Table of Contents
- Why Learning Multiple Ways Matters
- Method 1. Type Formulas Directly in a Cell
- Method 2. Insert Formulas Using the Formula Bar
- Method 3. Use the Insert Function (fx) Button
- Method 4. Use AutoSum and Quick Functions
- Method 5. Insert Formulas Using the Fill Handle
- Method 6. Insert Formulas Programmatically
- Comparison: Which Method Should You Choose?
- Summary
- FAQs About Inserting Formulas to Excel
Formulas are one of Excel’s most powerful features. They let you run calculations, analyze trends, automate repetitive work, and build dynamic reports. Whether you’re doing a quick sum, building nested conditional logic, or automating bulk spreadsheet generation, Excel gives you multiple ways to insert formulas — each suited to different skill levels and tasks.
In this article, we will walk through several easy and efficient ways to insert formulas into Excel , ranging from built-in UI methods to automation using Python (Spire.XLS). We will also include example use cases, step-by-step instructions, and a comparison table to help you decide which method works best for your workflow.
Method overview:
- Method 1: Type Formulas Directly in a Cell (Fastest for Simple Use)
- Method 2: Insert Formulas Using the Formula Bar (Best for Long or Complex Formulas)
- Method 3: Use the Insert Function (fx) Button (Most Beginner-Friendly)
- Method 4: Use AutoSum and Quick Functions (Extremely Efficient)
- Method 5: Insert Formulas Using the Fill Handle (Best for Repetition)
- Method 6: Insert Formulas Programmatically (Python – Spire.XLS)
Why Learning Multiple Ways Matters
Many Excel users only know how to type equations directly into a cell. While that works for simple calculations, it’s not always the fastest or most reliable method, especially when dealing with large datasets or complex formulas. Excel provides a variety of tools and shortcuts designed to speed up formula creation, improve accuracy, and avoid manual errors.
In addition, developers and data analysts often need automation solutions for generating or updating Excel files in bulk—something that scripting with Python can handle more efficiently than manual entry.
By learning multiple ways to insert formulas, you can:
- Work more efficiently with day-to-day spreadsheets
- Reduce errors caused by manual typing
- Take advantage of Excel’s built-in intelligence
- Automate repetitive tasks or large-scale Excel processing
Below are the six most efficient methods for inserting formulas into Excel, with practical guidance so you can apply them immediately.
Method 1. Type Formulas Directly in a Cell (Fastest for Simple Use)
Typing directly into a cell is the most common and straightforward way of inserting formulas. It’s fast, intuitive, and works perfectly for quick calculations.
Steps:
- Click the cell where you want the formula result to appear.
- Type an equal sign = to start the formula.
- Enter the formula—for example:
- =A1+B1
- =SUM(A1:A10)
- =A1*B1
- Press Enter to apply the formula.
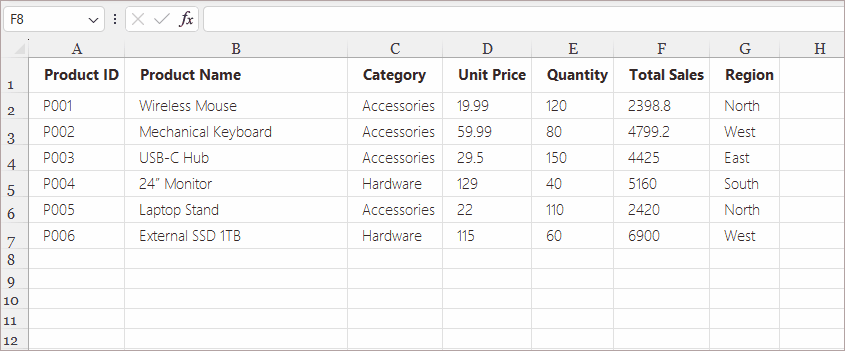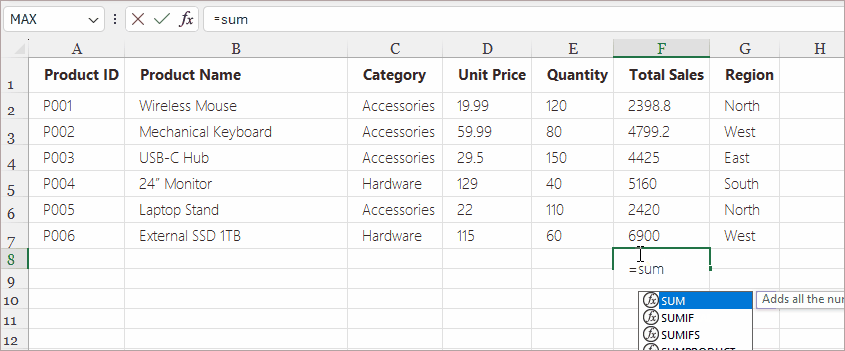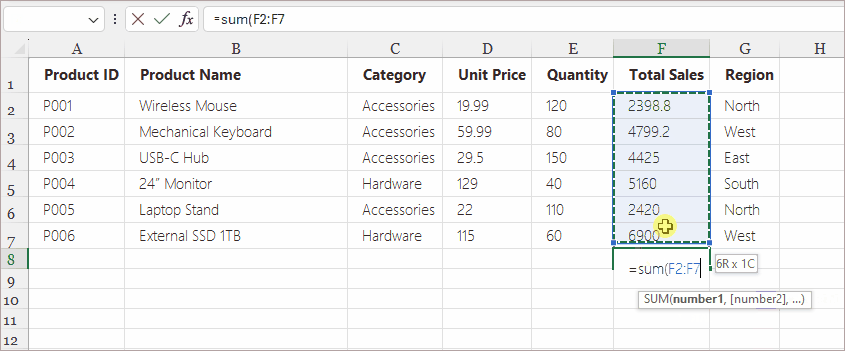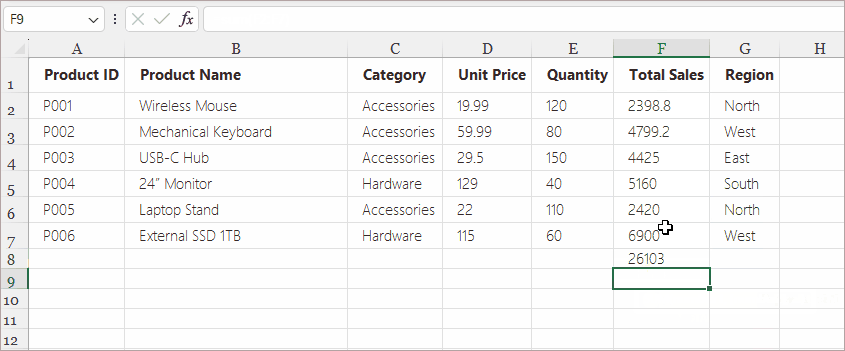
Example Use Cases:
- Adding or subtracting values
- Calculating totals
- Performing basic math operations
- Using simple functions (SUM, AVERAGE, MAX, MIN)
Why this method is useful:
- Extremely fast for simple tasks
- Great for small spreadsheets
- No additional tools or dialogs needed
However, this method becomes inefficient when you need to insert long or complex formulas that require more careful editing.
Method 2. Insert Formulas Using the Formula Bar (Best for Long or Complex Formulas)
The Formula Bar provides more space and clarity, making it ideal for editing long or complicated formulas without accidentally modifying the cell content itself.
Steps:
- Select the cell where your formula belongs.
- Click the Formula Bar at the top of Excel.
- Type or edit your formula.
- Press Enter .
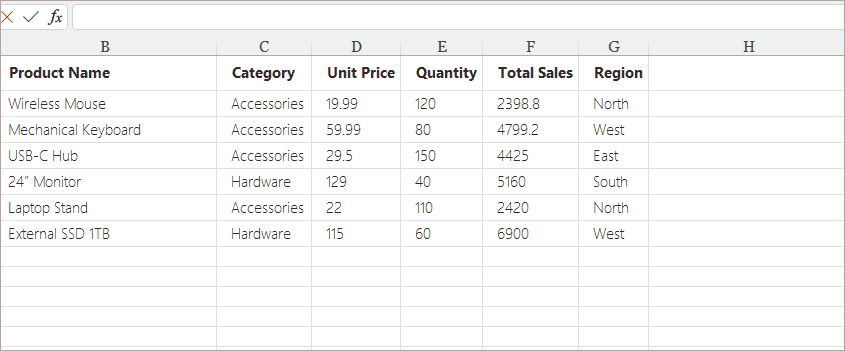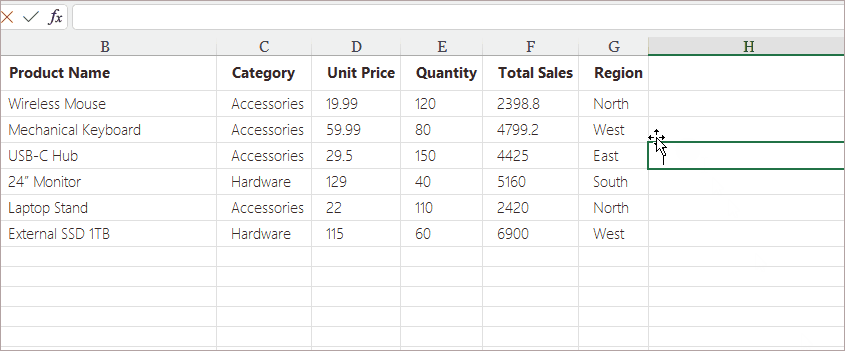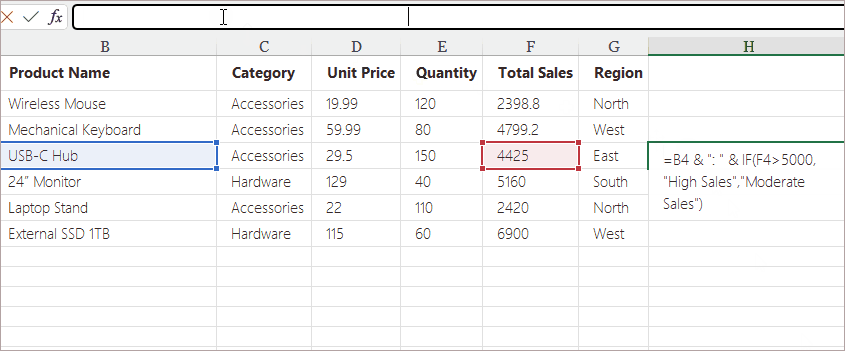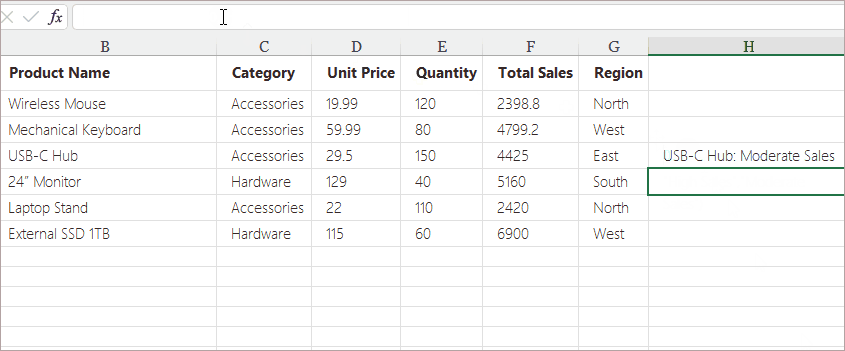
Example Use Cases:
- Nested IF statements
- VLOOKUP , INDEX + MATCH, XLOOKUP
- Concatenation formulas with multiple text segments
- Multi-condition logical formulas
Why this method is useful:
- Allows comfortable editing of long or multi-line formulas
- Reduces accidental cell changes
- Helps maintain a clean view of the worksheet
The Formula Bar also displays formula error warnings, making debugging easier.
Method 3. Use the Insert Function (fx) Button (Most Beginner-Friendly)
Excel’s Insert Function (fx) tool is specifically designed for users who are still learning formulas or prefer guided steps when building more complex functions.
Steps:
- Click the cell where you want the formula result.
- Click the fx button to the left of the Formula Bar.
- Choose a function category (Math, Text, Date & Time, Logical, Lookup, etc.).
- Select the desired function (e.g., SUMIFS , IF , LEFT , VLOOKUP ).
- Fill in the argument fields in the pop-up dialog.
- Click OK .
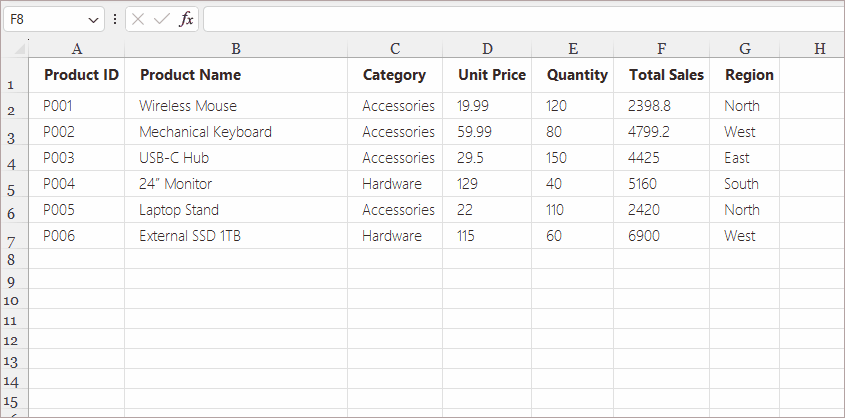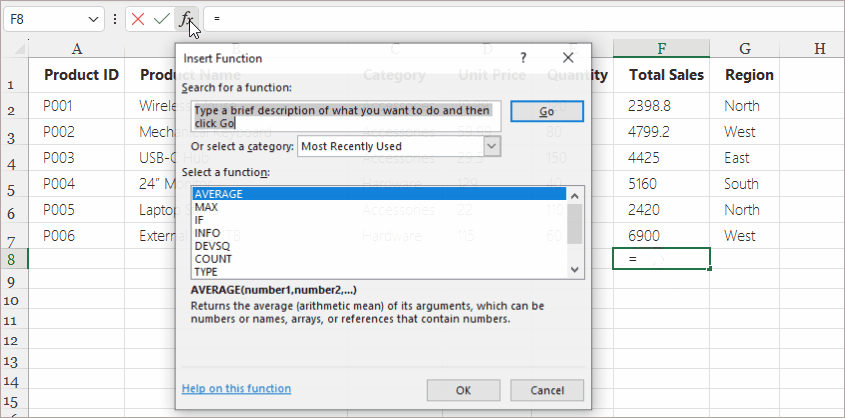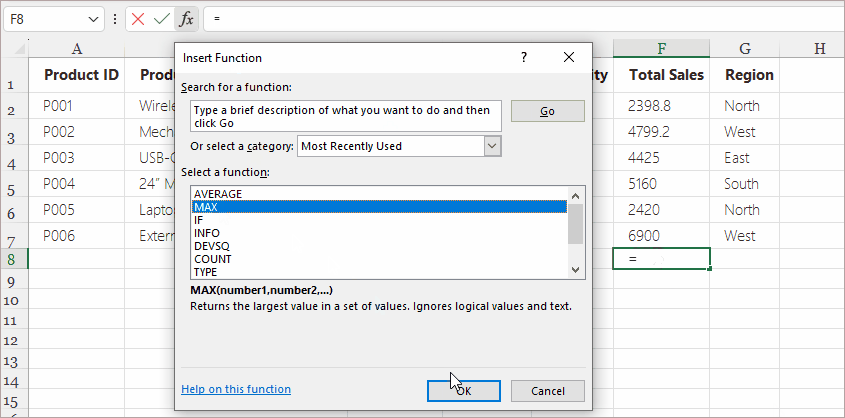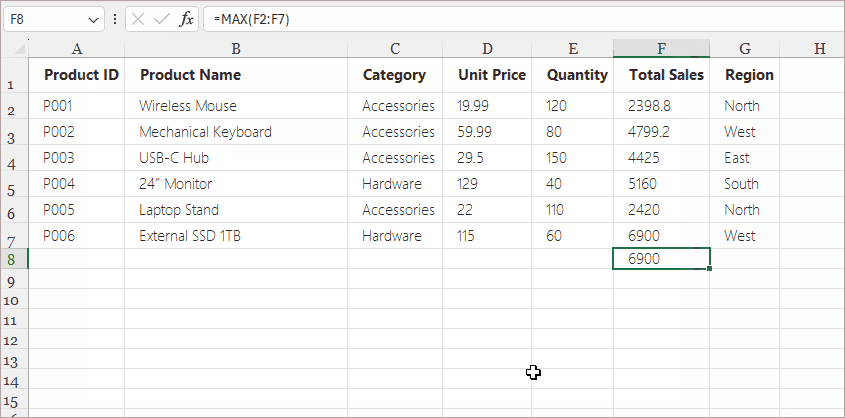
Example Use Cases:
- Learning how Excel functions work
- Formulas with multiple arguments
- Financial, date, and statistical calculations
- Anything where you want Excel to help guide the formula setup
Why this method is useful:
- Helps beginners avoid syntax errors
- Shows a description of each function and example usage
- Provides structured fields for entering arguments
This method is slower than direct entry but much more accurate when working with unfamiliar formulas.
Method 4. Use AutoSum and Quick Functions (Extremely Efficient)
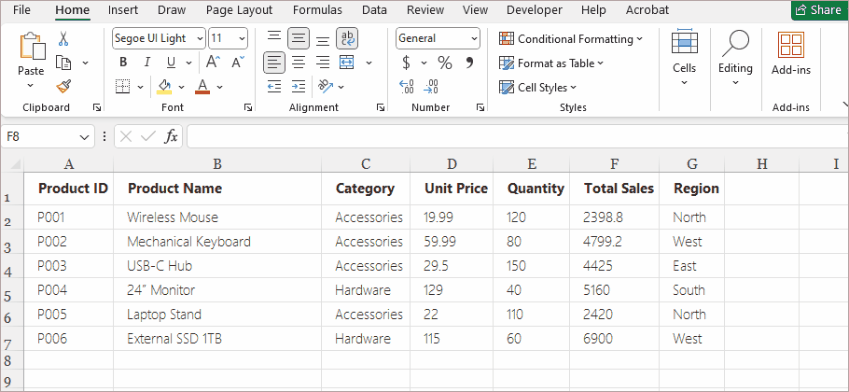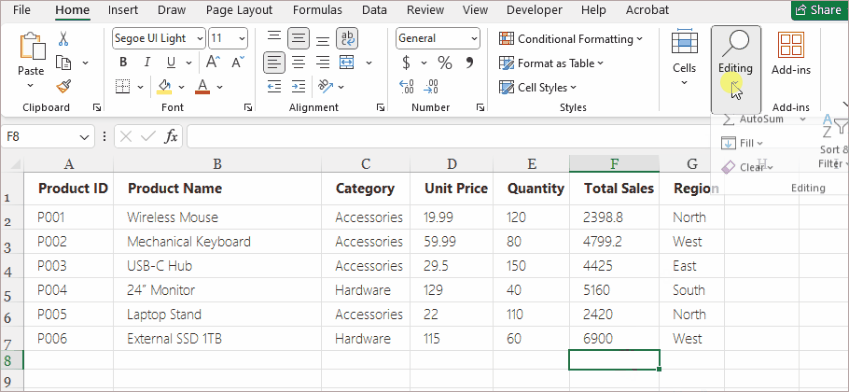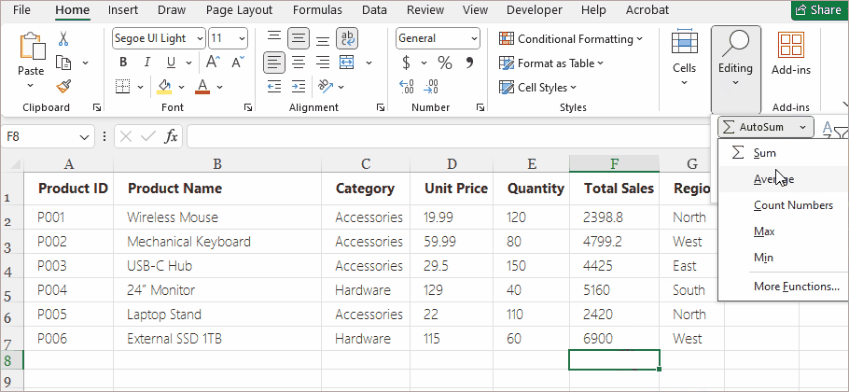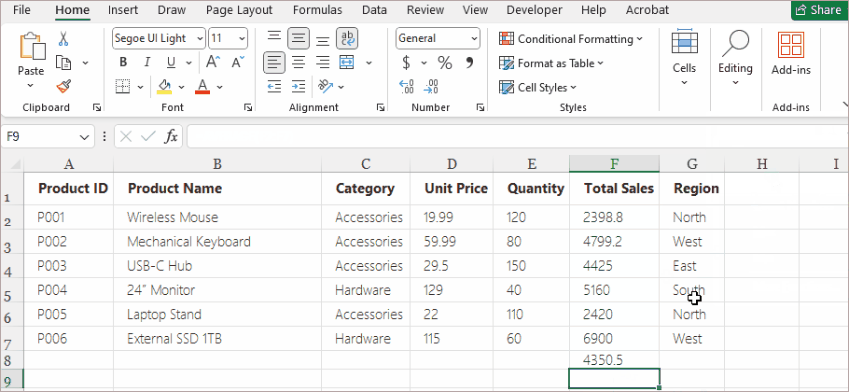
The AutoSum tool provides one-click shortcuts for commonly used functions such as:
- SUM
- AVERAGE
- COUNT
- MAX
- MIN
Steps:
- Select a cell below or beside your numeric data.
- Go to Home > Editing > AutoSum (or choose another function from the dropdown).
- Excel highlights a suggested range automatically.
- Press Enter to accept.
Example Use Cases:
- Summing a column of sales data
- Finding the highest or lowest value in a range
- Calculating an average score
- Counting how many numeric values appear in a dataset
Why this method is useful:
- Saves time—no typing needed
- Perfect for summary reports
- Excel auto-detects relevant cell ranges
- Reduces errors in range selection
If you frequently work with numeric reports, summary tables, or accounting files, AutoSum can speed up your workflow dramatically.
Method 5. Insert Formulas Using the Fill Handle (Best for Repetition)
Once a formula is entered, Excel’s Fill Handle can copy that formula across multiple rows or columns, automatically adjusting cell references.
Steps:
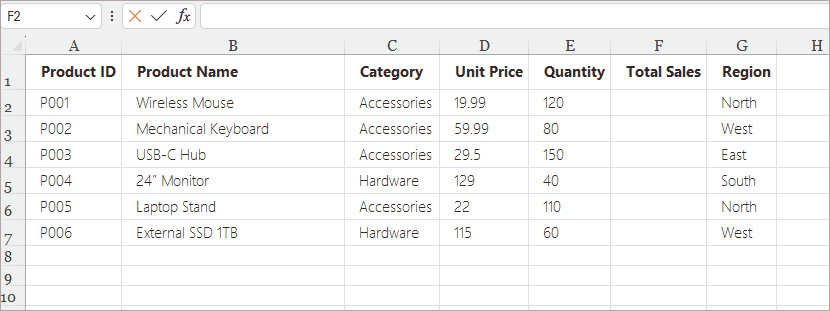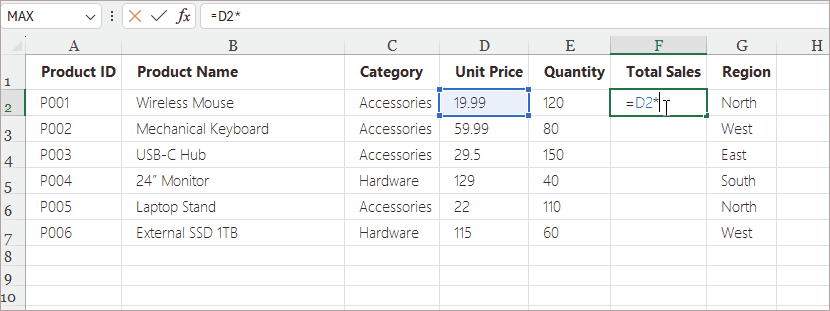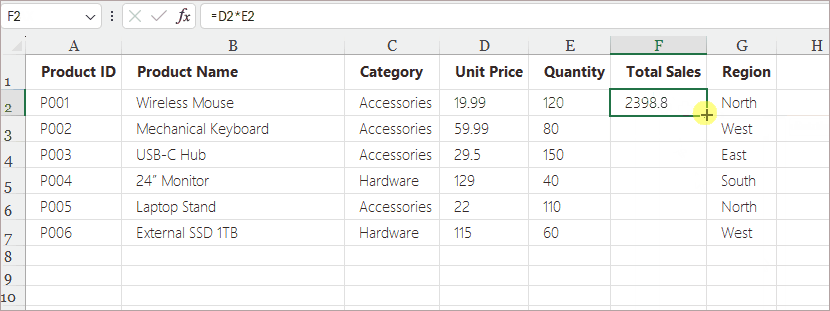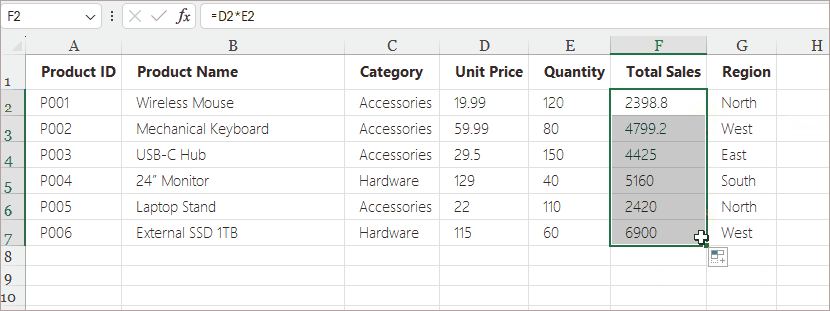
- Enter a formula in the first cell (e.g., =D2*E2).
- Hover over the bottom-right corner until the cursor turns into a small black cross.
- Drag down or across to fill adjacent cells.
- Release the mouse button.
Excel updates the references automatically:
- D2 becomes D3
- E2 becomes E3
- And so on
Example Use Cases:
- Calculating totals for hundreds of rows
- Applying the same logic to an entire dataset
- Generating sequences (e.g., =ROW(), =A1+10)
- Copying time or date calculations across cells
Why this method is useful:
- Extremely fast for repetitive calculations
- Automatically adjusts formulas based on position
- Reduces the need to manually type formulas in each row
This method is essential for data entry, financial modeling, budgeting, and any spreadsheet involving large datasets.
Method 6. Insert Formulas Programmatically (Python – Spire.XLS)
For automation, batch processing, or generating Excel files dynamically, inserting formulas programmatically is the most scalable approach. Using Python with Spire.XLS , you can create Excel files, insert formulas, and perform calculations automatically—without opening Excel.
Steps:
-
Install Spire.XLS for Python using pip.
pip install spire.xls -
Import the required module into your script.
-
Load an existing Excel file into a Workbook object.
-
Access the worksheet where you want to insert the formula.
-
Write the formula to the target cell using the Formula property.
-
Save the updated file to a new Excel workbook.
Example:
from spire.xls import *
# Create workbook and load an Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Insert a formula
sheet.Range["F8"].Formula = "=SUM(F2:F7)"
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Read further: Add or Read Formulas in Excel Using Python
Example Use Cases:
- Automated reporting
- Data transformation workflows
- Generating financial or sales reports for apps
- Batch processing thousands of Excel files
Why this method is useful:
- Eliminates manual work
- Ensures consistency across generated files
- Integrates Excel logic into larger software systems
This is the most powerful option for developers and analysts, as Spire.XLS for Python not only inserts formulas programmatically but also creates and edits workbooks, applies formatting, generates charts, converts Excel to PDF, and automates complex data tasks.
Comparison: Which Method Should You Choose?
| Method | Best For | Ease of Use | Speed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typing in Cell | Quick/basic formulas | Easy | Very fast | Ideal for small tasks |
| Formula Bar | Long or complex formulas | Easy | Medium | Offers more editing space |
| Insert Function (fx) | Beginners/complex functions | Very easy | Medium | Guided formula creation |
| AutoSum | Summaries & common functions | Very easy | Very fast | One-click totals |
| Fill Handle | Repeated formulas | Easy | Extremely fast | Auto-adjusts cell references |
| Python (Spire.XLS) | Automation & batch tasks | Medium | Fastest at scale | Best for developers |
Summary
Inserting formulas in Excel can be done in multiple simple and efficient ways, depending on your workflow. This article covered six practical methods — including using AutoSum, entering formulas through the Formula Bar, selecting functions from the Function Library, using the Fill Handle to copy formulas, typing manual formulas, and automating formula insertion with Spire.XLS for Python . Each method offers unique advantages, from quick calculations to scalable automation. By choosing the approach that best fits your needs, you can improve accuracy, streamline data processing, and make your Excel tasks more efficient.
FAQs About Inserting Formulas to Excel
Q1. My formula is not calculating and displays as text. Why?
The cell is formatted as Text. Change it to General and re-enter the formula.
Q2. What’s the fastest way to apply a formula to hundreds of rows?
Use the Fill Handle or automation via Python (Spire.XLS) .
Q3. Can Excel formulas reference other worksheets?
Yes. Example: =Sheet2!A1 + Sheet3!B5
Q4. Can formulas be generated automatically?
Yes. Tools like Spire.XLS for Python can insert formulas programmatically.