Generate Word Documents from Templates in Java
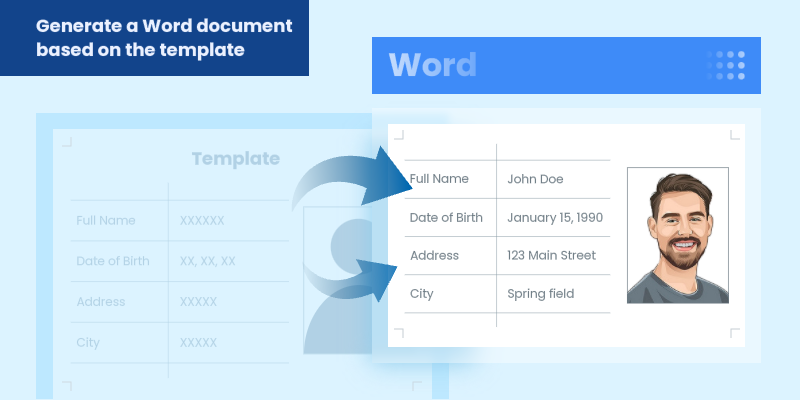
In modern software development, generating dynamic Word documents from templates is a common requirement for applications that produce reports, contracts, invoices, or other business documents. Java developers seeking efficient solutions for document automation can leverage Spire.Doc for Java, a robust library for processing Word files without requiring Microsoft Office.
This guide explores how to use Spire.Doc for Java to create Word documents from templates. We will cover two key approaches: replacing text placeholders and modifying bookmark content.
- Java Libray for Creating Word Documents
- Generate a Word Document by Replacing Text Placeholders
- Generate a Word Document by Modifying Bookmark Content
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Java Library for Generating Word Documents
Spire.Doc for Java is a powerful library that enables developers to create, manipulate, and convert Word documents. It provides an intuitive API that allows for various operations, including the modification of text, images, and bookmarks in existing documents.
To get started, download the library from our official website and import it into your Java project. If you're using Maven, include the following dependency in your pom.xml file:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
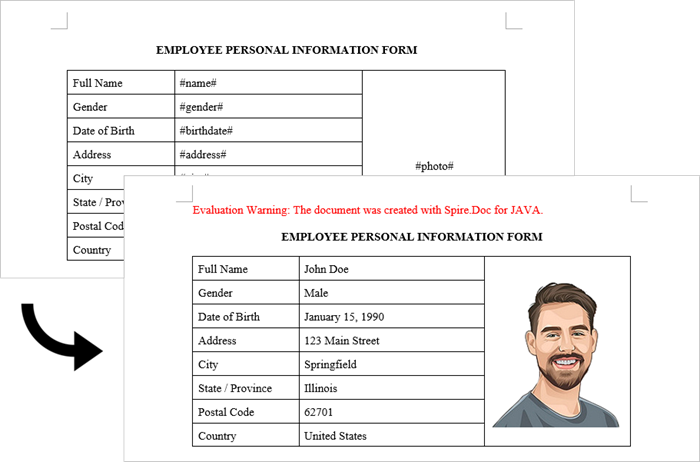
Generate a Word Document by Replacing Text Placeholders
This method uses a template document containing marked placeholders (e.g., #name#, #date#) that are dynamically replaced with real data. Spire.Doc's Document.replace() method handles text substitutions efficiently, while additional APIs enable advanced replacements like inserting images at specified locations.
Steps to generate Word documents from templates by replacing text placeholders:
- Initialize Document: A new Document object is created to work with the Word file.
- Load the template: The template document with placeholders is loaded.
- Create replacement mappings: A HashMap is created to store placeholder-replacement pairs.
- Perform text replacement: The replace() method finds and replaces all instances of each placeholder.
- Handle image insertion: The custom replaceTextWithImage() method replaces a text placeholder with an image.
- Save the result: The modified document is saved to a specified path.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.documents.TextSelection;
import com.spire.doc.fields.DocPicture;
import com.spire.doc.fields.TextRange;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ReplaceTextPlaceholders {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize a new Document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load the template Word file
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\template.docx");
// Map to hold text placeholders and their replacements
Map<String, String> replaceDict = new HashMap<>();
replaceDict.put("#name#", "John Doe");
replaceDict.put("#gender#", "Male");
replaceDict.put("#birthdate#", "January 15, 1990");
replaceDict.put("#address#", "123 Main Street");
replaceDict.put("#city#", "Springfield");
replaceDict.put("#state#", "Illinois");
replaceDict.put("#postal#", "62701");
replaceDict.put("#country#", "United States");
// Replace placeholders in the document with corresponding values
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : replaceDict.entrySet()) {
document.replace(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue(), true, true);
}
// Path to the image file
String imagePath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\portrait.png";
// Replace the placeholder “#photo#” with an image
replaceTextWithImage(document, "#photo#", imagePath);
// Save the modified document
document.saveToFile("output/ReplacePlaceholders.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Release resources
document.dispose();
}
// Method to replace a placeholder in the document with an image
static void replaceTextWithImage(Document document, String stringToReplace, String imagePath) {
// Load the image from the specified path
DocPicture pic = new DocPicture(document);
pic.loadImage(imagePath);
// Find the placeholder in the document
TextSelection selection = document.findString(stringToReplace, false, true);
// Get the range of the found text
TextRange range = selection.getAsOneRange();
int index = range.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().indexOf(range);
// Insert the image and remove the placeholder text
range.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().insert(index, pic);
range.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().remove(range);
}
}Output:
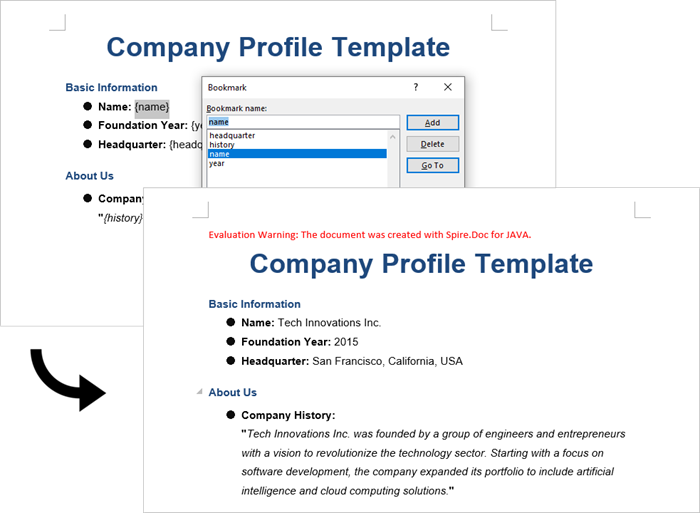
Generate a Word Document by Modifying Bookmark Content
This approach uses Word bookmarks to identify locations in the document where content should be inserted or modified. The BookmarksNavigator class in Spire.Doc streamlines the process by enabling direct access to bookmarks, allowing targeted content replacement while automatically preserving the document's original structure and formatting.
Steps to generate Word documents from templates by modifying bookmark content:
- Initialize Document: A new Document object is initialized.
- Load the template: The template document with predefined bookmarks is loaded.
- Set up replacements: A HashMap is created to map bookmark names to their replacement values.
- Navigate to bookmarks: A BookmarksNavigator is instantiated to navigate through bookmarks in the document.
- Replace content: The replaceBookmarkContent() method updates the bookmark's content.
- Save the result: The modified document is saved to a specified path.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ModifyBookmarkContent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize a new Document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load the template Word file
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\template.docx");
// Define bookmark names and their replacement values
Map<String, String> replaceDict = new HashMap<>();
replaceDict.put("name", "Tech Innovations Inc.");
replaceDict.put("year", "2015");
replaceDict.put("headquarter", "San Francisco, California, USA");
replaceDict.put("history", "Tech Innovations Inc. was founded by a group of engineers and " +
"entrepreneurs with a vision to revolutionize the technology sector. Starting " +
"with a focus on software development, the company expanded its portfolio to " +
"include artificial intelligence and cloud computing solutions.");
// Create a BookmarksNavigator to manage bookmarks in the document
BookmarksNavigator bookmarkNavigator = new BookmarksNavigator(document);
// Iterate through the bookmarks
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : replaceDict.entrySet()) {
// Navigate to a specific bookmark
bookmarkNavigator.moveToBookmark(entry.getKey());
// Replace content
bookmarkNavigator.replaceBookmarkContent(entry.getValue(), true);
}
// Save the modified document
document.saveToFile("output/ReplaceBookmarkContent.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Release resources
document.dispose();
}
}Output:
Conclusion
Both methods provide effective ways to generate documents from templates, but they suit different scenarios:
Text Replacement Method is best when:
- You need simple text substitutions
- You need to insert images at specific locations
- You want to replace text anywhere in the document (not just specific locations)
Bookmark Method is preferable when:
- You're working with complex documents where precise location matters
- You need to replace larger sections of content or paragraphs
- You want to preserve bookmarks for future updates
Spire.Doc also offers Mail Merge capabilities, enabling high-volume document generation from templates. This feature excels at producing personalized documents like mass letters or reports by merging template fields with external data sources like databases.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert the generated Word document to PDF?
A: Yes, Spire.Doc for Java supports converting documents to PDF and other formats. Simply use saveToFile() with FileFormat.PDF.
Q2: How can I handle complex formatting in generated documents?
A: Prepare your template with all required formatting in Word, then use placeholders or bookmarks in locations where dynamic content should appear. The formatting around these markers will be preserved.
Q3: What's the difference between mail merge and text replacement?
A: Mail merge is specifically designed for merging database-like data with documents and supports features like repeating sections for records. Text replacement is simpler but doesn't handle tabular data as elegantly.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Java without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
How to Generate Barcode in Python (Step-by-Step Guide)

Barcodes are essential in inventory management, retail systems, logistics, and many other data-driven fields. For Python developers, generating barcodes in Python can be complex—especially when working with multiple formats or large-scale automation. That’s why a reliable Python barcode generator library is necessary to ensure flexible and efficient barcode creation, with support for various barcode types and batch processing.
This article provides an accurate and efficient approach to generating barcodes in Python using Spire.Barcode for Python.
- Get Started with Spire.Barcode for Python
- How to Generate Barcode in Python
- Supported Barcode Types
- Frequently Asked Questions
Get Started with Spire.Barcode for Python
Why Choose Spire.Barcode?
Spire.Barcode for Python is a professional and user-friendly Python Barcode API designed for developers who want to add barcode generation or reading features to their Python applications. Here’s why it stands out:
- Supports multiple barcode symbologies including Code 128, QR Code, EAN-13, UPC, and more
- High-quality image output with complete customization settings
- Comprehensive and easy-to-integrate API
- No need for third-party dependencies
- One library to generate and scan barcodes
Installation and Importing
To install Spire.Barcode for Python, simply run:
pip install spire.barcodeYou can also install Free Spire.Barcode for Python for simple barcode generating tasks:
pip install spire.barcode.freeHow to Generate Barcode in Python
To generate a barcode in Python, you typically need to define the barcode type (such as Code 128 or QR Code) and the content to encode. Using a library like Spire.Barcode, you can configure them in just a few lines of code.
Key Classes and Methods:
- BarcodeSettings: Defines properties such as type, data, color, text, etc.
- BarCodeGenerator: Generates barcode images based on settings.
- GenerateImage(): Outputs barcode as an image stream.
Step 1: Import the Required Modules
To start coding your Python barcode generator, import the necessary classes.
- Python
from spire.barcode import BarcodeSettings, BarCodeType, BarCodeGenerator, Code128SetMode, FontStyle, ColorStep2: Configure Barcode Settings
Create a BarcodeSettings object and define barcode properties:
- Python
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
barcodeSettings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type
barcodeSettings.Type = BarCodeType.Code128
# Set the barcode data
barcodeSettings.Data = "ABC123456789"
# Set the barcode code128 set mode
barcodeSettings.Code128SetMode = Code128SetMode.Auto
# Choose the data display position
barcodeSettings.ShowTextOnBottom = True
# Set the bottom text and style
barcodeSettings.BottomText = "Code 128 Example"
barcodeSettings.SetTextFont("Arial", 12.0, FontStyle.Regular)
barcodeSettings.ShowBottomText = True
# Set the background color
barcodeSettings.BackColor = Color.get_Beige()Step 3: Generate the Barcode Image
Create a BarCodeGenerator object using the configured BarcodeSettings, then generate the barcode image as a stream and save it to a local file:
- Python
# Create a BarCodeGenerator object
barcodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(barcodeSettings)
# Generate the barcode image
barcodeImage = barcodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
# Save the image
with open("output/Code 128.png", "wb") as fp:
fp.write(barcodeImage)The generated barcode:

This script allows you to generate a Code 128 barcode and save it as an image. Just replace the BarCodeType and Data value to customize.
Generating Other Barcode Types
Spire.Barcode for Python supports a wide range of barcode symbologies, including the most commonly used types such as Code 39, UPC, QR Code, and EAN-13. This ensures developers can generate barcodes for various applications with compatibility and ease.
Barcode Type Support Overview
| Barcode Category | Barcode Types (Examples) | Free Version | Paid Version |
| 1D Linear Barcodes | Codabar, Code11, Code25, Interleaved25, Code39, Code39Extended, Code93, Code93Extended, Code128, EAN8, EAN13, EAN128, EAN14, UPCA, UPCE, MSI, PostNet, Planet, SCC14, SSCC18, ITF14, ITF6, PZN, OPC | ✅ (Partial) | ✅ (All) |
| 2D Barcodes | QRCode, DataMatrix, Pdf417, Pdf417Macro, Aztec, MicroQR | ✅ (QRCode only) | ✅ (All) |
| Stacked/Composite Codes | RSS14, RSS14Truncated, RSSLimited, RSSExpanded | ❌ | ✅ |
| Postal Barcodes | USPS, SwissPostParcel, DeutschePostIdentcode, DeutschePostLeitcode, RoyalMail4State, SingaporePost4State | ❌ | ✅ |
Advanced: Generate Barcodes in Bulk
You can easily generate multiple barcodes in bulk using Spire.Barcode for Python. This is especially useful for inventory management, batch labeling, or automated systems where each item requires a unique barcode.
Code Example
- Python
# Create a list of barcode data
data = ["Barcode 1", "Barcode 2", "Barcode 3"]
# Loop through the data to generate barcodes
for barcode_data in data:
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
settings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type and data
settings.Type = BarCodeType.Code39
settings.Data = barcode_data
# Create a BarCodeGenerator object
generator = BarCodeGenerator(settings)
# Save the barcode image
barcode_stream = generator.GenerateImage()
with open(f"output/{barcode_data}.png", "wb") as file:
file.write(barcode_stream)This Python script generates and saves a barcode image for each entry in the list, streamlining barcode creation workflow.
Conclusion
Generating barcodes in Python is simple and efficient with Spire.Barcode for Python. Whether you’re creating a single Code 128 barcode or automating batch QR code generation, this robust and flexible library gives you the control and quality needed for professional barcode integration. From supporting various symbologies to delivering high-quality output with minimal code, this Python barcode generator is an excellent tool for developers across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How to create a barcode in Python?
You can create a barcode using libraries like Spire.Barcode for Python, which supports a variety of symbologies like Code 128, QR Code, and more. Just install the package, configure barcode settings, and save the output image.
Q: How is barcode generated?
Barcodes are generated by encoding data into a visual pattern of bars or modules. With Python, this is done through barcode libraries like Spire.Barcode, which translate string input into a corresponding image.
Q: How to create a code generator in Python?
If you're referring to a barcode generator, define the barcode type (e.g., Code 128), provide the data, and use a library like Spire.Barcode to generate and save the image. You can automate this process using loops and functions.
Q: How to generate QR code by Python?
You can use Spire.Barcode for Python to generate QR codes quickly and efficiently. Here's a full example that creates a QR code with embedded data:
- Python
from spire.barcode import BarcodeSettings, BarCodeGenerator, BarCodeType
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
barcodeSettings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type to QRCode
barcodeSettings.Type = BarCodeType.QRCode
# Set the barcode data
barcodeSettings.Data = "ABC123456"
# Generate the barcode
barcodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(barcodeSettings)
barcodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
with open("output/QRCode.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(barcodeGenerator.GenerateImage())Result:

This enables you to embed URLs, text, or IDs into scannable QR images.
See Also: How to Generate and Scan QR Codes with Python
Get a Free License
Spire.Barcode for Python offers a free trial license that removes limitations and watermarking. Get a free license today and explore the full capabilities of this powerful Python barcode library.
Edit PDF Using Python: A Practical Guide to PDF Modification

PDFs are widely used in reports, invoices, and digital forms due to their consistent formatting across platforms. However, their fixed layout makes editing difficult without specialized tools. For developers looking to edit PDF using Python, Spire.PDF for Python provides a comprehensive and easy-to-use solution. This Python PDF editor enables you to modify PDF files programmatically—changing text, replacing images, adding annotations, handling forms, and securing files—without relying on Adobe Acrobat or any external software.
In this article, we will explore how to use Spire.PDF for Python to programmatically edit PDFs in Python applications.
- Why Use Python and Spire.PDF to Edit PDF Documents?
- Getting Started with Spire.PDF for Python
- How to Edit an Existing PDF Using Spire.PDF for Python
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Use Python and Spire.PDF to Edit PDF Documents?
Python is a highly versatile programming language that provides an excellent platform for automating and managing PDF documents. When it comes to edit PDF Python tasks, Spire.PDF for Python stands out as a comprehensive and easy-to-use solution for all your PDF manipulation needs.
Benefits of Using Python for PDF Editing
- Automation and Batch Processing: Streamline repetitive PDF editing tasks efficiently.
- Cost-Effective: Reduce manual work, saving time and resources when you Python-edit PDF files.
- Integration: Seamlessly incorporate PDF editing into existing Python-based systems and workflows.
Advantages of Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python is a standalone library that enables developers to create, read, edit, convert, and save PDF files without relying on external software. As a trusted Python PDF editor, it offers powerful features such as:
- Text and Image Editing
- Annotations and Bookmark Management
- Form Field Handling
- Security Settings (Encryption and Permissions)
- Conversion to Word, Excel, HTML, and Images
To learn more about these specific features, visit the Spire.PDF for Python tutorials.
With its intuitive API design, Spire.PDF makes it easier than ever to edit PDF files in Python quickly and effectively, ensuring a smooth development experience.
Getting Started with Spire.PDF for Python
Installation:
To install Spire.PDF for Python, simply run the following pip command:
pip install spire.pdf
Alternatively, you can install Free Spire.PDF for Python, a free version suitable for small projects, by running:
pip install spire.pdf.free
You can also download the library manually from the links.
Basic Setup Example:
The following example demonstrates how to create a simple PDF using Spire.PDF for Python:
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfFont, PdfBrushes, PdfFontFamily, PdfFontStyle
# Create a new PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a new page to the document
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create a font
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 28.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold)
# Create a brush
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Draw the string using the font and brush
page.Canvas.DrawString("Hello, World", font, brush, 100.0, 100.0)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/NewPDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result: The generated PDF displays the text "Hello, World" using Times Roman Bold.

With Spire.PDF installed, you're now ready to edit PDFs using Python. The sections below explain how to manipulate structure, content, security, and metadata.
How to Edit an Existing PDF Using Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides a simple yet powerful way to edit PDF using Python. With its intuitive API, developers can automate a wide range of PDF editing tasks including modifying document structure, page content, security settings, and properties. This section outlines the core categories of editing and their typical use cases.
Edit PDF Pages and Structure with Python
Structure editing lets you manipulate PDF page order, merge files, or insert/delete pages—ideal for document assembly workflows.
- Insert or Delete Pages
Use the Pages.Insert() and Pages.RemoveAt() methods of the PdfDocument class to insert or delete pages at specific positions.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfPageSize, PdfMargins, PdfPageRotateAngle
# Load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Insert and delete pages
# Insert at beginning
pdf.Pages.Insert(0, PdfPageSize.A4(), PdfMargins(50.0, 60.0), PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle90)
# Delete second page
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(1)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/InsertDeletePage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
- Merge Two PDF Files
The AppendPage() method allows you to combine PDFs by inserting pages from one document into another.
Code Example
- Python
import os
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Specify the PDF file path
pdfPath = "PDFs/"
# Read the PDF file names from the path and add them to a list
files = [pdfPath + file for file in os.listdir(pdfPath) if file.endswith(".pdf")]
# Load the first PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile(files[0])
# Iterate through the other PDF files
for i in range(1, len(files)):
# Load the current PDF file
pdf2 = PdfDocument()
pdf2.LoadFromFile(files[i])
# Append the pages from the current PDF file to the first PDF file
pdf.AppendPage(pdf2)
# Save the merged PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/MergePDFs.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
You may also like: Splitting PDF Files with Python Code
Edit PDF Content with Python
As a Python PDF editor, Spire.PDF supports a variety of content-level operations, including modifying text, images, annotations, and interactive forms.
- Replace Text in a PDF
The PdfTextReplacer class can be used to find and replace text from a page. Note that precise replacement may require case and layout-aware handling.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextReplacer, ReplaceActionType, Color
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Iterate through the pages
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create a PdfTextReplacer object
replacer = PdfTextReplacer(page)
# Set the replacement options
replacer.Options.ReplaceType = ReplaceActionType.IgnoreCase
# Replace the text
replacer.ReplaceAllText("drones", "ROBOTS", Color.get_Aqua()) # Setting the color is optional
# Save the merged PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceText.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:

- Replace Images in a PDF
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfImageHelper class to help you replace images in a PDF file with ease. By retrieving image information from a specific page, you can use the ReplaceImage() method to directly substitute the original image with a new one.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfImageHelper, PdfImage
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image info of the first image on the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)[0]
# Load a new image
newImage = PdfImage.FromFile("Image.png")
# Replace the image
imageHelper.ReplaceImage(imageInfo, newImage)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceImage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:

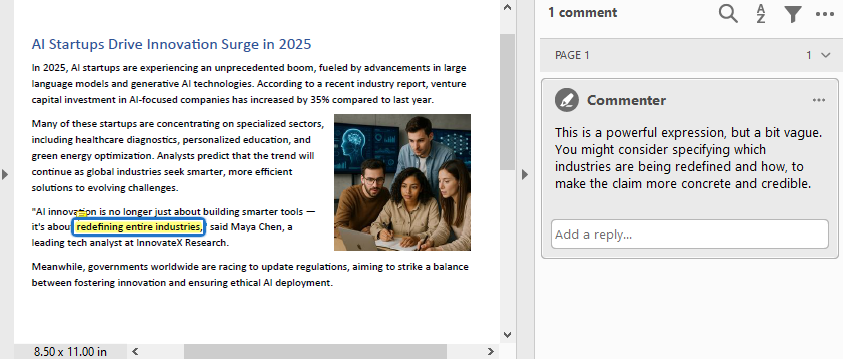
- Add Comments or Notes
To add comments or notes with Python, use the PdfTextMarkupAnnotation class and add it to the page’s AnnotationsWidget collection.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextFinder, PdfTextMarkupAnnotation, PdfRGBColor, Color
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
#Create a PdfTextFinder instance and set the options
finder = PdfTextFinder(page)
finder.Options.Parameter.IgnoreCase = False
finder.Options.Parameter.WholeWord = True
# Find the text to comment
text = finder.Find("redefining entire industries")[0]
# Get the bound of the text
bound = text.Bounds[0]
# Add comment
commentText = ("This is a powerful expression, but a bit vague. "
"You might consider specifying which industries are "
"being redefined and how, to make the claim more "
"concrete and credible.")
comment = PdfTextMarkupAnnotation("Commenter", commentText, bound)
comment.TextMarkupColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Yellow())
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(comment)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CommentNote.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
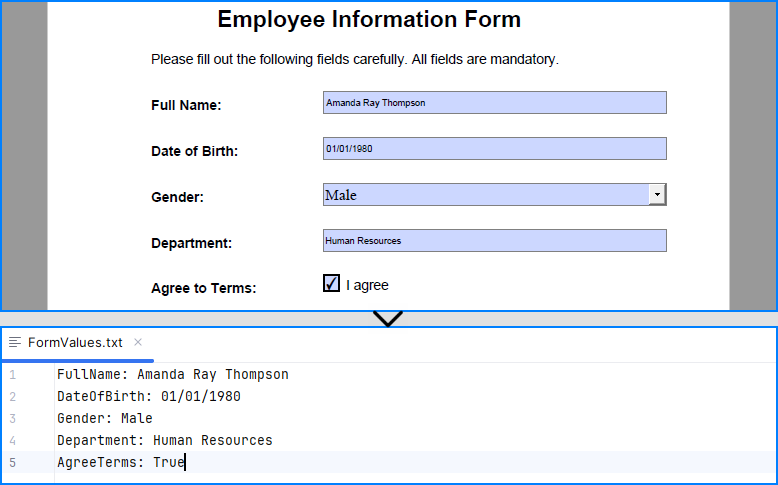
- Edit or Read Form Fields
Spire.PDF for Python allows you to programmatically fill out and read form fields in a PDF document. By accessing the FieldsWidget property of a PdfFormWidget object, you can iterate through all interactive form elements, such as text boxes, combo boxes, and checkboxes, and update or extract their values.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfFormWidget, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
forms = pdf.Form
formWidgets = PdfFormWidget(forms).FieldsWidget
# Fill the forms
for i in range(formWidgets.Count):
formField = formWidgets.get_Item(i)
if formField.Name == "FullName":
textBox = PdfTextBoxFieldWidget(formField)
textBox.Text = "Amanda Ray Thompson"
elif formField.Name == "DateOfBirth":
textBox = PdfTextBoxFieldWidget(formField)
textBox.Text = "01/01/1980"
elif formField.Name == "Gender":
comboBox = PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget(formField)
comboBox.SelectedIndex = [ 1 ]
elif formField.Name == "Department":
formField.Value = "Human Resources"
elif formField.Name == "AgreeTerms":
checkBox = PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget(formField)
checkBox.Checked = True
# Read the forms
formValues = []
for i in range(formWidgets.Count):
formField = formWidgets.get_Item(i)
if isinstance(formField, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + formField.Text)
elif isinstance(formField, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + formField.SelectedValue)
elif isinstance(formField, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + str(formField.Checked))
# Write the form values to a file
with open("output/FormValues.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("\n".join(formValues))
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/FilledForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
Explore more: How to Insert Page Numbers to PDF Using Python
Manage PDF Security with Python
PDF security editing is essential when dealing with sensitive documents. Spire.PDF supports encryption, password protection, digital signature handling, and permission settings.
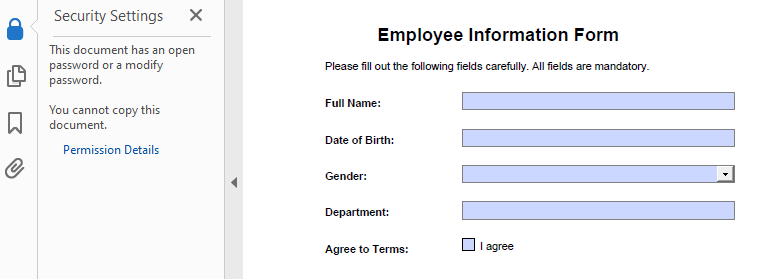
- Add a Password and Set Permissions
The Encrypt() method lets you secure a PDF with user/owner passwords and define allowed actions like printing or copying.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfEncryptionAlgorithm, PdfDocumentPrivilege, PdfPasswordSecurityPolicy
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Create a PdfSecurityPolicy object and set the passwords and encryption algorithm
securityPolicy = PdfPasswordSecurityPolicy("userPSD", "ownerPSD")
securityPolicy.EncryptionAlgorithm = PdfEncryptionAlgorithm.AES_128
# Set the document privileges
pdfPrivileges = PdfDocumentPrivilege.ForbidAll()
pdfPrivileges.AllowPrint = True
pdfPrivileges.AllowFillFormFields = True
# Apply the document privileges
securityPolicy.DocumentPrivilege = pdfPrivileges
# Encrypt the PDF with the security policy
pdf.Encrypt(securityPolicy)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EncryptedForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result
- Remove the Password from a PDF
To open a protected file, provide the user password when calling LoadFromFile(), use Decrypt() to decrypt the document, and save it again unprotected.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the encrypted PDF file with the owner password
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("output/EncryptedForm.pdf", "ownerPSD")
# Decrypt the PDF file
pdf.Decrypt()
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/DecryptedForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Recommended for you: Use Python to Add and Remove Digital Signature in PDF
Edit PDF Properties with Python
Use Spire.PDF to read and edit PDF metadata and viewer preferences—key features for document presentation and organization.
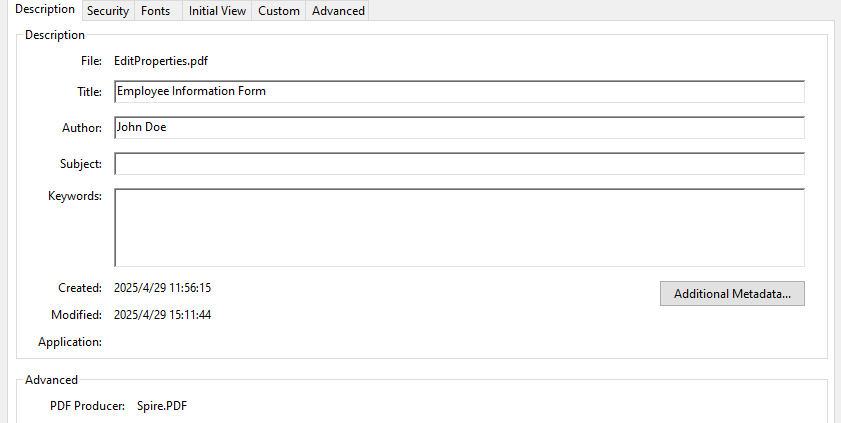
- Update Document Metadata
Update metadata such as title, author, or subject via the DocumentInformation property of the PDF document.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Set document metadata
pdf.DocumentInformation.Author = "John Doe"
pdf.DocumentInformation.Title = "Employee Information Form"
pdf.DocumentInformation.Producer = "Spire.PDF"
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EditProperties.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
- Set View Preferences
The ViewerPreferences property allows you to customize the viewing mode of a PDF (e.g., two-column layout).
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfPageLayout, PrintScalingMode
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Set the viewer preferences
pdf.ViewerPreferences.DisplayTitle = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideToolbar = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideWindowUI = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.FitWindow = False
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideMenubar = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.PrintScaling = PrintScalingMode.AppDefault
pdf.ViewerPreferences.PageLayout = PdfPageLayout.OneColumn
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EditViewerPreference.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
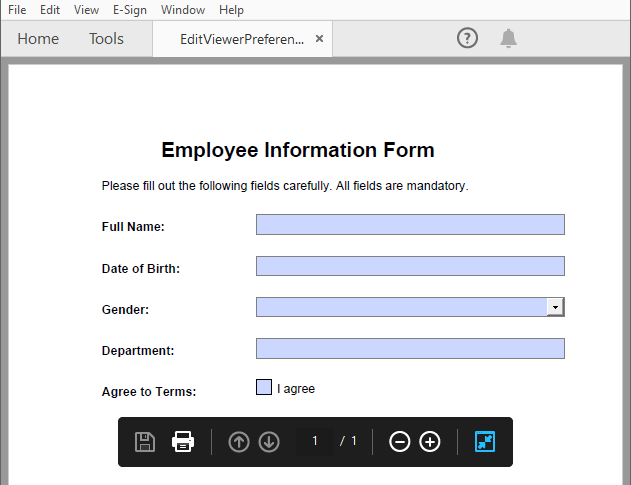
Similar topic: Change PDF Version Easily with Python Code
Conclusion
Editing PDFs using Python is both practical and efficient with Spire.PDF for Python. Whether you're building automation tools, editing digital forms, or securing sensitive reports, Spire.PDF equips you with a comprehensive suite of editing features—all accessible via clean and simple Python code.
With capabilities that span content editing, form interaction, document structuring, and security control, this Python PDF editor is a go-to solution for developers and organizations aiming to streamline their PDF workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I edit a PDF using Python?
A: Yes, Python offers powerful libraries like Spire.PDF for Python that enable you to edit text, images, forms, annotations, and even security settings in a PDF file.
Q: How to edit a PDF using coding?
A: By using libraries such as Spire.PDF for Python, you can load an existing PDF, modify its content or structure programmatically, and save the changes with just a few lines of code.
Q: What is the Python library for PDF editor?
A: Spire.PDF for Python is a popular choice. It offers comprehensive functionalities for creating, reading, editing, converting, and securing PDF documents without the need for additional software.
Q: Can I modify a PDF for free?
A: Yes, you can use the free edition of Spire.PDF for Python to edit PDF files, although it comes with some limitations, such as processing up to 10 pages per document. Additionally, you can apply for a 30-day temporary license that removes all limitations and watermarks for full functionality testing.
Spire.PDF 11.4.10 supports printing using .NET Standard DLL
We're pleased to announce the release of Spire.PDF 11.4.10. This version supports printing using .NET Standard DLL and retrieving PdfHideAction in buttons. Moreover, some known issues that occurred when converting PDF to images and saving files have also been successfully fixed. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREPDF-7372 | Supports retrieving PdfHideAction in buttons.
//Initialize an instance of the PdfDocument instance
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
//Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile);
//Initialize an instance of the StringBuilder class
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//Get the form from the document
PdfFormWidget formWidget = doc.Form as PdfFormWidget;
//Iterate through all fields in the form
for (int i = 0; i < formWidget.FieldsWidget.List.Count; i++)
{
PdfField field = formWidget.FieldsWidget.List[i] as PdfField;
//Get the ButtonField
if (field is PdfButtonWidgetFieldWidget)
{
PdfButtonWidgetFieldWidget buttonField = field as PdfButtonWidgetFieldWidget;
// Get the field name
string filename = buttonField.Name;
// Get the action
PdfAction action = buttonField.Actions.MouseDown;
if (buttonField.Actions.MouseDown != null && buttonField.Actions.MouseDown is PdfHideAction)
{
var btnAction = (PdfHideAction)buttonField.Actions.MouseDown;
sb.AppendLine(filename + "-MouseDown-Hide-" + btnAction.IsHide.ToString());
sb.AppendLine(filename + "-MouseDown-fname-" + btnAction.FieldName[0].ToString());
}
}
}
File.WriteAllText(outputFile, sb.ToString());
doc.Dispose();
|
| New feature | SPIREPDF-7376 SPIREPDF-7391 SPIREPDF-7467 | Supports printing on Windows and Linux systems using .NET Standard DLL.
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.LoadFromFile(pdffile);
doc.PrintSettings.SelectPageRange(1, 5);
if(doc.PrintSettings.CanDuplex)
{
doc.PrintSettings.Duplex = PdfDuplex.Vertical;
}
doc.Print();
|
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7361 | Fixes the issue that adding PdfTextMarkupAnnotation produced incorrect effects. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7380 | Fixes the issue where the text was garbled when converting PDF to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7388 | Fixes the issue where the application threw the “NullReferenceException” when accessing PdfDocumentLinkAnnotationWidget.Destination. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7414 | Fixes the issue where the text was truncated when entering multi-line content into PdfTextBoxField. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7420 | Fixes the issue where the application threw the “PdfDocumentException” when using the PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected() method. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7424 | Fixes the issue where the application threw the “ArgumentOutOfRangeException” when converting PDF to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7426 | Fixes the issue that the/DA structure was incorrect in TextBox fields. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7429 | Fixes the issue where the application threw the "Empty convert-string" error when saving PDF documents. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7431 | Fixes the issue where the result was incorrect when setting FieldsWidget.BorderColor = PdfRGBColor.Empty. |
Spire.Doc for Python 13.4.6 supports matching and finding all keywords within paragraphs
We are excited to announce the release of Spire.Doc for Python 13.4.6. The latest version supports matching and finding all keywords within paragraphs. Besides, some known bugs are fixed in this update, such as the issue that the text was garbled when converting Word to TXT. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREDOC-10348 SPIREDOC-11127 |
Supports matching and finding all keywords within paragraphs.
#Create word document
document = Document()
#Load the document from disk.
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Insert the paragraphs of document
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
section = document.Sections.get_Item(i)
for j in range(section.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(j)
textSelections = paragraph.FindAllString("The", False, True)
for selection in textSelections:
#highlight
selection.GetAsOneRange().CharacterFormat.HighlightColor = Color.get_Yellow()
#Save doc file.
document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx)
|
| New feature | SPIREDOC-10659 | Supports creating charts in Word.
def AppendCharts(section, chartType, width, heigh):
section.AddParagraph().AppendText("{0:s} chart.".format(chartType))
newPara = section.AddParagraph()
# Support adding the BarChart/LineChart/ColumnChart/Surface3DChart/BubbleChart/PieChart/ScatterChart type
shape = newPara.AppendChart(chartType, float(width), float(heigh))
chart = shape.Chart
chart.Series.Clear()
chart.Series.Add("E-iceblue Test Series 1", ["Word", "PDF", "Excel", "GoogleDocs", "Office"], [
float(1900000), float(850000), float(2100000), float(600000), float(1500000)])
chart.Series.Add("E-iceblue Test Series 2", ["Word", "PDF", "Excel", "GoogleDocs", "Office"], [
float(900000), float(50000), float(1100000), float(400000), float(2500000)])
chart.Series.Add("E-iceblue Test Series 3", ["Word", "PDF", "Excel", "GoogleDocs", "Office"], [
float(500000), float(820000), float(1500000), float(400000), float(100000)])
#Create word document
document = Document()
#Add section
section = document.AddSection()
AppendCharts(section, ChartType.Bar, 500, 300)
#Save
document.SaveToFile("AppendCharts.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
|
| New feature | SPIREDOC-10963 | Supports obtaining the line index position where the found content is located.
document = Document()
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
textSelections = document.FindAllString("Ceshi", True, True)
sb = []
ranges = []
for selection in textSelections:
tr = selection.GetAsOneRange()
ranges.append(tr)
layoutDoc = FixedLayoutDocument(document)
for tr in ranges:
spans = layoutDoc.GetLayoutEntitiesOfNode(tr)
for i in range(spans.Count):
tempSpan = spans[i]
fs = FixedLayoutSpan(tempSpan)
tempfl = fs.Parent
line = FixedLayoutLine(tempfl)
if line.Parent.Type == LayoutElementType.Column:
lines = line.Parent.Lines
index = lines.IndexOf(line)
# print(index)
sb.append("position:" + str(index))
File.AppendAllText(outputFile, sb)
|
| New feature | SPIREDOC-11001 | Supports enabling and disabling revision tracking mode.
document = Document()
#Load the file from disk.
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
document.TrackChanges = True
document.StartTrackRevisions("user")
range = document.LastParagraph.AppendText("Revise4")
range.InsertRevision.Author = "test01"
document.LastParagraph.Text = "remove"
range.DeleteRevision.Author = "test01"
document.StopTrackRevisions()
document.SaveToFile(outputFile)
|
| New feature | SPIREDOC-11015 | Supports setting "Document.LayoutOptions.UseHarfBuzzTextShaper" when converting Word to PDF.
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("input.docx");
doc.LayoutOptions.UseHarfBuzzTextShaper = true;
doc.SaveToFile("result.pdf", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.PDF);
|
| New feature | SPIREDOC-11114 | Supports detecting whether a document is encrypted.
value1 = Document.IsEncrypted(inputFile_1) |
| New feature | SPIREDOC-11157 | Supports converting OfficeMath to MathMLCode.
doc = Document()
section=doc.AddSection()
officeMath = OfficeMath(doc)
officeMath.FromLatexMathCode("x^{2}+\\sqrt{{x^{2}+1}}+1")
officeMath.ToMathMLCode()
|
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10502 | Fixes the issue where adding and extracting formulas would throw an "Arg_InvalidCastException" exception. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10646 | Fixes the issue that the text was garbled when converting Word to TXT. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10860 | Fixes the issue where using FixedLayoutRow.Table would throw an "Arg_NullReferenceException" exception. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10886 | Fixes the issue that the return value of Document.IsContainMacro was incorrect. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10924 | Fixes the issue that "Cannot remove because there is no parent" exception occurred when converting HTML to Word. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-10996 | Fixes the issue that "System.ArgumentNullException" occurred when converting Word to HTML. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11014 | Fixes the issue where PreserveFormFields=True did not take effect. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11077 SPIREDOC-11101 | Fixes the issue that list numbering was incorrect when converting Word to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11166 | Fixes the issue that the "'Document' is not defined" error occurred when using Span.ParentNode. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11168 | Fixes the issue that formulas were blurry when converting Word to HTML. |
Spire.PDF for Android via Java 10.4.0 adds a new feature
We are delighted to announce the release of Spire.PDF for Android via Java 10.4.0. This version supports setting 'PreserveAllowedMetadata=true' when using PdfStandardsConverter. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREPDF-6921 | Supports setting 'PreserveAllowedMetadata=true' when using PdfStandardsConverter.
PdfStandardsConverter converter = new PdfStandardsConverter(stream); converter.Options.PreserveAllowedMetadata = true; |
Spire.XLS 15.4.4 adds support for several formulas
We're pleased to announce the release of Spire.XLS 15.4.4. This version adds support for several new formulas, and also supports auto-fitting row height in merged cells spanning multiple columns in a single row. Besides, some issues that occurred when converting Excel to PDF and saving files have been successfully fixed. More details are shown below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5697 | Supports auto-fitting row height in merged cells spanning multiple columns in a single row.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook(); workbook.LoadFromFile(@"in.xlsx"); Worksheet sheet= workbook.Worksheets[0]; AutoFitterOptions options = new AutoFitterOptions(); options.AutoFitMergedCells = true; //the first parameter is the merged row sheet.AutoFitRow(9, 1, sheet.LastColumn, options); workbook.SaveToFile(@"out.xlsx", Spire.Xls.FileFormat.Version2016); workbook.Dispose(); |
| New feature | SPIREXLS-5746 SPIREXLS-5768 SPIREXLS-5769 SPIREXLS-5774 |
Supports the GAMMALN.PRECISE, LOGNORM.INV, LOGNORM.DIST, and GAUSS formulas.
sheet.Range["C2"].Formula = "=GAUSS(A1)"; sheet.Range["C3"].Formula = "=LOGNORM.DIST(A2, A3, A4, A5)"; sheet.Range["C4"].Formula = "=GAMMALN.PRECISE(1.5)"; sheet.Range["C5"].Formula = "=LOGNORM.INV(0.5, 0, 1)"; |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5555 | Fixes the issue where data was incomplete when converting Excel to PDF with the SheetFitToPage=true property. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5724 | Fixes the inconsistency issue when converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5725 | Fixes the issue where the text was displayed incorrectly when converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5767 | Fixes the issue that the XML data for ColumnWidth did not comply with OpenXML standards. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5775 | Fixes the issue that it was where failed to update the associated sheets when modifying the row count in a sheet. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5777 | Fixes the issue where shapes were incorrect in the saved Excel file. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5778 | Fixed the issue that the IFERROR formula returned incorrect values. |
Spire.Office for Java 10.4.0 is released
We are excited to announce the release of Spire.Office for Java 10.4.0. In this version, Spire.Doc for Java enhances the conversions from Word to HTML/PDF; Spire.XLS for Java supports creating a slicer using table data; Spire.Presentation for Java enhances the conversion from PowerPoint to images; Spire.PDF for Java supports signing with "digitalsignatures.PdfCertificate" using byte[] certificate data. Besides, a lot of known issues are fixed successfully in this version. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
Spire.Doc for Java
| New feature | SPIREDOC-11117 | Optimizes the time-consuming issue of Word to PDF conversion.
|
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11123 | Fixes the issue that the program threw the "AssertionError" exception when converting Word documents to HTML. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11139 | Fixes the issue that the program threw an exception when retrieving content of the saved documents. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11144 | Fixes the issue that the program threw the "NullPointerException" exception when converting Word documents to HTML. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11153 | Fixes the issue that the result was incorrect when obtaining OLE NativeDataBytes. |
| Bug | SPIREDOC-11162 | Fixes the issue that the layout was incorrect when converting Word to PDF. |
Spire.XLS for Java
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | - | Supports creating a slicer using table data.
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet of workbook
Worksheet worksheet = wb.getWorksheets().get(0);
worksheet.getRange().get("A1").setValue("fruit");
worksheet.getRange().get("A2").setValue("grape");
worksheet.getRange().get("A3").setValue("blueberry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A4").setValue("kiwi");
worksheet.getRange().get("A5").setValue("cherry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A6").setValue("grape");
worksheet.getRange().get("A7").setValue("blueberry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A8").setValue("kiwi");
worksheet.getRange().get("A9").setValue("cherry");
worksheet.getRange().get("B1").setValue("year");
worksheet.getRange().get("B2").setValue2(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B3").setValue2(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B4").setValue2(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B5").setValue2(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B6").setValue2(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B7").setValue2(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B8").setValue2(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B9").setValue2(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("C1").setValue("amount");
worksheet.getRange().get("C2").setValue2(50);
worksheet.getRange().get("C3").setValue2(60);
worksheet.getRange().get("C4").setValue2(70);
worksheet.getRange().get("C5").setValue2(80);
worksheet.getRange().get("C6").setValue2(90);
worksheet.getRange().get("C7").setValue2(100);
worksheet.getRange().get("C8").setValue2(110);
worksheet.getRange().get("C9").setValue2(120);
//Get slicer collection
XlsSlicerCollection slicers = worksheet.getSlicers();
//Create a super table with the data from the specific cell range.
IListObject table = worksheet.getListObjects().create("Super Table", worksheet.getRange().get("A1:C9"));
int count = 3;
int index = 0;
for (Object styletype : SlicerStyleType.values())
{
SlicerStyleType type = (SlicerStyleType)styletype;
count += 5;
//Add a Slicer through pivot table data : here invoke Add(IListObject, string, int) api.
String range = "E" + count;
index = slicers.add(table, range.toString(), 0);
//Style setting
XlsSlicer xlsSlicer = slicers.get(index);
xlsSlicer.setName("slicers_" + count);
xlsSlicer.setStyleType(type);
}
//Save to file
wb.saveToFile(outputFile_xlsx, ExcelVersion.Version2013);
|
| New feature | - | Supports creating a slicer using pivot table data.
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet of workbook
Worksheet worksheet = wb.getWorksheets().get(0);
worksheet.getRange().get("A1").setValue("fruit");
worksheet.getRange().get("A2").setValue("grape");
worksheet.getRange().get("A3").setValue("blueberry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A4").setValue("kiwi");
worksheet.getRange().get("A5").setValue("cherry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A6").setValue("grape");
worksheet.getRange().get("A7").setValue("blueberry");
worksheet.getRange().get("A8").setValue("kiwi");
worksheet.getRange().get("A9").setValue("cherry");
worksheet.getRange().get("B1").setValue("year");
worksheet.getRange().get("B2").setValue2(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B3").setValue2(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B4").setValue2(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B5").setValue2(2020);
worksheet.getRange().get("B6").setValue2(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B7").setValue2(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B8").setValue2(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("B9").setValue2(2021);
worksheet.getRange().get("C1").setValue("amount");
worksheet.getRange().get("C2").setValue2(50);
worksheet.getRange().get("C3").setValue2(60);
worksheet.getRange().get("C4").setValue2(70);
worksheet.getRange().get("C5").setValue2(80);
worksheet.getRange().get("C6").setValue2(90);
worksheet.getRange().get("C7").setValue2(100);
worksheet.getRange().get("C8").setValue2(110);
worksheet.getRange().get("C9").setValue2(120);
// Get pivot table collection
PivotTablesCollection pivotTables = worksheet.getPivotTables();
//Add a PivotTable to the worksheet
CellRange dataRange = worksheet.getRange().get("A1:C9");
PivotCache cache = wb.getPivotCaches().add(dataRange);
//Cell to put the pivot table
PivotTable pt = worksheet.getPivotTables().add("TestPivotTable", worksheet.getRange().get("A12"), cache);
//Drag the fields to the row area.
IPivotField pf = pt.getPivotFields().get("fruit");
pf.setAxis(AxisTypes.Row);
IPivotField pf2 = pt.getPivotFields().get("year");
pf2.setAxis(AxisTypes.Column);
//Drag the field to the data area.
pt.getDataFields().add(pt.getPivotFields().get("amount"), "SUM of Count", SubtotalTypes.Sum);
//Set PivotTable style
pt.setBuiltInStyle(PivotBuiltInStyles.PivotStyleMedium10);
//Get slicer collection
XlsSlicerCollection slicers = worksheet.getSlicers();
//Add a Slicer through pivot table data: here invoke Add(IPivotTable, string, int) api.
int index = slicers.add(pt, "E12", 0);
XlsSlicer xlsSlicer = slicers.get(index);
xlsSlicer.setName("test_xlsSlicer");
xlsSlicer.setWidth(100);
xlsSlicer.setHeight(120);
xlsSlicer.setStyleType(SlicerStyleType.SlicerStyleLight2);
xlsSlicer.isPositionLocked(true);
//Get SlicerCache object of current slicer
XlsSlicerCache slicerCache = xlsSlicer.getSlicerCache();
slicerCache.setCrossFilterType(SlicerCacheCrossFilterType.ShowItemsWithNoData);
//Style setting
XlsSlicerCacheItemCollection slicerCacheItems = xlsSlicer.getSlicerCache().getSlicerCacheItems();
XlsSlicerCacheItem xlsSlicerCacheItem = slicerCacheItems.get(0);
xlsSlicerCacheItem.isSelected(false);
XlsSlicerCollection slicers_2 = worksheet.getSlicers();
IPivotField r1 = pt.getPivotFields().get("year");
int index_2 = slicers_2.add(pt, "I12", r1);
XlsSlicer xlsSlicer_2 = slicers.get(index_2);
xlsSlicer_2.setRowHeight(40);
xlsSlicer_2.setStyleType(SlicerStyleType.SlicerStyleLight3);
xlsSlicer_2.isPositionLocked(false);
//Get SlicerCache object of current slicer
XlsSlicerCache slicerCache_2 = xlsSlicer_2.getSlicerCache();
slicerCache_2.setCrossFilterType(SlicerCacheCrossFilterType.ShowItemsWithDataAtTop);
//Style setting
XlsSlicerCacheItemCollection slicerCacheItems_2 = xlsSlicer_2.getSlicerCache().getSlicerCacheItems();
XlsSlicerCacheItem xlsSlicerCacheItem_2 = slicerCacheItems_2.get(1);
xlsSlicerCacheItem_2.isSelected(false);
pt.calculateData();
//Save to file
wb.saveToFile("out.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
|
| New feature | - | Supports retrieving slicer information.
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.loadFromFile(inputFile);
// Get slicer collection of first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = wb.getWorksheets().get(0);
XlsSlicerCollection slicers = worksheet.getSlicers();
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("slicers.Count:" + slicers.getCount()+"\r\n");
XlsSlicer xlsSlicer = slicers.get(1);
builder.append("xlsSlicer.Name:" + xlsSlicer.getName()+"\r\n");
builder.append("xlsSlicer.Caption:" + xlsSlicer.getCaption()+"\r\n");
builder.append("xlsSlicer.NumberOfColumns:" + xlsSlicer.getNumberOfColumns()+"\r\n");
builder.append("xlsSlicer.ColumnWidth:" + xlsSlicer.getColumnWidth()+"\r\n");
builder.append("xlsSlicer.RowHeight:" + xlsSlicer.getRowHeight()+"\r\n");
builder.append("xlsSlicer.ShowCaption:" + xlsSlicer.isShowCaption()+"\r\n");
builder.append("xlsSlicer.PositionLocked:" + xlsSlicer.isPositionLocked()+"\r\n");
builder.append("xlsSlicer.Width:" + xlsSlicer.getWidth()+"\r\n");
builder.append("xlsSlicer.Height:" + xlsSlicer.getHeight()+"\r\n");
//Get SlicerCache object of current slicer
XlsSlicerCache slicerCache = xlsSlicer.getSlicerCache();
builder.append("slicerCache.SourceName:" + slicerCache.getSourceName()+"\r\n");
builder.append("slicerCache.IsTabular:" + slicerCache.isTabular()+"\r\n");
builder.append("slicerCache.Name:" + slicerCache.getName()+"\r\n");
XlsSlicerCacheItemCollection slicerCacheItems = slicerCache.getSlicerCacheItems();
XlsSlicerCacheItem xlsSlicerCacheItem = slicerCacheItems.get(1);
builder.append("xlsSlicerCacheItem.Selected:" + xlsSlicerCacheItem.isSelected() +"\r\n");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(outputFile_T);
fw.write(builder.toString());
fw.flush();
fw.close();
wb.dispose();
|
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5569 | Fixes the issue that OLE objects failed to open correctly after converting Excel to XLSB format. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5673 | Fixes the issue that alignment was incorrect when converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5752 | Optimizes the text rendering effect of grouped shapes when converting Excel to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREXLS-5757 | Fixes the issue that some formula values were calculated incorrectly when converting Excel to images. |
Spire.Presentation for Java
| New feature | SPIREPPT-2668 | Fixes the issue where the content was incorrect when converting PowerPoint to images.
|
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2669 | Fixes the issue where the text shadow effect was lost when converting PowerPoint to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2672 | Fixes the issue where the text layout was incorrect when converting PowerPoint to images. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2693 | Fixes the issue where the layout was incorrect when opening merged PowerPoint documents in WPS. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2731 | Fixes the issue where the charts were incorrect when converting PowerPoint to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2732 | Fixes the issue where the program hung when running the packaged .jar file after setting setCustomFontsFolder while converting a PowerPoint to HTML. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2779 | Fixes the issue where the content auto-fit effect was incorrect in merged PowerPoint documents. |
Spire.PDF for Java
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREPDF-7460 | Supports using the byte[] certificate data when signing with "digitalsignatures. PdfCertificate".
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
pdf.loadFromFile(inputFile);
FileInputStream instream = new FileInputStream(inputFile_pfx);
byte[] data = FileUtil.getStreamBytes(instream);
PdfCertificate x509 = new PdfCertificate(data, "e-iceblue");
PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker signatureMaker = new PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker(pdf, x509);
signatureMaker.makeSignature("signName");
pdf.saveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PDF);
pdf.dispose();
|
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7457 | Fixes the problem that the program threw “NullPointerException” when setting isFlatten(true). |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7458 | Fixes the issue that some contents were incorrect after converting PDF to PDF/A. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7463 | Fixes the issue that the format and font were incorrect after converting PDF to PowerPoint. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7462 | Fixes the issue that the data extracted from tables was incorrect. |
Spire.PDF for Java 11.4.2 supports signing with "digitalsignatures.PdfCertificate" using byte[] certificate data
We are excited to announce the release of Spire.PDF for Java 11.4.2. This version supports using the byte[] certificate data when signing with "digitalsignatures. PdfCertificate". It also enhances the conversion from PDF to PDF/A and PowerPoint. Moreover, some known issues are fixed successfully in this version, such as the issue that the data extracted from tables was incorrect. More details are listed below.
Here is a list of changes made in this release
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREPDF-7460 | Supports using the byte[] certificate data when signing with "digitalsignatures. PdfCertificate".
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
pdf.loadFromFile(inputFile);
FileInputStream instream = new FileInputStream(inputFile_pfx);
byte[] data = FileUtil.getStreamBytes(instream);
PdfCertificate x509 = new PdfCertificate(data, "e-iceblue");
PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker signatureMaker = new PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker(pdf, x509);
signatureMaker.makeSignature("signName");
pdf.saveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PDF);
pdf.dispose();
|
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7457 | Fixes the problem that the program threw “NullPointerException” when setting isFlatten(true). |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7458 | Fixes the issue that some contents were incorrect after converting PDF to PDF/A. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7463 | Fixes the issue that the format and font were incorrect after converting PDF to PowerPoint. |
| Bug | SPIREPDF-7462 | Fixes the issue that the data extracted from tables was incorrect. |
Spire.Presentation 10.4.6 supports inserting formulas in table cells
We're glad to announce the release of Spire.Presentation 10.4.6. This version supports inserting formulas in table cells and reading CustomerData of Shape. In addition, some issues that occurred when converting PPTX to PDF/SVG and opening PowerPoint files have been successfully fixed. Check below for more details.
Here is a list of all changes made in this release.
| Category | ID | Description |
| New feature | SPIREPPT-2772 | Supports reading CustomerData of Shape.
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
ppt.LoadFromFile(inputFile);
List dataList = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes[1].CustomerDataList;
Console.WriteLine(dataList.Count);
for(int i = 0; i < dataList.Count; i++)
{
string name = dataList[i].Name;
string content = dataList[i].XML;
File.WriteAllText(outputFile + name, content);
}
|
| New feature | SPIREPPT-2782 | Supports inserting formulas in table cells.
//Create a PPT document
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
Double[] widths = new double[] { 100, 100, 150, 100, 100 };
Double[] heights = new double[] { 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15 };
//Add new table to PPT
ITable table = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendTable(presentation.SlideSize.Size.Width / 2 - 275, 90, widths, heights);
String[,] dataStr = new String[,]{
{"Name", "Capital", "Continent", "Area", "Population"},
{"Venezuela", "Caracas", "South America", "912047", "19700000"},
{"Bolivia", "La Paz", "South America", "1098575", "7300000"},
{"Brazil", "Brasilia", "South America", "8511196", "150400000"},
{"Canada", "Ottawa", "North America", "9976147", "26500000"},
{"Chile", "Santiago", "South America", "756943", "13200000"},
{"Colombia", "Bagota", "South America", "1138907", "33000000"},
{"Cuba", "Havana", "North America", "114524", "10600000"},
{"Ecuador", "Quito", "South America", "455502", "10600000"},
{"Paraguay", "Asuncion","South America", "406576", "4660000"},
{"Peru", "Lima", "South America", "1285215", "21600000"},
{"Jamaica", "Kingston", "North America", "11424", "2500000"},
{"Mexico", "Mexico City", "North America", "1967180", "88600000"}
};
//Add data to table
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
//Fill the table with data
table[j, i].TextFrame.Text = dataStr[i, j];
//Set the Font
table[j, i].TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].LatinFont = new TextFont("Arial Narrow");
}
//Set the alignment of the first row to Center
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
table[i, 0].TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Center;
}
string latexMathCode = @"x^{2}+\sqrt{x^{2}+1}=2";
table[2, 3].TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexMathCode);
//Set the style of table
table.StylePreset = TableStylePreset.LightStyle3Accent1;
//Save the document
presentation.SaveToFile("Output.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
|
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2421 | Fixes the issue where the text was garbled when converting PowerPoint to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2691 | Fixes the issue that the application threw a "System.NullReferenceException" error when adding a GroupShape to a new PowerPoint file. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2798 | Fixes the issue where the text was lost when converting PowerPoint to PDF. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2804 | Fixes the issue where opening a file saved using the Presentation.GetStream() method would cause an error. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2824 | Fixes the issue where the position of shapes changed after using the Ungroup() method. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2840 | Fixes the issue that the application threw a "NullReferenceException" error when converting PowerPoint to SVG. |
| Bug | SPIREPPT-2851 | Fixes the issue where the shapes were incorrect when converting PowerPoint to SVG. |