
Program Guide (108)
Children categories
Efficiently emphasizing critical data within Excel workbooks is essential for swift analysis. This process not only draws immediate attention to the most relevant information but also aids in identifying trends, anomalies, and key metrics. By using Python to handle Excel workbooks, users can automate the search and highlight functions, enhancing productivity and ensuring precision. This article explores how to leverage Python for finding and highlighting data in Excel worksheets using Spire.XLS for Python library.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Find and Highlight Data in Excel Worksheets
Using Spire.XLS for Python, we can find all cells containing a specific string and return them as a list by using the Worksheet.FindAllString(stringValue: str, formula: bool, formulaValue: bool) method. After that, we can iterate through the found cells and apply a highlight color by setting it via the CellRange.Style.Color property.
The detailed steps for finding and highlighting data in an Excel worksheet are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class and load an Excel workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Find all the cells containing the string to be highlighted using Worksheet.FindAllString() method.
- Iterate through the results to highlight the cells by setting a fill color through CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Find the data to be highlighted
cellRanges = sheet.FindAllString("Urgent", False, True)
# Iterate through the found ranges
for cellRange in cellRanges:
# Highlight the data
cellRange.Style.Color = Color.get_LightYellow()
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/FindHighlightDataExcel.xlsx")
workbook.Dispose()
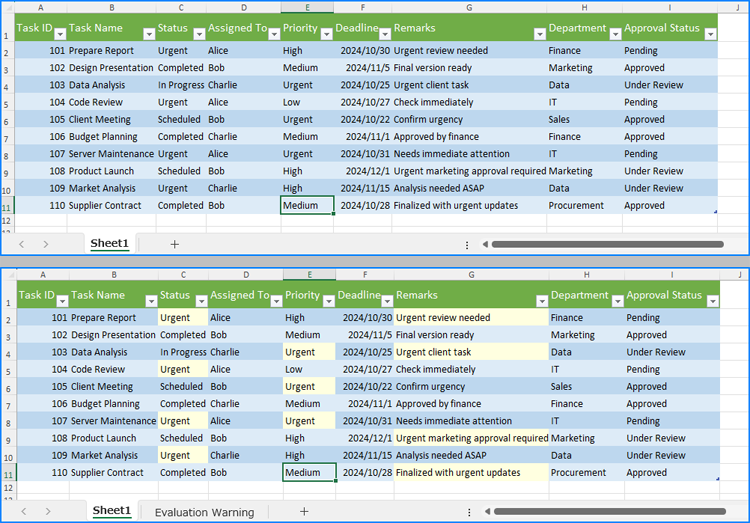
Find and Highlight Data in a Specific Cell Range
In addition to searching for data across the entire worksheet, we can use the CellRange.FindAllString(stringValue: str, formula: bool, formulaValue: bool) method to find and highlight data within a specified cell range. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Get a cell range through Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Find all the cells containing the string to be highlighted using CellRange.FindAllString() method.
- Iterate through the results to highlight the cells by setting a fill color through CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get the cell range
findRange = sheet.Range["C1:C11"]
# Find the data to be highlighted
cellRanges = findRange.FindAllString("Urgent", False, True)
# Iterate the found ranges
for cellRange in cellRanges:
# Highlight the data
cellRange.Style.Color = Color.get_LightYellow()
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/FindHighlightRange.xlsx")
workbook.Dispose()
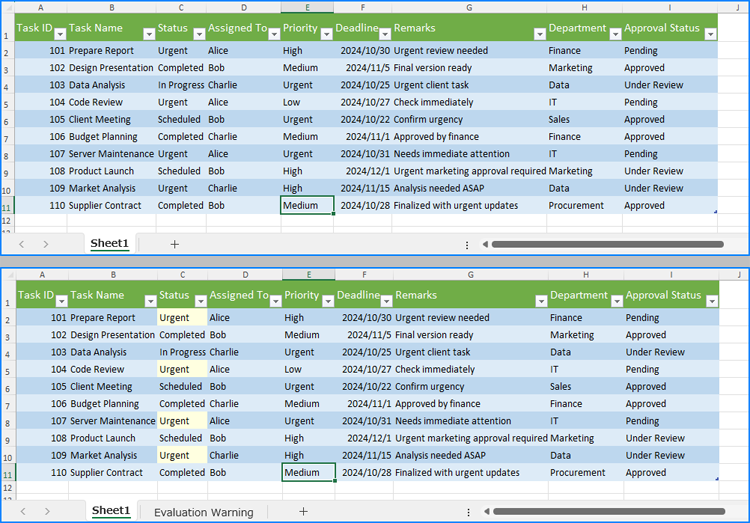
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Digital signatures serve as a critical layer of security, ensuring that an Excel file has not been altered since it was signed and verifying the identity of its originator. However, there are scenarios where the detection and removal of these digital signatures become necessary, such as when consolidating multiple documents, updating content, or preparing files for systems that do not support digitally signed documents. This article shows how to detect and remove digital signatures in Excel files with Python code using Spire.XLS for Python, providing a simple way to batch process Excel file digital signatures.
- Detecting the Presence of Digital Signatures in Excel Files
- Removing Digital Signatures from Excel Files
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Detecting the Presence of Digital Signatures in Excel Files
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Workbook class to deal with Excel files and the Workbook.IsDigitallySigned property to check if an Excel file has digital signatures. Developers can use the Boolean value returned by this property to determine whether the Excel file contains a digital signature.
The detailed steps for detecting if an Excel file has digital signatures are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Check whether the workbook is digitally signed by the value of the Workbook.IsDigitallySigned property.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Check whether the workbook is digitally signed
if workbook.IsDigitallySigned is False:
print("The workbook is not digitally signed.")
else:
print("The workbook is digitally signed.")
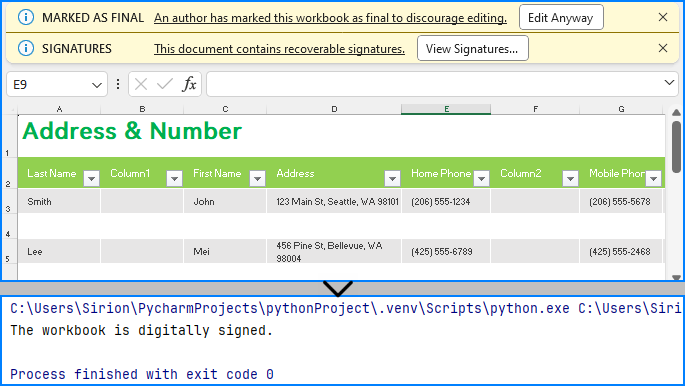
Removing Digital Signatures from Excel Files
Developers can use the Workbook.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures() method to effortlessly delete all digital signatures in an Excel workbook. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove all digital signatures from the workbook using Workbook.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures() method.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Remove digital signatures
workbook.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures()
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("output/RemoveExcelDigitalSignature.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A pie chart is a circular statistical graphic that is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a category's contribution to the whole, making it an effective way to visualize relative sizes. In this article, you will learn how to create a standard pip chart, an exploded pip chart, and a pie of pie chart in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Pie Chart in Excel
- Create an Exploded Pie Chart in Excel
- Create a Pie of Pie Chart in Excel
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Pie Chart in Excel in Python
To add a pie chart to a worksheet, use the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Pie) method, which returns a Chart object. You can then set various properties, such as DataRange, ChartTitle, LeftColumn, TopRow, and Series to define the chart's data, title, position, and series formatting.
Here are the steps to create a pie chart in Excel:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Insert values into the worksheet cells that will be used as chart data.
- Add a pie chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Pie) method.
- Set the chart data using Chart.DataRange property.
- Define the chart's position and size using Chart.LeftColumn, Chart.TopRow, Chart.RightColumn, and Chart.BottomRow properties.
- Set the chart title using Chart.ChartTitle property.
- Access and format the series through Chart.Series property.
- Save the workbook as an Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set values of the specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Year"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "2002"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "2003"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "2004"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "2005"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Sales"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 4000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 6000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 7000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500
# Format the cells
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].RowHeight = 15
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Color = Color.get_DarkGray()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:B5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a pie chart
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Pie)
# Set region of chart data
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["B2:B5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4
chart.TopRow = 2
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 20
# Set chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales by year"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Get the first series
cs = chart.Series[0]
# Set category labels for the series
cs.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A5"]
# Set values for the series
cs.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B5"]
# Show vales in data labels
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/PieChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
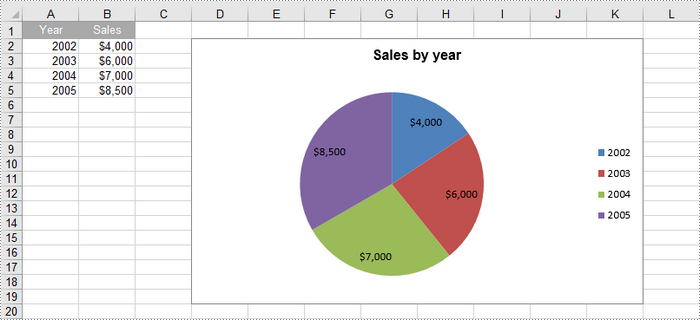
Create an Exploded Pie Chart in Excel in Python
An exploded pie chart is a variation of the standard pie chart where one or more slices are separated or "exploded" from the main chart. To create an exploded pie chart, you can use the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieExploded) method.
The steps to create an exploded pip chart in Excel are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Insert values into the worksheet cells that will be used as chart data.
- Add an exploded pie chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType. PieExploded) method.
- Set the chart data using Chart.DataRange property.
- Define the chart's position and size using Chart.LeftColumn, Chart.TopRow, Chart.RightColumn, and Chart.BottomRow properties.
- Set the chart title using Chart.ChartTitle property.
- Access and format the series through Chart.Series property.
- Save the workbook as an Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set values of the specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Year"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "2002"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "2003"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "2004"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "2005"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Sales"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 4000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 6000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 7000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500
# Format the cells
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].RowHeight = 15
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Color = Color.get_DarkGray()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:B5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add an exploded pie chart
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieExploded)
# Set region of chart data
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["B2:B5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4
chart.TopRow = 2
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 20
# Set chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales by year"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Get the first series
cs = chart.Series[0]
# Set category labels for the series
cs.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A5"]
# Set values for the series
cs.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B5"]
# Show vales in data labels
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ExplodedPieChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
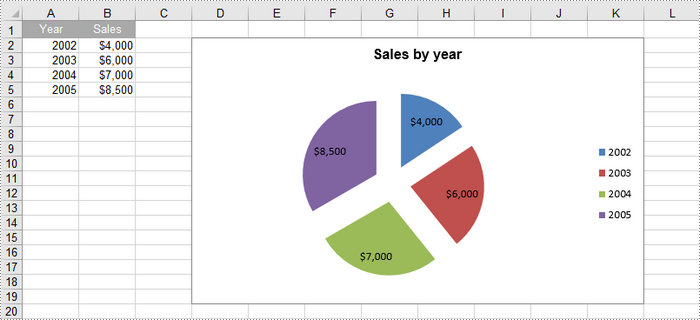
Create a Pie of Pie Chart in Excel in Python
A pie of pie chart is a specialized type of pie chart that allows for more detailed representation of data by providing a secondary pie chart for specific categories. To add a pip of pie chart to a worksheet, use the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieOfPie) method.
The detailed steps to create a pie of pie chart in Excel are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Insert values into the worksheet cells that will be used as chart data.
- Add a pie of pie chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieOfPie) method.
- Set the chart data, position, size, title using the properties under the Chart object.
- Access the first series using Chart.Series[0] property.
- Set the split value that determines what displays in the secondary pie using Series.Format.Options.SplitValue property.
- Save the workbook as an Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set values of the specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Product"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Coffee"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Biscuits"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Tea"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Vegetables"
sheet.Range["A6"].Value = "Fruits"
sheet.Range["A7"].Value = "Chips"
sheet.Range["A8"].Value = "Drinks"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Sales Percentage"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 0.27
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 0.13
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 0.26
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 0.25
sheet.Range["B6"].NumberValue = 0.03
sheet.Range["B7"].NumberValue = 0.05
sheet.Range["B8"].NumberValue = 0.01
# Autofit column width
sheet.AutoFitColumn(2)
# Format the cells
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].RowHeight = 15
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Color = Color.get_DarkGray()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:B8"].Style.NumberFormat = "0%"
# Add a pie of pie chart
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieOfPie)
# Set region of chart data
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["B2:B58"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4
chart.TopRow = 2
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 20
# Chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales Percentage"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Get the first series
cs = chart.Series[0]
# Set category labels for the series
cs.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A8"]
# Set values for the series
cs.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B8"]
# Show vales in data labels
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set the size of the secondary pie
cs.Format.Options.PieSecondSize = 50
# Set the split value, which determines what displays in the secondary pie
cs.Format.Options.SplitType = SplitType.Percent
cs.Format.Options.SplitValue = 10
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/PieOfPieChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
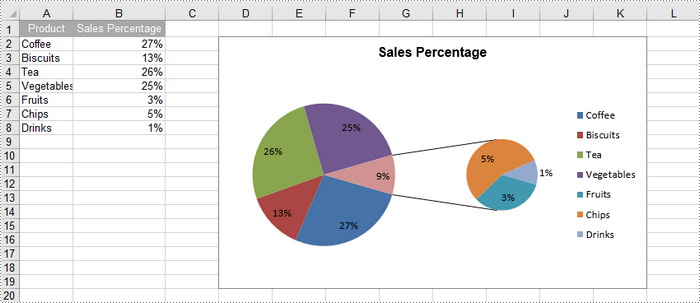
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Sparklines in Excel are small, lightweight charts that fit inside individual cells of a worksheet. They are particularly useful for showing variations in data across rows or columns, allowing users to quickly identify trends without taking up much space. In this article, we'll demonstrate how to insert, modify, and delete sparklines in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Insert a Sparkline in Excel in Python
- Modify a Sparkline in Excel in Python
- Delete Sparklines from Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Insert a Sparkline in Excel in Python
Excel offers 3 main types of sparklines:
- Line Sparkline: Shows data trends as a line, similar to a miniature line graph.
- Column Sparkline: Displays data as vertical bars, emphasizing individual data points.
- Win/Loss Sparkline: Illustrates positive and negative values, useful for tracking binary outcomes like wins or losses.
Spire.XLS for Python supports inserting all of the above types of sparklines. Below are the detailed steps for inserting a sparkline in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add a sparkline group to the worksheet using Worksheet.SparklineGroups.AddGroup() method.
- Specify the sparkline type, color, and data point color for the sparkline group.
- Add a sparkline collection to the group using SparklineGroup.Add() method, and then add a sparkline to the collection using SparklineCollection.Add() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet in the workbook
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a sparkline group to the worksheet
sparkline_group1 = sheet.SparklineGroups.AddGroup()
# Set the sparkline type to line
sparkline_group1.SparklineType = SparklineType.Line
# Set the sparkline color
sparkline_group1.SparklineColor = Color.get_Orange()
# Set the highest data point color
sparkline_group1.HighPointColor = Color.get_Red()
# Add a sparkline collection
sparklines1 = sparkline_group1.Add()
# Add a sparkline to the collection, define the data range for the sparkline and the target cell for displaying the sparkline
sparklines1.Add(sheet.Range["A3:L3"], sheet.Range["M3"])
# Add a sparkline group to the worksheet
sparkline_group2 = sheet.SparklineGroups.AddGroup()
# Set the sparkline type to column
sparkline_group2.SparklineType = SparklineType.Column
# Set the sparkline color
sparkline_group2.SparklineColor = Color.get_BlueViolet()
# Set the highest data point color
sparkline_group2.HighPointColor = Color.get_Red()
# Add a sparkline collection
sparklines2 = sparkline_group2.Add()
# Add a sparkline to the collection, define the data range for the sparkline and the target cell for displaying the sparkline
sparklines2.Add(sheet.Range["A4:L4"], sheet.Range["M4"])
# Add a sparkline group to the worksheet
sparkline_group3 = sheet.SparklineGroups.AddGroup()
# Set the sparkline type to stacked (win/loss)
sparkline_group3.SparklineType = SparklineType.Stacked
# Set the sparkline color
sparkline_group3.SparklineColor = Color.get_DarkBlue()
# Set the negative data point color
sparkline_group3.NegativePointColor = Color.get_Red()
# Add a sparkline collection
sparklines3 = sparkline_group3.Add()
# Add a sparkline to the collection, define the data range for the sparkline and the target cell for displaying the sparkline
sparklines3.Add(sheet.Range["A8:L8"], sheet.Range["M8"])
# Save the resulting workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddSparklines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
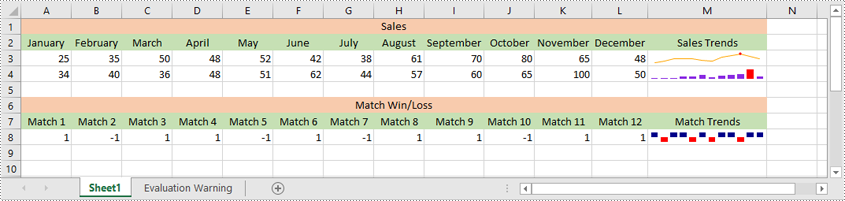
Modify a Sparkline in Excel in Python
After inserting a sparkline, you can modify its type, color, and data source to make it more effective at displaying the information you need.
The following steps explain how to modify a sparkline in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific sparkline group in the worksheet using Worksheet.SparklineGroups[index] property.
- Change the sparkline type and color for the sparkline group using SparklineGroup.SparklineType and SparklineGroup.SparklineColor properties.
- Get a specific sparkline in the group and change its data source using ISparklines.RefreshRanges() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file that contains sparklines
workbook.LoadFromFile("AddSparklines.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet in the workbook
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the second sparkline group
sparklineGroup = sheet.SparklineGroups[1]
# Change the sparkline type
sparklineGroup.SparklineType = SparklineType.Line
# Change the sparkline color
sparklineGroup.SparklineColor = Color.get_ForestGreen()
# Change the data range of the sparkline
sparklines = sparklineGroup[0]
sparklines.RefreshRanges(sheet.Range["A4:F4"], sheet.Range["M4"])
# Save the resulting workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("ModifySparklines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
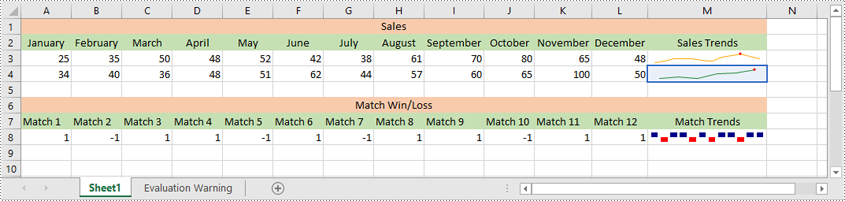
Delete Sparklines from Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python allows you to remove specific sparklines from a sparkline group and to remove the entire sparkline group from an Excel worksheet.
The following steps explain how to remove an entire sparkline group or specific sparklines from a sparkline group using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific sparkline group in the worksheet using Worksheet.SparklineGroups[index] property.
- Delete the entire sparkline group using Worksheet.SparklineGroups.Clear() method. Or delete a specific sparkline using ISparklines.Remove() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file that contains sparklines
workbook.LoadFromFile("AddSparklines.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet in the workbook
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first sparkline group in the worksheet
sparklineGroup = sheet.SparklineGroups[0]
# Remove the first sparkline group from the worksheet
sheet.SparklineGroups.Clear(sparklineGroup)
# # Remove the first sparkline
# sparklines = sparklineGroup[0]
# sparklines.Remove(sparklines[0])
# Save the resulting workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("RemoveSparklines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
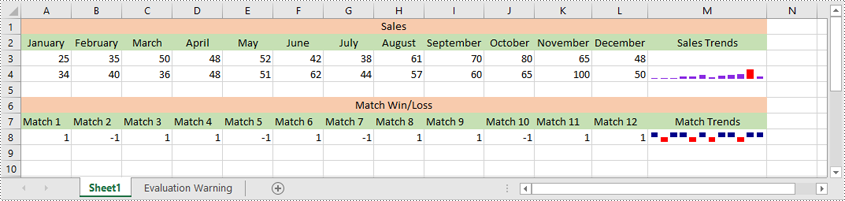
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
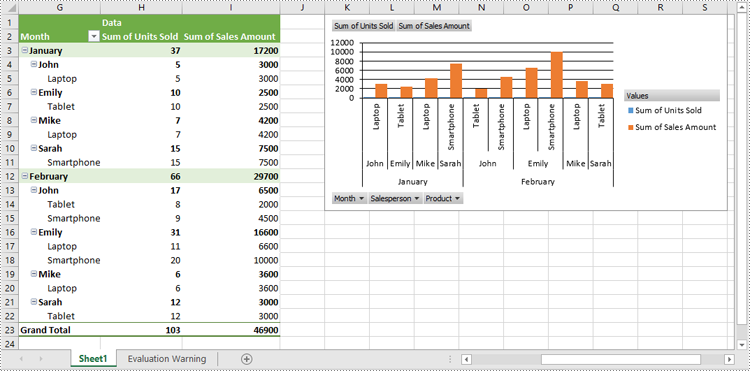
Pivot charts are a powerful tool in Excel that allows you to visualize data from pivot tables in an easy-to-understand format. They enable users to summarize large datasets, highlight trends, and make data-driven decisions through interactive graphs. Whether you're analyzing sales figures, performance metrics, or any other form of data, pivot charts provide a dynamic way to represent complex data visually. In this article, we will demonstrate how to create pivot charts in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create Pivot Charts in Excel in Python
- Show or Hide Field Buttons in Pivot Charts in Excel in Python
- Format Pivot Chart Series in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
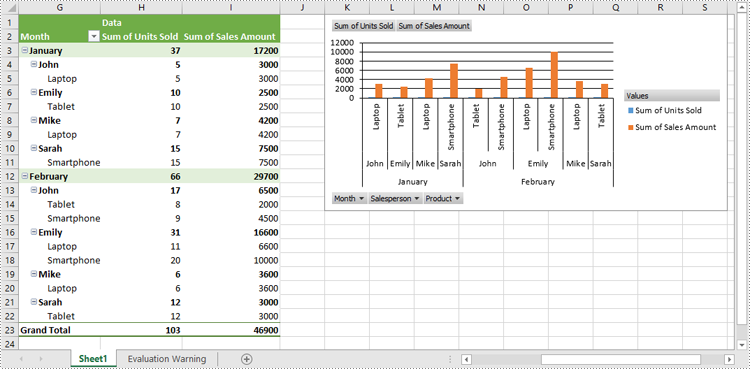
Create Pivot Charts in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.Charts.Add(pivotChartType:ExcelChartType, pivotTable:IPivotTable) method to create a pivot chart based on a specific pivot table in Excel. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the Excel file using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific pivot table in the worksheet using Worksheet.PivotTables[index] property.
- Add a pivot chart based on the pivot table to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(pivotChartType:ExcelChartType, pivotTable:IPivotTable) method.
- Set the position and title of the pivot chart.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("PivotTable.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first pivot table in the worksheet
pivotTable = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Create a clustered column chart based on the pivot table
pivotChart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered, pivotTable)
# Set chart position
pivotChart.TopRow = 1
pivotChart.LeftColumn = 11
pivotChart.RightColumn = 20
pivotChart.BottomRow = 15
# Set chart title to null
pivotChart.ChartTitle = ""
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("CreatePivotChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
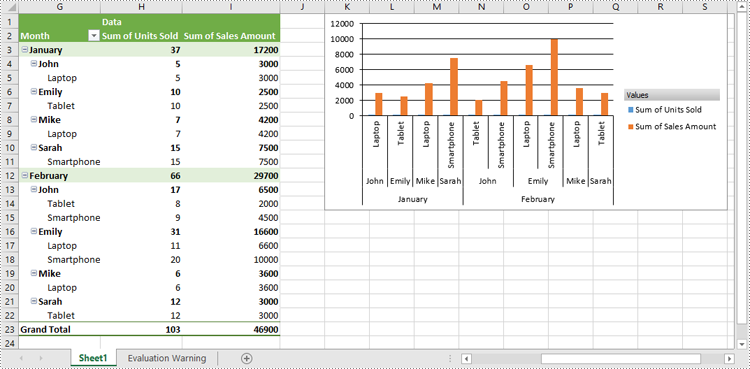
Show or Hide Field Buttons in Pivot Charts in Excel in Python
You can show or hide the following field buttons in a pivot chart with Spire.XLS for Python:
- Entire Field Buttons
- Report Filter Field Buttons
- Legend Field Buttons
- Axis Field Buttons
- Value Field Buttons
The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the Excel file using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific pivot table in the worksheet using Worksheet.PivotTables[index] property.
- Add a pivot chart based on the pivot table to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(pivotChartType:ExcelChartType, pivotTable:IPivotTable) method.
- Set the position and title of the pivot chart.
- Hide specific field buttons in the pivot chart, such as the axis field buttons and the value field buttons, using Chart.DisplayAxisFieldButtons and Chart.DisplayValueFieldButtons properties.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("CreatePivotChart.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first pivot table in the worksheet
pivotTable = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Create a clustered column chart based on the pivot table
pivotChart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered, pivotTable)
# Set chart position
pivotChart.TopRow = 1
pivotChart.LeftColumn = 11
pivotChart.RightColumn = 20
pivotChart.BottomRow = 15
# Set chart title to null
pivotChart.ChartTitle = ""
# Hide specific field buttons
pivotChart.DisplayAxisFieldButtons = False
pivotChart.DisplayValueFieldButtons = False
# pivotChart.DisplayLegendFieldButtons = False
# pivotChart.ShowReportFilterFieldButtons = False
# pivotChart.DisplayEntireFieldButtons = False
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("HideFieldButtons.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Format Pivot Chart Series in Excel in Python
When generating a pivot chart using a pivot table as the data source with Spire.XLS for Python, the chart series are not automatically created. You need to add the series to the pivot chart and then apply the desired formatting. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the Excel file using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific pivot table in the worksheet using Worksheet.PivotTables[index] property.
- Add a pivot chart based on the pivot table to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(pivotChartType:ExcelChartType, pivotTable:IPivotTable) method.
- Set the position and title of the pivot chart.
- Add series to the chart using Chart.Series.Add() method and then apply the desired formatting to the series.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("CreatePivotChart.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first pivot table in the worksheet
pivotTable = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Create a clustered column chart based on the pivot table
pivotChart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered, pivotTable)
# Set chart position
pivotChart.TopRow = 1
pivotChart.LeftColumn = 11
pivotChart.RightColumn = 20
pivotChart.BottomRow = 15
# Set chart title to null
pivotChart.ChartTitle = ""
# Add chart series
series = pivotChart.Series.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered)
# Set bar width
series.GetCommonSerieFormat().GapWidth = 10
# Set overlap
# series.GetCommonSerieFormat().Overlap = 100
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("FormatChartSeries.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
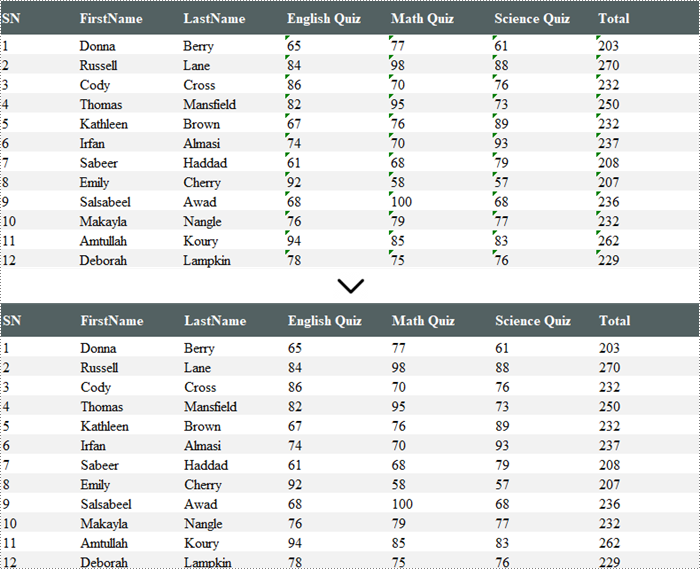
Converting text to numbers and vice versa in Excel is crucial for efficient data management. When you convert text to numbers, you enable accurate calculations and data processing, which is essential for tasks like financial reporting and statistical analysis. On the other hand, converting numbers to text can be beneficial for formatting outputs, creating clear and readable labels, and presenting data in a more user-friendly manner.
In this article, you will learn how to convert text to numbers and numbers to text in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Convert Text to Numbers in Excel
If you import data from another source into Excel, a small green triangle may appear in the upper-left corner of the cell. This error indicator indicates that the number is stored as text. Numbers that are stored as text can cause unexpected results, like an uncalculated formula showing instead of a result.
To convert numbers stored as text to numbers, you can simply use the CellRange.ConvertToNumber() method. The CellRange object can represent a single cell or a range of cells.
The steps to convert text to numbers in Excel are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a cell or a range of cells using Worksheet.Range property.
- Convert the text in the cell(s) into numbers using CellRange.ConvertToNumber() method.
- Save the document to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a cell range
range = worksheet.Range["D2:G13"]
# Convert text to number
range.ConvertToNumber()
# Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/TextToNumbers.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
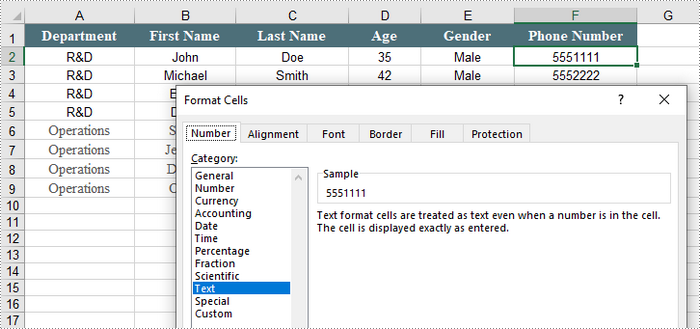
Convert Numbers to Text in Excel
When working with numerical data in Excel, you might encounter situations where you need to convert numbers to text. This is particularly important when dealing with data that requires specific formatting, such as IDs or phone numbers that must retain leading zeros.
To convert the number in a cell into text, you can set the CellRange.NumberFormat to @. The CellRange object represents a single cell or a range of cells.
The detailed steps to convert numbers to text in Excel are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell or a range of cells using Worksheet.Range property.
- Convert the numbers in the cell(s) into text by setting CellRange.NumberFormat to @.
- Save the document to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Employee.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a cell range
cellRange = worksheet.Range["F2:F9"]
# Convert numbers in the cell range to text
cellRange.NumberFormat = "@"
# Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/NumbersToText.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
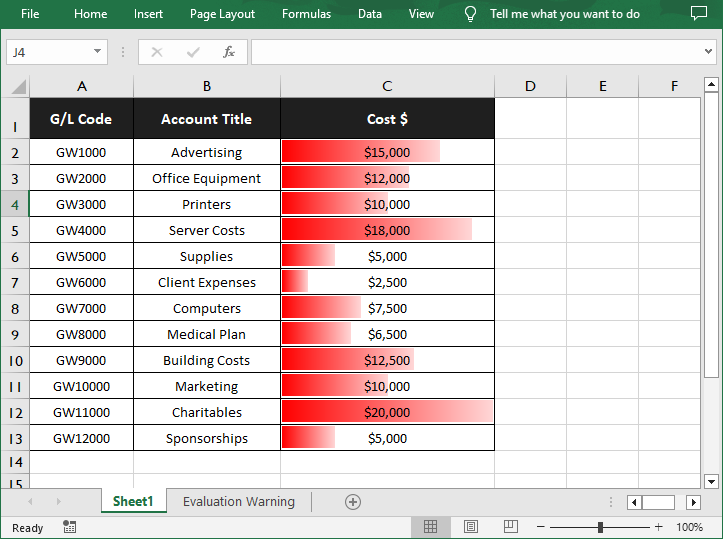
Data Bars in Excel is a feature within the Conditional Formatting tool that allows you to visually represent numerical data through a series of bars. This feature is particularly useful for comparing values at a glance, as the length of the bar corresponds to the magnitude of the value it represents. In this article, you will learn how to add data bars in an Excel cell range in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Data Bars in Excel in Python
With Spire.XLS for Python, you are allowed to add a data bar to a specified data range and also set its format. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worsheets[index] property.
- Add a conditional formatting to the worksheet using Worksheet.ConditionalFormats.Add() method and return an object of XlsConditionalFormats class.
- Set the cell range where the conditional formatting will be applied using XlsConditionalFormats.AddRange() method.
- Add a condition using XlsConditionalFormats.AddCondition() method, and then set its format type to DataBar using IConditionalFormat.FormatType property.
- Set the fill effect and color of the data bars using IConditionalFormat.DataBar.BarFillType and IConditionalFormat.DataBar.BarColor properties.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a conditional format to the worksheet
xcfs = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add()
# Set the range where the conditional format will be applied
xcfs.AddRange(sheet.Range["C2:C13"])
# Add a condition and set its format type to DataBar
format = xcfs.AddCondition()
format.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.DataBar
# Set the fill effect and color of the data bars
format.DataBar.BarFillType = DataBarFillType.DataBarFillGradient
format.DataBar.BarColor = Color.get_Red()
# Save the result document
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplyDataBarsToCellRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Charts and shapes in Excel are vital tools for clear and effective data presentation. Sometimes, it's beneficial to convert these visual elements into images. Perhaps you need to include a specific chart in a report or presentation outside of Excel. Or maybe you want to use an Excel-created infographic on your company's website. Regardless of the use case, knowing how to export these visuals as standalone image files can be invaluable. In this guide, we will explore how to convert charts and shapes in Excel to images in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to Image in Python
- Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Python
- Convert a Chart Sheet in Excel to Image in Python
- Convert Shapes in Excel to Images in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to Image in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet, chartIndex: int) method, allowing you to convert a specific chart within a worksheet into an image stream. This image stream can then be saved as an image file in various formats, including PNG, JPG, BMP, and more. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Save a specific chart in the worksheet to an image stream using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet, chartIndex: int) method.
- Save the image stream to an image file using the Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Charts.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Save the first chart in the worksheet to an image stream
image_stream = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet, 0)
# Save the image stream to a PNG image file
image_stream.Save("Output/chart.png")
workbook.Dispose()
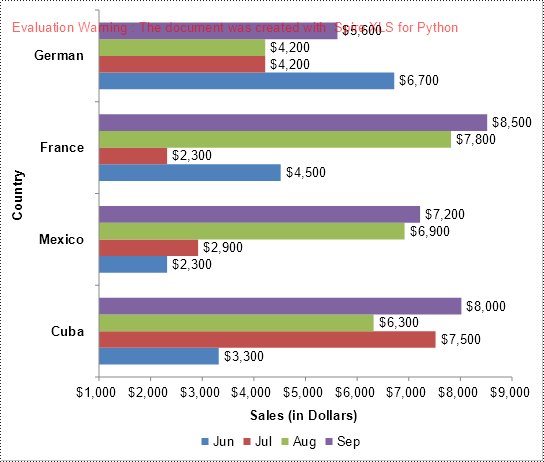
Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Python
To convert all charts in an Excel worksheet to images, you can use the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Save all charts in the worksheet to a list of image streams using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet) method.
- Iterate through the image streams in the list and save them to separate image files.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Charts.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
image_streams = []
# Save the charts in the worksheet to a list of image streams
image_streams = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet)
# Save the image streams to PNG image files
for i, image_stream in enumerate(image_streams):
image_stream.Save(f"Output/chart-{i}.png")
workbook.Dispose()
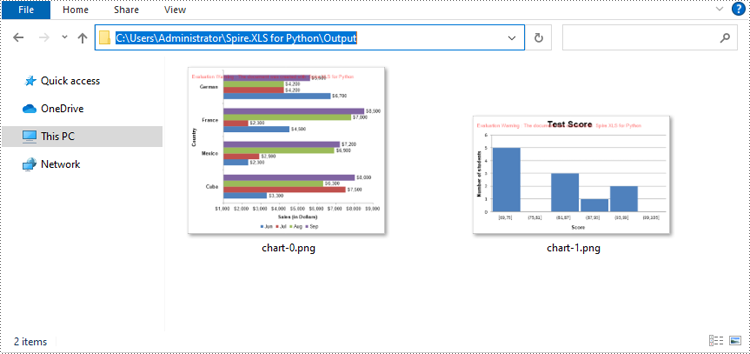
Convert a Chart Sheet in Excel to Image in Python
In Microsoft Excel, a chart sheet is a special type of sheet that is dedicated to displaying a single chart or graph. You can convert a chart sheet in an Excel workbook to an image using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(chartSheet: ChartSheet) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific chart sheet in the file using the Workbook.Chartsheets[] property.
- Save the chart sheet to an image stream using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(chartSheet: ChartSheet) method.
- Save the image stream to an image file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ChartSheet.xlsx")
# Get the first chart sheet
chart_sheet = workbook.Chartsheets[0]
# Save the chart sheet to an image stream
image_stream = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(chart_sheet)
# Save the image stream to a PNG image file
image_stream.Save("Output/chartSheet.png")
workbook.Dispose()
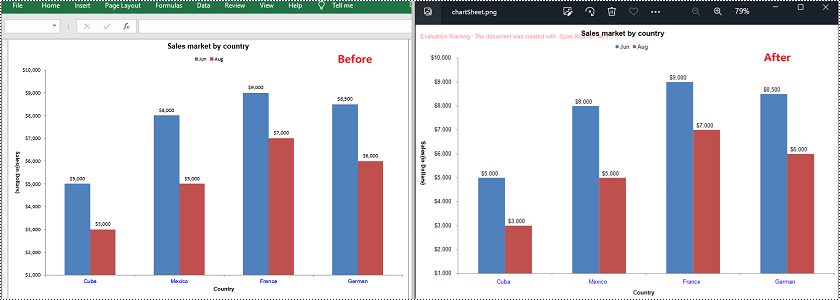
Convert Shapes in Excel to Images in Python
In addition to converting charts or chart sheets to images, you can also convert shapes in an Excel worksheet to images by using the XlsShape.SaveToImage() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Iterate through all the shapes in the worksheet.
- Typecast the shape to an XlsShape object.
- Save the shape to an image stream using the XlsShape.SaveToImage() method.
- Save the image stream to an image file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Shapes.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Iterate through all the shapes in the worksheet
for i, shape in enumerate(sheet.PrstGeomShapes):
xls_shape = XlsShape(shape)
# Save the shape to an image stream
image_stream = shape.SaveToImage()
# Save the image stream to a PNG image file
image_stream.Save(f"Output/shape_{i}.png")
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Page setup in Excel refers to the various settings that control how an Excel worksheet will be printed or displayed in a print preview. These settings determine the appearance and layout of the printed document, ensuring that it meets the desired formatting and readability standards. Page setup options include page margins, orientation, paper size, print area, headers, footers, scaling, and other print-related settings. In this article, we will explain how to set page setup options in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Set Page Margins in Excel in Python
- Set Page Orientation in Excel in Python
- Set Paper Size in Excel in Python
- Set Print Area in Excel in Python
- Set Scaling Factor in Excel in Python
- Set FitToPages Options in Excel in Python
- Set Headers and Footers in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
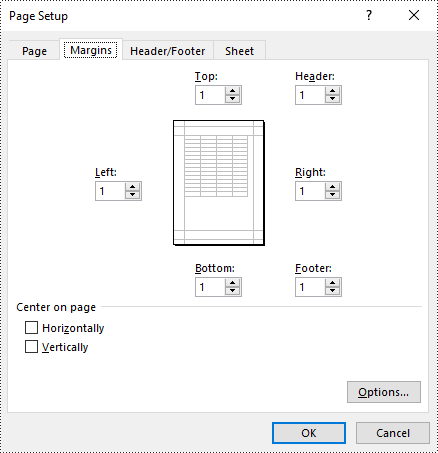
Set Page Margins in Excel in Python
In Spire.XLS for Python, the PageSetup class is used to configure page setup options for Excel worksheets. You can access the PageSetup object of a worksheet through the Worksheet.PageSetup property. Then, you can use properties like PageSetup.TopMargin, PageSetup.BottomMargin, PageSetup.LeftMargin, PageSetup.RightMargin, PageSetup.HeaderMarginInch, and PageSetup.FooterMarginInch to set the respective margins for the worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the top, bottom, left, right, header, and footer margins using PageSetup.TopMargin, PageSetup.BottomMargin, PageSetup.LeftMargin, PageSetup.RightMargin, PageSetup.HeaderMarginInch, and PageSetup.FooterMarginInch properties.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set top, bottom, left, and right page margins for the worksheet
# The measure of the unit is Inch (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
pageSetup.TopMargin = 1
pageSetup.BottomMargin = 1
pageSetup.LeftMargin = 1
pageSetup.RightMargin = 1
pageSetup.HeaderMarginInch= 1
pageSetup.FooterMarginInch= 1
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPageMargins.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
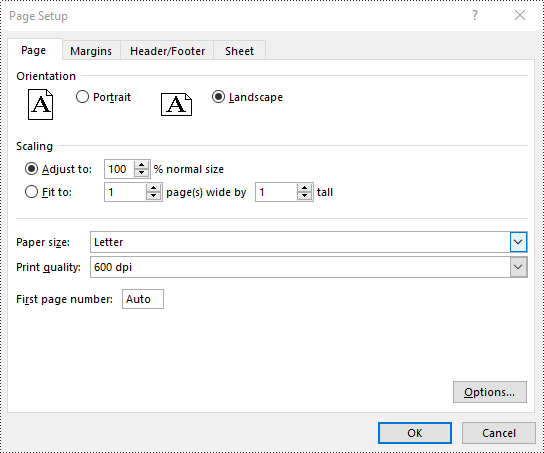
Set Page Orientation in Excel in Python
To set the page orientation for an Excel worksheet, you can use the PageSetup.Orientation property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the page orientation using PageSetup.Orientation property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set the page orientation for printing the worksheet to landscape mode
pageSetup.Orientation = PageOrientationType.Landscape
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPageOrientation.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
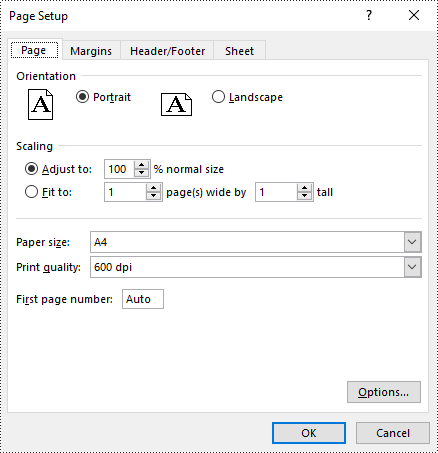
Set Paper Size in Excel in Python
You can set a wide range of paper sizes, such as A3, A4, A5, B4, B5, Letter, Legal, and Tabloid for printing an Excel worksheet using the PageSetup.PaperSize property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the paper size using PageSetup.PaperSize property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set the paper size to A4
pageSetup.PaperSize = PaperSizeType.PaperA4
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPaperSize.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
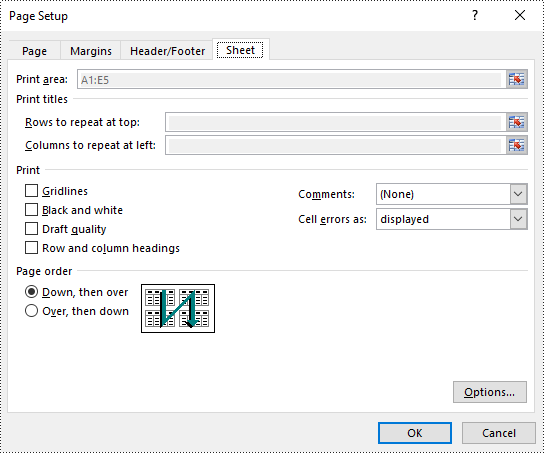
Set Print Area in Excel in Python
The print area of an Excel worksheet can be customized using the PageSetup.PringArea property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the print area using PageSetup.PringArea property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set the print area of the worksheet to "A1:E5"
pageSetup.PrintArea = "A1:E5"
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPrintArea.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
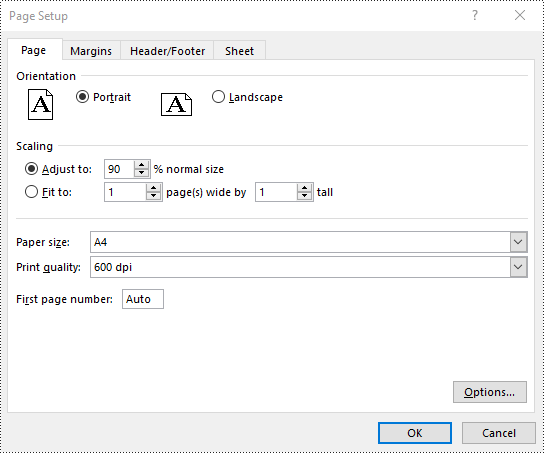
Set Scaling Factor in Excel in Python
You can scale the content of a worksheet to a specific percentage of its original size with the PageSetup.Zoom property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the scaling factor using PageSetup.Zoom property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set the scaling factor of the worksheet to 90%
pageSetup.Zoom = 90
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetScalingFactor.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
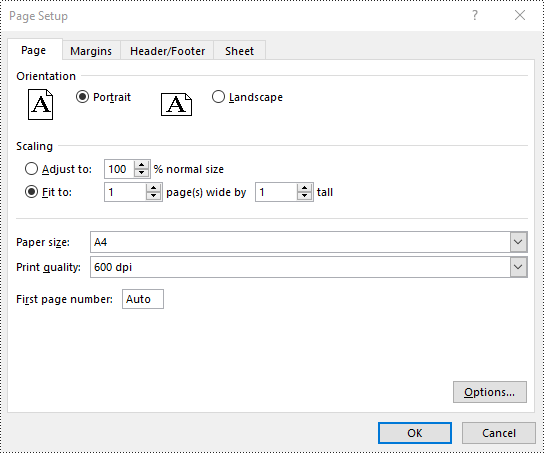
Set FitToPages Options in Excel in Python
In addition to scaling the content of a worksheet to a specific percentage of its original size, you can also fit the content of a worksheet to a specific number of pages using PageSetup.FitToPagesTall and PageSetup.FitToPagesWide properties. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Fit the content of the worksheet to one page using PageSetup.FitToPagesTall and PageSetup.FitToPagesWide properties.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Fit the content of the worksheet within one page vertically (i.e., all rows will fit on a single page)
pageSetup.FitToPagesTall = 1
# Fit the content of the worksheet within one page horizontally (i.e., all columns will fit on a single page)
pageSetup.FitToPagesWide = 1
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("FitToPages.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Set Headers and Footers in Excel in Python
For setting headers and footers in Excel, please check this article: Python: Add Headers and Footers to Excel.
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Converting XLS files to various formats is necessary for data management and presentation. ODS, XPS, PostScript, and PDF/A-1b offer unique advantages and are suitable for different scenarios.
ODS is widely used for compatibility with many office suites. XPS preserves document fidelity and is ideal for sharing and archiving. PostScript is a versatile page description language often used for printing and graphic design. PDF/A-1b ensures long-term archiving by complying with strict preservation standards.
This guide will illustrate how to convert Excel to ODS, XPS, PostScript, and PDF/A-1b with Python using Spire.XLS for Python, leveraging their specific strengths to meet diverse needs.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install it, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows.
Convert Excel to ODS, XPS, and PostScript with Python
To convert Excel to ODS, XPS, and PostScript documents, you can utilize Workbook.SaveToFile() method. It supports converting CSV to Excel and PDF, Excel to PDF and XLSX, etc. By using this method provided by Spire.XLS for Python, you can seamlessly transform your documents into these formats while maintaining accuracy without data loss. Read the following steps to learn more:
Steps to convert Excel to ODS, XPS, and PostScript:
- Create a new Workbook object.
- Import the file to be converted from the disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert it to ODS, XPS, or PostScript with Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
Here is the code example for reference:
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the file from the disk
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx")
# Save the document to an ODS file
workbook.SaveToFile("to_ods.ods", FileFormat.ODS)
# Save the document as an XPS file
workbook.SaveToFile("to_xps.xps", FileFormat.XPS)
# Save the document as a PostScript file
workbook.SaveToFile("to_postscript.ps", FileFormat.PostScript)
workbook.Dispose()
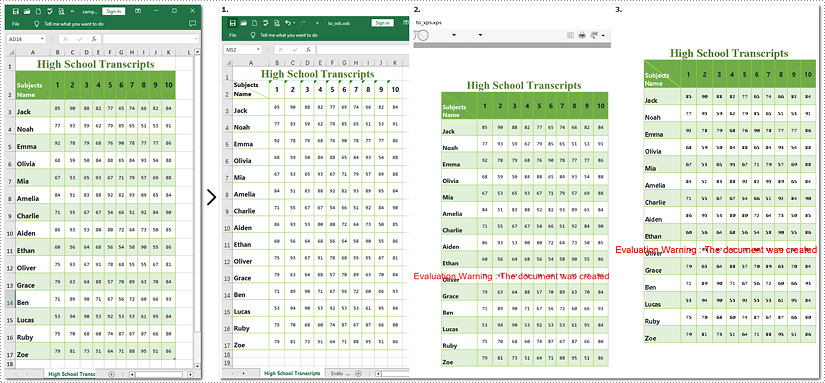
Note: Images 1, 2, and 3 show the results of converting Excel files to ODS, XPS, and PostScript formats, respectively.
How to Convert Excel Documents to PDF/A-1b Format
If you need to convert Excel to PDF/A-1b Format with Python, call Workbook.SaveToFile will help you. The steps to transform Excel documents to PDF/A-1b are similar to those above, except the former involves an additional step. This tutorial will guide you through the process with detailed steps and a code example.
Steps to convert Excel to PDF/A-1b
- Instantiate a new Workbook object.
- Read the Excel document from the disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the PDF conformance level to PDF/A-1b.
- Save the generated document as PDF with Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
Here is the code example for you:
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Open the file from the disk
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx")
# Set the PDF conformance to PDF/A-1b
workbook.ConverterSetting.PdfConformanceLevel = PdfConformanceLevel.Pdf_A1B
# Convert the Excel document to PDF/A-1b
workbook.SaveToFile("to_pdfa1b", FileFormat.PDF)
workbook.Dispose()
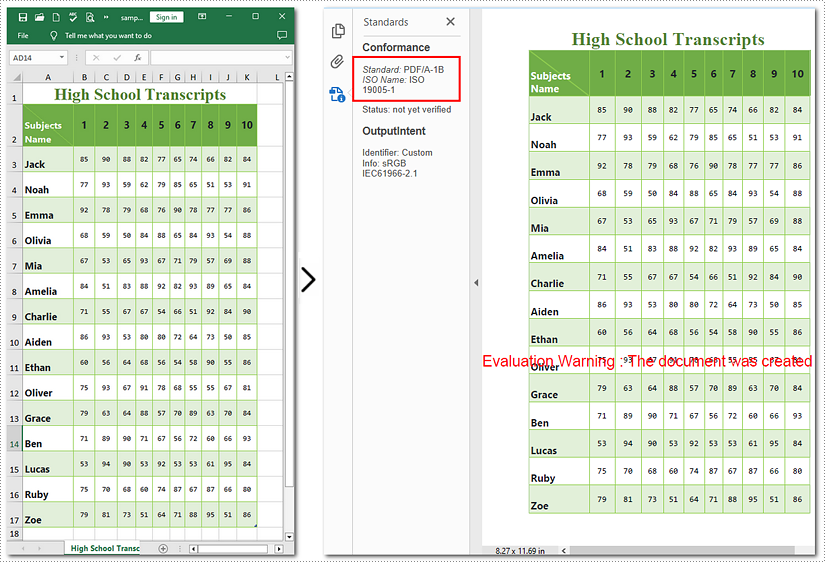
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
