
Program Guide (108)
Children categories
Pivot tables provide a flexible way to organize, manipulate, and summarize data from different perspectives, enabling users to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions. With pivot tables, you can easily rearrange and summarize data based on various criteria, such as categories, dates, or numerical values. This feature is particularly useful when dealing with complex datasets or when you need to compare and analyze data from different angles. In this article, you will learn how to create or operate pivot tables in an Excel document using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Pivot Table in Excel in Python
- Sort Pivot Table by Column Values in Python
- Expand or Collapse Rows in Pivot Table in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Pivot Table in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the PivotTable class to work with pivot tables in an Excel document. To create a pivot table based on the data in an existing Excel worksheet, follow the steps below.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Specify the range of cells on which the pivot table will be created using Worksheet.Range property
- Create an object of PivotCache using Workbook.PivotCaches.Add() method.
- Add a pivot table to the worksheet using Worksheet.PivotTables.Add() method.
- Add fields to rows area.
- Add fields to values area.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Select the data source range
cellRange = sheet.Range["C1:F11"]
piVotCache = workbook.PivotCaches.Add(cellRange)
# Add a PivotTable to the worksheet and set the location and cache of it
pivotTable = sheet.PivotTables.Add("Pivot Table", sheet.Range["H1"], piVotCache)
# Add "Region" and "Product" fields to rows area
regionField = pivotTable.PivotFields["Region"]
regionField.Axis = AxisTypes.Row
pivotTable.Options.RowHeaderCaption = "Region"
productField = pivotTable.PivotFields["Product"]
productField.Axis = AxisTypes.Row
# Add "Quantity" and "Amount" fields to values area
pivotTable.DataFields.Add(pivotTable.PivotFields["Quantity"], "SUM of Quantity", SubtotalTypes.Sum)
pivotTable.DataFields.Add(pivotTable.PivotFields["Amount"], "SUM of Amount", SubtotalTypes.Sum)
# Apply a built-in style to the pivot table
pivotTable.BuiltInStyle = PivotBuiltInStyles.PivotStyleMedium11
# Set column width
sheet.SetColumnWidth(8, 16);
sheet.SetColumnWidth(9, 16);
sheet.SetColumnWidth(10, 16);
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("output/PivotTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
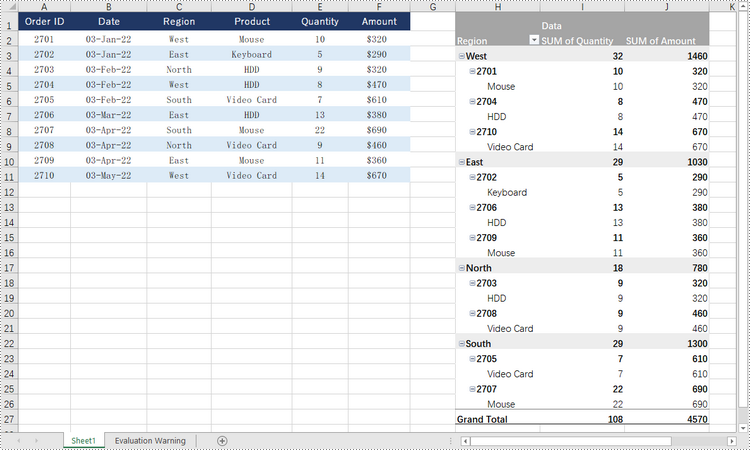
Sort Pivot Table by Column Values in Python
A specific field can be accessed through the PivotTable.PivotFields[index] property, and then you can set its sort type using the PivotField.SortType property. The following are the steps to sort pivot table by the values of a specific field.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific pivot table from the worksheet through Worksheet.PivotTables[index] property.
- Get a specific field through PivotTable.PivotFields[fieldName] property.
- Sort data in the field through PivotField.SortType property.
- Save the workbook to a different file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PivotTable.xlsx");
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the specified pivot table
pivotTable = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Get the specified field
idField = pivotTable.PivotFields["Order ID"]
# Sort data in the column of "Order ID" field
idField.SortType = PivotFieldSortType.Descending
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("output/SortData.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
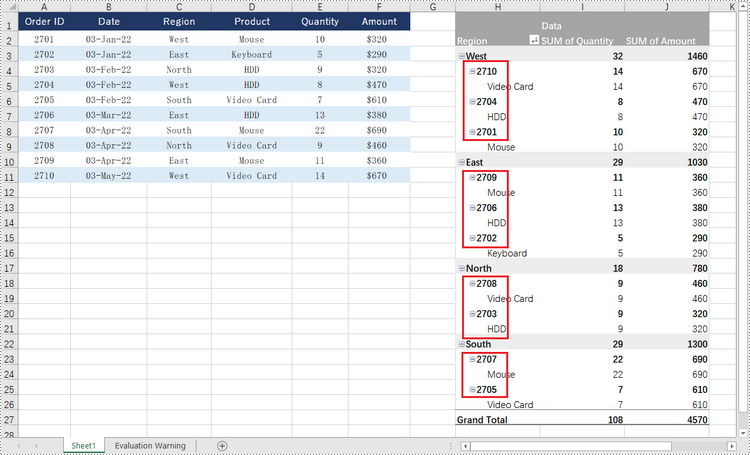
Expand or Collapse Rows in Pivot Table in Python
To collapse the details under a certain pivot field, use PivotField.HideItemDetail(string itemValue, bool isHiddenDetail) method and set the second parameter to true; to show the details, set the second parameter to false. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific pivot table from the worksheet through Worksheet.PivotTables[index] property.
- Get a specific field through PivotTable.PivotFields[fieldName] property.
- Collapse or expand rows of the field using PivotField.HideItemDetail(string itemValue, bool isHiddenDetail) method.
- Save the workbook to a different file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PivotTable.xlsx");
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the specified pivot table
pivotTable = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Get the specified field
regoinField = pivotTable.PivotFields["Region"]
# Hide details under the selected item of the region
regoinField.HideItemDetail("West", True)
regoinField.HideItemDetail("East", True)
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("output/CollapseRows.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
By default, Excel uses column letters and row numbers to refer to cells and ranges (for example, A1, B2:C5). While this approach is functional, it can become inconvenient, particularly when dealing with large datasets or complex formulas. Named ranges provide a solution to this problem by allowing users to assign custom names to cells or ranges, making them easier to identify, reference, and work with. In this article, we will explain how to create, edit and delete named ranges in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Named Range in Excel in Python
- Edit an Existing Named Range in Excel in Python
- Delete a Named Range from Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Named Range in Excel in Python
You can use the Workbook.NameRanges.Add() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python to add a named range to an Excel workbook. Once the named range is added, you can define the cell or range of cells it refers to using the INamedRange.RefersToRange property.
The following steps explain how to create a named range in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a named range to the workbook using the Workbook.NameRanges.Add() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the workbook using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set the cell range that the named range refers to using the INamedRange.RefersToRange property.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Add a named range to the workbook
namedRange = workbook.NameRanges.Add("Amount")
# Get a specific worksheet in the workbook
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the cell range that the named range references
namedRange.RefersToRange = sheet.Range["D2:D5"]
# Save the resulting file to a specific location
workbook.SaveToFile("CreateNamedRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Edit an Existing Named Range in Excel in Python
After you've created a named range, you may want to modify its name or adjust the cells it refers to.
The following steps explain how to modify the name and cell references of an existing named range in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific named range in the workbook using the Workbook.NameRanges[] property.
- Modify the name of the named range using the INamedRange.Name property.
- Modify the cells that the named range refers to using the INamedRange.RefersToRange property.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("CreateNamedRange.xlsx")
# Get the first named range in the workbook
namedRange = workbook.NameRanges[0]
# Change the name of the named range
namedRange.Name = "MonitorAmount"
# Change the cell range that the named range references
namedRange.RefersToRange = workbook.Worksheets[0].Range["D2"]
# Save the resulting file to a specific location
workbook.SaveToFile("ModifyNamedRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Delete a Named Range from Excel in Python
If you have made significant changes to the structure or layout of your spreadsheet, it might be necessary to delete a named range that is no longer relevant or accurate.
The following steps explain how to delete a named range from Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific named range by its index or name using the Workbook.NameRanges.RemoveAt() or Workbook.NameRanges.Remove() method.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("CreateNamedRange.xlsx")
# Remove the first named range by its index
workbook.NameRanges.RemoveAt(0)
# Remove the first named range by its name
# workbook.NameRanges.Remove("Amount");
# Save the resulting file to a specific location
workbook.SaveToFile("RemoveNamedRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
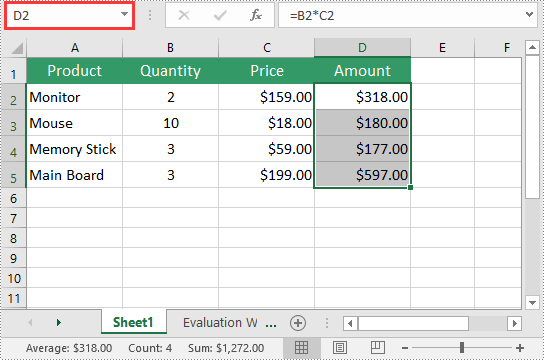
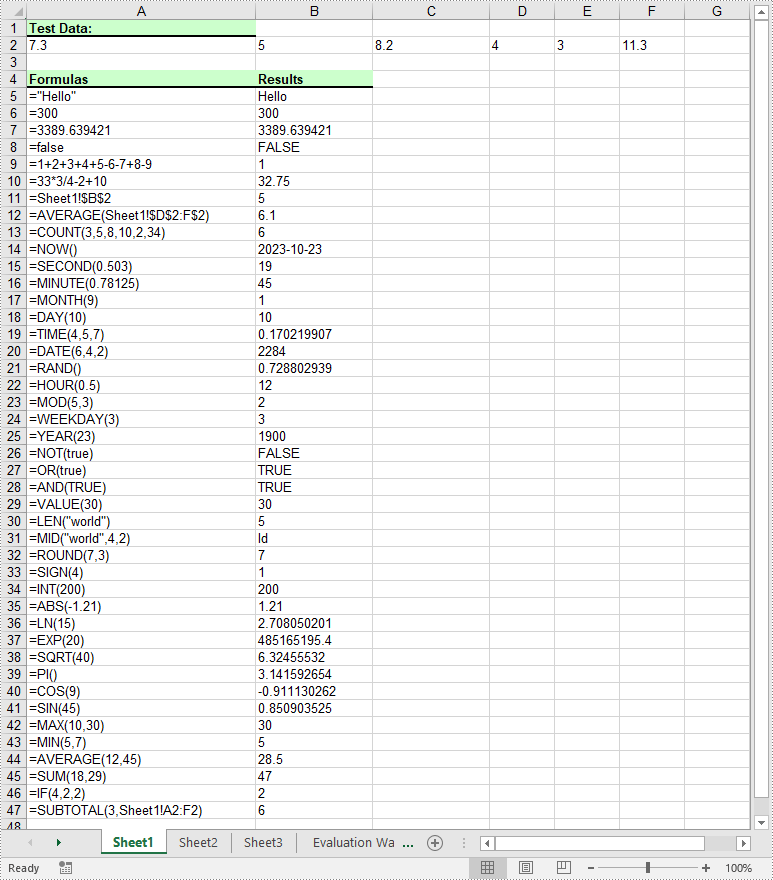
Formulas in Excel are equations or expressions that perform calculations on data within a spreadsheet. They allow you to perform basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as more advanced functions like statistical analysis, date and time calculations, and logical evaluations. By incorporating formulas into your Excel spreadsheets, you can save time, eliminate errors, and gain valuable insights from your data. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add or read formulas in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
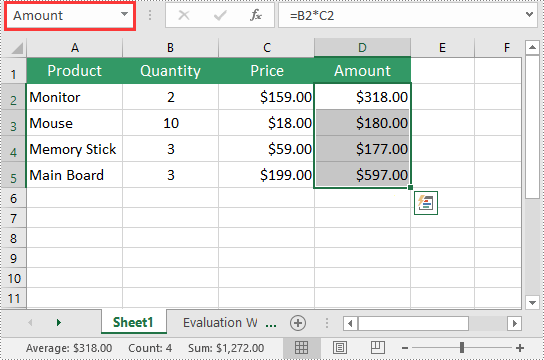
Add Formulas to Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].Formula property to add formulas to specific cells in an Excel worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add some text and numeric data to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].Text and Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].NumberValue properties.
- Add text and formulas to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].Text and Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].Formula properties.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Declare two variables: currentRow, currentFormula
currentRow = 1
currentFormula = ""
# Add text to the worksheet and set cell style
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "Test Data:"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.FillPattern = ExcelPatternType.Solid
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightGreen1
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Medium
currentRow += 1
# Add some numeric data to the worksheet
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].NumberValue = 7.3
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].NumberValue = 5
sheet.Range[currentRow, 3].NumberValue = 8.2
sheet.Range[currentRow, 4].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range[currentRow, 5].NumberValue = 3
sheet.Range[currentRow, 6].NumberValue = 11.3
currentRow += 2
# Add text to the worksheet and set cell style
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "Formulas"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Text = "Results"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightGreen1
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.FillPattern = ExcelPatternType.Solid
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Medium
currentRow += 1
# Add text and formulas to the worksheet
# Str
currentFormula = "=\"Hello\""
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Int
currentFormula = "=300"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Float
currentFormula = "=3389.639421"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Bool
currentFormula = "=false"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Expressions
currentFormula = "=1+2+3+4+5-6-7+8-9"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
currentFormula = "=33*3/4-2+10"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Cell reference
currentFormula = "=Sheet1!$B$2"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Functions
# AVERAGE
currentFormula = "=AVERAGE(Sheet1!$D$2:F$2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# COUNT
currentFormula = "=COUNT(3,5,8,10,2,34)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# NOW
currentFormula = "=NOW()"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Style.NumberFormat = "yyyy-MM-DD"
currentRow += 1
# SECOND
currentFormula = "=SECOND(0.503)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MINUTE
currentFormula = "=MINUTE(0.78125)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MONTH
currentFormula = "=MONTH(9)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# DAY
currentFormula = "=DAY(10)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# TIME
currentFormula = "=TIME(4,5,7)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# DATE
currentFormula = "=DATE(6,4,2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# RAND
currentFormula = "=RAND()"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# HOUR
currentFormula = "=HOUR(0.5)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MOD
currentFormula = "=MOD(5,3)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# WEEKDAY
currentFormula = "=WEEKDAY(3)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# YEAR
currentFormula = "=YEAR(23)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# NOT
currentFormula = "=NOT(true)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# OR
currentFormula = "=OR(true)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# AND
currentFormula = "=AND(TRUE)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# VALUE
currentFormula = "=VALUE(30)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# LEN
currentFormula = "=LEN(\"world\")"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MID
currentFormula = "=MID(\"world\",4,2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# ROUND
currentFormula = "=ROUND(7,3)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SIGN
currentFormula = "=SIGN(4)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# INT
currentFormula = "=INT(200)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# ABS
currentFormula = "=ABS(-1.21)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# LN
currentFormula = "=LN(15)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# EXP
currentFormula = "=EXP(20)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SQRT
currentFormula = "=SQRT(40)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# PI
currentFormula = "=PI()"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# COS
currentFormula = "=COS(9)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SIN
currentFormula = "=SIN(45)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MAX
currentFormula = "=MAX(10,30)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MIN
currentFormula = "=MIN(5,7)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# AVERAGE
currentFormula = "=AVERAGE(12,45)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SUM
currentFormula = "=SUM(18,29)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# IF
currentFormula = "=IF(4,2,2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SUBTOTAL
currentFormula = "=SUBTOTAL(3,Sheet1!A2:F2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Set width of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd columns
sheet.SetColumnWidth(1, 32)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(2, 16)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(3, 16)
# Create a cell style
style = workbook.Styles.Add("Style")
# Set the horizontal alignment as left
style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
# Apply the style to the worksheet
sheet.ApplyStyle(style)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddFormulas.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
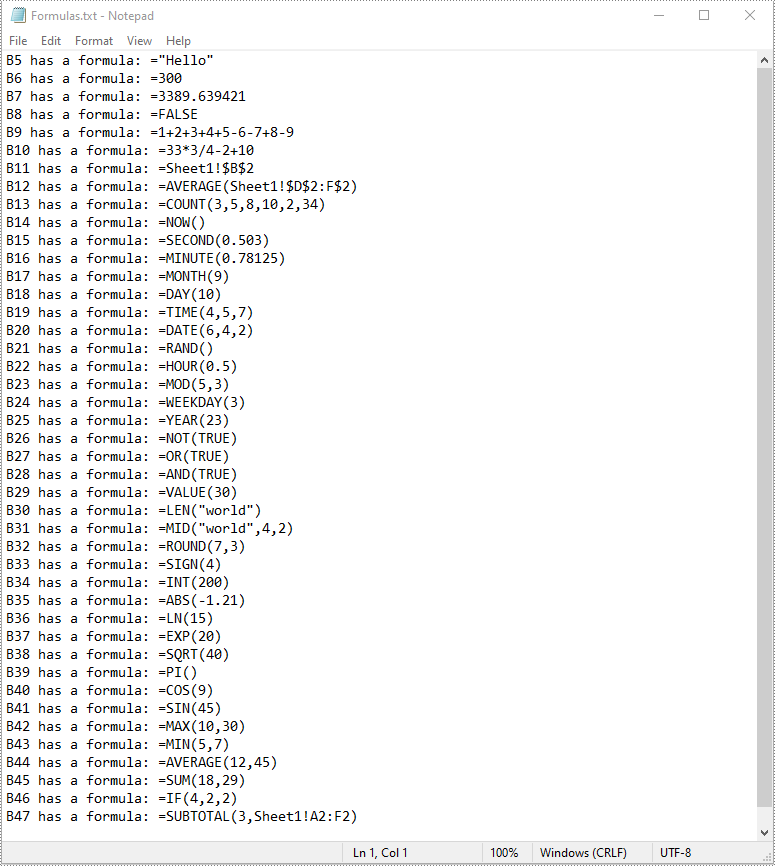
Read Formulas in Excel in Python
To read formulas in an Excel worksheet, you need to loop through all the cells in the worksheet, after that, find the cells containing formulas using the Cell.HasFormula property, and then get the formulas of the cells using the CellRange.Formula property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Get the used range of the worksheet using the Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Create an empty list.
- Loop through all the cells in the used range.
- Find the cells containing formulas using the Cell.HasFormula property.
- Get the names and the formulas of the cells using the CellRange.RangeAddressLocal and CellRange.Formula properties.
- Append the cell names and formulas to the list.
- Write the items in the list into a text file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("AddFormulas.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the used range of the worksheet
usedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Create an empty list
list = []
# Loop through the cells in the used range
for cell in usedRange:
# Check if the cell has a formula
if(cell.HasFormula):
# Get the cell name
cellName = cell.RangeAddressLocal
# Get the formula
formula = cell.Formula
# Append the cell name and formula to the list
list.append(cellName + " has a formula: " + formula)
# Write the items in the list into a text file
with open("Formulas.txt", "w", encoding = "utf-8") as text_file:
for item in list:
text_file.write(item + "\n")
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Headers and footers are areas located at the top and bottom of each page in a document, used to add additional information or elements. Headers typically include document titles, company names, dates, and other information, while footers often contain page numbers, file paths, copyright statements, and other details. By setting headers and footers in Excel, documents can be made more professional and organized. In this article, we will show you how to add headers and footers to Excel by using Spire.XLS for Python.
Spire.XLS for Python provides the PageSetup class to work with the page setup in Excel including headers and footers. Specifically, it contains LeftHeader property, CenterHeader property, RightHeader property, LeftFooter property, etc. to represent the left section, center section and right section of a header or footer. To add fields to headers or footers, or to apply formatting to text, you'll need to use the scripts listed in the following table.
| Script | Description |
| &P | The current page numbers. |
| &N | The total number of pages. |
| &D | The current data. |
| &T | The current time. |
| &G | A picture. |
| &A | The worksheet name. |
| &F | The file name. |
| &B | Make text bold. |
| &I | Italicize text. |
| &U | Underline text. |
| &"font name" | Represents a font name, for example, &"Arial". |
| & + Integer | Represents font size, for example, &12. |
| &K + Hex color code | Represents font color, for example, &KFF0000. |
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Text to the Header or Footer in Excel
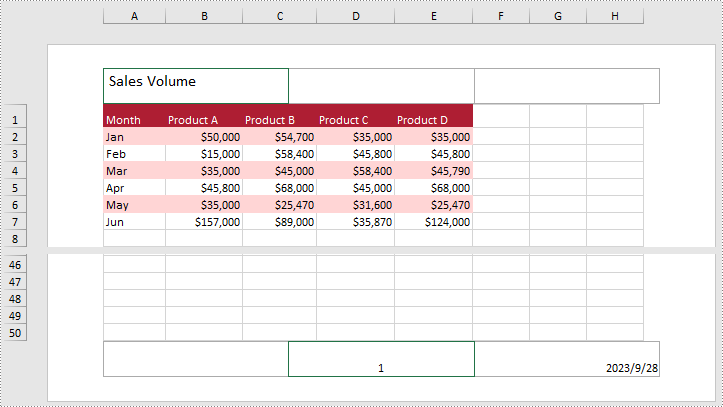
Spire.XLS for Python allows you to add formatted text to the certain section of the header or footer. In this way, you can set different elements in Excel, such as file titles, page numbers or date. Here are the detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specific worksheet by Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add text to the left header by setting PageSetup.LeftHeader property as you like.
- Add page number to the center footer by setting PageSetup.CenterFooter property to &P.
- Add the current date to the right footer by setting PageSetup.RightFooter property to &D.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "sample.xlsx" outputFile = "TextHeaderFooter.xlsx" #Create an object of Workbook class workbook = Workbook() #Load a sample file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first worksheet of this file Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Add text to the left header Worksheet.PageSetup.LeftHeader = "&\"Calibri\"&14 Sales Volume" #Add page number to the center footer Worksheet.PageSetup.CenterFooter = "&P" #Add the current date to the right footer Worksheet.PageSetup.RightFooter = "&D" #Set the view mode of the sheet Worksheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Layout #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2010) workbook.Dispose()
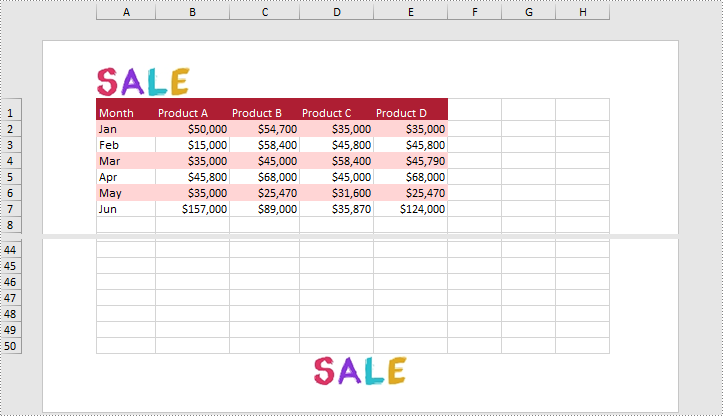
Add Images to the Header or Footer in Excel
What's more, Spire.XLS for Python also supports adding images to the header or footer. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specific worksheet by Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Load an image and set it as the image source of the left header by PageSetup.LeftHeaderImage property.
- Display the image in the left header section by setting PageSetup.LeftHeader property to “&G”.
- Set it as the image source of the center footer by PageSetup.CenterFooterImage property.
- Display the image in the center footer section by setting PageSetup.CenterFooter property to “&G”.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.common import * inputFile = "sample.xlsx" inputImage = "Logo.png" outputFile = "ImageHeaderFooter.xlsx" #Create an object of workbook class workbook = Workbook() #Load a sample file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first sheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Load an image from disk image = Image.FromFile(inputImage) #Add the image to the left header sheet.PageSetup.LeftHeaderImage = image sheet.PageSetup.LeftHeader = "&G" #Add the image to the center footer sheet.PageSetup.CenterFooterImage = image sheet.PageSetup.CenterFooter = "&G" #Set the view mode of the sheet sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Layout #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2010) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A workbook can consist of one or more worksheets, and each worksheet is independent. When dealing with an existing Excel file or creating a new Excel file from scratch, we can add worksheets as needed to better manage and analyze data. In this article, we will show you how to add worksheets to Excel programmatically by using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Add a Worksheet to an Existing Excel file
- Add a Worksheet to a New Excel file
- Add Multiple Worksheets to a New Excel file
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
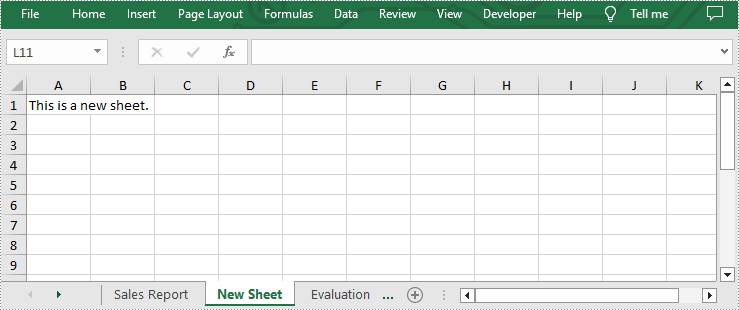
Add a Worksheet to an Existing Excel file
Spire.XLS for Python allows users to add a new worksheet to an existing Excel file by using Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName) method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a new sheet to this file using Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName) method.
- Add desired text to cell A1 by Worksheet.Range[cellName].Text property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "AddWorksheet.xlsx"
#Create an object of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Load an Excel file from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Add a new worksheet to this file
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("New Sheet")
#Add desired text to cell A1
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "This is a new sheet."
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Add a Worksheet to a New Excel file
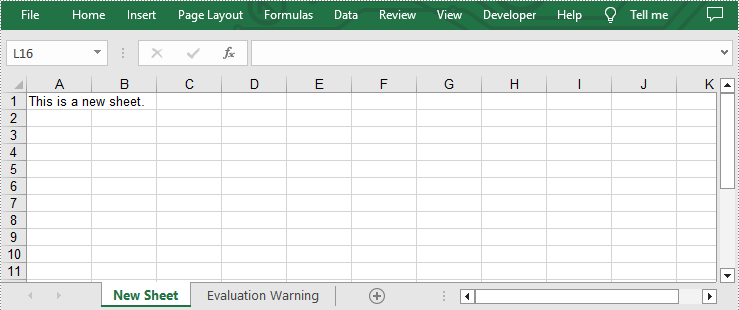
In addition to adding worksheets to existing Excel files, you can also add worksheets to a newly created Excel files with the same method. You just need to clear the default worksheet before adding by calling Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Clear the default worksheets using Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Add a new sheet to the new workbook by using Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName) method.
- Add desired text to cell A1 by Worksheet.Range[cellName].Text property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
outputFile = "AddWorksheet.xlsx"
#Create an object of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Clear the default sheets
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
#Add a new worksheet to the new file
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("New Sheet")
#Add desired text to cell A1
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "This is a new sheet."
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
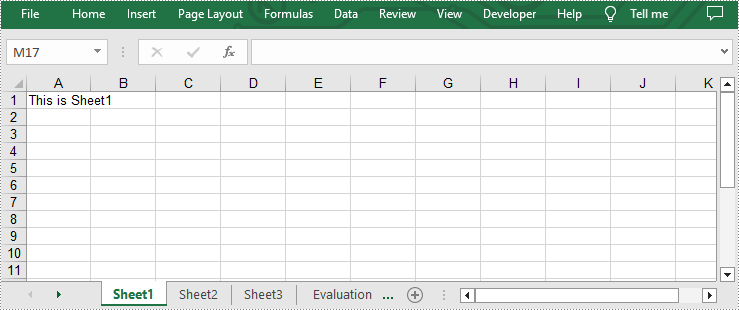
Add Multiple Worksheets to a New Excel file
If you want to add multiple worksheets to a newly created Excel file, you can use Workbook.CreateEmptySheets(sheetCount) method to add a specified number of worksheets. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Add three sheets to this file by using Workbook.CreateEmptySheets(sheetCount) method.
- Loop through the added worksheets and add text to cell A1 in each worksheet by Worksheet.Range[cellName].Text property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
outputFile = "AddWorksheet.xlsx"
#Create an object of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Add three sheets to this file
sheetCount = 3
workbook.CreateEmptySheets(sheetCount)
#Loop through the added worksheets
for i in range(sheetCount):
#Add text to cell A1 in each worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[i]
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "This is Sheet{}".format(i+1)
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Textboxes in Excel provide a flexible way to add textual information or annotations to worksheets, charts, or other objects. They allow users to display explanatory text, labels, or comments that are not directly related to the data itself. In this guide, we will explore how to add, update, and delete textboxes in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Add a Textbox to Excel in Python
- Update a Textbox in Excel in Python
- Delete a Textbox in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
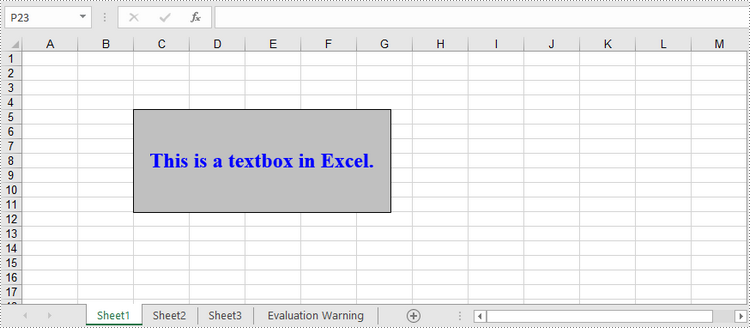
Add a Textbox to Excel in Python
A textbox can be added to the specified location of a worksheet using Worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox() method. The TextBox object has a set of properties that allow you to set the text and formatting of the textbox. The detailed steps to create a textbox using Spire.XLS for Python are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add a textbox to the worksheet at the specified location using Worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox() method.
- Set text of the textbox through TextBox.Text property.
- Set formatting of the text through other properties under the TextBox object.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a textbox to the worksheet, specifying location and size
textBox = sheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox(5, 3, 120, 300)
# Set fill color of the textbox
textBox.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.SolidColor
textBox.Fill.ForeKnownColor = ExcelColors.Gray25Percent
# Add text to the textbox and set the text alignment
textBox.Text = "This is a textbox in Excel."
textBox.HAlignment = CommentHAlignType.Center
textBox.VAlignment = CommentVAlignType.Center
# Set font for the text
font = workbook.CreateFont()
font.FontName = "Times New Roman"
font.Size = 18
font.IsBold = True
font.Color = Color.get_Blue()
richText = textBox.RichText
rt = RichText(richText)
rt.SetFont(0, len(textBox.Text) - 1, font)
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile('output/InsertTextbox.xlsx', ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
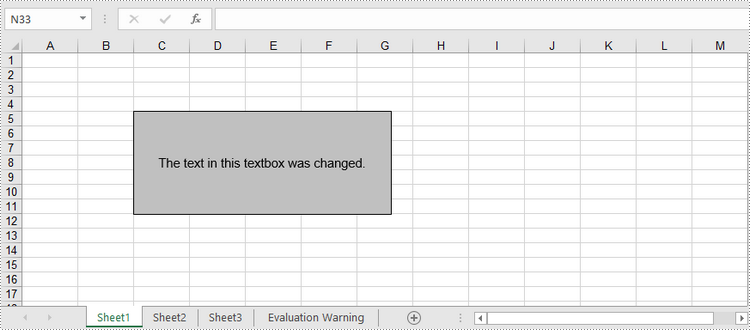
Update a Textbox in Excel in Python
A certain textbox can be accessed through Worksheet.TextBoxes[index] property and the text inside the box can be obtained or modified through TextBox.Text property. The following are the steps to update a textbox using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add a textbox to the worksheet at the specified location using Worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox() method.
- Reset text of the textbox through TextBox.Text property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile('C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Textbox.xlsx')
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first textbox
tb = sheet.TextBoxes[0]
# Change the text of textbox
tb.Text = "The text in this textbox was changed."
# Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile('output/UpdateTextbox.xlsx', ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Delete a Textbox in Excel in Python
To remove a specific textbox, you use Worksheet.TextBox[index].Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific sheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Remove a specific textbox by using Worksheet.TextBoxes[index].Remove() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile('C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Textbox.xlsx')
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Remove the first textbox
sheet.TextBoxes[0].Remove()
# Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile('output/RemoveTextbox.xlsx', ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Proper row height and column width are essential for optimizing data readability and ensuring that all content is fully visible in Excel. While the default row height and column width settings may be suitable in some cases, they may not be sufficient when dealing with lengthy text, large numbers, or complex formulas. In such cases, it becomes necessary to set appropriate row heights and column widths. In this article, we will explain how to set row height and column width in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set Row Height in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.SetRowHeight() method to set the height for a specific row. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set the height of a specific row using Worksheet.SetRowHeight() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the height of the first row
worksheet.SetRowHeight(1, 25)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetRowHeight.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Set Column Width in Excel in Python
To set the width of a specific column, you can use the Worksheet.SetColumnWidth() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set the width of a specific column using Worksheet.SetColumnWidth() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the width of the third column
worksheet.SetColumnWidth(3, 15)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetColumnWidth.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
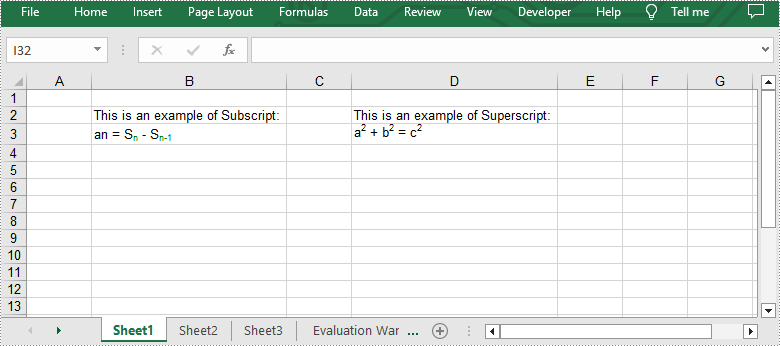
Superscript and subscript are formatting styles used in typography and writing to position characters or numbers above or below the normal line of text. Superscript is a smaller-sized text or symbol that is raised above the baseline. It is commonly used for mathematical exponents, footnotes, and ordinal indicators. Subscript, on the other hand, is a smaller-sized text or symbol that is positioned below the baseline. It is often used for chemical formulas, mathematical expressions and some linguistic notations. These formatting styles can help users distinguish specific elements within text and convey information more effectively. In this article, we will show you how to apply superscript and subscript in Excel by using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Apply Superscript and Subscript in Excel
To apply the superscript or subscript style to specific characters in excel, you need to create a custom font first and set the superscript or subscript property of it. And then assign the font to the specific characters within the cell using CellRange.RichText.SetFont() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet of it using Workbook.Worksheets[int index] property.
- Get the specific cells using Worksheet.Range[string name] property and add desired text to them.
- Get a cell by using Worksheet.Range[string name] property and add rich text to it by CellRange.RichText.Text property.
- Create a custom font using Workbook.CreateFont() method.
- Enable the subscript property of the font by setting ExcelFont.IsSubscript property to true.
- Assign the font to specific characters of the added rich text in the cell by calling CellRange.RichText.SetFont() method.
- Likewise, get another cell using Worksheet.Range[string name] property and add rich text to it by CellRange.RichText.Text property.
- Create a custom font using Workbook.CreateFont() method.
- Enable the superscript property of the font by setting ExcelFont.IsSuperscript property to true.
- Assign the font to specific characters of the added rich text in the cell by calling CellRange.RichText.SetFont() method.
- Automatically adjust column widths to fit text length using Worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.common import * from spire.xls.common import * outputFile = "ApplySubscriptAndSuperscript.xlsx" #Create an object of Workbook class workbook = Workbook() #Get the first worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Add text to the specific cells sheet.Range["B2"].Text = "This is an example of Subscript:" sheet.Range["D2"].Text = "This is an example of Superscript:" #Add rich text to a specific cell range = sheet.Range["B3"] range.RichText.Text = "an = Sn - Sn-1" #Create a custom font font = workbook.CreateFont() #Enable the subscript property of the font by setting the IsSubscript property to "true" font.IsSubscript = True #Set the font color font.Color = Color.get_Green() #Assign the font to specific characters of the added rich text range.RichText.SetFont(6, 6, font) range.RichText.SetFont(11, 13, font) #Add rich text to another cell range = sheet.Range["D3"] range.RichText.Text = "a2 + b2 = c2" #Create a custom font font = workbook.CreateFont() #Enable the superscript property of the font by setting the IsSuperscript property to "true" font.IsSuperscript = True #Assign the font to specific characters of the added rich text range.RichText.SetFont(1, 1, font) range.RichText.SetFont(6, 6, font) range.RichText.SetFont(11, 11, font) #Autofit the column widths sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns() #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
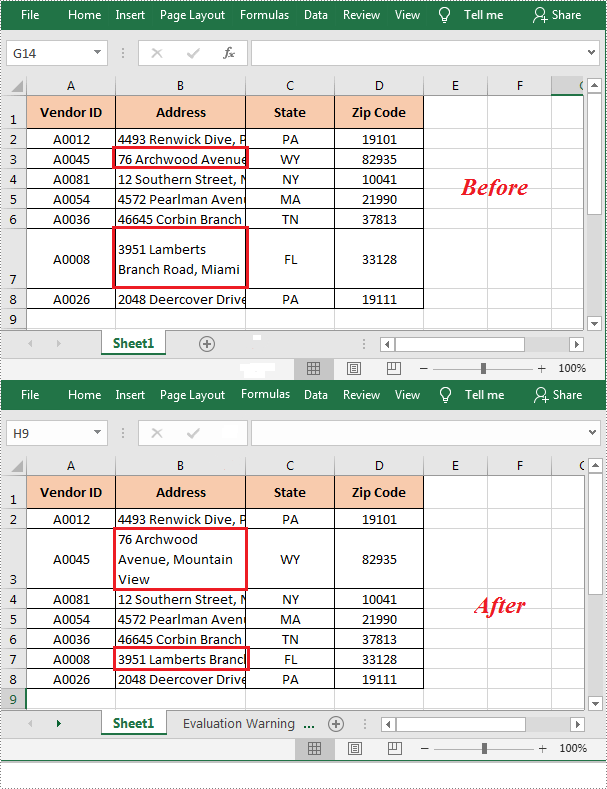
Text wrapping and unwrapping are powerful formatting options in Microsoft Excel that offer flexibility in displaying text within cells. When text wrapping is enabled, long text is automatically wrapped into multiple lines within a cell, which ensures that the entire content is visible without truncation. This feature is particularly useful for presenting lengthy descriptions, notes, or paragraphs within a confined cell space. On the other hand, text unwrapping allows you to remove line breaks and display the text in a single line within the cell. This can be beneficial in scenarios where you need to fit the text into a specific layout or when exporting data to other applications or file formats that may not handle wrapped text correctly. In this article, we will demonstrate how to wrap or unwrap text in Excel cells in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Wrap or Unwrap Text in Excel Cells in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the CellStyle.WrapText property to control whether the text should be wrapped or unwrapped within a cell. If you want to wrap text in a cell, you can set the property as True. Conversely, if you want to unwrap text in a cell, you can set the property as False.
The following steps explain how to wrap or unwrap text in an Excel cell using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get a specified cell using Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Get the style of the specified cell using CellRange.Style property.
- Wrap the text in the cell by setting the CellStyle.WrapText property to True. Or unwrapping the text in the cell by setting the CellStyle.WrapText property to False.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet of the file
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Wrap the text in cell B3
sheet.Range["B3"].Style.WrapText = True
# Unwrap the text in cell B7
sheet.Range["B7"].Style.WrapText = False
#Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("WrapOrUnwrapTextInCells.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The Excel workbook is a powerful spreadsheet that enables the creation, manipulation, and analysis of data in a variety of ways. One of the useful features that workbooks offer is the ability to hide or unhide worksheets in a workbook. Hiding worksheets can help protect sensitive or confidential information, reduce clutter, or organize data more efficiently. And when users need to re-display the hidden worksheets, they can also unhide them with simple operations. This article is going to explain how to hide or unhide worksheets in Excel workbooks through Python programs using Sprie.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
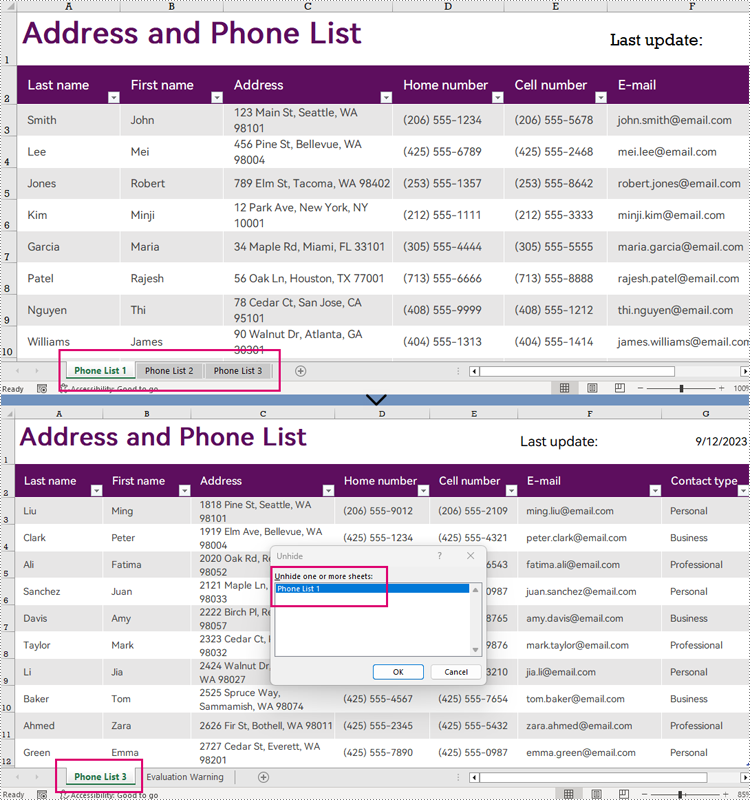
Hide Excel Worksheets in Python
The Worksheet.Visibility property in Spire.XLS for Python can be used to set the visibility of a worksheet. By assigning WorksheetVisibility.Hidden or WorksheetVisibility.StrongHidden to this property, users can change the visibility of a worksheet to hidden or very hidden (completely not shown in Excel and can only be unhidden through code).
The detailed steps for hiding worksheets are as follows:
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load a workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Change the status of the first worksheet to hidden by assigning WorksheetVisibility.Hidden to the Workbook.Worksheets[].Visibility property.
- Change the status of the second worksheet to very hidden by assigning WorksheetVisibility.StrongHidden to the Workbook.Worksheets[].Visibility property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.common import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Hide the first worksheet
workbook.Worksheets[0].Visibility = WorksheetVisibility.Hidden
# Change the second worksheet to very hidden
workbook.Worksheets[1].Visibility = WorksheetVisibility.StrongHidden
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/HideWorksheets.xlsx")
Unhide Excel Worksheets in Python
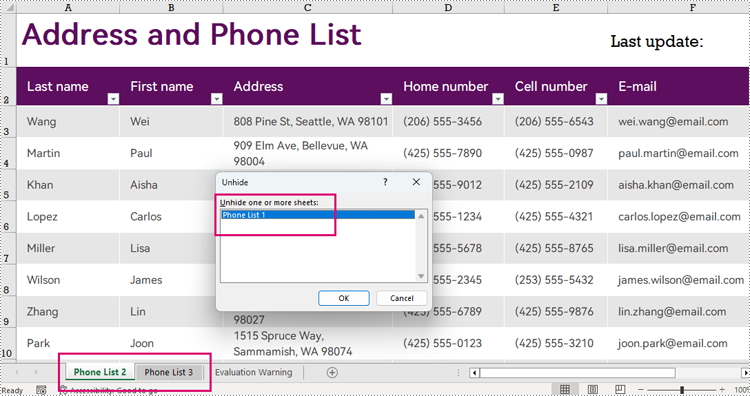
Unhiding a worksheet can be done by assigning WorksheetVisibility.Visible to the Workbook.Worksheets[].Visibility property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load a workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Unhide the very hidden worksheet by assigning WorksheetVisibility.Visible to the Workbook.Worksheets[].Visibility property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.common import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("output/HideWorksheets.xlsx")
# Unhide the second worksheet
workbook.Worksheets[1].Visibility = WorksheetVisibility.Visible
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/UnhideWorksheet.xlsx")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
