Python: Set or Remove Table Borders in PowerPoint
Table borders in PowerPoint refer to the visible lines or outlines that surround the cells within a table. These borders provide a visual separation between cells and help define the boundaries of the table. By setting or modifying table borders, you can customize the appearance of tables in your PowerPoint presentations. In this article, we will guide you on how to set and remove table borders in PowerPoint in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Set Table Borders in PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the ITable.SetTableBorder() method, which allows you to set borders for a table in PowerPoint. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Get the first slide of the presentation using Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Add a table to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendTable() method.
- Add borders to the table and set the border type, width, and color using ITable.SetTableBorder() method.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Get the first slide of the presentation
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Specify the number and size of rows and columns in table
widths = [100, 100, 100, 100, 100]
heights = [20, 20]
# Add a table to the first slide
table = slide.Shapes.AppendTable(100, 100, widths, heights)
# Add borders to the table and set the border type, width, and color
table.SetTableBorder(TableBorderType.All, 1, Color.get_Blue())
# Save the result presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("SetBorders.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
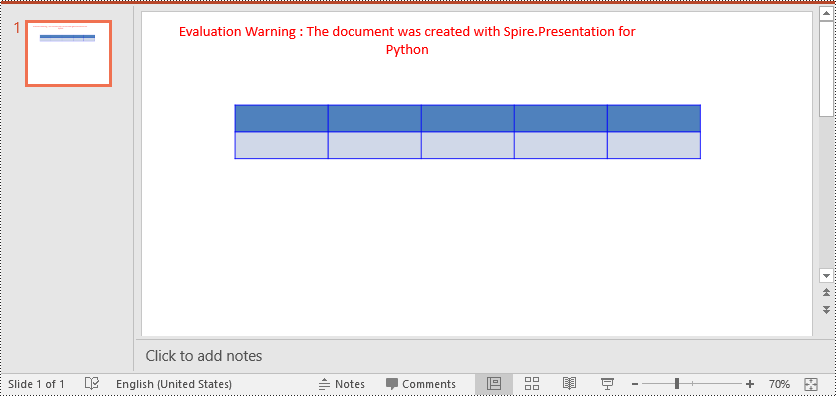
Remove Table Borders in PowerPoint in Python
To remove borders from a table, you need to iterate through the cells in the table and then remove the borders from each cell. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide of the presentation using Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Get the table on the slide.
- Iterate through the rows in the table and the cells in each row.
- Remove the borders from each cell by setting the fill type of the top, bottom, left and right borders of the cell as none.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a PowerPoint presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("SetBorders.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Get the table on the slide
table = slide.Shapes[0] if isinstance(slide.Shapes[0], ITable) else None
table = (ITable)(table)
# Iterate through the rows and cells in the table
for row in table.TableRows:
for cell in row:
# Remove borders from each cell by setting the fill type of the top, bottom, left and right borders of the cell as none
cell.BorderTop.FillType = FillFormatType.none
cell.BorderBottom.FillType = FillFormatType.none
cell.BorderLeft.FillType = FillFormatType.none
cell.BorderRight.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Save the result presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("RemoveBorders.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
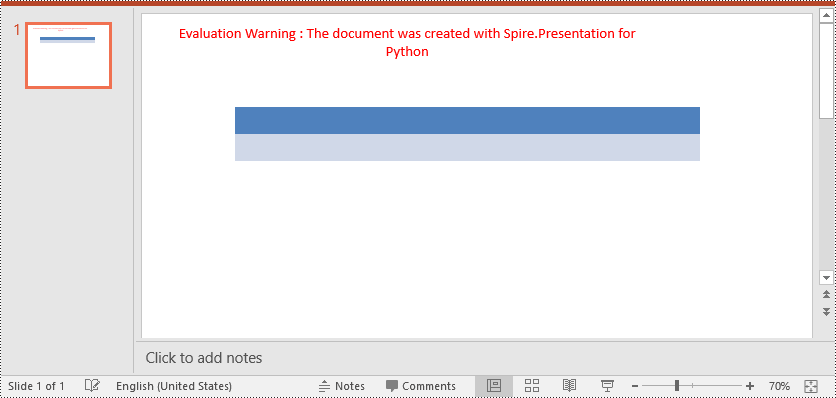
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Change the Margins of a PDF Document
Margins in a PDF document refer to the blank spaces surrounding the content on each page. They act as a buffer zone between the text or images and the edges of the page. Changing the margins of a PDF document can be a useful task when you want to adjust the layout, accommodate annotations or comments, or prepare the document for printing or presentation.
This article introduces how to modify the margins of a PDF document using the Spire.PDF for Python library. You will discover techniques to both increase and reduce the margins of your PDFs, enabling you to customize the layout according to your specific requirements.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Increase the Margins of a PDF Document in Python
In Spire.PDF for Python, there isn't a direct method to modify the margins of an existing PDF document. However, you can increase the margins by creating a new PDF document with a page size equal to the original document's page size plus the increased margin values. Then, copy and paste (draw) each page of the original document into the appropriate place on the new document page.
The following are the steps to increase the margins of a PDF document using Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object called "originalPdf" and load the original PDF document.
- Create another PdfDocument object called "newPdf" for creating a new PDF document.
- Specify the desired increase values for the top, bottom, left, and right margins.
- Calculate the new page size by adding the margin increase values to the original page dimensions.
- Create a template based on the original PDF page using PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Add a new page to the "newPdf" document with the calculated page size using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Draw the template onto the new page at the appropriate location to using PdfTemplate.Draw() method.
- Repeat steps 5-7 for each page in the original PDF document.
- Save the "newPdf" object to a PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
originalPdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
originalPdf.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf")
# Get the first page
"firstPage = originalPdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create another PdfDocument object for creating new document
newPdf = PdfDocument()
# Set the increase values of the margins
marginsToAdd = newPdf.PageSettings.Margins
marginsToAdd.Top = 40
marginsToAdd.Bottom = 40
marginsToAdd.Left = 40
marginsToAdd.Right = 40
# Calculate the new page size
sizeF = SizeF(firstPage.Size.Width + marginsToAdd.Left + marginsToAdd.Right, firstPage.Size.Height + marginsToAdd.Top + marginsToAdd.Bottom)
# Iterate through the pages in the original document
for i in range(originalPdf.Pages.Count):
# Create a template based on a specific page
pdfTemplate = originalPdf.Pages.get_Item(i).CreateTemplate()"
# Add a page to the new PDF
page = newPdf.Pages.Add(sizeF)
# Draw template on the page
pdfTemplate.Draw(page, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save the new document
newPdf.SaveToFile("Output/IncreaseMargins.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose resources
originalPdf.Dispose()
newPdf.Dispose()

Reduce the Margins of a PDF Document in Python
Similarly, you can reduce the margins by creating a new PDF document with a page size equal to the page size of the original document minus the margin value to be reduced. Then, copy and paste (draw) each page of the original document into the appropriate place on the new document page.
To reduce the margins of a PDF document using Python, follow these steps:
- Create a PdfDocument object called "originalPdf" and load the original PDF document.
- Create another PdfDocument object called "newPdf" for creating a new PDF document.
- Specify the desired reduction values for the top, bottom, left, and right margins.
- Calculate the new page size by subtracting the margin value to be reduced from the original page size.
- Create a template based on the original PDF page using PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Add a new page to the "newPdf" document with the calculated page size using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Draw the template onto the new page at the appropriate location using PdfTemplate.Draw() method.
- Repeat steps 5-7 for each page in the original PDF document.
- Save the "newPdf" object to a PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
originalPdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
originalPdf.LoadFromFile(""C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf"")
# Get the first page
firstPage = originalPdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create another PdfDocument object
newPdf = PdfDocument()
# Set the reduction value of the margins
topToReduce = 20.0
bottomToReduce = 20.0
leftToReduce = 20.0
rightToReduce = 20.0
# Calculate the new page size
sizeF = SizeF(firstPage.Size.Width - leftToReduce - rightToReduce, firstPage.Size.Height - topToReduce - bottomToReduce)
# Iterate through the pages in the original document
for i in range(originalPdf.Pages.Count):
# Create a template based on a specific page
pdfTemplate = originalPdf.Pages.get_Item(i).CreateTemplate()
# Add a page to the new PDF
page = newPdf.Pages.Add(sizeF, PdfMargins(0.0))
# Draw template on the page
pdfTemplate.Draw(page, -leftToReduce, -topToReduce)
# Save the new document
newPdf.SaveToFile(""Output/ReduceMargins.pdf"", FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose resources
originalPdf.Dispose()
newPdf.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Read Content from a Word Document
Extracting content from Word documents plays a crucial role in both work and study. Extracting one page of content helps in quickly browsing and summarizing key points, while extracting content from one section aids in in-depth study of specific topics or sections. Extracting the entire document allows you to have a comprehensive understanding of the document content, facilitating deep analysis and comprehensive comprehension. This article will introduce how to use Spire.Doc for Java to read a page, a section, and the entire content of a Word document in a Java project.
- Read a Page from a Word Document in Java
- Read a Section from a Word Document in Java
- Read the Entire Content from a Word Document in Java
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Read a Page from a Word Document in Java
Using the FixedLayoutDocument class and FixedLayoutPage class makes it easy to extract content from a specified page. To facilitate viewing the extracted content, the following example code saves the extracted content to a new Word document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create a FixedLayoutDocument object.
- Obtain a FixedLayoutPage object for a page in the document.
- Use the FixedLayoutPage.getSection() method to get the section where the page is located.
- Get the index position of the first paragraph on the page within the section.
- Get the index position of the last paragraph on the page within the section.
- Create another Document object.
- Add a new section using Document.addSection().
- Clone the properties of the original section to the new section using Section.cloneSectionPropertiesTo(newSection) method.
- Copy the content of the page from the original document to the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.pages.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
public class ReadOnePage {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load document content from the specified file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a fixed layout document object
FixedLayoutDocument layoutDoc = new FixedLayoutDocument(document);
// Get the first page
FixedLayoutPage page = layoutDoc.getPages().get(0);
// Get the section where the page is located
Section section = page.getSection();
// Get the first paragraph of the page
Paragraph paragraphStart = page.getColumns().get(0).getLines().getFirst().getParagraph();
int startIndex = 0;
if (paragraphStart != null) {
// Get the index of the paragraph in the section
startIndex = section.getBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(paragraphStart);
}
// Get the last paragraph of the page
Paragraph paragraphEnd = page.getColumns().get(0).getLines().getLast().getParagraph();
int endIndex = 0;
if (paragraphEnd != null) {
// Get the index of the paragraph in the section
endIndex = section.getBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(paragraphEnd);
}
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Add a new section
Section newSection = newdoc.addSection();
// Clone the properties of the original section to the new section
section.cloneSectionPropertiesTo(newSection);
// Copy the content of the original document's page to the new document
for (int i = startIndex; i <=endIndex; i++)
{
newSection.getBody().getChildObjects().add(section.getBody().getChildObjects().get(i).deepClone());
}
// Save the new document to the specified file
newdoc.saveToFile("Content of One Page.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document
newdoc.close();
newdoc.dispose();
// Close and release the original document
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}
Read a Section from a Word Document in Java
Using Document.Sections[index], you can access specific Section objects that contain the header, footer, and body content of a document. The following example demonstrates a simple method to copy all content from one section to another document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Use Document.getSections().get(1) to retrieve the second section of the document.
- Create another new Document object.
- Clone the default style of the original document to the new document using Document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc) method.
- Use Document.getSections().add(section.deepClone()) to clone the content of the second section of the original document to the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
public class ReadOneSection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document from a file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Get the second section of the document
Section section = document.getSections().get(1);
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Clone the default style to the new document
document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc);
// Clone the second section to the new document
newdoc.getSections().add(section.deepClone());
// Save the new document to a file
newdoc.saveToFile("Content of One Section.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document object
newdoc.close();
newdoc.dispose();
// Close and release the original document object
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}
Read the Entire Content from a Word Document in Java
This example demonstrates how to iterate through each section of the original document to read the entire content of the document and clone each section into a new document. This method can help you quickly replicate both the structure and content of the entire document, preserving the format and layout of the original document in the new document. Such operations are very useful for maintaining the integrity and consistency of the document structure. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create another new Document object.
- Clone the default style of the original document to the new document using the Document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc) method.
- Iterate through each section of the original document using a for loop and clone it into the new document.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
public class ReadOneDocument {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document from a file
document.loadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Create a new document object
Document newdoc = new Document();
// Clone the default style to the new document
document.cloneDefaultStyleTo(newdoc);
// Iterate through each section in the original document and clone it to the new document
for (Section sourceSection : (Iterable<Section>) document.getSections()) {
newdoc.getSections().add(sourceSection.deepClone());
}
// Save the new document to a file
newdoc.saveToFile("Content of the entire document.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close and release the new document object
newdoc.close();
newdoc.dispose();
// Close and release the original document object
document.close();
document.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Insert or Extract Images in Word Tables
Images are an effective tool for conveying complex information. By inserting images into tables, you can enhance data presentation with charts, graphs, diagrams, illustrations, and more. This not only enables readers to easily comprehend the information being presented but also adds visual appeal to your document. In certain cases, you may also come across situations where you need to extract images from tables for various purposes. For example, you might want to reuse an image in a presentation, website, or another document. Extracting images allows you to repurpose them, streamlining your content creation process and increasing efficiency. In this article, we will explore how to insert and extract images in Word tables in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert Images into a Word Table in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the TableCell.Paragraphs[index].AppendPicture() method to add an image to a specific table cell. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section in the document using the Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific table in the section using the Section.Tables[index] property.
- Access a specific cell in the table using the Table.Row[index].Cells[index] property.
- Add an image to the cell using the TableCell.Paragraphs[index].AppendPicture() method and set the image width and height.
- Save the result document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Table2.docx")
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the first table in the section
table = section.Tables.get_Item(0)
# Add an image to the 3rd cell of the second row in the table
cell = table.Rows[1].Cells[2]
picture = cell.Paragraphs[0].AppendPicture("doc.png")
# Set image width and height
picture.Width = 100
picture.Height = 100
# Add an image to the 3rd cell of the 3rd row in the table
cell = table.Rows[2].Cells[2]
picture = cell.Paragraphs[0].AppendPicture("xls.png")
# Set image width and height
picture.Width = 100
picture.Height = 100
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("AddImagesToTable.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()
Extract Images from a Word Table in Python
To extract images from a Word table, you need to iterate through all objects in the table and identify the ones of the DocPicture type. Once the DocPicture objects are found, you can access their image bytes using the DocPicture.ImageBytes property, and then save the image bytes to image files. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section in the document using the Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific table in the section using the Section.Tables[index] property.
- Create a list to store the extracted image data.
- Iterate through all rows in the table.
- Iterate through all cells in each row.
- Iterate through all paragraphs in each cell.
- Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph.
- Check if the current child object is of DocPicture type.
- Get the image bytes of the DocPicture object using the DocPicture.ImageBytes property and append them to the list.
- Save the image bytes in the list to image files.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("AddImagesToTable.docx")
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the first table in the section
table = section.Tables.get_Item(0)
# Create a list to store image bytes
image_data = []
# Iterate through all rows in the table
for i in range(table.Rows.Count):
row = table.Rows.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all cells in each row
for j in range(row.Cells.Count):
cell = row.Cells[j]
# Iterate through all paragraphs in each cell
for k in range(cell.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = cell.Paragraphs[k]
# Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph
for o in range(paragraph.ChildObjects.Count):
child_object = paragraph.ChildObjects[o]
# Check if the current child object is of DocPicture type
if isinstance(child_object, DocPicture):
picture = child_object
# Get the image bytes
bytes = picture.ImageBytes
# Append the image bytes to the list
image_data.append(bytes)
# Save the image bytes in the list to image files
for index, item in enumerate(image_data):
image_Name = f"Images/Image-{index}.png"
with open(image_Name, 'wb') as imageFile:
imageFile.write(item)
doc.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
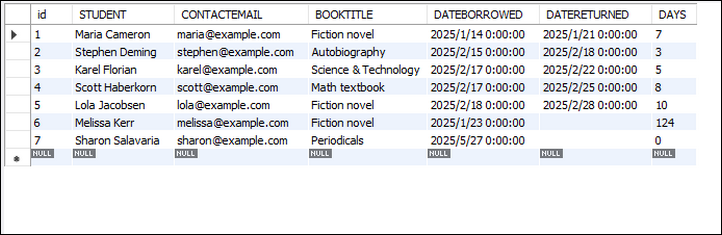
C# para ler arquivos Excel e exportar dados para DataTable e banco de dados
Índice
Instalar com Nuget
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Links Relacionados
Ler arquivos Excel em C# é um requisito comum para muitas aplicações, seja para análise de dados, relatórios ou integração com banco de dados. Embora as bibliotecas Interop da Microsoft possam ser usadas, elas têm limitações (como exigir que o Excel esteja instalado). Em vez disso, exploraremos uma abordagem mais eficiente usando o Spire.XLS, uma biblioteca .NET que permite ler e escrever arquivos Excel sem Interop. Este artigo aborda:
- Biblioteca C# .NET para Ler Excel Sem Interop
- Como Ler um Arquivo Excel em C#
- Ler Dados do Excel para um DataTable
- Ler Dados do Excel para um Banco de Dados
- Conclusão
- Perguntas Frequentes
Biblioteca C# .NET para Ler Excel Sem Interop
O Excel Interop da Microsoft exige que o Excel esteja instalado na máquina, tornando-o inadequado para aplicações do lado do servidor. Em vez disso, bibliotecas como o Spire.XLS oferecem uma solução leve e de alto desempenho, sem dependências do Excel.
Por que usar o Spire.XLS?
- Nenhuma Instalação do Excel Necessária – Funciona de forma independente.
- Suporta .NET Core & .NET Framework – Compatibilidade multiplataforma.
- Ler/Escrever Arquivos Excel – Suporta .xls, .xlsx e .xlsm.
- Importar para DataTable & Bancos de Dados – Integração perfeita com ADO.NET.
Instalação do Spire.XLS
Para começar, instale a biblioteca via Gerenciador de Pacotes NuGet:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Alternativamente, você pode baixar o Spire.XLS for .NET do nosso site oficial e referenciar o arquivo DLL manualmente.
Como Ler um Arquivo Excel em C#
Esta seção demonstra como ler um arquivo Excel em C# usando a biblioteca Spire.XLS. O processo envolve carregar o arquivo, acessar planilhas e recuperar valores de células programaticamente. Isso é útil para automatizar a extração de dados, processar relatórios do Excel ou integrar dados de planilhas em aplicações.
Passo 1. Importar Namespace Necessário
Para utilizar a funcionalidade do Spire.XLS, você precisa importar seu namespace. Isso dá acesso a classes como Workbook e Worksheet, que são essenciais para operações com arquivos Excel.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;Passo 2. Carregar um Arquivo Excel
Para carregar um arquivo Excel, crie um objeto Workbook e chame o método LoadFromFile. Isso lê o arquivo na memória, permitindo manipulação posterior.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");Passo 3. Obter uma Planilha Específica
Arquivos Excel podem conter várias planilhas. Você pode acessar uma planilha específica indexando a coleção Worksheets (baseada em zero). A primeira planilha está no índice 0, a segunda no 1, e assim por diante.
- C#
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]; //Primeira planilhaPasso 4. Recuperar Valor de uma Célula Específica
Para recuperar o valor de uma célula, use a propriedade CellRange.Value. Especifique os índices de linha e coluna (começando em 1) para localizar a célula. Isso é útil para extrair dados estruturados como cabeçalhos ou registros individuais.
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1]; // Linha1, Coluna 1 (A1)
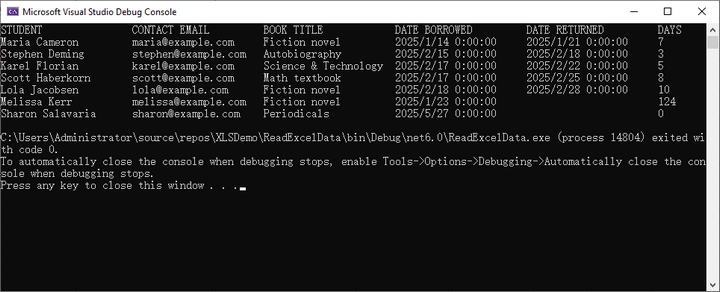
string value = cell.Value;Abaixo está um exemplo completo de leitura de dados de uma planilha inteira e impressão no console:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ReadExcelData
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Get the cell range containing data
CellRange locatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange;
// Iterate through the rows
for (int i = 0; i < locatedRange.Rows.Length; i++)
{
// Iterate through the columns
for (int j = 0; j < locatedRange.Rows[i].ColumnCount; j++)
{
// Get data of a specific cell
string cellValue = locatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value?.ToString() ?? "N/A";
// Align output with a width of 22
Console.Write($"{cellValue,-22}");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}Resultado:
Ler Dados do Excel para um DataTable
Exportar dados do Excel para um DataTable permite uma integração perfeita com controles de UI como DataGridView ou processamento de dados de backend. O Spire.XLS simplifica este processo com seu método integrado ExportDataTable(), que converte automaticamente os dados da planilha em um DataTable estruturado, preservando os cabeçalhos das colunas e os tipos de dados.
Passo 1. Importar Namespace Necessário
Inclua o namespace Spire.XLS para acessar as classes essenciais.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;Passo 2. Criar um Formulário e Evento de Clique de Botão
Crie um formulário (por exemplo, Form1) e adicione um botão com um manipulador de eventos para ler o arquivo Excel.
- C#
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// O código irá aqui
}
}Passo 3. Carregar o Workbook
Dentro do evento de clique do botão, crie um objeto Workbook e carregue o arquivo Excel.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");Passo 4. Exportar Dados para DataTable
Acesse uma planilha específica por seu índice e exporte seus dados para um DataTable usando o método ExportDataTable.
- C#
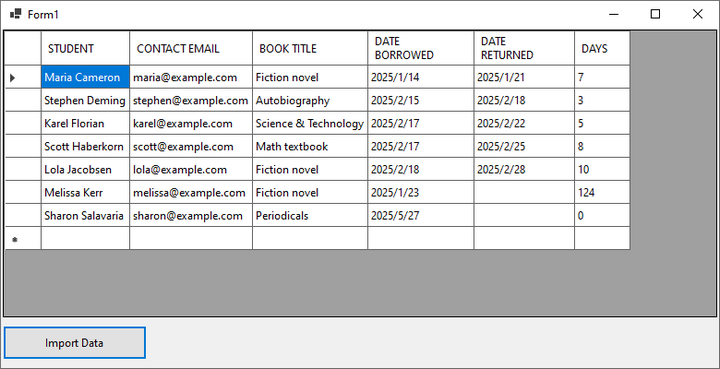
DataTable dataTable = wb.Worksheets[0].ExportDataTable();Passo 5. Vincular Dados ao DataGridView
Supondo que você tenha um controle DataGridView em seu formulário, vincule o DataTable ao DataGridView para exibir os dados.
- C#
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;O seguinte é o código completo para ler dados de um arquivo Excel em um DataTable e exibi-lo em um controle DataGridView do Windows Forms:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
namespace ReadExcelIntoDataTable
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Export data from worksheet into a DataTable
DataTable dataTable = sheet.ExportDataTable();
// Bind DataTable to DataGridView
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;
// Dispose resources
wb.Dispose();
}
}
}Resultado:
Ler Dados do Excel para um Banco de Dados
A integração de dados do Excel com um banco de dados pode otimizar o gerenciamento de dados. Abaixo, vamos percorrer o processo de leitura de um arquivo Excel e importação de seu conteúdo para um banco de dados MySQL. Este método é ideal para automatizar a migração de dados, relatórios ou sincronizar dados do Excel com um banco de dados estruturado.
Passo 1. Instalar a Biblioteca de Dados MySQL
Para interagir com bancos de dados MySQL em suas aplicações .NET, você precisará instalar a biblioteca MySql.Data. Este pacote NuGet fornece as classes e métodos necessários para conectar e manipular bancos de dados MySQL.
- C#
Install-Package MySql.DataPasso 2. Importar Namespaces Necessários
Antes de trabalhar com arquivos Excel e MySQL, você deve incluir os namespaces necessários. O Spire.XLS é usado para operações com Excel, enquanto o MySql.Data.MySqlClient permite a conectividade com o banco de dados MySQL.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;Passo 3. Extrair Cabeçalhos e Dados do Excel
O trecho de código a seguir demonstra como extrair cabeçalhos e dados do arquivo Excel. Os cabeçalhos são limpos para evitar conflitos de nomenclatura de colunas do MySQL, enquanto os dados são armazenados em um formato estruturado para inserção posterior.
- C#
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific sheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Retrieve headers
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Removing spaces to avoid conflicts with MySQL column names
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Retrieve data
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++) {
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}Passo 4. Conectar a um Banco de Dados MySQL
Uma conexão com o banco de dados MySQL é estabelecida usando uma string de conexão, que inclui detalhes do servidor, credenciais e o nome do banco de dados de destino. A instrução using garante a liberação adequada dos recursos.
- C#
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=yourpassword;database=yourdatabase;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// A conexão está estabelecida; execute as operações do banco de dados aqui
}Passo 5. Criar Dinamicamente uma Tabela no MySQL
Este passo gera dinamicamente uma tabela MySQL com colunas que correspondem aos cabeçalhos do Excel. Por simplicidade, todas as colunas são definidas como VARCHAR(255), mas os tipos de dados podem ser ajustados com base nos requisitos.
- C#
// Create a table with dynamic columns based on headers
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Assuming all header values are VARCHAR for simplicity; adjust types as needed
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Create a table in database
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Execute the create table query
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}Passo 6. Preencher a Tabela com Dados
Os dados extraídos do Excel são inseridos na tabela MySQL usando consultas parametrizadas para prevenir injeção de SQL. Cada linha do arquivo Excel é mapeada para um registro de banco de dados correspondente.
- C#
// Prepare the SQL INSERT statement
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Insert data into the table
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}Aqui está o código completo para importar dados de um arquivo Excel para uma tabela MySQL:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;
namespace ExcelToMySQL
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific sheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Retrieve headers
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Removing spaces to avoid conflicts with MySQL column names
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Retrieve data
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}
// Establish a connection to the MySQL database
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=admin;database=excel_db;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// Create a table with dynamic columns based on headers
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Assuming all header values are VARCHAR for simplicity; adjust types as needed
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Create a table in database
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Execute the create table query
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
// Prepare the SQL INSERT statement
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Insert data into the table
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Dados exportados com sucesso!");
}
}
}Resultado:
Conclusão
Ler arquivos Excel em C# nunca foi tão fácil, graças a bibliotecas como o Spire.XLS. Este guia o orientou no processo de carregar arquivos Excel, ler seu conteúdo e até mesmo importar os dados para um banco de dados MySQL. Com essas técnicas, você pode aprimorar significativamente as capacidades de manipulação de dados de suas aplicações.
Perguntas Frequentes
Q1: Posso ler arquivos Excel protegidos por senha?
R: Sim, o Spire.XLS suporta a leitura de arquivos Excel criptografados usando:
- C#
wb.OpenPassword = "psd";
wb.LoadFromFile("file.xlsx");Q2: Como leio os resultados da fórmula em vez da própria fórmula?
R: Você tem duas opções para recuperar os resultados da fórmula:
Para células individuais:
Verifique se uma célula contém uma fórmula usando CellRange.HasFormula e obtenha o valor com CellRange.FormulaValue:
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1];
if (cell.HasFormula)
{
string result = cell.FormulaValue.ToString();
}Para exportação em massa para DataTable:
Use Worksheet.ExportDataTable() com computedFormulaValue: true para exportar valores calculados:
- C#
DataTable data = sheet.ExportDataTable(range, exportColumnNames: true, computedFormulaValue: true);Q3: Como posso ler dados do Excel para um DataTable?
R: Use o método Worksheet.ExportDataTable() fornecido pelo Spire.XLS.
Q4: Como posso ler um arquivo Excel linha por linha?
R: Consulte o seguinte código:
- C#
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
for (int row = 1; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string cellValue = sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty;
Console.WriteLine(cellValue);
}
}Obtenha uma Licença Gratuita
Para experimentar plenamente as capacidades do Spire.XLS for .NET sem quaisquer limitações de avaliação, você pode solicitar uma licença de avaliação gratuita de 30 dias.
Veja Também
C# zum Lesen von Excel-Dateien und zum Exportieren von Daten in DataTable und Datenbank
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Mit Nuget installieren
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Verwandte Links
Das Lesen von Excel-Dateien in C# ist eine häufige Anforderung für viele Anwendungen, sei es für Datenanalyse, Berichterstattung oder Datenbankintegration. Während die Interop-Bibliotheken von Microsoft verwendet werden können, haben sie Einschränkungen (z. B. die Notwendigkeit, dass Excel installiert ist). Stattdessen werden wir einen effizienteren Ansatz mit Spire.XLS untersuchen, einer .NET-Bibliothek, die das Lesen und Schreiben von Excel-Dateien ohne Interop ermöglicht. Dieser Artikel behandelt:
- C# .NET-Bibliothek zum Lesen von Excel ohne Interop
- Wie man eine Excel-Datei in C# liest
- Excel-Daten in eine DataTable einlesen
- Excel-Daten in eine Datenbank einlesen
- Fazit
- FAQs
C# .NET-Bibliothek zum Lesen von Excel ohne Interop
Microsofts Excel Interop erfordert, dass Excel auf dem Computer installiert ist, was es für serverseitige Anwendungen ungeeignet macht. Stattdessen bieten Bibliotheken wie Spire.XLS eine leichtgewichtige, hochleistungsfähige Lösung ohne Abhängigkeiten von Excel.
Warum Spire.XLS verwenden?
- Keine Excel-Installation erforderlich – Funktioniert unabhängig.
- Unterstützt .NET Core & .NET Framework – Plattformübergreifende Kompatibilität.
- Excel-Dateien lesen/schreiben – Unterstützt .xls, .xlsx und .xlsm.
- Import in DataTable & Datenbanken – Nahtlose Integration mit ADO.NET.
Installation von Spire.XLS
Um zu beginnen, installieren Sie die Bibliothek über den NuGet Package Manager:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Alternativ können Sie Spire.XLS für .NET von unserer offiziellen Website herunterladen und die DLL-Datei manuell referenzieren.
Wie man eine Excel-Datei in C# liest
Dieser Abschnitt zeigt, wie man eine Excel-Datei in C# mit der Spire.XLS-Bibliothek liest. Der Prozess umfasst das Laden der Datei, den Zugriff auf Arbeitsblätter und das programmgesteuerte Abrufen von Zellwerten. Dies ist nützlich für die Automatisierung der Datenextraktion, die Verarbeitung von Excel-Berichten oder die Integration von Tabellenkalkulationsdaten in Anwendungen.
Schritt 1. Notwendigen Namespace importieren
Um die Funktionalität von Spire.XLS zu nutzen, müssen Sie dessen Namespace importieren. Dies ermöglicht den Zugriff auf Klassen wie Workbook und Worksheet, die für Excel-Dateioperationen unerlässlich sind.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;Schritt 2. Eine Excel-Datei laden
Um eine Excel-Datei zu laden, erstellen Sie ein Workbook-Objekt und rufen Sie die Methode LoadFromFile auf. Dadurch wird die Datei in den Speicher gelesen, was eine weitere Bearbeitung ermöglicht.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");Schritt 3. Ein bestimmtes Arbeitsblatt abrufen
Excel-Dateien können mehrere Arbeitsblätter enthalten. Sie können auf ein bestimmtes Blatt zugreifen, indem Sie die Worksheets-Sammlung indizieren (nullbasiert). Das erste Blatt befindet sich am Index 0, das zweite am Index 1 und so weiter.
- C#
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]; //Erstes BlattSchritt 4. Wert einer bestimmten Zelle abrufen
Um den Wert einer Zelle abzurufen, verwenden Sie die Eigenschaft CellRange.Value. Geben Sie die Zeilen- und Spaltenindizes (beginnend bei 1) an, um die Zelle zu lokalisieren. Dies ist nützlich zum Extrahieren strukturierter Daten wie Kopfzeilen oder einzelner Datensätze.
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1]; // Zeile1, Spalte 1 (A1)
string value = cell.Value;Unten finden Sie ein vollständiges Beispiel zum Lesen von Daten aus einem gesamten Arbeitsblatt und zum Ausgeben in der Konsole:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ReadExcelData
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Erstellen Sie ein Workbook-Objekt
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Laden Sie eine vorhandene Excel-Datei
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Holen Sie sich das erste Arbeitsblatt
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Holen Sie sich den Zellbereich, der Daten enthält
CellRange locatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange;
// Iterieren Sie durch die Zeilen
for (int i = 0; i < locatedRange.Rows.Length; i++)
{
// Iterieren Sie durch die Spalten
for (int j = 0; j < locatedRange.Rows[i].ColumnCount; j++)
{
// Holen Sie sich die Daten einer bestimmten Zelle
string cellValue = locatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value?.ToString() ?? "N/A";
// Richten Sie die Ausgabe mit einer Breite von 22 aus
Console.Write($"{cellValue,-22}");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}Ergebnis:

Excel-Daten in eine DataTable einlesen
Das Exportieren von Excel-Daten in eine DataTable ermöglicht eine nahtlose Integration mit UI-Steuerelementen wie DataGridView oder der Backend-Datenverarbeitung. Spire.XLS vereinfacht diesen Prozess mit seiner integrierten Methode ExportDataTable(), die Arbeitsblattdaten automatisch in eine strukturierte DataTable konvertiert und dabei Spaltenüberschriften und Datentypen beibehält.
Schritt 1. Notwendigen Namespace importieren
Fügen Sie den Spire.XLS-Namespace hinzu, um auf wesentliche Klassen zuzugreifen.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;Schritt 2. Ein Formular und ein Button-Klick-Ereignis erstellen
Erstellen Sie ein Formular (z. B. Form1) und fügen Sie eine Schaltfläche mit einem Ereignishandler zum Lesen der Excel-Datei hinzu.
- C#
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Der Code kommt hierher
}
}Schritt 3. Das Arbeitsbuch laden
Erstellen Sie innerhalb des Button-Klick-Ereignisses ein Workbook-Objekt und laden Sie die Excel-Datei.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");Schritt 4. Daten in DataTable exportieren
Greifen Sie über seinen Index auf ein bestimmtes Arbeitsblatt zu und exportieren Sie seine Daten mit der Methode ExportDataTable in eine DataTable.
- C#
DataTable dataTable = wb.Worksheets[0].ExportDataTable();Schritt 5. Daten an DataGridView binden
Angenommen, Sie haben ein DataGridView-Steuerelement in Ihrem Formular, binden Sie die DataTable an das DataGridView, um die Daten anzuzeigen.
- C#
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;Das Folgende ist der vollständige Code zum Lesen von Daten aus einer Excel-Datei in eine DataTable und zum Anzeigen in einem Windows Forms DataGridView-Steuerelement:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
namespace ReadExcelIntoDataTable
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Erstellen Sie ein Workbook-Objekt
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Laden Sie eine vorhandene Excel-Datei
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Holen Sie sich das erste Arbeitsblatt
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Exportieren Sie Daten aus dem Arbeitsblatt in eine DataTable
DataTable dataTable = sheet.ExportDataTable();
// Binden Sie die DataTable an das DataGridView
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;
// Geben Sie Ressourcen frei
wb.Dispose();
}
}
}Ergebnis:

Excel-Daten in eine Datenbank einlesen
Die Integration von Excel-Daten in eine Datenbank kann die Datenverwaltung optimieren. Im Folgenden führen wir Sie durch den Prozess des Lesens einer Excel-Datei und des Imports ihres Inhalts in eine MySQL-Datenbank. Diese Methode ist ideal für die Automatisierung der Datenmigration, die Berichterstellung oder die Synchronisierung von Excel-Daten mit einer strukturierten Datenbank.
Schritt 1. MySQL-Datenbibliothek installieren
Um mit MySQL-Datenbanken in Ihren .NET-Anwendungen zu interagieren, müssen Sie die Bibliothek MySql.Data installieren. Dieses NuGet-Paket stellt die notwendigen Klassen und Methoden zur Verfügung, um eine Verbindung zu MySQL-Datenbanken herzustellen und diese zu bearbeiten.
- C#
Install-Package MySql.DataSchritt 2. Notwendige Namespaces importieren
Bevor Sie mit Excel-Dateien und MySQL arbeiten, müssen Sie die erforderlichen Namespaces einbinden. Spire.XLS wird für Excel-Operationen verwendet, während MySql.Data.MySqlClient die Konnektivität zu MySQL-Datenbanken ermöglicht.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;Schritt 3. Kopfzeilen und Daten aus Excel extrahieren
Der folgende Codeausschnitt zeigt, wie Kopfzeilen und Daten aus der Excel-Datei extrahiert werden. Die Kopfzeilen werden bereinigt, um Konflikte bei der Benennung von MySQL-Spalten zu vermeiden, während die Daten in einem strukturierten Format für das spätere Einfügen gespeichert werden.
- C#
// Erstellen Sie ein Workbook-Objekt
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Laden Sie ein Excel-Dokument
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Holen Sie sich ein bestimmtes Blatt
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Rufen Sie die Kopfzeilen ab
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Leerzeichen entfernen, um Konflikte mit MySQL-Spaltennamen zu vermeiden
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Rufen Sie die Daten ab
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++) {
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}Schritt 4. Mit einer MySQL-Datenbank verbinden
Eine Verbindung zur MySQL-Datenbank wird über eine Verbindungszeichenfolge hergestellt, die Serverdetails, Anmeldeinformationen und den Namen der Zieldatenbank enthält. Die using-Anweisung stellt die ordnungsgemäße Freigabe von Ressourcen sicher.
- C#
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=yourpassword;database=yourdatabase;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// Die Verbindung ist hergestellt; führen Sie hier Datenbankoperationen durch
}Schritt 5. Dynamisch eine Tabelle in MySQL erstellen
Dieser Schritt generiert dynamisch eine MySQL-Tabelle mit Spalten, die den Excel-Kopfzeilen entsprechen. Der Einfachheit halber werden alle Spalten als VARCHAR(255) festgelegt, aber die Datentypen können je nach Anforderungen angepasst werden.
- C#
// Erstellen Sie eine Tabelle mit dynamischen Spalten basierend auf den Kopfzeilen
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Annahme, dass alle Kopfzeilenwerte zur Vereinfachung VARCHAR sind; passen Sie die Typen nach Bedarf an
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Erstellen Sie eine Tabelle in der Datenbank
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Führen Sie die Abfrage zum Erstellen der Tabelle aus
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}Schritt 6. Die Tabelle mit Daten füllen
Die extrahierten Excel-Daten werden mithilfe parametrisierter Abfragen in die MySQL-Tabelle eingefügt, um SQL-Injection zu verhindern. Jede Zeile aus der Excel-Datei wird einem entsprechenden Datenbankdatensatz zugeordnet.
- C#
// Bereiten Sie die SQL-INSERT-Anweisung vor
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Fügen Sie Daten in die Tabelle ein
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}Hier ist der vollständige Code zum Importieren von Daten aus einer Excel-Datei in eine MySQL-Tabelle:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;
namespace ExcelToMySQL
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Erstellen Sie ein Workbook-Objekt
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Laden Sie ein Excel-Dokument
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Holen Sie sich ein bestimmtes Blatt
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Rufen Sie die Kopfzeilen ab
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Leerzeichen entfernen, um Konflikte mit MySQL-Spaltennamen zu vermeiden
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Rufen Sie die Daten ab
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}
// Stellen Sie eine Verbindung zur MySQL-Datenbank her
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=admin;database=excel_db;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// Erstellen Sie eine Tabelle mit dynamischen Spalten basierend auf den Kopfzeilen
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Annahme, dass alle Kopfzeilenwerte zur Vereinfachung VARCHAR sind; passen Sie die Typen nach Bedarf an
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Erstellen Sie eine Tabelle in der Datenbank
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Führen Sie die Abfrage zum Erstellen der Tabelle aus
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
// Bereiten Sie die SQL-INSERT-Anweisung vor
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Fügen Sie Daten in die Tabelle ein
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Daten erfolgreich exportiert!");
}
}
}Ergebnis:

Fazit
Das Lesen von Excel-Dateien in C# war noch nie einfacher, dank Bibliotheken wie Spire.XLS. Dieser Leitfaden hat Sie durch den Prozess des Ladens von Excel-Dateien, des Lesens ihrer Inhalte und sogar des Imports der Daten in eine MySQL-Datenbank geführt. Mit diesen Techniken können Sie die Datenverarbeitungsfähigkeiten Ihrer Anwendungen erheblich verbessern.
FAQs
F1: Kann ich passwortgeschützte Excel-Dateien lesen?
A: Ja, Spire.XLS unterstützt das Lesen verschlüsselter Excel-Dateien mit:
- C#
wb.OpenPassword = "psd";
wb.LoadFromFile("file.xlsx");F2: Wie lese ich Formelergebnisse anstelle der Formel selbst?
A: Sie haben zwei Möglichkeiten, Formelergebnisse abzurufen:
Für einzelne Zellen:
Prüfen Sie mit CellRange.HasFormula, ob eine Zelle eine Formel enthält, und rufen Sie den Wert mit CellRange.FormulaValue ab:
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1];
if (cell.HasFormula)
{
string result = cell.FormulaValue.ToString();
}Für den Massenexport in eine DataTable:
Verwenden Sie Worksheet.ExportDataTable() mit computedFormulaValue: true, um berechnete Werte zu exportieren:
- C#
DataTable data = sheet.ExportDataTable(range, exportColumnNames: true, computedFormulaValue: true);F3: Wie kann ich Excel-Daten in eine DataTable einlesen?
A: Verwenden Sie die von Spire.XLS bereitgestellte Methode Worksheet.ExportDataTable().
F4: Wie kann ich eine Excel-Datei zeilenweise lesen?
A: Beziehen Sie sich auf den folgenden Code:
- C#
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
for (int row = 1; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string cellValue = sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty;
Console.WriteLine(cellValue);
}
}Holen Sie sich eine kostenlose Lizenz
Um die Funktionen von Spire.XLS für .NET ohne Evaluierungseinschränkungen vollständig zu erleben, können Sie eine kostenlose 30-Tage-Testlizenz anfordern.
Siehe auch
C# per leggere file Excel ed esportare dati in DataTable e database
Indice
Installa con Nuget
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Link Correlati
La lettura di file Excel in C# è un requisito comune per molte applicazioni, sia per l'analisi dei dati, la reportistica o l'integrazione di database. Sebbene sia possibile utilizzare le librerie Interop di Microsoft, esse presentano delle limitazioni (come la necessità che Excel sia installato). Esploreremo invece un approccio più efficiente utilizzando Spire.XLS, una libreria .NET che consente di leggere e scrivere file Excel senza Interop. Questo articolo tratta:
- Libreria C# .NET per Leggere Excel Senza Interop
- Come Leggere un File Excel in C#
- Leggere Dati Excel in una DataTable
- Leggere Dati Excel in un Database
- Conclusione
- Domande Frequenti
Libreria C# .NET per Leggere Excel Senza Interop
L'Interop di Excel di Microsoft richiede che Excel sia installato sulla macchina, rendendolo inadatto per le applicazioni lato server. Invece, librerie come Spire.XLS offrono una soluzione leggera e ad alte prestazioni senza dipendenze da Excel.
Perché usare Spire.XLS?
- Nessuna Installazione di Excel Richiesta – Funziona in modo indipendente.
- Supporta .NET Core e .NET Framework – Compatibilità multipiattaforma.
- Leggi/Scrivi File Excel – Supporta .xls, .xlsx e .xlsm.
- Importa in DataTable e Database – Integrazione perfetta con ADO.NET.
Installazione di Spire.XLS
Per iniziare, installa la libreria tramite il NuGet Package Manager:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
In alternativa, puoi scaricare Spire.XLS per .NET dal nostro sito ufficiale e fare riferimento manualmente al file DLL.
Come Leggere un File Excel in C#
Questa sezione dimostra come leggere un file Excel in C# utilizzando la libreria Spire.XLS. Il processo prevede il caricamento del file, l'accesso ai fogli di lavoro e il recupero programmatico dei valori delle celle. Ciò è utile per automatizzare l'estrazione dei dati, elaborare report di Excel o integrare i dati dei fogli di calcolo nelle applicazioni.
Passaggio 1. Importa lo Spazio dei Nomi Necessario
Per utilizzare la funzionalità di Spire.XLS, è necessario importare il suo spazio dei nomi. Ciò dà accesso a classi come Workbook e Worksheet, che sono essenziali per le operazioni sui file Excel.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;Passaggio 2. Carica un File Excel
Per caricare un file Excel, crea un oggetto Workbook e chiama il metodo LoadFromFile. Questo legge il file in memoria, consentendo ulteriori manipolazioni.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");Passaggio 3. Ottieni un Foglio di Lavoro Specifico
I file Excel possono contenere più fogli di lavoro. È possibile accedere a un foglio specifico indicizzando la raccolta Worksheets (in base zero). Il primo foglio si trova all'indice 0, il secondo all'1, e così via.
- C#
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]; //Primo foglioPassaggio 4. Recupera il Valore di una Cella Specifica
Per recuperare il valore di una cella, utilizzare la proprietà CellRange.Value. Specificare gli indici di riga e colonna (a partire da 1) per individuare la cella. Ciò è utile per estrarre dati strutturati come intestazioni o record individuali.
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1]; // Riga 1, Colonna 1 (A1)
string value = cell.Value;Di seguito è riportato un esempio completo di lettura dei dati da un intero foglio di lavoro e della loro stampa sulla console:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ReadExcelData
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Crea un oggetto Workbook
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Carica un file Excel esistente
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Ottieni il primo foglio di lavoro
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Ottieni l'intervallo di celle contenente i dati
CellRange locatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange;
// Itera attraverso le righe
for (int i = 0; i < locatedRange.Rows.Length; i++)
{
// Itera attraverso le colonne
for (int j = 0; j < locatedRange.Rows[i].ColumnCount; j++)
{
// Ottieni i dati di una cella specifica
string cellValue = locatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value?.ToString() ?? "N/A";
// Allinea l'output con una larghezza di 22
Console.Write($"{cellValue,-22}");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}Risultato:

Leggi i Dati di Excel in una DataTable
L'esportazione dei dati di Excel in una DataTable consente un'integrazione perfetta con i controlli dell'interfaccia utente come DataGridView o l'elaborazione dei dati di backend. Spire.XLS semplifica questo processo con il suo metodo integrato ExportDataTable(), che converte automaticamente i dati del foglio di lavoro in una DataTable strutturata preservando le intestazioni delle colonne e i tipi di dati.
Passaggio 1. Importa lo Spazio dei Nomi Necessario
Includi lo spazio dei nomi Spire.XLS per accedere alle classi essenziali.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;Passaggio 2. Crea un Modulo e un Evento Click del Pulsante
Crea un modulo (ad es. Form1) e aggiungi un pulsante con un gestore di eventi per la lettura del file Excel.
- C#
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Il codice andrà qui
}
}Passaggio 3. Carica la Cartella di Lavoro
All'interno dell'evento click del pulsante, crea un oggetto Workbook e carica il file Excel.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");Passaggio 4. Esporta i Dati in DataTable
Accedi a un foglio di lavoro specifico tramite il suo indice ed esporta i suoi dati in una DataTable utilizzando il metodo ExportDataTable.
- C#
DataTable dataTable = wb.Worksheets[0].ExportDataTable();Passaggio 5. Associa i Dati a DataGridView
Supponendo di avere un controllo DataGridView sul modulo, associa la DataTable al DataGridView per visualizzare i dati.
- C#
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;Di seguito è riportato il codice completo per leggere i dati da un file Excel in una DataTable e visualizzarli in un controllo DataGridView di Windows Forms:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
namespace ReadExcelIntoDataTable
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Crea un oggetto Workbook
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Carica un file Excel esistente
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Ottieni il primo foglio di lavoro
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Esporta i dati dal foglio di lavoro in una DataTable
DataTable dataTable = sheet.ExportDataTable();
// Associa la DataTable a DataGridView
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;
// Rilascia le risorse
wb.Dispose();
}
}
}Risultato:

Leggi i Dati di Excel in un Database
L'integrazione dei dati di Excel con un database può semplificare la gestione dei dati. Di seguito, illustreremo il processo di lettura di un file Excel e di importazione del suo contenuto in un database MySQL. Questo metodo è ideale per automatizzare la migrazione dei dati, la creazione di report o la sincronizzazione dei dati di Excel con un database strutturato.
Passaggio 1. Installa la Libreria Dati MySQL
Per interagire con i database MySQL nelle tue applicazioni .NET, dovrai installare la libreria MySql.Data. Questo pacchetto NuGet fornisce le classi e i metodi necessari per connettersi e manipolare i database MySQL.
- C#
Install-Package MySql.DataPassaggio 2. Importa gli Spazi dei Nomi Necessari
Prima di lavorare con file Excel e MySQL, è necessario includere gli spazi dei nomi richiesti. Spire.XLS viene utilizzato per le operazioni su Excel, mentre MySql.Data.MySqlClient abilita la connettività al database MySQL.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;Passaggio 3. Estrai Intestazioni e Dati da Excel
Il seguente frammento di codice dimostra come estrarre intestazioni e dati dal file Excel. Le intestazioni vengono pulite per evitare conflitti di denominazione delle colonne MySQL, mentre i dati vengono archiviati in un formato strutturato per un inserimento successivo.
- C#
// Crea un oggetto Workbook
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Carica un documento Excel
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Ottieni un foglio specifico
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Recupera intestazioni
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Rimozione degli spazi per evitare conflitti con i nomi delle colonne MySQL
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Recupera dati
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++) {
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}Passaggio 4. Connettiti a un Database MySQL
Viene stabilita una connessione al database MySQL utilizzando una stringa di connessione, che include i dettagli del server, le credenziali e il nome del database di destinazione. L'istruzione using garantisce il corretto smaltimento delle risorse.
- C#
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=yourpassword;database=yourdatabase;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// La connessione è stabilita; eseguire qui le operazioni sul database
}Passaggio 5. Crea Dinamicamente una Tabella in MySQL
Questo passaggio genera dinamicamente una tabella MySQL con colonne corrispondenti alle intestazioni di Excel. Per semplicità, tutte le colonne sono impostate come VARCHAR(255), ma i tipi di dati possono essere regolati in base ai requisiti.
- C#
// Crea una tabella con colonne dinamiche basate sulle intestazioni
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Supponendo che tutti i valori di intestazione siano VARCHAR per semplicità; regolare i tipi secondo necessità
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Crea una tabella nel database
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Esegui la query di creazione della tabella
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}Passaggio 6. Popola la Tabella con i Dati
I dati Excel estratti vengono inseriti nella tabella MySQL utilizzando query con parametri per prevenire l'iniezione di SQL. Ogni riga del file Excel viene mappata a un record di database corrispondente.
- C#
// Prepara l'istruzione SQL INSERT
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Inserisci i dati nella tabella
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}Ecco il codice completo per importare i dati da un file Excel in una tabella MySQL:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;
namespace ExcelToMySQL
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Crea un oggetto Workbook
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Carica un documento Excel
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Ottieni un foglio specifico
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Recupera intestazioni
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Rimozione degli spazi per evitare conflitti con i nomi delle colonne MySQL
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Recupera dati
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}
// Stabilisci una connessione al database MySQL
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=admin;database=excel_db;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// Crea una tabella con colonne dinamiche basate sulle intestazioni
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Supponendo che tutti i valori di intestazione siano VARCHAR per semplicità; regolare i tipi secondo necessità
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Crea una tabella nel database
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Esegui la query di creazione della tabella
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
// Prepara l'istruzione SQL INSERT
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Inserisci i dati nella tabella
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Dati esportati con successo!");
}
}
}Risultato:

Conclusione
Leggere file Excel in C# non è mai stato così facile, grazie a librerie come Spire.XLS. Questa guida ti ha illustrato il processo di caricamento dei file Excel, la lettura del loro contenuto e persino l'importazione dei dati in un database MySQL. Con queste tecniche, puoi migliorare notevolmente le capacità di gestione dei dati delle tue applicazioni.
Domande Frequenti
D1: Posso leggere file Excel protetti da password?
R: Sì, Spire.XLS supporta la lettura di file Excel crittografati utilizzando:
- C#
wb.OpenPassword = "psd";
wb.LoadFromFile("file.xlsx");D2: Come posso leggere i risultati delle formule invece della formula stessa?
R: Hai due opzioni per recuperare i risultati delle formule:
Per singole celle:
Verifica se una cella contiene una formula usando CellRange.HasFormula e ottieni il valore con CellRange.FormulaValue:
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1];
if (cell.HasFormula)
{
string result = cell.FormulaValue.ToString();
}Per l'esportazione di massa in DataTable:
Usa Worksheet.ExportDataTable() con computedFormulaValue: true per esportare i valori calcolati:
- C#
DataTable data = sheet.ExportDataTable(range, exportColumnNames: true, computedFormulaValue: true);D3: Come posso leggere i dati di Excel in una DataTable?
R: Usa il metodo Worksheet.ExportDataTable() fornito da Spire.XLS.
D4: Come posso leggere un file Excel riga per riga?
R: Fare riferimento al seguente codice:
- C#
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
for (int row = 1; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string cellValue = sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty;
Console.WriteLine(cellValue);
}
}Ottieni una Licenza Gratuita
Per sperimentare appieno le funzionalità di Spire.XLS per .NET senza alcuna limitazione di valutazione, puoi richiedere una licenza di prova gratuita di 30 giorni.
Vedi Anche
Python: Add or Remove Sections in PowerPoint
In PowerPoint, sections are a powerful tool for organizing and managing slides. By dividing slides into different sections, you can better organize content, navigate through your presentation, and present information in a more structured manner. This article will demonstrate how to add and remove sections in a PowerPoint presentation using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Add a Section at the End of a PowerPoint
- Insert a Section Before a Specified Section
- Add a Section Before a Specified Slide in PowerPoint
- Remove a Section from a PowerPoint
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Add a Section at the End of a PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the Presentation.SectionList.Append(section_name) method to add a section at the end of a presentation. Here are the specific steps to perform this operation:
- Create a Presentation class instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a section at the end using the Presentation.SectionList.Append() method.
- Save the document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a new presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a sample PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Append a new section
presentation.SectionList.Append("New Section")
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("AddSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Dispose of the presentation object
presentation.Dispose()
Insert a Section Before a Specified Section in Python
You can also use the Presentation.SectionList.Insert(index, section_name) method to insert a new section before a specific section. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation class instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Insert a new section before a specific section using the Presentation.SectionList.Insert() method, where index is the position of the specific section.
- Save the document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a new presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a sample PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Insert a new section before the second section
presentation.SectionList.Insert(1," New Section")
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("AddSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Dispose of the presentation object
presentation.Dispose()
Add a Section Before a Specified Slide in Python
You can also use the Presentation.SectionList.Add(section_name, slide) method to insert a new section before a specific slide. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation class instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Insert a new section before a specific slide using the Presentation.SectionList.Add() method
- Save the document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a new presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a sample PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Get the second slide
slide=presentation.Slides[1]
# Add a new section before the second slide
presentation.SectionList.Add("New Section",slide)
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("AddSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Dispose of the presentation object
presentation.Dispose()
Remove a Section from a PowerPoint in Python
If you don't need a specific section, you can simply remove it using the Presentation.SectionList.RemoveAt(index_to_remove) method. Please note that removing a section does not delete the slides within that section. Here are the steps to delete a specific section while preserving its slides:
- Create a Presentation class instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific section using the Presentation.SectionList.RemoveAt(index_to_remove) method, which takes an integer index as a parameter. You can also remove all sections using the Presentation.Slides.RemoveAll() method.
- Save the document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a new presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a sample PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Remove the second section
presentation.SectionList.RemoveAt(1)
# # Remove all sections
# presentation.SectionList.RemoveAll()
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("RemoveSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Dispose of the presentation object
presentation.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Attach Files to a PDF Document
By incorporating supplemental resources directly into the PDF, it consolidates all relevant information in a single file, making it easier to organize, share, and archive. This feature enables users to seamlessly share supporting documents, images, or multimedia elements, eliminating the need for separate file transfers or external links. It streamlines communication, improves efficiency, and ensures that recipients have convenient access to all the necessary resources within the PDF itself. In this article, you will learn how to attach files to a PDF document in Python with the help of Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Background Knowledge
There are generally two types of attachments in PDF, namely document level attachment and annotation attachment. Both are supported by Spire.PDF for Python. The table below lists the differences between them.
| Attachment type | Represented by | Definition |
| Document level attachment | PdfAttachment class | A file attached to a PDF at the document level won't appear on a page, but can be viewed in the "Attachments" panel of a PDF reader. |
| Annotation attachment | PdfAnnotationAttachment class | A file attached as an annotation can be found on a page or in the "Attachment" panel. An Annotation attachment is shown as a paper clip icon on the page; reviewers can double-click the icon to open the file. |
Attach Files to a PDF Document in Python
To attach files to PDFs at the document level, you first need to create a PdfAttachment object based on an external file, and then you can add it to a PDF document using the PdfDocument.Attachments.Add() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PdfAttachment object based on an external file.
- Add the attachment to the document using PdfDocument.Attachments.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf")
# Create PdfAttachment objects based on external files
attachment_one = PdfAttachment("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx")
attachment_two = PdfAttachment("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png")
# Add the attachments to PDF
doc.Attachments.Add(attachment_one)
doc.Attachments.Add(attachment_two)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Attachment.pdf")
Attach Files as Annotations in PDF in Python
An annotation attachment is represented by the PdfAttachmentAnnotation class. Create an instance of this class, specify its attributes such as bounds, flag and text, and then add it to a specified page using the PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
Below are the steps to attach files as annotations in PDF using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific page to add annotation through PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Create a PdfAttachmentAnnotation object based on an external file.
- Add the annotation attachment to the page using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Draw a string on PDF
str = ""Here is the report:""
font = PdfTrueTypeFont(""Times New Roman"", 16.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
x = 50.0
y = doc.Pages.get_Item(0).ActualSize.Height - 300.0
page.Canvas.DrawString(str, font, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
# Create a PdfAttachmentAnnotation object based on an external file
data = Stream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx")
size = font.MeasureString(str);
bounds = RectangleF((x + size.Width + 5.0), y, 10.0, 15.0)
annotation = PdfAttachmentAnnotation(bounds, "Report.docx", data);
# Set color, flag, icon and text of the annotation
annotation.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
annotation.Flags = PdfAnnotationFlags.Default
annotation.Icon = PdfAttachmentIcon.Graph
annotation.Text = "Click to open the file"
# Add the attachment annotation to PDF
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(annotation)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/AnnotationAttachment.pdf")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Split a PDF Page into Multiple Pages
Sometimes, when dealing with PDF documents, there is a need to split a page into different sections based on content or layout. For instance, splitting a mixed-layout page with both horizontal and vertical content into two separate parts. This type of splitting is not commonly available in basic PDF management functions but can be important for academic papers, magazine ads, or mixed-layout designs. This article explains how to use Spire.PDF for Python to perform horizontal or vertical PDF page splitting.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Split PDF Page Horizontally or Vertically with Python
Spire.PDF for Python not only supports splitting a PDF document into multiple PDF documents, but also allows splitting a specific page within a PDF into two or more pages. Here are the detailed steps to split a page:
- Create an instance of the PdfDocument class.
- Load the source PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the page(s) to be split using PdfDocument.Pages[].
- Create a new PDF document and set its page margins to 0.
- Set the width or height of the new document to half of the source document.
- Add a page to the new PDF document using the PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a template for the source document's page using the PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Draw the content of the source page onto the new page using the PdfTemplate.Draw() method.
- Save the split document using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Terms of service.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a new PDF document and remove the page margins
newpdf = PdfDocument()
newpdf.PageSettings.Margins.All=0
# Horizontal splitting: Set the width of the new document's page to be the same as the width of the first page of the original document, and the height to half of the first page's height
newpdf.PageSettings.Width=page.Size.Width
newpdf.PageSettings.Height=page.Size.Height/2
'''
# Vertical splitting: Set the width of the new document's page to be half of the width of the first page of the original document, and the height to the same as the first page's height
newpdf.PageSettings.Width=page.Size.Width/2
newpdf.PageSettings.Height=page.Size.Height
'''
# Add a new page to the new PDF document
newPage = newpdf.Pages.Add()
# Set the text layout format
format = PdfTextLayout()
format.Break=PdfLayoutBreakType.FitPage
format.Layout=PdfLayoutType.Paginate
# Create a template based on the first page of the original document and draw it onto the new page of the new document, automatically paginating when the page is filled
page.CreateTemplate().Draw(newPage, PointF(0.0, 0.0), format)
# Save the document
newpdf.SaveToFile("HorizontalSplitting.pdf")
# Close the objects
newpdf.Close()
pdf.Close()
The result of horizontal splitting is as follows:
The result of vertical splitting is as follows:

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.