Table of Contents
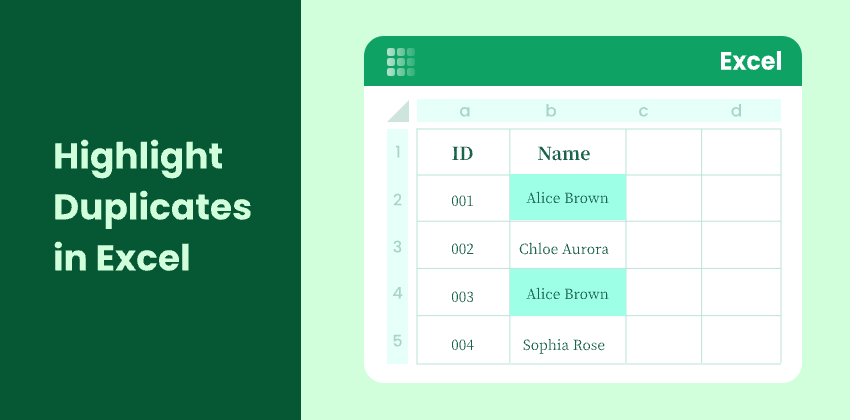
Duplicate values are a common issue in Excel spreadsheets. Whether you’re working with customer lists, product inventories, invoices, or survey results, duplicate data can lead to errors, inaccurate reports, and poor decisions.
Fortunately, Excel provides several simple and effective ways to highlight duplicates so you can easily spot and manage them. In this article, you’ll learn four easy methods to find and highlight duplicate values in Excel—from built-in tools to automated solutions using Python.
Method overview:
- Method 1. Conditional Formatting (Built-in – Easiest Way)
- Method 2. Use a Formula with Conditional Formatting
- Method 3. Use a Helper Column with COUNTIF
- Method 4. Use Python with Spire.XLS for Automation
Method 1: Conditional Formatting (Built-in – Easiest Way)
This is the fastest and most beginner-friendly way to highlight duplicates in Excel. It uses Excel’s built-in visual rules, so no formulas or technical skills are required. With just a few clicks, Excel automatically scans your selected range and marks duplicate values. This method is ideal for quick checks and small to medium-sized datasets.
Steps
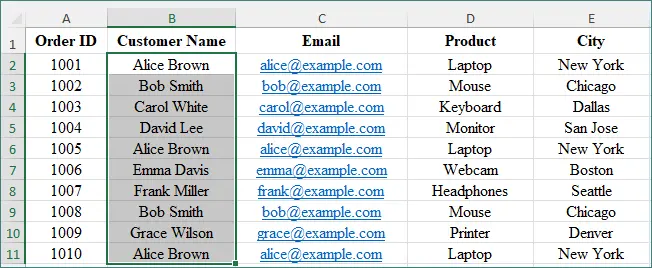
-
Select the cell range you want to check (for example, B2:B11).
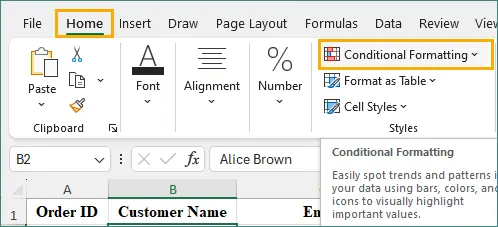
-
Go to Home → Conditional Formatting.
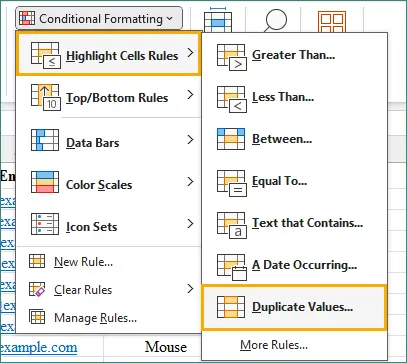
-
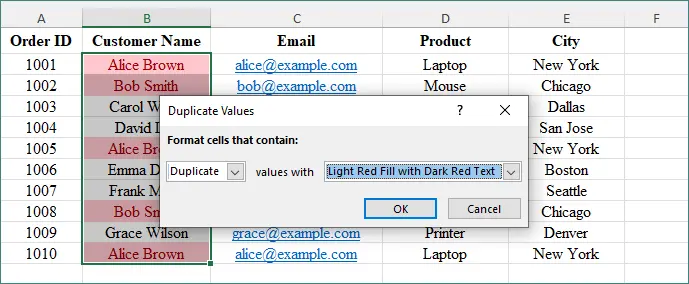
Click Highlight Cells Rules → Duplicate Values.
-
Choose a formatting style (fill color, text color).
-
Click OK.
Excel will instantly highlight all duplicate values in the selected range.
Key Benefits
- Best for quick, visual checks
- No formulas required
Method 2: Use a Formula with Conditional Formatting
This method lets you define exactly how Excel identifies duplicates, such as highlighting only repeated values or excluding the first occurrence. It requires a basic understanding of formulas but gives you much greater flexibility than built-in rules. This approach works especially well for structured or complex datasets.
Example Formula
To highlight all duplicate values (including the first occurrence):
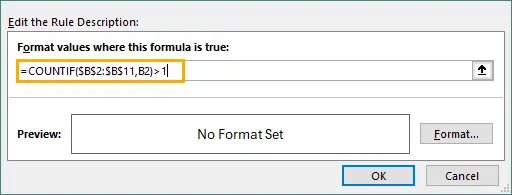
=COUNTIF($B$2:$B$11,B2)>1
What this formula means:
- COUNTIF($B$2:$B$11, B2) counts how many times the value in cell B2 appears in the range B2:B11.
- If the count is greater than 1, Excel treats the value as a duplicate.
In simple terms, this formula tells Excel to highlight any cell whose value appears more than once in the selected range. The dollar signs ($) lock the search range so it stays fixed when the rule is applied to other cells.
For more COUNTIF examples, see Microsoft’s official documentation.
Steps
-
Select your data range.
-
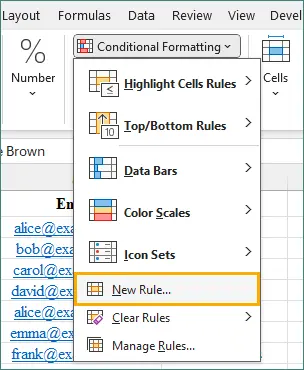
Go to Conditional Formatting → New Rule.
-
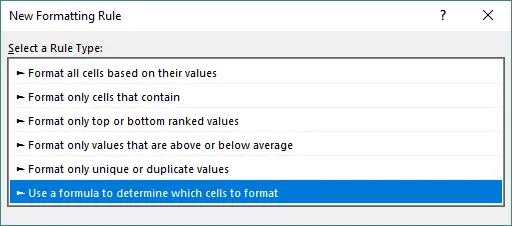
Select Use a formula to determine which cells to format.
-
Enter the formula above.
-
Choose a format and click OK.

This method is useful when you want to customize how Excel treats duplicates.
Key Benefits
- More flexibility
- Works well with complex datasets
Method 3: Use a Helper Column with COUNTIF
This method relies on a helper column to count how many times each value appears in your dataset. It provides a clear, transparent view of duplicates that is easy to audit and validate. Because the results update automatically, it is ideal for dynamic worksheets that change frequently. This approach works well when accuracy and traceability are important.
Steps
-
In a blank column (for example, F2), enter:
=COUNTIF($B:$B,B2)
-
Then drag the formula down.
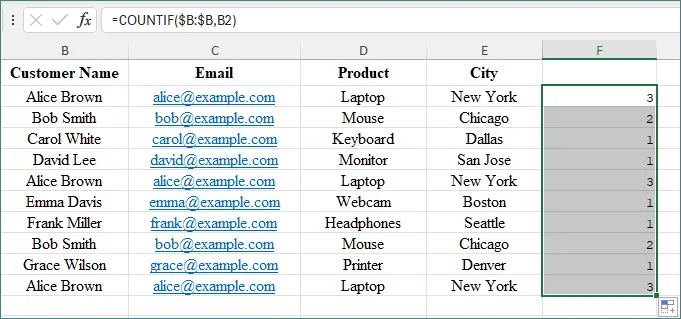
How It Works
- A result of 1 means the value is unique.
- A result greater than 1 means it’s a duplicate.
You can then apply conditional formatting to the helper column to visually highlight duplicates.
Key Benefits
- Great for dynamic, updatable reports
- Easy to audit and track duplicates
Method 4: Use Python with Spire.XLS for Automation
If you frequently work with large Excel files or repetitive tasks, you can use Python with Spire.XLS for automation. This method allows you to programmatically scan and highlight duplicates without manual effort. It helps save time, reduce human error, and process files in bulk. This approach is ideal for developers or teams that need scalable Excel solutions.
What Is Spire.XLS for Python?
Spire.XLS for Python is a powerful library that allows you to read, write, format, and manipulate Excel files using Python—no Microsoft Excel installation required.
Installation
pip install spire.xls
Sample Code to Highlight Duplicates
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Load the Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Use conditional formatting to highlight duplicate values in the specified cell range
conditional_format = sheet.Range["B2:B11"].ConditionalFormats.AddCondition()
conditional_format.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.DuplicateValues
conditional_format.BackColor = Color.get_Yellow()
# Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("HighlightDuplicates.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
output:
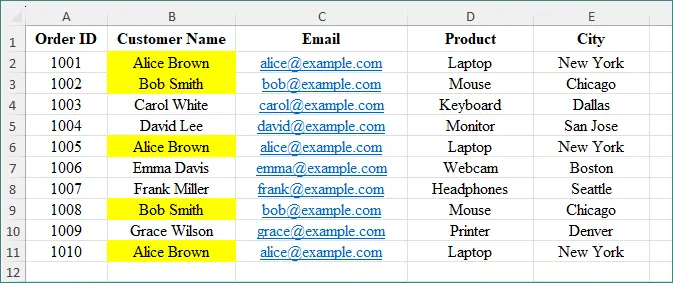
Key Benefits
- Ideal for batch processing
- Perfect for enterprise automation workflows
Conditional formatting can do much more than highlight duplicates in Excel. It also allows you to apply alternating row colors and highlight top or bottom ranked values. To learn more, see this tutorial: Apply Conditional Formatting in Excel in Python.
Comparison of the Methods
| Method | Ease of Use | Best For | Automation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conditional Formatting | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Quick visual checks | x |
| Formula + Conditional Formatting | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Custom logic | x |
| Helper Column (COUNTIF) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Dynamic reports | x |
| Python + Spire.XLS | ⭐⭐ | Large files, batch work | √ |
Final Thoughts
Highlighting duplicates in Excel helps improve data accuracy and reduces costly errors. If you only need a quick visual scan, built-in Conditional Formatting is the fastest option. For more advanced control, formulas and helper columns work well.
If you handle large files frequently, using Python with Spire.XLS can dramatically improve efficiency through automation.
The best method depends on your workload, file size, and technical comfort level.
FAQs About Highlighting Duplicates in Excel
Q1. Can Excel highlight duplicates automatically?
Yes. The built-in Conditional Formatting feature highlights duplicates instantly.
Q2. Can I highlight duplicates across multiple columns?
Yes. You can select multiple columns before applying Conditional Formatting or use a custom formula.
Q3. Does highlighting duplicates delete data?
No. Highlighting only changes cell formatting and does not affect the underlying data.
Q4. What is the best method for large Excel files?
For large datasets or repeated tasks, automation using Python and Spire.XLS is the most efficient approach.