
Spire.Doc for Python (98)
During the process of document creation, it is common to encounter numerous blank lines. These empty spaces can disrupt the flow of the content, clutter the layout, and undermine the overall aesthetic presentation of the document. In order to optimize the reading experience and ensure a well-structured document, it becomes crucial to eliminate the blank lines. This article will demonstrate how to delete blank lines from Word documents through Python programs using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Remove Blank Lines from Word Documents
Blank lines in a Word document appear as blank paragraphs, which are child objects of sections. Therefore, removing blank lines simply requires iterating through the sections, identifying and deleting empty paragraphs within them. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each section and each child object of the sections.
- First, check if a child object is of paragraph type. If it is, continue to check if the sub-object is an instance of the "Paragraph" class. If it is, further check if the paragraph has no text. If there is no text, delete the paragraph using Section.Body.ChildObjects.Remove() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Iterate through each section in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
j = 0
# Iterate through each child object in the section
while j < section.Body.ChildObjects.Count:
# Check if the child object is of type Paragraph
if section.Body.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph:
objItem = section.Body.ChildObjects[j]
# Check if the child object is an instance of the Paragraph class
if isinstance(objItem, Paragraph):
paraObj = Paragraph(objItem)
# Check if the paragraph text is empty
if len(paraObj.Text) == 0:
# If the paragraph text is empty, remove the object from the section's child objects list
section.Body.ChildObjects.Remove(objItem)
j -= 1
j += 1
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveBlankLines.docx")

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Hyperlinks are an essential component of creating dynamic and interactive Word documents. By linking specific text or objects to other documents, web pages, email addresses, or specific locations within the same document, hyperlinks allow users to navigate through information seamlessly. In this article, you will learn how to add or remove hyperlinks in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add Hyperlinks to Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Paragraph.AppendHyperlink() method to add a web link, an email link, a file link, or a bookmark link to a piece of text or an image inside a paragraph. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section and a paragraph to it.
- Insert a hyperlink based on text using Paragraph.AppendHyerplink(link: str, text: str, type: HyperlinkType) method.
- Add an image to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method.
- Insert a hyperlink based on the image using Paragraph.AppendHyerplink(link: str, picture: DocPicture, type: HyperlinkType) method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Word document
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
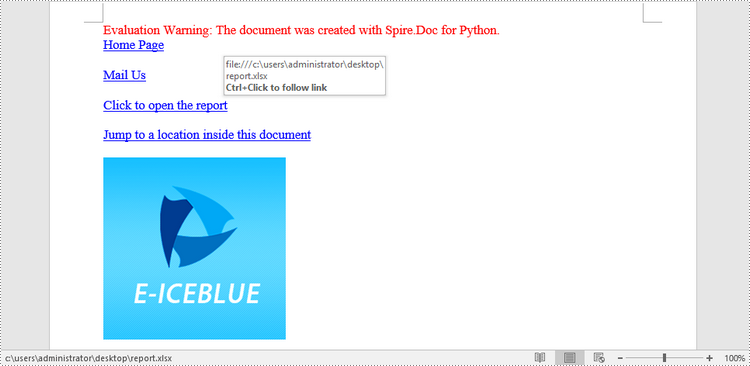
paragraph.AppendHyperlink("https://www-iceblue.com/", "Home Page", HyperlinkType.WebLink)
# Append line breaks
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add an email link
paragraph.AppendHyperlink("mailto:support@e-iceblue.com", "Mail Us", HyperlinkType.EMailLink)
# Append line breaks
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add a file link
filePath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\report.xlsx"
paragraph.AppendHyperlink(filePath, "Click to open the report", HyperlinkType.FileLink)
# Append line breaks
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add another section and create a bookmark
section2 = doc.AddSection()
bookmarkParagrapg = section2.AddParagraph()
bookmarkParagrapg.AppendText("Here is a bookmark")
start = bookmarkParagrapg.AppendBookmarkStart("myBookmark")
bookmarkParagrapg.Items.Insert(0, start)
bookmarkParagrapg.AppendBookmarkEnd("myBookmark")
# Link to the bookmark
paragraph.AppendHyperlink("myBookmark", "Jump to a location inside this document", HyperlinkType.Bookmark)
# Append line breaks
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add an image link
image = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png"
picture = paragraph.AppendPicture(image)
paragraph.AppendHyperlink("https://www.e-iceblue.com/", picture, HyperlinkType.WebLink)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/CreateHyperlinks.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019);
doc.Dispose()
Remove Hyperlinks from Word in Python
To delete all hyperlinks in a Word document at once, you'll need to find all the hyperlinks in the document and then create a custom method FlattenHyperlinks() to flatten them. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a sample Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find all the hyperlinks in the document using custom method FindAllHyperlinks().
- Loop through the hyperlinks and flatten all of them using custom method FlattenHyperlinks().
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Find all the hyperlinks in a document
def FindAllHyperlinks(document):
hyperlinks = []
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
section = document.Sections.get_Item(i)
for j in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
sec = section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
if sec.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph:
for k in range((sec if isinstance(sec, Paragraph) else None).ChildObjects.Count):
para = (sec if isinstance(sec, Paragraph)
else None).ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
if para.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Field:
field = para if isinstance(para, Field) else None
if field.Type == FieldType.FieldHyperlink:
hyperlinks.append(field)
return hyperlinks
# Flatten the hyperlink fields
def FlattenHyperlinks(field):
ownerParaIndex = field.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.IndexOf(
field.OwnerParagraph)
fieldIndex = field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field)
sepOwnerPara = field.Separator.OwnerParagraph
sepOwnerParaIndex = field.Separator.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.IndexOf(
field.Separator.OwnerParagraph)
sepIndex = field.Separator.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(
field.Separator)
endIndex = field.End.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field.End)
endOwnerParaIndex = field.End.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.IndexOf(
field.End.OwnerParagraph)
FormatFieldResultText(field.Separator.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody,
sepOwnerParaIndex, endOwnerParaIndex, sepIndex, endIndex)
field.End.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(endIndex)
for i in range(sepOwnerParaIndex, ownerParaIndex - 1, -1):
if i == sepOwnerParaIndex and i == ownerParaIndex:
for j in range(sepIndex, fieldIndex - 1, -1):
field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j)
elif i == ownerParaIndex:
for j in range(field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.Count - 1, fieldIndex - 1, -1):
field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j)
elif i == sepOwnerParaIndex:
for j in range(sepIndex, -1, -1):
sepOwnerPara.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j)
else:
field.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(i)
# Convert fields to text range and clear the text formatting
def FormatFieldResultText(ownerBody, sepOwnerParaIndex, endOwnerParaIndex, sepIndex, endIndex):
for i in range(sepOwnerParaIndex, endOwnerParaIndex + 1):
para = ownerBody.ChildObjects[i] if isinstance(
ownerBody.ChildObjects[i], Paragraph) else None
if i == sepOwnerParaIndex and i == endOwnerParaIndex:
for j in range(sepIndex + 1, endIndex):
if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[j], TextRange):
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j])
elif i == sepOwnerParaIndex:
for j in range(sepIndex + 1, para.ChildObjects.Count):
if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[j], TextRange):
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j])
elif i == endOwnerParaIndex:
for j in range(0, endIndex):
if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[j], TextRange):
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j])
else:
for j, unusedItem in enumerate(para.ChildObjects):
if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[j], TextRange):
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j])
# Format text
def FormatText(tr):
tr.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Black()
tr.CharacterFormat.UnderlineStyle = UnderlineStyle.none
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.docx")
# Get all hyperlinks
hyperlinks = FindAllHyperlinks(doc)
# Flatten all hyperlinks
for i in range(len(hyperlinks) - 1, -1, -1):
FlattenHyperlinks(hyperlinks[i])
# Save to a different file
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveHyperlinks.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Adding or removing rows and columns in a Word table allows you to adjust the table's structure to accommodate your data effectively. By adding rows and columns, you can effortlessly expand the table as your data grows, ensuring that all relevant information is captured and displayed in a comprehensive manner. On the other hand, removing unnecessary rows and columns allows you to streamline the table, eliminating any redundant or extraneous data that may clutter the document. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add or delete table rows and columns in Word in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Add or Insert a Row into a Word Table in Python
- Add or Insert a Column into a Word Table in Python
- Delete a Row from a Word Table in Python
- Delete a Column from a Word Table in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add or Insert a Row into a Word Table in Python
You can add a row to the end of a Word table or insert a row at a specific location of a Word table using the Table.AddRow() or Table.InsertRow() method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section of the document using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get the first table of the section using Section.Tables[] property.
- Insert a row at a specific location of the table using Table.Rows.Insert() method.
- Add data to the newly inserted row.
- Add a row to the end of the table using Table.AddRow() method.
- Add data to the newly added row.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Table1.docx")
# Get the first section of the document
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the first table of the first section
table = section.Tables.get_Item(0) if isinstance(section.Tables.get_Item(0), Table) else None
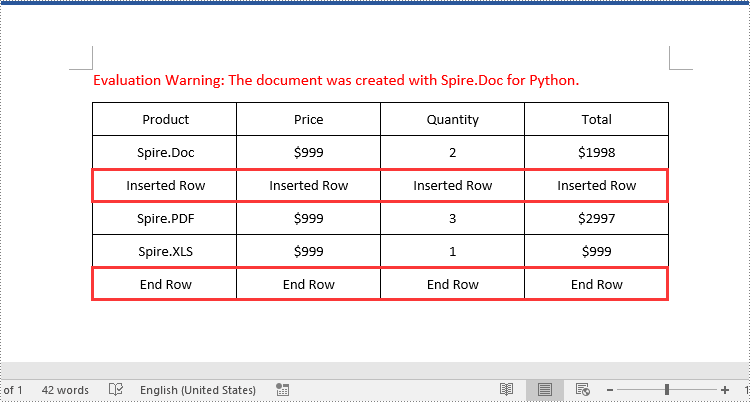
# Insert a row into the table as the third row
table.Rows.Insert(2, table.AddRow())
# Get the inserted row
insertedRow = table.Rows[2]
# Add data to the row
for i in range(insertedRow.Cells.Count):
cell = insertedRow.Cells[i]
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Inserted Row")
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
# Add a row at the end of the table
addedRow = table.AddRow()
# Add data to the row
for i in range(addedRow.Cells.Count):
cell = addedRow.Cells[i]
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("End Row")
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("AddRows.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
Add or Insert a Column into a Word Table in Python
Spire.Doc for Python doesn't offer a direct method to add or insert a column into a Word table. But you can achieve this by adding or inserting cells at a specific location of each table row using TableRow.Cells.Add() or TableRow.Cells.Insert() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section of the document using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get the first table of the section using Section.Tables[] property.
- Loop through each row of the table.
- Create a TableCell object, then insert it at a specific location of each row using TableRow.Cells.Insert() method and set cell width.
- Add data to the cell and set text alignment.
- Add a cell to the end of each row using TableRow.AddCell() method and set cell width.
- Add data to the cell and set text alignment.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Table1.docx")
# Get the first section of the document
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the first table of the first section
table = section.Tables.get_Item(0) if isinstance(section.Tables.get_Item(0), Table) else None
# Loop through the rows of the table
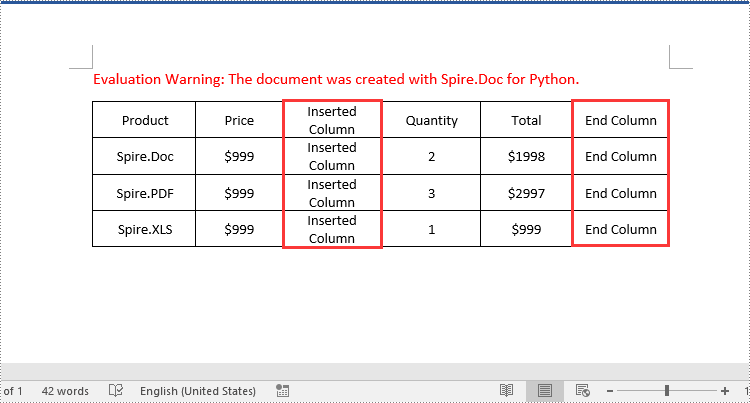
for i in range(table.Rows.Count):
row = table.Rows.get_Item(i)
# Create a TableCell object
cell = TableCell(document)
# Insert the cell as the third cell of the row and set cell width
row.Cells.Insert(2, cell)
cell.Width = row.Cells[0].Width
# Add data to the cell
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Inserted Column")
# Set text alignment
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
# Add a cell to the end of the row and set cell width
cell = row.AddCell()
cell.Width = row.Cells[1].Width
# Add data to the cell
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("End Column")
# Set text alignment
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("AddColumns.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
Delete a Row from a Word Table in Python
To delete a specific row from a Word table, you can use the Table.Rows.RemoveAt() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section of the document using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get the first table of the section using Section.Tables[] property.
- Remove a specific row from the table using Table.Rows.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("AddRows.docx")
# Get the first section of the document
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the first table of the first section
table = section.Tables.get_Item(0) if isinstance(section.Tables.get_Item(0), Table) else None
# Remove the third row
table.Rows.RemoveAt(2)
# Remove the last row
table.Rows.RemoveAt(table.Rows.Count - 1)
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveRows.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
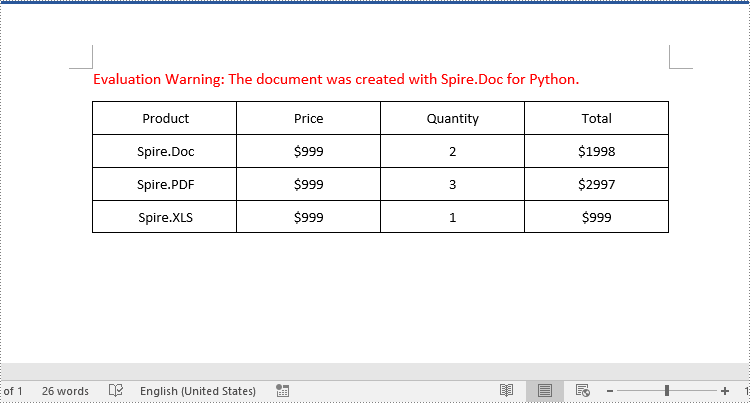
Delete a Column from a Word Table in Python
To delete a specific column from a Word table, you need to remove the corresponding cell from each table row using the TableRow.Cells.RemoveAt() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section of the document using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get the first table of the section using Section.Tables[] property.
- Loop through each row of the table.
- Remove a specific cell from each row using TableRow.Cells.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("AddColumns.docx")
# Get the first section of the document
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the first table of the first section
table = section.Tables.get_Item(0) if isinstance(section.Tables.get_Item(0), Table) else None
# Loop through the rows of the table
for i in range(table.Rows.Count):
row = table.Rows.get_Item(i)
# Remove the third cell from the row
row.Cells.RemoveAt(2)
# Remove the last cell from the row
row.Cells.RemoveAt(row.Cells.Count - 1)
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveColumns.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
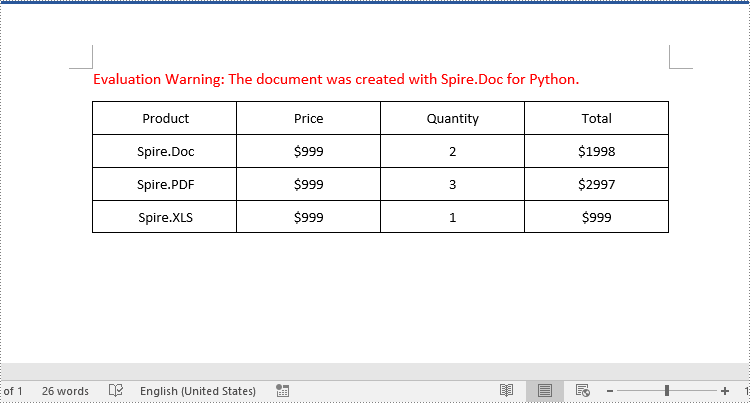
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Converting a Word document into images can be a useful and convenient option when you want to share or present the content without worrying about formatting issues or compatibility across devices. By converting a Word document into images, you can ensure that the text, images, and formatting remain intact, making it an ideal solution for sharing documents on social media, websites, or through email. In this article, you will learn how to convert Word to PNG, JPEG or SVG in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
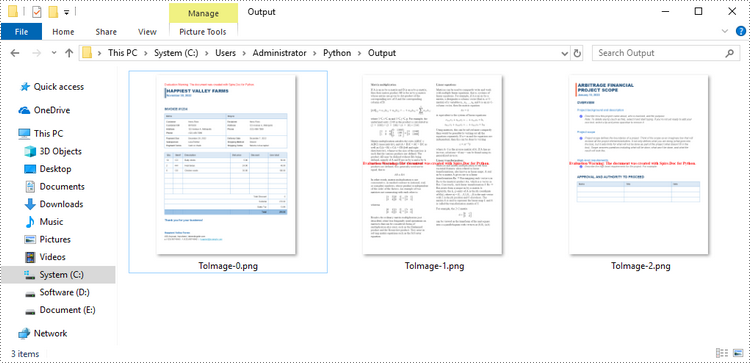
Convert Word to PNG or JPEG in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Document.SaveImageToStream() method to convert a certain page into a bitmap image. Afterwards, you can save the bitmap image to a popular image format such as PNG, JPEG, or BMP. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve each page in the document, and convert a specific page into a bitmap image using Document.SaveImageToStreams() method.
- Save the bitmap image into a PNG or JPEG file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Loop through the pages in the document
for i in range(document.GetPageCount()):
# Convert a specific page to bitmap image
imageStream = document.SaveImageToStreams(i, ImageType.Bitmap)
# Save the bitmap to a PNG file
with open('Output/ToImage-{0}.png'.format(i),'wb') as imageFile:
imageFile.write(imageStream.ToArray())
document.Close()
Convert Word to SVG in Python
To convert a Word document into multiple SVG files, you can simply use the Document.SaveToFile() method. Here are the steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert it to individual SVG files using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Convert it to SVG files
document.SaveToFile("output/ToSVG.svg", FileFormat.SVG)
document.Close()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Watermarks in Word documents serve as overlayed text or pictures that are typically used to indicate documents’ status, confidentiality, draft nature, etc. While they are useful in certain contexts, watermarks often become a hindrance when it comes to presenting documents. They can be distracting, obscuring the readability, and reduce the overall quality of the document. This article will show how to remove watermarks from Word documents in Python programs using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Remove the Watermark from a Word Document
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Document.Watermark property which allows users to deal with the watermark of a Word document. Users can assign a null value to this property to remove the watermark of Word document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove the watermark by assigning a null value to Document.Watermark property.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Remove the watermark
doc.Watermark = None
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveWatermark.docx", FileFormat.Auto)

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Images in Word documents can break up large blocks of text and make the content more visually interesting. In addition, they can also effectively illustrate complex ideas or concepts that are difficult to explain solely through text. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically add images to a Word document using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert an Image in a Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Paragraph.AppendPicture() method to insert an image into a Word document. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add two paragraphs to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraphs and set formatting.
- Load an image and add it to a specified paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method.
- Set width and height for the image using DocPicture.Width and DocPicture.Height properties.
- Set a text wrapping style for the image using DocPicture.TextWrappingStyle property.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Add a seciton
section = document.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph
paragraph1 = section.AddParagraph()
# Add text to the paragraph and set formatting
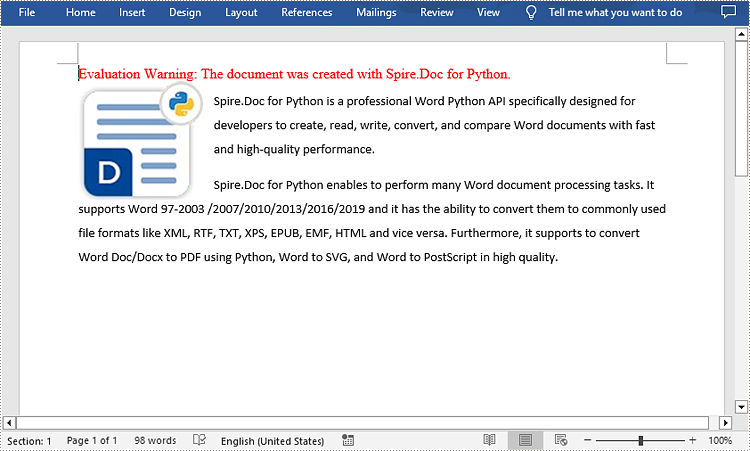
tr = paragraph1.AppendText("Spire.Doc for Python is a professional Word Python API specifically designed for developers to create, read, write, convert, and compare Word documents with fast and high-quality performance.")
tr.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri"
tr.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11
paragraph1.Format.LineSpacing = 18
paragraph1.Format.BeforeSpacing = 10
paragraph1.Format.AfterSpacing = 10
# Add another paragraph
paragraph2 = section.AddParagraph()
tr = paragraph2.AppendText("Spire.Doc for Python enables to perform many Word document processing tasks. It supports Word 97-2003 /2007/2010/2013/2016/2019 and it has the ability to convert them to commonly used file formats like XML, RTF, TXT, XPS, EPUB, EMF, HTML and vice versa. Furthermore, it supports to convert Word Doc/Docx to PDF using Python, Word to SVG, and Word to PostScript in high quality.")
# Add text to the paragraph and set formatting
tr.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri"
tr.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11
paragraph2.Format.LineSpacing = 18
# Add an image to the specified paragraph
picture = paragraph1.AppendPicture("Spire.Doc.jpg")
# Set image width and height
picture.Width = 100
picture.Height = 100
# Set text wrapping style for the image
picture.TextWrappingStyle = TextWrappingStyle.Square
#Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("InsertImage.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
document.Close()
Insert an Image at a Specified Location in a Word document in Python
If you wish to place the image at a specified location in the Word document, you can set its position through the DocPicture.HorizontalPosition and DocPicture.VerticalPosition properties. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraph and set formatting.
- Add an image to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method.
- Set width and height for the image using DocPicture.Width and DocPicture.Height properties.
- Set the horizontal position and vertical position for the image using DocPicture.HorizontalPosition and DocPicture.VerticalPosition properties.
- Set a text wrapping style for the image using DocPicture.TextWrappingStyle property.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph to the section
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Add text to the paragraph and set formatting
paragraph.AppendText("The sample demonstrates how to insert an image at a specified location in a Word document.")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading2)
# Add an image to the paragraph
picture = paragraph.AppendPicture("pic.jpg")
# Set image position
picture.HorizontalPosition = 150.0
picture.VerticalPosition = 60.0
# Set image size
picture.Width = 120.0
picture.Height = 180.0
# Set a text wrapping style for the image (note that the position settings are not applicable when the text wrapping style is Inline)
picture.TextWrappingStyle = TextWrappingStyle.Through
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("WordImage.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Text files are a common file type that contain only plain text without any formatting or styles. If you want to apply formatting or add images, charts, tables, and other media elements to text files, one of the recommended solutions is to convert them to Word files.
Conversely, if you want to efficiently extract content or reduce the file size of Word documents, you can convert them to text format. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically convert text files to Word format and convert Word files to text format using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Convert Text (TXT) to Word in Python
Conversion from TXT to Word is quite simple that requires only a few lines of code. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a text file using Document.LoadFromFile(string fileName) method.
- Save the text file as a Word file using Document.SaveToFile(string fileName, FileFormat fileFormat) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a TXT file
document.LoadFromFile("input.txt")
# Save the TXT file as Word
document.SaveToFile("TxtToWord.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Convert Word to Text (TXT) in Python
The Document.SaveToFile(string fileName, FileFormat.Txt) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python allows you to export a Word file to text format. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file using Document.LoadFromFile(string fileName) method.
- Save the Word file in txt format using Document.SaveToFile(string fileName, FileFormat.Txt) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file from disk
document.LoadFromFile("Input.docx")
# Save the Word file in txt format
document.SaveToFile("WordToTxt.txt", FileFormat.Txt)
document.Close()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
By extracting text from Word documents, you can effortlessly obtain the written information contained within them. This allows for easier manipulation, analysis, and organization of textual content, enabling tasks such as text mining, sentiment analysis, and natural language processing. Extracting images, on the other hand, provides access to visual elements embedded within Word documents, which can be crucial for tasks like image recognition, content extraction, or creating image databases. In this article, you will learn how to extract text and images from a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Extract Text from a Specific Paragraph in Python
- Extract Text from an Entire Word Document in Python
- Extract Images from an Entire Word Document in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Extract Text from a Specific Paragraph in Python
To get a certain paragraph from a section, use Section.Paragraphs[index] property. Then, you can get the text of the paragraph through Paragraph.Text property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph through Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Get text from the paragraph through Paragraph.Text property.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(2)
# Get text from the paragraph
str = paragraph.Text
# Print result
print(str)
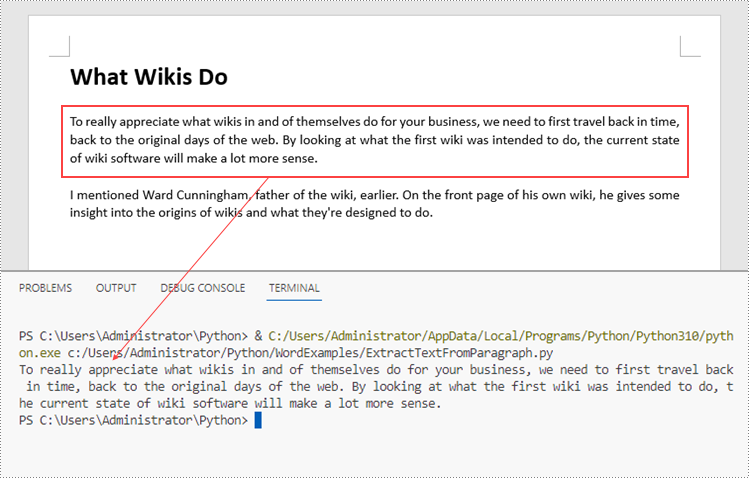
Extract Text from an Entire Word Document in Python
If you want to get text from a whole document, you can simply use Document.GetText() method. Below are the steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get text from the document using Document.GetText() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get text from the entire document
str = doc.GetText()
# Print result
print(str)

Extract Images from an Entire Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python does not provide a straightforward method to get images from a Word document. You need to iterate through the child objects in the document, and determine if a certain a child object is a DocPicture. If yes, you get the image data using DocPicture.ImageBytes property and then save it as a popular image format file. The main steps are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through the child objects in the document.
- Determine if a specific child object is a DocPicture. If yes, get the image data through DocPicture.ImageBytes property.
- Write the image data as a PNG file.
- Python
import queue
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Create a Queue object
nodes = queue.Queue()
nodes.put(doc)
# Create a list
images = []
while nodes.qsize() > 0:
node = nodes.get()
# Loop through the child objects in the document
for i in range(node.ChildObjects.Count):
child = node.ChildObjects.get_Item(i)
# Determine if a child object is a picture
if child.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Picture:
picture = child if isinstance(child, DocPicture) else None
dataBytes = picture.ImageBytes
# Add the image data to the list
images.append(dataBytes)
elif isinstance(child, ICompositeObject):
nodes.put(child if isinstance(child, ICompositeObject) else None)
# Loop through the images in the list
for i, item in enumerate(images):
fileName = "Image-{}.png".format(i)
with open("ExtractedImages/"+fileName,'wb') as imageFile:
# Write the image to a specified path
imageFile.write(item)
doc.Close()
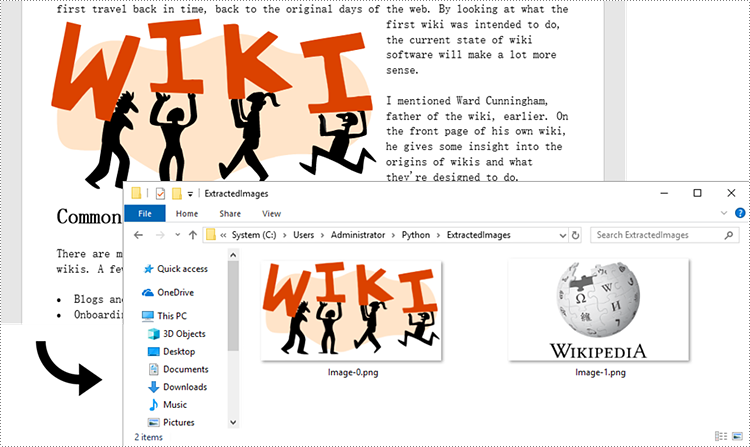
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Creating, reading, and updating Word documents is a common need for many developers working with the Python programming language. Whether it's generating reports, manipulating existing documents, or automating document creation processes, having the ability to work with Word documents programmatically can greatly enhance productivity and efficiency. In this article, you will learn how to create, read, or update Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Word Document from Scratch in Python
- Read Text of a Word Document in Python
- Update a Word Document in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create a Word Document from Scratch in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Document class to represent a Word document model. A document must contain at least one section (represented by the Section class) and each section is a container for various elements such as paragraphs, tables, charts, and images. This example shows you how to create a simple Word document containing several paragraphs using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Set the page margins through Section.PageSetUp.Margins property.
- Add several paragraphs to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraphs using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Create a ParagraphStyle object, and apply it to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Set the page margins
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 40
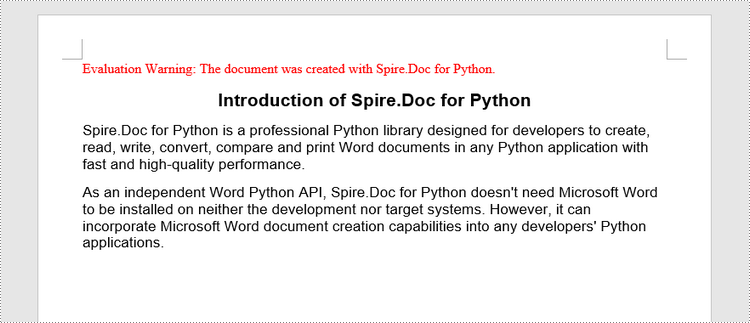
# Add a title
titleParagraph = section.AddParagraph()
titleParagraph.AppendText("Introduction of Spire.Doc for Python")
# Add two paragraphs
bodyParagraph_1 = section.AddParagraph()
bodyParagraph_1.AppendText("Spire.Doc for Python is a professional Python library designed for developers to " +
"create, read, write, convert, compare and print Word documents in any Python application " +
"with fast and high-quality performance.")
bodyParagraph_2 = section.AddParagraph()
bodyParagraph_2.AppendText("As an independent Word Python API, Spire.Doc for Python doesn't need Microsoft Word to " +
"be installed on neither the development nor target systems. However, it can incorporate Microsoft Word " +
"document creation capabilities into any developers' Python applications.")
# Apply heading1 to the title
titleParagraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading1)
# Create a style for the paragraphs
style2 = ParagraphStyle(doc)
style2.Name = "paraStyle"
style2.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
style2.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 13
doc.Styles.Add(style2)
bodyParagraph_1.ApplyStyle("paraStyle")
bodyParagraph_2.ApplyStyle("paraStyle")
# Set the horizontal alignment of the paragraphs
titleParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
bodyParagraph_1.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
bodyParagraph_2.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
# Set the after spacing
titleParagraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 10
bodyParagraph_1.Format.AfterSpacing = 10
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/WordDocument.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
Read Text of a Word Document in Python
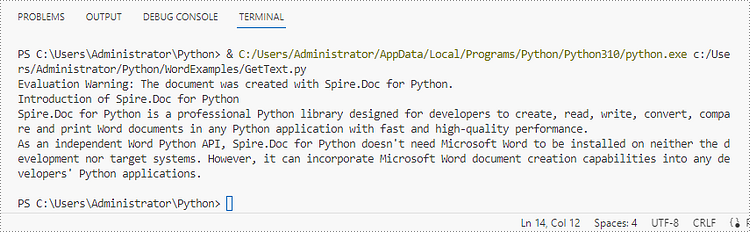
To get the text of an entire Word document, you could simply use Document.GetText() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get text from the entire document using Document.GetText() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\WordDocument.docx")
# Get text from the entire document
text = doc.GetText()
# Print text
print(text)
Update a Word Document in Python
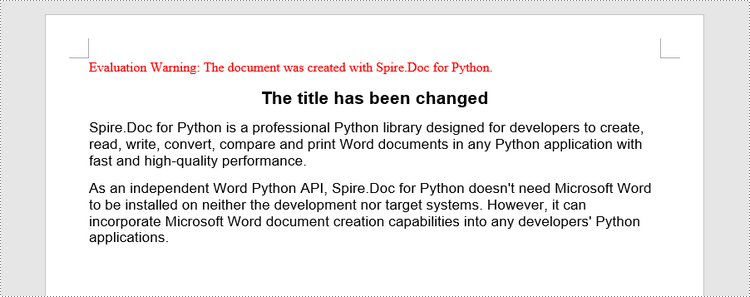
To access a specific paragraph, you can use the Section.Paragraphs[index] property. If you want to modify the text of the paragraph, you can reassign text to the paragraph through the Paragraph.Text property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph through Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Change the text of the paragraph through Paragraph.Text property.
- Save the document to another Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\WordDocument.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(1)
# Change the text of the paragraph
paragraph.Text = "The title has been changed"
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Updated.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A watermark is a semitransparent text or an image placed behind the content of a document. In Word, you can add a watermark to protect the intellectual property of the document, for example to include a copyright symbol, author's name or company logo. Or you can use it to indicate the status of a document, such as "Draft", "Confidential", or "Final". This article will demonstrate how to add text watermarks and image watermarks to Word in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add a Text Watermark to a Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the TextWatermark class to set a text watermark, and then you can add it to Word document through Document.Watermark property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a sample Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create an instance of TextWatermark class.
- Set the text, font size, color and layout of the text watermark using the methods of TextWatermark class.
- Add the text watermark to the Word document using Document.Watermark property.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("test.docx")
# Create a TextWatermark object
txtWatermark = TextWatermark()
# Set the format of the text watermark
txtWatermark.Text = "DO NOT COPY"
txtWatermark.FontSize = 65
txtWatermark.Color = Color.get_Red()
txtWatermark.Layout = WatermarkLayout.Diagonal
# Add the text watermark to document
document.Watermark = txtWatermark
#Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("Output/TextWatermark.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
document.Close()
Add an Image Watermark in a Word Document in Python
To set the image watermark, you can use the methods of PictureWatermark class. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a sample Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create an instance of PictureWatermark class.
- Load an image as the image watermark using PictureWatermark.SetPicture() method, and then set scaling as well as washout property of the image watermark.
- Add the image watermark to the Word document using Document.Watermark property.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("test.docx")
# Create a PictureWatermark object
picture = PictureWatermark()
# Set the format of the picture watermark
picture.SetPicture("logo.png")
picture.Scaling = 100
picture.IsWashout = False
# Add the image watermark to document
document.Watermark = picture
#Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("Output/ImageWatermark.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
document.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
