
Program Guide (108)
Children categories
How to Filter Excel Pivot Tables with Python: Step-by-Step Guide
2025-05-16 10:01:44 Written by Administrator
Introduction
Pivot Tables in Excel are versatile tools that enable efficient data summarization and analysis. They allow users to explore data, uncover insights, and generate reports dynamically. One of the most powerful features of Pivot Tables is filtering, which lets users focus on specific data subsets without altering the original data structure.
What This Tutorial Covers
This tutorial provides a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to programmatically apply various types of filters to a Pivot Table in Excel using Python with the Spire.XLS for Python library. It covers the following topics:
- Benefits of Filtering Data in Pivot Tables
- Install Python Excel Library – Spire.XLS for Python
- Add Report Filter to Pivot Table
- Apply Row Field Filter in Pivot Table
- Apply Column Field Filter in Pivot Table
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Benefits of Filtering Data in Pivot Tables
Filtering is an essential feature of Pivot Tables that provides the following benefits:
- Enhanced Data Analysis: Quickly focus on specific segments or categories of your data to draw meaningful insights.
- Dynamic Data Updates: Filters automatically adjust to reflect changes when the underlying data is refreshed, keeping your analysis accurate.
- Improved Data Organization: Display only relevant data in your reports without altering or deleting the original dataset, preserving data integrity.
Install Python Excel Library – Spire.XLS for Python
Before working with Pivot Tables in Excel using Python, ensure the Spire.XLS for Python library is installed. The quickest way to do this is using pip, Python’s package manager. Simply run the following command in your terminal or command prompt:
pip install spire.xlsOnce installed, you’re ready to start automating Pivot Table filtering in your Python projects.
Add Report Filter to Pivot Table
A report filter allows you to filter the entire Pivot Table based on a particular field and value. This type of filter is useful when you want to display data for a specific category or item globally across the Pivot Table, without changing the layout.
Steps to Add a Report Filter
- Initialize the Workbook: Create a Workbook object to manage your Excel file.
- Load the Excel File: Use Workbook.LoadFromFile() to load an existing file containing a Pivot Table.
- Access the Worksheet: Use Workbook.Worksheets[] to select the desired worksheet.
- Locate the Pivot Table: Use Worksheet.PivotTables[] to access the specific Pivot Table.
- Define the Report Filter: Create a PivotReportFilter object specifying the field to filter.
- Apply the Report Filter: Add the filter to the Pivot Table using XlsPivotTable.ReportFilters.Add().
- Save the Updated File: Use Workbook.SaveToFile() to save your changes.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an existing Excel file containing a Pivot Table
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Access the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Access the first Pivot Table in the worksheet
pt = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Create a report filter for the field "Product"
reportFilter = PivotReportFilter("Product", True)
# Add the report filter to the pivot table
pt.ReportFilters.Add(reportFilter)
# Save the updated workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddReportFilter.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()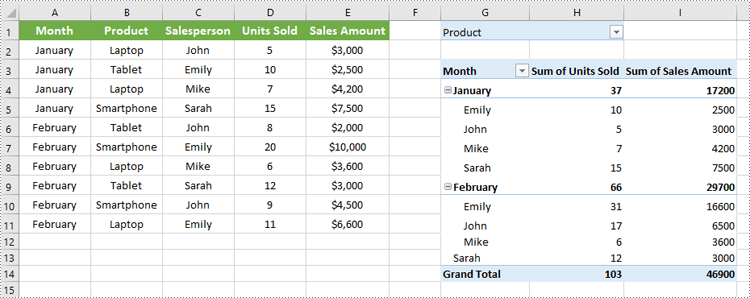
Apply Row Field Filter in Pivot Table
Row field filters allow you to filter data displayed in the row fields of an Excel Pivot Table. These filters can be based on labels (specific text values) or values (numeric criteria).
Steps to Add a Row Field Filter
- Initialize the Workbook: Create a Workbook object to manage the Excel file.
- Load the Excel File: Use Workbook.LoadFromFile() to load your target file containing a Pivot Table.
- Access the Worksheet: Select the desired worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[].
- Locate the Pivot Table: Access the specific Pivot Table using Worksheet.PivotTables[].
- Add a Row Field Filter: Add a label filter or value filter using
XlsPivotTable.RowFields[].AddLabelFilter() or
XlsPivotTable.RowFields[].AddValueFilter().
- Calculate Pivot Table Data: Use XlsPivotTable.CalculateData() to calculate the pivot table data.
- Save the Updated File: Save your changes using Workbook.SaveToFile().
Code Example
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first pivot table
pt = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Add a value filter to the first row field in the pivot table
pt.RowFields[0].AddValueFilter(PivotValueFilterType.GreaterThan, pt.DataFields[0], Int32(5000), None)
# Or add a label filter to the first row field in the pivot table
# pt.RowFields[0].AddLabelFilter(PivotLabelFilterType.Equal, "Mike", None)
# Calculate the pivot table data
pt.CalculateData()
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddRowFieldFilter.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()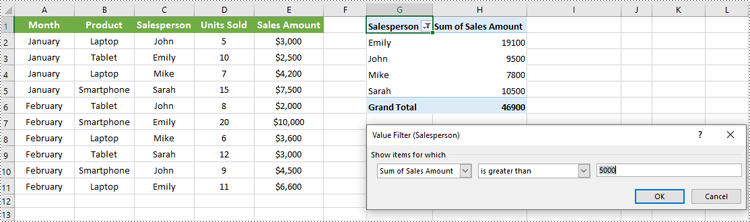
Apply Column Field Filter in Pivot Table
Column field filters in Excel Pivot Tables allow you to filter data displayed in the column fields. Similar to row field filters, column field filters can be based on labels (text values) or values (numeric criteria).
Steps to Add Column Field Filter
- Initialize the Workbook: Create a Workbook object to manage your Excel file.
- Load the Excel File: Use Workbook.LoadFromFile() to open your file containing a Pivot Table.
- Access the Worksheet: Select the target worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[].
- Locate the Pivot Table: Use Worksheet.PivotTables[] to access the desired Pivot Table.
- Add a Column Field Filter: Add a label filter or value filter using
XlsPivotTable.ColumnFields[].AddLabelFilter() or
XlsPivotTable.ColumnFields[].AddValueFilter().
- Calculate Pivot Table Data: Use XlsPivotTable.CalculateData() to calculate the Pivot Table data.
- Save the Updated File: Save your changes using Workbook.SaveToFile().
Code Example
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Access the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Access the first Pivot Table
pt = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Add a label filter to the first column field
pt.ColumnFields[0].AddLabelFilter(PivotLabelFilterType.Equal, String("Laptop"), None)
# # Or add a value filter to the first column field
# pt.ColumnFields[0].AddValueFilter(PivotValueFilterType.Between, pt.DataFields[0], Int32(5000), Int32(10000))
# Calculate the pivot table data
pt.CalculateData()
# Save the updated workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("AddColumnFieldFilter.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()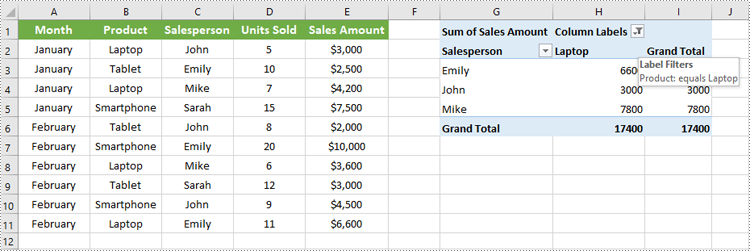
Conclusion
Filtering Pivot Tables in Excel is crucial for effective data analysis, allowing users to zoom in on relevant information without disrupting the table’s structure. Using Spire.XLS for Python, developers can easily automate adding, modifying, and managing filters on Pivot Tables programmatically. This tutorial covered the primary filter types—report filters, row field filters, and column field filters—with detailed code examples to help you get started quickly.
FAQs
Q: Can I add multiple filters to the same Pivot Table?
A: Yes, you can add multiple report filters, row filters, and column filters simultaneously to customize your data views with Spire.XLS.
Q: Do filters update automatically if the source data changes?
A: Yes, after refreshing the Pivot Table or recalculating with CalculateData(), filters will reflect the latest data.
Q: Can I filter based on custom conditions?
A: Spire.XLS supports many filter types including label filters (equals, begins with, contains) and value filters (greater than, less than, between).
Q: Is it possible to remove filters programmatically?
A: Yes, you can remove filters by clearing or resetting the respective filter collections or fields.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for .NET without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
In Microsoft Excel, each worksheet acts as a unique space for organizing distinct sets of data, projects, or analyses. Efficient management of these worksheets is crucial for quick navigation and effective data handling. By renaming worksheets, users can create intuitive labels that clearly indicate the content of each sheet, making it easier to locate specific information. Furthermore, customizing tab colors enhances visual organization, allowing users to differentiate between various sections or categories at a glance.
In this article, we will demonstrate how to change worksheet names and set tab colors in Excel using Python and the Spire.XLS for Python library.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
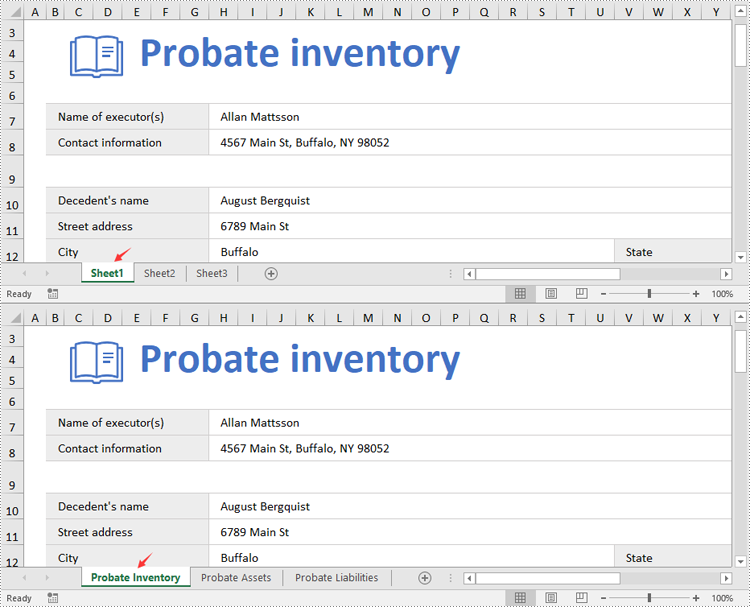
Change Worksheet Names in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.Name property to rename a worksheet in an Excel file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using the Worbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Rename the worksheet using the Worksheet.Name property.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "Sample1.xlsx" outputFile = "RenameWorksheets.xlsx" # Create an object of the Workbook class workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Rename the first worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] sheet.Name = "Probate Inventory" # Rename the second worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[1] sheet.Name = "Probate Assets" # Rename the third worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[2] sheet.Name = "Probate Liabilities" # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Set Worksheet Tab Colors in Excel in Python
The Worksheet.TabColor property allows setting a tab color for a worksheet in an Excel file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using the Worbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Rename the worksheet using the Worksheet.TabColor property.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "Sample2.xlsx" outputFile = "SetTabColor.xlsx" # Create an object of the Workbook class workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Set the tab color for the first worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] worksheet.TabColor = Color.get_Red() # Set the tab color for the second worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[1] worksheet.TabColor = Color.get_Green() # Set the tab color for the third worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[2] worksheet.TabColor = Color.get_LightBlue() # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Worksheet names can be used as unique identifiers for different collections of data in a workbook. When working with large Excel files that contain multiple worksheets, knowing the name of each worksheet can help you quickly identify where specific types of information are stored. In this article, you will learn how to get worksheet names in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Get All Worksheet Names in Excel in Python
The Worksheet.Name property returns the name of a Worksheet. To retrieve the names of all the worksheets in Excel (including hidden ones), you can iterate through each worksheet and get their names with this property. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store the retrieved worksheet names.
- Iterate through each worksheet.
- Get the name of each worksheet through Worksheet.Name property and append it to the list.
- Write the contents of the list to a text file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Specifiy the input and output file paths
inputFile = "BudgetSum.xlsx"
outputFile = "GetWorksheetNames.txt"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a list to store the worksheet names
names = []
# Iterate through each worksheet
for sheet in workbook.Worksheets:
# Get each worksheet name and add it to the list
names.append(sheet.Name)
# Write to a txt file
with open(outputFile, "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
file.write("\n".join(names))

Get Hidden Worksheet Names in Excel in Python
If you only need to retrieve the names of the hidden worksheets, you can first iterate through each worksheet to determine whether a worksheet is hidden, and if so, get its name through the Worksheet.Name property. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store the retrieved worksheet names.
- Iterate through each worksheet and find the hidden worksheets.
- Get the names of the hidden worksheets through Worksheet.Name property and append them to the list.
- Write the contents of the list to a text file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Specifiy the input and output file paths
inputFile = "BudgetSum.xlsx"
outputFile = "GetHiddenWorksheetNames.txt"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a list to store the worksheet names
names = []
# Iterate through each worksheet
for sheet in workbook.Worksheets:
# Detect the hidden worksheet
if sheet.Visibility == WorksheetVisibility.Hidden:
# Get the hidden worksheet name and add it to the list
names.append(sheet.Name)
# Write to a txt file
with open(outputFile, "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
file.write("\n".join(names))

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
In today's data-driven world, efficiently transferring data into Excel is essential. Python's versatile ecosystem automates the process, eliminating manual entry, reducing errors, and handling large datasets beyond Excel's limits. Whether pulling data from APIs, databases, or unstructured sources, Python creates dynamic workflows that ensure consistency and scalability. Its compatibility with various data formats transforms raw data into structured Excel files, bridging complex data pipelines with user-friendly outputs while boosting productivity and enabling professionals to focus on high-value analysis. This article will demonstrate how to use Spire.XLS for Python to import data into Excel workbooks within Python applications.
- How to Write Data into Excel Files with Spire.XLS for Python
- Import CSV Data into Excel Worksheets
- Transfer Data and Worksheets Between Excel Files
- Import JSON Data into Excel Worksheets
- Import XML Data into Excel Worksheets
- Import Database Records into Excel Worksheets
- Import HTML Table Data into Excel Worksheets
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
How to Write Data into Excel Files with Spire.XLS for Python
Spire.XLS for Python is an Excel file processing library that supports reading, editing, and writing Excel files. With this library, you can effortlessly write data into Excel worksheets, apply formatting, and save the workbook as a file.
Before writing data into Excel worksheets, Python provides a variety of built-in and third-party libraries-such as json, xml.etree.ElementTree, and BeautifulSoup-that allow you to read and process data from different file formats, including TXT, CSV, JSON, XML, and HTML. These libraries help transform raw or semi-structured data into lists, dictionaries, or dataframes that are easy to work with in Python.
Once the data is extracted and structured, Spire.XLS for Python can be used to write it into Excel workbooks. The library offers precise control over worksheet creation, cell-level data entry, formatting, and file export in Excel-compatible formats.
Steps to Write Data into Excel Using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Initialize a Workbook
Create an instance of the Workbook class to generate a new Excel workbook with three default worksheets, or use the Workbook.LoadFromFile(filePath: str) method to load an existing Excel file. - Create or Clear Worksheets
Use the Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method to get worksheets, or the Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName: str) method to add worksheets. - Prepare the Data
Use Python libraries such as json, csv, or xml.etree.ElementTree to extract and organize your data into row and column structures. - Write Headers and Data
Iterate through your data and use the Worksheet.Range.get_Item(row: int, col: int).Value property to assign values to specific cells. - Format the Worksheet (Optional)
Apply styles using the CellRange.ApplyStyle() method, autofit columns using the Worksheet.AutoFitColumn() method, and set borders or colors to improve the appearance and readability of the worksheet. - Save the Workbook
Save the final Excel file using the Workbook.SaveToFile(filePath: str, format: FileFormat) method in your preferred Excel version.
Import CSV Data into Excel Worksheets
Importing data from CSV files into Excel is a fundamental task in data preparation. With Spire.XLS for Python, you can easily load structured data from CSV files using the Workbook.LoadFromFile(filePath: str, separator: str) method of the Workbook class and convert it into a well-formatted Excel workbook. In fact, data from text files can be imported in the same way. This method supports custom cell styling, header addition, and ensures the data is clean and ready for analysis or reporting.
Steps to import CSV data into Excel workbooks:
- Create an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load the CSV table data using the Workbook.LoadFromFile(filePath: str, separator: str) method and specify the file path and the column separator (e.g., comma or tab).
- Access the first worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(index: int) method.
- Optionally, read the table from the first worksheet and write it into another using the Worksheet.Range.get_Item(row: int, col: int).Value property of the Worksheet class.
- Format the worksheet as needed and save the result using the Workbook.SaveToFile(filePath: str, fileFormat) method.
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat, BuiltInStyles
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the table from the CSV or text file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.csv", ",")
# workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.txt", "\t")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Format the table
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Heading4
for i in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows.get_Item(i).BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Accent4_20
for j in range(sheet.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(j + 1)
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/TextCSVToExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Transfer Data and Worksheets Between Excel Files
Working with multiple Excel files often requires copying data or entire worksheets from one workbook to another. With Spire.XLS for Python, you can perform these operations programmatically using the Workbook and Worksheet classes, allowing you to preserve formatting, formulas, and data structure when consolidating or merging information from different sources.
Steps to copy data and worksheets between Excel workbooks:
- Create a new instance of the Workbook class and load the source Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile(filePath: str) method.
- Create another Workbook instance and clear the default worksheets using the Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- To copy data only:
- Iterate through worksheets in the source workbook and create new worksheets in the destination using the Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName: str) method.
- Use the Worksheet.Range.get_Item(row, col).Value property to read from the source worksheet and write into the destination worksheet.
- To copy entire worksheets:
- Use the Worksheet.CopyFrom(sourceWorksheet) method to duplicate the content of each source worksheet into a new worksheet.
- Save the new workbook using the Workbook.SaveToFile(filePath: str, ileFormat: FileFormat) method.
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat
# Create a Workbook object and load an Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Create another Workbook object and load an Excel file
newWorkbook = Workbook()
newWorkbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Read data from one workbook and insert it into another
for i in range(workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0).Rows.Count):
for j in range(workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0).Columns.Count):
# Add a new worksheet
sheet = newWorkbook.Worksheets.Add(workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0).Name)
# Write data
sheet.Range.get_Item(i + 1, j + 1).Value = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0).Range.get_Item(i + 1, j + 1).Value
# Copy worksheets from the first workbook to the second workbook
for i in range(workbook.Worksheets.Count):
# Add a new worksheet
newSheet = newWorkbook.Worksheets.Add(workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(i).Name + "-Copy")
# Copy all contents to the new worksheet
newSheet.CopyFrom(workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(i))
# Save the workbook
newWorkbook.SaveToFile("output/ExcelToExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
newWorkbook.Dispose()

Import JSON Data into Excel Worksheets
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a popular format for structured data, commonly used in APIs and modern web applications. With Python's built-in json module, you can easily parse JSON files and extract table-like data. This data can then be written into an Excel worksheet using Spire.XLS for Python, which allows you to format, edit, and organize the content for easier analysis, visualization, or sharing.
A code example demonstrates how to import JSON data into Excel files:
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat, BuiltInStyles
import json
# Load JSON data
with open("Sample.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
jsonData = json.load(f)
headers = list(jsonData[0].keys())
rows = [[str(item[key]) for key in headers] for item in jsonData]
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Clear the default worksheets and add new one
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("JSON Data")
# Write headers and rows into the new worksheet
for col, header in enumerate(headers):
sheet.Range[1, col + 1].Value = header
for row_idx, row_data in enumerate(rows):
for col_idx, value in enumerate(row_data):
sheet.Range[row_idx + 2, col_idx + 1].Value = value
# Apply styles and auto-fit columns
sheet.Rows[0].BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Heading2
for row in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows[row].BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Accent2_40
for col in range(sheet.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(col + 1)
# Save Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/JSONToExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Import XML Data into Excel Worksheets
XML is a widely used format for representing hierarchical data in enterprise systems and data feeds. With Python's xml.etree.ElementTree module, you can navigate and extract the desired elements and attributes. Once the data is retrieved, Spire.XLS for Python allows you to write the data into Excel worksheets, mapping the hierarchical structure into rows and columns. This makes it easier to present, filter, and analyze complex XML content in a tabular format.
The following example shows how to extract XML data and write it into an Excel worksheet with Spire.XLS for Python:
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat, BuiltInStyles
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# Load XML data
tree = ET.parse("Sample.xml")
root = tree.getroot()
first_order = root.find("order")
headers = [elem.tag.replace('_', ' ').title() for elem in first_order]
rows = [
[order.find(tag.lower().replace(" ", "_")).text or "" for tag in headers]
for order in root.findall("order")
]
# Use Spire.XLS for Python to create and write to workbook
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("XML Data")
# Write headers and rows
for col, header in enumerate(headers):
sheet.Range[1, col + 1].Value = header
for row_idx, row_data in enumerate(rows):
for col_idx, value in enumerate(row_data):
sheet.Range[row_idx + 2, col_idx + 1].Value = value
# Apply styles and auto-fit columns
sheet.Rows[0].BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Heading4
for row in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows[row].BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Accent4_40
for col in range(sheet.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(col + 1)
# Save Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/XMLToExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Import Database Records into Excel Worksheets
Importing database records into Excel is a common requirement in reporting and business intelligence. You can use database connector libraries in Python, such as sqlite3, pyodbc, or pymysql, to establish connections with various relational databases and retrieve records via SQL queries.
Once data is fetched from the database, it can be written into Excel using the Workbook class and the Worksheet.Range.get_Item().Value property in Spire.XLS. This enables you to convert relational datasets into readable and portable Excel workbooks that are ideal for reports, dashboards, and archival.
An example demonstrates how to fetch rows from a SQLite database and populate an Excel worksheet:
- Python
import sqlite3
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat, BuiltInStyles
# Connect to the SQLite database
conn = sqlite3.connect("Sample.db")
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Get all table names in the database
cursor.execute("SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type='table';")
tables = [row[0] for row in cursor.fetchall()]
# Create an Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear() # Clear the default worksheets
# Loop through each table and export to a worksheet
for table_name in tables:
# Fetch all data from the table
cursor.execute(f"SELECT * FROM {table_name}")
rows = cursor.fetchall()
# Get column names
column_names = [desc[0] for desc in cursor.description]
# Add a new worksheet with the table name
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(table_name)
# Write header row
for col_index, column_name in enumerate(column_names):
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(1, col_index + 1)
cell.Value = str(column_name)
# Write data rows
for row_index, row in enumerate(rows, start=2):
for col_index, value in enumerate(row):
sheet.Range.get_Item(row_index, col_index + 1).Value = str(value)
# Apply styles
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Heading4
for i in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows.get_Item(i).BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Accent4_20
for j in range(sheet.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(j + 1)
# Close the database connection
conn.close()
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/SQDBToExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Import HTML Table Data into Excel Worksheets
Many web pages display data in HTML table format. By using the BeautifulSoup library in Python, you can scrape table data from web content and convert it into structured data. This data can then be written into Excel worksheets using the Spire.XLS for Python library.
With optional styling and formatting capabilities, you can preserve the tabular structure and create professional-looking reports from online sources such as stock data, weather updates, or product listings.
A code example demonstrates how to extract table data from HTML and write it into Excel worksheets:
- Python
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat, BuiltInStyles
# Read HTML file
with open("Sample.html", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
soup = BeautifulSoup(f, "html.parser")
# Find the table
table = soup.find("table")
rows = table.find_all("tr")
# Extract data from table as a 2D list
data = []
for row in rows:
cells = row.find_all(["th", "td"])
data.append([cell.get_text(strip=True) for cell in cells])
# Create a new Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Iterate through the data
for row_index, row in enumerate(data, start=1):
for col_index, cell_value in enumerate(row, start=1):
# Write the table data to the cells in the worksheet
sheet.Range.get_Item(row_index, col_index).Value = str(cell_value)
# Format the table
sheet.Rows.get_Item(0).BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Heading4
for i in range(1, sheet.Rows.Count):
sheet.Rows.get_Item(i).BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Accent4_20
for j in range(sheet.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(j + 1)
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/HTMLToExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Applying styles is one of the simplest ways to enhance the professionalism and readability of Excel spreadsheets. Excel provides a wide range of built-in styles that allow users to quickly format cells, ranges, or worksheets. Additionally, users can create custom styles to specify fonts, colors, borders, number formats, and more, tailored to their individual preferences. Whether you're designing professional reports, sales presentations, or project management plans, knowing how to use styles effectively helps make data more visually appealing and easier to understand.
In this guide, you will learn how to apply styles to cells or worksheets in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Apply a Built-in Style to Cells in Excel in Python
- Apply a Custom Style to Cells in Excel in Python
- Apply a Custom Style to a Worksheet in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Apply a Built-in Style to Cells in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the CellRange.BuiltInStyle property, which enables developers to apply built-in styles, such as Title, Heading 1, and Heading 2 to individual cells or ranges in Excel. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired cell or range of cells using the Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Apply a built-in style to the cell or range of cells using the CellRange.BuiltInStyle property.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the desired cell range
range = sheet.Range["A1:H1"]
# Apply a built-in style to the cell range
range.BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Heading2
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplyBuiltinStyle.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
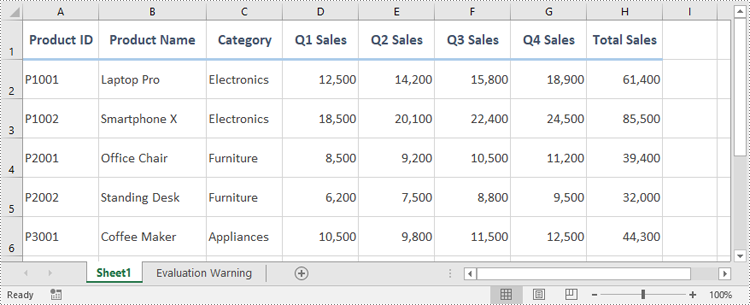
Apply a Custom Style to Cells in Excel in Python
Developers can use the Workbook.Styles.Add() method to create a custom style, which can then be applied to individual cells or ranges using the CellRange.Style property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired cell or range of cells using the Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Add a custom style to the workbook using the Workbook.Styles.Add() method.
- Define the formatting, such as the font size, font color, text alignment, cell borders and cell background color, using the properties of the CellStyle class.
- Apply the custom style to the cell or range of cells using the CellRange.Style property.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the desired cell range
range = sheet.Range["A1:H1"]
# Add a custom style to the workbook
style = workbook.Styles.Add("CustomCellStyle")
# Set the font size
style.Font.Size = 13
# Set the font color
style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
# Bold the text
style.Font.IsBold = True
# Set the vertical text alignment
style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Bottom
# Set the horizontal text alignment
style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
# Set the bottom border color
style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.get_GreenYellow()
# Set the bottom border type
style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Medium
# Set the background color
style.Color = Color.get_CornflowerBlue()
# Apply the custom style to the cell range
range.Style = style
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplyCustomStyle.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
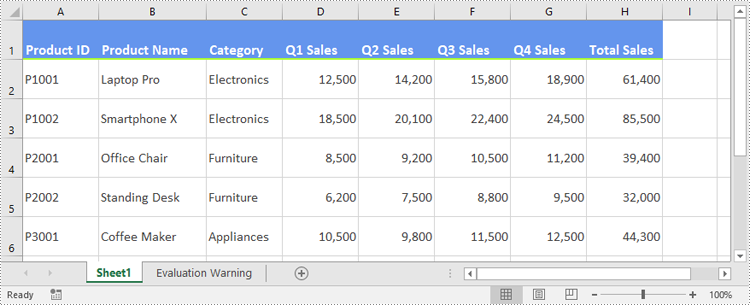
Apply a Custom Style to a Worksheet in Excel in Python
In certain cases, it may be necessary to apply a custom style to an entire worksheet rather than to specific cells or ranges. This can be accomplished using the Worksheet.ApplyStyle() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add a custom style to the workbook using the Workbook.Styles.Add() method.
- Define the formatting, such as the font size, font color, and cell background color, using the properties of the CellStyle class.
- Apply the custom style to the worksheet using the Worksheet.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a custom style to the workbook
style = workbook.Styles.Add("CustomSheetStyle")
# Set the font size
style.Font.Size = 12
# Set the font color
style.Font.Color = Color.FromRgb(91, 155, 213)
# Set the cell background color
style.Color = Color.FromRgb(242, 242, 242)
# Apply the custom style to the worksheet
sheet.ApplyStyle(style)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplyCustomStyleToSheet.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
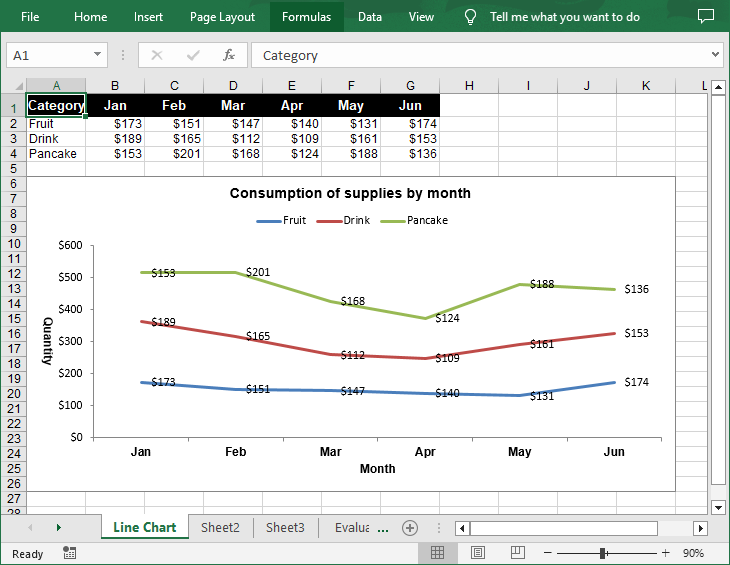
A line chart is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points connected by straight line segments. It's particularly useful for showing changes over time. For example, if you're tracking monthly sales figures, a line chart can help you identify trends, peaks, and troughs. In this article, you will learn how to create a line chart in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Simple Line Chart in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line) method to add a simple line chart to an Excel worksheet. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Add the chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a simple line chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, title, axis and other attributes of the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet and set its name
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Name = "Line Chart"
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Category"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Fruit"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Drink"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Pancake"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jan"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 173
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 189
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 153
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Feb"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 151
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 165
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 201
sheet.Range["D1"].Value = "Mar"
sheet.Range["D2"].NumberValue = 147
sheet.Range["D3"].NumberValue = 112
sheet.Range["D4"].NumberValue = 168
sheet.Range["E1"].Value = "Apr"
sheet.Range["E2"].NumberValue = 140
sheet.Range["E3"].NumberValue = 109
sheet.Range["E4"].NumberValue = 124
sheet.Range["F1"].Value = "May"
sheet.Range["F2"].NumberValue = 131
sheet.Range["F3"].NumberValue = 161
sheet.Range["F4"].NumberValue = 188
sheet.Range["G1"].Value = "Jun"
sheet.Range["G2"].NumberValue = 174
sheet.Range["G3"].NumberValue = 153
sheet.Range["G4"].NumberValue = 136
# Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].RowHeight = 20
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.Size = 11
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:G4"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a line chart to the worksheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line)
# Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:G4"]
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 27
# Set and format chart title
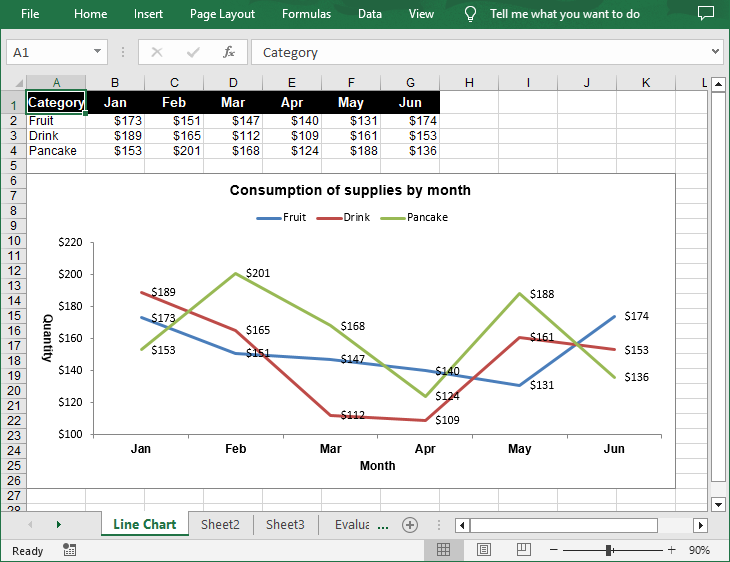
chart.ChartTitle = "Consumption of supplies by month"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set the category axis of the chart
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Month"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Set the value axis of the chart
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Quantity"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 100
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Set series colors and data labels
for cs in chart.Series:
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("LineChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Create a Stacked Line Chart in Excel in Python
A stacked line chart stacks the values of each category on top of each other. This makes it easier to visualize how each data series contributes to the overall trend. The following are the steps to create a stacked line chart using Python:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Add the chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a stacked line chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.LineStacked) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, title, axis and other attributes of the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet and set its name
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Name = "Line Chart"
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Category"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Fruit"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Drink"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Pancake"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jan"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 173
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 189
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 153
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Feb"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 151
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 165
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 201
sheet.Range["D1"].Value = "Mar"
sheet.Range["D2"].NumberValue = 147
sheet.Range["D3"].NumberValue = 112
sheet.Range["D4"].NumberValue = 168
sheet.Range["E1"].Value = "Apr"
sheet.Range["E2"].NumberValue = 140
sheet.Range["E3"].NumberValue = 109
sheet.Range["E4"].NumberValue = 124
sheet.Range["F1"].Value = "May"
sheet.Range["F2"].NumberValue = 131
sheet.Range["F3"].NumberValue = 161
sheet.Range["F4"].NumberValue = 188
sheet.Range["G1"].Value = "Jun"
sheet.Range["G2"].NumberValue = 174
sheet.Range["G3"].NumberValue = 153
sheet.Range["G4"].NumberValue = 136
# Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].RowHeight = 20
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.Size = 11
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:G4"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a stacked line chart to the worksheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.LineStacked)
# Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:G4"]
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 27
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Consumption of supplies by month"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set the category axis of the chart
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Month"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Set the value axis of the chart
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Quantity"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Set series colors and data labels
for cs in chart.Series:
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("StackedLineChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Editing an Excel document involves a variety of actions, such as inputting and formatting text, applying formulas, generating visualizations, and organizing data for clarity and insight. Being able to edit Excel documents programmatically is a crucial skill that empowers developers to enhance their data management capabilities.
In this article, you will learn how to edit an existing Excel document in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Read and Write Excel Files in Python
- Apply Formatting to Excel Cells in Python
- Find and Replace Text in Excel in Python
- Add Formulas and Charts to Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Read and Write Excel Files in Python
A key task when handling Excel files in Python is the efficient reading and writing of data, which is essential for numerous applications such as data analysis and report generation. Spire.XLS for Python simplifies this process by offering the CellRange.Value property. This feature allows developers to easily retrieve values from individual cells and reassign them as needed.
Here are the steps to read and write an Excel file using Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell using the Worksheet.Range property
- Get or set the cell value using the CellRange.Value property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific cell
cell = worksheet.Range["A1"]
# Read the cell value
cellValue = cell.Value
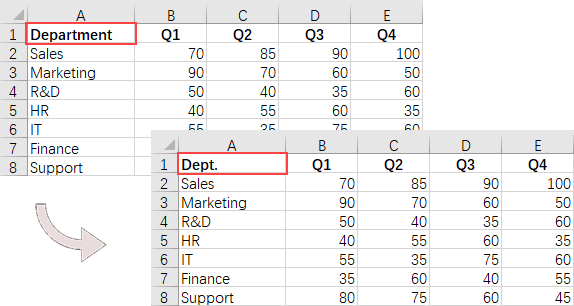
# Determine if the cell value is "Department"
if (cellValue == "Department"):
# Update the cell value
cell.Value = "Dept."
# Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("ModifyExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Apply Formatting to Excel Cells in Python
Formatting Excel documents is essential for producing professional-looking reports that effectively communicate information. Spire.XLS for Python offers a comprehensive suite of APIs within the CellRange class, empowering developers to manage various formatting options seamlessly. This includes adjusting font styles, selecting cell colors, aligning text, and modifying row heights and column widths.
Here are the steps to apply styles and formats to Excel cells using Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get all located range using the Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Get a specific row using the CellRange.Rows[index] property, and set the cell color, text color, text alignment, and row height using the properties under the CellRange object.
- Get a specific column using the CellRange.Columns[index] property, and set the column width using the ColumnWidth property under the CellRange object.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get all located range from the worksheet
allocatedRange = worksheet.AllocatedRange
#Iterate through the rows
for rowNum in range(0, allocatedRange.RowCount):
if rowNum == 0:
# Apply cell color to the header row
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Change the font color of the header row
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
else:
# Apply alternate colors to other rows
if rowNum % 2 == 1:
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Color = Color.get_LightGray()
else:
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Color = Color.get_White()
# Align text to center
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
# Set the row height
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].RowHeight = 20
# Iterate through the columns
for columnNum in range(0, allocatedRange.ColumnCount):
if (columnNum > 0):
# Set the column width
allocatedRange.Columns[columnNum].ColumnWidth = 10
# Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("FormatExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()

Find and Replace Text in Excel in Python
The find and replace functionality in Excel enables users to swiftly locate specific text within their spreadsheets and substitute it with new content, which is particularly useful for data corrections and updates. With Spire.XLS for Python, you can efficiently locate a cell containing a specific string using the Worksheet.FindString() method. Once identified, you can easily replace its value using the CellRange.Value property.
Here are the steps to find and replace text in Excel using Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Find the cell that contains a specified string using the Worksheet.FindString() method.
- Update the cell value using the CellRange.Value property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
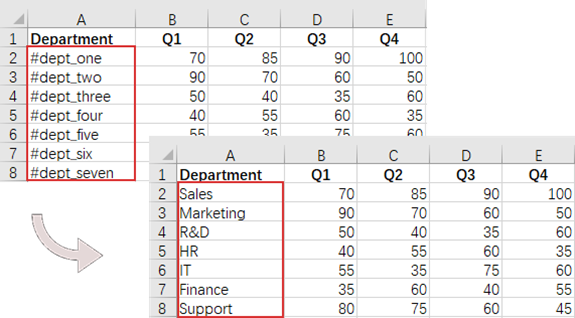
# Define a list of department names for replacement
departments = ["Sales", "Marketing", "R&D", "HR", "IT", "Finance", "Support"]
# Define a list of placeholders that will be replaced in the Excel sheet
placeholders = ["#dept_one", "#dept_two", "#dept_three", "#dept_four", "#dept_five", "#dept_six", "#dept_seven"]
# Iterate through the placeholder strings
for i in range (0, len(placeholders)):
# Find the cell containing the current placeholder string
cell = worksheet.FindString(placeholders[i], False, False)
# Replace the value in the found cell with the corresponding department name
cell.Value = departments[i]
# Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("ReplaceText.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Add Formulas and Charts to Excel in Python
In addition to basic file operations, Spire.XLS for Python provides a variety of advanced techniques for working with Excel files. For example, you can insert formulas into cells using the CellRange.Formula property, which allows for real-time calculations and data analysis directly within your spreadsheet. Furthermore, it allows you to create visually appealing data presentations by adding charts to your worksheets using the Worksheet.Charts.Add() method.
Here are the steps to add formulas and charts to Excel using Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell using the Worksheet.Range property.
- Add a formula to the cell using the CellRange.Formula property.
- Add a column chart to the worksheet using the Worksheet.Charts.Add() method.
- Set the chart data range, position, title and other attributes using the properties under the Chart object.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get all located range
allocatedRange = worksheet.AllocatedRange
#Iterate through the rows
for rowNum in range(0, allocatedRange.RowCount):
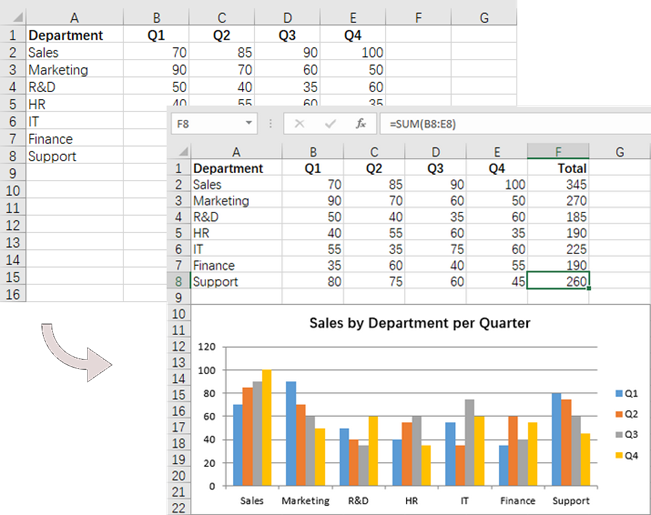
if (rowNum == 0):
# Write text to cell G1
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Text = "Total"
# Apply style to the cell
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Style.Font.IsBold = True
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Right
else:
# Add formulas to the cells from G2 to G8
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Formula = f"=SUM(B{rowNum + 1}:E{rowNum + 1})"
# Add a clustered column chart
chart = worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered)
# Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = worksheet.Range["A1:E8"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 10
chart.RightColumn = 8
chart.BottomRow = 23
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales by Department per Quarter"
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 13
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
# Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("AddFormulaAndChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Dynamically Create, Read, and Modify Excel Files by Byte Streams
2025-01-07 01:19:20 Written by KoohjiIn Excel file processing, using byte streams in Python to create, read, and modify Excel files enables efficient data manipulation and automation. This approach eliminates reliance on physical storage or local filesystems, making it ideal for cloud-based or memory-constrained environments. It also supports real-time data exchange, system integration, and instant feedback in web applications, promoting rapid development and adaptable workflows. In this article, we will explore how to use Spire.XLS for Python to dynamically process Excel workbooks by byte streams with simple Python code.
- Create Excel Files and Save as Byte Streams in Python
- Read Excel Files from Byte Streams in Python
- Modify Excel Files from Byte Streams in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create Excel Files and Save as Byte Streams in Python
With Spire.XLS for Python, we can create an Excel workbook by initializing a Workbook instance and populating it with data. Once the workbook is ready, we can save it to a Stream object and convert that stream into a bytes object for further use or storage. This method allows us to efficiently generate Excel files in memory without the need for disk storage.
Below are the steps for creating an Excel file and saving it as a byte stream with Python:
- Create an instance of the Workbook class to initialize a new Excel workbook. The new workbook includes three default worksheets.
- Retrieve a worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Create a data list or obtain it from another source.
- Iterate through rows and columns to populate the worksheet with data using the Worksheet.Range.get_Item().Value or NumberValue properties.
- Format cells using the properties available in CellRange.Style.
- Create a Stream object and save the workbook to it using the Workbook.SaveToStream() method.
- Convert the stream to a bytes object using the Stream.ToArray() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat, Stream, Color, HorizontalAlignType
# Create an instance of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Create a 2D list of data or read data from other sources
data = [
["Country", "Capital", "Population (Millions)", "Area (km²)", "Continent"],
["United States", "Washington, D.C.", 331, 9833520, "North America"],
["Canada", "Ottawa", 38, 9984670, "North America"],
["Brazil", "Brasília", 213, 8515767, "South America"],
["United Kingdom", "London", 68, 243610, "Europe"],
["Germany", "Berlin", 83, 357022, "Europe"],
["India", "New Delhi", 1391, 3287263, "Asia"],
["China", "Beijing", 1441, 9596961, "Asia"],
["Australia", "Canberra", 26, 7692024, "Oceania"],
["South Africa", "Pretoria", 60, 1219090, "Africa"],
["Japan", "Tokyo", 126, 377975, "Asia"]
]
# Insert the data into the worksheet
for i, row in enumerate(data):
for j, value in enumerate(row):
if isinstance(value, str):
sheet.Range.get_Item(i + 1, j + 1).Value = value
else:
sheet.Range.get_Item(i + 1, j + 1).NumberValue = value
# Format the header row with new colors
headerRow = sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.get_Item(0)
headerRow.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(0, 102, 204) # Blue color for the header
headerRow.Style.Font.FontName = "Calibri"
headerRow.Style.Font.Size = 14
headerRow.Style.Font.IsBold = True
headerRow.Style.Font.Color = Color.FromRgb(255, 255, 255) # White text
headerRow.Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
# Format the data rows with new alternating colors
for i in range(1, sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.Count):
row = sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.get_Item(i)
row.Style.Font.FontName = "Times New Roman"
row.Style.Font.Size = 12
row.Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
if i % 2 == 0:
row.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(229, 243, 255) # Light blue for even rows
else:
row.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(255, 255, 204) # Light yellow for odd rows
# Auto-fit the columns
for i in range(sheet.AllocatedRange.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(i + 1)
# Create a Stream object
stream = Stream()
# Save the workbook to the stream
workbook.SaveToStream(stream, FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
# Convert the stream to bytes
bytes_data = stream.ToArray()
# Write the bytes to a file or use them as needed
with open("output/CreateExcelByStream.xlsx", "wb") as file:
file.write(bytes_data)
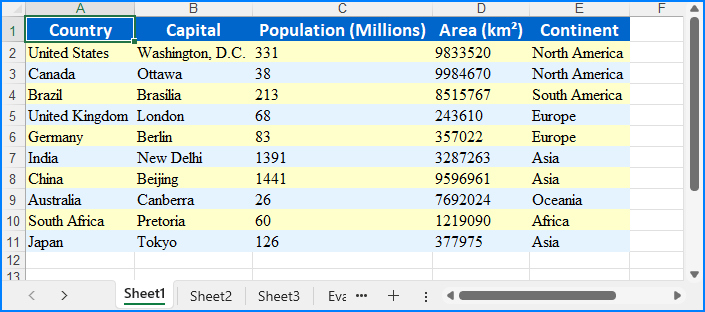
Read Excel Files from Byte Streams in Python
To load an Excel workbook from a byte stream, we can convert the byte data into a Stream object and load it into a Workbook instance. Then, we can then access the worksheet data to extract and utilize the data within the Python application seamlessly.
The steps for reading Excel files from byte streams using Python are as follows:
- Create or convert to a bytes object for the Excel file, or use an existing one.
- Create a Stream object from the bytes.
- Instantiate the Workbook class and load the Excel file from the Stream object using the Workbook.LoadFromStream() method.
- Retrieve a worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Iterate through rows and columns to access cell values using the Worksheet.AllocatedRange.get_Item().Value property.
- Output the values or utilize them as needed.
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, Stream
# Create a bytes object or use an existing one
with open("output/CreateExcelByStream.xlsx", "rb") as file:
bytes_data = file.read()
# Create an instance of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file from the byte stream
workbook.LoadFromStream(Stream(bytes_data))
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Read data from the worksheet
# Create a list to store the data
data = []
for i in range(sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.Count):
# Retrieve a row of data
row = sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.get_Item(i)
# Create a list to store the row's data
row_data = []
for j in range(row.Cells.Count):
# Get the value of the cell
cellValue = sheet.AllocatedRange.get_Item(i + 1, j + 1).Value
row_data.append(cellValue)
data.append(row_data)
# Display the data or use it as needed
for row in data:
print(row)
# Release resources
workbook.Dispose()
Modify Excel Files from Byte Streams in Python
Modifying Excel files from byte streams enables us to update or enhance data dynamically without saving it to disk. This method involves loading the byte stream into a Workbook instance, making changes to its content or formatting, and saving the changes back to a byte stream for reuse.
The following steps show how to modify an Excel workbook from a byte stream using Python:
- Create or convert to a bytes object of the Excel file, or use an existing one.
- Initialize a Stream object from the bytes and load it into a Workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromStream() method.
- Access a worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Modify cell values with the Worksheet.AllocatedRange.get_Item().Value property.
- Format cells using properties in CellRange.Style and add borders with the CellRange.BorderAround() method or the CellRange.BorderInside() method.
- Auto-fit column widths using the Worksheet.AutoFitColumn() method.
- Save the workbook to a new Stream object using the Workbook.SaveToStream() method and convert it back to bytes or bytearray using Stream.ToArray() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, Stream, HorizontalAlignType, Color, FileFormat
# Create a bytes object or use an existing one
with open("output/CreateExcelByStream.xlsx", "rb") as file:
bytes_data = file.read()
# Create an instance of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file from the byte stream
stream = Stream(bytes_data)
workbook.LoadFromStream(stream)
stream.Close()
# Remove unnecessary worksheets (commented out in this case)
#for i in range(1, workbook.Worksheets.Count):
# workbook.Worksheets.RemoveAt(i)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Modify the style of the header row
headerRow = sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.get_Item(0)
headerRow.Style.Font.Bold = False
headerRow.Style.Font.FontName = "Arial"
headerRow.Style.Font.Size = 12
headerRow.Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
headerRow.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(173, 216, 230) # Light blue background color
# Add outline borders for the header row
headerRow.BorderAround()
# Modify the style of the data rows
for i in range(1, sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.Count):
row = sheet.AllocatedRange.Rows.get_Item(i)
row.Style.Font.FontName = "Consolas"
row.Style.Font.Size = 11
if i % 2 == 0:
row.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(240, 240, 240) # Light gray background color for even rows
else:
row.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(255, 255, 255) # White background color for odd rows
# Auto-adjust the column widths
for i in range(sheet.AllocatedRange.Columns.Count):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(i + 1)
# Save the modified Excel file
streamTemp = Stream()
workbook.SaveToStream(streamTemp, FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
# Convert the stream to bytes
bytes_data = streamTemp.ToArray()
# Write the bytes to a file or use them as needed
with open("output/ModifiedExcel.xlsx", "wb") as file:
file.write(bytes_data)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
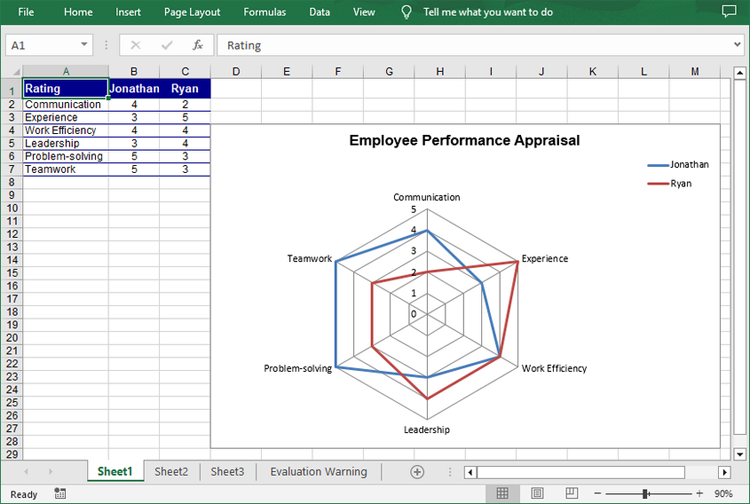
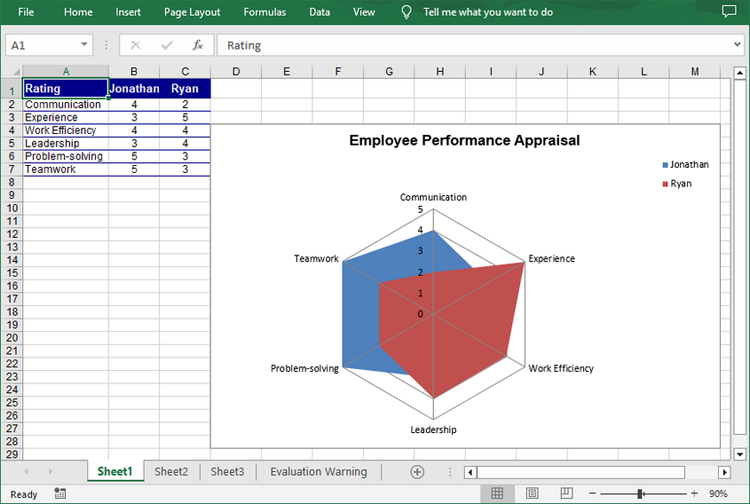
A radar chart, also known as a spider chart, is a graphical method of displaying multivariate data in two dimensions. Each spoke on the chart represents a different variable, and data points are plotted along these spokes. Radar charts are particularly useful for comparing the performance of different entities across several criteria. This article will demonstrate how to create a radar chart in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Simple Radar Chart in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Radar) method to add a standard radar chart to an Excel worksheet. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Add the chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a simple radar chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Radar) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, legend and title of the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
*from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Rating"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Communication"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Experience"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Work Efficiency"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Leadership"
sheet.Range["A6"].Value = "Problem-solving"
sheet.Range["A7"].Value = "Teamwork"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jonathan"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 3
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 3
sheet.Range["B6"].NumberValue = 5
sheet.Range["B7"].NumberValue = 5
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Ryan"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 2
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 5
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range["C6"].NumberValue = 3
sheet.Range["C7"].NumberValue = 3
# Set font styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Size = 11
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
# Set row height and column width
sheet.Rows[0].RowHeight = 20
sheet.Range["A1:C7"].Columns[0].ColumnWidth = 15
# Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.get_DarkBlue()
sheet.Range["A2:C7"].Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin
sheet.Range["A2:C7"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.get_DarkBlue()
sheet.Range["B1:C7"].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:C7"].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
# Add a radar chart to the worksheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Radar)
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4
chart.TopRow = 4
chart.RightColumn = 14
chart.BottomRow = 29
# Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C7"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Employee Performance Appraisal"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 14
chart.PlotArea.Fill.Visible = False
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Corner
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("CreateRadarChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Create a Filled Radar Chart in Excel in Python
A filled radar chart is a variation of a standard radar chart, with the difference that the area between each data point is filled with color. The following are the steps to create a filled radar chart using Python:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Add the chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a filled radar chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.RadarFilled) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, legend and title of the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Rating"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Communication"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Experience"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Work Efficiency"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Leadership"
sheet.Range["A6"].Value = "Problem-solving"
sheet.Range["A7"].Value = "Teamwork"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jonathan"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 3
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 3
sheet.Range["B6"].NumberValue = 5
sheet.Range["B7"].NumberValue = 5
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Ryan"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 2
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 5
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range["C6"].NumberValue = 3
sheet.Range["C7"].NumberValue = 3
# Set font styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Size = 11
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
# Set row height and column width
sheet.Rows[0].RowHeight = 20
sheet.Range["A1:C7"].Columns[0].ColumnWidth = 15
# Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.get_DarkBlue()
sheet.Range["A2:C7"].Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin
sheet.Range["A2:C7"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.get_DarkBlue()
sheet.Range["B1:C7"].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:C7"].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
# Add a filled radar chart to the worksheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.RadarFilled)
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4
chart.TopRow = 4
chart.RightColumn = 14
chart.BottomRow = 29
# Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C7"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Employee Performance Appraisal"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 14
chart.PlotArea.Fill.Visible = False
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Corner
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("FilledRadarChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Charts in Excel are powerful tools that transform raw data into visual insights, making it easier to identify trends and patterns. Often, you may need to manage or adjust these charts to better suit your needs. For instance, you might need to extract the data behind a chart for further analysis, resize a chart to fit your layout, move a chart to a more strategic location, or remove outdated charts to keep your workbook organized and clutter-free. In this article, you will learn how to extract, resize, move, and remove charts in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Extract the Data Source of a Chart in Excel
- Resize a Chart in Excel
- Move a Chart in Excel
- Remove a Chart from Excel
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Extract the Data Source of a Chart in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Chart.DataRange property, which allows you to define or retrieve the cell range used as the data source for a chart. After retrieving this range, you can access the data it contains for further processing or analysis. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the worksheet containing the chart using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the chart using the Worksheet.Charts[index] property.
- Get the cell range that is used as the data source of the chart using the Chart.DataRange property.
- Loop through the rows and columns in the cell range and get the data of each cell.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ChartSample.xlsx")
# Get the worksheet containing the chart
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the chart
chart = sheet.Charts[0]
# Get the cell range that the chart uses
cellRange = chart.DataRange
# Iterate through the rows and columns in the cell range
for i in range(len(cellRange.Rows)):
for j in range(len(cellRange.Rows[i].Columns)):
# Get the data of each cell
print(cellRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value + " ", end='')
print("")
workbook.Dispose()
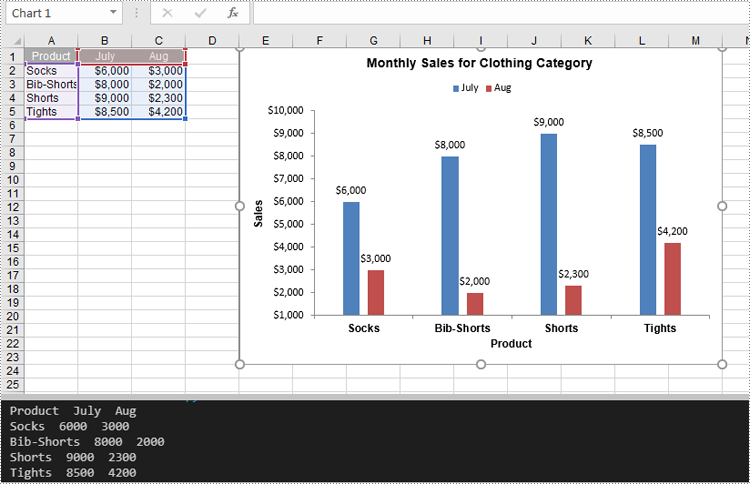
Resize a Chart in Excel in Python
Resizing a chart allows you to adjust its dimensions to fit specific areas of your worksheet or enhance its readability. With Spire.XLS for Python, you can adjust the chart's dimensions using the Chart.Width and Chart.Height properties. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the worksheet containing the chart using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the chart using the Worksheet.Charts[index] property.
- Adjust the chart’s dimensions using the Chart.Width and Chart.Height properties.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ChartSample.xlsx")
# Get the worksheet containing the chart
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the chart
chart = sheet.Charts[0]
# Resize the chart
chart.Width = 450
chart.Height = 300
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ResizeChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
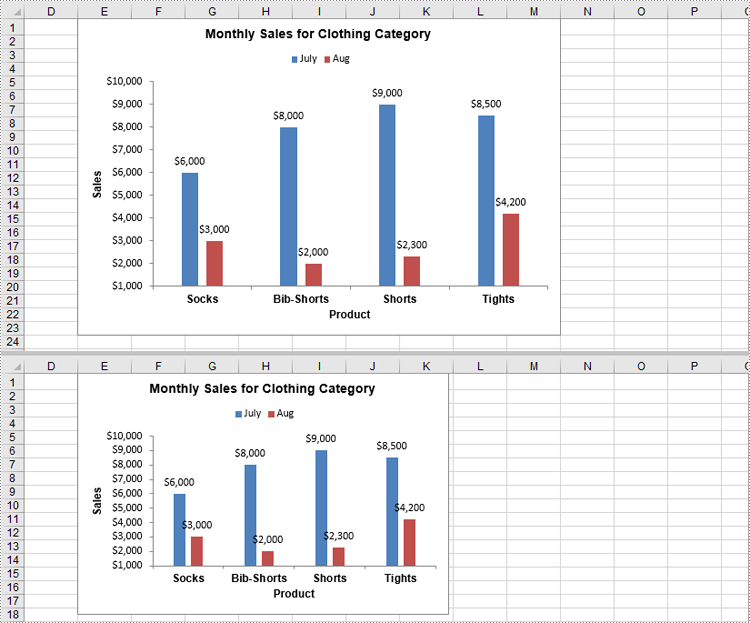
Move a Chart in Excel in Python
Moving a chart lets you reposition it for better alignment or to relocate it to another sheet. You can use the Chart.LeftColumn, Chart.TopRow, Chart.RightColumn, and Chart.BottomRow properties to specify the new position of the chart. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the worksheet containing the chart using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the chart using the Worksheet.Charts[index] property.
- Set the new position of the chart using the Chart.LeftColumn, Chart.TopRow, Chart.RightColumn, and Chart.BottomRow properties.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ChartSample.xlsx")
# Get the worksheet containing the chart
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the chart
chart = sheet.Charts[0]
# Set the new position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 7
chart.RightColumn = 9
chart.BottomRow = 30
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("MoveChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
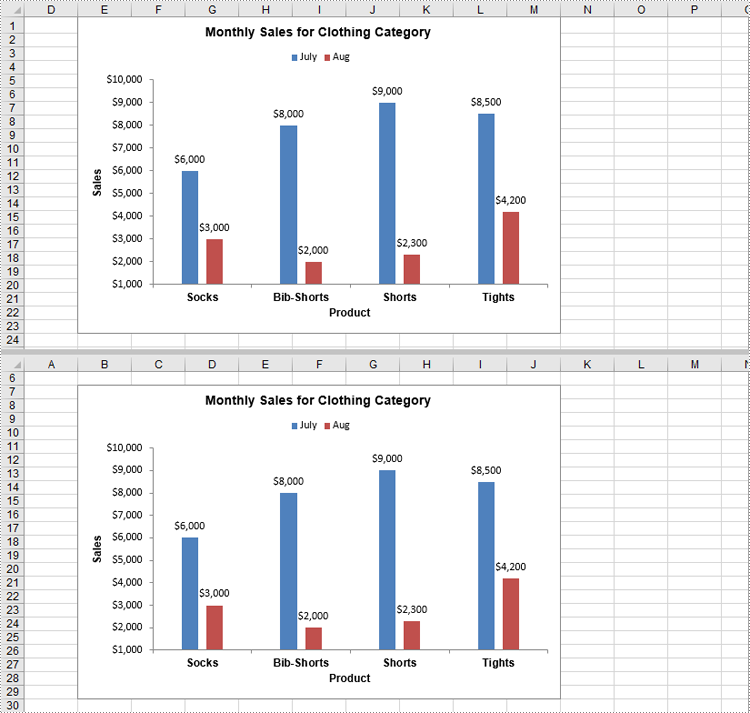
Remove a Chart from Excel in Python
Removing unnecessary or outdated charts from your worksheet helps keep your document clean and organized. In Spire.XLS for Python, you can use the Chart.Remove() method to delete a chart from an Excel worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the worksheet containing the chart using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the chart using the Worksheet.Charts[index] property.
- Remove the chart using the Chart.Remove() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ChartSample.xlsx")
# Get the worksheet containing the chart
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the chart
chart = sheet.Charts[0]
# Remove the chart
chart.Remove()
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("RemoveChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
