
Spire.Doc for Python (98)
In Word, each paragraph should convey a unique idea or point, helping to organize information in a way that is easy for readers to understand. Inserting new paragraphs allows you to introduce new concepts or expand on different aspects of a topic, making the text clearer. In this article, you will learn how to insert a new paragraph in Word in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Add a Paragraph at the End of a Word Document in Python
- Insert a Paragraph at a Specified Location in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add a Paragraph at the End of a Word Document in Python
To add a new paragraph at the end, you need to get the last section of the Word document through the Document.LastSection property, and then add a paragraph at the end of the section through the Section.AddParagraph() method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the last section of the document using Document.LastSection property.
- Add a paragraph at the end of the section using Section.AddParagraph() method, and then add text to it using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Create a ParagraphStyle object and set the font name, size, style of the paragraph text.
- Apply the paragraph style using Paragraph.ApplyStyle() method
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Test.docx")
# Get the first section
section = doc.LastSection
# Add a paragraph at the end and set its text content
para = section.AddParagraph()
para.AppendText("Add a paragraph to the end of the document.")
# Set the paragraph style
style = ParagraphStyle(doc)
style.Name = "Style1"
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
style.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
style.CharacterFormat.Bold= True
doc.Styles.Add(style)
para.ApplyStyle("Style1")
para.Format.BeforeSpacing = 10
# Save the result file
doc.SaveToFile("AddParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
doc.Close()

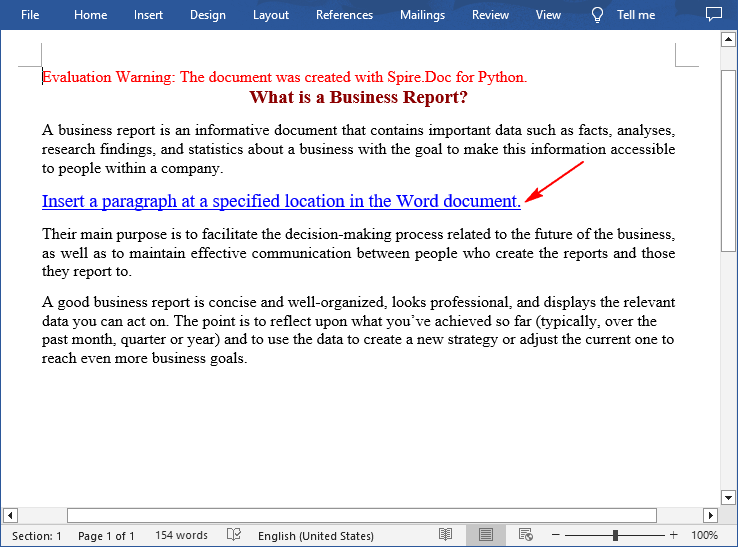
Insert a Paragraph at a Specified Location in Word in Python
You can also add a paragraph and then insert it to a specified position in Word through the Section.Paragraphs.Insert(index: int, paragraph: IParagraph) method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Add a paragraph using Section.AddParagraph() method, and then add text to it using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Set the font name, size, style of the paragraph text.
- Insert the newly added paragraph at a specified index using Section.Paragraphs.Insert(index: int, paragraph: IParagraph) method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Test.docx")
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Add a paragraph and set its text content
para = section.AddParagraph()
textRange = para.AppendText("Insert a paragraph at a specified location in the Word document.")
# Set the font name, size, color and style
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 14
textRange.CharacterFormat.UnderlineStyle = UnderlineStyle.Single
# Insert the paragraph as the third paragraph
section.Paragraphs.Insert(2, para)
# Set spacing after the paragraph
para.Format.AfterSpacing = 10
# Save the result file
doc.SaveToFile("InsertParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
MS Word allows users to view hyperlinks but lacks a built-in feature for extracting hyperlinks with a single click. This limitation makes extracting multiple links from a document time-consuming. Thankfully, Python can streamline this process significantly. In this article, we'll show you how to use Spire.Doc for Python to easily extract hyperlinks from Word documents with Python, either individual or batch, saving you time and effort.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows.
Extract Hyperlinks from Word Documents: Specified Links
Whether you're looking to retrieve just one important link or filter out certain URLs, this section will guide you through the process step by step. Using the Field.FieldText and the Field.Code properties provided by Spire.Doc, you can efficiently target and extract specified hyperlinks, making it easier to access the information you need.
Steps to extract specified hyperlinks from Word documents:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Read a Word document from files using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through elements to find all hyperlinks in this Word document.
- Get a certain hyperlink from the hyperlink collection.
- Retrieve the hyperlink text with Field.FieldText property.
- Extract URLs from the hyperlink in the Word document using Field.Code property.
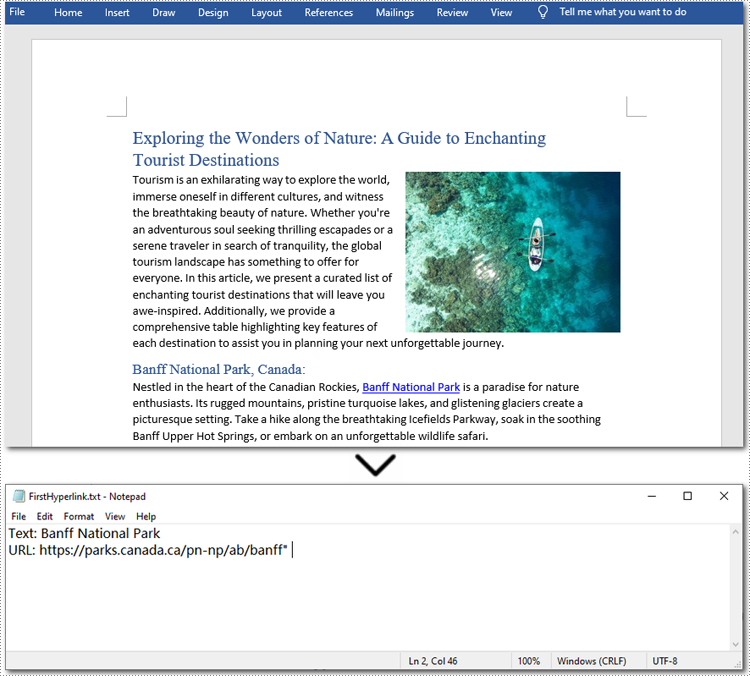
Here is the code example of extracting the first hyperlink in a Word document:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("/sample.docx")
# Find all hyperlinks in the Word document
hyperlinks = []
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
for j in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
sec = section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
if sec.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph:
for k in range((sec if isinstance(sec, Paragraph) else None).ChildObjects.Count):
para = (sec if isinstance(sec, Paragraph) else None).ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
if para.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Field:
field = para if isinstance(para, Field) else None
if field.Type == FieldType.FieldHyperlink:
hyperlinks.append(field)
# Get the first hyperlink text and URL
if hyperlinks:
first_hyperlink = hyperlinks[0]
hyperlink_text = first_hyperlink.FieldText
hyperlink_url = first_hyperlink.Code.split('HYPERLINK ')[1].strip('"')
# Save to a text file
with open("/FirstHyperlink.txt", "w") as file:
file.write(f"Text: {hyperlink_text}\nURL: {hyperlink_url}\n")
# Close the document
doc.Close()
Extract All Hyperlinks from Word Documents
After checking out how to extract specified hyperlinks, let's move on to extracting all hyperlinks from your Word documents. This is especially helpful when you need a list of all links, whether to check for broken ones or for other purposes. By automating this process with Spire.Doc(short for Spire Doc for Python), you can save time and ensure accuracy. Let's take a closer look at the steps and code example. Steps to extract all hyperlinks from Word documents:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document from the local storage with Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through elements to find all hyperlinks in the Word document.
- Iterate through all hyperlinks in the collection.
- Use Field.FieldText property to extract the hyperlink text from each link.
- Use Field.Code property to get URLs from hyperlinks.
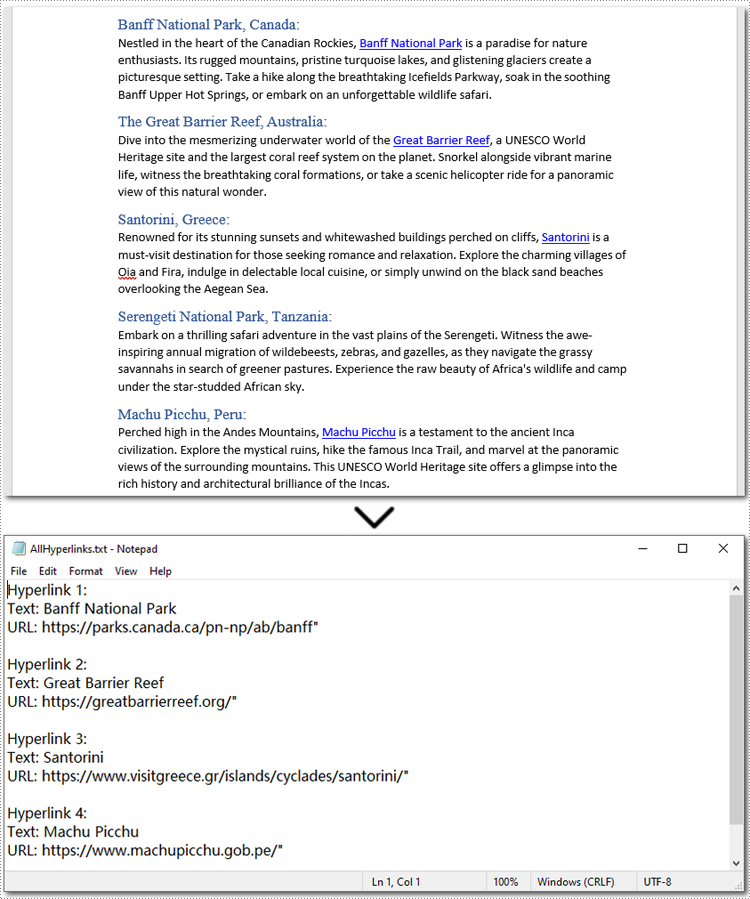
Below is a code example of extracting all hyperlinks from a Word document:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("/sample.docx")
# Find all hyperlinks in the Word document
hyperlinks = []
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
for j in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
sec = section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
if sec.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph:
for k in range((sec if isinstance(sec, Paragraph) else None).ChildObjects.Count):
para = (sec if isinstance(sec, Paragraph) else None).ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
if para.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Field:
field = para if isinstance(para, Field) else None
if field.Type == FieldType.FieldHyperlink:
hyperlinks.append(field)
# Save all hyperlinks text and URL to a text file
with open("/AllHyperlinks.txt", "w") as file:
for i, hyperlink in enumerate(hyperlinks):
hyperlink_text = hyperlink.FieldText
hyperlink_url = hyperlink.Code.split('HYPERLINK ')[1].strip('"')
file.write(f"Hyperlink {i+1}:\nText: {hyperlink_text}\nURL: {hyperlink_url}\n\n")
# Close the document
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Macros in Word documents are small programs created using the Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) language. They are designed to automate repetitive tasks or add advanced functionality. While these macros can be powerful tools for improving productivity, they also pose security risks if used maliciously. Therefore, it is essential to detect and remove potentially harmful macros from Word documents, especially when handling files from untrusted sources. In this article, we will explain how to detect and remove VBA macros in Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Detect Whether a Word Document Contains VBA Macros in Python
- Remove VBA Macros from a Word Document in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
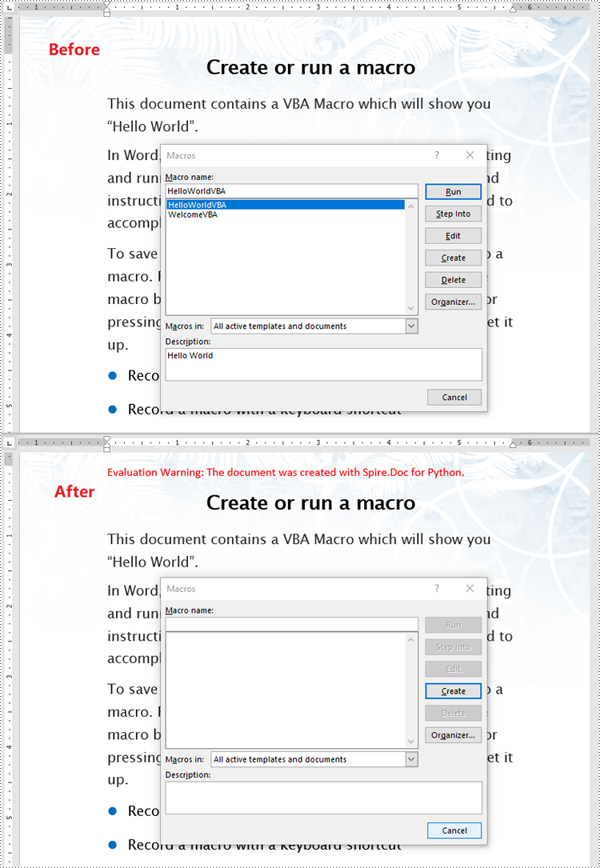
Detect Whether a Word Document Contains VBA Macros in Python
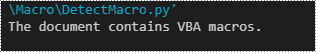
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Document.IsContainMacro property, enabling developers to check whether a Word document contains VBA macros easily. This property returns a boolean value: True indicates that the document includes one or more VBA macros, while False indicates that no macros are present in the document.
The following steps explain how to detect whether a Word document contains VBA macros using Spire.Doc for Python:
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Detect whether the document includes VBA macros using the Document.IsContainMacro property.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Initialize an instance of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Test.docm")
# Detect if the document contains VBA macros
if document.IsContainMacro:
print("The document contains VBA macros.")
else:
print("The document does not contain any VBA macros.")
document.Close()
Remove VBA Macros from a Word Document in Python
Developers can remove all macros from a Word document at once by using the Document.ClearMacros() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove all macros from the document using the Document.ClearMacros() method.
- Save the result document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Initialize an instance of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Test.docm")
# Remove all VBA macros from the document
document.ClearMacros()
# Save the modified document to a docm file
document.SaveToFile("RemoveMacros.docm", FileFormat.Docm2016)
document.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Textboxes in a Word document serve as versatile containers for text, enabling users to enhance layout and design. They allow for the separation of content from the main body, making documents more visually appealing and organized. Extracting or updating textboxes can be essential for improving document efficiency, ensuring information is current, and facilitating data analysis.
In this article, you will learn how to extract or update textboxes in a Word document using Python and Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
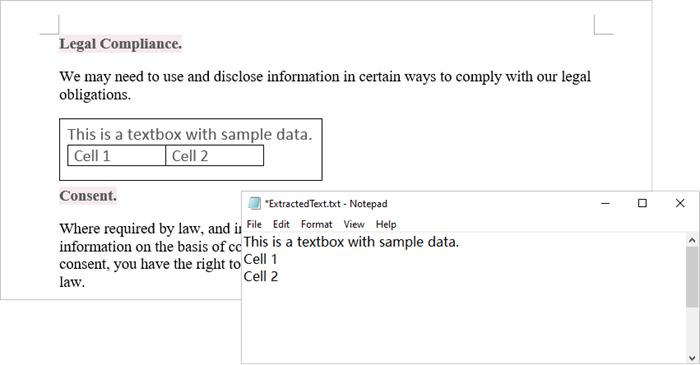
Extract Text from a Textbox in Word
Using Spire.Doc for Python, you can access a specific text box in a document by utilizing the Document.TextBoxes[index] property. After retrieving the text box, you can iterate through its child objects to identify whether each one is a paragraph or a table. If the object is a paragraph, you can retrieve its text using the Paragraph.Text property. In cases where the object is a table, you will need to loop through each cell to extract text from every individual cell within that table.
The steps to extract text from a text box in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- load a Word file by using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access a specific text box using Document.TextBoxes[index] property.
- Iterate through the child objects within the text box.
- Determine if a child object is a paragraph. If it is, retrieve the text from the paragraph using Paragraph.Text property.
- Check if a child object is a table. If so, iterate through the cells in the table to extract text from each cell.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get a specific textbox
textBox = document.TextBoxes.get_Item(0)
with open('ExtractedText.txt','w') as sw:
# Iterate through the child objects in the textbox
for i in range(textBox.ChildObjects.Count):
# Get a specific child object
object = textBox.ChildObjects.get_Item(i)
# Determine if the child object is paragraph
if object.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph:
# Write paragraph text to txt file
sw.write((object if isinstance(object, Paragraph) else None).Text + "\n")
# Determine if the child object is table
if object.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Table:
table = object if isinstance(object, Table) else None
for i in range(table.Rows.Count):
row = table.Rows[i]
for j in range(row.Cells.Count):
cell = row.Cells[j]
for k in range(cell.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = cell.Paragraphs.get_Item(k)
# Write paragrah text of a specific cell to txt file
sw.write(paragraph.Text + "\n")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
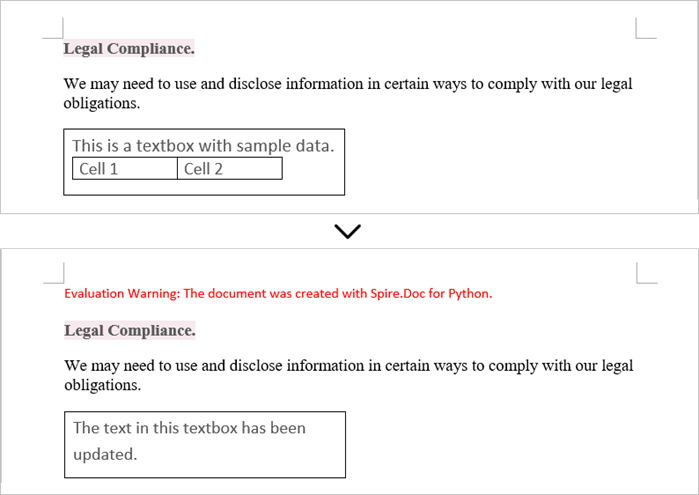
Update Text in a Textbox in Word
To update a textbox in a Word document, start by clearing its existing content with the TextBox.ChildObjects.Clear() method. This action removes all child objects, including any paragraphs or tables currently contained within the textbox. After clearing the content, you can add a new paragraph to the text box. Once the paragraph is created, set its text to the desired value.
The steps to update a textbox in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific textbox using Document.TextBoxes[index] property
- Remove existing content of the textbox using TextBox.ChildObjects.Clear() method.
- Add a paragraph to the textbox using TextBox.Body.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Get a specific textbox
textBox = document.TextBoxes.get_Item(0)
# Remove child objects of the textbox
textBox.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Add a new paragraph to the textbox
paragraph = textBox.Body.AddParagraph()
# Set line spacing
paragraph.Format.LineSpacing = 15.0
# Add text to the paragraph
textRange = paragraph.AppendText("The text in this textbox has been updated.")
# Set font size
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 15.0
# Save the document to a different Word file
document.SaveToFile("UpdateTextbox.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019);
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Programmatic editing of Word documents involves using code to alter or modify the contents of these documents. This approach enables automation and customization, making it particularly advantageous for handling large document collections. Through the use of Spire.Doc library, developers can perform a wide range of operations, including text manipulation, formatting changes, and the addition of images or tables.
The following sections will demonstrate how to edit or modify a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Modify Text in a Word Document
- Change Formatting of Text in a Word Document
- Add New Elements to a Word Document
- Remove Paragraphs from a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Modify Text in a Word Document in Python
In order to alter the content of a paragraph, the initial step is to obtain the desired paragraph from a specific section through the use of the Section.Paragraphs[index] property. Following this, you can replace the existing text with the new content by assigning it to the Paragraph.Text property of the chosen paragraph.
Here are the steps to edit text in a Word document with Python:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph using Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Reset the text of the paragraph using Paragraph.Text property.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load an existing Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections[0]
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs[0]
# Modify the text of the paragraph
paragraph.Text = "The text has been modified"
# Save the document to a different Word file
document.SaveToFile("output/ModifyText.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Dispose resource
document.Dispose()

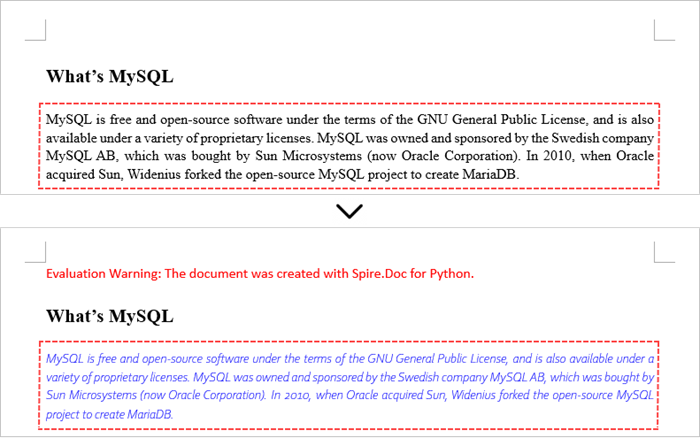
Change Formatting of Text in a Word Document in Python
To alter the text appearance of a particular paragraph, you first need to obtain the specified paragraph. Next, go through its child objects to find the individual text ranges. The formatting of each text range can then be updated using the TextRange.CharacterFormat property.
The steps to change text formatting in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph using Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph.
- Determine if a child object is a text range.
- Get a specific text range.
- Reset the text formatting using TextRange.CharacterFormat property.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(0)
# Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for i in range(paragraph.ChildObjects.Count):
# Determine if a child object is text range
if isinstance(paragraph.ChildObjects[i], TextRange):
# Get a specific text range
textRange = paragraph.ChildObjects[i]
# Reset font name
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Corbel Light"
# Reset font size
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11.0
# Reset text color
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
# Apply italic to the text range
textRange.CharacterFormat.Italic = True
# Save the document to a different Word file
doc.SaveToFile("output/ChangeFormatting.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
# Dispose resource
doc.Dispose()
Add New Elements to a Word Document in Python
In a Word document, most elements—such as text, images, lists, and charts—are fundamentally organized around the concept of a paragraph. To insert a new paragraph into a specific section, use the Section.AddParagraph() method.
After creating the new paragraph, you can add various elements to it by leveraging the methods and properties of the Paragraph object.
The steps to add new elements (text and images) to a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Add an image to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Get the last section
lastSection = doc.LastSection
# Add a paragraph to the section
paragraph = lastSection.AddParagraph()
# Add an image to the paragraph
picture = paragraph.AppendPicture("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png");
# Set text wrap style
picture.TextWrappingStyle = TextWrappingStyle.TopAndBottom
# Add text to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("This text and the image above are added by Spire.Doc for Python.")
# Create a paragraph style
style = ParagraphStyle(doc)
style.Name = "FontStyle"
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
doc.Styles.Add(style)
# Apply the style to the paragraph
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Save the document to a different Word file
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddNewElements.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
# Dispose resource
doc.Dispose()

Remove Paragraphs from a Word Document in Python
To eliminate a specific paragraph from a document, simply invoke the ParagraphCollection.RemoveAt() method and supply the index of the paragraph you intend to delete.
The steps to remove paragraphs from a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Remove a specific paragraph from the section using Section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Remove a specific paragraph
section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt(0)
# Save the document to a different Word file
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
# Dispose resource
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Superscript and subscript are formatting options that allow you to raise or lower characters in relation to the main text. Superscript is typically used for mathematical expressions, footnotes, ordinal indicators (such as "1st" or "2nd"), and chemical formulas. Subscript is commonly employed in chemical equations, mathematical notation, and certain linguistic elements. By adding superscripts and subscripts, you can enhance the readability and professionalism of your documents, especially in scientific, mathematical, and technical writing. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add superscripts and subscripts to Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Add Superscript and Subscript Text to Word in Python
- Apply Superscript and Subscript Formatting to Existing Text in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add Superscript and Subscript Text to Word in Python
You can add text to a paragraph using the Paragraph.AppentText() method. After that, you can apply superscript or subscript formatting to the text through the TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Add a section to the document using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add normal text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Add superscript or subscript text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Apply superscript or subscript formatting to the superscript or subscript text using TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Add a section to the document
section = document.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph to the section
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Add normal text to the paragraph
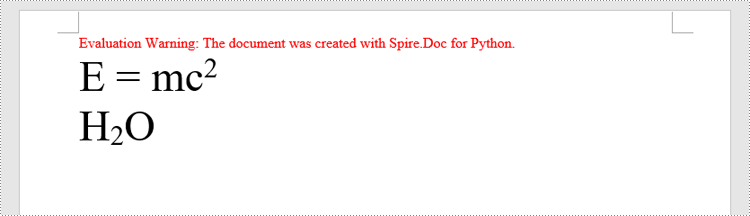
paragraph.AppendText("E = mc")
# Add superscript text to the paragraph
superscript_text = paragraph.AppendText("2")
# Apply superscript formatting to the superscript text
superscript_text.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SuperScript
# Start a new line
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add normal text to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("H")
# Add subscript text to the paragraph
subscript_text = paragraph.AppendText("2")
# Apply subscript formatting to the subscript text
subscript_text.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SubScript
# Add normal text to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("O")
# Set the font size for the text in the paragraph
for i in range(paragraph.Items.Count):
item = paragraph.Items[i]
if isinstance(item, TextRange):
text_range = item
text_range.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 36
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("AddSuperscriptAndSubscriptText.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
Apply Superscript and Subscript Formatting to Existing Text in Word in Python
To apply superscript or subscript formatting to a specific text, you need to search for the text using the Document.FindAllString() method, then apply superscript or subscript formatting to the instances of that text through the TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find a specific text in the document using Document.FindAllString() method. This method will return a list of TextSelection objects, each representing an instance of the text in the document.
- Get the first instance of the text as a single text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method, then apply superscript formatting to the text range by setting the TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property to SubSuperScript.SuperScript.
- Get the second instance of the text as a single text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method, then apply subscript formatting to the text range by setting the TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property to SubSuperScript.SubScript.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Find a specific number in the document
text_selections = document.FindAllString("2", False, False)
# Apply superscript formatting to the first instance of the number
superscript_text = text_selections[0].GetAsOneRange()
superscript_text.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SuperScript
# Apply subscript formatting to the second instance of the number
subscript_text = text_selections[1].GetAsOneRange()
subscript_text.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SubScript
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("ApplySuperscriptAndSubscriptFormatting.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Create and Execute Conditional Mail Merges in Word Documents
2024-08-09 00:54:29 Written by KoohjiConditional mail merge in Word documents is a powerful method for personalized communication at scale. Unlike other mail merges that apply the same template to all recipients, conditional mail merge allows users to customize content based on specific criteria or conditions, ensuring that each recipient receives information that is directly relevant to them. By leveraging Python, users can automate the creation and execution of conditional mail merges.
This article will show how to create and execute conditional mail merges in Word documents through Python code using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
- Execute Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
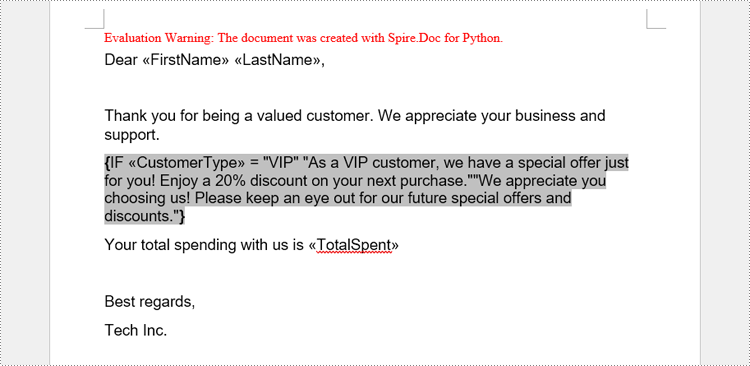
A conditional mail merge uses an If field containing a mail merge field, which alters the merge results based on the data. To add a conditional mail merge to a Word document, insert an If field, then include a mail merge field within the If field’s code, and finish by adding the field end mark to complete the setup. The condition is controlled by the code within the If field.
The detailed steps for adding a conditional mail merge to a Word document are as follows:
- Create an instance of the Document class to generate a Word document.
- Add a section to the document and configure the page setup.
- Create paragraph styles, add paragraphs, and set their formats.
- Create an IfField object, set its starting code through the IfField.Code property, and insert it into a paragraph using the Paragraph.Items.Add() method.
- Append a mail merge field to the paragraph using the Paragraph.AppendField() method.
- Append the remaining code to the paragraph using the Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Append a field end mark to end the If field using the Paragraph.AppendFieldMark() method.
- Set the end mark as the end mark of the If field through the IfField.End property.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
# Create an instance of Document
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document
section = doc.AddSection()
# Set the page size and margins
section.PageSetup.PageSize = PageSize.A4()
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 50
# Create a paragraph style
style = ParagraphStyle(doc)
style.Name = "Style1"
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 14
style.ParagraphFormat.BeforeSpacing = 5
style.ParagraphFormat.AfterSpacing = 10
doc.Styles.Add(style)
# Add paragraphs and set the style
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Dear ")
paragraph.AppendField("FirstName", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.AppendText(" ")
paragraph.AppendField("LastName", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.AppendText(",")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("\r\nThank you for being a valued customer. We appreciate your business and support.")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Add an If field to a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
ifField = IfField(doc)
ifField.Type = FieldType.FieldIf
ifField.Code = "IF "
paragraph.Items.Add(ifField)
# Add a mail merge field in the code of the If field
paragraph.AppendField("CustomerType", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.AppendText(" = ")
paragraph.AppendText("\"VIP\"")
paragraph.AppendText(" \"As a VIP customer, we have a special offer just for you! Enjoy a 20% discount on your next "
"purchase.\"")
paragraph.AppendText("\"We appreciate you choosing us! Please keep an eye out for our future special offers and "
"discounts.\"")
# Add a field end mark at the end to end the If field
endIf = paragraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldEnd)
ifField.End = endIf
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Add paragraphs and set the style
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Your total spending with us is ")
paragraph.AppendField("TotalSpent", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("\r\nBest regards,\r\nTech Inc.")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/ConditionalMailMerge.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
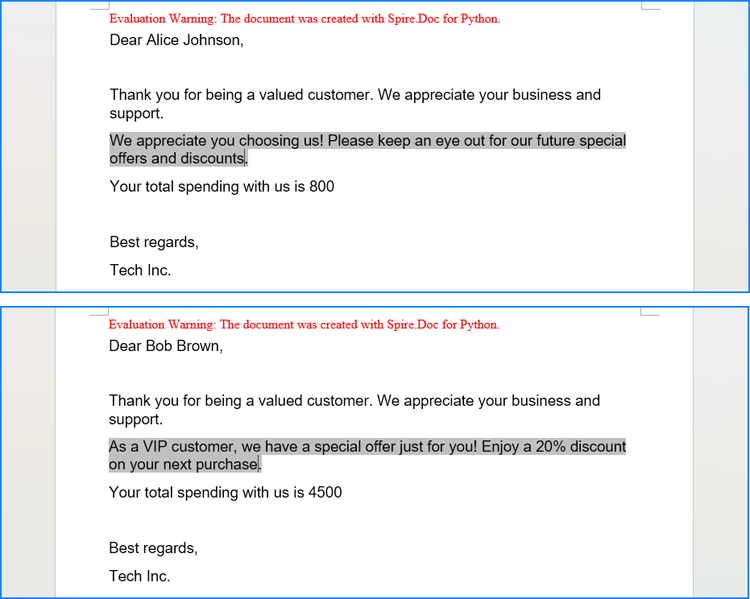
Execute Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
The Document.MailMerge.Execute(fieldNames: list[str], fieldValues: list[str]) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python allows for mail merge operations within Word documents. After the merge, you can update the results of conditional mail merges by setting the Document.IsUpdateFields property to True. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Read the data in the table used for the merge as a two-dimensional list.
- Iterate through the data rows, skipping the header:
- Create an instance of the Document class and load the Word document to be merged.
- Get the names of the mail merge fields as a list using the Document.MailMerge.GetMergeFieldNames() method.
- Execute the mail merge with the data using the Document.MailMerge.Execute() method.
- Update the If field by setting the Document.IsUpdateFields property to True.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
import csv
# Read the data from a CSV file
data = []
with open("Customers.csv", "r") as csvfile:
read = csv.reader(csvfile)
for row in read:
data.append(row)
# Iterate through the data rows by skipping the header
for i in range(1, len(data)):
# Create an instance of Document and load a Word document
doc = Document("output/ConditionalMailMerge.docx")
# Get the field names from the document
fieldNames = doc.MailMerge.GetMergeFieldNames()
# Execute the mail merge
doc.MailMerge.Execute(fieldNames, data[i])
# Update the If field
doc.IsUpdateFields = True
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile(f"output/Customers/{data[i][0]} {data[i][1]}.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In Microsoft Word, adding, adjusting, and removing page borders is an effective strategy to enhance the aesthetics and professionalism of your documents. The inclusion of borders can lend a page a more refined and dignified appearance, particularly suitable for formal contexts such as reports, certificates, or invitations, conveying a sense of meticulous elegance. By customizing the color, pattern, and thickness of borders, users can ingeniously integrate personal creativity according to the document theme, crafting a unique design style that makes the content more captivating. Conversely, opting to remove borders can achieve a streamlined page layout, effectively eliminating unnecessary visual clutter—a practice especially fitting for those pursuing minimalist aesthetics or aiming to save on printing costs. This article will introduce how to add, modify, or remove Word page borders in Python projects using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your VS Code through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
Python Add Word Page Borders
When setting page borders in a Word document using the Spire.Doc library, you can achieve this by invoking the Section.PageSetup.Borders property. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Use a for loop to iterate through each section (Section) in the document.
- Apply borders to all pages by setting the Section.PageSetup.PageBordersApplyType property to PageBordersApplyType.AllPages.
- Set the page border style using the Secton.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.DashDotStroker) method.
- Define the border width using the Section.PageSetup.Borders.LineWidth(2) method.
- Set the border color using the Section.PageSetup.Borders.Color(Color.get_Orange()) method.
- Set the distance between the border and the page content using the Section.PageSetup.Borders.Top.Space, Bottom.Space, Left.Space, and Right.Space properties.
- Save the changes to a Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load an existing Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample01.docx")
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
# Set borders for all pages in the current section
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.PageBordersApplyType = PageBordersApplyType.AllPages
# Set border style
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.DashDotStroker)
# Set border width
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.LineWidth(2)
# Set border color
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Color(Color.get_Orange())
# Set the distance between the top border and page content
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Top.Space = 20.0
# Set the distance between the bottom border and page content
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Bottom.Space = 20.0
# Set the distance between the left border and page content
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Left.Space = 20.0
# Set the distance between the right border and page content
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Right.Space = 20.0
# Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("AddWordPageBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Release resources used by the Document object
doc.Dispose()

Python Modify Word Page Borders
Leveraging the Spire.Doc library, we can extensively customize the page borders in Word documents, including the style, hue, width, and other visual attributes of the borders. By tweaking these properties, achieving the desired visual presentation becomes effortless. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the first section of the document using Document.Sections.get_Item(0).
- Alter the page border style using the Section.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.DoubleWave) method.
- Change the color of the page border with the Section.PageSetup.Borders.Color(Color.get_Orange()) method.
- Adjust the width of the page border through the Section.PageSetup.Borders.LineWidth(2) method.
- Save the changes to a Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load an existing Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample02.docx")
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Set border style
section.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.DoubleWave)
# Set border color
section.PageSetup.Borders.Color(Color.get_Orange())
# Set border width
section.PageSetup.Borders.LineWidth(2)
# Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifyWordPageBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Release resources occupied by the Document object
doc.Dispose()

Python Remove Word Page Borders
To remove page borders in Word, you can use the Section.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.none) method. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Use a for loop to iterate through each section (Section) in the document.
- Apply the Section.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.none) method to remove the page borders.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load an existing Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample02.docx")
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
# Remove page borders
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.none)
# Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("RemoveWordPageBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Release the resources occupied by the Document object
doc.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is widely used for its structured format and readability on different platforms and systems. Its self-descriptive tags enable you to process data more easily. Meanwhile, Word XML focuses specifically on storing and exchanging Microsoft Word documents. It allows Word documents to transfer without loss. They both show flexibility under various scenarios that Word documents cannot achieve.
On the page, you will learn how to convert Word to XML and Word XML formats using Python with Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows.
Convert Word to XML in Python with Spire.Doc for Python
This part will explain how to convert Word documents to XML in Python with step-by-step instructions and a code example. Spire.Doc for Python provides the Document.SaveToFile() method to make it easy to save Word as XML. Check out the steps below and start processing your Word documents without effort!
Steps to Convert Word to XML:
- Create a new Document object.
- Load the Word document that you wish to be operated using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Covert it to XML by calling Document.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Word document object
document = Document()
# Load the file from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx")
# Save the document to an XML file
document.SaveToFile("WordtoXML.xml", FileFormat.Xml)
document.Close()

Convert Word to Word XML in Python
To convert Word to Word XML, you can utilize the Document.SaveToFile() method provided by Spire.Doc for Python. It not only helps to convert Word documents to Word XML but also to many other formats, such as PDF, XPS, HTML, RTF, etc.
Steps to Convert Word to Word XML:
- Create a new Document object.
- Load the Word document by Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert it to Word XML using Document.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example for you:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Word document object
document = Document()
# Load the file from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx")
# For Word 2003
document.SaveToFile("WordtoWordML.wordml", FileFormat.WordML)
# For Word 2007-2013
document.SaveToFile("WordtoWordXML.wordxml", FileFormat.WordXml)
document.Close()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
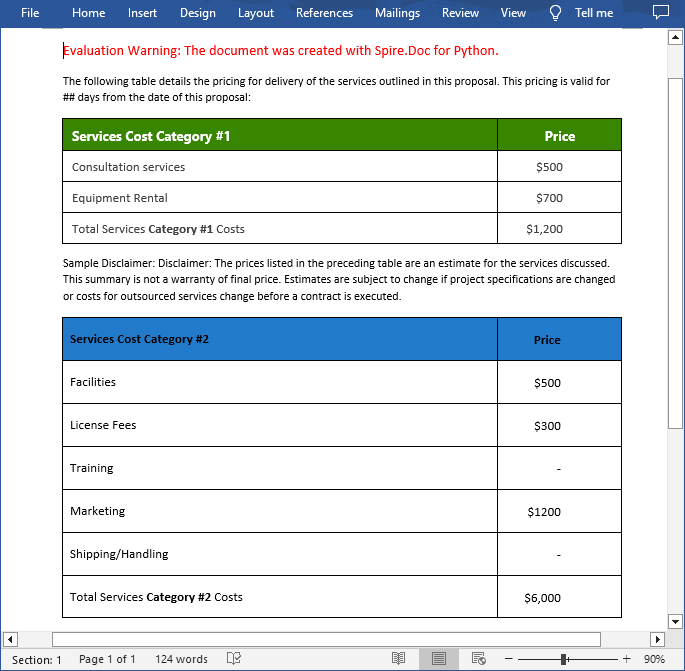
Merge tables in Word can be useful when you want to combine data from multiple tables into a single, larger table to create a more comprehensive view of the information. On the contrary, split tables can help you divide a large table into smaller, more manageable sections so you can focus on specific data sets. This article will demonstrate how to merge or split tables in Word in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Merge Tables in Word in Python
With Spire.Doc for Python, you can combine two or more tables into one by copying all rows from other tables to the target table and then deleting the other tables. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get two tables in the section using Section.Tables[] property.
- Iterate through all rows in the second table and copy them using Table.Rows[].Clone() method.
- Add the rows of the second table to the first table using Table.Rows.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "Cost.docx"
outputFile = "CombineTables.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Get the first and second table in the section
table1 = section.Tables[0] if isinstance(section.Tables[0], Table) else None
table2 = section.Tables[1] if isinstance(section.Tables[1], Table) else None
# Add rows of the second table to the first table
for i in range(table2.Rows.Count):
table1.Rows.Add(table2.Rows[i].Clone())
# Remove the second table
section.Tables.Remove(table2)
# Save the result document
section.Document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()
Spilt a Table in Word in Python
To split a table into two or more tables, you need to create a new table, then copy the specified rows from the original table to the new table, and then delete those rows from the original table. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get a specified table in the section using Section.Tables[] property.
- Specify the row index where the table will be split.
- Create a new instance of the Table class.
- Iterate through the specified rows in the original table and copy them using Table.Rows[].Clone() method.
- Add the specified rows to the new table using Table.Rows.Add() method.
- Iterate through the copied rows and remove each row from the original table using Table.Rows.RemoveAt() method.
- Add the new table to the section using Section.Tables.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "CombineTables.docx"
outputFile = "SplitTable.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Get the first table in the section
table = section.Tables[0] if isinstance(section.Tables[0], Table) else None
# Specify to split the table from the fifth row
splitIndex = 4
# Create a new table
newTable = Table(section.Document, True)
# Adds rows (from the 5th to the last row) to the new table
for i in range(splitIndex, table.Rows.Count):
newTable.Rows.Add(table.Rows[i].Clone())
# Delete rows from the original table
for i in range(table.Rows.Count - 1, splitIndex - 1, -1):
table.Rows.RemoveAt(i)
# Add the new table to the section
section.Tables.Add(newTable)
# Save the result document
section.Document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
