met:
- Python 3.7 or above
Ensure that Python (version 3.7 or later) is installed on your system. You can download it from the official Python website. - Spire.PDF for Python
This is a powerful PDF library that allows you to programmatically create, manipulate, and compress PDF documents—without relying on external software like Adobe Acrobat.
To install Spire.PDF for Python, run the following command in your terminal or command prompt:
pip install spire.pdf
Need help with the installation? See our step-by-step guide: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows_
Practical PDF Compression Techniques in Python
In this section, you'll explore five practical techniques for reducing PDF file size:
- Font compression and unembedding
- Image compression
- Full-document compression
- Metadata and attachment removal
- Batch compressing multiple PDFs
Font Compression and Unembedding
Fonts embedded in a PDF—especially those from large font libraries or multilingual character sets—can significantly increase the file size. Spire.PDF allows you to:
- Compress embedded fonts to minimize space usage
- Unembed fonts that are not essential for rendering
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfCompressor object and load the PDF file
compressor = PdfCompressor("C:/Users/Administrator/Documents/Example.pdf")
# Get the OptimizationOptions object
compression_options = compressor.OptimizationOptions
# Enable font compression
compression_options.SetIsCompressFonts(True)
# Optional: unembed fonts to further reduce size
# compression_options.SetIsUnembedFonts(True)
# Compress the PDF and save the result
compressor.CompressToFile("CompressFonts.pdf")
Image Compression
Spire.PDF lets you reduce the size of all images in a PDF by creating a PdfCompressor instance, enabling the image resizing and compression options, and specifying the image quality level. This approach applies compression uniformly across the entire document.
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfCompressor object and load the PDF file
compressor = PdfCompressor("C:/Users/Administrator/Documents/Example.pdf")
# Get the OptimizationOptions object
compression_options = compressor.OptimizationOptions
# Enable image resizing
compression_options.SetResizeImages(True)
# Enable image compression
compression_options.SetIsCompressImage(True)
# Set image quality (available options: Low, Medium, High)
compression_options.SetImageQuality(ImageQuality.Medium)
# Compress and save the PDF file
compressor.CompressToFile("Compressed.pdf")
Full Document Compression
Beyond optimizing individual elements, Spire.PDF also supports full-document compression. By adjusting the document's CompressionLevel and disabling incremental updates, you can apply comprehensive optimization to reduce overall file size.
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Documents/Example.pdf")
# Disable incremental update
pdf.FileInfo.IncrementalUpdate = False
# Set the compression level to the highest
pdf.CompressionLevel = PdfCompressionLevel.Best
# Save the optimized PDF
pdf.SaveToFile("OptimizeDocumentContent.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Removing Metadata and Attachments
Cleaning up metadata and removing embedded attachments is a quick way to reduce PDF size. Spire.PDF lets you remove unnecessary information like author/title fields and attached files:
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the PDF
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Example.pdf")
# Disable the incremental update
pdf.FileInfo.IncrementalUpdate = False
# Remove metadata
pdf.DocumentInformation.Author = ""
pdf.DocumentInformation.Title = ""
# Remove attachments
pdf.Attachments.Clear()
# Save the optimized PDF
pdf.SaveToFile("Cleaned.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Batch Compressing Multiple PDFs
You can compress multiple PDFs at once by looping through files in a folder and applying the same optimization settings:
import os
from spire.pdf import *
# Folder containing the PDF files to compress
input_folder = "C:/PDFs/"
# Loop through all files in the input folder
for file in os.listdir(input_folder):
# Process only PDF files
if file.endswith(".pdf"):
# Create a PdfCompressor instance and load the file
compressor = PdfCompressor(os.path.join(input_folder, file))
# Access compression options
opt = compressor.OptimizationOptions
# Enable image resizing
opt.SetResizeImages(True)
# Enable image compression
opt.SetIsCompressImage(True)
# Set image quality to medium (options: Low, Medium, High)
opt.SetImageQuality(ImageQuality.Medium)
# Define output file path with "compressed_" prefix
output_path = os.path.join(input_folder, "compressed_" + file)
# Perform compression and save the result
compressor.CompressToFile(output_path)
Summary
Reducing the size of PDF files is a practical step toward faster workflows, especially when dealing with email sharing, web uploads, and large-scale archiving. With Spire.PDF for Python, developers can implement smart compression techniques—ranging from optimizing images and fonts to stripping unnecessary elements like metadata and attachments.
Whether you're building automation scripts, integrating PDF handling into backend services, or preparing documents for long-term storage, these tools give you the flexibility to control file size without losing visual quality. By combining multiple strategies—like full-document compression and batch processing—you can keep your PDFs lightweight, efficient, and ready for distribution across platforms.
Want to explore more ways to work with PDFs in Python? Explore the full range of Spire.PDF for Python tutorials to learn how to merge/split PDFs, convert PDF to PDF/A, add password protection, and more.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I use Spire.PDF for Python on Linux or macOS?
A1: Yes. Spire.PDF for Python is compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Q2: Is Spire.PDF for Python free?
A2: Spire.PDF for Python offers a free version suitable for small-scale and non-commercial use. For full functionality, including unrestricted use in commercial applications, a commercial version is available. You can request a free 30-day trial license to explore all its premium features.
Q3: Will compressing the PDF reduce the visual quality?
A3: Not necessarily. Spire.PDF’s compression methods are designed to preserve visual fidelity while optimizing file size. You can fine-tune image quality or leave it to the default settings.
Extract Tables from PDF Using Python - Easy Table Parsing Guide
2024-05-15 01:10:42 Written by Koohji
Extracting tables from PDF using Python typically involves understanding how content is visually laid out in rows and columns. Many PDF tables are defined using cell borders, making them easier to detect programmatically. In such cases, a layout-aware library that reads content positioning—rather than just raw text—is essential for accurate PDF table extraction in Python.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn a reliable method to extract tables from PDF using Python, no OCR or machine learning required. Whether your PDF contains clean grids or complex layouts, we'll show how to turn table data into structured formats like Excel or pandas DataFrames for further analysis.
Table of Contents
- Install and Set Up Spire.PDF for Python
- Extract Tables from PDF
- Tips for Better Accuracy
- Common Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Handling Table Extraction from PDF in Python
Unlike Excel or CSV files, PDF documents don’t store tables as structured data. To extract tables from PDF files using Python, you need a library that can analyze the layout and detect tabular structures.
Spire.PDF for Python simplifies this process by providing built-in methods to extract tables page by page. It works best with clearly formatted tables and helps developers convert PDF content into usable data formats like Excel or CSV.
You can install the library with:
pip install Spire.PDF
Or install the free version for smaller PDF table extraction tasks:
pip install spire.pdf.free
Extracting Tables from PDF – Step-by-Step
To extract tables from a PDF file using Python, we start by loading the document and analyzing each page individually. With Spire.PDF for Python, you can detect tables based on their layout structure and extract them programmatically—even from multi-page documents.
Load PDF and Extract Tables
Here's a basic example that shows how to read tables from a PDF using Python. This method uses Spire.PDF to extract each table from the document page by page, making it ideal for developers who want to programmatically extract tabular data from PDFs.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
# Load PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a PdfTableExtractor object
table_extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
# Extract tables from each page
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
tables = table_extractor.ExtractTable(i)
for table_index, table in enumerate(tables):
print(f"Table {table_index + 1} on page {i + 1}:")
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
row_data = []
for col in range(table.GetColumnCount()):
text = table.GetText(row, col).replace("\n", " ")
row_data.append(text.strip())
print("\t".join(row_data))
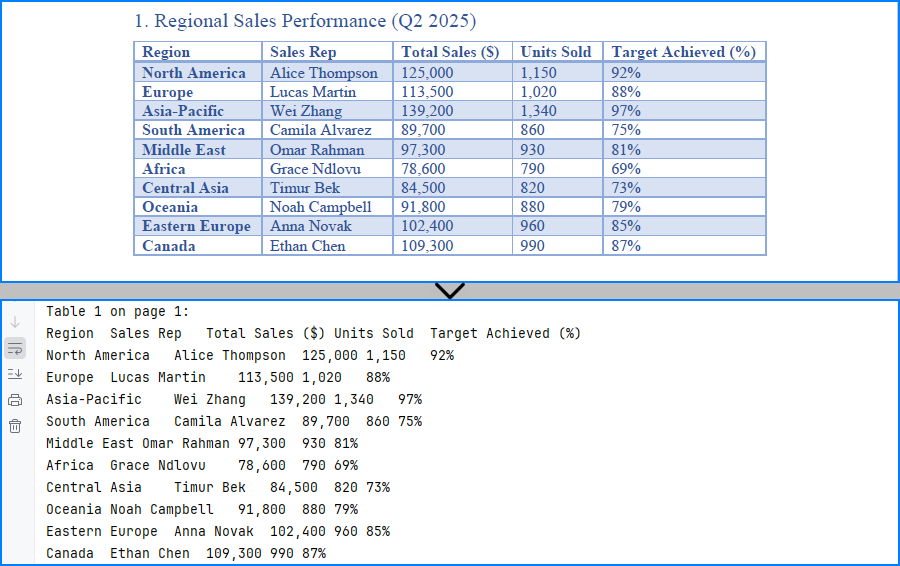
This method works reliably for bordered tables. However, for tables without visible borders—especially those with multi-line cells or unmarked headers—the extractor may fail to detect the tabular structure.
The result of extracting table data from a PDF using Python and Spire.PDF is shown below:
Export Tables to Excel and CSV
If you want to analyze or store the extracted PDF tables, you can convert them to Excel and CSV formats using Python. In this example, we use Spire.XLS for Python to create a spreadsheet for each table, allowing easy data processing or sharing. You can install the library from pip: pip install spire.xls.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat
# Load PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("G:/Documents/Sample101.pdf")
# Set up extractor and Excel workbook
extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Extract tables page by page
for page_index in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
tables = extractor.ExtractTable(page_index)
for t_index, table in enumerate(tables):
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(f"Page{page_index+1}_Table{t_index+1}")
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
for col in range(table.GetColumnCount()):
text = table.GetText(row, col).replace("\n", " ").strip()
sheet.Range.get_Item(row + 1, col + 1).Value = text
sheet.AutoFitColumn(col + 1)
# Save all tables to one Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/Sample.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
As shown below, the extracted PDF tables are converted to Excel and CSV using Spire.XLS for Python.

You may also like: How to Insert Data into Excel Files in Python
Tips to Improve PDF Table Extraction Accuracy in Python
Extracting tables from PDFs can sometimes yield imperfect results—especially when dealing with complex layouts, page breaks, or inconsistent formatting. Below are a few practical techniques to help improve table extraction accuracy in Python and get cleaner, more structured output.
1. Merging Multi-Page Tables
Spire.PDF extracts tables on a per-page basis. If a table spans multiple pages, you can combine them manually by appending the rows:
Example:
# Extract and combine tables
combined_rows = []
for i in range(start_page, end_page + 1):
tables = table_extractor.ExtractTable(i)
if tables:
table = tables[0] # Assuming one table per page
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
cells = [table.GetText(row, col).strip().replace("\n", " ") for col in range(table.GetColumnCount())]
combined_rows.append(cells)
You can then convert combined_rows into Excel or CSV if you prefer analysis via these formats.
2. Filtering Out Empty or Invalid Rows
Tables may contain empty rows or columns, or the extractor may return blank rows depending on layout. You can filter them out before exporting.
Example:
# Step 1: Filter out empty rows
filtered_rows = []
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
row_data = [table.GetText(row, col).strip().replace("\n", " ") for col in range(table.GetColumnCount())]
if any(cell for cell in row_data): # Skip completely empty rows
filtered_rows.append(row_data)
# Step 2: Transpose and filter out empty columns
transposed = list(zip(*filtered_rows))
filtered_columns = [col for col in transposed if any(cell.strip() for cell in col)]
# Step 3: Transpose back to original row-column format
filtered_data = list(zip(*filtered_columns))
This helps improve accuracy when working with noisy or inconsistent layouts.
Common Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I extract both text and tables from a PDF?
Yes, use PdfTextExtractor to retrieve the full page text and PdfTableExtractor to extract structured tables.
Q: Why aren't my tables detected?
Make sure the PDF is text-based (not scanned images) and that the layout follows a logical row-column format. Spire.PDF for Python detects only bordered tables; unbordered tables are often not recognized.
If you are handling an image-based PDF document, you can use Spire.OCR for Python to extract table data. Please refer to: How to Extract Text from Images Using Python.
Q: How to extract tables without borders from PDF documents?
Spire.PDF may have difficulty extracting tables without visible borders. If the tables are not extracted correctly, consider the following approaches:
- Using
PdfTextExtractorto extract raw text and then writing custom logic to identify rows and columns. - Using a large language model API (e.g., GPT) to interpret the structure from extracted plain text and return only structured table data.
- Consider adding visible borders to tables in the original document before generating the PDF, as this makes it easier to extract them using Python code.
Q: How do I convert extracted tables to a pandas DataFrame?
While Spire.PDF doesn’t provide native DataFrame output, you can collect cell values into a list of lists and then convert:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(table_data)
This lets you convert PDF tables into pandas DataFrames using Python for data analysis.
Q: Is Spire.PDF for Python free to use?
Yes, there are two options available:
- Free Spire.PDF for Python – a permanently free version with limited features (e.g., page count limits). You can install it via pip or download it from the official Free Spire.PDF for Python page.
- Temporary Free License – to unlock all features of the commercial version for evaluation or internal use, you can apply for a temporary free license here.
Conclusion
Whether you're working with structured reports, financial data, or standardized forms, extracting tables from PDFs in Python can streamline your workflow. With a layout-aware parser like Spire.PDF for Python, you can reliably detect and export tables—no OCR or manual formatting needed. By converting tables to Excel, CSV, or DataFrame, you unlock their full potential for automation and analysis.
In summary, extracting tables from PDFs in Python becomes much easier with Spire.PDF, especially when converting them into structured formats like Excel and CSV for analysis.
TIFF is a popular image format used in scanning and archiving due to its high quality and support for a wide range of color spaces. On the other hand, PDFs are widely used for document exchange because they preserve the layout and formatting of a document while compressing the file size. Conversion between these formats can be useful for various purposes such as archival, editing, or sharing documents.
In this article, you will learn how to convert PDF to TIFF and TIFF to PDF using the Spire.PDF for Python and Pillow libraries.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This situation relies on the combination of Spire.PDF for Python and Pillow (PIL). Spire.PDF is used to read, create and convert PDF documents, while the PIL library is used for handling TIFF files and accessing their frames.
The libraries can be easily installed on your device through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF pip install pillow
Convert PDF to TIFF in Python
To complete the PDF to TIFF conversion, you first need to load the PDF document and convert the individual pages into image streams using Spire.PDF. Subsequently, these image streams are then merged together using the functionality of the PIL library, resulting in a consolidated TIFF image.
The following are the steps to convert PDF to TIFF using Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document from a specified file path.
- Iterate through the pages in the document.
- Convert each page into an image stream using PdfDocument.SaveAsImage() method.
- Convert the image stream into a PIL image.
- Combine these PIL images into a single TIFF image.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
from PIL import Image
from io import BytesIO
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf")
# Create an empty list to store PIL Images
images = []
# Iterate through all pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Convert a specific page to an image stream
with doc.SaveAsImage(i) as imageData:
# Open the image stream as a PIL image
img = Image.open(BytesIO(imageData.ToArray()))
# Append the PIL image to list
images.append(img)
# Save the PIL Images as a multi-page TIFF file
images[0].save("Output/ToTIFF.tiff", save_all=True, append_images=images[1:])
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Convert TIFF to PDF in Python
With the assistance of the PIL library, you can load a TIFF file and transform each frame into distinct PNG files. Afterwards, you can utilize Spire.PDF to draw these PNG files onto pages within a PDF document.
To convert a TIFF image to a PDF document using Python, follow these steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a TIFF image.
- Iterate though the frames in the TIFF image.
- Get a specific frame, and save it as a PNG file.
- Add a page to the PDF document.
- Draw the image on the page at the specified location using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawImage() method.
- Save the document to a PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
from PIL import Image
import io
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the page margins to 0
doc.PageSettings.SetMargins(0.0)
# Load a TIFF image
tiff_image = Image.open("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\TIFF.tiff")
# Iterate through the frames in it
for i in range(tiff_image.n_frames):
# Go to the current frame
tiff_image.seek(i)
# Extract the image of the current frame
frame_image = tiff_image.copy()
# Save the image to a PNG file
frame_image.save(f"temp/output_frame_{i}.png")
# Load the image file to PdfImage
image = PdfImage.FromFile(f"temp/output_frame_{i}.png")
# Get image width and height
width = image.PhysicalDimension.Width
height = image.PhysicalDimension.Height
# Add a page to the document
page = doc.Pages.Add(SizeF(width, height))
# Draw image at (0, 0) of the page
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0, width, height)
# Save the document to a PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("Output/TiffToPdf.pdf",FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PDF files often contain bookmarks, which are clickable links that make navigating lengthy documents easier. Extracting these bookmarks can be beneficial for creating an outline of the document, analyzing document structure, or identifying key topics or sections. In this article, you will learn how to extract PDF bookmarks with Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Extract Bookmarks from PDF Using Python
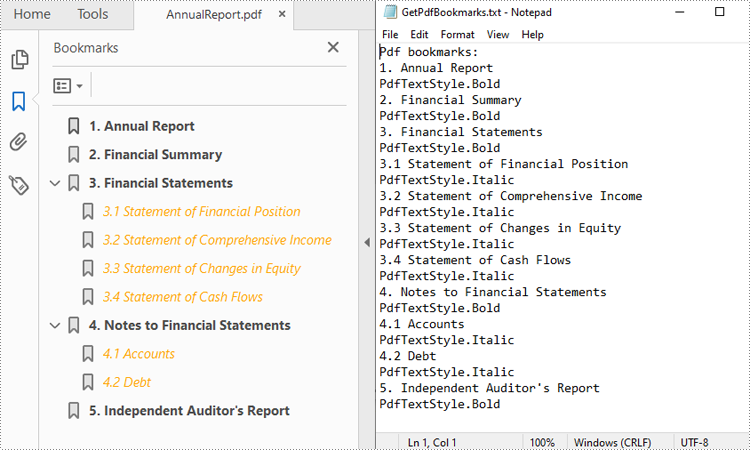
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can create custom methods GetBookmarks() and GetChildBookmark() to get the title and text styles of both parent and child bookmarks in a PDF file, then export them to a TXT file. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get bookmarks collection in the PDF file using PdfDocument.Bookmarks property.
- Call custom methods GetBookmarks() and GetChildBookmark() to get the text content and text style of parent and child bookmarks.
- Export the extracted PDF bookmarks to a TXT file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
inputFile = "AnnualReport.pdf"
result = "GetPdfBookmarks.txt"
def GetChildBookmark(parentBookmark, content):
if parentBookmark.Count > 0:
# Iterate through each child bookmark in the parent bookmarks
for i in range(parentBookmark.Count):
childBookmark = parentBookmark.get_Item(i)
# Get the title
content.append(childBookmark.Title)
# Get the text style
textStyle = str(childBookmark.DisplayStyle)
content.append(textStyle)
cldBk = PdfBookmarkCollection(childBookmark)
GetChildBookmark(cldBk, content)
def GetBookmarks(bookmarks, result):
# Create an object of StringBuilder
content = []
# Get PDF bookmarks information
if bookmarks.Count > 0:
content.append("Pdf bookmarks:")
# Iterate through each parent bookmark
for i in range(bookmarks.Count):
parentBookmark = bookmarks.get_Item(i)
# Get the title
content.append(parentBookmark.Title)
# Get the text style
textStyle = str(parentBookmark.DisplayStyle)
content.append(textStyle)
cldBk = PdfBookmarkCollection(parentBookmark)
GetChildBookmark(cldBk, content)
# Save to a TXT file
with open(result, "w") as file:
file.write("\n".join(content))
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file from disk.
pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get bookmarks collection of the PDF file
bookmarks = pdf.Bookmarks
# Get the contents of bookmarks and save them to a TXT file
GetBookmarks(bookmarks, result)
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
