Table of Contents

Whether you’re preparing reports, cleaning datasets, or automating invoices, sometimes you need numbers to behave like text in Excel. For example, you may want to preserve leading zeros in ZIP codes, display IDs as text, or format numeric values with specific symbols and patterns.
Converting numbers to text ensures that Excel stops treating those values as numeric data—preventing automatic rounding, unwanted calculations, or scientific notation formatting. Fortunately, Excel provides several built-in and programmatic ways to handle this.
In this article, we’ll explore five effective methods to convert numbers to text in Excel—from simple formatting tricks to automated solutions using VBA and Python (Spire.XLS). Each method serves a different need, so you can choose the one that fits your workflow best.
Method overview:
- Method 1. Using Excel Cell Formatting Tools
- Method 2. Using Text-to-Columns Tool
- Method 3. Using Excel Functions that Return Text
- Method 4. Using VBA Macro
- Method 5. Using Python Automation
Why Convert Numbers to Text?
Numbers in Excel are typically stored in numeric form, which allows for calculations, formulas, and charting. However, in many real-world cases, you need them as text strings instead. Here are a few reasons why:
- Preserve data integrity: Keep phone numbers, employee IDs, or postal codes exactly as entered (e.g., “00123” instead of “123”).
- Avoid calculation errors: When merging datasets, numeric values can accidentally sum or round; converting them to text prevents this.
- Improve formatting flexibility: Text-formatted numbers allow for custom prefixes, suffixes, and display styles (e.g., “USD 123.00”).
- Ensure consistency for exports: When exporting data to other systems (databases, CSVs, or APIs), text format ensures values remain intact.
- Enable automation and scripting: Some automated processes require string inputs instead of numeric ones.
Method 1. Using Excel Cell Formatting Tools
One of the easiest ways to convert numbers to text is through Excel’s Format Cells feature. This method doesn’t require formulas or code, and it’s suitable for small to medium datasets.
Steps:
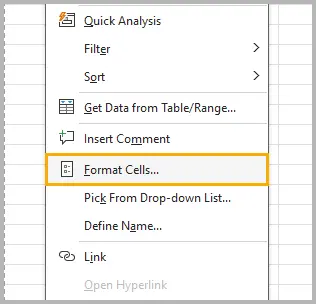
- Select the cells containing numbers.
- Right-click and choose Format Cells .
- In the Number tab, select Text .
- Click OK .
- Re-enter the numbers (or press F2 → Enter to refresh existing values).

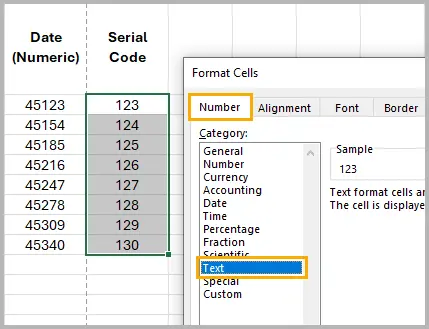
Excel will now treat those values as text instead of numbers. You can confirm this by checking that the cell content is left-aligned and that a small green triangle (text indicator) appears in the upper-left corner.
Alternative:
If you prefer a manual approach, you can add an apostrophe (') before the number. Excel interprets this as text but hides the apostrophe when displayed.
Pros:
- Quick and intuitive.
- No formulas or coding required.
Cons:
- Not ideal for very large datasets.
- Must be repeated if new data is added.
Method 2. Using Text-to-Columns Tool
If you want to convert numbers to text without using formulas or coding, Excel’s Text-to-Columns feature is a quick and practical method. It allows you to reformat numeric values into plain text within their original cells.
Steps:
- Select the range that contains the numbers you want to convert.
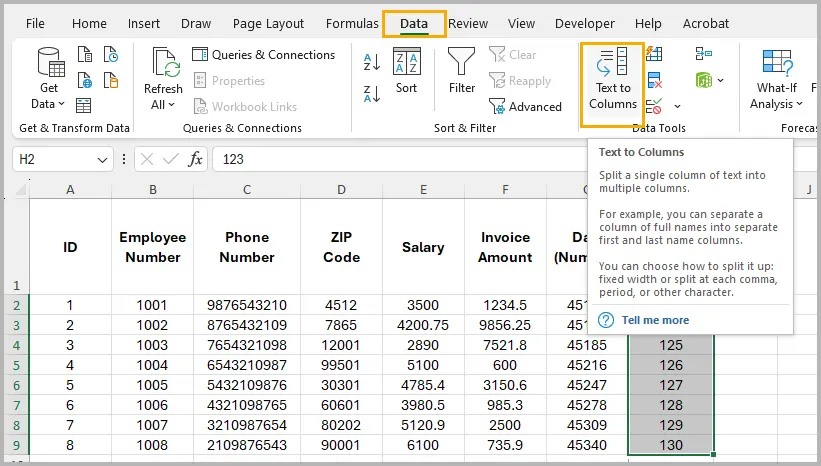
- Go to the Data tab → click Text to Columns .
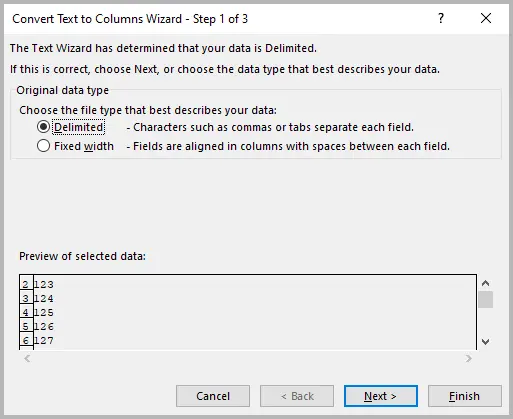
- In the Convert Text to Columns Wizard , choose Delimited → click Next .
- Skip delimiter options → click Next again.
- In Column Data Format , select Text .
- Click Finish .
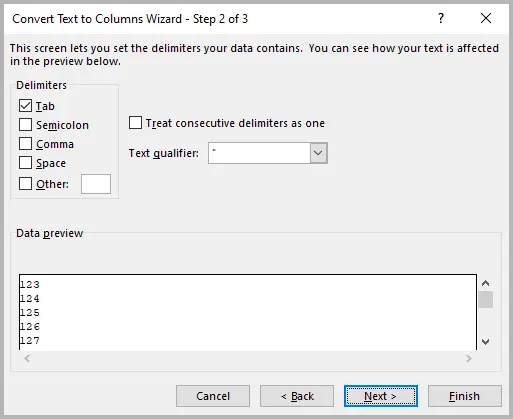
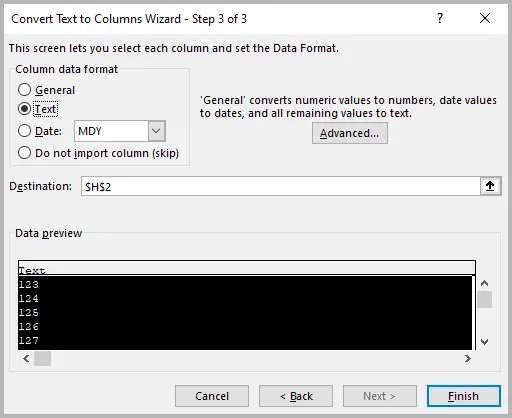
After applying Text-to-Columns, the numbers are stored as text values directly in their original cells (indicated by a small green triangle in the corner).
Pros:
- Converts numbers to text in place.
- No need for helper columns or formulas.
- Works in all Excel versions.
Cons:
- Manual process (not dynamic).
- Must be repeated when new data is added.
Method 3. Using Excel Functions that Return Text
Excel offers several functions that can convert numbers to text directly in formulas. Two of the most useful are TEXT() and VALUETOTEXT() .
Option 1: TEXT Function
The TEXT() function converts a numeric value into text while allowing you to specify a custom format.
Syntax:
=TEXT(value, format_text)
Examples:
| A (Original) | B (Formula) |
|---|---|
| 1234.5 | =TEXT(A1, "0.00") → “1234.50” |
| 5678 | =TEXT(A2, "$#,##0") → “$5,678” |
The TEXT() function is especially powerful when you want your text output to follow a specific numeric, date, or currency pattern.
Tip: Combine TEXT() with other text functions like CONCAT(), TEXTJOIN(), or the ampersand (&) operator to create descriptive strings:
="Total amount: " & TEXT(A1, "$#,##0.00")
Option 2: VALUETOTEXT Function (Excel 365 / Excel 2021 and Later)
If you’re using a modern Excel version, the VALUETOTEXT() function provides a more direct and flexible conversion.
Syntax:
=VALUETOTEXT(value, [format])Parameters:
- value — The number you want to convert.
- [format] — Optional; use 0 for simple text or 1 for JSON-compatible output.
Examples:
| A (Original) | B (Formula) |
|---|---|
| 9876 | =VALUETOTEXT(A1) → “9876” |
| 543.21 | =VALUETOTEXT(A2,1) → “543.21” |
This function is particularly useful when you’re working with dynamic arrays, automation scripts, or exporting data that needs to remain textual.
Pros:
- Formula-based and flexible.
- Works dynamically with changing data.
- Supports formatting customization.
Cons:
- VALUETOTEXT() requires newer Excel versions.
- Results depend on correct format strings.
Tip: Replace the Original Numbers with Text Values
When you use formulas such as TEXT() or VALUETOTEXT(), Excel only displays the converted text in the formula cells — it doesn’t overwrite your original numbers.
To permanently replace numbers with text equivalents:
- Enter the formula in a blank column (e.g., column B).
- Verify the results look correct.
- Select the formula cells and copy them.
- Right-click the original numeric column → choose Paste Special → Values .
- Delete the helper column if you no longer need it.
Method 4. Using VBA Macro
For users who frequently need to convert numbers to text, creating a VBA macro offers automation and flexibility. With just a few lines of code, you can convert an entire range in one click.
Steps:
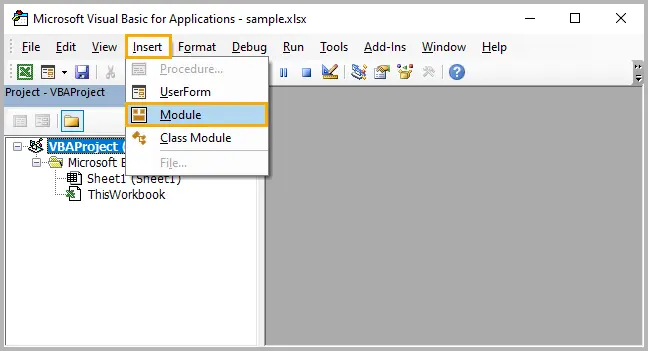
- Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
- Click Insert → Module .
- Paste the following code:
- Close the editor and return to Excel.
- Select the range of numbers you want to convert.
- Press Alt + F8 , choose ConvertNumbersToText , and click Run .
Sub ConvertNumbersToText()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Selection
If IsNumeric(cell.Value) Then
cell.Value = CStr(cell.Value)
End If
Next cell
End Sub
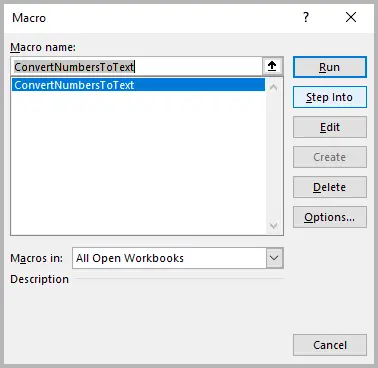
Excel will loop through your selection and convert all numeric values into text strings using VBA’s CStr() function.
Pros:
- Fully automated.
- Works on large data ranges.
- Can be reused anytime.
Cons:
- Requires enabling macros.
- May be restricted by some organizational policies.
Tip: If you want to preserve the original numeric formatting, you can enhance the macro with additional logic using Format() instead of CStr().
Method 5. Using Python Automation (with Spire.XLS for Python)
If you’re working with Excel files programmatically, Spire.XLS for Python provides a straightforward and reliable way to convert numbers to text directly in your scripts. This approach is especially valuable for large-scale automation, batch processing, or web-based systems.
Example Code:
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Employee.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a cell range
cellRange = worksheet.Range["F2:F9"]
# Convert numbers in the cell range to text
cellRange.NumberFormat = "@"
# Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/NumbersToText.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
How It Works
- Workbook Management: The Workbook object allows you to load and work with existing Excel files using the
LoadFromFilemethod. - Worksheet Access: Each workbook can contain multiple worksheets, which you can access by index.
- Cell Range Selection: The
Rangemethod identifies specific rows and columns for data manipulation. - Formatting Cells: Setting the
NumberFormatproperty to"@"converts the cell format from numeric to text. - Saving Changes: The
SaveToFilemethod saves the modified workbook to a new or existing file.
For more detailed instructions, check out the full tutorial: Convert Text to Numbers and Numbers to Text in Excel in Python
Pros:
- Ideal for bulk and automated conversions.
- Works without launching Excel.
- Easily integrated into data pipelines or web applications.
Cons:
- Requires installing and using Spire.XLS.
- Best suited for users comfortable with Python scripting.
As a comprehensive Python Excel library, Spire.XLS enables programmers to easily manage and customize Excel formatting through code. Want to learn more? Check out this tutorial: Format Excel with Python
Comparison Table: Which Method Should You Choose?
| Method | Type | Works In-Place? | Automation Level | Difficulty | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Formatting | Manual | Yes | None | ★☆☆☆☆ | Simple formatting only |
| Text-to-Columns | Manual | Yes | None | ★★☆☆☆ | One-time conversion |
| TEXT / VALUETOTEXT | Formula | No | Low | ★★☆☆☆ | Dynamic conversion |
| VBA Macro | Code | Yes | High | ★★★☆☆ | Frequent conversions |
| Python (Spire.XLS) | Code | Yes | Very High | ★★★★☆ | Automated batch processing |
Summary
Converting numbers to text in Excel can be as simple—or as advanced—as you need it to be. For most users, Excel’s cell formatting tools and the Text-to-Columns feature provide quick, built-in ways to change numeric data into text without using any formulas.
If you want more control or need formatted text outputs, Excel’s TEXT and VALUETOTEXT functions are flexible options that let you customize display styles or combine numbers with descriptive text. For larger or recurring conversion tasks, automation through VBA macros or Spire.XLS for Python offers speed, accuracy, and scalability—perfect for enterprise-level workflows.
When selecting a method, consider how often you’ll perform the task, whether you need dynamic updates, and if automation is a priority. With these five methods, you can convert numbers to text in Excel efficiently, no matter your skill level or data size.
FAQs
Q1: Will converting numbers to text affect calculations?
Yes. Once a value is text, Excel will no longer treat it as numeric in formulas like SUM or AVERAGE.
Q2: Does changing the cell format to “Text” convert existing numbers automatically?
No. You’ll need to re-enter or refresh values (press F2 → Enter) after changing the format.
Q3: Can I convert numbers to text without losing formatting?
Yes. Use the TEXT() function and specify your desired format string (e.g., "0.00" or "$#,##0.00").
Q4: Can I reverse the process and turn text back into numbers?
Absolutely. Use the VALUE() function or convert the column format back to “Number.”
Q5: Is Spire.XLS free to use?
Spire.XLS offers both a free and a commercial version. The free version supports most common features for small to medium tasks.