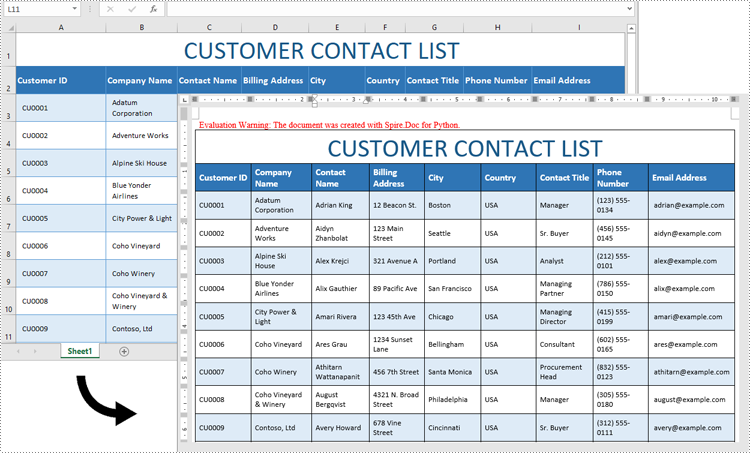
Python: Convert Excel Data to Word Table with Formatting
Excel is ideal for data calculations, analysis, and organization, while Word shines at creating polished, well-formatted documents and reports. Transferring data from Excel to Word is often necessary for professionals preparing reports or presentations, as it allows for advanced formatting options that enhance readability and create a more professional look. In this guide, you will learn how to convert data in an Excel sheet to a Word table with formatting in Python using Spire.Office for Python.
Install Spire.Office for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Office for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Office
Convert Excel Data to Word Table with Formatting in Python
This process uses two libraries in the Spire.Office for Python package. They’re Spire.XLS for Python and Spire.Doc for Python. The former is used to read data and formatting from an Excel worksheet, and the latter is used to create a Word document and write data, including formatting, into a table. To make this code example easy to understand, we have defined the following two custom methods that handle specific tasks:
- MergeCells() - Merge the corresponding cells in the Word table based on the merged cells in the Excel sheet.
- CopyStyle() - Copy various cell styles from the Excel worksheet to the Word table, including font style, background color, and text alignment.
The following steps demonstrate how to convert data from an Excel sheet to a Word table with formatting using Spire.Office for Python.
- Create an object of the Workbook class and load a sample Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Create a new Word document using the Document class, and add a section to it.
- Add a table to the Word document using the Section.AddTable() method.
- Detect the merged cells in the worksheet and merge the corresponding cells in the Word tale using the custom method MergeCells().
- Iterate through the cells in the worksheet, read the data of the cells through the CellRange.Value property and add the data to Word table cells using the TableCell.AddParagraph().AppendText() method.
- Copy the cell styles from the Excel worksheet to the Word table using the custom method CopyStyle().
- Save the Word document to a file using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.doc import *
def MergeCells(sheet, table):
"""Merge cells in the Word table based on merged cells in the Excel sheet."""
if sheet.HasMergedCells:
ranges = sheet.MergedCells
for i in range(len(ranges)):
startRow = ranges[i].Row
startColumn = ranges[i].Column
rowCount = ranges[i].RowCount
columnCount = ranges[i].ColumnCount
if rowCount > 1 and columnCount > 1:
for j in range(startRow, startRow + rowCount):
table.ApplyHorizontalMerge(j - 1, startColumn - 1, startColumn - 1 + columnCount - 1)
table.ApplyVerticalMerge(startColumn - 1, startRow - 1, startRow - 1 + rowCount - 1)
if rowCount > 1 and columnCount == 1:
table.ApplyVerticalMerge(startColumn - 1, startRow - 1, startRow - 1 + rowCount - 1)
if columnCount > 1 and rowCount == 1:
table.ApplyHorizontalMerge(startRow - 1, startColumn - 1, startColumn - 1 + columnCount - 1)
def CopyStyle(wTextRange, xCell, wCell):
"""Copy cell styling from Excel to Word."""
# Copy font style
wTextRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.FromRgb(xCell.Style.Font.Color.R, xCell.Style.Font.Color.G, xCell.Style.Font.Color.B)
wTextRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = float(xCell.Style.Font.Size)
wTextRange.CharacterFormat.FontName = xCell.Style.Font.FontName
wTextRange.CharacterFormat.Bold = xCell.Style.Font.IsBold
wTextRange.CharacterFormat.Italic = xCell.Style.Font.IsItalic
# Copy background color
if xCell.Style.FillPattern is not ExcelPatternType.none:
wCell.CellFormat.Shading.BackgroundPatternColor=Color.FromRgb(xCell.Style.Color.R, xCell.Style.Color.G, xCell.Style.Color.B)
# Copy horizontal alignment
if xCell.HorizontalAlignment == HorizontalAlignType.Left:
wTextRange.OwnerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
elif xCell.HorizontalAlignment == HorizontalAlignType.Center:
wTextRange.OwnerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
elif xCell.HorizontalAlignment == HorizontalAlignType.Right:
wTextRange.OwnerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Right
# Copy vertical alignment
if xCell.VerticalAlignment == VerticalAlignType.Bottom:
wCell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Bottom
elif xCell.VerticalAlignment == VerticalAlignType.Center:
wCell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
elif xCell.VerticalAlignment == VerticalAlignType.Top:
wCell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Top
# Load an Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Contact list.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create a Word document
doc = Document()
section = doc.AddSection()
section.PageSetup.Orientation = PageOrientation.Landscape
# Add a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
table.ResetCells(sheet.LastRow, sheet.LastColumn)
# Merge cells
MergeCells(sheet, table)
# Export data and styles from Excel to Word table
for r in range(1, sheet.LastRow + 1):
table.Rows[r - 1].Height = float(sheet.Rows[r - 1].RowHeight)
for c in range(1, sheet.LastColumn + 1):
xCell = sheet.Range[r, c]
wCell = table.Rows[r - 1].Cells[c - 1]
# Add text from Excel to Word table cell
textRange = wCell.AddParagraph().AppendText(xCell.NumberText)
# Copy font and cell style
CopyStyle(textRange, xCell, wCell)
# Save the document to a Word file
doc.SaveToFile("ConvertExcelDataToWordTable.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Find and Highlight Data in Excel Worksheets
Efficiently emphasizing critical data within Excel workbooks is essential for swift analysis. This process not only draws immediate attention to the most relevant information but also aids in identifying trends, anomalies, and key metrics. By using Python to handle Excel workbooks, users can automate the search and highlight functions, enhancing productivity and ensuring precision. This article explores how to leverage Python for finding and highlighting data in Excel worksheets using Spire.XLS for Python library.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Find and Highlight Data in Excel Worksheets
Using Spire.XLS for Python, we can find all cells containing a specific string and return them as a list by using the Worksheet.FindAllString(stringValue: str, formula: bool, formulaValue: bool) method. After that, we can iterate through the found cells and apply a highlight color by setting it via the CellRange.Style.Color property.
The detailed steps for finding and highlighting data in an Excel worksheet are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class and load an Excel workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Find all the cells containing the string to be highlighted using Worksheet.FindAllString() method.
- Iterate through the results to highlight the cells by setting a fill color through CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Find the data to be highlighted
cellRanges = sheet.FindAllString("Urgent", False, True)
# Iterate through the found ranges
for cellRange in cellRanges:
# Highlight the data
cellRange.Style.Color = Color.get_LightYellow()
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/FindHighlightDataExcel.xlsx")
workbook.Dispose()
Find and Highlight Data in a Specific Cell Range
In addition to searching for data across the entire worksheet, we can use the CellRange.FindAllString(stringValue: str, formula: bool, formulaValue: bool) method to find and highlight data within a specified cell range. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Get a cell range through Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Find all the cells containing the string to be highlighted using CellRange.FindAllString() method.
- Iterate through the results to highlight the cells by setting a fill color through CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get the cell range
findRange = sheet.Range["C1:C11"]
# Find the data to be highlighted
cellRanges = findRange.FindAllString("Urgent", False, True)
# Iterate the found ranges
for cellRange in cellRanges:
# Highlight the data
cellRange.Style.Color = Color.get_LightYellow()
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/FindHighlightRange.xlsx")
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Extract or Update Textboxes in a Word Document
Textboxes in a Word document serve as versatile containers for text, enabling users to enhance layout and design. They allow for the separation of content from the main body, making documents more visually appealing and organized. Extracting or updating textboxes can be essential for improving document efficiency, ensuring information is current, and facilitating data analysis.
In this article, you will learn how to extract or update textboxes in a Word document using Python and Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
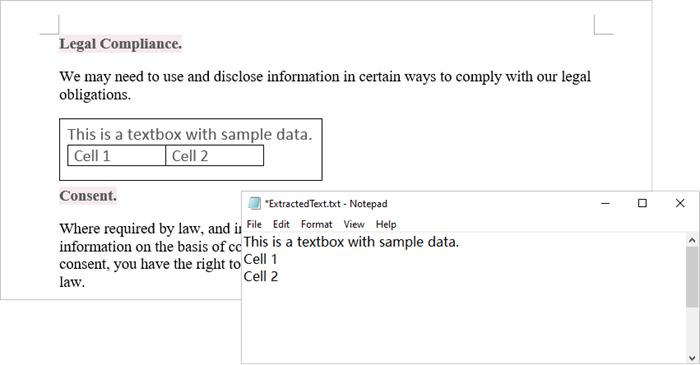
Extract Text from a Textbox in Word
Using Spire.Doc for Python, you can access a specific text box in a document by utilizing the Document.TextBoxes[index] property. After retrieving the text box, you can iterate through its child objects to identify whether each one is a paragraph or a table. If the object is a paragraph, you can retrieve its text using the Paragraph.Text property. In cases where the object is a table, you will need to loop through each cell to extract text from every individual cell within that table.
The steps to extract text from a text box in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- load a Word file by using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access a specific text box using Document.TextBoxes[index] property.
- Iterate through the child objects within the text box.
- Determine if a child object is a paragraph. If it is, retrieve the text from the paragraph using Paragraph.Text property.
- Check if a child object is a table. If so, iterate through the cells in the table to extract text from each cell.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get a specific textbox
textBox = document.TextBoxes.get_Item(0)
with open('ExtractedText.txt','w') as sw:
# Iterate through the child objects in the textbox
for i in range(textBox.ChildObjects.Count):
# Get a specific child object
object = textBox.ChildObjects.get_Item(i)
# Determine if the child object is paragraph
if object.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph:
# Write paragraph text to txt file
sw.write((object if isinstance(object, Paragraph) else None).Text + "\n")
# Determine if the child object is table
if object.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Table:
table = object if isinstance(object, Table) else None
for i in range(table.Rows.Count):
row = table.Rows[i]
for j in range(row.Cells.Count):
cell = row.Cells[j]
for k in range(cell.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = cell.Paragraphs.get_Item(k)
# Write paragrah text of a specific cell to txt file
sw.write(paragraph.Text + "\n")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
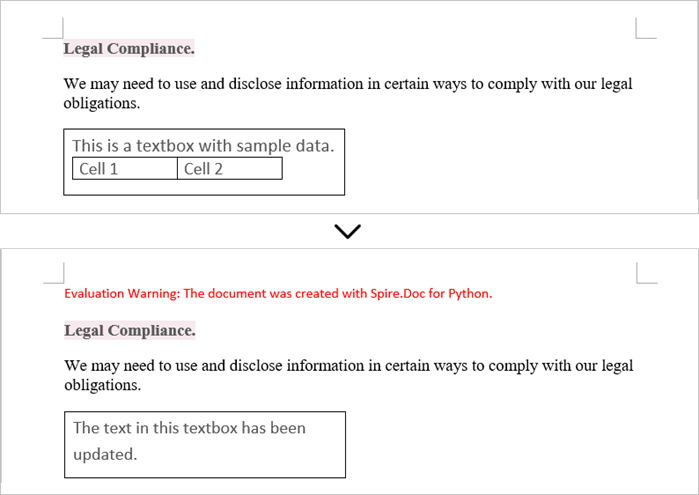
Update Text in a Textbox in Word
To update a textbox in a Word document, start by clearing its existing content with the TextBox.ChildObjects.Clear() method. This action removes all child objects, including any paragraphs or tables currently contained within the textbox. After clearing the content, you can add a new paragraph to the text box. Once the paragraph is created, set its text to the desired value.
The steps to update a textbox in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific textbox using Document.TextBoxes[index] property
- Remove existing content of the textbox using TextBox.ChildObjects.Clear() method.
- Add a paragraph to the textbox using TextBox.Body.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Get a specific textbox
textBox = document.TextBoxes.get_Item(0)
# Remove child objects of the textbox
textBox.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Add a new paragraph to the textbox
paragraph = textBox.Body.AddParagraph()
# Set line spacing
paragraph.Format.LineSpacing = 15.0
# Add text to the paragraph
textRange = paragraph.AppendText("The text in this textbox has been updated.")
# Set font size
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 15.0
# Save the document to a different Word file
document.SaveToFile("UpdateTextbox.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019);
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Crop Pages in PDF
When dealing with PDF files, you might sometimes need to crop pages in the PDF to remove unnecessary margins, borders, or unwanted content. By doing so, you can make the document conform to specific design requirements or page sizes, ensuring a more aesthetically pleasing or functionally optimized output. This article will introduce how to crop pages in PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python. It can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Crop a PDF Page in Python
Spire.PDF for Python allows you specify a rectangular area, and then use the PdfPageBase.CropBox property to crop page to the specified area. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Crop the page to the specified area using PdfPageBase.CropBox property.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample1.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Crop the page by the specified area
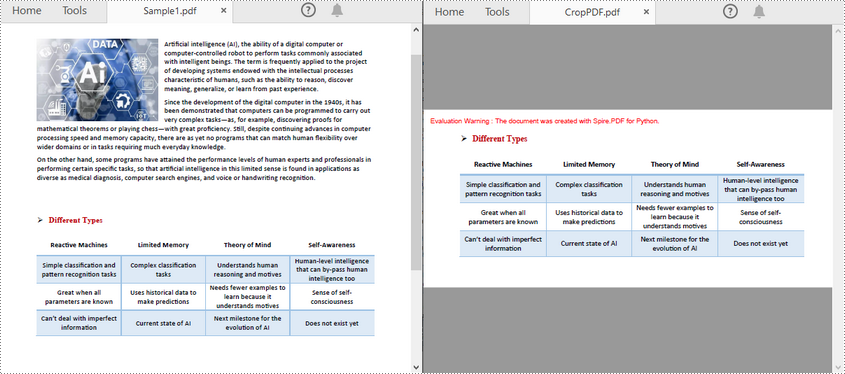
page.CropBox = RectangleF(0.0, 300.0, 600.0, 260.0)
# Save the result file
pdf.SaveToFile("CropPDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Crop a PDF Page and Export as an Image in Python
To accomplish this task, you can use the PdfDocument.SaveAsImage(pageIndex: int) method to convert a cropped PDF page to an image stream. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Crop the page to the specified area using PdfPageBase.CropBox property.
- Convert the cropped page to an image stream using PdfDocument.SaveAsImage() method.
- Save the image as a PNG, JPG or BMP file using Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample1.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Crop the page by the specified area
page.CropBox = RectangleF(0.0, 300.0, 600.0, 260.0)
# Convert the page to an image
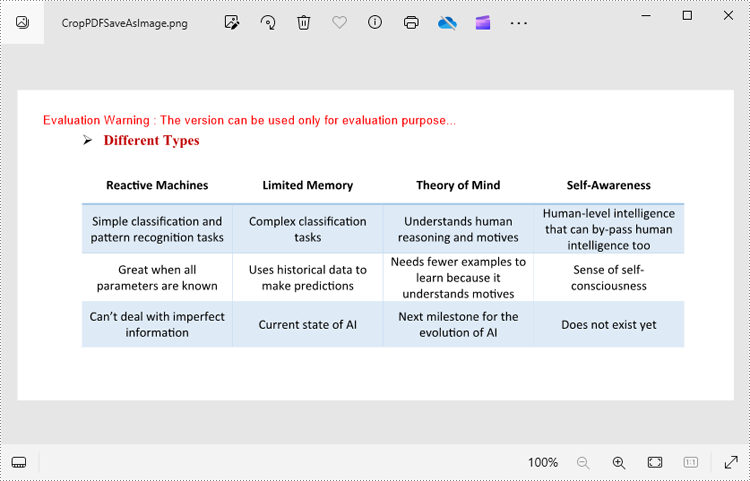
with pdf.SaveAsImage(0) as imageS:
# Save the image as a PNG file
imageS.Save("CropPDFSaveAsImage.png")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Set the Transparency of PDF Images
Setting the transparency of images in PDF documents is crucial for achieving professional-grade output, which allows for layering images without hard edges and creating a seamless integration with the background or underlying content. This not only enhances the visual appeal but also creates a polished and cohesive look, especially in graphics-intensive documents. This article will demonstrate how to effectively set the transparency of PDF images using Spire.PDF for Python in Python programs.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add Images with Specified Transparency to PDF
Developers can utilize the PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawImage() method in Spire.PDF for Python to draw an image at a specified location on a PDF page. Before drawing, developers can set the transparency of the canvas using PdfPageBase.Canvas.SetTransparency() method, which in turn sets the transparency level of the image being drawn. Below are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a page in the document using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Load an image using PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Set the transparency of the canvas using PdfPageBase.Canvas.SetTransparency() method.
- Draw the image on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawImage() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Load an image
image = PdfImage.FromFile("Screen.jpg")
# Set the transparency of the canvas
page.Canvas.SetTransparency(0.2)
# Draw the image at the specified location
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, PointF(80.0, 80.0))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/AddTranslucentPicture.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Adjust the Transparency of Existing Images in PDF
To adjust the transparency of an existing image on a PDF page, developers can retrieve the image along with its bounds, delete the image, and finally redraw the image in the same location with the specified transparency. This process allows for the adjustment of the image's opacity while maintaining its original placement. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a page in the document using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Get an image on the page as a stream through PdfPageBase.ImagesInfo[].Image property and get the bounds of the image through PdfPageBase.ImagesInfo[].Bounds property.
- Remove the image from the page using PdfPageBase.DeleteImage() method.
- Create a PdfImage instance with the stream using PdfImage.FromStream() method.
- Set the transparency of the canvas using PdfPageBase.Canvas.SetTransparency() method.
- Redraw the image in the same location with the specified transparency using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawImage() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample1.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get the first image on the page as a stream and the bounds of the image
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
imageInformation = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)
bounds = imageInformation[0].Bounds
imageStream =imageInformation[0].Image
# Delete the original image
imageHelper.DeleteImage(imageInformation[0])
# Create a PdfImage instance using the image stream
image = PdfImage.FromStream(imageStream)
# Create a PdfImage instance using the image stream
image = PdfImage.FromStream(imageStream)
# Set the transparency of the canvas
page.Canvas.SetTransparency(0.3)
# Draw the new image at the same location using the canvas
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, bounds)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/SetExistingImageTransparency.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#: Set Page Setup Options in Excel
When printing Excel spreadsheets, particularly those containing complex datasets or detailed reports, configuring the page setup properly is crucial. Excel’s page setup options enable you to adjust key factors such as page margins, orientation, paper size, and scaling, ensuring your documents are tailored to fit various printing needs. By customizing these settings, you can control how your content is displayed on the page, making sure it appears polished and professional. In this article, we will demonstrate how to set page setup options in Excel in C# using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Set Page Margins in Excel in C#
- Set Page Orientation in Excel in C#
- Set Paper Size in Excel in C#
- Set Print Area in Excel in C#
- Set Scaling Factor in Excel in C#
- Set Fit-to-Pages Options in Excel in C#
- Set Headers and Footers in Excel in C#
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Set Page Margins in Excel in C#
The PageSetup class in Spire.XLS for .NET is used to configure page setup options for Excel worksheets. You can access the PageSetup object of a worksheet through the Worksheet.PageSetup property. Then, use properties like PageSetup.TopMargin, PageSetup.BottomMargin, PageSetup.LeftMargin, PageSetup.RightMargin, PageSetup.HeaderMarginInch, and PageSetup.FooterMarginInch to set the corresponding margins for the worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the top, bottom, left, right, header, and footer margins using PageSetup.TopMargin, PageSetup.BottomMargin, PageSetup.LeftMargin, PageSetup.RightMargin, PageSetup.HeaderMarginInch, and PageSetup.FooterMarginInch properties.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetPageMargins
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup;
// Set top, bottom, left, and right page margins for the worksheet
// The measure of the unit is Inch (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
pageSetup.TopMargin = 1;
pageSetup.BottomMargin = 1;
pageSetup.LeftMargin = 1;
pageSetup.RightMargin = 1;
pageSetup.HeaderMarginInch = 1;
pageSetup.FooterMarginInch = 1;
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPageMargins.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Set Page Orientation in Excel in C#
The PageSetup.Orientation property lets you determine how the page should be oriented when printed. You can choose between two options: portrait mode or landscape mode. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the page orientation using PageSetup.Orientation property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetPageOrientation
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup;
// Set the page orientation for printing the worksheet to landscape mode
pageSetup.Orientation = PageOrientationType.Landscape;
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPageOrientation.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
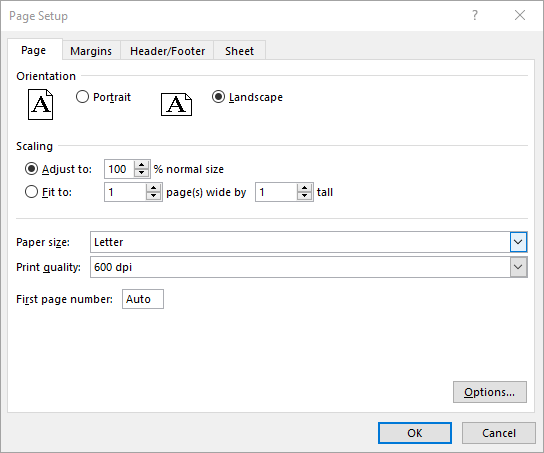
Set Paper Size in Excel in C#
The PageSetup.PaperSize property enables you to select from a variety of paper sizes for printing your worksheet. These options include A3, A4, A5, B4, B5, letter, legal, tabloid, and more. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the paper size using PageSetup.PaperSize property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetPaperSize
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup;
// Set the paper size to A4
pageSetup.PaperSize = PaperSizeType.PaperA4;
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPaperSize.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
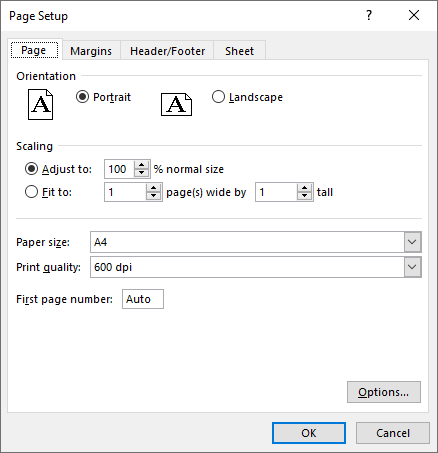
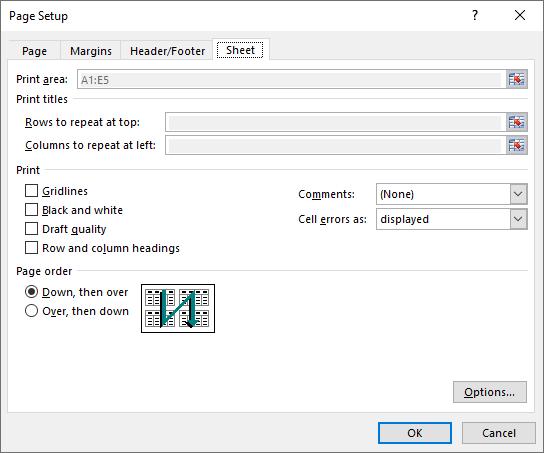
Set Print Area in Excel in C#
You can specify the exact area that you want to print using the PageSetup.PringArea property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the print area using PageSetup.PringArea property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetPrintArea
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup;
// Set the print area of the worksheet to "A1:E5"
pageSetup.PrintArea = "A1:E5";
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPrintArea.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
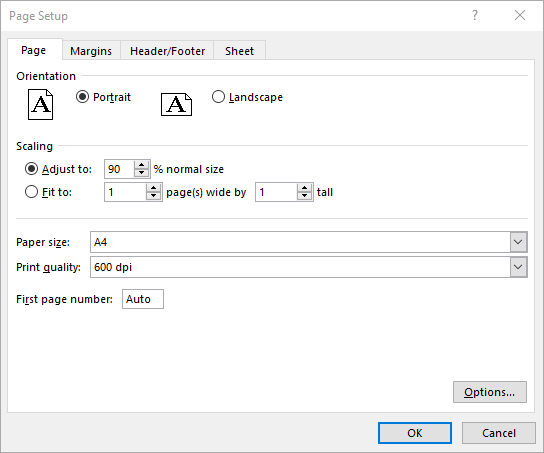
Set Scaling Factor in Excel in C#
If you want to scale the content of your worksheet to a specific percentage of its original size, use the PageSetup.Zoom property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the scaling factor using PageSetup.Zoom property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetScalingFactor
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup;
// Set the scaling factor of the worksheet to 90%
pageSetup.Zoom = 90;
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetScalingFactor.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Set Fit-to-Pages Options in Excel in C#
Spire.XLS also enables you to fit your worksheet content to a specific number of pages by using the PageSetup.FitToPagesTall and PageSetup.FitToPagesWide properties. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Fit the content of the worksheet to one page using PageSetup.FitToPagesTall and PageSetup.FitToPagesWide properties.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetFitToPages
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup;
// Fit the content of the worksheet within one page vertically (i.e., all rows will fit on a single page)
pageSetup.FitToPagesTall = 1;
// Fit the content of the worksheet within one page horizontally (i.e., all columns will fit on a single page)
pageSetup.FitToPagesWide = 1;
// Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("FitToPages.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
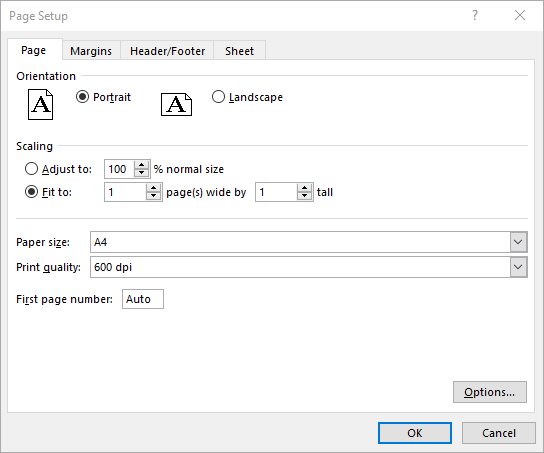
Set Headers and Footers in Excel in C#
For setting headers and footers in Excel, please check this article: C#/VB.NET: Add Headers and Footers to Excel.
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add Page Numbers to a PDF Document
Adding page numbers to a PDF enhances its organization and readability, making it easier for readers to navigate the document. Whether for reports, manuals, or e-books, page numbers provide a professional touch and help maintain the flow of information. This process involves determining the placement, alignment, and style of the numbers within the footer or header.
In this article, you will learn how to add page numbers to the PDF footer using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add Left-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
- Add Center-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
- Add Right-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Coordinate System in PDF
When using Spire.PDF for Python to modify a PDF document, the coordinate system's origin is at the top-left corner of the page. The x-axis extends to the right, while the y-axis extends downward.
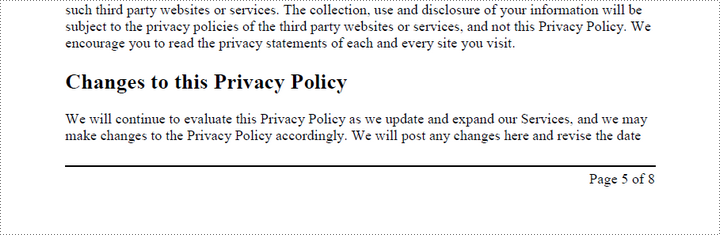
Page numbers are usually positioned in the header or footer. Thus, it's important to consider the page size and margins when determining the placement of the page numbers.
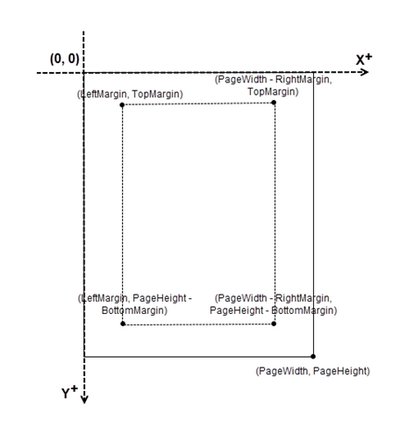
Classes and Methods for Creating Page Numbers
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfPageNumberField and PdfPageCountField classes to retrieve the current page number and total page count. These can be merged into a single PdfCompositeField that formats the output as "Page X of Y", where X represents the current page number and Y indicates the total number of pages.
To position the PdfCompositeField on the page, use the Location property, and render it with the Draw() method.
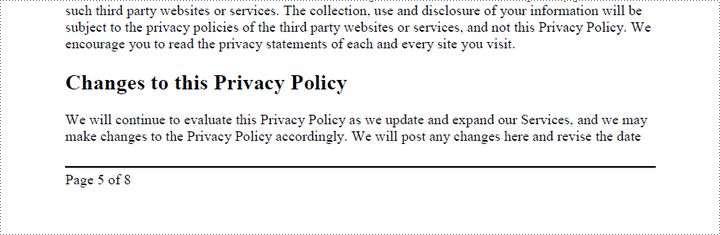
Add Left-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
To add left-aligned page numbers in the footer, you need to consider the left and bottom page margins as well as the page height. For example, you can use coordinates such as (LeftMargin, PageHeight – BottomMargin + SmallNumber). This ensures that the page numbers align with the left side of the text while keeping a comfortable distance from both the content and the edges of the page.
The steps to add left-aligned page numbers to PDF footer are as follows:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file from a specified path.
- Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object.
- Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string.
- Set the position of the composite field through PdfCompositeField.Location property to ensure the page number aligns with the left side of the text.
- Iterate through the pages in the document, and draw the composite field on each page at the specified location.
- Save the document to a different PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Privacy Policy.pdf")
# Create font, brush and pen
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
pen = PdfPen(brush, 1.0)
# Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object
pageNumberField = PdfPageNumberField()
pageCountField = PdfPageCountField()
# Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string
compositeField = PdfCompositeField(font, brush, "Page {0} of {1}", [pageNumberField, pageCountField])
# Get the page size
pageSize = doc.Pages.get_Item(0).Size
# Specify the blank areas around the page
leftMargin = 54.0
rightMargin = 54.0
bottomMargin = 72.0
# Set the location of the composite field
compositeField.Location = PointF(leftMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 18.0)
# Iterate through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Draw a line at the specified position
page.Canvas.DrawLine(pen, leftMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0, pageSize.Width - rightMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0)
# Draw the composite field on the page
compositeField.Draw(page.Canvas, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save to a different PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("Output/LeftAlignedPageNumbers.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Add Center-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
To position the page number in the center of the footer, you first need to measure the width of the page number itself. Once you have this measurement, you can calculate the appropriate X coordinate by using the formula (PageWidth - PageNumberWidth) / 2. This ensures the page number is horizontally centered within the footer.
The steps to add center-aligned page numbers to PDF footer are as follows:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file from a specified path.
- Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object.
- Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string.
- Set the position of the composite field through PdfCompositeField.Location property to ensure the page number is perfectly centered in the footer.
- Iterate through the pages in the document, and draw the composite field on each page at the specified location.
- Save the document to a different PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Privacy Policy.pdf")
# Create font, brush and pen
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
pen = PdfPen(brush, 1.0)
# Specify the blank margins around the page
leftMargin = 54.0
rightMargin = 54.0
bottomMargin = 72.0
# Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object
pageNumberField = PdfPageNumberField()
pageCountField = PdfPageCountField()
# Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single field
compositeField = PdfCompositeField(font, brush, "Page {0} of {1}", [pageNumberField, pageCountField])
# Iterate through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Get the page size
pageSize = doc.Pages.get_Item(i).Size
# Draw a line at the specified position
page.Canvas.DrawLine(pen, leftMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0, pageSize.Width - rightMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0)
# Measure the size the "Page X of Y"
pageNumberSize = font.MeasureString("Page {} of {}".format(i + 1, doc.Pages.Count))
# Set the location of the composite field
compositeField.Location = PointF((pageSize.Width - pageNumberSize.Width)/2, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 18.0)
# Draw the composite field on the page
compositeField.Draw(page.Canvas, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save to a different PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("Output/CenterAlignedPageNumbers.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Add Right-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
To add a right-aligned page number in the footer, measure the width of the page number. Then, calculate the X coordinate using the formula PageWidth - PageNumberWidth - RightMargin. This ensures that the page number aligns with the right side of the text.
The following are the steps to add right-aligned page numbers to PDF footer:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file from a specified path.
- Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object.
- Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string.
- Set the position of the composite field through PdfCompositeField.Location property to ensure the page number aligns with the right side of the text.
- Iterate through the pages in the document, and draw the composite field on each page at the specified location.
- Save the document to a different PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Privacy Policy.pdf")
# Create font, brush and pen
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
pen = PdfPen(brush, 1.0)
# Specify the blank margins around the page
leftMargin = 54.0
rightMargin = 54.0
bottomMargin = 72.0
# Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object
pageNumberField = PdfPageNumberField()
pageCountField = PdfPageCountField()
# Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string
compositeField = PdfCompositeField(font, brush, "Page {0} of {1}", [pageNumberField, pageCountField])
# Iterate through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Get the page size
pageSize = doc.Pages.get_Item(i).Size
# Draw a line at the specified position
page.Canvas.DrawLine(pen, leftMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0, pageSize.Width - rightMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0)
# Measure the size the "Page X of Y"
pageNumberSize = font.MeasureString("Page {} of {}".format(i + 1, doc.Pages.Count))
# Set the location of the composite field
compositeField.Location = PointF(pageSize.Width - pageNumberSize.Width - rightMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 18.0)
# Draw the composite field on the page
compositeField.Draw(page.Canvas, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save to a different PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("Output/RightAlignedPageNumbers.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Edit or Modify a Word Document
Programmatic editing of Word documents involves using code to alter or modify the contents of these documents. This approach enables automation and customization, making it particularly advantageous for handling large document collections. Through the use of Spire.Doc library, developers can perform a wide range of operations, including text manipulation, formatting changes, and the addition of images or tables.
The following sections will demonstrate how to edit or modify a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Modify Text in a Word Document
- Change Formatting of Text in a Word Document
- Add New Elements to a Word Document
- Remove Paragraphs from a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Modify Text in a Word Document in Python
In order to alter the content of a paragraph, the initial step is to obtain the desired paragraph from a specific section through the use of the Section.Paragraphs[index] property. Following this, you can replace the existing text with the new content by assigning it to the Paragraph.Text property of the chosen paragraph.
Here are the steps to edit text in a Word document with Python:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph using Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Reset the text of the paragraph using Paragraph.Text property.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load an existing Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections[0]
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs[0]
# Modify the text of the paragraph
paragraph.Text = "The text has been modified"
# Save the document to a different Word file
document.SaveToFile("output/ModifyText.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Dispose resource
document.Dispose()

Change Formatting of Text in a Word Document in Python
To alter the text appearance of a particular paragraph, you first need to obtain the specified paragraph. Next, go through its child objects to find the individual text ranges. The formatting of each text range can then be updated using the TextRange.CharacterFormat property.
The steps to change text formatting in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph using Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph.
- Determine if a child object is a text range.
- Get a specific text range.
- Reset the text formatting using TextRange.CharacterFormat property.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(0)
# Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for i in range(paragraph.ChildObjects.Count):
# Determine if a child object is text range
if isinstance(paragraph.ChildObjects[i], TextRange):
# Get a specific text range
textRange = paragraph.ChildObjects[i]
# Reset font name
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Corbel Light"
# Reset font size
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11.0
# Reset text color
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
# Apply italic to the text range
textRange.CharacterFormat.Italic = True
# Save the document to a different Word file
doc.SaveToFile("output/ChangeFormatting.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
# Dispose resource
doc.Dispose()
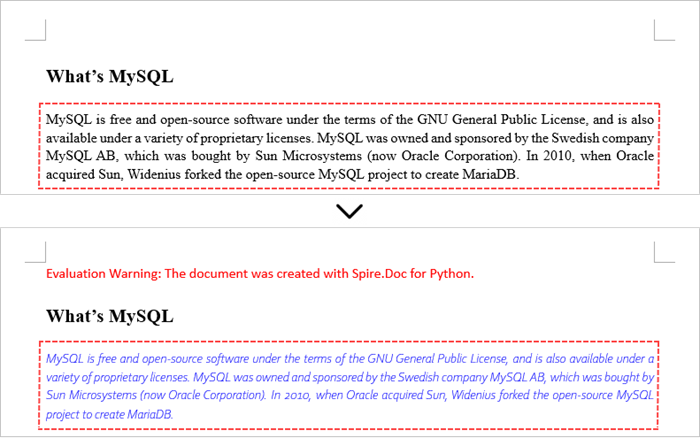
Add New Elements to a Word Document in Python
In a Word document, most elements—such as text, images, lists, and charts—are fundamentally organized around the concept of a paragraph. To insert a new paragraph into a specific section, use the Section.AddParagraph() method.
After creating the new paragraph, you can add various elements to it by leveraging the methods and properties of the Paragraph object.
The steps to add new elements (text and images) to a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Add an image to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Get the last section
lastSection = doc.LastSection
# Add a paragraph to the section
paragraph = lastSection.AddParagraph()
# Add an image to the paragraph
picture = paragraph.AppendPicture("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png");
# Set text wrap style
picture.TextWrappingStyle = TextWrappingStyle.TopAndBottom
# Add text to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("This text and the image above are added by Spire.Doc for Python.")
# Create a paragraph style
style = ParagraphStyle(doc)
style.Name = "FontStyle"
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
doc.Styles.Add(style)
# Apply the style to the paragraph
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Save the document to a different Word file
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddNewElements.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
# Dispose resource
doc.Dispose()

Remove Paragraphs from a Word Document in Python
To eliminate a specific paragraph from a document, simply invoke the ParagraphCollection.RemoveAt() method and supply the index of the paragraph you intend to delete.
The steps to remove paragraphs from a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Remove a specific paragraph from the section using Section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Remove a specific paragraph
section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt(0)
# Save the document to a different Word file
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
# Dispose resource
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Detect Page Orientation or Rotation Angle in PDF
Proper presentation of a PDF document is critical for maintaining its accuracy and professionalism. By checking the orientation and rotation of each PDF page, you can confirm that all elements, including diagrams and images, are displayed correctly as intended on the viewing device or platform, thus avoiding confusion or misinterpretation of content. In this article, you will learn how to detect the orientation and rotation angle of a PDF page in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python. It can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
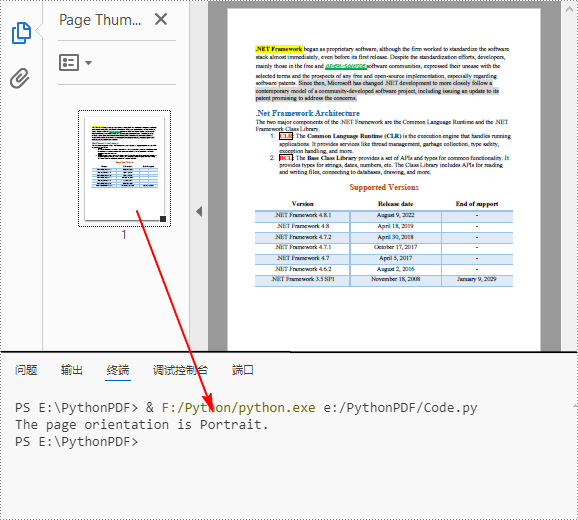
Detect PDF Page Orientation in Python
Page orientation is determined by the relationship between page width and height. Using Spire.PDF for Python, you can compare these two values to detect whether a page is landscape (width greater than height) or portrait (width less than height). The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the width and height of the PDF page using PdfPageBase.Size.Width and PdfPageBase.Size.Height properties.
- Compare the values of page width and height to detect the page orientation.
- Print out the result.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("SamplePDF.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get the width and height of the page
Width = page.Size.Width
Height = page.Size.Height
# Compare the values of page width and height
if Width > Height:
print("The page orientation is Landscape.")
else:
print("The page orientation is Portrait.")
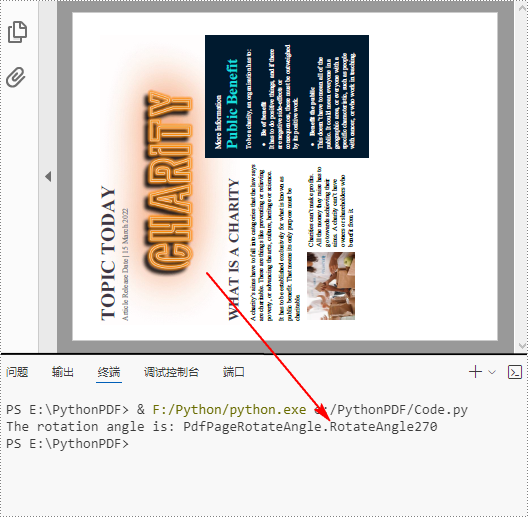
Detect PDF Page Rotation Angle in Python
PDF pages can be rotated by a certain angle. To detect the rotation angle of a PDF page, you can use the PdfPageBase.Rotation property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the rotation angle of the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation property, and then convert it to text string.
- Print out the result.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get the rotation angle of the current page
rotationAngle = page.Rotation
rotation = str(rotationAngle)
# Print out the result
print("The rotation angle is: " + rotation)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add or Remove Digital Signatures in PDF
Digital signatures are vital for maintaining the authenticity and integrity of PDF documents. They provide a reliable way to verify the signer's identity and ensure that the document's content has not been tampered with since the signature was applied. By using digital signatures, you can enhance the security and trustworthiness of your documents. In this article, we will explore how to add and remove digital signatures in PDF files in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add a Digital Signature to PDF in Python
- Add an Invisible Digital Signature to PDF in Python
- Remove Digital Signature from PDF in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
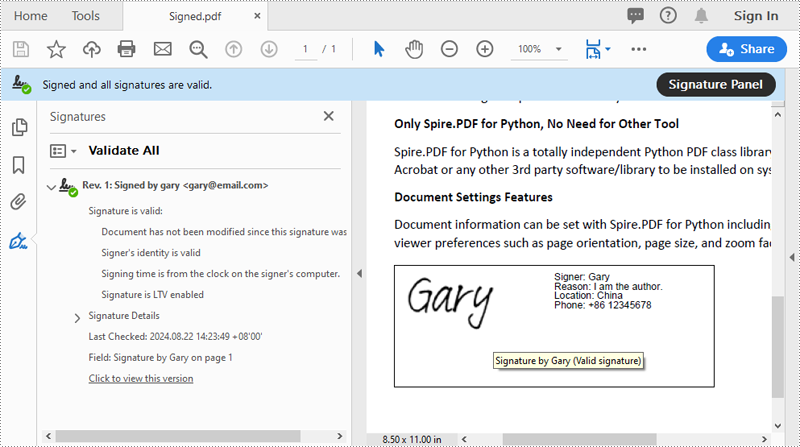
Add a Digital Signature to PDF in Python
You can use the PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker.MakeSignature(sigFieldName: str, page: PdfPageBase, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float, signatureAppearance: IPdfSignatureAppearance) method to add a visible digital signature with a custom appearance to a specific page of a PDF document. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker instance and pass the PdfDocument object, certificate (.pfx) file path and certificate password to the class instructor as parameters.
- Set signature details, such as the signer’s name, contact information, location, and signature reason, using the properties of the PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker class.
- Create a PdfSignatureAppearance instance for the signature, and then customize the labels for the signature and set the signature image.
- Get a specific page in the PDF document using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Call the PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker.MakeSignature(sigFieldName: str, page: PdfPageBase, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float, signatureAppearance: IPdfSignatureAppearance) method to add the digital signature to a specific location of the page.
- Save the result document using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a signature maker
signatureMaker = PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker(doc, "gary.pfx", "e-iceblue")
# Configure the signature properties like the signer's name, contact information, location and signature reason
signature = signatureMaker.Signature
signature.Name = "Gary"
signature.ContactInfo = "+86 12345678"
signature.Location = "China"
signature.Reason = "I am the author."
# Create a custom signature appearance
appearance = PdfSignatureAppearance(signature)
# Set label for the signer's name
appearance.NameLabel = "Signer: "
# Set label for the contact information
appearance.ContactInfoLabel = "Phone: "
# Set label for the location
appearance.LocationLabel = "Location: "
# Set label for the signature reason
appearance.ReasonLabel = "Reason: "
# Set signature image
appearance.SignatureImage = PdfImage.FromFile("SigImg.png")
# Set the graphic render/display mode for the signature
appearance.GraphicMode = GraphicMode.SignImageAndSignDetail
# Set the layout for the signature image
appearance.SignImageLayout = SignImageLayout.none
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Add the signature to a specified location of the page
signatureMaker.MakeSignature("Signature by Gary", page, 90.0, 600.0, 260.0, 100.0, appearance)
# Save the signed document
doc.SaveToFile("Signed.pdf")
doc.Close()
Add an Invisible Digital Signature to PDF in Python
An invisible signature in a PDF is a type of digital signature that provides all the security and authentication benefits of a standard digital signature but does not appear visibly on the document itself. Using the PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker.MakeSignature(sigFieldName: str) method of Spire.PDF for Python, you can add an invisible digital signature to a PDF document. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker instance and pass the PdfDocument object, certificate (.pfx) file path and password to the class instructor as parameters.
- Add an invisible digital signature to a PDF document using the PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker.MakeSignature(sigFieldName: str) method
- Save the result document using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("test2.pdf")
# Create a signature maker
signatureMaker = PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker(doc, "gary.pfx", "e-iceblue")
# Add an invisible signature to the document
signatureMaker.MakeSignature("Signature by Gary")
# Save the signed document
doc.SaveToFile("InvisibleSignature.pdf")
doc.Close()
Remove Digital Signature from PDF in Python
To remove digital signatures from a PDF document, you need to iterate through all form fields in the document, find the form fields that are of PdfSignatureFieldWidget type and then remove them from the document. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the form field collection of the document using PdfDocument.Form property.
- Iterate through the form fields in the collection from the last to the first.
- Check if the field is a PdfSignatureFieldWidget object.
- If the result is True, remove the field from the document using PdfFormFieldWidgetCollection.FieldsWidget.RemoveAt(index) method.
- Save the result document using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("Signed.pdf")
# Get form field collection from the document
pdfForm = doc.Form
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(pdfForm)
# Check if there are any form fields in the collection
if formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count > 0:
# Loop through all form fields from the last to the first
for i in range(formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count - 1, -1, -1):
field = formWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item(i)
# Check if the field is a PdfSignatureFieldWidget
if isinstance(field, PdfSignatureFieldWidget):
# Remove the field
formWidget.FieldsWidget.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("RemoveSignature.pdf")
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.