
Program Guide (108)
Children categories
When working with large amounts of information, the ability to quickly sort data can be very beneficial at times. By arranging data in ascending, descending, or customized order, users can easily spot trends, analyze relationships, and extract valuable insights. In this article, you will learn how to sort columns or rows in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Sort By Columns in Excel in Python
- Sort By Custom List in Excel in Python
- Sort By Rows in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Sort By Columns in Excel in Python
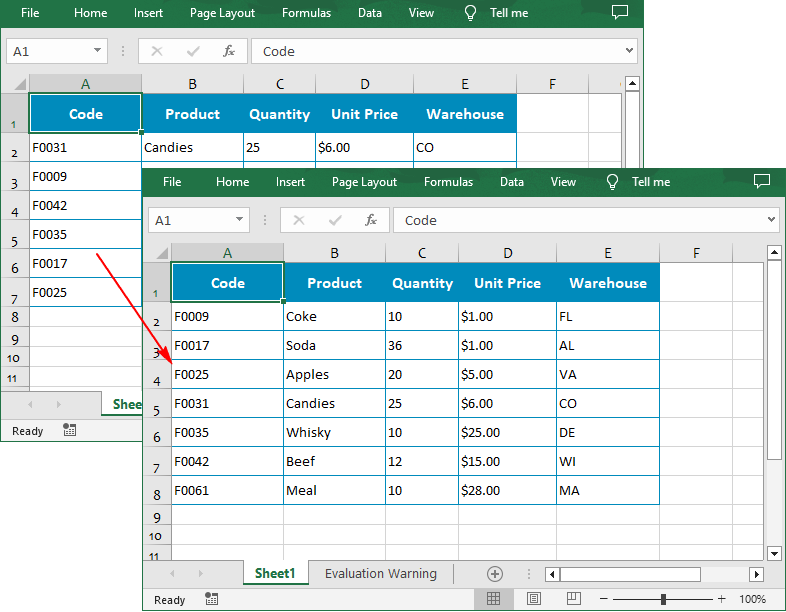
The Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(key: int, sortComparsionType: SortComparsionType, orderBy: OrderBy) method provided by Spire.XLS for Python allows users to sort data based on different criteria. For example, you can sort cell values, cell colors or font colors in ascending, descending, or other order.
The following are the steps to sort the values in a specified column:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Specify the sorting mode using Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add() method.
- Sort data in a specified cell range using Workbook.DataSorter.Sort() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Budget.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Sort values in the specified column in ascending order
workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(0, SortComparsionType.Values, OrderBy.Ascending)
# Sort in the specified cell range
workbook.DataSorter.Sort(worksheet["A1:E7"])
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("SortByColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Sort By Custom List in Excel in Python
You can also create a custom list and then sort data based on it using the Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(key: int, customSortOrder: List[str]) method.
The following are the steps to sort data using a custom list:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Create a custom sort list, and then sort a specified column using it though Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add() method.
- Sort data in a specified cell range using Workbook.DataSorter.Sort() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Budget.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create a custom sort list
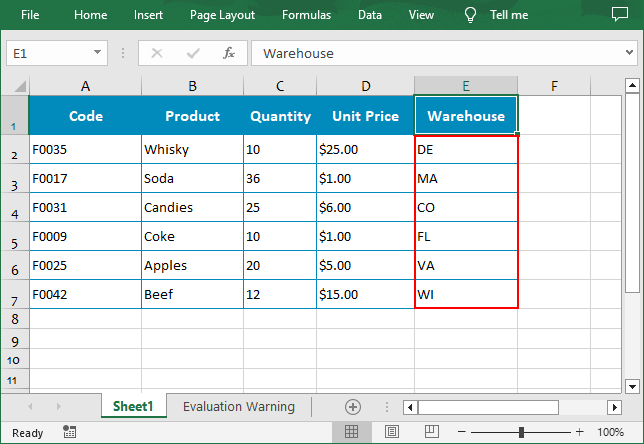
customList = ["DE","MA", "CO", "FL", "VA", "WI"]
# Sort a specified column using the custom list
workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(4, customList )
# Sort in the specified cell range
workbook.DataSorter.Sort(worksheet["A1:E7"])
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("CustomSortList.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Sort By Rows in Excel in Python
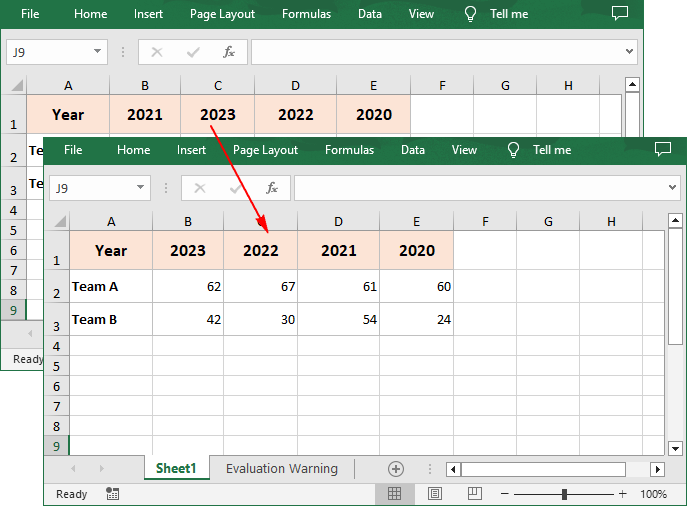
To sort a specified row in Excel, you need to set the sort orientation to LeftToRight, specify the sort mode and sort row data accordingly.
The following are the steps to sort the values in a specified row:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set whether to include titles when sorting using Workbook.DataSorter.IsIncludeTitle property.
- Set the sort orientation using Workbook.DataSorter.Orientation property.
- Specify the sorting mode, and then sort data in the first row using Workbook.DataSorter.Sort(Worksheet.Rows[0]) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Year.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set whether to include titles when sorting
workbook.DataSorter.IsIncludeTitle = True
# Set the sort orientation
workbook.DataSorter.Orientation = SortOrientationType.LeftToRight
# Specify the sorting mode
workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(0,SortComparsionType.Values,OrderBy.Descending)
# Sort data in the first row
workbook.DataSorter.Sort(sheet.Rows[0])
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("SortByRows.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Setting the number format for cells in Excel worksheets is crucial for data management and presentation, which enhances readability, ensures consistency, and facilitates accurate data analysis. Proper number formatting allows users to distinguish between different types of numerical data, such as currency, percentages, dates, and scientific notations, making complex datasets more comprehensible at a glance. In this article, we will explore how to automate the process of setting the number format for cells in Excel worksheets with Spire.XLS for Python in Python programs.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set the Number Format for Cells in Excel Worksheets
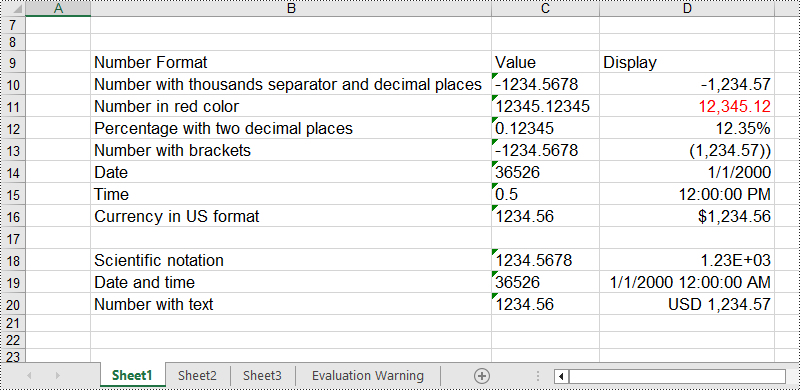
In an Excel workbook, the number format of a cell is determined by its format code. Developers can utilize various symbols in format code to define how numerical data, date and time, currency, etc. are displayed. Below are some commonly used symbols in number format codes:
- #: Represents a digit placeholder that displays only non-zero digits.
- 0: Represents a digit placeholder and always occupies at least one position.
- ; (semicolon): Separates formats for positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero.
- / (slash): In date formats, separates year, month, and day.
- $: Currency symbol, used for representing monetary values, adaptable to system regional settings.
- () (parentheses): Formats negative numbers by enclosing them in parentheses.
- [ ] (square brackets): Utilized in conditional formatting, such as color settings [Red] or conditions like [<=100]"Low";[>100]"High".
Spire.XLS for Python provides the CellRange.NumberValue property to set the number value of a cell and the CellRange.NumberFormat property to set the number format with format code. Below are the steps for setting the number format for cells in Excel worksheets with Python:
- Create an instance of Workbook class to create an Excel workbook.
- Get the first default worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Add text to header row through Worksheet.Range[].Text property.
- Add number value to cells through Worksheet.Range[].NumberValue property and set the number format for the cells with format code through Worksheet.Range[].NumberFormat property.
- Save the Excel workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Set the header row
sheet.Range["B9"].Text = "Number Format"
sheet.Range["C9"].Text = "Value"
sheet.Range["D9"].Text = "Display"
# Number with thousands separator and decimal places
sheet.Range["B10"].Text = "Number with thousands separator and decimal places"
sheet.Range["C10"].Text = "-1234.5678"
sheet.Range["D10"].NumberValue = -1234.5678
sheet.Range["D10"].NumberFormat = "#,##0.00"
# Number in red color
sheet.Range["B11"].Text = "Number in red color"
sheet.Range["C11"].Text = "12345.12345"
sheet.Range["D11"].NumberValue = 12345.12345
sheet.Range["D11"].NumberFormat = "[Red]#,##0.00"
# Percentage with two decimal places
sheet.Range["B12"].Text = "Percentage with two decimal places"
sheet.Range["C12"].Text = "0.12345"
sheet.Range["D12"].NumberValue = 0.12345
sheet.Range["D12"].NumberFormat = "0.00%"
# Number with brackets
sheet.Range["B13"].Text = "Number with brackets"
sheet.Range["C13"].Text = "-1234.5678"
sheet.Range["D13"].NumberValue = -1234.5678
sheet.Range["D13"].NumberFormat = "(#,##0.00;(#,##0.00))"
# Date
sheet.Range["B14"].Text = "Date"
sheet.Range["C14"].Text = "36526"
sheet.Range["D14"].NumberValue = 36526
sheet.Range["D14"].NumberFormat = "m/d/yyyy"
# Time
sheet.Range["B15"].Text = "Time"
sheet.Range["C15"].Text = "0.5"
sheet.Range["D15"].NumberValue = 0.5
sheet.Range["D15"].NumberFormat = "h:mm:ss AM/PM"
# Currency in US format
sheet.Range["B16"].Text = "Currency in US format"
sheet.Range["C16"].Text = "1234.56"
sheet.Range["D16"].NumberValue = 1234.56
sheet.Range["D16"].NumberFormat = "$#,##0.00"
# Scientific notation
sheet.Range["B18"].Text = "Scientific notation"
sheet.Range["C18"].Text = "1234.5678"
sheet.Range["D18"].NumberValue = 1234.5678
sheet.Range["D18"].NumberFormat = "0.00E+00"
# Date and time
sheet.Range["B19"].Text = "Date and time"
sheet.Range["C19"].Text = "36526"
sheet.Range["D19"].NumberValue = 36526
sheet.Range["D19"].NumberFormat = "m/d/yyyy h:mm:ss AM/PM"
# Number with text
sheet.Range["B20"].Text = "Number with text"
sheet.Range["C20"].Text = "1234.56"
sheet.Range["D20"].NumberValue = 1234.5678
sheet.Range["D20"].NumberFormat = "\"USD \"#,##0.00"
# Set the font size and autofit rows and columns
sheet.AllocatedRange.Style.Font.Size = 13
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitRows()
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/SetNumberFormatExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Copying data in Excel is a fundamental feature that allows you to quickly and efficiently reproduce data. It can be especially valuable when building spreadsheets with similar structures, or needing to propagate the same information across multiple areas of your workbook. By mastering the art of copying in Excel, you can boost your productivity and reduce the risk of manual data entry errors. In this article, we will explain how to copy rows, columns and cells in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
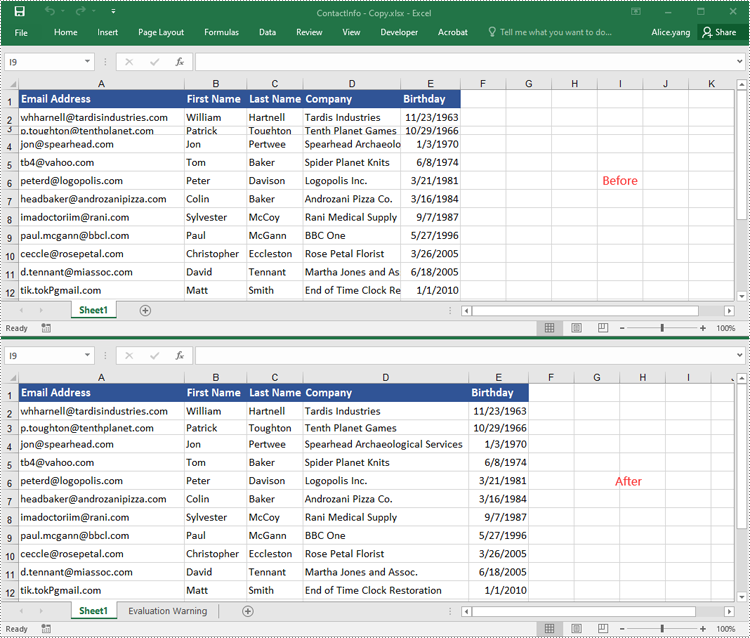
Copy Rows in Excel in Python
You can use the Worksheet.CopyRow(sourceRow, destSheet, destRowIndex, copyOptions) method provided by Spire.XLS for Python to easily copy a row in the same or between different worksheets in Excel. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired row that you want to copy using the Worksheet.Rows[index] property.
- Copy the row and its format from the source worksheet to the destination worksheet using the Worksheet.CopyRow(sourceRow, destSheet, destRowIndex, copyOptions) method.
- Copy the column widths of cells in the source row to the corresponding cells in the destination row.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx")
# Get the source worksheet
sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the destination worksheet
sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the desired row that you want to copy
row = sheet1.Rows[0]
# Copy the row from the source worksheet to the first row of the destination worksheet
sheet1.CopyRow(row, sheet2, 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
columns = sheet1.Columns.Length
# Copy the column widths of the cells in the source row to the corresponding cells in the destination row
for i in range(columns):
column_width = row.Columns[i].ColumnWidth
sheet2.Rows[0].Columns[i].ColumnWidth = column_width
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyRow.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
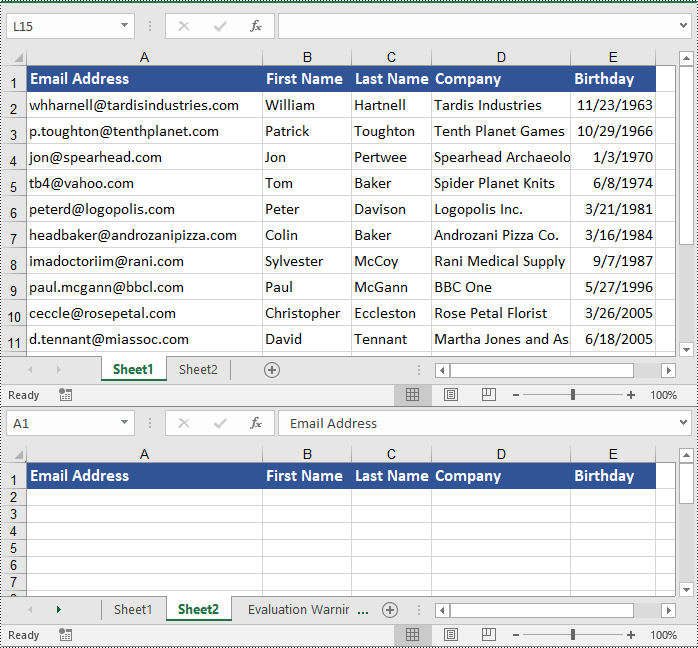
Copy Columns in Excel in Python
To copy a column in an Excel worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.CopyColumn(sourceColumn, destSheet, destColIndex, copyOptions) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired column that you want to copy using the Worksheet.Columns[index] property.
- Copy the column and its format from the source worksheet to the destination worksheet using the Worksheet.CopyColumn(sourceColumn, destSheet, destColIndex, copyOptions) method.
- Copy the row heights of cells in the source column to the corresponding cells in the destination column.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx")
# Get the source worksheet
sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the destination worksheet
sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the desired column that you want to copy
column = sheet1.Columns[0]
# Copy the column from the source worksheet to the first column of the destination worksheet
sheet1.CopyColumn(column, sheet2, 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
rows = column.Rows.Length
# Copy the row heights of cells in the source column to the corresponding cells in the destination column
for i in range(rows):
row_height = column.Rows[i].RowHeight
sheet2.Columns[0].Rows[i].RowHeight = row_height
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyColumn.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
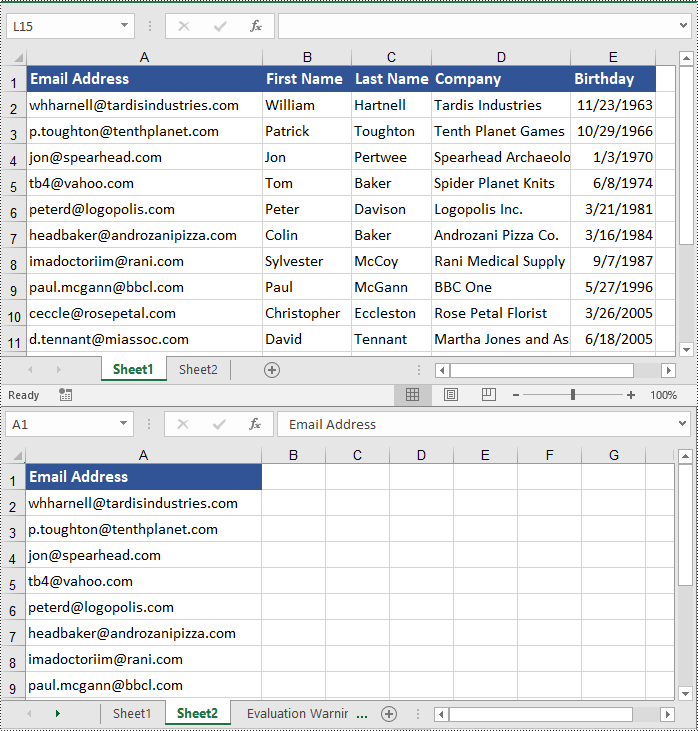
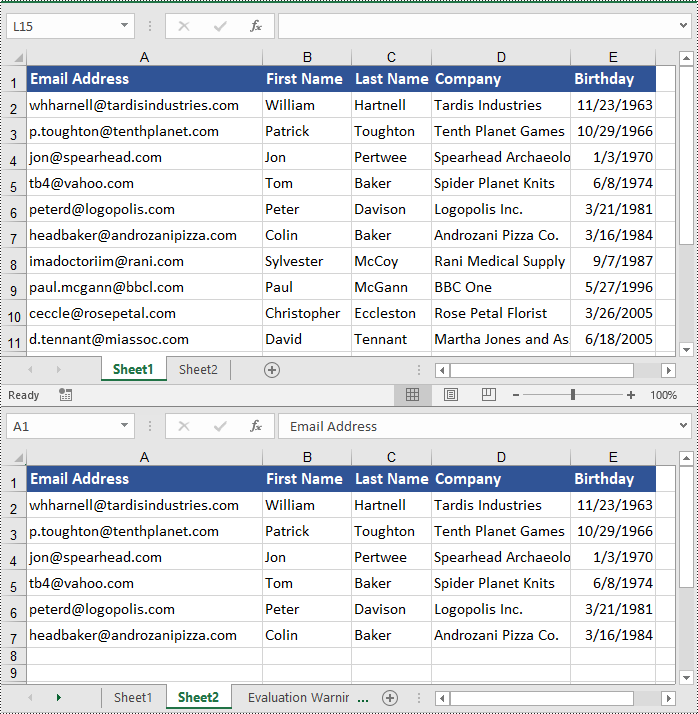
Copy Cells in Excel in Python
In addition to copying entire rows and columns, you are also able to copy an individual cell or a range of cells using the CellRange.Copy(destRange, copyOptions) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the source cell range and the destination cell range using the Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Copy the source cell range and its format from the source worksheet to the destination cell range in the destination worksheet using the CellRange.Copy(destRange, copyOptions) method.
- Copy the row heights and column widths of the source cell range to the destination cell range.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx")
# Get the source worksheet
sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the destination worksheet
sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the source cell range
range1 = sheet1.Range["A1:E7"]
# Get the destination cell range
range2 = sheet2.Range["A1:E7"]
# Copy the source cell range from the source worksheet to the destination cell range in the destination worksheet
range1.Copy(range2, CopyRangeOptions.All)
# Copy the row heights and column widths of the source cell range to the destination cell range
for i, row in enumerate(range1.Rows):
for j, column in enumerate(row.Columns):
range2.Rows[i].Columns[j].ColumnWidth = column.ColumnWidth
range2.Rows[i].RowHeight = row.RowHeight
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyCells.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Drop-down lists in Excel worksheets are an indispensable tool for enhancing data accuracy, efficiency, and usability in spreadsheet management. By offering pre-defined options within a cell, they not only streamline data entry processes but also enforce consistency, reducing the likelihood of input errors. This feature is particularly valuable when working with large datasets or collaborative projects where maintaining uniformity across multiple entries is crucial. This article demonstrates how to create customized drop-down lists within Excel worksheets using Spire.XLS for Python, empowering users to create organized and user-friendly worksheets.
- Create Drop-Down Lists Based on Cell Values Using Python
- Create Drop-Down Lists Based on Strings Using Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create Drop-Down Lists Based on Cell Values Using Python
In Excel worksheets, creating drop-down lists is accomplished through the data validation feature. With Spire.XLS for Python, developers can use the CellRange.DataValidation.DataRange property to create drop-down lists within cells and use the data from the specified cell range as list options.
The detailed steps for creating a drop-down list based on cell values are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Get a specific cell range through Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Set the data range for data validation of the cell range through CellRange.DataValidation.DataRange property to create drop-down lists with cell values.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific cell range
cellRange = sheet.Range["C3:C7"]
# Set the data range for data validation to create drop-down lists in the cell range
cellRange.DataValidation.DataRange = sheet.Range["F4:H4"]
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/DropDownListExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
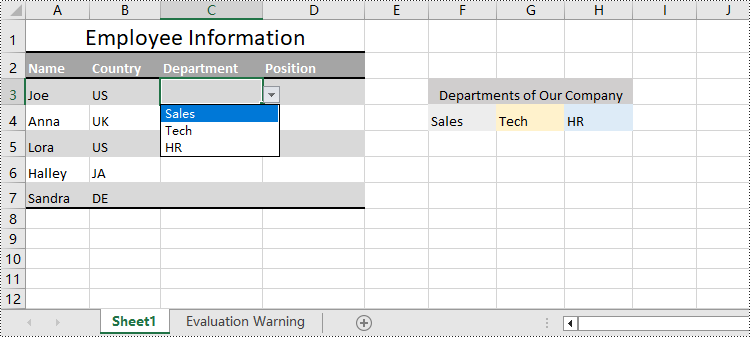
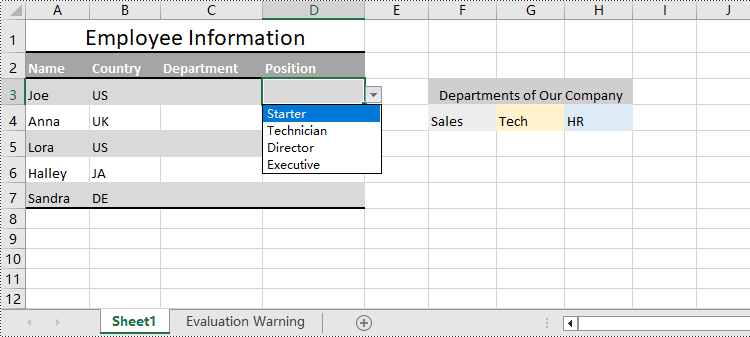
Create Drop-Down Lists Based on String Using Python
Spire.XLS for Python also provides the CellRange.DataValidation.Values property to create drop-down lists in cells directly using string lists.
The detailed steps for creating drop-down lists based on values are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Get a specific cell range through Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Set a string list as the values of data validation in the cell range through CellRange.DataValidation.Values property to create drop-down lists based on strings.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get a cell range
cellRange = sheet.Range["D3:D7"]
# Set the value for data validation to create drop-down lists
cellRange.DataValidation.Values = ["Starter", "Technician", "Director", "Executive"]
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ValueDropDownListExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Excel files often contain a wealth of comments that can provide valuable context and insights. These comments may include important text notes, instructions, or even embedded images that can be incredibly useful for various data analysis and reporting tasks. Extracting this information from the comments can be a valuable step in unlocking the full potential of the data. In this article, we will demonstrate how to effectively extract text and images from comments in Excel files in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
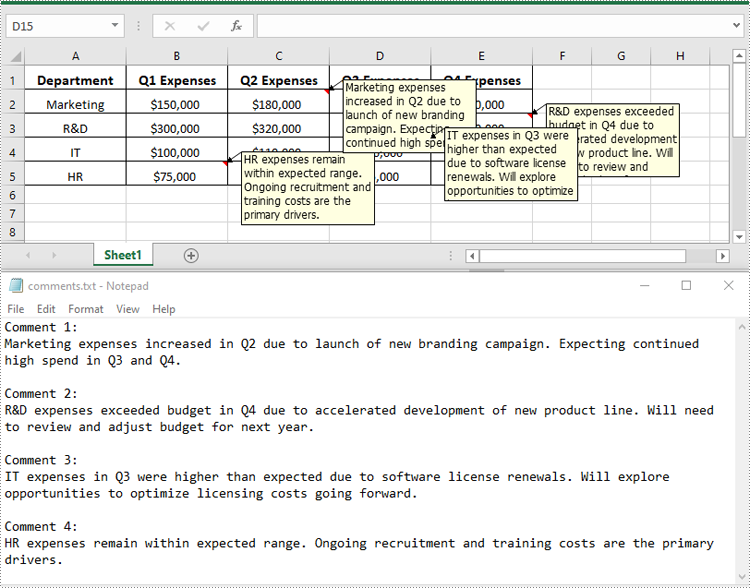
Extract Text from Comments in Excel in Python
You can get the text of comments using the ExcelCommentObject.Text property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store the extracted comment text.
- Get the comments in the worksheet using Worksheet.Comments property.
- Traverse through the comments.
- Get the text of each comment using ExcelCommentObject.Text property and append it to the list.
- Save the content of the list to a text file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Comments.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create a list to store the comment text
comment_text = []
# Get all the comments in the worksheet
comments = worksheet.Comments
# Extract the text from each comment and add it to the list
for i, comment in enumerate(comments, start=1):
comment_text.append(f"Comment {i}:")
text = comment.Text
comment_text.append(text)
comment_text.append("")
# Write the comment text to a file
with open("comments.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
file.write("\n".join(comment_text))
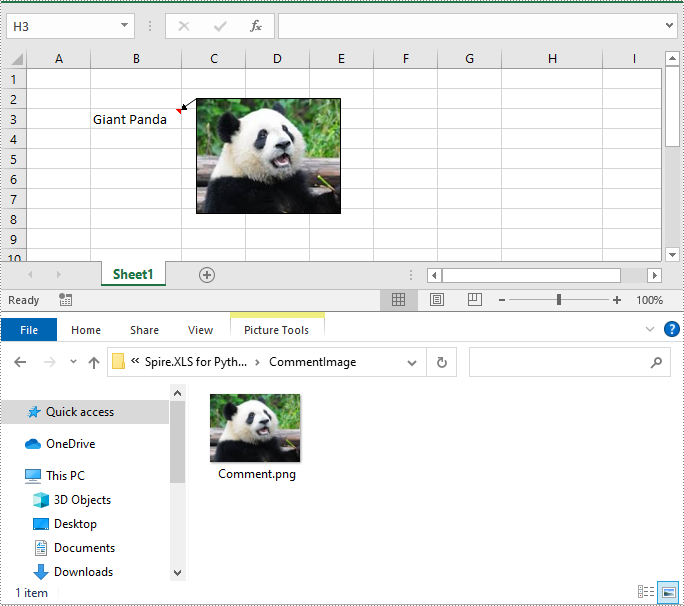
Extract Images from Comments in Excel in Python
To get the images embedded in Excel comments, you can use the ExcelCommentObject.Fill.Picture property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific comment in the worksheet using Worksheet.Comments[index] property.
- Get the embedded image in the comment using ExcelCommentObject.Fill.Picture property.
- Save the image to an image file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ImageComment.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific comment in the worksheet
comment = worksheet.Comments[0]
# Extract the image from the comment and save it to an image file
image = comment.Fill.Picture
image.Save("CommentImage/Comment.png")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Excel has been a widely used tool for data organization and analysis for many years. Over time, Microsoft has introduced different file formats for storing Excel data, the most common being the older XLS format and the more modern XLSX format.
The XLS format, introduced in the late 1990s, had certain limitations, such as a file size limit of 65,536 rows and 256 columns, and a maximum of 65,000 unique styles. The XLSX format, introduced in 2007, addressed these limitations by allowing for larger file sizes, more rows and columns, and expanded style capabilities. While XLSX is now the standard format, there are still many existing XLS files that need to be accessed and used, which makes the ability to convert between these formats an essential skill. In this article, we will explain how to convert Excel XLS to XLSX and vice versa in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Convert XLSX to XLS in Python
To convert an XLSX file to XLS format, you can use the Workbook.SaveToFile(fileName, ExcelVersion.Version97to2003) method. The ExcelVersion.Version97to2003 parameter specifies that the workbook should be saved in the Excel 97-2003 (XLS) format. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an XLSX file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the XLSX file to XLS format using the Workbook.SaveToFile(fileName, ExcelVersion.Version97to2003) method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "Sample1.xlsx" outputFile = "XlsxToXls.xls" # Create a Workbook object workbook = Workbook() # Load the XLSX file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Save the XLSX file to XLS format workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version97to2003) workbook.Dispose()
Convert XLS to XLSX in Python
To convert an XLS file to XLSX format, you need to specify the target Excel version to a version higher than 97-2003, such as 2007 (ExcelVersion.Version2007), 2010 (ExcelVersion.Version2010), 2013 (ExcelVersion.Version2013), or 2016 (ExcelVersion.Version2016). The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an XLS file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the XLS file to an Excel 2016 (XLSX) file using the Workbook.SaveToFile(fileName, ExcelVersion.Version2016) method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "Sample2.xls" outputFile = "XlsToXlsx.xlsx" # Create a Workbook object workbook = Workbook() # Load the XLS file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Save the XLS file to XLSX format workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
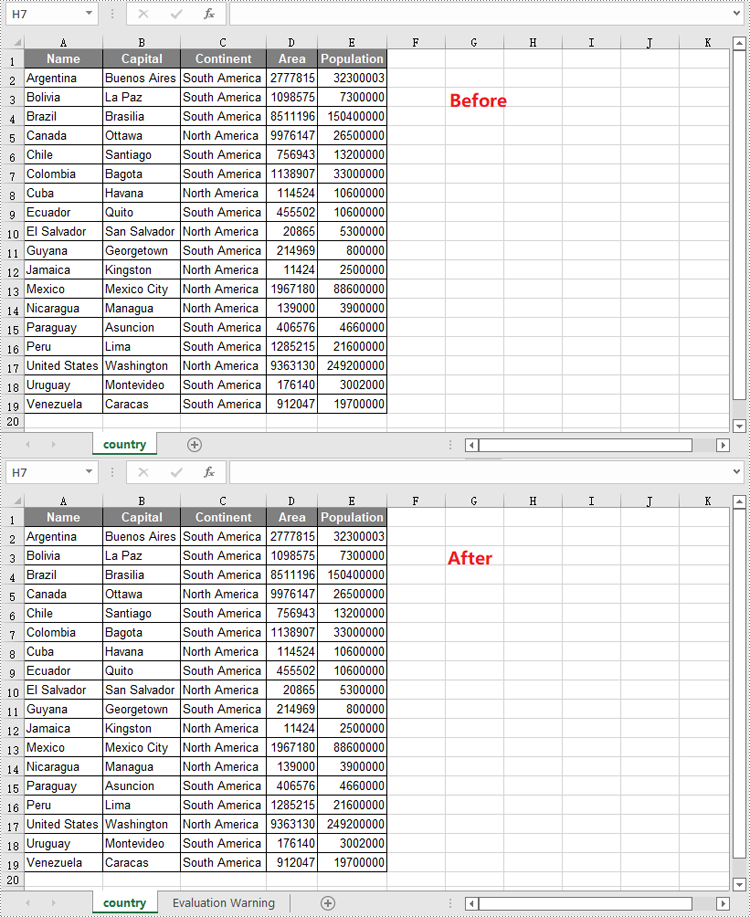
Reordering columns or rows in Excel is a simple process that allows you to change the arrangement of data within your spreadsheet. This can be useful for better organizing your data or aligning it with other columns or rows. You can reorder by using drag-and-drop, cut and paste, or keyboard shortcuts depending on the version of Excel you are using.
This article focus on introducing how to programmatically reorder columns or rows in an Excel worksheet in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your system through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Reorder Columns in Excel in Python
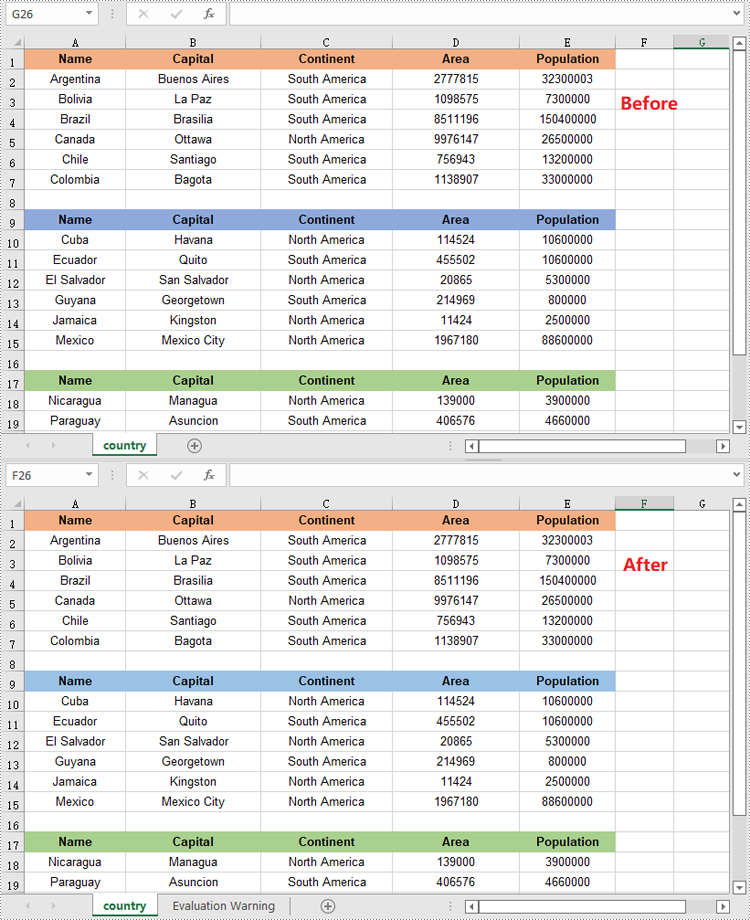
Spire.XLS does not provide a straightforward way to reorganize the order of columns or rows within an Excel worksheet. The solution requires creating a duplicate of the target worksheet. Then, you can copy the columns or rows from the copied worksheet and paste them into the original worksheet in the new preferred column or row sequence.
The following are the steps to reorder columns in an Excel worksheet using Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified file path.
- Get the target worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Specify the new column order within a list.
- Create a temporary sheet and copy the data from the target sheet into it.
- Copy the columns from the temporary worksheet to the target worksheet in the desired order using Worksheet.Columns[index].Copy() method.
- Remove the temporary sheet.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel document.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
targetSheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Specify the new column order in a list (the column index starts from 0)
newColumnOrder = [3, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5 ,6, 7]
# Add a temporary worksheet
tempSheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("temp")
# Copy data from the target worksheet to the temporary sheet
tempSheet.CopyFrom(targetSheet)
# Iterate through the newColumnOrder list
for i in range(len(newColumnOrder)):
# Copy the column from the temporary sheet to the target sheet in the new order
tempSheet.Columns[newColumnOrder[i]].Copy(targetSheet.Columns[i], True, True)
# Reset the column width in the target sheet
targetSheet.Columns[i].ColumnWidth = tempSheet.Columns[newColumnOrder[i]].ColumnWidth
# Remove the temporary sheet
workbook.Worksheets.Remove(tempSheet)
# Save the workbook to another Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ReorderColumns.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
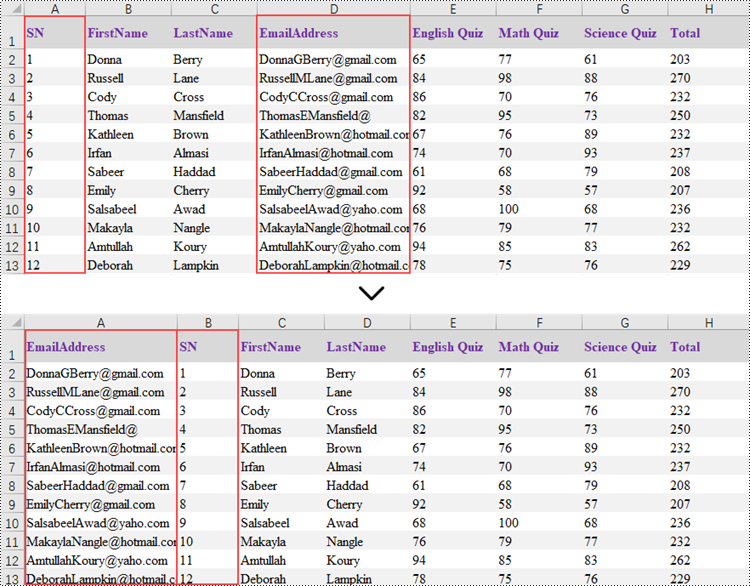
Reorder Rows in Excel in Python
Rearranging the rows in an Excel spreadsheet follows a similar approach to reorganizing the columns. The steps to reorder the rows within an Excel worksheet are as outlined below.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified file path.
- Get the target worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Specify the new row order within a list.
- Create a temporary sheet and copy the data from the target sheet into it.
- Copy the rows from the temporary worksheet to the target worksheet in the desired order using Worksheet.Rows[index].Copy() method.
- Remove the temporary sheet.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel document.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
targetSheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Specify the new row order in a list (the row index starts from 0)
newRowOrder = [0, 2, 3, 1, 4, 5 ,6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]
# Add a temporary worksheet
tempSheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("temp")
# Copy data from the first worksheet to the temporary sheet
tempSheet.CopyFrom(targetSheet)
# Iterate through the newRowOrder list
for i in range(len(newRowOrder)):
# Copy the row from the temporary sheet to the target sheet in the new order
tempSheet.Rows[newRowOrder[i]].Copy(targetSheet.Rows[i], True, True)
# Reset the row height in the target sheet
targetSheet.Rows[i].RowHeight = tempSheet.Rows[newRowOrder[i]].RowHeight
# Remove the temporary sheet
workbook.Worksheets.Remove(tempSheet)
# Save the workbook to another Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ReorderRows.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Document properties provide additional information about an Excel file, such as author, title, subject, and other metadata associated with the file. Retrieving these properties from Excel can help users gain insight into the file content and history, enabling better organization and management of files. At times, users may also need to remove document properties to protect the privacy and confidentiality of the information contained in the file. In this article, you will learn how to read or remove document properties in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Read Standard and Custom Document Properties in Excel
- Remove Standard and Custom Document Properties in Excel
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
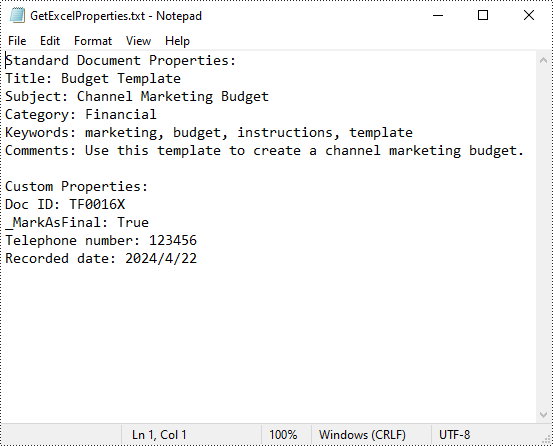
Read Standard and Custom Document Properties in Excel in Python
Excel properties are divided into two main categories:
- Standard Properties: These are predefined properties that are built into Excel files. They typically include basic details about the file such as title, subject, author, keywords, etc.
- Custom Properties: These are user-defined attributes that can be added to Excel to track additional information about the file based on your specific needs.
Spire.XLS for Python allows to read both the standard and custom document properties of an Excel file. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a StringBuilder instance.
- Get a collection of all standard document properties using Workbook.DocumentProperties property.
- Get specific standard document properties using the properties of the BuiltInDocumentProperties class and append them to the StringBuilder instance.
- Get a collection of all custom document properties using Workbook.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Iterate through the collection.
- Get the name, type, and value of each custom document property using ICustomDocumentProperties[].Name, ICustomDocumentProperties[].PropertyType and ICustomDocumentProperties[].Value properties.
- Determine the specific property type, and then convert the property value to the value of the corresponding data type.
- Append the property name and converted property value to the StringBuilder instance using StringBuilde.append() method.
- Write the content of the StringBuilder instance into a txt file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
def AppendAllText(fname: str, text: List[str]):
fp = open(fname, "w")
for s in text:
fp.write(s + "\n")
fp.close()
inputFile = "Budget Template.xlsx"
outputFile = "GetExcelProperties.txt"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a StringBuilder instance
builder = []
# Get a collection of all standard document properties
standardProperties = workbook.DocumentProperties
# Get specific standard properties and append them to the StringBuilder instance
builder.append("Standard Document Properties:")
builder.append("Title: " + standardProperties.Title)
builder.append("Subject: " + standardProperties.Subject)
builder.append("Category: " + standardProperties.Category)
builder.append("Keywords: " + standardProperties.Keywords)
builder.append("Comments: " + standardProperties.Comments)
builder.append("")
# Get a collection of all custom document properties
customProperties = workbook.CustomDocumentProperties
builder.append("Custom Properties:")
# Iterate through the collection
for i in range(len(customProperties)):
# Get the name, type, and value of each custom document property
name = customProperties[i].Name
type = customProperties[i].PropertyType
obj = customProperties[i].Value
# Determine the specific property type, and then convert the property value to the value of the corresponding data type
value = None
if type == PropertyType.Double:
value = Double(obj).Value
elif type == PropertyType.DateTime:
value = DateTime(obj).ToShortDateString()
elif type == PropertyType.Bool:
value = Boolean(obj).Value
elif type == PropertyType.Int:
value = Int32(obj).Value
elif type == PropertyType.Int32:
value = Int32(obj).Value
else:
value = String(obj).Value
# Append the property name and converted property value to the StringBuilder instance
builder.append(name + ": " + str(value))
# Write the content of the StringBuilder instance into a text file
AppendAllText(outputFile, builder)
workbook.Dispose()
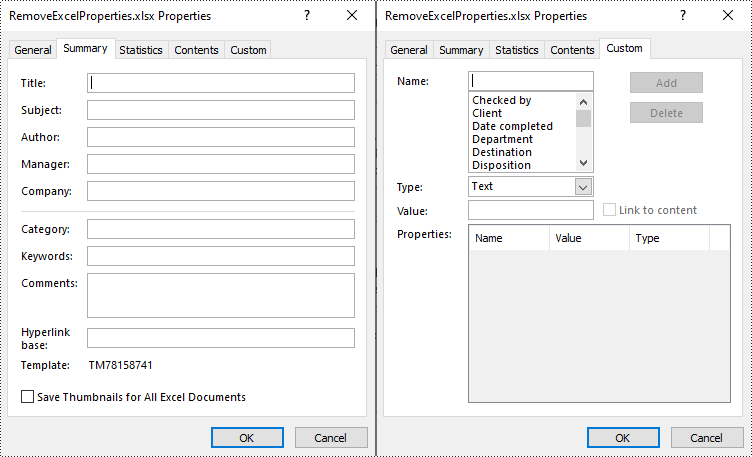
Remove Standard and Custom Document Properties in Excel in Python
You can easily delete standard document properties from an Excel file by setting their values as empty. For custom document properties, you can use the ICustomDocumentProperties.Remove() method to delete them. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a collection of all standard document properties using Workbook.DocumentProperties property.
- Set the values of specific standard document properties as empty through the corresponding properties of the BuiltInDocumentProperties class.
- Get a collection of all custom document properties using Workbook.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Iterate through the collection.
- Delete each custom property from the collection by its name using ICustomDocumentProperties.Remove() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "Budget Template.xlsx"
outputFile = "RemoveExcelProperties.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get a collection of all standard document properties
standardProperties = workbook.DocumentProperties
# Set the value of each standard document property as empty
standardProperties.Title = ""
standardProperties.Subject = ""
standardProperties.Category = ""
standardProperties.Keywords = ""
standardProperties.Comments = ""
# Get a collection of all custom document properties
customProperties = workbook.CustomDocumentProperties
# Iterate through the collection
for i in range(len(customProperties) - 1, -1, -1):
# Delete each custom document property from the collection by its name
customProperties.Remove(customProperties[i].Name)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In Microsoft Excel, text alignment and text orientation are crucial formatting options for optimizing the presentation of text within cells. Text alignment determines the horizontal or vertical positioning of text within a cell, while text orientation controls the tilt angle or display direction of the text. By flexibly utilizing these formatting options, you can customize the appearance of text within cells to create professional and visually appealing spreadsheets. In this article, we will demonstrate how to set text alignment and orientation in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set Text Alignment and Orientation in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the CellRange.Style.HorizontalAlignment and CellRange.Style.VerticalAlignment properties that enable you to customize the horizontal and vertical alignment of text in a single cell or range of cells. Additionally, it allows you to change the orientation of text by applying rotation to cells using the CellRange.Style.Rotation property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
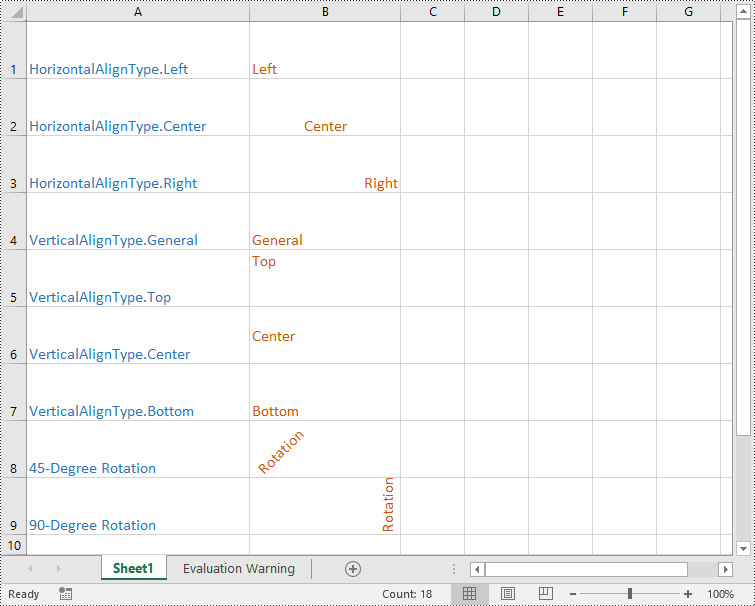
- Set the horizontal alignment for text in specific cells to Left, Center, Right, or General using the CellRange.Style.HorizontalAlignment property.
- Set the vertical alignment for text in specific cells to Top, Center, or Bottom using the CellRange.Style.VerticalAlignment property.
- Change the orientation for text in specific cells using the CellRange.Style.Rotation property.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Example.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to Left
sheet.Range["B1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
# Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to Center
sheet.Range["B2"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
# Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to Right
sheet.Range["B3"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Right
# Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to General
sheet.Range["B4"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.General
# Set the vertical alignment for text in a specific cell to Top
sheet.Range["B5"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Top
# Set the vertical alignment for text in a specific cell to Center
sheet.Range["B6"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
# Set the vertical alignment for text in a specific cell to Bottom
sheet.Range["B7"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Bottom
# Change the text orientation in specific cells by applying rotation
sheet.Range["B8"].Style.Rotation = 45
sheet.Range["B9"].Style.Rotation = 90
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("TextAlignmentAndOrientation.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The AutoFit feature in Microsoft Excel is a handy tool that allows you to automatically adjust the height of rows or the width of columns in an Excel spreadsheet to fit the content within them. This feature is particularly useful when you have data that may vary in length or when you want to ensure that all the content is visible without having to manually adjust the column widths or row heights. In this article, we will explain how to AutoFit rows and columns in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
AutoFit a Specific Row and Column in Python
To AutoFit a specific row and column in an Excel worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.AutoFitRow() and Worksheet.AutoFitColumn() methods. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- AutoFit a specific row and column in the worksheet by its index (1-based) using Worksheet.AutoFitRow(rowIndex) and Worksheet.AutoFitColumn(columnIndex) methods.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Automatically adjust the height of the 3rd row in the worksheet
sheet.AutoFitRow(3)
# Automatically adjust the width of the 4th column in the worksheet
sheet.AutoFitColumn(4)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("AutoFitSpecificRowAndColumn.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
AutoFit Multiple Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
To AutoFit multiple rows and columns within a cell range, you can use the CellRange.AutoFitRows() and CellRange.AutoFitColumns() methods. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFroFmFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell range in the worksheet using Worksheet.Range[] property.
- AutoFit the rows and columns in the cell range using CellRange.AutoFitRows() and CellRange.AutoFitColumns() methods.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific cell range in the worksheet
range = sheet.Range["A1:E14"]
# Or get the used cell range in the worksheet
# range = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Automatically adjust the heights of all rows in the cell range
range.AutoFitRows()
# Automatically adjust the widths of all columns in the cell range
range.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("AutoFitMultipleRowsAndColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
