Detect and Remove Blank Pages from PDF Files in Python
PDF documents may occasionally include blank pages. These pages can affect the reading experience, increase the file size and lead to paper waste during printing. To improve the professionalism and usability of a PDF document, detecting and removing blank pages is an essential step.
This article shows how to accurately detect and remove blank pages—including those that appear empty but actually contain invisible elements—using Python, Spire.PDF for Python, and Pillow.
Install Required Libraries
This tutorial requires two Python libraries:
- Spire.PDF for Python: Used for loading PDFs and detecting/removing blank pages.
- Pillow: A library for image processing that helps detect visually blank pages, which may contain invisible content.
You can easily install both libraries using pip:
pip install Spire.PDF Pillow
Need help installing Spire.PDF? Refer to this guide:
How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
How to Effectively Detect and Remove Blank Pages from PDF Files in Python
Spire.PDF provides a method called PdfPageBase.IsBlank() to check if a page is completely empty. However, some pages may appear blank but actually contain hidden content like white text, watermarks, or background images. These cannot be reliably detected using the PdfPageBase.IsBlank() method alone.
To ensure accuracy, this tutorial adopts a two-step detection strategy:
- Use the PdfPageBase.IsBlank() method to identify and remove fully blank pages.
- Convert non-blank pages to images and analyze them using Pillow to determine if they are visually blank.
⚠️ Important:
If you don’t use a valid license during the PDF-to-image conversion, an evaluation watermark will appear on the image, potentially affecting the blank page detection.
Contact the E-iceblue sales team to request a temporary license for proper functionality.
Steps to Detect and Remove Blank Pages from PDF in Python
Follow these steps to implement blank page detection and removal in Python:
1. Define a custom is_blank_image() Method
This custom function uses Pillow to check whether the converted image of a PDF page is blank (i.e., if all pixels are white).
2. Load the PDF Document
Load the PDF using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
3. Iterate Through Pages
Loop through each page to check if it’s blank using two methods:
- If the PdfPageBase.IsBlank() method returns True, remove the page directly.
- If not, convert the page to an image using the PdfDocument.SaveAsImage() method and analyze it with the custom is_blank_image() method.
4. Save the Result PDF
Finally, save the PDF with blank pages removed using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Code Example
- Python
import io
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
from PIL import Image
# Custom function: Check if the image is blank (whether all pixels are white)
def is_blank_image(image):
# Convert to RGB mode and then get the pixels
img = image.convert("RGB")
# Get all pixel points and check if they are all white
white_pixel = (255, 255, 255)
return all(pixel == white_pixel for pixel in img.getdata())
# Load the PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample1111.pdf")
# Iterate through each page in reverse order to avoid index issues when deleting
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count - 1, -1, -1):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Check if the current page is completely blank
if page.IsBlank():
# If it's completely blank, remove it directly from the document
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(i)
else:
# Convert the current page to an image
with pdf.SaveAsImage(i) as image_data:
image_bytes = image_data.ToArray()
pil_image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_bytes))
# Check if the image is blank
if is_blank_image(pil_image):
# If it's a blank image, remove the corresponding page from the document
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the resulting PDF
pdf.SaveToFile("RemoveBlankPages.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is considered a blank page in a PDF file?
A: A blank page may be truly empty or contain hidden elements such as white text, watermarks, or transparent objects. This solution detects both types using a dual-check strategy.
Q2: Can I use this method without a Spire.PDF license?
A: Yes, you can run it without a license. However, during PDF-to-image conversion, an evaluation watermark will be added to the output images, which may affect the accuracy of blank page detection. It's best to request a free temporary license for testing.
Q3: What versions of Python are compatible with Spire.PDF?
A: Spire.PDF for Python supports Python 3.7 and above. Ensure that Pillow is also installed to perform image-based blank page detection.
Q4: Can I modify the script to only detect blank pages without deleting them?
A: Absolutely. Just remove or comment out the pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(i) line and use print() or logging to list detected blank pages for further review.
Conclusion
Removing unnecessary blank pages from PDF files is an important step in optimizing documents for readability, file size, and professional presentation. With the combined power of Spire.PDF for Python and Pillow, developers can precisely identify both completely blank pages and pages that appear empty but contain invisible content. Whether you're generating reports, cleaning scanned files, or preparing documents for print, this Python-based solution ensures clean and efficient PDFs.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Lock Cells, Rows, and Columns in Excel with JavaScript in React
When working with Excel, you may sometimes need to protect critical data while allowing users to edit other parts of the worksheet. This is especially important for scenarios where certain formulas, headers, or reference values must remain unchanged to ensure data integrity. By locking specific areas, you can prevent accidental modifications, maintain consistency, and control access to key information within the spreadsheet. In this article, you will learn how to lock cells, rows, and columns in Excel in React using JavaScript and the Spire.XLS for JavaScript library.
Install Spire.XLS for JavaScript
To get started with locking cells, rows, and columns in Excel files within a React application, you can either download Spire.XLS for JavaScript from our website or install it via npm with the following command:
npm i spire.xls
After that, copy the "Spire.Xls.Base.js" and "Spire.Xls.Base.wasm" files to the public folder of your project. Additionally, include the required font files to ensure accurate and consistent text rendering.
For more details, refer to the documentation: How to Integrate Spire.XLS for JavaScript in a React Project
Lock Cells in Excel
Spire.XLS for JavaScript offers the Worksheet.Range.get().Style.Locked property, allowing you to protect critical data cells while enabling edits to the rest of the worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object using the wasmModule.Workbook.Create() method.
- Load a sample Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get() method.
- Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.Range.Style.Locked property to "false".
- Set text for specific cells using the Worksheet.Range.get().Text property and then lock them by setting the Worksheet.Range.get().Style.Locked property to "true".
- Protect the worksheet with a password using the Worksheet.Protect() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- JavaScript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
// State to hold the loaded WASM module
const [wasmModule, setWasmModule] = useState(null);
// useEffect hook to load the WASM module when the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
const loadWasm = async () => {
try {
// Access the Module and spirexls from the global window object
const { Module, spirexls } = window;
// Set the wasmModule state when the runtime is initialized
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
setWasmModule(spirexls);
};
} catch (err) {
// Log any errors that occur during loading
console.error('Failed to load WASM module:', err);
}
};
// Create a script element to load the WASM JavaScript file
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/Spire.Xls.Base.js`;
script.onload = loadWasm;
// Append the script to the document body
document.body.appendChild(script);
// Cleanup function to remove the script when the component unmounts
return () => {
document.body.removeChild(script);
};
}, []);
// Function to lock specific cells in Excel
const LockExcelCells = async () => {
if (wasmModule) {
// Load the ARIALUNI.TTF font file into the virtual file system (VFS)
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS('ARIALUNI.TTF', '/Library/Fonts/', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/`);
// Load the input Excel file into the virtual file system (VFS)
const inputFileName = 'Sample.xlsx';
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS(inputFileName, '', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/`);
// Create a new workbook
const workbook = wasmModule.Workbook.Create();
// Load the Excel file from the virtual file system
workbook.LoadFromFile({fileName: inputFileName});
// Get the first worksheet
let sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get(0);
// Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet.Range.Style.Locked = false;
// Lock a specific cell in the worksheet
sheet.Range.get("A1").Text = "Locked";
sheet.Range.get("A1").Style.Locked = true;
// Lock a specific cell range in the worksheet
sheet.Range.get("C1:E3").Text = "Locked";
sheet.Range.get("C1:E3").Style.Locked = true;
// Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet.Protect({password: "123", options: wasmModule.SheetProtectionType.All});
let outputFileName = "LockCells.xlsx";
// Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile({ fileName: outputFileName, version: wasmModule.ExcelVersion.Version2013 });
// Read the saved file and convert it to a Blob object
const modifiedFileArray = wasmModule.FS.readFile(outputFileName);
const modifiedFile = new Blob([modifiedFileArray], { type: 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet' });
// Create a URL for the Blob and initiate the download
const url = URL.createObjectURL(modifiedFile);
const a = document.createElement('a');
a.href = url;
a.download = outputFileName;
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.click();
document.body.removeChild(a);
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
// Clean up resources used by the workbooks
workbook.Dispose();
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', height: '300px' }}>
<h1>Lock Specific Cells in Excel Using JavaScript in React</h1>
<button onClick={LockExcelCells} disabled={!wasmModule}>
Lock
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Run the code to launch the React app at localhost:3000. Once it's running, click on the "Lock" button to lock specific cells in the Excel file:
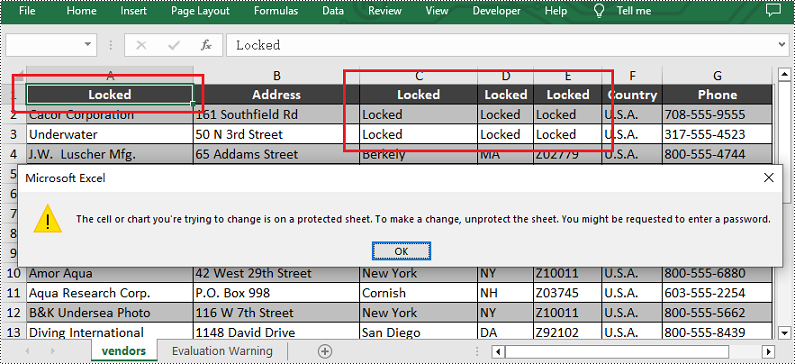
Upon opening the output Excel sheet and attempting to edit the protected cells, a dialog box will appear, notifying you that the cell you're trying to change is on a protected sheet:
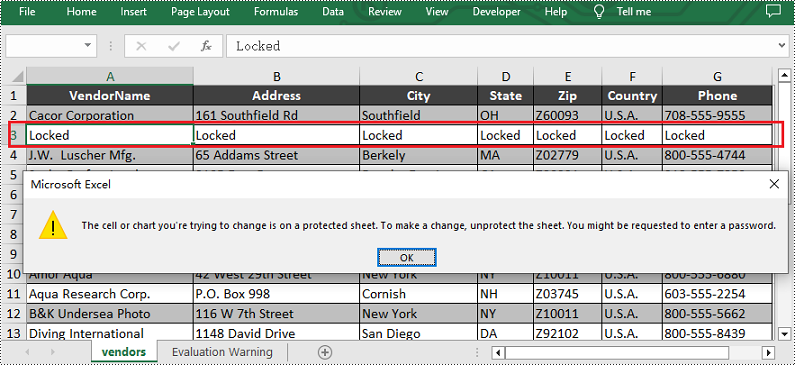
Lock Rows in Excel
If you need to preserve row-based data, such as headers or summaries, you can lock entire rows using the Worksheet.Rows.get().Style.Locked property in Spire.XLS for JavaScript. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object using the wasmModule.Workbook.Create() method.
- Load a sample Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get() method.
- Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.Range.Style.Locked property to "false".
- Set text for a specific row using the Worksheet.Rows.get().Text property and then lock it by setting the Worksheet.Rows.get().Style.Locked property to "true".
- Protect the worksheet with a password using the Worksheet.Protect() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- JavaScript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
// State to hold the loaded WASM module
const [wasmModule, setWasmModule] = useState(null);
// useEffect hook to load the WASM module when the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
const loadWasm = async () => {
try {
// Access the Module and spirexls from the global window object
const { Module, spirexls } = window;
// Set the wasmModule state when the runtime is initialized
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
setWasmModule(spirexls);
};
} catch (err) {
// Log any errors that occur during loading
console.error('Failed to load WASM module:', err);
}
};
// Create a script element to load the WASM JavaScript file
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/Spire.Xls.Base.js`;
script.onload = loadWasm;
// Append the script to the document body
document.body.appendChild(script);
// Cleanup function to remove the script when the component unmounts
return () => {
document.body.removeChild(script);
};
}, []);
// Function to lock specific rows in Excel
const LockExcelRows = async () => {
if (wasmModule) {
// Load the ARIALUNI.TTF font file into the virtual file system (VFS)
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS('ARIALUNI.TTF', '/Library/Fonts/', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/`);
// Load the input Excel file into the virtual file system (VFS)
const inputFileName = 'Sample.xlsx';
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS(inputFileName, '', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/`);
// Create a new workbook
const workbook = wasmModule.Workbook.Create();
// Load the Excel file from the virtual file system
workbook.LoadFromFile({fileName: inputFileName});
// Get the first worksheet
let sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get(0);
// Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet.Range.Style.Locked = false;
// Lock the third row in the worksheet
sheet.Rows.get(2).Text = "Locked";
sheet.Rows.get(2).Style.Locked = true;
// Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet.Protect({password: "123", options: wasmModule.SheetProtectionType.All});
let outputFileName = "LockRows.xlsx";
// Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile({ fileName: outputFileName, version: wasmModule.ExcelVersion.Version2013 });
// Read the saved file and convert it to a Blob object
const modifiedFileArray = wasmModule.FS.readFile(outputFileName);
const modifiedFile = new Blob([modifiedFileArray], { type: 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet' });
// Create a URL for the Blob and initiate the download
const url = URL.createObjectURL(modifiedFile);
const a = document.createElement('a');
a.href = url;
a.download = outputFileName;
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.click();
document.body.removeChild(a);
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
// Clean up resources used by the workbooks
workbook.Dispose();
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', height: '300px' }}>
<h1>Lock Specific Rows in Excel Using JavaScript in React</h1>
<button onClick={LockExcelRows} disabled={!wasmModule}>
Lock
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
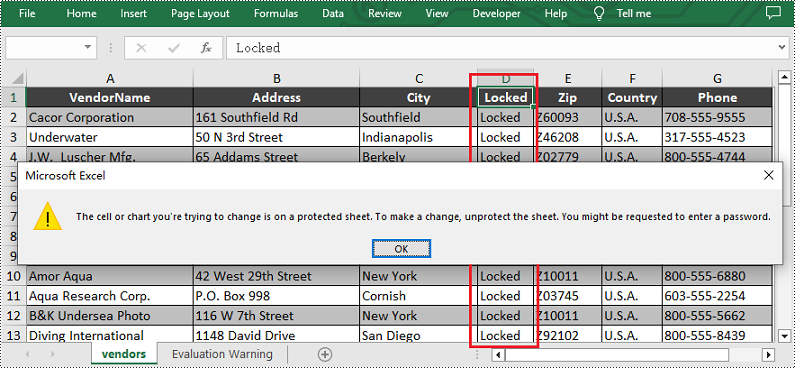
Lock Columns in Excel
To maintain the integrity of key vertical data, such as fixed identifiers or category labels, you can lock entire columns using the Worksheet.Columns.get().Style.Locked property in Spire.XLS for JavaScript. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object using the wasmModule.Workbook.Create() method.
- Load a sample Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get() method.
- Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.Range.Style.Locked property to "false".
- Set text for a specific column using the Worksheet.Columns.get().Text property and then lock it by setting the Worksheet.Columns.get().Style.Locked property to "true".
- Protect the worksheet with a password using the Worksheet.Protect() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- JavaScript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
// State to hold the loaded WASM module
const [wasmModule, setWasmModule] = useState(null);
// useEffect hook to load the WASM module when the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
const loadWasm = async () => {
try {
// Access the Module and spirexls from the global window object
const { Module, spirexls } = window;
// Set the wasmModule state when the runtime is initialized
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
setWasmModule(spirexls);
};
} catch (err) {
// Log any errors that occur during loading
console.error('Failed to load WASM module:', err);
}
};
// Create a script element to load the WASM JavaScript file
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/Spire.Xls.Base.js`;
script.onload = loadWasm;
// Append the script to the document body
document.body.appendChild(script);
// Cleanup function to remove the script when the component unmounts
return () => {
document.body.removeChild(script);
};
}, []);
// Function to lock specific columns in Excel
const LockExcelColumns = async () => {
if (wasmModule) {
// Load the ARIALUNI.TTF font file into the virtual file system (VFS)
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS('ARIALUNI.TTF', '/Library/Fonts/', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/`);
// Load the input Excel file into the virtual file system (VFS)
const inputFileName = 'Sample.xlsx';
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS(inputFileName, '', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/`);
// Create a new workbook
const workbook = wasmModule.Workbook.Create();
// Load the Excel file from the virtual file system
workbook.LoadFromFile({fileName: inputFileName});
// Get the first worksheet
let sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get(0);
// Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet.Range.Style.Locked = false;
// Lock the fourth column in the worksheet
sheet.Columns.get(3).Text = "Locked";
sheet.Columns.get(3).Style.Locked = true;
// Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet.Protect({password: "123", options: wasmModule.SheetProtectionType.All});
let outputFileName = "LockColumns.xlsx";
// Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile({ fileName: outputFileName, version: wasmModule.ExcelVersion.Version2013 });
// Read the saved file and convert it to a Blob object
const modifiedFileArray = wasmModule.FS.readFile(outputFileName);
const modifiedFile = new Blob([modifiedFileArray], { type: 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet' });
// Create a URL for the Blob and initiate the download
const url = URL.createObjectURL(modifiedFile);
const a = document.createElement('a');
a.href = url;
a.download = outputFileName;
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.click();
document.body.removeChild(a);
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
// Clean up resources used by the workbooks
workbook.Dispose();
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', height: '300px' }}>
<h1>Lock Specific Columns in Excel Using JavaScript in React</h1>
<button onClick={LockExcelColumns} disabled={!wasmModule}>
Lock
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for JavaScript without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Spire.Presentation for Java 10.2.2 enhances the conversion from PowerPoint to images
We are delighted to announce the release of Spire.Presentation for Java 10.2.2. This version enhances the conversion from PowerPoint documents to images. Moreover, some known issues are fixed successfully in this version, such as the issue that it threw "Value cannot be null" when saving a PowerPoint document. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2669 | Fixes the issue that the shadow effect of text was lost when converting PowerPoint to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2717 | Optimizes the function of adding annotations for specific text. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2718 | Fixes the issue that it threw "StringIndexOutOfBoundsException" when adding annotations for specific text. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2719 | Fixes the issue that the effect of converting PowerPoint to images was incorrect. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2722 | Fixes the issue that it threw "Value cannot be null" when saving a PowerPoint document. |
Spire.Doc 13.2.3 optimizes the time and resource consumption when converting Word to PDF
We're pleased to announce the release of Spire.Doc 13.2.3. This version optimizes the time and resource consumption when converting Word to PDF, and also adds new interfaces for reading and writing chart titles, data labels, axis, legends, data tables and other chart attributes. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | - | Adds new interfaces for reading and writing chart titles, chart data labels, chart axis, chart legends, chart data tables and other attributes.
|
| New feature | - | Namespace changes:
Spire.Doc.Formatting.RowFormat.TablePositioning->Spire.Doc.Formatting.TablePositioning Spire.Doc.Printing.PagesPreSheet->Spire.Doc.Printing.PagesPerSheet |
| New feature | - | Optimizes the time and resource consumption when converting Word to PDF, especially when working with large files or complex layouts. |
Spire.XLS for Java 15.2.1 enhances conversions from Excel to images and PDF
We are excited to announce the release of the Spire.XLS for Java 15.2.1. The latest version enhances conversions from Excel to images and PDF. Besides, this update fixes the issue that the program threw a "NullPointerException" when loading an XLSX document. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5575 | Fixes the issue that the program threw a "NullPointerException" when loading an XLSX document. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5668 | Fixes the issue that incorrect colors existed when converting Excel to images. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5685 | Fixes the issue that incomplete content displayed when converting Excel to PDF. |
Python: Recognize Text from Images
In today's digital world, extracting text from images has become essential for many fields, including business, education, and data analysis. OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology makes this process effortless by converting text in images into editable and searchable formats quickly and accurately. Whether it's turning handwritten notes into digital files or pulling key information from scanned documents, OCR simplifies tasks and makes work more efficient. In this article, we will demonstrate how to recognize text from images in Python using Spire.OCR for Python.
Install Spire.OCR for Python
This scenario requires Spire.OCR for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.OCR
Download the Model of Spire.OCR for Python
Spire.OCR for Python provides different recognition models for different operating systems. Download the model suited to your system from one of the links below:
- Windows: win-x64.zip
- Linux: linux.zip
- macOS: mac.zip
- linux_aarch: linux_aarch.zip
After downloading, extract the package and save it to a specific directory on your system.
Recognize Text from Images in Python
Spire.OCR for Python offers the OcrScanner.Scan() method to recognize text from images. Once the recognition is complete, you can use the OcrScanner.Text property to retrieve the recognized text and then save it to a file for further use. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the OcrScanner class to handle OCR operations.
- Create an instance of the ConfigureOptions class to configure the OCR settings.
- Specify the file path to the model and the desired recognition language through the ConfigureOptions.ModelPath and ConfigureOptions.Language properties.
- Apply the configuration settings to the OcrScanner instance using the OcrScanner.ConfigureDependencies() method.
- Call the OcrScanner.Scan() method to perform text recognition on the image.
- Retrieve the recognized text using the OcrScanner.Text property.
- Save the extracted text to a file for further use.
- Python
from spire.ocr import *
# Create an instance of the OcrScanner class
scanner = OcrScanner()
# Configure OCR settings
configureOptions = ConfigureOptions()
# Set the file path to the model
configureOptions.ModelPath = r'D:\OCR\win-x64'
# Set the recognition language. Supported languages include English, Chinese, Chinesetraditional, French, German, Japanese, and Korean.
configureOptions.Language = 'English'
# Apply the settings to the OcrScanner instance
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(configureOptions)
# Recognize text from the image
scanner.Scan(r'Sample.png')
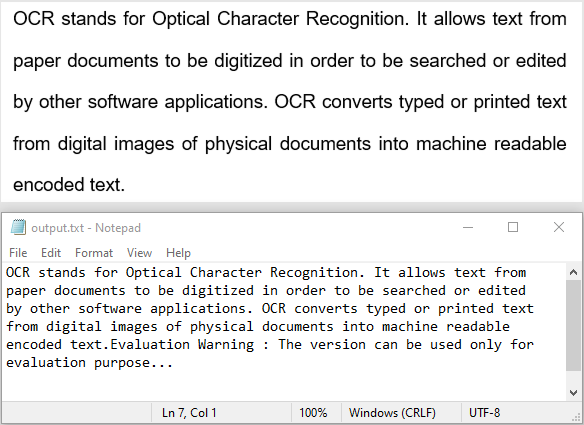
# Retrieve the recognized text and save it to a file
text = scanner.Text.ToString() + '\n'
with open('output.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text + '\n')
Recognize Text with Coordinates from Images in Python
In scenarios where you need the exact position of text in an image, such as for layout analysis or advanced data processing, extracting coordinate information is essential. With Spire.OCR for Python, you can retrieve recognized text block by block. Each text block includes detailed positional data such as the x and y coordinates, width, and height. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the OcrScanner class to handle OCR operations.
- Create an instance of the ConfigureOptions class to configure the OCR settings.
- Specify the file path to the model and the desired recognition language through the ConfigureOptions.ModelPath and ConfigureOptions.Language properties.
- Apply the configuration settings to the OcrScanner instance using the OcrScanner.ConfigureDependencies() method.
- Call the OcrScanner.Scan() method to perform text recognition on the image.
- Retrieve the recognized text using the OcrScanner.Text property.
- Iterate through the text blocks in the recognized text. For each block, use the IOCRTextBlock.Text property to get the text and the IOCRTextBlock.Box property to retrieve positional details (x, y, width, and height).
- Save the results to a text file for further analysis.
- Python
from spire.ocr import *
# Create an instance of the OcrScanner class
scanner = OcrScanner()
# Configure OCR settings
configureOptions = ConfigureOptions()
# Set the file path to the model
configureOptions.ModelPath = r'D:\OCR\win-x64'
# Set the recognition language. Supported languages include English, Chinese, Chinesetraditional, French, German, Japanese, and Korean.
configureOptions.Language = 'English'
# Apply the settings to the OcrScanner instance
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(configureOptions)
# Recognize text from the image
scanner.Scan(r'sample.png')
# Retrieve the recognized text
text = scanner.Text
# Iterate through the text blocks in the recognized text. For each text block, retrieve its text and positional data (x, y, width, and height)
block_text = ""
for block in text.Blocks:
rectangle = block.Box
block_info = f'{block.Text} -> x: {rectangle.X}, y: {rectangle.Y}, w: {rectangle.Width}, h: {rectangle.Height}'
block_text += block_info + '\n'
# Save the results to a file
with open('output.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(block_text + '\n')

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add, Extract and Remove Custom Document Properties in Word Documents
Custom document properties are user-defined fields within a Word document that store specific metadata. Unlike standard properties, such as title, author, or subject, which are predefined by Microsoft Word, these custom properties provide users with the flexibility to define and manage additional metadata fields according to their specific requirements. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add, extract, and remove custom document properties in Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Add Custom Document Properties to Word in Python
- Extract Custom Document Properties in Word in Python
- Remove Custom Document Properties from Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add Custom Document Properties to Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the CustomDocumentProperties.Add() method, which enables developers to assign different types of values, such as text, time, numeric, or yes or no, to the custom properties of a Word document. The steps below demonstrate how to add custom document properties with different types of values to a Word document using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the custom document properties of the document through the Document.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Add custom document properties with different data types to the document using the CustomDocumentProperties.Add(name, value) method.
- Save the result document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Example.docx")
# Add custom document properties with different types of values to the document
customProperties = document.CustomDocumentProperties
customProperties.Add("DocumentCategory", String("Technical Report"))
customProperties.Add("RevisionNumber", Int32(5))
customProperties.Add("LastReviewedDate", DateTime(2024, 12, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0))
customProperties.Add("RequiresFollowUp", Boolean(False))
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AddCustomDocumentProperties.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Extract Custom Document Properties in Word in Python
Extracting custom document properties allows developers to access metadata for further analysis, reporting, or integration into other applications. Spire.Doc for Python makes it simple to retrieve the details of these properties using the CustomDocumentProperty.Name and CustomDocumentProperty.Value properties. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the custom document properties of the document through the Document.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Iterate through the custom document properties.
- Extract the name and value of each custom document property.
- Save the extracted data to a text file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("AddCustomDocumentProperties.docx")
# Open a text file to save the extracted custom properties
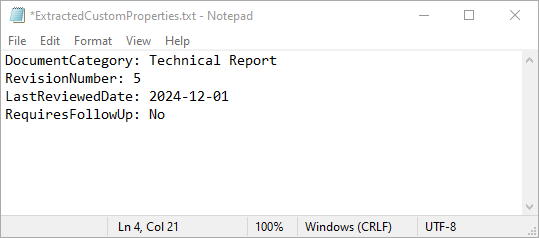
with open("ExtractedCustomProperties.txt", "w") as output_file:
# Iterate through all custom document properties
for i in range(document.CustomDocumentProperties.Count):
# Extract the name and value of each custom property
property_name = document.CustomDocumentProperties.get_Item(i).Name
property_value = document.CustomDocumentProperties.get_Item(i).Value
# Write the property details to the text file
output_file.write(f"{property_name}: {property_value}\n")
document.Close()
Remove Custom Document Properties from Word in Python
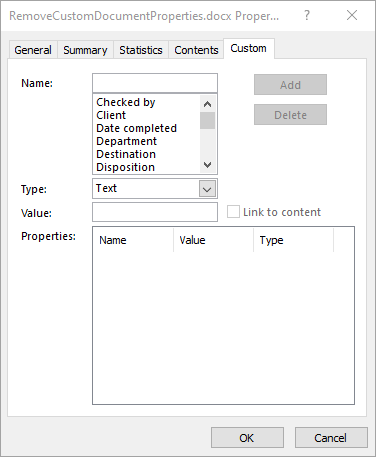
Cleaning up custom document properties is crucial for maintaining confidentiality, reducing file size, and ensuring metadata does not contain outdated or irrelevant information. Spire.Doc for Python allows developers to remove custom properties from a Word document using the DocumentProperties.Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the custom document properties of the document through the Document.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Iterate through the custom document properties.
- Remove each custom document property through its name using the DocumentProperties.Remove() method.
- Save the result document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("AddCustomDocumentProperties.docx")
# Iterate through all custom document properties
customProperties = document.CustomDocumentProperties
for i in range(customProperties.Count - 1, -1, -1):
# Remove each custom document property by its name
customProperties.Remove(customProperties[i].Name)
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveCustomDocumentProperties.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Insert, Retrieve, Reorder, and Remove Slides in PowerPoint Sections
PowerPoint presentations are a powerful tool for presenting information in an organized and engaging manner. To further enhance the organization of slides, PowerPoint allows users to group slides into sections. This feature makes navigating and managing large presentations much easier. In this article, we'll show you how to manage slides within PowerPoint sections in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python. Specifically, we'll cover how to add, retrieve, reorder, and remove slides in these sections.
- Insert Slides into a PowerPoint Section in Python
- Retrieve Slides from a PowerPoint Section in Python
- Reorder Slides in a PowerPoint Section in Python
- Remove Slides from a PowerPoint Section in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Insert Slides into a PowerPoint Section in Python
Inserting slides is essential when you want to introduce new content to a section. Using Spire.Presentation for Python, you can quickly insert a slide into a section with the Section.Insert() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section through its index (0-based) using the Presentation.SectionList(index) property.
- Add a new slide to the presentation, then insert it into the section using the Section.Insert() method.
- Remove the added slide from the presentation.
- Save the resulting presentation using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Example.pptx")
# Access the first section
first_section = presentation.SectionList.get_Item(0)
# Add a new slide to the presentation and insert it at the start of the section
slide = presentation.Slides.Append()
first_section.Insert(0, slide)
# Remove the added slide from the presentation
presentation.Slides.Remove(slide)
# Save the modified presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("InsertSlidesInSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
# Close the Presentation object
presentation.Dispose()
Retrieve Slides from a PowerPoint Section in Python
Retrieving slides from a specific section allows you to focus on a smaller group of slides for tasks such as reordering or applying custom formatting. Using the Section.GetSlides() method in Spire.Presentation for Python, you can easily access all the slides in a particular section. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section through its index (0-based) using the Presentation.SectionList(index) property.
- Retrieve the slides within the section using the Section.GetSlides() method.
- Iterate through the retrieved slides and get the slide number (1-based) of each slide.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Example.pptx")
# Retrieve the slides in the 3rd section
section = presentation.SectionList.get_Item(2)
slides = section.GetSlides()
output_content = "The slide numbers in this section are:\n"
# Get the slide number of each slide in the section
for slide in slides:
output_content += str(slide.SlideNumber) + " "
# Save the slide number to a text file
with open("slide_numbers.txt", "w") as file:
file.write(output_content)

Reorder Slides in a PowerPoint Section in Python
Reordering slides is important to ensure related content is in the right order. Spire.Presentation for Python offers the Section.Move() method, which allows you to move a slide to a new position within a section. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section through its index (0-based) using the Presentation.SectionList(index) property.
- Move a specific slide in the section to another position using the Section.Move() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Example.pptx")
# Access the 3rd section
section = presentation.SectionList.get_Item(2)
# Retrieve the slides in the section
slides = section.GetSlides()
# Move the 1st slide in the section to the specified position
section.Move(2, slides[0])
# Save the modified presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("ReorderSlidesInSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
# Close the Presentation object
presentation.Dispose()
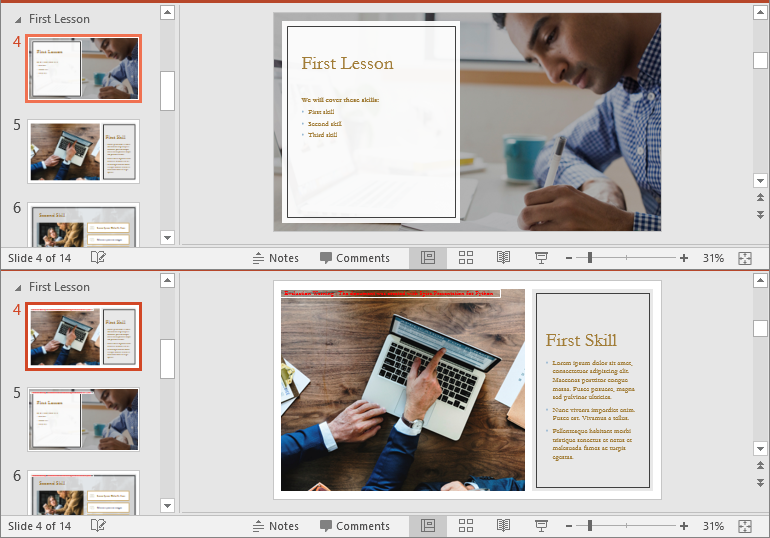
Remove Slides from a PowerPoint Section in Python
Removing slides from a section streamlines your presentation, particularly when some slides become outdated or unnecessary. With Spire.Presentation for Python, you can easily remove a single slide or multiple slides from a section using the Section.RemoveAt() or Section.RemoveRange() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section through its index (0-based) using the Presentation.SectionList(index) property.
- Remove a specific slide or a range of slides from the presentation using the Section.RemoveAt() or Section.RemoveRange() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Example.pptx")
# Access the 3rd section
section = presentation.SectionList.get_Item(2)
# Remove the first slide from the section
section.RemoveAt(0)
# Or remove a range of slides from the section
# section.RemoveRange(0, 2)
# Save the modified presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("RemoveSlidesInSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
# Close the Presentation object
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Extract Annotations from PDF
Annotations in PDF documents play a crucial role in enhancing collaboration, emphasizing key points, or providing additional context. Extracting annotations is essential for efficiently analyzing PDF content, but manual extraction can be tedious. This guide demonstrates how to extract annotations from PDF with Python using Spire.PDF for Python, providing a faster and more flexible solution to access important information.
- Extract Specified Annotations from PDF Documents
- Extract All Annotations from a PDF Page
- Extract All Annotations from PDF Files
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install it, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows.
Extract Specified Annotations from PDF Documents
Although Adobe Acrobat offers a built-in one-click annotation extraction feature, it lacks flexibility when handling specific annotations. If you only need to extract one or a few annotations, you must manually locate and copy them, which can be inefficient, especially when working with PDFs containing multiple annotations. Spire.PDF (short for Spire.PDF for Python), however, provides the PdfAnnotationCollection.get_item() method, enabling targeted extraction of specific annotations, making PDF annotation management more flexible and efficient.
Steps to extract specified annotations from PDF:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF document from the local storage with PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property, and access the annotations collection with PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget property.
- Create a list to store annotation information.
- Access the specified annotation using PdfAnnotationCollection.get_Item() method.
- Append annotation details to the list.
- Save the list as a Text file.
Here is the code example of exporting the first annotation on the third page:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a new PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile( "Sample.pdf")
# Get the third page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(2)
# Access the annotations on the page
annotations = page.AnnotationsWidget
# Create a list to save information of annotations
sb = []
# Access the first annotation on the page
annotation = annotations.get_Item(0)
# Append the annotation details to the list
sb.append("Annotation information: ")
sb.append("Text: " + annotation.Text)
modifiedDate = annotation.ModifiedDate.ToString()
sb.append("ModifiedDate: " + modifiedDate)
# Save the list as a Text file
with open("GetSpecificAnnotation.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
file.write("\n".join(sb))
# Close the PDF file
pdf.Close()
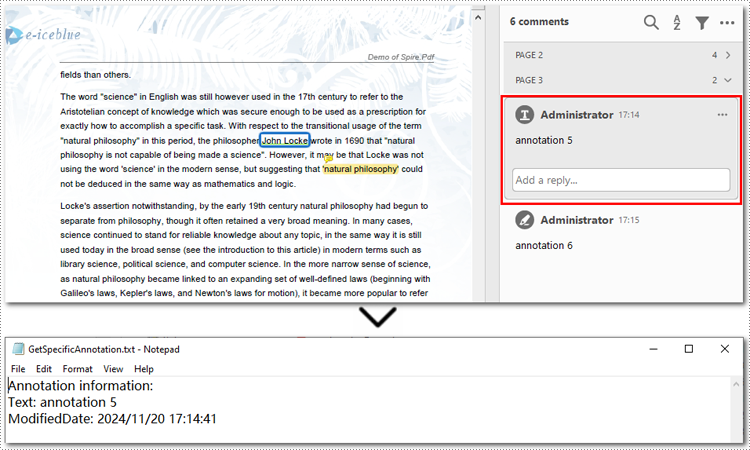
Extract All Annotations from a PDF Page
To export all annotations from a specified PDF page, you can still use the PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget property along with the PdfAnnotationCollection.get_item() method. However, you will need to iterate through all the annotations on the page to ensure none are missed. Below are the steps and code examples to guide you through the process.
Steps to extract annotations from PDF pages:
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Read a PDF document from the local storage with PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the annotation collection on the specified page using PdfDocument.Pages.AnnotationsWidget property.
- Create a list to store annotation information.
- Loop through annotations on a certain page.
- Retrieve each annotation using PdfAnnotationCollection.get_Item() method.
- Add annotation details to the list.
- Save the list as a Text file.
Below is the code example of extracting all annotations on the second page:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a new PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get all annotations from the second page
annotations = pdf.Pages.get_Item(1).AnnotationsWidget
# Create a list to maintain annotation details
sb = []
# Loop through annotations on the page
if annotations.Count > 0:
for i in range(annotations.Count):
# Get the current annotation
annotation = annotations.get_Item(i)
# Get the annotation details
if isinstance(annotation, PdfPopupAnnotationWidget):
continue
sb.append("Annotation information: ")
sb.append("Text: " + annotation.Text)
modifiedDate = annotation.ModifiedDate.ToString()
sb.append("ModifiedDate: " + modifiedDate)
# Save annotations as a Text file
with open("GetAllAnnotationsFromPage.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
file.write("\n".join(sb))
# Release resources
pdf.Close()
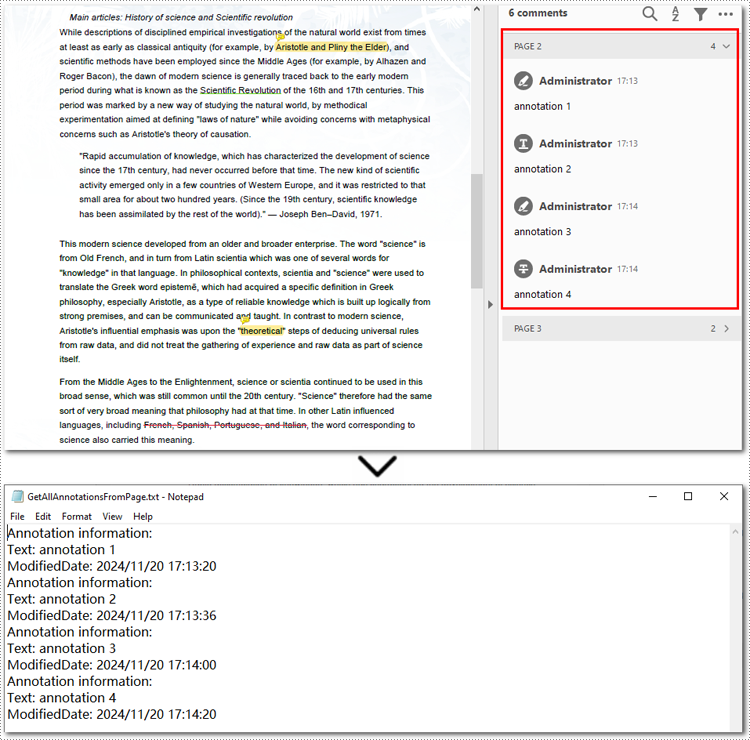
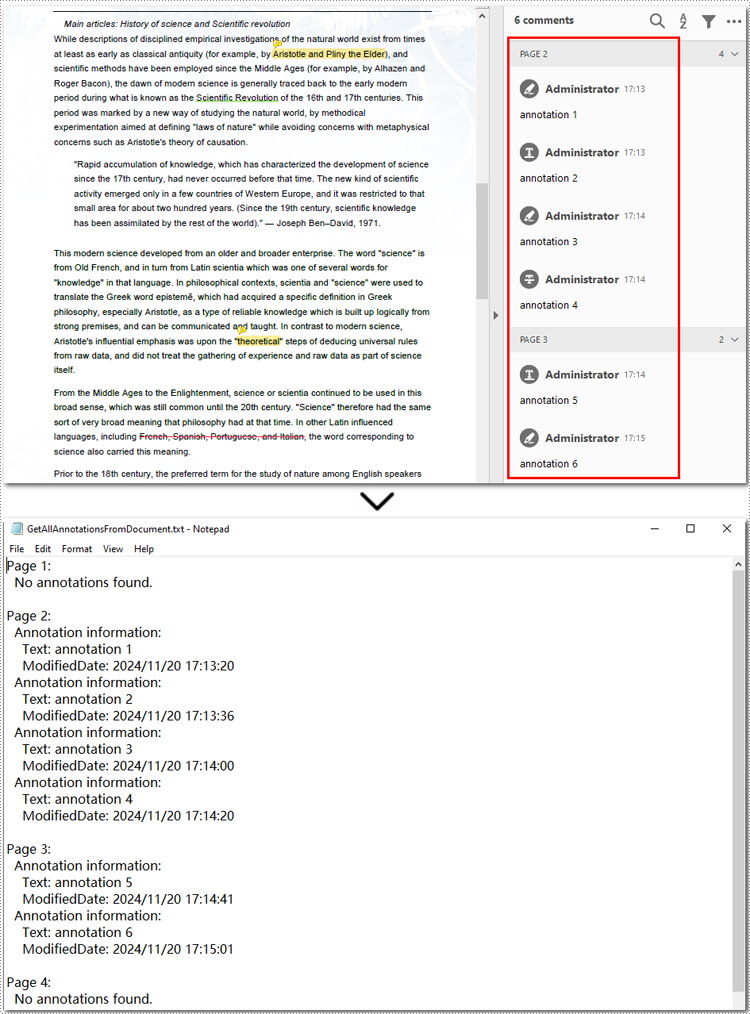
Extract All Annotations from PDF Files
The final section of this guide illustrates how to extract all annotations from a PDF document using Python. The process is similar to exporting annotations from a single page but involves iterating through each page, traversing all annotations, and accessing their details. Finally, the extracted annotation details are saved to a text file for further use. Let’s take a closer look at the detailed steps.
Steps to extract all annotations from a PDF document:
- Create an instance of PdfDocument class.
- Read a PDF document from the disk with PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Initialize a list to store annotation information.
- Loop through all pages and access the annotation collection with PdfDocument.Pages.AnnotationsWidget property.
- Iterate each annotation in the collection and get annotations using PdfAnnotationCollection.get_item() method.
- Append annotation details to the list.
- Output the list as a Text file.
Here is an example of exporting all annotations from a PDF file:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a new PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a list to save annotation details
sb = []
# Iterate through all pages in the PDF document
for pageIndex in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
sb.append(f"Page {pageIndex + 1}:")
# Access the annotation collection of the current page
annotations = pdf.Pages.get_Item(pageIndex).AnnotationsWidget
# Loop through annotations in the collection
if annotations.Count > 0:
for i in range(annotations.Count):
# Get the annotations of the current page
annotation = annotations.get_Item(i)
# Skip invalid annotations (empty text and default date)
if not annotation.Text.strip() and annotation.ModifiedDate.ToString() == "0001/1/1 0:00:00":
continue
# Extract annotation information
sb.append("Annotation information: ")
sb.append("Text: " + (annotation.Text.strip() or "N/A"))
modifiedDate = annotation.ModifiedDate.ToString()
sb.append("ModifiedDate: " + modifiedDate)
else:
sb.append("No annotations found.")
# Add a blank line after each page
sb.append("")
# Save all annotations to a file
with open("GetAllAnnotationsFromDocument.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
file.write("\n".join(sb))
# Close the PDF document
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Split PowerPoint Presentations
Splitting a PowerPoint presentation into smaller files or individual sections can be useful in various situations. For instance, when collaborating with a team, each member may only need a specific section of the presentation to work on. Additionally, breaking a large presentation into smaller parts can simplify sharing over email or uploading to platforms with file size restrictions. In this article, we'll show you how to split PowerPoint presentations by slides, slide ranges, and sections in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Split PowerPoint Presentations by Slides in Python
- Split PowerPoint Presentations by Slide Ranges in Python
- Split PowerPoint Presentations by Sections in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Split PowerPoint Presentations by Slides in Python
Developers can use Spire.Presentation for Python to split a PowerPoint presentation into individual slides by iterating through the slides in the presentation and adding each slide to a new presentation. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through all slides in the presentation:
- Access the current slide through the Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Create a new PowerPoint presentation using the Presentation class and remove its default slide using the Presentation.Slides.RemoveAt(0) method.
- Append the current slide to the new presentation using the Presentation.Slides.AppendBySlide() method.
- Save the new presentation as a file using the ISlide.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Iterate through all slides in the presentation
for i in range(presentation.Slides.Count):
# Get the current slide
slide = presentation.Slides[i]
# Create a new PowerPoint presentation and remove its default slide
newPresentation = Presentation()
newPresentation.Slides.RemoveAt(0)
# Append the current slide to the new presentation
newPresentation.Slides.AppendBySlide(slide)
# Save the new presentation as a file
newPresentation.SaveToFile(f"output/Presentations/Slide-{i + 1}.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
newPresentation.Dispose()
presentation.Dispose()
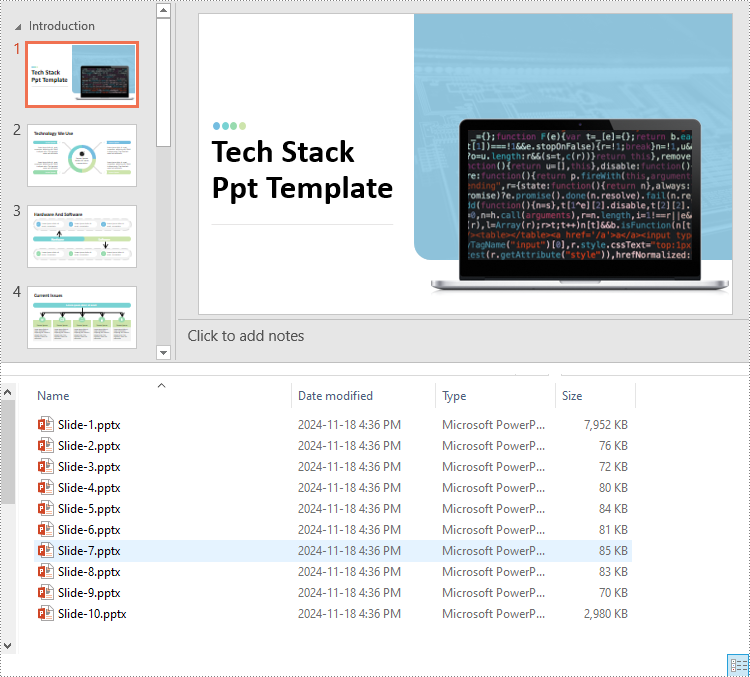
Split PowerPoint Presentations by Slide Ranges in Python
Apart from splitting a PowerPoint presentation into individual slides, developers can also divide it into specific ranges of slides by adding the desired slides to new presentations. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create new PowerPoint presentations using the Presentation class and remove the default slides within them using the Presentation.Slides.RemoveAt(0) method.
- Append specified ranges of slides to the new presentations using the Presentation.Slides.AppendBySlide() method.
- Save the new presentations as files using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Create two new PowerPoint presentations and remove their default slides
presentation1 = Presentation()
presentation2 = Presentation()
presentation1.Slides.RemoveAt(0)
presentation2.Slides.RemoveAt(0)
# Append slides 1-3 to the first new presentation
for i in range(3):
presentation1.Slides.AppendBySlide(presentation.Slides[i])
# Append the remaining slides to the second new presentation
for i in range(3, presentation.Slides.Count):
presentation2.Slides.AppendBySlide(presentation.Slides[i])
# Save the new presentations as files
presentation1.SaveToFile("output/Presentations/SlideRange1.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation2.SaveToFile("output/Presentations/SlideRange2.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation1.Dispose()
presentation2.Dispose()
presentation.Dispose()
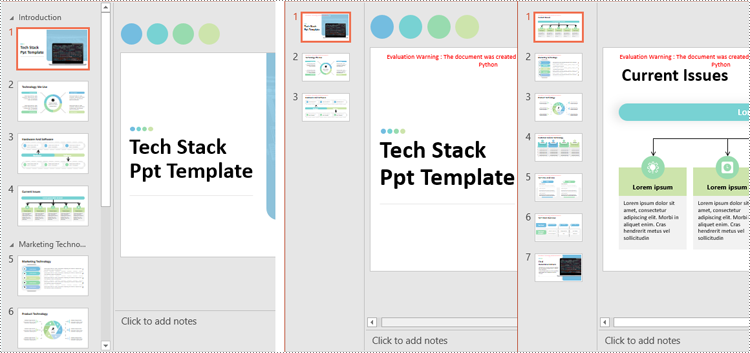
Split PowerPoint Presentations by Sections in Python
Sections in PowerPoint are often used to organize slides into manageable groups. With Spire.Presentation for Python, developers can split a PowerPoint presentation into sections by iterating through the sections in the presentation and adding the slides within each section to a new presentation. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through all sections in the presentation:
- Access the current section through the Presentation.SectionList[] property.
- Create a new PowerPoint presentation using the Presentation class and remove its default slide using the Presentation.Slides.RemoveAt(0) method.
- Add a section to the new presentation with the same name using the Presentation.SectionList.Append() method.
- Retrieve the slides of the current section using the Section.GetSlides() method.
- Iterate through the retrieved slides and add them to the section of the new presentation using the Section.Insert() method.
- Save the new presentation as a file using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Iterate through all sections
for i in range(presentation.SectionList.Count):
# Get the current section
section = presentation.SectionList.get_Item(0)
# Create a new PowerPoint presentation and remove its default slide
newPresentation = Presentation()
newPresentation.Slides.RemoveAt(0)
# Add a section to the new presentation
newSection = newPresentation.SectionList.Append(section.Name)
# Retrieve the slides of the current section
slides = section.GetSlides()
# Insert each retrieved slide into the section of the new presentation
for slide_index, slide in enumerate(slides):
newSection.Insert(slide_index, slide)
# Save the new presentation as a file
newPresentation.SaveToFile(f"output/Presentations/Section-{i + 1}.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2019)
newPresentation.Dispose()
presentation.Dispose()
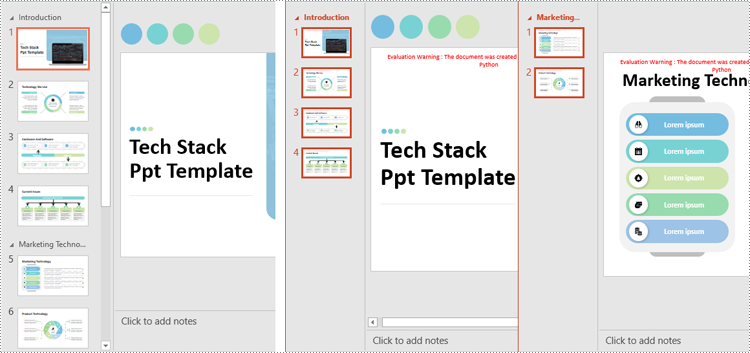
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.