
Program Guide (108)
Children categories
Python: Set the Background Color and Image for Excel Worksheets
2024-03-15 08:01:56 Written by KoohjiFor data analysis and reporting, visual aesthetics play a significant role in presenting information effectively. When working with Excel worksheets, the ability to set background colors and images enhances the overall readability and impact of the data. By leveraging the power of Python, developers can effortlessly manipulate Excel files and customize the appearance of their worksheets. This article demonstrates how to use Spire.XLS for Python to set the background color and image for Excel worksheets with Python programs.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set the Background Color for an Excel Worksheet
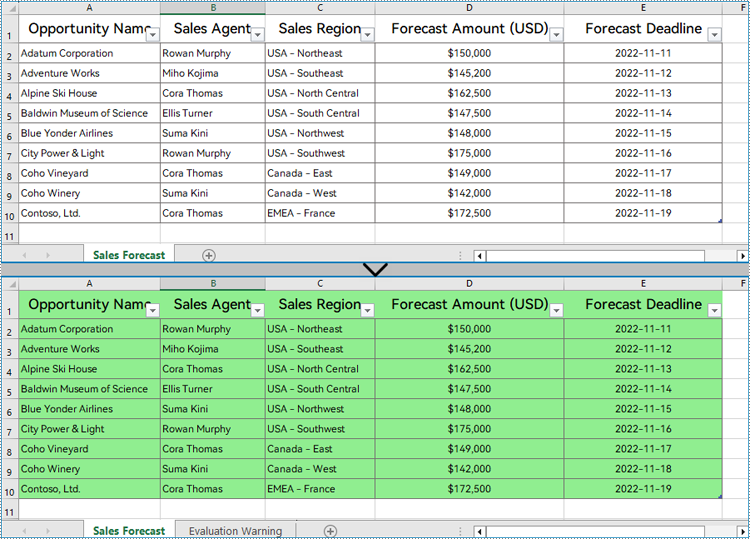
With Spire.XLS for Python, developers can set the background color for a specified cell range through CellRange.Style.Color property. The detailed steps for setting the background color for the used cell range in a worksheet are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Get the used range in the worksheet through Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Set the background color of the used range through CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook class
wb = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get a worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get the used range of the worksheet
usedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Set the background color of the used range to a light and soft color
usedRange.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(144, 238, 144)
# Save the workbook
wb.SaveToFile("output/ExcelBackgroundColor.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
wb.Dispose()
Set the Background Image for an Excel Worksheet
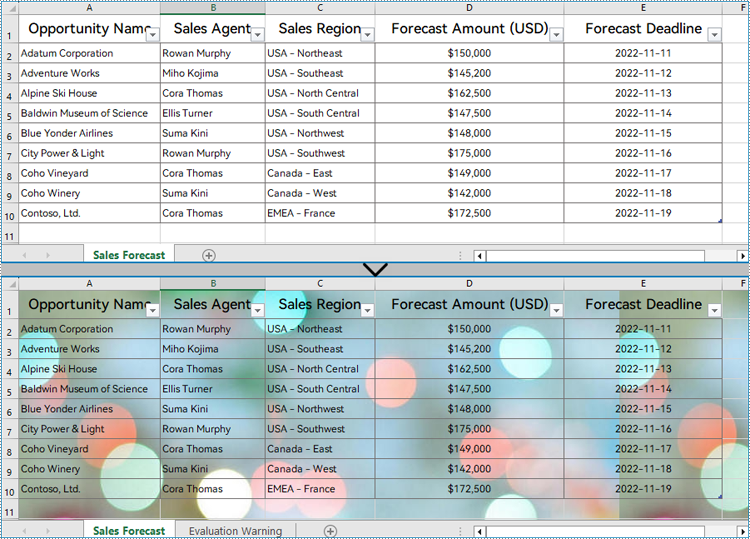
Setting a background image for an Excel worksheet can be accomplished through PageSetup class. Using the Worksheet.PageSetup.BackgroundImage property, developers can set the image background for the entire worksheet. Detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Load an image using Stream() method.
- Set the background image of the worksheet through Worksheet.PageSetup.BackgroundImage property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook class
wb = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get a worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Load an image
image = Stream("BackgroundImage.jpg")
# Set the background of the worksheet
sheet.PageSetup.BackgoundImage = image
# Save the workbook
wb.SaveToFile("output/ExcelBackgroundImage.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
wb.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Shapes are a powerful tool in Excel that enables you to transform raw data into visually appealing and informative representations. By inserting and customizing shapes, you can create clear, engaging, and visually impactful spreadsheets that effectively communicate your data and captivate your audience. In this article, we will demonstrate how to insert and remove shapes in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Insert Shapes in Excel in Python
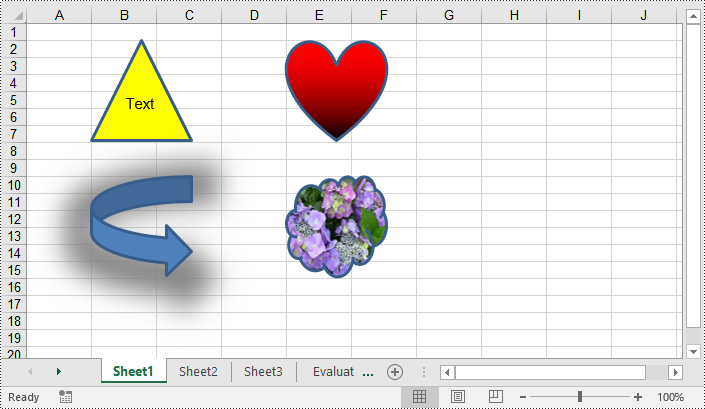
You can add numerous types of shapes, such as lines, rectangles, triangles, and stars, to an Excel worksheet by using the Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. Once added, you can customize the shapes, such as adding text to the shapes, filling the shapes with solid or gradient colors or images, and setting shadow styles for the shapes. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Add a shape to the worksheet using Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape() method.
- Add text to the shape using IPrstGeomShape.Text property.
- Fill the shape with a color using IPrstGeomShape.Fill.ForeColor property.
- Set the fill type of the shape as solid using IPrstGeomShape.Fill.FillType property.
- Repeat the above steps to add more shapes to the worksheet.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a triangle shape to the worksheet
triangle = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(2, 2, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.Triangle)
# Add text to the shape
triangle.Text = "Text"
# Fill the triangle with a solid color
triangle.Fill.ForeColor = Color.get_Yellow()
triangle.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.SolidColor
# Add a heart shape to the worksheet
heart = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(2, 5, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.Heart)
# Fill the heart with a gradient color
heart.Fill.ForeColor = Color.get_Red()
heart.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.Gradient
# Add an arrow shape with the default color to the worksheet
arrow = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(10, 2, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.CurvedRightArrow)
# Set shadow style for the arrow
arrow.Shadow.Angle = 90
arrow.Shadow.Distance = 10
arrow.Shadow.Size = 150
arrow.Shadow.Color = Color.get_Gray()
arrow.Shadow.Blur = 30
arrow.Shadow.Transparency = 1
arrow.Shadow.HasCustomStyle = True
# Add a cloud shape to the worksheet
cloud = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(10, 5, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.Cloud)
# Fill the cloud with a custom picture
cloud.Fill.CustomPicture(Image.FromFile("Hydrangea.jpg"), "Hydrangea.jpg")
cloud.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.Picture
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("InsertShapes.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Remove Shapes from Excel in Python
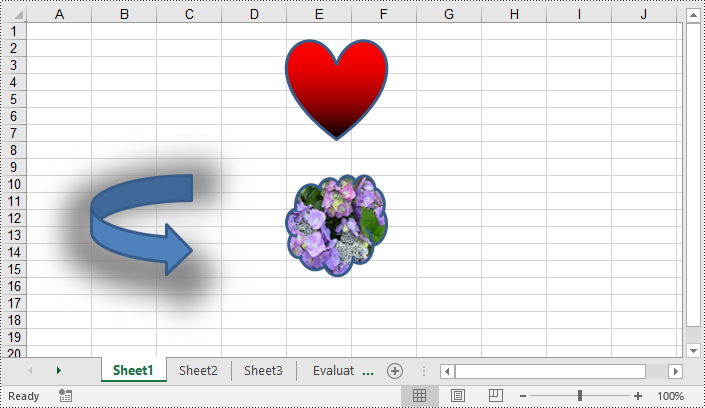
Shapes can improve the visual appearance of your workbook, but they can also increase the file size of it. Removing unnecessary shapes helps reduce the file size, making it more manageable and easier to share or store. Spire.XLS for Python enables you to remove specific shapes from a worksheet effortlessly by using the Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes[index].Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific shape from the Worksheet using Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes[index].Remove() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("InsertShapes.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Remove the first shape from the worksheet
sheet.PrstGeomShapes[0].Remove()
#Save to file.
workbook.SaveToFile("RemoveShapes.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
If you have additional pieces of information to include in your spreadsheet, inserting rows or columns can provide room for these new fields. In addition,
adding blank rows or columns between data sets can also help to effectively separate different categories of information, making them easier to read and analyze. This article will demonstrate how to insert rows and columns in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Insert a Row and a Column in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int) and Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int) methods for inserting a blank row and a blank column in an Excel worksheet. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
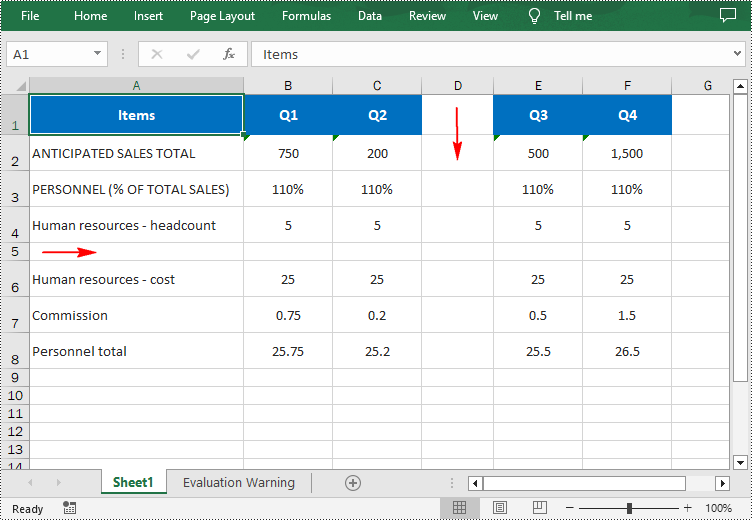
- Insert a row into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int) method.
- Insert a column into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "input.xlsx" outputFile = "InsertRowAndColumn.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel document workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get a specified worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Insert a blank row as the 5th row in the worksheet worksheet.InsertRow(5) # Insert a blank column as the 4th column in the worksheet worksheet.InsertColumn(4) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
Insert Multiple Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
To insert multiple rows and columns into a worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int, rowCount: int) and Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int, columnCount: int) methods. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
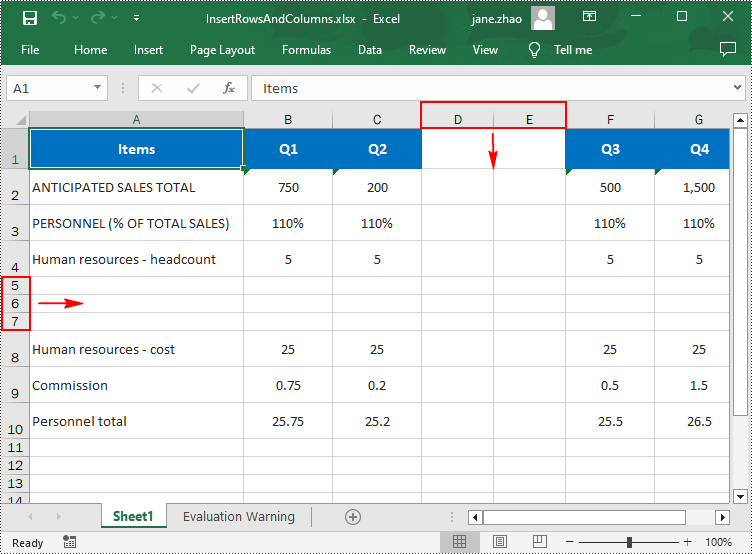
- Insert multiple rows into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int, rowCount: int) method.
- Insert multiple columns into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int, columnCount: int) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "input.xlsx" outputFile = "InsertRowsAndColumns.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel document workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get a specified worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Insert three blank rows into the worksheet worksheet.InsertRow(5, 3) #Insert two blank columns into the worksheet worksheet.InsertColumn(4, 2) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Moving and deleting worksheets in Excel are essential operations that allow you to organize and manage your workbook efficiently. Moving worksheets enables you to adjust the order of worksheets to match your specific needs or bring related information together. While deleting worksheets helps you eliminate unwanted or redundant sheets, creating a cleaner and more organized workspace. In this article, we will demonstrate how to move and delete worksheets in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Move a Worksheet in Excel in Python
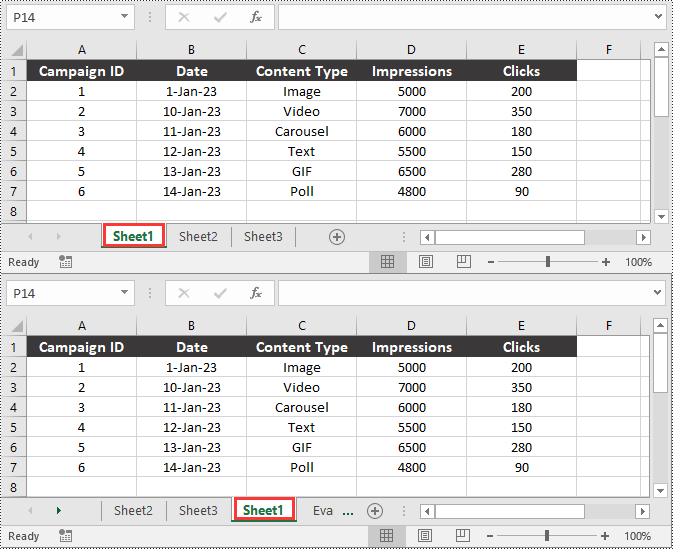
You can easily move a worksheet in an Excel file to another position by using the Worksheet.MoveWorksheet() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheet[] property.
- Move the worksheet to another position in the file using the Worksheet.MoveWorksheet() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet in the file by its index
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Or get a specific worksheet in the file by its name
# sheet = workbook.Worksheets["Sheet1"]
# Move the worksheet to the 3rd position in the file
sheet.MoveWorksheet(2)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("MoveWorksheet.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Delete a Worksheet in Excel in Python
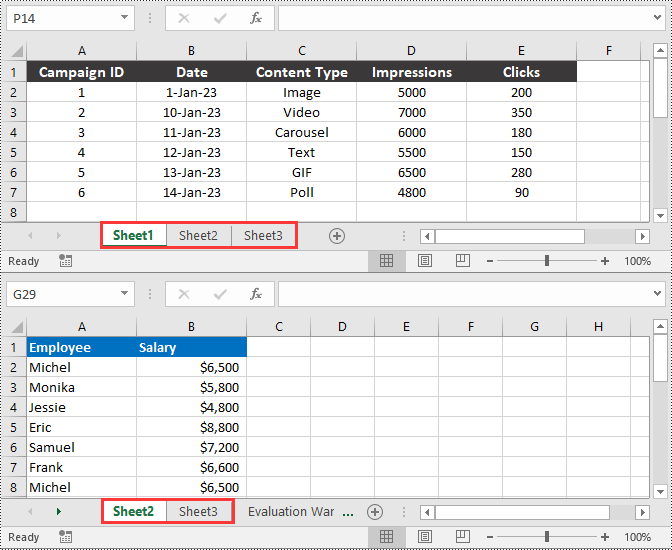
You can delete a specific worksheet from an Excel file by using the Workbook.Worksheets.RemoveAt() or Workbook.Worksheets.Remove() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific worksheet from the file using the Workbook.Worksheets.RemoveAt() or Workbook.Worksheets.Remove() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Remove a specific worksheet in the file by its index
workbook.Worksheets.RemoveAt(0)
# Or get a specific worksheet in the file by its name and then remove it
# worksheet = workbook.Worksheets["Sheet1"]
# workbook.Worksheets.Remove(worksheet)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("DeleteWorksheet.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Cell borders play a crucial role in enhancing the visual clarity and organization of data in Excel spreadsheets. Adding borders to cells can help draw attention to specific data points, highlight headers, or create clear boundaries between different sections of your worksheet. On the other hand, removing borders can provide a sleek and seamless appearance, especially when you want to eliminate distractions and focus solely on the data itself.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the process of adding or removing cell borders in Excel by using the Spire.XLS for Python library.
- Add Borders to a Selected Cell or Cell Range in a Worksheet
- Add Borders to the Cell Range Containing Data in a Worksheet
- Add Left, Top, Right, Bottom, Diagonal Borders to a Cell
- Remove Borders of a Cell or Cell Range in a Worksheet
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Borders to a Selected Cell or Cell Range in a Worksheet in Python
Borders can be applied to individual cells, groups of cells, or even entire ranges to create clear boundaries and make data stand out. By adding borders, you can effectively organize and structure your data, making it easier to analyze and understand.
With Spire.XLS for Python, accessing specific cells or cell ranges is made easy through the Worksheet.Range[name: str] property. Once you have obtained the desired cell or cell range, you can apply an outside border using the CellRange.BorderAround() method. Additionally, you can apply inside borders to a cell range using the CellRange.BorderInside() method.
To apply borders to a cell or cell range, follow the steps below.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Get a cell or cell range using Worksheet.Range[name: str] property.
- Apply outside borders to the cell or cell range using CellRange.BorderAround() method.
- Apply inside borders to the cell range using CellRange.BorderInside() method.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific cell
cell = worksheet.Range["C11"]
# Apply borders to the cell
cell.BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium, Color.get_Black())
# Get a cell range
cellRange = worksheet.Range["B2:C6"]
# Apply outside borders to the cell range
cellRange.BorderAround(LineStyleType.Thin, Color.get_Black())
# Apply inside borders to the cell range
cellRange.BorderInside(LineStyleType.Thin, Color.get_Black())
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("Output/AddBordersToCellRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
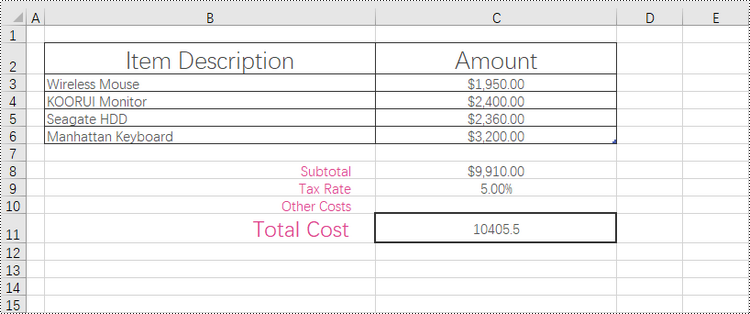
Add Borders to the Cell Range Containing Data in a Worksheet in Python
The range that contains data in a worksheet is commonly referred to as the "allocated range" or "used range". It represents the rectangular area that encompasses all the cells with data, including text, numbers, formulas, and other types of content.
To retrieve the cell range having data, use the Worksheet.AllocatedRange property. Then, you can easily apply borders to this range using the BorderAround() and BorderInside() methods.
The steps to add borders to the cell range containing data are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Get the cell range that contains data using Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Apply outside borders to the cell or cell range using CellRange.BorderAround() method.
- Apply inside borders to the cell range using CellRange.BorderInside() method.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the cell range that contains data
locatedRange = worksheet.AllocatedRange
# Apply outside borders to the cell range
locatedRange .BorderAround(LineStyleType.MediumDashed, Color.get_Black())
# Apply inside borders to the cell range
locatedRange .BorderInside(LineStyleType.Thin, Color.get_Black())
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("Output/AddBordersToLocatedRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
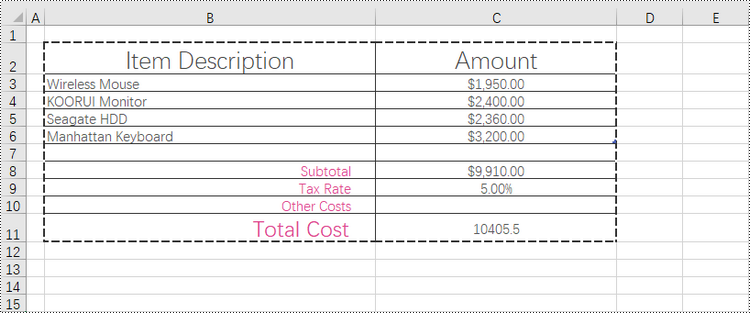
Add Left, Top, Right, Bottom, Diagonal Borders to a Cell in Python
In addition to applying outside and inside borders, you have the option to add left, top, right, bottom, and diagonal borders to individual cells or cell ranges. This feature allows you to go beyond basic border customization and provides additional flexibility to highlight important information, separate sections within your worksheet, or provide a visual structure to your data.
Spire.XLS provides convenient access to specific borders, including the left, right, top, bottom, and diagonal borders, through properties such as CellRange.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft]. Once you have obtained the desired border, you have the flexibility to customize its appearance by utilizing the IBorder.LineStyle property and the IBorder.Color property.
To add left, top, right, bottom, diagonal borders to a cell, follow the following steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Get a specific cell using Worksheet.Range property.
- Get the left, top, right, bottom and diagonal borders of the cell using the properties such as CellRange.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].
- Set the line style of the border using IBorder.LineStyle property
- Set the color of the border using IBorder.Color property.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a cell
cell = worksheet.Range["B11"]
# Get the left, top, right, bottom border of the cell
leftBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft]
topBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop]
rightBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight]
bottomBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom]
# Set the border type respectively
leftBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thick
topBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.Dotted
rightBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.SlantedDashDot
bottomBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.Double
# Set the border color respectively
leftBorder.Color = Color.get_Red()
topBorder.Color = Color.get_Brown()
rightBorder.Color = Color.get_DarkGray()
bottomBorder.Color = Color.get_OrangeRed()
# Get a specific cell
cell = worksheet.Range["C10"]
# Get the diagonal border of the cell
diagonalBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.DiagonalDown]
# Set the border style
diagonalBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("Output/BorderOfEdge.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
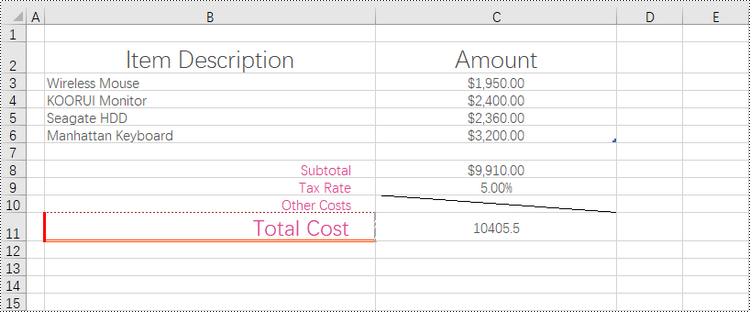
Remove Borders of a Cell or Cell Range in a Worksheet in Python
Borders can be removed from individual cells, groups of cells, or even entire ranges, allowing you to reduce visual noise and clutter, making your data easier to interpret and analyze. Additionally, you can choose to remove borders from specific sides of a cell, such as the left, top, right, or bottom, which can alter the visual appearance and enhance the overall presentation.
To eliminate borders surrounding or within a cell or cell range, you can easily achieve this by setting the CellRange.Borders.LineStyle property to LineStyleType.none. Similarly, if you want to remove a border on a specific side, such as the left side, you can accomplish this by setting the CellRange.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].LineStyle property to LineStyleType.none.
The steps to remove borders of a cell or cell range as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Get a specific cell or cell range using Worksheet.Range property.
- Remove all borders of the cell or cell range by setting CellRange.Borders.LineStyle property to LineStyleType.none.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\BorderExample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a cell
cell = worksheet.Range["C11"]
# Remove borders by setting line style to none
cell.Borders.LineStyle = LineStyleType.none
# Remove border on a specific side
# cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].LineStyle = LineStyleType.none
# Get a cell range
cellRange = worksheet.Range["B2:C6"]
# Remove borders by setting line style to none
cellRange.Borders.LineStyle = LineStyleType.none
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("Output/RemoveBorders.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
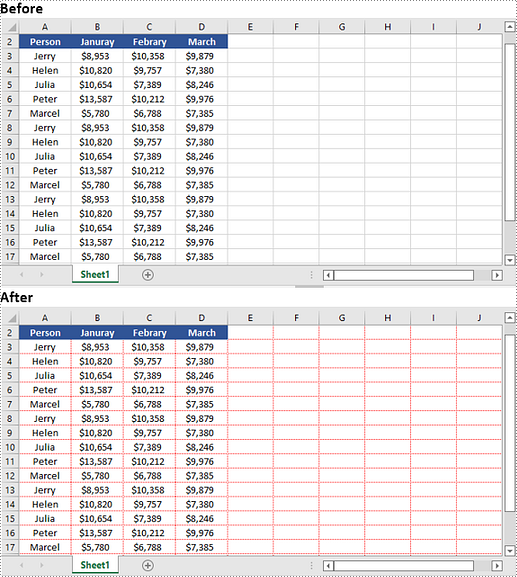
Gridlines in Microsoft Excel provide a visual aid that helps users navigate through data and maintain a structured layout. By default, Excel displays gridlines in a light color to separate cells, making it easier to distinguish and locate specific data. However, there are instances when you may want to hide or even modify the appearance of gridlines to suit your specific needs. In this article, we will explore how to hide, show, and change gridlines in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
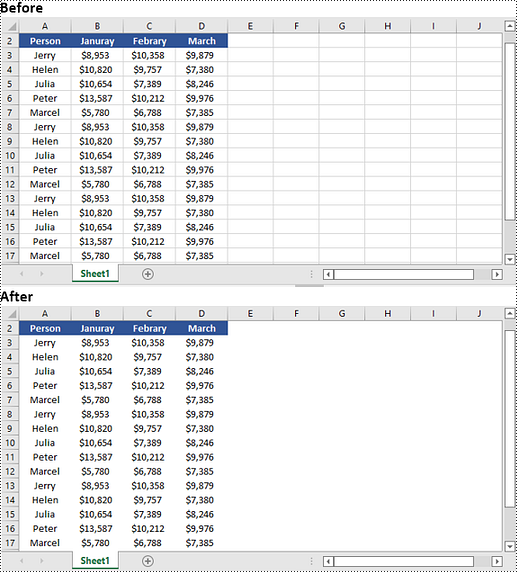
Hide or Show Gridlines in Excel in Python
The Worksheet.GridLinesVisible property provided by Spire.XLS for Python is used to control the visibility of gridlines in an Excel worksheet. If you want to hide the gridlines in the worksheet, set this property to False. Conversely, if you wish to make the hidden gridlines visible again, set this property to True. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Hide or show the gridlines in the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.GridLinesVisible property as False or True.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Hide the gridlines in the worksheet
sheet.GridLinesVisible = False
# Show the hidden gridlines in the worksheet
# sheet.GridLinesVisible = True
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("HideGridlines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Change Gridlines in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.GridLineColor property, which allows you to customize the color of gridlines in an Excel worksheet. By using this property, you can change the default color of gridlines to your desired choice. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Change the color of the gridlines in the worksheet using the Worksheet.GridLineColor property.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Change the color of the gridlines in the worksheet
sheet.GridLineColor = ExcelColors.Red
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ChangeGridlineColor.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
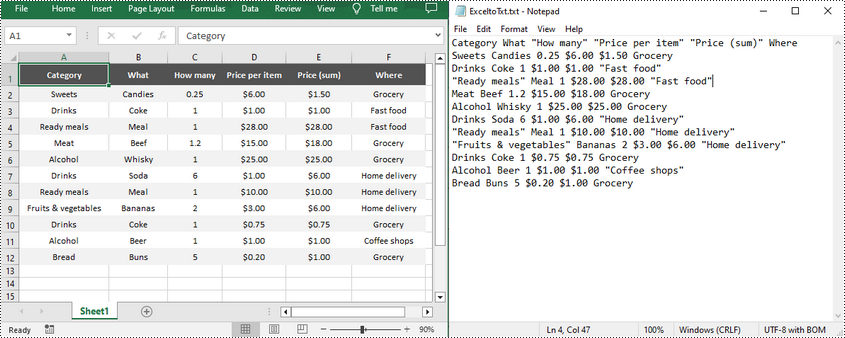
Text files have a distinct advantage over Excel spreadsheets in terms of simplicity as they don't contain complex formatting, macros or formulas. This streamlined nature not only enhances portability, but also reduces the possibility of file corruption. Consequently, converting Excel files to text files can greatly facilitates data parsing and ensures compatibility with various applications. In this article, you will learn how to convert Excel to TXT text file in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Convert Excel to TXT in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Worksheet.SaveToFile(fileName: str, separator: str, encoding: Encoding) method to convert a specified worksheet to a TXT text file. The three parameters represent:
- fileName: Specifies the path and the name of the output text file.
- separator: Specifies the separator for the output text file. Common separators include commas (,), tabs, semicolons (;), etc.
- encoding: Specifies the encoding format of the file, e.g. UTF-8, Unicode, ASCII, etc. You need to use the correct encoding format to ensure that the text is represented and interpreted correctly.
The following are the detailed steps to convert Excel to text files in Python.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet by its index using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Convert the Excel worksheet to a TXT file using Worksheet.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
import os import sys curPath = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) rootPath = os.path.split(curPath)[0] sys.path.append(rootPath) from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "Inventories.xlsx" outputFile = "ExceltoTxt.txt" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel document from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Save the worksheet as a txt file sheet.SaveToFile(outputFile, " ", Encoding.get_UTF8()) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Images in Excel can enhance data visualization and help convey information effectively. Apart from inserting/deleting images in Excel with Spire.XLS for Python, you can also use the library to replace existing images with new ones, or extract images for reuse or backup. This article will demonstrate how to replace or extract images in Excel in Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Replace Images in Excel with Python
To replace a picture in Excel, you can load a new picture and then set it as the value of the ExcelPicture.Picture property. The following are the detailed steps to replace an Excel image with another one.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get a specified picture from the worksheet using Worksheet.Pictures[] property.
- Load an image and then replace the original picture with it using ExcelPicture.Picture property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile ("ExcelImg.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first picture from the worksheet
excelPicture = sheet.Pictures[0]
# Replace the picture with another one
excelPicture.Picture = Image.FromFile("logo.png")
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ReplaceImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)

Extract Images from Excel with Python
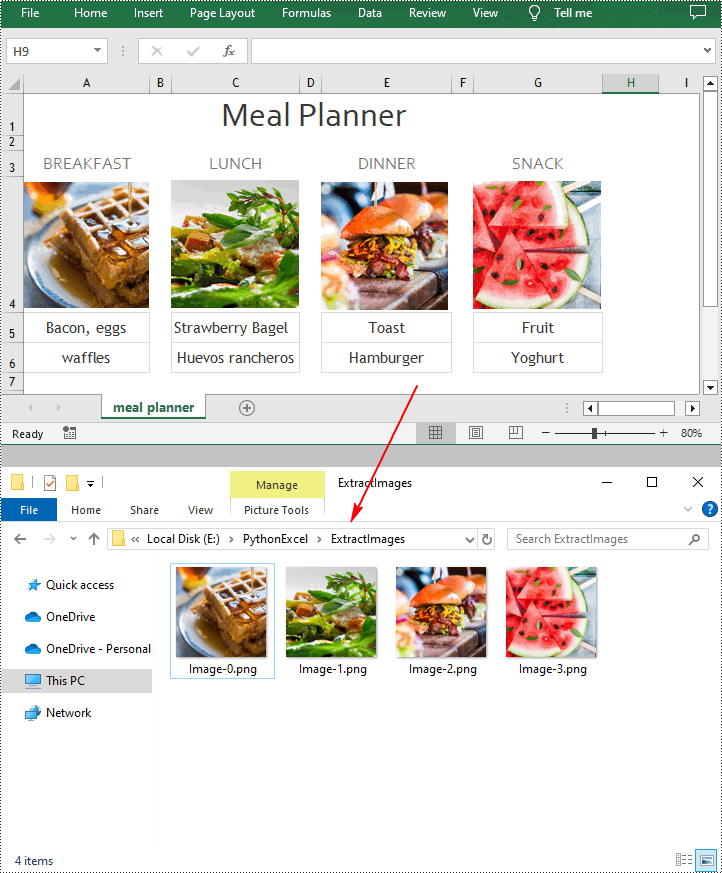
Spire.XLS for Python provides the ExcelPicture.Picture.Save() method to save the images in Excel to a specified file path. The following are the detailed steps to extract all images in an Excel worksheet at once.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Loop through to get all pictures in the worksheet using Worksheet.Pictures property.
- Extract pictures and save them to a specified file path using ExcelPicture.Picture.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Test.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get all images in the worksheet
for i in range(sheet.Pictures.Count - 1, -1, -1):
pic = sheet.Pictures[i]
# Save each image as a PNG file
pic.Picture.Save("ExtractImages\\Image-{0:d}.png".format(i), ImageFormat.get_Png())
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is a flexible file format widely used on the web. Unlike traditional image formats, SVG files are not based on pixels. Instead, they use mathematical equations to define shapes, lines, and colors. This unique characteristic allows SVG files to be scaled up or down without any loss of quality, making them an excellent choice for creating interactive and visually appealing graphics. By converting Excel files to SVG, you can seamlessly embed the resulting SVG files into web pages, ensuring smooth integration and display of your Excel data on the web. In this article, we will demonstrate how to convert Excel to SVG format in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Convert a Worksheet in Excel to SVG in Python
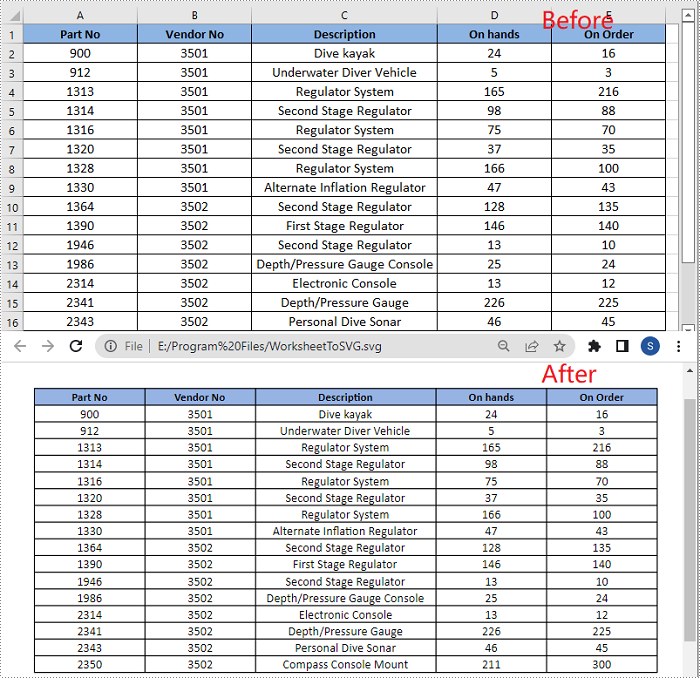
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.ToSVGStream() method to convert an Excel worksheet to SVG. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index through Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Create an object of the Stream class.
- Save the worksheet to an SVG using Worksheet.ToSVGStream() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample1.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Save the worksheet to an SVG
stream = Stream("WorksheetToSVG.svg")
worksheet.ToSVGStream(stream, 0, 0, 0, 0)
stream.Flush()
stream.Close()
workbook.Dispose()
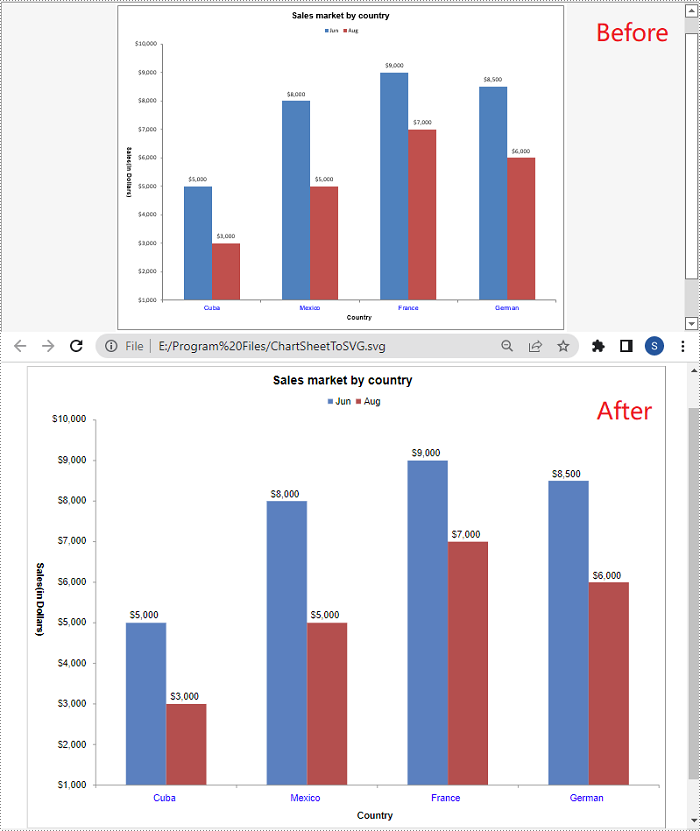
Convert a Chart Sheet in Excel to SVG in Python
A chart sheet in Excel is a separate sheet within an Excel workbook that is dedicated to displaying a chart. Spire.XLS for Python allows you to convert a chart sheet to SVG by using the ChartSheet.ToSVGStream() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific chart sheet using Workbook.GetChartSheetByName() method.
- Create an object of the Stream class.
- Save the chart sheet to an SVG using ChartSheet.ToSVGStream() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample2.xlsx")
# Get a specific chart sheet
chartSheet = workbook.GetChartSheetByName("Chart1")
# Save the chart sheet to an SVG
stream = Stream("ChartSheetToSVG.svg")
chartSheet.ToSVGStream(stream)
stream.Flush()
stream.Close()
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Accepting and rejecting tracked changes in Excel are essential features that empower users to effectively manage and control modifications made by multiple contributors. Accepting changes allows users to include modifications in the spreadsheet, facilitating collaboration and ensuring that the final version reflects collective input. Conversely, rejecting changes enables users to maintain the original content and avoid incorporating incorrect or unnecessary modifications. These functions provide users with the ability to maintain data integrity, ensure document accuracy, and streamline the collaborative process in Excel. In this article, we will demonstrate how to accept and reject tracked changes in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Accept Tracked Changes in Excel in Python
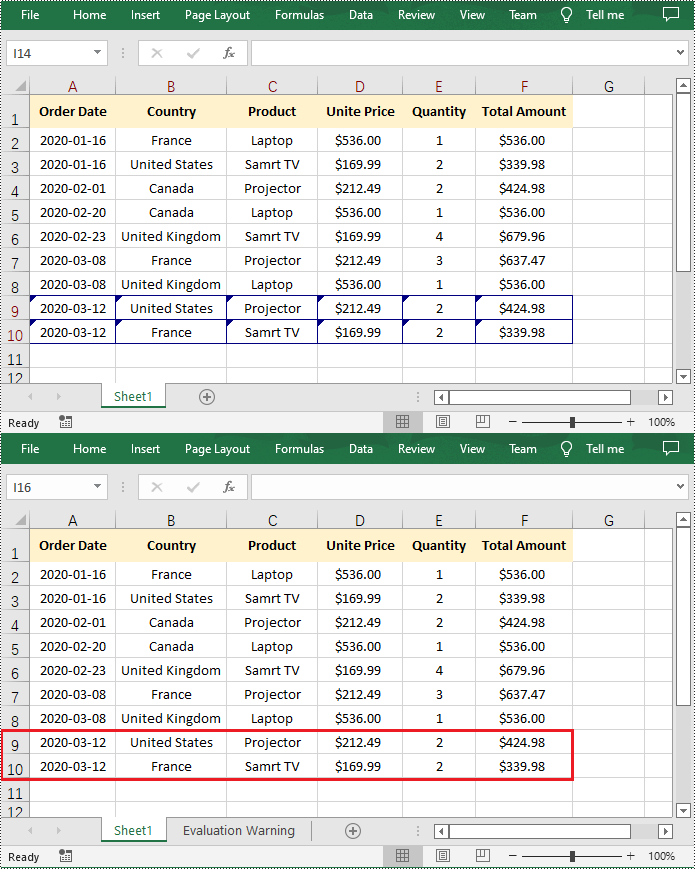
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Workbook.HasTrackedChanges property to determine whether an Excel workbook has tracked changes or not. If the property returns True, you can use the Workbook.AcceptAllTrackedChanges() method to accept these changes at once.
The following steps explain how to accept all tracked changes in an Excel workbook using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Check if the workbook has tracked changes using Workbook.HasTrackedChanges property.
- Accept all tracked changes in the workbook using Workbook.AcceptAllTrackedChanges() method.
- Save the result workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "AcceptChanges.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Check if the file has tracked changes
if workbook.HasTrackedChanges:
# Accept all tracked changes in the file
workbook.AcceptAllTrackedChanges()
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Reject Tracked Changes in Excel in Python
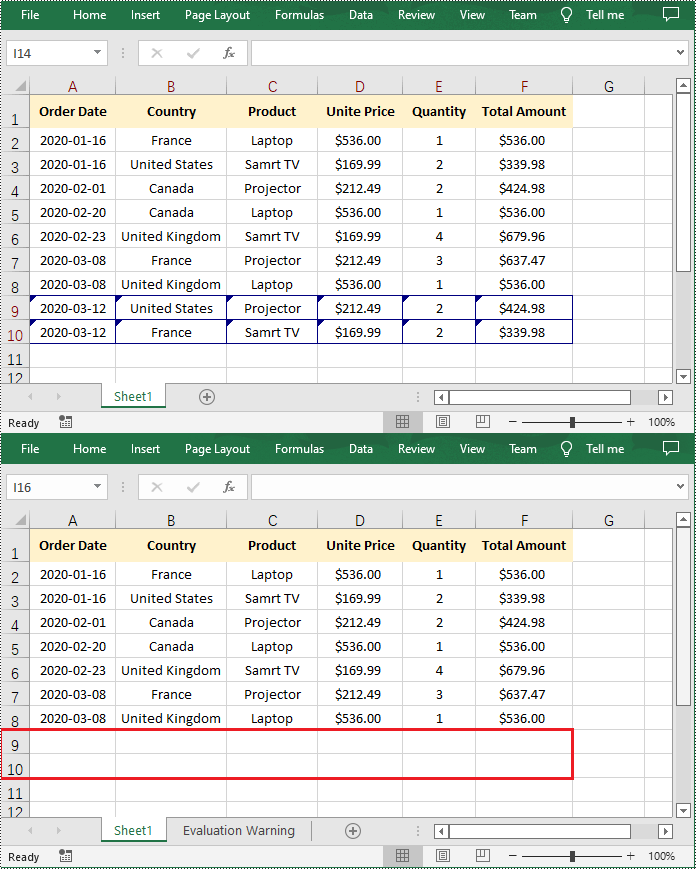
If the changes made to a workbook compromise the integrity of the data, such as introducing errors, inconsistencies, or inaccuracies, you can reject these changes by using the Workbook.RejectAllTrackedChanges() method.
The following steps explain how to reject all tracked changes in an Excel workbook using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Check if the workbook has tracked changes using Workbook.HasTrackedChanges property.
- Reject all tracked changes in the workbook using Workbook.RejectAllTrackedChanges() method.
- Save the result workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "RejectChanges.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Check if the file has tracked changes
if workbook.HasTrackedChanges:
# Reject all tracked changes in the file
workbook.RejectAllTrackedChanges()
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
