Extracting content from Word documents plays a crucial role in both work and study. Extracting one page of content helps in quickly browsing and summarizing key points, while extracting content from one section aids in in-depth study of specific topics or sections. Extracting the entire document allows you to have a comprehensive understanding of the document content, facilitating deep analysis and comprehensive comprehension. This article will introduce how to use Spire.Doc for Java to read a page, a section, and the entire content of a Word document in a Java project.
- Read a Page from a Word Document in Java
- Read a Section from a Word Document in Java
- Read the Entire Content from a Word Document in Java
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.2.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
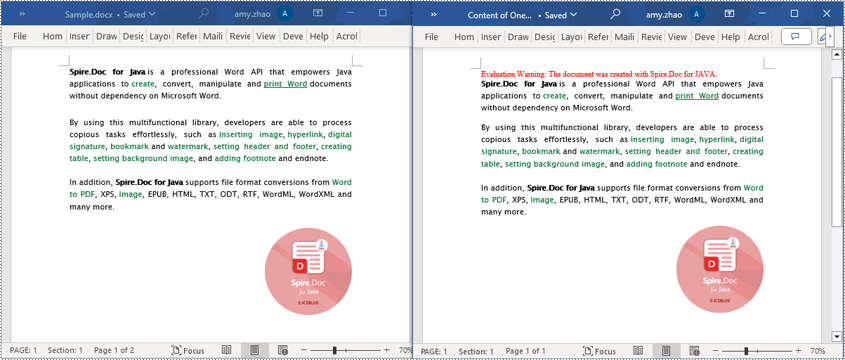
Read a Page from a Word Document in Java
Using the FixedLayoutDocument class and FixedLayoutPage class makes it easy to extract content from a specified page. To facilitate viewing the extracted content, the following example code saves the extracted content to a new Word document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create a FixedLayoutDocument object.
- Obtain a FixedLayoutPage object for a page in the document.
- Use the FixedLayoutPage.getSection() method to get the section where the page is located.
- Get the index position of the first paragraph on the page within the section.
- Get the index position of the last paragraph on the page within the section.
- Create another Document object.
- Add a new section using Document.addSection().
- Clone the properties of the original section to the new section using Section.cloneSectionPropertiesTo(newSection) method.
- Copy the content of the page from the original document to the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.pages.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
public class ReadOnePage {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load document content from the specified file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a fixed layout document object
FixedLayoutDocument layoutDoc = new FixedLayoutDocument(document);
// Get the first page
FixedLayoutPage page = layoutDoc.getPages().get(0);
// Get the section where the page is located
Section section = page.getSection();
// Get the first paragraph of the page
Paragraph paragraphStart = page.getColumns().get(0).getLines().getFirst().getParagraph();
int startIndex = 0;
if (paragraphStart != null) {
// Get the index of the paragraph in the section
startIndex = section.getBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(paragraphStart);
}
// Get the last paragraph of the page
Paragraph paragraphEnd = page.getColumns().get(0).getLines().getLast().getParagraph();
int endIndex = 0;
if (paragraphEnd != null) {
// Get the index of the paragraph in the section
endIndex = section.getBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(paragraphEnd);
}
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Add a new section
Section newSection = newdoc.addSection();
// Clone the properties of the original section to the new section
section.cloneSectionPropertiesTo(newSection);
// Copy the content of the original document's page to the new document
for (int i = startIndex; i <=endIndex; i++)
{
newSection.getBody().getChildObjects().add(section.getBody().getChildObjects().get(i).deepClone());
}
// Save the new document to the specified file
newdoc.saveToFile("Content of One Page.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document
newdoc.close();
newdoc.dispose();
// Close and release the original document
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}
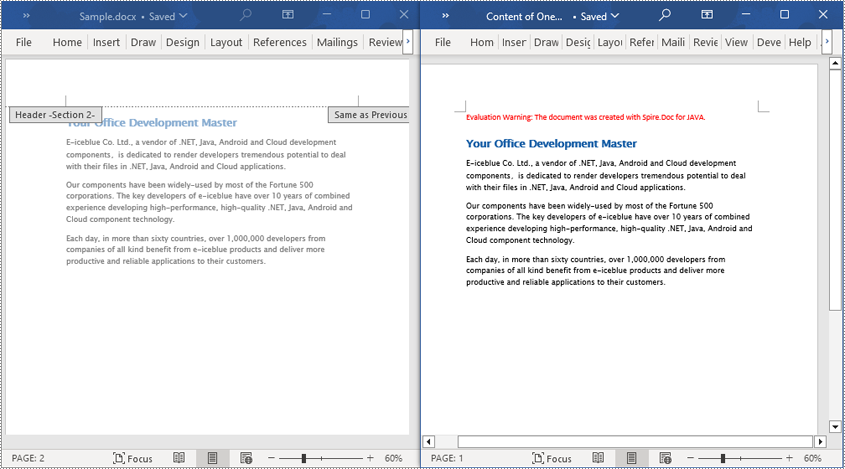
Read a Section from a Word Document in Java
Using Document.Sections[index], you can access specific Section objects that contain the header, footer, and body content of a document. The following example demonstrates a simple method to copy all content from one section to another document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Use Document.getSections().get(1) to retrieve the second section of the document.
- Create another new Document object.
- Clone the default style of the original document to the new document using Document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc) method.
- Use Document.getSections().add(section.deepClone()) to clone the content of the second section of the original document to the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
public class ReadOneSection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document from a file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Get the second section of the document
Section section = document.getSections().get(1);
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Clone the default style to the new document
document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc);
// Clone the second section to the new document
newdoc.getSections().add(section.deepClone());
// Save the new document to a file
newdoc.saveToFile("Content of One Section.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document object
newdoc.close();
newdoc.dispose();
// Close and release the original document object
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}
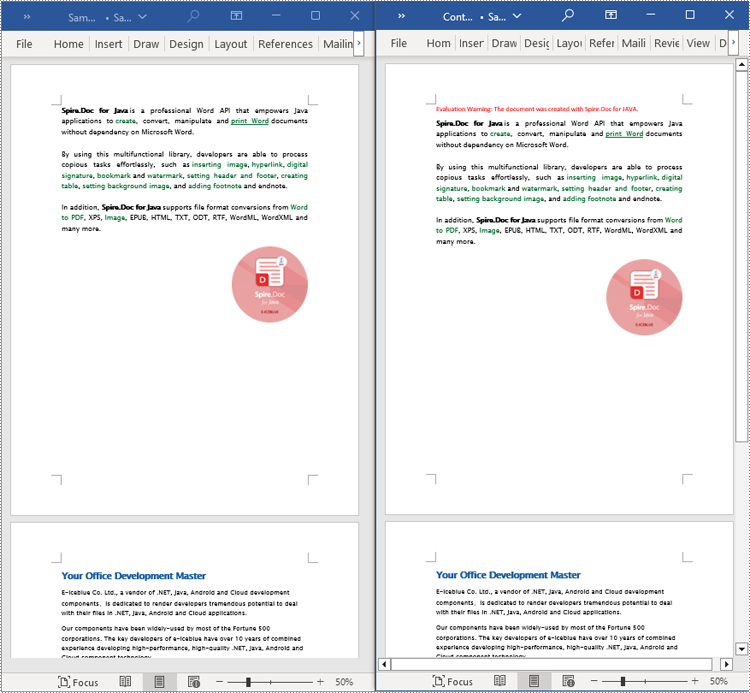
Read the Entire Content from a Word Document in Java
This example demonstrates how to iterate through each section of the original document to read the entire content of the document and clone each section into a new document. This method can help you quickly replicate both the structure and content of the entire document, preserving the format and layout of the original document in the new document. Such operations are very useful for maintaining the integrity and consistency of the document structure. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create another new Document object.
- Clone the default style of the original document to the new document using the Document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc) method.
- Iterate through each section of the original document using a for loop and clone it into the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
public class ReadOneDocument {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document from a file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Clone the default style to the new document
document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc);
// Iterate through each section in the original document and clone it to the new document
for (Section sourceSection : (Iterable<Section>) document.getSections()) {
newdoc.getSections().add(sourceSection.deepClone());
}
// Save the new document to a file
newdoc.saveToFile("Content of the entire document.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document object
newdoc.close();
newdoc.dispose();
// Close and release the original document object
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.