
Program Guide (86)
Children categories
Making PDF content accessible on the web enhances usability, searchability, and compatibility across devices. Whether you're developing a PDF viewer, automating document workflows, or republishing content online, converting PDF to HTML using Python can significantly improve the user experience.
This comprehensive guide demonstrates how to convert PDF to HTML using Python. It covers everything from basic conversions and advanced customization to stream-based output—each section includes practical, easy-to-follow code snippets to help you get started quickly.
Table of Contents
- Why Export PDF as HTML
- Install Python PDF to HTML Converter Library
- Basic PDF to HTML Conversion in Python
- Customize the HTML Output
- Save PDF to HTML Stream
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Export PDF as HTML?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the foundation of web content. By exporting PDFs into HTML, you enable seamless viewing, editing, and indexing of document content online. Key advantages include:
- Improved Web Accessibility: HTML renders natively in all browsers.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Search engines can index content better than in PDFs.
- Responsive Layouts: HTML adjusts to different screen sizes.
- Interactive Enhancements: HTML allows for styling, scripts, and better user interaction.
- Plugin-Free Viewing: No need for third-party PDF viewers.
Install Python PDF to HTML Converter Library
To start exporting PDFs to HTML using Python, you’ll need a reliable library that supports PDF processing and HTML export. For this tutorial, we’re using Spire.PDF for Python, a high-performance PDF library that supports reading, editing, and converting PDF files in various formats, including HTML, with minimal effort.
Installation
The library can be installed easily via pip. Open your terminal and run the following command:
pip install Spire.PDF
This will download and install the latest version of the package along with its dependencies.
Need help with the installation? Follow this step-by-step guide: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Basic PDF to HTML Conversion in Python
Spire.PDF makes it easy to export an entire PDF document to HTML using the SaveToFile() method.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Initialize a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load your PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Convert and save it as HTML
doc.SaveToFile("PdfToHtml.html", FileFormat.HTML)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
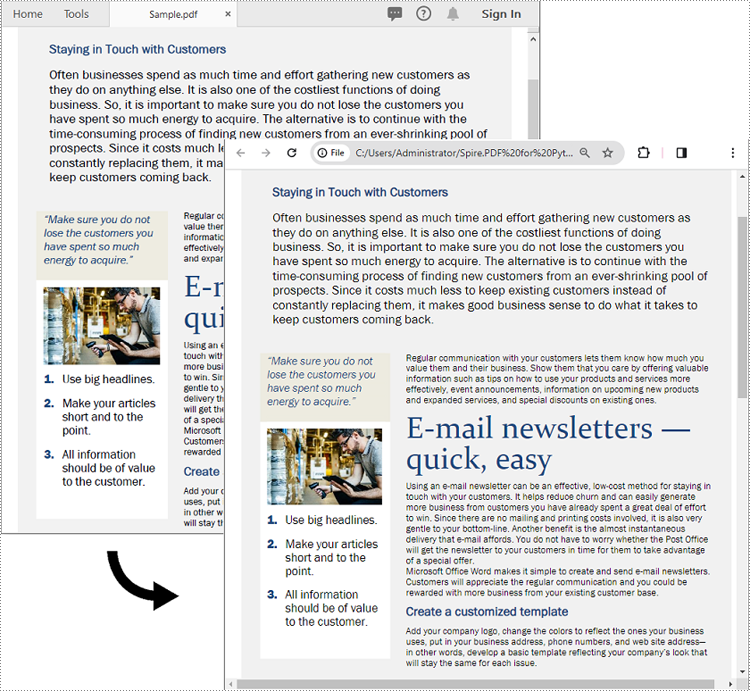
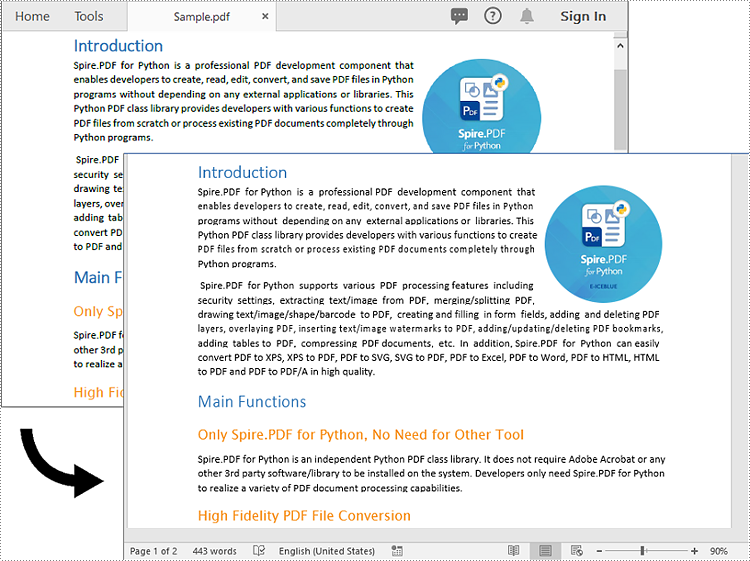
This approach generates a single HTML file that preserves the layout and structure of the original PDF.
The screenshot below showcases the input PDF and the output HTML file:
Customize the HTML Output
If you need more control over the conversion process, the SetPdfToHtmlOptions() method lets you fine-tune the HTML output.
You can customize various aspects of the conversion—such as image embedding, page splitting, and SVG quality—using the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| useEmbeddedSvg | bool | If True, embeds SVG for vector content. |
| useEmbeddedImg | bool | If True, embeds images. Effective only if useEmbeddedSvg is False. |
| maxPageOneFile | bool | Limits HTML output to one page per file (if not using SVG). |
| useHighQualityEmbeddedSvg | bool | Enables high-resolution SVG (only when useEmbeddedSvg is True). |
Example Code
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Initialize a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load your PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Access conversion settings
options = doc.ConvertOptions
# Customize conversion: use image embedding, one page per file
options.SetPdfToHtmlOptions(False, True, 1, False)
# Save the PDF to HTML with the custom options
doc.SaveToFile("PdfToHtmlWithOptions.html", FileFormat.HTML)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
This configuration disables SVG and instead embeds images, outputting each page as a separate HTML file.
Save PDF to HTML Stream
In web or cloud-based applications, you might prefer to write the HTML output to a stream (e.g., for serving over HTTP) instead of saving directly to the file system. This can be achieved with the SaveToStream() method.
Example Code
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Initialize a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load your PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a stream to save the HTML output
fileStream = Stream("PdfToHtmlStream.html")
# Save the PDF to HTML stream
doc.SaveToStream(fileStream, FileFormat.HTML)
# Close the stream and the document
fileStream.Close()
doc.Close()
This approach is ideal for web servers, APIs, or any application that handles files dynamically in memory or over the network.
Conclusion
Converting PDF to HTML using Python is an effective way to make your documents web-compatible and more interactive. With Spire.PDF for Python, you get full control over the conversion process, from simple exports to advanced configurations like embedded images or SVGs and stream output.
Ready to transform your PDFs into interactive web content? Give Spire.PDF for Python a try and streamline your document-to-HTML workflow today.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert password-protected PDFs to HTML?
A1: Yes, Spire.PDF allows you to open encrypted PDFs using doc.LoadFromFile("file.pdf", "password").
Q2: Does this method support multi-page PDFs?
A2: Yes. By default, it converts all pages. You can control how many pages appear per HTML file using the maxPageOneFile parameter.
Q3: Are images and fonts preserved in HTML output?
A3: Yes, depending on the conversion settings (e.g., embedding images or SVGs), visual fidelity is preserved as closely as possible.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
In PDF, you can change the page size to make the document meet different needs. For example, a smaller page size is required when creating handouts or compact versions of documents, while a larger page size could be useful for designing posters or graphics-intensive materials. In some cases, you may also need to get the page dimensions (width and height) to determine if the document is resized optimally. In this article, you will learn how to change or get PDF page size programmatically in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Change PDF Page Size to a Standard Paper Size with Python
- Change PDF Page Size to a Custom Paper Size with Python
- Get PDF Page Size with Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Change PDF Page Size to a Standard Paper Size with Python
The way to change the page size of a PDF file is to create a new PDF file and add pages of the desired size to it, then create templates based on the pages in the original PDF file and draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF file. This process will preserve text, images, and other elements present in the original PDF file.
Spire.PDF for Python supports a variety of standard paper size, such as letter, legal, A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, B0, B1, B2, B3, B4 and so on. The following are the steps to change the page size of a PDF file to a standard paper size:
- Initialize a PdfDocument instance and load the original PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Initialize another PdfDocument instance to create a new PDF file.
- Loop through the pages in the original PDF.
- Add pages of the desired size to the new PDF file using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Initialize a PdfTextLayout instance and set the text layout as one page through PdfTextLayout.Layout property.
- Create templates based on the pages in the original PDF using PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF file with the specified text layout using PdfTemplate.Draw() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
inputFile = "Sample1.pdf"
outputFile = "ChangePageSizeToA3.pdf"
# Create a PdfDocument instance
originalPdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the original PDF document
originalPdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a new PDF document
newPdf = PdfDocument()
# Loop through the pages in the original PDF
for i in range(originalPdf.Pages.Count):
page = originalPdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Add pages of size A3 to the new PDF
newPage = newPdf.Pages.Add(PdfPageSize.A3(), PdfMargins(0.0))
# Create a PdfTextLayout instance
layout = PdfTextLayout()
# Set text layout as one page (if not set the content will not scale to fit page size)
layout.Layout = PdfLayoutType.OnePage
# Create templates based on the pages in the original PDF
template = page.CreateTemplate()
# Draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF
template.Draw(newPage, PointF.Empty(), layout)
# Save the result document
newPdf.SaveToFile(outputFile)
newPdf.Close()
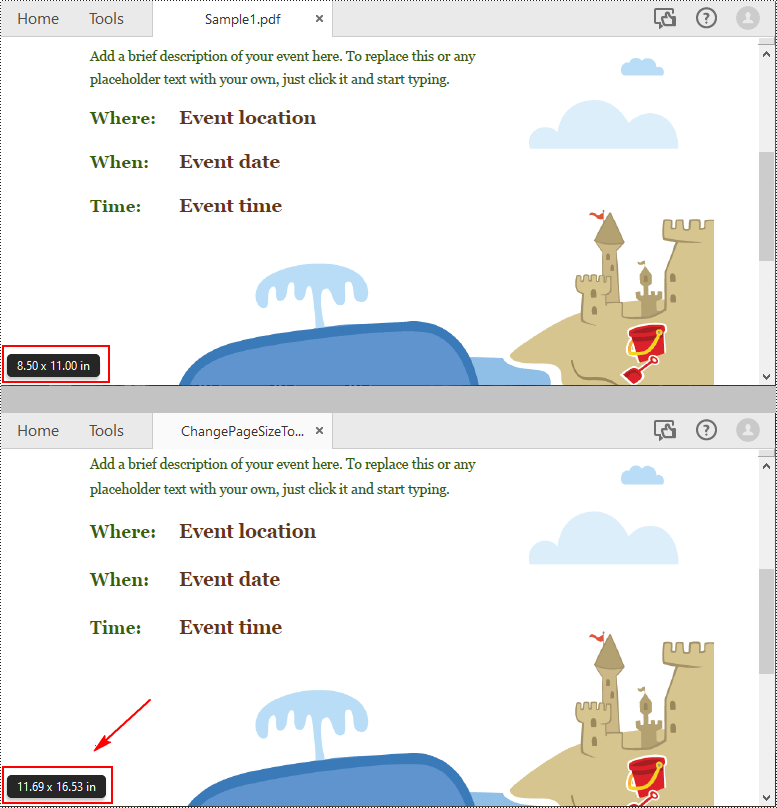
Change PDF Page Size to a Custom Paper Size with Python
Spire.PDF for Python uses point (1/72 of an inch) as the unit of measure. If you need to change the page size of a PDF to a custom paper size in other units of measure like inches or millimeters, you can use the PdfUnitConvertor class to convert them to points.
The following are steps to change the page size of a PDF file to a custom paper size in inches:
- Initialize a PdfDocument instance and load the original PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Initialize another PdfDocument instance to create a new PDF file.
- Initialize a PdfUnitConvertor instance, then convert the custom size in inches to points using PdfUnitConvertor.ConvertUnits() method.
- Initialize a SizeF instance from the custom size.
- Loop through the pages in the original PDF.
- Add pages of the custom size to the new PDF file using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Initialize a PdfTextLayout instance and set the text layout as one page through PdfTextLayout.Layout property.
- Create templates based on the pages in the original PDF using PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF file with the specified text layout using PdfTemplate.Draw() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
inputFile = "Sample1.pdf"
outputFile = "CustomizePdfPageSize.pdf"
# Create a PdfDocument instance
originalPdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the original PDF document
originalPdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a new PDF document
newPdf = PdfDocument()
# Create a PdfUnitConvertor instance
unitCvtr = PdfUnitConvertor()
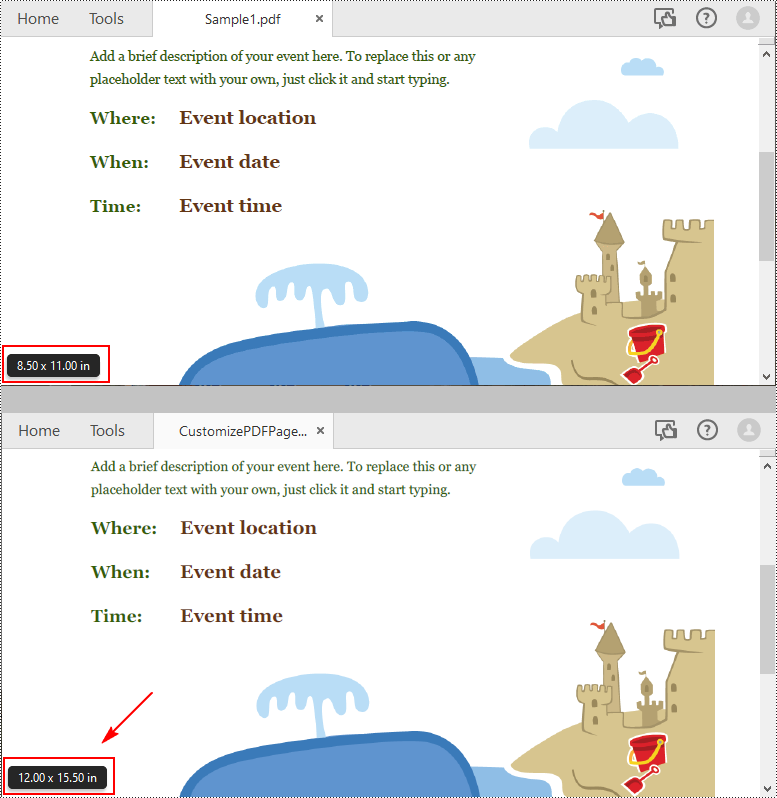
# Convert the custom size in inches to points
width = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(12.0, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
height = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(15.5, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
#Create a new SizeF instance from the custom size, then it will be used as the page size of the new PDF
size = SizeF(width, height)
# Loop through the pages in the original PDF
for i in range(originalPdf.Pages.Count):
page = originalPdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Add pages of the custom size (12.0*15.5 inches) to the new PDF
newPage = newPdf.Pages.Add(size, PdfMargins(0.0))
# Create a PdfTextLayout instance
layout = PdfTextLayout()
# Set text layout as one page (if not set the content will not scale to fit page size)
layout.Layout = PdfLayoutType.OnePage
# Create templates based on the pages in the original PDF
template = page.CreateTemplate()
# Draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF
template.Draw(newPage, PointF.Empty(), layout)
# Save the result document
newPdf.SaveToFile(outputFile)
newPdf.Close()
Get PDF Page Size with Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfPageBase.Size.Width and PdfPageBase.Size.Height properties to get the width and height of a PDF page in points. If you want to convert the default unit of measure to other units, you can use the PdfUnitConvertor class.
The following are the steps to get the PDF page size:
- Initialize a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the width and height of the PDF page using PdfPageBase.Size.Width and PdfPageBase.Size.Height properties.
- Initialize a PdfUnitConvertor instance, and then convert the size units from points to other units of measure using PdfUnitConvertor.ConvertUnits() method.
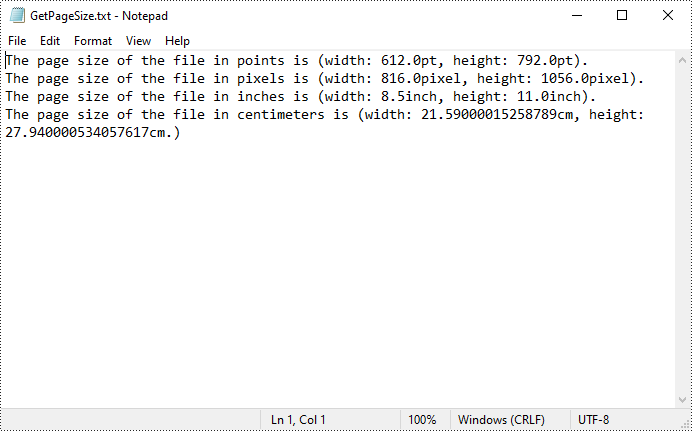
- Add the size information to a StringBuilder instance, and then save the result to a TXT file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def AppendAllText(fname: str, text: List[str]):
fp = open(fname, "w")
for s in text:
fp.write(s + "\n")
fp.close()
inputFile = "Sample1.pdf"
outputFile = "GetPageSize.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first page of the file
page = pdf.Pages[0]
# Get the width and height of page based on "point"
pointWidth = page.Size.Width
pointHeight = page.Size.Height
# Create PdfUnitConvertor to convert the unit
unitCvtr = PdfUnitConvertor()
# Convert size units from points to pixels
pixelWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointWidth, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel)
pixelHeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointHeight, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel)
# Convert size units from points to inches
inchWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointWidth, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch)
inchHeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointHeight, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch)
# Convert size units from points to centimeters
centimeterWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointWidth, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Centimeter)
centimeterHeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointHeight, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Centimeter)
# Add the size information to a StringBuilder instance
content = []
content.append("The page size of the file in points is (width: " +
str(pointWidth) + "pt, height: " + str(pointHeight) + "pt).")
content.append("The page size of the file in pixels is (width: " +
str(pixelWidth) + "pixel, height: " + str(pixelHeight) + "pixel).")
content.append("The page size of the file in inches is (width: " +
str(inchWidth) + "inch, height: " + str(inchHeight) + "inch).")
content.append("The page size of the file in centimeters is (width: " +
str(centimeterWidth) + "cm, height: " + str(centimeterHeight) + "cm.)")
# Save to a txt file
AppendAllText(outputFile, content)
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PDF files are designed to preserve the formatting and layout of the original document, making them ideal for sharing and printing. However, they are typically not editable without specialized software. Converting a PDF to a Word document allows you to make changes, add or delete text, modify formatting, and customize content as needed. This is particularly useful when you want to update or revise existing PDF files. In this article, we will explain how to convert PDF to Word DOC or DOCX formats in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Convert PDF to Word DOC or DOCX in Python
- Setting Document Properties While Converting PDF to Word in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert PDF to Word DOC or DOCX in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, fileFormat:FileFormat) method to convert PDF documents to a wide range of file formats, including Word DOC, DOCX, and more. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert the PDF document to a Word DOCX or DOC file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, fileFormat:FileFormat) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Convert the PDF document to a Word DOCX file
doc.SaveToFile("ToDocx.docx", FileFormat.DOCX)
# Or convert the PDF document to a Word DOC file
doc.SaveToFile("ToDoc.doc", FileFormat.DOC)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Setting Document Properties While Converting PDF to Word in Python
Document properties are attributes or information associated with a document that provide additional details about the file. These properties offer insights into various aspects of the document, such as its author, title, subject, version, keywords, category, and more.
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfToDocConverter class which allows developers to convert a PDF document to a Word DOCX file and set document properties for the file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfToDocConverter class.
- Set document properties, such as title, subject, comment and author, for the converted Word DOCX file using the properties of the PdfToDocConverter class.
- Convert the PDF document to a Word DOCX file using PdfToDocConverter.SaveToDocx() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfToDocConverter class
converter = PdfToDocConverter("Sample.pdf")
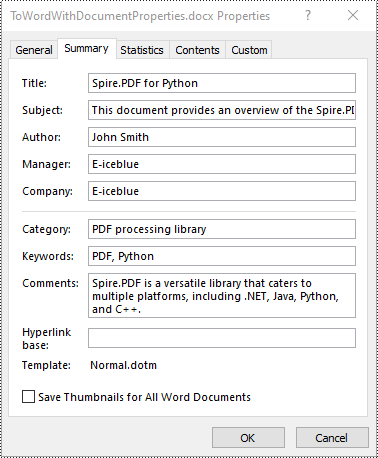
# Set document properties such as title, subject, author and keywords for the converted .DOCX file
converter.DocxOptions.Title = "Spire.PDF for Python"
converter.DocxOptions.Subject = "This document provides an overview of the Spire.PDF for Python product."
converter.DocxOptions.Tags = "PDF, Python"
converter.DocxOptions.Categories = "PDF processing library"
converter.DocxOptions.Commments = "Spire.PDF is a versatile library that caters to multiple platforms, including .NET, Java, Python, and C++."
converter.DocxOptions.Authors = "John Smith"
converter.DocxOptions.LastSavedBy = "Alexander Johnson"
converter.DocxOptions.Revision = 8
converter.DocxOptions.Version = "V4.0"
converter.DocxOptions.ProgramName = "Spire.PDF for Python"
converter.DocxOptions.Company = "E-iceblue"
converter.DocxOptions.Manager = "E-iceblue"
# Convert the PDF document to a Word DOCX file
converter.SaveToDocx("ToWordWithDocumentProperties.docx")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Creating a form in PDF not only ensures a professional appearance but also allows users to fill out and submit data electronically, streamlining data entry processes. Whether you are collecting survey responses, gathering client information, or creating employment applications, the ability to generate interactive PDF forms offers a seamless and organized way to capture, store, and manage valuable data. In this article, you will learn how to create a fillable PDF form as well as how to fill in a PDF form using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Create a Fillable Form in PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides a range of helpful classes that enable programmers to generate and modify different types of form fields in PDF files. These include text boxes, check boxes, combo boxes, list boxes, and radio buttons. The table below lists some of the classes involved in this tutorial.
| Class | Description |
| PdfForm | Represents interactive form of the PDF document. |
| PdfField | Represents field of the PDF document's interactive form. |
| PdfTextBoxField | Represents text box field in the PDF form. |
| PdfCheckBoxField | Represents check box field in the PDF form. |
| PdfComboBoxField | Represents combo box field in the PDF Form. |
| PdfListBoxField | Represents list box field of the PDF form. |
| PdfListFieldItem | Represents an item of a list field. |
| PdfRadioButtonListField | Represents radio button field in the PDF form. |
| PdfRadioButtonListItem | Represents an item of a radio button list. |
| PdfButtonField | Represents button field in the PDF form. |
To generate a PDF form, start by creating an instance of the respective field class. Set the field's size and position in the document using the Bounds property, and finally, add it to the PDF using the PdfFormFieldCollection.Add() method. The following are the main steps to create various types of form fields in a PDF document using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a page using PdfDocuemnt.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a PdfTextBoxField object, set the properties of the field including Bounds, Font and Text, and then add it to the document using PdfFormFieldCollection.Add() method.
- Repeat the step 3 to add check box, combo box, list box, radio button, and button to the document.
- Save the document to a PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Initialize x and y coordinates
baseX = 100.0
baseY = 30.0
# Create two brush objects
brush1 = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue()))
brush2 = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Black()))
# Create a font
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular)
# Add a textbox
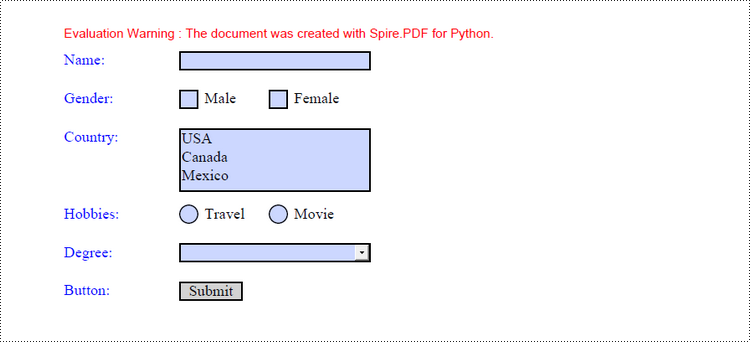
page.Canvas.DrawString("Name:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
tbxBounds = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 150.0, 15.0)
textBox = PdfTextBoxField(page, "name")
textBox.Bounds = tbxBounds
textBox.Font = font
doc.Form.Fields.Add(textBox)
baseY += 30.0
# add two checkboxes
page.Canvas.DrawString("Gender:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY));
checkboxBound1 = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 15.0, 15.0)
checkBoxField1 = PdfCheckBoxField(page, "male")
checkBoxField1.Bounds = checkboxBound1
checkBoxField1.Checked = False
page.Canvas.DrawString("Male", font, brush2, PointF(baseX + 20.0, baseY))
checkboxBound2 = RectangleF(baseX + 70.0, baseY, 15.0, 15.0)
checkBoxField2 = PdfCheckBoxField(page, "female")
checkBoxField2.Bounds = checkboxBound2
checkBoxField2.Checked = False
page.Canvas.DrawString("Female", font, brush2, PointF(baseX + 90.0, baseY))
doc.Form.Fields.Add(checkBoxField1)
doc.Form.Fields.Add(checkBoxField2)
baseY += 30.0
# Add a listbox
page.Canvas.DrawString("Country:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
listboxBound = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 150.0, 50.0)
listBoxField = PdfListBoxField(page, "country")
listBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("USA", "usa"))
listBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Canada", "canada"))
listBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Mexico", "mexico"))
listBoxField.Bounds = listboxBound
listBoxField.Font = font
doc.Form.Fields.Add(listBoxField)
baseY += 60.0
# Add two radio buttons
page.Canvas.DrawString("Hobbies:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
radioButtonListField = PdfRadioButtonListField(page, "hobbies")
radioItem1 = PdfRadioButtonListItem("travel")
radioBound1 = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 15.0, 15.0)
radioItem1.Bounds = radioBound1
page.Canvas.DrawString("Travel", font, brush2, PointF(baseX + 20.0, baseY))
radioItem2 = PdfRadioButtonListItem("movie")
radioBound2 = RectangleF(baseX + 70.0, baseY, 15.0, 15.0)
radioItem2.Bounds = radioBound2
page.Canvas.DrawString("Movie", font, brush2, PointF(baseX + 90.0, baseY))
radioButtonListField.Items.Add(radioItem1)
radioButtonListField.Items.Add(radioItem2)
doc.Form.Fields.Add(radioButtonListField)
baseY += 30.0
# Add a combobox
page.Canvas.DrawString("Degree:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
cmbBounds = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 150.0, 15.0)
comboBoxField = PdfComboBoxField(page, "degree")
comboBoxField.Bounds = cmbBounds
comboBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Bachelor", "bachelor"))
comboBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Master", "master"))
comboBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Doctor", "doctor"))
comboBoxField.Font = font
doc.Form.Fields.Add(comboBoxField)
baseY += 30.0
# Add a button
page.Canvas.DrawString("Button:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
btnBounds = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 50.0, 15.0)
buttonField = PdfButtonField(page, "button")
buttonField.Bounds = btnBounds
buttonField.Text = "Submit"
buttonField.Font = font
submitAction = PdfSubmitAction("https://www.e-iceblue.com/getformvalues.php")
buttonField.Actions.MouseDown = submitAction
doc.Form.Fields.Add(buttonField)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Form.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
Fill in a PDF Form in Python
In order to fill in a form, the necessary steps include obtaining all form fields from the PDF document, locating a specific field based on its type and name, and subsequently entering or selecting a value from a predetermined list. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the form from the document through PdfDocument.Form property.
- Get the form widget collection through PdfFormWidget.FieldsWidget property.
- Get a specific form field by its type and name.
- Enter a value or select a value from the predefined list for the field.
- Save the document to a PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document contaning form fields
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Form.pdf")
# Get form from the document
form = doc.Form
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(form)
# Get form widget collection
formWidgetCollection = formWidget.FieldsWidget
# If the collection is nut null
if formWidgetCollection.Count > 0:
# Loop through the elements in the form widget collection
for i in range(formWidgetCollection.Count):
# Get a specific field
field = formWidgetCollection.get_Item(i)
# Determine if a field is a textbox
if isinstance(field, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget):
textBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget) else None
# Determine if the name of the text box is "name"
if textBoxField.Name == "name":
# Add text to the text box
textBoxField.Text = "Jackson Green"
# Choose an item from the list box
if isinstance(field, PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
listBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
if listBoxField.Name == "country":
index = [1]
listBoxField.SelectedIndex = index
# Choose an item from the combo box
if isinstance(field, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
comBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
if comBoxField.Name == "degree":
items = [0]
comBoxField.SelectedIndex = items
# Select an item in the radio buttons
if isinstance(field, PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget):
radioBtnField = field if isinstance(field, PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget) else None
if radioBtnField.Name == "hobbies":
radioBtnField.SelectedIndex = 1
# Check the specified check box
if isinstance(field, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
checkBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
if checkBoxField.Name == "male":
checkBoxField.Checked = True
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/FillForm.pdf")
doc.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Lists are a fundamental data structure in PDF documents as they allow users to efficiently store and arrange collections of items. The three most commonly utilized list types in PDFs are ordered lists, unordered lists (also known as bulleted lists), and nested lists. These lists facilitate the presentation of information in a well-organized and visually appealing manner within PDF documents. In this article, we will explore how to use Spire.PDF for Python to create ordered, unordered, and nested lists in PDF documents for generating professional-looking PDF documents.
- Create Ordered Lists in PDF with Python
- Create Unordered Lists with Symbol Markers in PDF Using Python
- Create Unordered Lists with Image Markers in PDF Using Python
- Create Nested Lists in PDF with Python
In Spire.PDF for Python, the PdfSortedList class and PdfList class are available for generating various types of lists in PDF documents, such as ordered lists, unordered lists, and nested lists. By utilizing the functionalities provided by Spire.PDF for Python, developers can easily format and incorporate these lists into their PDF pages. The following are the key classes and properties that are particularly useful for creating lists within PDF documents:
| Class or property | Description |
| PdfSortedList class | Represents an ordered list in a PDF document. |
| PdfList class | Represents an unordered list in a PDF document. |
| Brush property | Gets or sets a list's brush. |
| Font property | Gets or sets a list's font. |
| Indent property | Gets or sets a list's indent. |
| TextIndent property | Gets or sets the indent from the marker to the list item text. |
| Items property | Gets items of a list. |
| Marker property | Gets or sets the marker of a list. |
| Draw() method | Draw list on the canvas of a page at the specified location. |
| PdfOrderedMarker class | Represents the marker style of an ordered list, such as numbers, letters, and roman numerals. |
| PdfMarker class | Represents bullet style for an unordered list. |
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Create Ordered Lists in PDF with Python
Developers can use the PdfSortedList class in Spire.PDF for Python to create ordered lists and format them using the properties available under this class. Afterwards, the list can be drawn on a PDF page using the PdfSortedList.Draw() method. Here is a detailed step-by-step guide for how to create ordered lists in PDF documents:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create fonts and the brush for the title and the list and draw the list title on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Initialize an instance of PdfSortedList class to create an ordered list with specified items.
- Initialize an instance of PdfOrderedMarker class to create an ordered marker for the list.
- Set the font, item indent, text-indent, brush, and marker for the list using properties under PdfSortedList class.
- Draw the list on the page using PdfSortedList.Draw() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page to the document with specified page size and margins
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create tile font and list font
titleFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 14.0, 1, True)
listFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 12.0, 0, True)
# Create a brush to draw the list
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Specify the initial coordinate
x = 10.0
y = 20.0
# Draw the title
title = "Introduction to Common Fruits:"
page.Canvas.DrawString(title, titleFont, brush, x, y)
# Create a numbered list
listItems = "Apples are fruits that are commonly eaten and come in various varieties.\n" \
+ "Bananas are tropical fruits that are rich in potassium and are a popular snack.\n" \
+ "Oranges are citrus fruits known for their high vitamin C content and refreshing taste.\n"\
+ "Grapes are small, juicy fruits that come in different colors, such as green, red, and purple."
list = PdfSortedList(listItems)
# Create a marker for the list
marker = PdfOrderedMarker(PdfNumberStyle.UpperRoman, listFont)
# Format the list
list.Font = listFont
list.Indent = 2
list.TextIndent = 4
list.Brush = brush
list.Marker = marker
# Draw the list on the page
list.Draw(page.Canvas, x, y + float(titleFont.MeasureString(title).Height + 5))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CreateNumberedList.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Create Unordered Lists with Symbol Markers in PDF Using Python
Creating an unordered list in a PDF document with Spire.PDF for Python involves PdfList class and the properties under this class. When creating an unordered list, developers need to set the marker style and font for the unordered list using the PdfList.Marker.Style and PdfList.Marker.Font properties. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create fonts and the brush for the title, the marker, and the list, and draw the list title on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Initialize an instance of PdfList class to create an unordered list with specified items.
- Set the font, item indent, text indent, and brush for the list using properties under PdfList class.
- Set the marker style and font through PdfList.Marker.Style property and PdfList.Marker.Font property.
- Draw the list on the page using PdfList.Draw() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page to the document with specified page size and margins
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create tile font and list font
titleFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 14.0, 1, True)
listFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 12.0, 0, True)
markerFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 8.0, 0, True)
# Create a brush to draw the list
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Specify the initial coordinate
x = 10.0
y = 20.0
# Draw the title
title = "Colors:"
page.Canvas.DrawString(title, titleFont, brush, x, y)
# Create an unordered list
listContent = "Red is a vibrant color often associated with love, passion, and energy.\n" \
+ "Green is a color symbolizing nature, growth, and harmony.\n" \
+ "Pink is a color associated with femininity, love, and tenderness."
list = PdfList(listContent)
# Format the list
list.Font = listFont
list.Indent = 2
list.TextIndent = 4
list.Brush = brush
# Format the marker
list.Marker.Style = PdfUnorderedMarkerStyle.Asterisk
list.Marker.Font = markerFont
# Draw the list on the page
list.Draw(page.Canvas, x, float(y + titleFont.MeasureString(title).Height + 5))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CreateSymbolBulletedList.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Create Unordered Lists with Image Markers in PDF Using Python
Creating an unordered list with image markers follows similar steps to creating a list with symbol markers. Developers just need to set the item marker style to an image through PdfList.Marker.Style property. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create fonts and the brush for the title, the marker, and the list, and draw the list title on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Initialize an instance of PdfList class to create an unordered list with specified items.
- Set the font, item indent, text-indent, and brush for the list using properties under PdfList class.
- Load an image using PdfImage.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the marker style as PdfUnorderedMarkerStyle.CustomImage through PdfList.Marker.Style property and set the loaded image as the marker through PdfList.Marker.Image property.
- Draw the list on the page using PdfList.Draw() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page to the document with specified page size and margins
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create tile font and list font
titleFont = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.Helvetica, 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold)
listFont = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.Helvetica, 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular)
# Create a brush to draw the list
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Specify the initial coordinate
x = 10.0
y = 20.0
# Draw the title
title = "Colors:"
page.Canvas.DrawString(title, titleFont, brush, x, y)
# Create an unordered list
listContent = "Blue is a calming color often associated with tranquility, trust, and stability.\n" \
+ "Purple is a color associated with royalty, luxury, and creativity.\n" \
+ "Brown is a natural earthy color often associated with stability, reliability, and warmth."
list = PdfList(listContent)
# Format the list
list.Font = listFont
list.Indent = 2
list.TextIndent = 4
list.Brush = brush
# Load an image
image = PdfImage.FromFile("Marker.png")
# Set the marker as a custom image
list.Marker.Style = PdfUnorderedMarkerStyle.CustomImage
list.Marker.Image = image
# Draw the list on the page
list.Draw(page.Canvas, x, float(y + titleFont.MeasureString(title).Height + 5))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CreateImageBulletedList.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Create Nested Lists in PDF with Python
When creating a nested list, both the parent list and each level of sublists can be created as either unordered or ordered lists. Once the lists at each level are created, the PdfListItem.Sublist property can be used to set a list as the sublist of a corresponding item in the parent list. Here are the steps to create a nested list:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create fonts and the brush for the title, the marker, and the list, and draw the list title on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Create an unordered list as the parent list and format the list and the marker.
- Create three sublists for the items in the parent list and format the list.
- Get an item in the parent list using PdfList.Items.get_Item() method.
- Set a specified list as the sublist of the item through PdfListItem.SubList property.
- Draw the list on the page using PdfList.Draw() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page to the document with specified page size and margins
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create tile font and list font
titleFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 14.0, 1, True)
listFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 12.0, 0, True)
markerFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 12.0, 0, True)
# Create brushs to draw the title and lists
titleBrush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
firstListBrush = PdfBrushes.get_Purple()
secondListBrush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Specify the initial coordinate
x = 10.0
y = 20.0
# Draw the title
title = "Nested List:"
page.Canvas.DrawString(title, titleFont, titleBrush, x, y)
# Create a parent list
parentListContent = "Fruits:\n" + "Colors:\n" + "Days of the week:"
parentList = PdfList(parentListContent)
# Format the parent list
indent = 4
textIndent = 4
parentList.Font = listFont
parentList.Indent = indent
parentList.TextIndent = textIndent
# Set the parent list marker
parentList.Marker.Style = PdfUnorderedMarkerStyle.Square
parentList.Marker.Font = markerFont
# Create nested sublists and format them
subListMarker = PdfOrderedMarker(PdfNumberStyle.LowerLatin, markerFont)
subList1Content = "Apples\n" + "Bananas\n" + "Oranges"
subList1 = PdfSortedList(subList1Content, subListMarker)
subList1.Font = listFont
subList1.Indent = indent * 2
subList1.TextIndent = textIndent
subList2Content = "Red\n" + "Green"
subList2 = PdfSortedList(subList2Content, subListMarker)
subList2.Font = listFont
subList2.Indent = indent * 2
subList2.TextIndent = textIndent
subList3Content = "Monday\n" + "Tuesday\n" + "Wednesday"
subList3 = PdfSortedList(subList3Content, subListMarker)
subList3.Font = listFont
subList3.Indent = indent * 2
subList3.TextIndent = textIndent
# Set the created list as the nested sublist of each item in the parent list
item1 = parentList.Items.get_Item(0)
item1.SubList = subList1
item2 = parentList.Items.get_Item(1)
item2.SubList = subList2
item3 = parentList.Items.get_Item(2)
item3.SubList = subList3
# Draw the list
parentList.Draw(page.Canvas, x, float(y + titleFont.MeasureString(title).Height + 5))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CreateNestedList.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Hyperlinks in PDF documents are commonly used tools for navigating to internal or external related information. However, these links need to be accurate and up-to-date in order to be effective. Document editors are supposed to have the power to change or delete hyperlinks to update outdated references, rectify errors, comply with evolving web standards, or enhance accessibility. This article will demonstrate how to use Spire.PDF for Python to modify or remove hyperlinks in PDF documents to ensure accurate information dissemination, seamless navigation, and inclusive user experience.
- Update the Target Address of Hyperlinks in PDF Using Python
- Remove Hyperlinks in PDF Documents Using Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Update the Target Address of Hyperlinks in PDF Using Python
In PDF documents, hyperlinks are annotations displayed on the linked content on a page. Therefore, to modify hyperlinks in PDF documents, it is needed to retrieve all annotations on a page through PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget property. Then, a specific hyperlink annotation can be obtained from the annotation list and the target address can be updated through PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget.Url property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a page of the document using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Get all annotations on the page through PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget property.
- Get a hyperlink annotation and cast it to a PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget object.
- Set a new target address for the hyperlink annotation through PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget.Url property.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page of the document
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get all annotations on the page
widgetCollection = page.AnnotationsWidget
# Get the second hyperlink annotation
annotation = widgetCollection.get_Item(1)
# Cast the hyperlink annotation to a PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget object
link = PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget(annotation)
# Set a new target address for the second hyperlink
link.Url = "https://www.mcafee.com/learn/understanding-trojan-viruses-and-how-to-get-rid-of-them/"
#Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ModifyPDFHyperlink.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Remove Hyperlinks in PDF Documents Using Python
Spire.PDF for Python enables developers to effortlessly remove specific hyperlinks on a page using the PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method. Additionally, developers can also iterate through each page and its annotations to identify and eliminate all hyperlink annotations in the entire PDF document with the help of Spire.PDF for Python. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- To remove a specific hyperlink, get a page in the document using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method and remove the hyperlink annotation using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method.
- To remove all hyperlinks in the document, loop through the pages in the document to get the annotations on each page through PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget property.
- Loop through the annotations to check if each annotation is an instance of PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget class. If it is, remove it using PdfAnnotationCollection.Remove() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# # Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Remove the first hyperlink on the first page
#page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
#page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt(0)
# Remove all hyperlinks
# Loop through the pages in the document
for j in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Get each page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(j)
# Get the annotations on each page
annotations = page.AnnotationsWidget
# Check if there is any annotations on a page
if annotations.Count > 0:
# Loop through the annotations
i = annotations.Count - 1
while i >=0:
# Get an annotation
annotation = annotations.get_Item(i)
# Check if each annotation is a hyperlink
if isinstance(annotation, PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget):
# Remove hyperlink annotations
annotations.Remove(annotation)
i -= 1
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/RemovePDFHyperlink.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A PDF portfolio is a collection of files assembled into a single PDF document. It serves as a comprehensive and interactive showcase of various types of content, such as documents, images, presentations, videos, and more. Unlike a traditional PDF document, a PDF portfolio allows you to present multiple files in a cohesive and organized manner, providing a seamless browsing experience for the viewer. In this article, we will demonstrate how to create a PDF portfolio and how to identify if a PDF is a portfolio in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Create a PDF Portfolio with Python
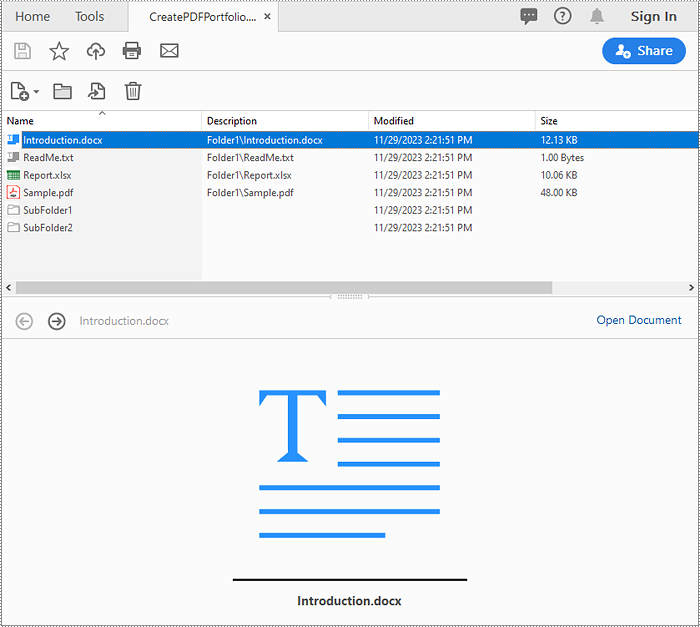
Spire.PDF for Python allows you to generate a PDF portfolio by adding files to a PDF using the PdfDocument.Collection.AddFile() method. Furthermore, you can organize the files within the PDF portfolio by adding folders using the PdfDocument.Collection.Folders.CreateSubfolder() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the output file path and the folders where the files to be included in the PDF portfolio are located.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Iterate through the files in the first folder and add them to the PDF portfolio using the PdfDocument.Collection.AddFile() method.
- Iterate through the files in the second folder. For each file, create a separate folder within the PDF portfolio using the PdfDocument.Collection.Folders.CreateSubfolder() method, and then add the file to the corresponding folder using the PdfFolder.AddFile() method.
- Save the resulting PDF portfolio using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
import glob
# Specify the folders where the files to be included in the PDF portfolio are located
input_folder1 = "Folder1/*"
input_folder2 = "Folder2/*"
# Specify the output file path
output_file = "CreatePDFPortfolio.pdf"
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Get the list of file paths in the first folder
files1 = glob.glob(input_folder1)
# Loop through the files in the list
for i, file in enumerate(files1):
# Add each file to the PDF portfolio
doc.Collection.AddFile(file)
# Get the list of file paths in the second folder
files2 = glob.glob(input_folder2)
# Loop through the files in the list
for j, file in enumerate(files2):
# Create a separate folder for each file
folder = doc.Collection.Folders.CreateSubfolder(f"SubFolder{j + 1}")
# Add the file to the folder
folder.AddFile(file)
# Save the resulting PDF portfolio to the specified file path
doc.SaveToFile(output_file)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Identify if a PDF is a Portfolio with Python
You can use the PdfDocument.IsPortfolio property to easily identify whether a PDF document is a portfolio or not. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input and output file paths.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Identify whether the document is a portfolio or not using the PdfDocument.IsPortfolio property.
- Save the result to a text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
input_file = "CreatePDFPortfolio.pdf"
output_file = "IsPDFPortfolio.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile(input_file)
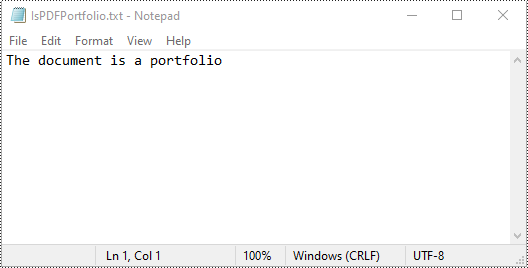
# Identify whether the document is a portfolio or not
if doc.IsPortfolio:
st = "The document is a portfolio"
else:
st = "The document is not a portfolio"
# Save the result to a text file
with open(output_file, "w") as text_file:
text_file.write(st)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
To get the number of pages in a PDF file, you can open the file in a PDF viewer such as Adobe, which has a built-in page count feature. However, when there is a batch of PDF files, opening each file to check how many pages it contains is a time-consuming task. In this article, you will learn how to quicky count the number of pages in a PDF file through programming using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Count the Number of Pages in a PDF File in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfDocument.Pages.Count property to quickly count the number of pages in a PDF file without opening it. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Count the number of pages in the PDF document using PdfDocument.Pages.Count property.
- Write the result to a TXT file or print it out directly.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def AppendText(fname: str, text: str):
fp = open(fname, "w")
fp.write(text + "\n")
fp.close()
# Specify the input and output files
inputFile = "contract.pdf"
outputFile = "GetNumberOfPages.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
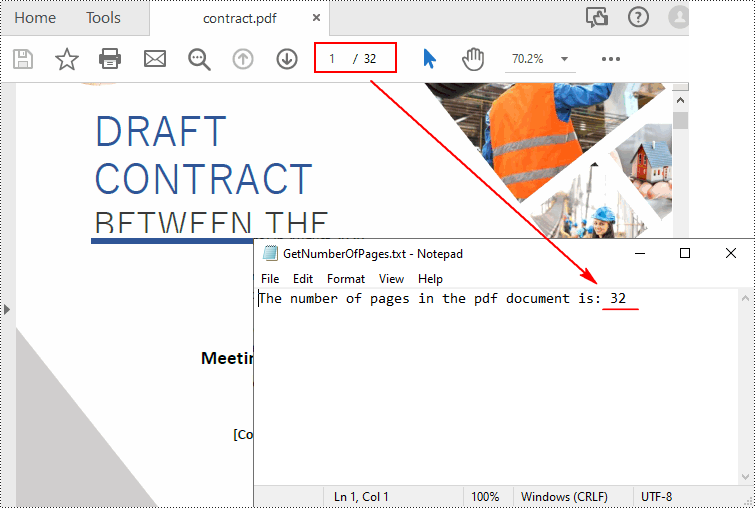
# Count the number of pages in the document
count = pdf.Pages.Count
# Print the result
print("Total Pages:", count)
# Write the result to a TXT file
AppendText(
outputFile, "The number of pages in the pdf document is: " + str(count))
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Hyperlinks in PDF are interactive elements that, when clicked, can jump to a specific location in the document, to an external website, or to other resources. By inserting hyperlinks in a PDF document, you can provide supplementary information and enhance the overall integrity of the document. This article will demonstrate how to add hyperlinks to PDF files in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add Hyperlinks to a PDF Document in Python
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can add web links, email links and file links to a PDF document. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a pdf document and add a page to it.
- Specify a URL address and draw it directly on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Create a PdfTextWebLink object.
- Set the link's display text, URL address, and the font and brush used to draw it using properties of PdfTextWebLink class.
- Draw the link on the page using PdfTextWebLink.DrawTextWebLink() method.
- Create a PdfFileLinkAnnotation object and with a specified file.
- Add the file link to the page annotations using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add(PdfFileLinkAnnotation) method.
- Draw hypertext of the file link using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Initialize x, y coordinates
y = 30.0
x = 10.0
# Create true type fonts
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0,PdfFontStyle.Regular,True)
font1 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Underline,True)
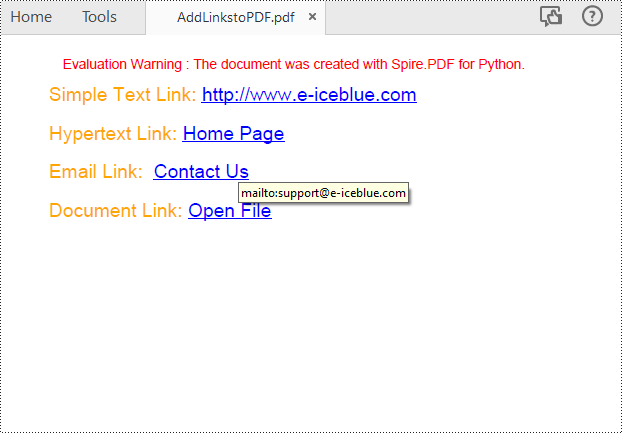
# Add a simply link
label = "Simple Text Link: "
format = PdfStringFormat()
format.MeasureTrailingSpaces = True
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
url = "http://www.e-iceblue.com"
page.Canvas.DrawString(url, font1, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
y = y + 28
# Add a hypertext link
label = "Hypertext Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
webLink = PdfTextWebLink()
webLink.Text = "Home Page"
webLink.Url = url
webLink.Font = font1
webLink.Brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
webLink.DrawTextWebLink(page.Canvas, PointF(x, y))
y = y + 28
# Add an Email link
label = "Email Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
link = PdfTextWebLink()
link.Text = "Contact Us"
link.Url = "mailto:support@e-iceblue.com"
link.Font = font1
link.Brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
link.DrawTextWebLink(page.Canvas, PointF(x, y))
y = y + 28
# Add a file link
label = "Document Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
text = "Open File"
location = PointF(x, y)
size = font1.MeasureString(text)
linkBounds = RectangleF(location, size)
fileLink = PdfFileLinkAnnotation(linkBounds,"C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Report.xlsx")
fileLink.Border = PdfAnnotationBorder(0.0)
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(fileLink)
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font1, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
#Save the result pdf file
pdf.SaveToFile("AddLinkstoPDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Insert Hyperlinks into Existing Text in PDF in Python
Adding a hyperlink to existing text in a PDF document requires locating the text first. Once the location has been obtained, an object of PdfUriAnnotation class with the link can be created and added to the position. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first page using PdfDocument.Pages property.
- Find all occurrences of the specified text on the page using PdfPageBase.FindText() method.
- Loop through all occurrences of the found text and create a PdfUriAnnotation instance based on the text bounds of each occurrence.
- Set the hyperlink URL, border, and border color using properties under PdfUriAnnotation class.
- Insert the hyperlink to the page annotations using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add(PdfUriAnnotation) method.
- Save the PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("input.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages[0]
# Find all occurrences of the specified text on the page
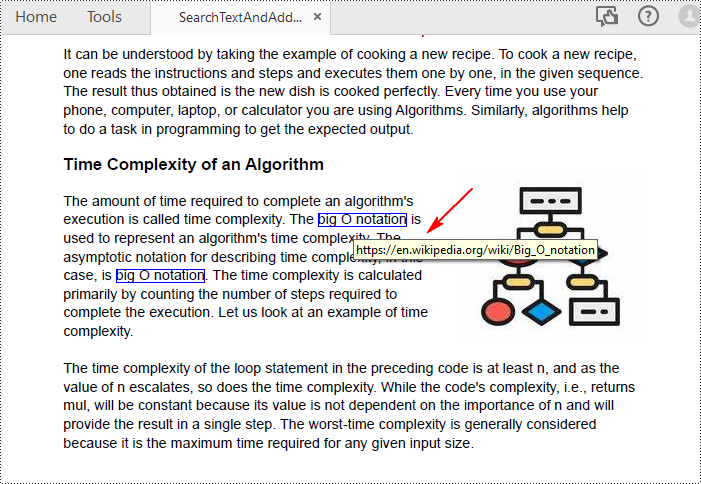
collection = page.FindText("big O notation", TextFindParameter.IgnoreCase)
# Loop through all occurrences of the specified text
for find in collection.Finds:
# Create a hyperlink annotation
uri = PdfUriAnnotation(find.Bounds)
# Set the URL of the hyperlink
uri.Uri = "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_O_notation"
# Set the border of the hyperlink annotation
uri.Border = PdfAnnotationBorder(1.0)
# Set the color of the border
uri.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
# Add the hyperlink annotation to the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(uri)
#Save the result file
pdf.SaveToFile("SearchTextAndAddHyperlink.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Layers in PDF are similar to layers in image editing software, where different elements of a document can be organized and managed separately. Each layer can contain different content, such as text, images, graphics, or annotations, and can be shown or hidden independently. PDF layers are often used to control the visibility and positioning of specific elements within a document, making it easier to manage complex layouts, create dynamic designs, or control the display of information. In this article, you will learn how to add, hide, remove layers in a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add a Layer to PDF in Python
- Set Visibility of a Layer in PDF in Python
- Remove a Layer from PDF in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add a Layer to PDF in Python
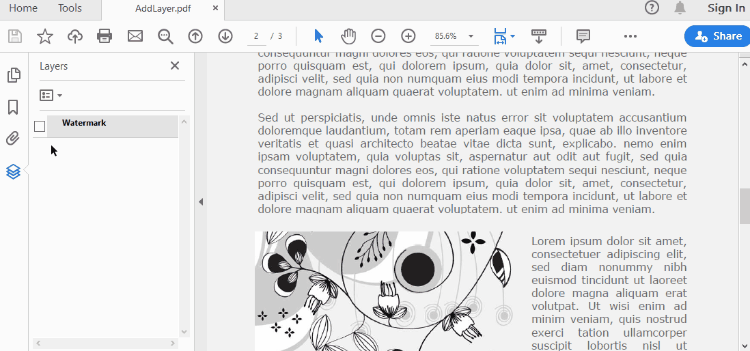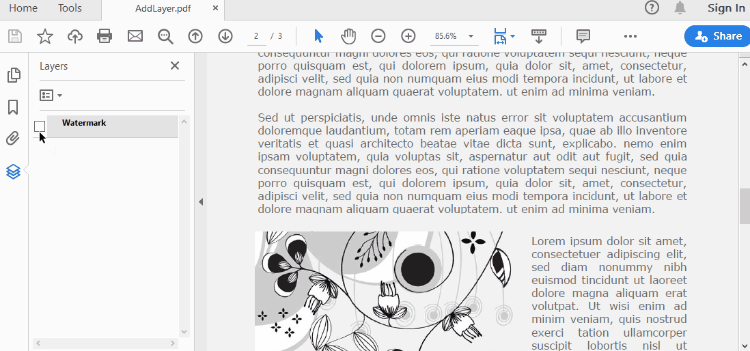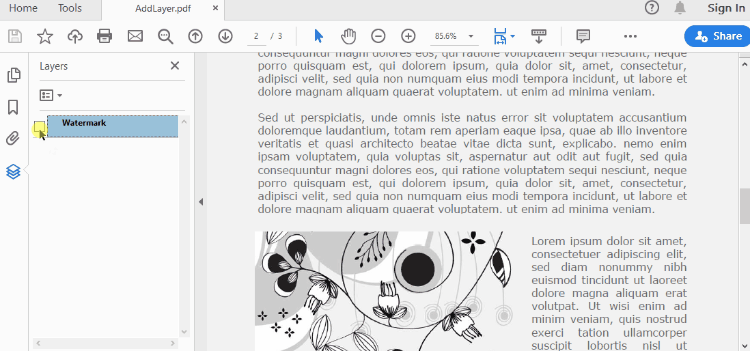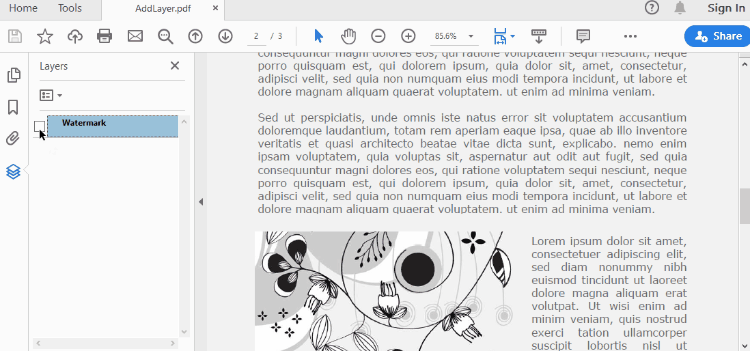
A layer can be added to a PDF document using the Document.Layers.AddLayer() method. After the layer object is created, you can draw text, images, fields, or other elements on it to form its appearance. The detailed steps to add a layer to PDF using Spire.PDF for Java are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a layer using Document.Layers.AddLayer() method.
- Get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Create a canvas for the layer based on the page using PdfLayer.CreateGraphics() method.
- Draw text on the canvas using PdfCanvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def AddLayerWatermark(doc):
# Create a layer named "Watermark"
layer = doc.Layers.AddLayer("Watermark")
# Create a font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Bodoni MT Black", 50.0, 1, True)
# Specify watermark text
watermarkText = "DO NOT COPY"
# Get text size
fontSize = font.MeasureString(watermarkText)
# Get page count
pageCount = doc.Pages.Count
# Loop through the pages
for i in range(0, pageCount):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages[i]
# Create canvas for layer
canvas = layer.CreateGraphics(page.Canvas)
# Draw sting on the graphics
canvas.DrawString(watermarkText, font, PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), (canvas.Size.Width - fontSize.Width)/2, (canvas.Size.Height - fontSize.Height)/2 )
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Invoke AddLayerWatermark method to add a layer
AddLayerWatermark(doc)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Set Visibility of a Layer in PDF in Python
To control the visibility of layers in a PDF document, you can use the PdfDocument.Layers[index].Visibility property. Set it to off to hide a layer, or set it to on to unhide a layer. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the visibility of a certain layer through Document.Layers[index].Visibility property.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Layer.pdf")
# Hide a layer by setting the visibility to off
doc.Layers[0].Visibility = PdfVisibility.Off
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/HideLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Remove a Layer from PDF in Python
If a layer is no more wanted, you can remove it using the PdfDocument.Layers.RmoveLayer() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific layer through PdfDocument.Layers[index] property.
- Remove the layer from the document using PdfDcument.Layers.RemoveLayer(PdfLayer.Name) method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Layer.pdf")
# Delete the specific layer
doc.Layers.RemoveLayer(doc.Layers[0].Name)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
