
.NET (1317)
Children categories
Change the color or remove underline from hyperlink in Word with C#
2016-05-12 08:14:23 Written by KoohjiBy default, hyperlink in Word shows up as blue and underlined. In some cases, users may want to modify the hyperlink style so as to get better looking with the whole document. This article is going to introduce how we can remove the underline or change the color of hyperlinks using Spire.Doc in C#.
Code Snippets:
Step 1: Create a new object of Document class, add a section to it.
Document document = new Document(); Section section = document.AddSection();
Step 2: Add a paragraph and append a hyperlink to the paragraph. In order to format the hyperlink, we return the value of hyperlink in a TextRange.
Paragraph para= section.AddParagraph();
TextRange txtRange = para1.AppendHyperlink("www.e-iceblue.com", "www.e-iceblue.com", HyperlinkType.WebLink);
Step 3: Format the hyperlink with the specified the font name, font size, color and underline style.
txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"; txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12; txtRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Red; txtRange.CharacterFormat.UnderlineStyle = UnderlineStyle.None;
Step 4: Save the file.
document.SaveToFile("result.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
Output:
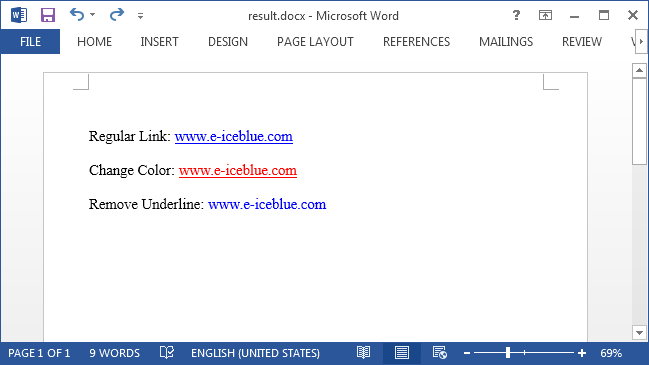
Full Code:
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace FormatHyperlink
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document document = new Document();
Section section = document.AddSection();
Paragraph para1= section.AddParagraph();
para1.AppendText("Regular Link: ");
TextRange txtRange1 = para1.AppendHyperlink("www.e-iceblue.com", "www.e-iceblue.com", HyperlinkType.WebLink);
txtRange1.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman";
txtRange1.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12;
Paragraph blankPara1 = section.AddParagraph();
Paragraph para2 = section.AddParagraph();
para2.AppendText("Change Color: ");
TextRange txtRange2 = para2.AppendHyperlink("www.e-iceblue.com", "www.e-iceblue.com", HyperlinkType.WebLink);
txtRange2.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman";
txtRange2.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12;
txtRange2.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Red;
Paragraph blankPara2 = section.AddParagraph();
Paragraph para3 = section.AddParagraph();
para3.AppendText("Remove Underline: ");
TextRange txtRange3 = para3.AppendHyperlink("www.e-iceblue.com", "www.e-iceblue.com", HyperlinkType.WebLink);
txtRange3.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman";
txtRange3.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12;
txtRange3.CharacterFormat.UnderlineStyle = UnderlineStyle.None;
document.SaveToFile("result.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.docx");
}
}
}
How to create a formula to apply conditional formatting in Excel in C#
2016-05-11 07:40:52 Written by KoohjiWe always use conditional formatting to highlight the cells with certain color from the whole data in the Excel worksheet. Spire.XLS also supports to create a formula to apply conditional formatting in Excel in C#. This article will show you how to apply a conditional formatting rule.
View the steps of Microsoft Excel set the conditional formatting.
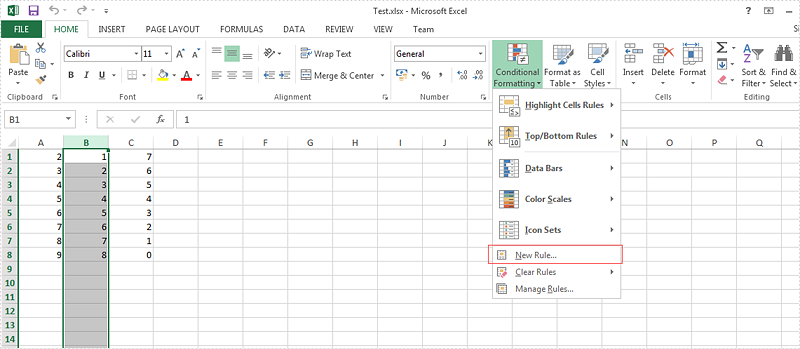
Step 1: Choose the column B and then click "New Rule" under "Conditional Formatting"
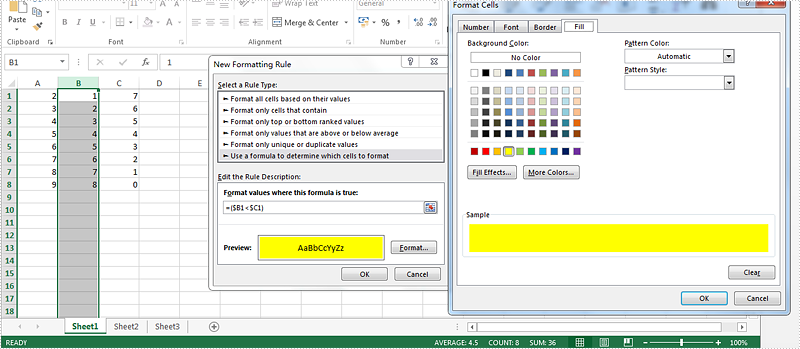
Step 2: Select the rule type, enter the rule by adding the formula and then add the highlight color for the format.
Here comes to the steps of how to set the conditional formatting rule by Spire.XLS in C#.
Step 1: Create a new excel workbook and load the document from file.
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("Test.xlsx");
Step 2: Get the first worksheet and the second column from the workbook.
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]; CellRange range = sheet.Columns[1];
Step 3: Set the conditional formatting formula and apply the rule to the chosen cell range.
XlsConditionalFormats xcfs = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add(); xcfs.AddRange(range); IConditionalFormat conditional = xcfs.AddCondition(); conditional.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.Formula; conditional.FirstFormula = "=($B1<$C1)"; conditional.BackKnownColor = ExcelColors.Yellow;
Step 4: Save the document to file.
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Effective screenshot:
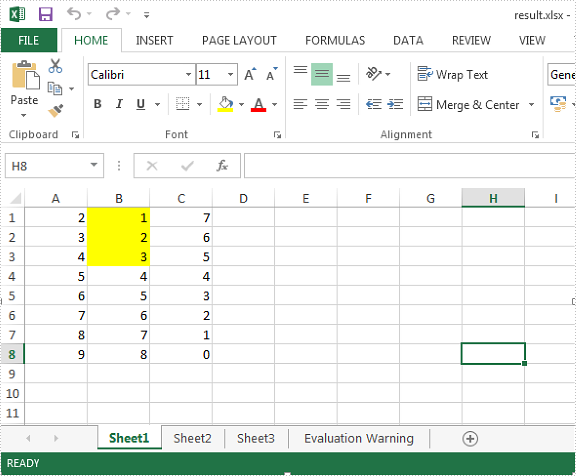
Full codes:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace CreateFormula
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("Test.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
CellRange range = sheet.Columns[1];
XlsConditionalFormats xcfs = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add();
xcfs.AddRange(range);
IConditionalFormat conditional = xcfs.AddCondition();
conditional.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.Formula;
conditional.FirstFormula = "=($B1<$C1)";
conditional.BackKnownColor = ExcelColors.Yellow;
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace CreateFormula
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim wb As New Workbook()
wb.LoadFromFile("Test.xlsx")
Dim sheet As Worksheet = wb.Worksheets(0)
Dim range As CellRange = sheet.Columns(1)
Dim xcfs As XlsConditionalFormats = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add()
xcfs.AddRange(range)
Dim conditional As IConditionalFormat = xcfs.AddCondition()
conditional.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.Formula
conditional.FirstFormula = "=($B1<$C1)"
conditional.BackKnownColor = ExcelColors.Yellow
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Spire.Xls enables developers to quickly find specific data, highlight the data as well as replace them with new data in excel files. We've already introduced how to find and highlight excel data, so this article is aimed to demonstrate how to replace selected data in excel on WPF applications using Spire.Xls for WPF.
Detail steps and code snippets:
Step 1: Create a WPF Application, add two buttons, three text boxes, two text blocks into the Main Window and align them like below.
Step 2: Double click the Browse button, add following codes to initialize a new OpenFileDialog object and set its properties to select excel file, and save its file name to the first text box.
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog1 = new OpenFileDialog();
openFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = @"E:\";
openFileDialog1.Title = "Select Excel Files";
openFileDialog1.DefaultExt = "xlsx";
openFileDialog1.Filter = "Excel files (*.xls;*.xlsx)|*.xls;*.xlsx|All files (*.*)|*.*";
openFileDialog1.FilterIndex = 1;
openFileDialog1.CheckFileExists = true;
openFileDialog1.CheckPathExists = true;
openFileDialog1.RestoreDirectory = true;
openFileDialog1.ReadOnlyChecked = true;
openFileDialog1.ShowReadOnly = true;
if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog().Value)
{
textBox1.Text = openFileDialog1.FileName;
}
Step 3: Double click the Replace All button, add following codes to load the excel file, replace all of the text entered in the find box with new text entered in the replace box, then save the changes and launch the file.
//Load the sample excel file
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile(textBox1.Text);
//Get the first worksheet of the excel file
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Call Worksheet.FindAllString(string stringValue, bool formula, bool formulaValue) method to find all of the specific text from the first worksheet and save the results to a CellRange array
CellRange[] ranges = sheet.FindAllString(this.FindBox.Text, false, false);
//Loop through the array, replace the selected text with new text
foreach (CellRange range in ranges)
{
range.Text = this.ReplaceBox.Text;
}
//Save the changes and launch the file
workbook.SaveToFile("Replaced.xlsx");
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Replaced.xlsx");
Result:
Run the project, you will get the following dialog box, Click Browse to choose excel file, then input the text that you want to find and the text used to replace, next click the Replace All button.
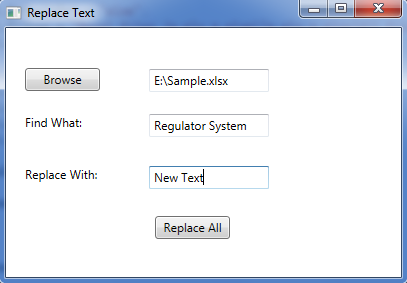
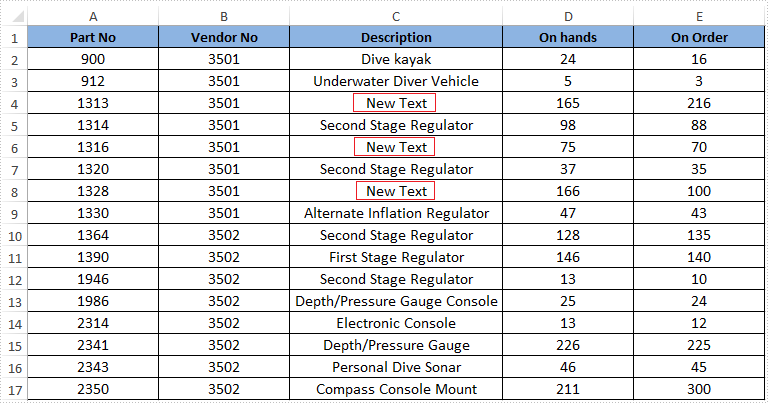
Effective screenshot of the result excel file:
Full codes:
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using Microsoft.Win32;
using Spire.Xls;
namespace Replace_Selected_Excel_Data_in_WPF
{
///
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
///
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void BrowseBtn_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog1 = new OpenFileDialog();
openFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = @"E:\";
openFileDialog1.Title = "Select Excel Files";
openFileDialog1.DefaultExt = "xlsx";
openFileDialog1.Filter = "Excel files (*.xls;*.xlsx)|*.xls;*.xlsx|All files (*.*)|*.*";
openFileDialog1.FilterIndex = 1;
openFileDialog1.CheckFileExists = true;
openFileDialog1.CheckPathExists = true;
openFileDialog1.RestoreDirectory = true;
openFileDialog1.ReadOnlyChecked = true;
openFileDialog1.ShowReadOnly = true;
if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog().Value)
{
textBox1.Text = openFileDialog1.FileName;
}
}
private void ReplaceBtn_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile(textBox1.Text);
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
CellRange[] ranges = sheet.FindAllString(this.FindBox.Text, false, false);
foreach (CellRange range in ranges)
{
range.Text = this.ReplaceBox.Text;
}
workbook.SaveToFile("Replaced.xlsx");
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Replaced.xlsx");
}
}
}
Excel version 2013 added a fantastic feature in Chart Data Label option that you can custom data labels from a column/row of data. The chart below uses labels from the data in cells C2: C5 next to the plotted values. This article will present how to add labels to data points using the values from cells in C#.
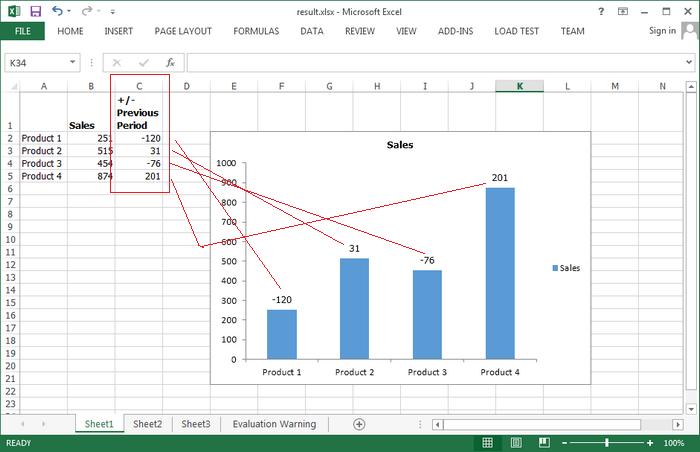
Code Snippets:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Workbook class and set the Excel version as 2013.
Workbook wb = new Workbook(); wb.Version = ExcelVersion.Version2013;
Step 2: Get the first sheet from workbook.
Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets[0];
Step 3: Insert data.
ws.Range["A2"].Text = "Product 1"; ws.Range["A3"].Text = "Product 2"; ws.Range["A4"].Text = "Product 3"; ws.Range["A5"].Text = "Product 4"; ws.Range["B1"].Text = "Sales"; ws.Range["B1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true; ws.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 251; ws.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 515; ws.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 454; ws.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 874; ws.Range["C1"].Text = "+/-\nPrevious\nPeriod"; ws.Range["C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true; ws.Range["C2"].NumberValue = -120; ws.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 31; ws.Range["C4"].NumberValue = -76; ws.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 201; ws.SetRowHeight(1, 40);
Step 4: Insert a Clustered Column Chart in Excel based on the data range from A1:B5.
Chart chart = ws.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered); chart.DataRange = ws.Range["A1:B5"]; chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
Step 5: Set chart position.
chart.LeftColumn = 5; chart.TopRow = 2; chart.RightColumn = 13; chart.BottomRow = 22;
Step 6: Add labels to data points using the values from cell range C2:C5.
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.ValueFromCell = ws.Range["C2:C5"];
Step 7: Save and launch the file.
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace CustomLabels
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.Version = ExcelVersion.Version2013;
Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets[0];
ws.Range["A2"].Text = "Product 1";
ws.Range["A3"].Text = "Product 2";
ws.Range["A4"].Text = "Product 3";
ws.Range["A5"].Text = "Product 4";
ws.Range["B1"].Text = "Sales";
ws.Range["B1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
ws.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 251;
ws.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 515;
ws.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 454;
ws.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 874;
ws.Range["C1"].Text = "+/-\nPrevious\nPeriod";
ws.Range["C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
ws.Range["C2"].NumberValue = -120;
ws.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 31;
ws.Range["C4"].NumberValue = -76;
ws.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 201;
ws.SetRowHeight(1, 40);
Chart chart = ws.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
chart.DataRange = ws.Range["A1:B5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
chart.LeftColumn = 5;
chart.TopRow = 2;
chart.RightColumn = 13;
chart.BottomRow = 22;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.ValueFromCell = ws.Range["C2:C5"];
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
}
}
}
Manually adjusting table columns can be time-consuming, especially if you have a large document with multiple tables. This is where the AutoFit tables feature in Word comes into play. It allows you to adjust the size of your table automatically, eliminating the need for manual adjustments. By setting AutoFit, the table will always adapt to display the content in the most suitable way. In this article, you will learn how to autofit tables in a Word document in C# using Spire.Doc for .NET.
- Set Tables to AutoFit to Contents in Word in C#
- Set Tables to AutoFit to Window in Word in C#
- Set Tables to Fixed Column Width in Word in C#
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Set Tables to AutoFit to Contents in Word in C#
The AutoFit to Contents option in Word adjusts the size of table columns and rows according to the content within the cells. Once set, each column is automatically resized to ensure that all content is displayed completely without excessive empty space.
With Spire.Doc for .NET, you can use the Table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.AutoFitToContents) method to autofit tables to content. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section in the document through Document.Sections[] property.
- Get a specified table in the section through Section.Tables[] property.
- AutoFit the table to contents using Table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.AutoFitToContents) method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
namespace AutoFitToContents
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Document instance
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("TableTemp.docx");
// Get the first section in the document
Section section = doc.Sections[0];
// Get the first table in the section
Table table = section.Tables[0] as Table;
// AutoFit the table to contents
table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.AutoFitToContents);
// Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("AutoFitToContents.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
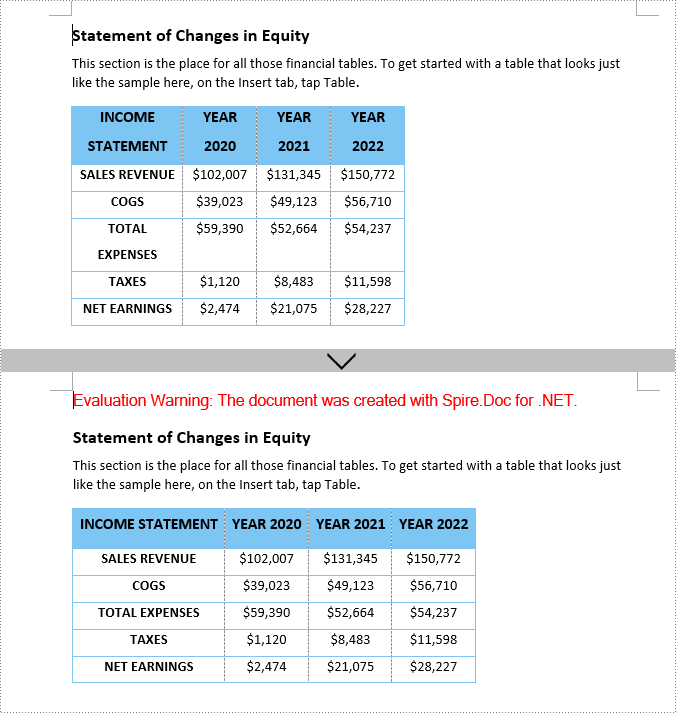
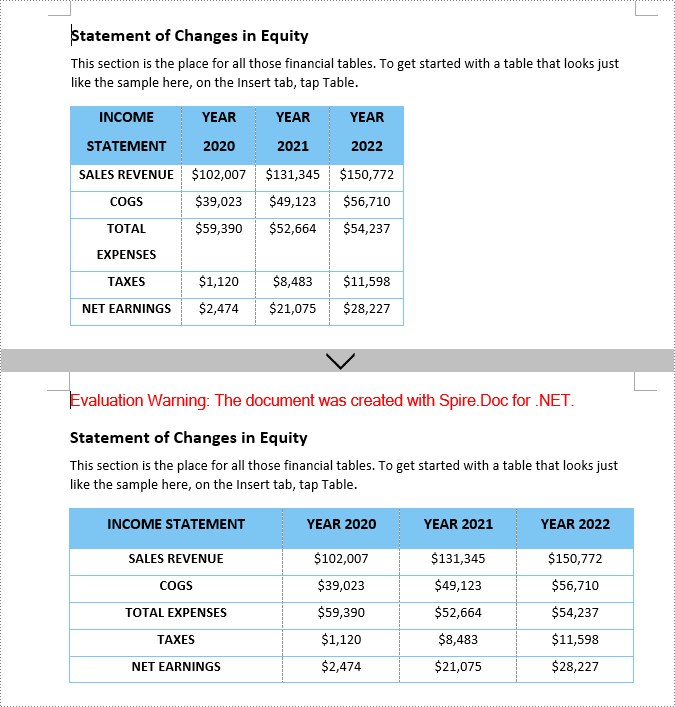
Set Tables to AutoFit to Window in Word in C#
The AutoFit to Window option in Word enables the table to automatically adjust its width to fit the width of the Word window. Once set, the table will expand or contract to fill the entire page width (between the left and right margins).
To autofit tables to page, use the Table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.AutoFitToWindow) method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section in the document through Document.Sections[] property.
- Get a specified table in the section through Section.Tables[] property.
- AutoFit the table to Word window using Table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.AutoFitToWindow) method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
namespace AutoFitToWindow
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Document instance
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("TableTemp.docx");
// Get the first section in the document
Section section = doc.Sections[0];
// Get the first table in the section
Table table = section.Tables[0] as Table;
// AutoFit the table to page
table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.AutoFitToWindow);
// Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("AutoFitToWindow.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
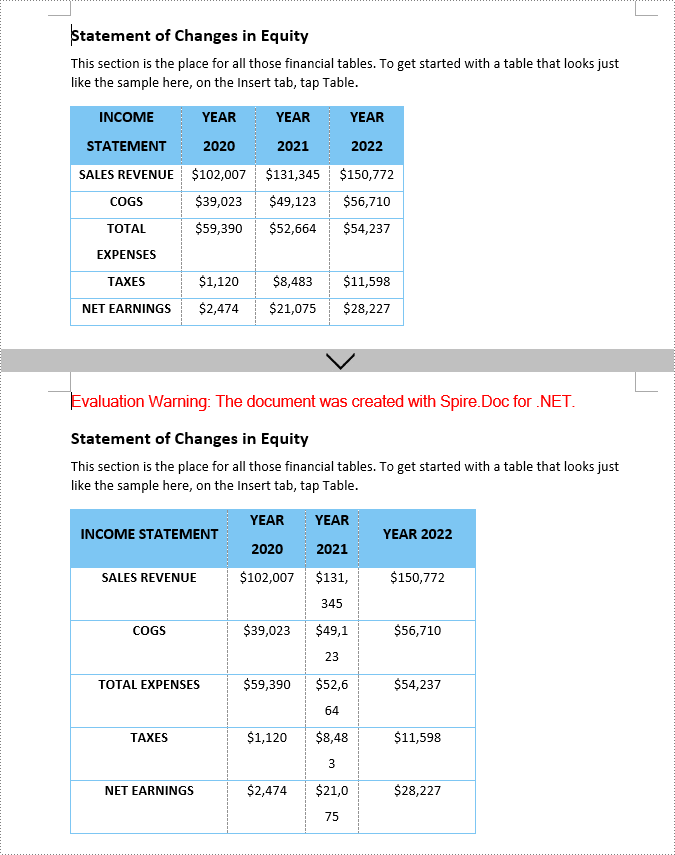
Set Tables to Fixed Column Width in Word in C#
The Fixed Column Width option in Word allows you to maintain a specific, unchanging width for each column in the table. Once set, the column width of the table will remain fixed regardless of any changes to the content within the cells or the size of the document window.
The Table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.FixedColumnWidths) method can be used to set fixed column width for Word tables. The following are the detailed steps to:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section in the document through Document.Sections[] property.
- Get a specified table in the section through Section.Tables[] property.
- Fix the column widths of the table using Table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.FixedColumnWidths) method.
- Iterate through each row and then set the new column widths using Table.Rows[index].Cells[index].SetCellWidth() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
namespace FixedColumnWidth
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Document instance
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("TableTemp.docx");
// Get the first section in the document
Section section = doc.Sections[0];
// Get the first table in the section
Table table = section.Tables[0] as Table;
// Set to fixed column width
table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.FixedColumnWidths);
// Iterate through each row in the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.Rows.Count; i++)
{
// Reset the width of the first column
table.Rows[i].Cells[0].SetCellWidth(120f, CellWidthType.Point);
// Reset the width of the second column
table.Rows[i].Cells[1].SetCellWidth(60f, CellWidthType.Point);
// Reset the width of the third column
table.Rows[i].Cells[2].SetCellWidth(40f, CellWidthType.Point);
// Reset the width of the fourth column
table.Rows[i].Cells[3].SetCellWidth(90f, CellWidthType.Point);
}
// Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("FixedColumnWidth.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for .NET without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
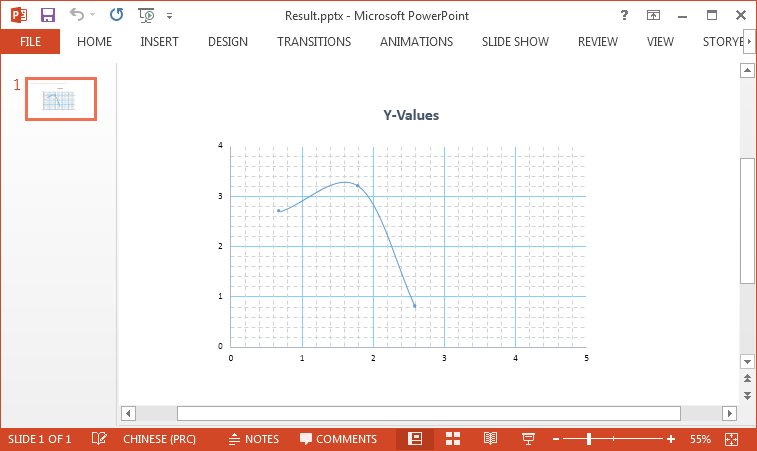
Axis is a significant part of charts. In order to make the data easier to read, we may need to modify the axis values or display the minor grid lines. This article demonstrates how to format axis of chart in PowerPoint using Spire.Presenation.
Here is the test document:
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Presentation class and load a sample PowerPoint document.
Presentation ppt = new Presentation(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Test.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
Step 2: Get the chart from the document.
IChart chart = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes[0] as IChart;
Step 3: Set bounds of axis value. Before we assign values, we must set IsAutoMax and IsAutoMin as false, otherwise MS PowerPoint will automatically set the values.
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMax = false; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMin= false; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMax = false; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMin= false; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 0f; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MaxValue = 5.0f; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinValue = 0f; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MaxValue = 4.0f;
Step 4: For the same reason, IsAutoMajor and IsAutoMinor must be set as false before assigning values to MajorUnit and MinorUnit.
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMajor = false; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMinor= false; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMajor = false; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMinor = false; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorUnit = 1.0f; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorUnit = 0.2f; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MajorUnit = 1.0f; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorUnit =0.2f;
Step 5: Set and format minor grid lines.
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.Width = 0.1f; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.Width = 0.1f; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightGray; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightGray; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.DashStyle = LineDashStyleType.Dash; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.DashStyle = LineDashStyleType.Dash;
Step 6: Set and format major grid lines.
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.Width = 0.3f; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightSkyBlue; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.Width = 0.3f; chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightSkyBlue;
Step 7: Save the file.
ppt.SaveToFile("Result.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
Output:
Full Code:
using Spire.Presentation;
using Spire.Presentation.Charts;
using Spire.Presentation.Drawing;
using System.Drawing;
namespace FormatAxis
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Presentation ppt = new Presentation(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Test.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
IChart chart = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes[0] as IChart;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMax = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMin = false;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMax = false;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMin = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 0f;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MaxValue = 5.0f;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinValue = 0f;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MaxValue = 4.0f;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMajor = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMinor = false;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMajor = false;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMinor = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorUnit = 1.0f;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorUnit = 0.2f;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MajorUnit = 1.0f;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorUnit = 0.2f;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.Width = 0.1f;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.Width = 0.1f;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightGray;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightGray;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.DashStyle = LineDashStyleType.Dash;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.DashStyle = LineDashStyleType.Dash;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.Width = 0.3f;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightSkyBlue;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.Width = 0.3f;
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightSkyBlue;
ppt.SaveToFile("Result.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Result.pptx");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Presentation
Imports Spire.Presentation.Charts
Imports Spire.Presentation.Drawing
Imports System.Drawing
Namespace FormatAxis
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim ppt As New Presentation("C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Test.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010)
Dim chart As IChart = TryCast(ppt.Slides(0).Shapes(0), IChart)
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMax = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMin = False
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMax = False
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMin = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 0F
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MaxValue = 5F
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinValue = 0F
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MaxValue = 4F
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMajor = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.IsAutoMinor = False
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMajor = False
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.IsAutoMinor = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorUnit = 1F
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorUnit = 0.2F
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MajorUnit = 1F
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorUnit = 0.2F
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.Width = 0.1F
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.Width = 0.1F
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightGray
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightGray
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.DashStyle = LineDashStyleType.Dash
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MinorGridLines.DashStyle = LineDashStyleType.Dash
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.Width = 0.3F
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightSkyBlue
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.Width = 0.3F
chart.SecondaryValueAxis.MajorGridTextLines.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.LightSkyBlue
ppt.SaveToFile("Result.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Result.pptx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
How to Copy a Page within a PDF File or between PDF Files in WPF
2016-04-29 08:43:03 Written by KoohjiIn some cases, we need to copy one or more pages of a pdf file, while copy pdf pages can be classified into two categories: copy pages within a pdf file and copy pages between pdf files. With the help of Spire.PDF, we can easily achieve this task programmatically instead of using Adobe Acrobat and dragging the page to copy it manually.
This article will demonstrate how to copy a page within a pdf file or between pdf files in WPF using Spire.PDF for WPF.
Before using the code, please add the following namespace first:
using System.Drawing; using System.Windows; using Spire.Pdf; using Spire.Pdf.Graphics;
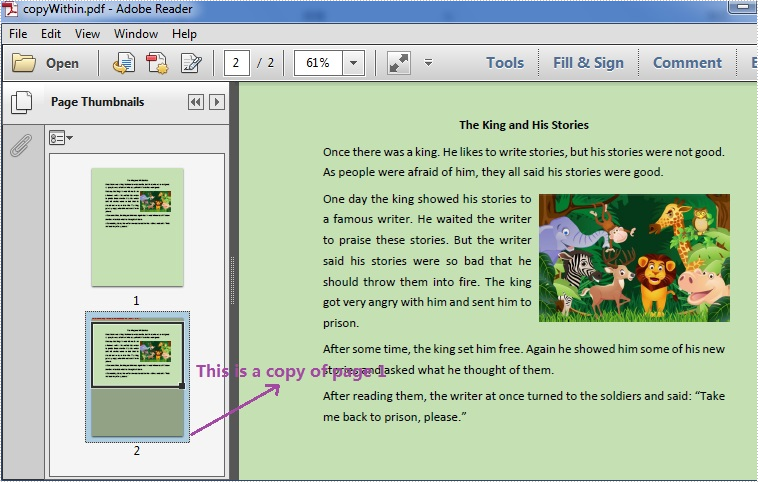
Copy Page within a PDF File
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of PdfDocument class and load the sample pdf file.
PdfDocument doc1 = new PdfDocument();
doc1.LoadFromFile("Stories.pdf");
Step 2: Get the first page of the pdf file, then get its page size and call CreateTemplate() method to create a new pdf template based on the first page.
PdfPageBase page = doc1.Pages[0]; SizeF size = page.Size; PdfTemplate template = page.CreateTemplate();
Step 3: Copy the first page within the pdf file.
Add a new page that is the same size as the first page to the pdf file, draw the template to the new page by invoking DrawTemplate(PdfTemplate template, PointF location) method.
page = doc1.Pages.Add(size, new PdfMargins(0,0)); page.Canvas.DrawTemplate(template,new PointF(0,0));
Step 4: Save and launch the file.
doc1.SaveToFile("copyWithin.pdf");
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("copyWithin.pdf");
Effective Screenshot:
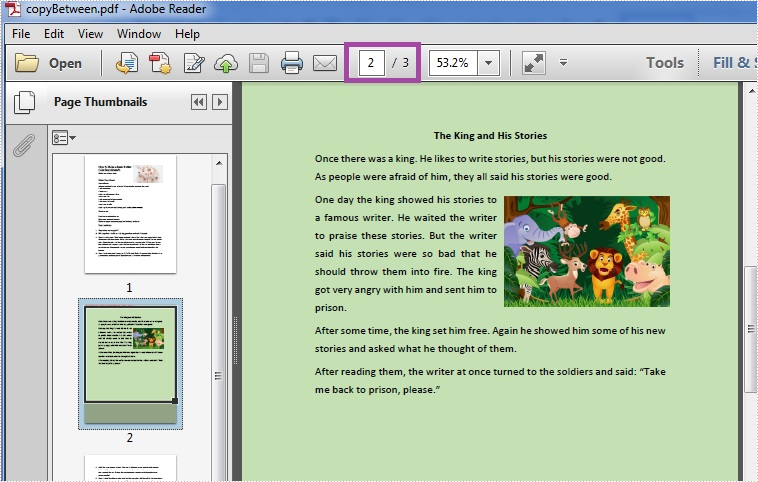
Copy Page between PDF Files
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of PdfDocument class named doc1 and load the first pdf file.
PdfDocument doc1 = new PdfDocument();
doc1.LoadFromFile("Stories.pdf");
Step 2: Initialize a new instance of PdfDocument class named doc2 and load the second pdf file.
PdfDocument doc2 = new PdfDocument();
doc2.LoadFromFile("Instruction.pdf");
Step 3: Get the first page of doc1, then get its page size and create a new template based on the first page.
PdfPageBase page = doc1.Pages[0]; SizeF size = page.Size; PdfTemplate template = page.CreateTemplate();
Step 4: Copy the first page from doc1 to doc2.
Invoking Insert(int index, SizeF size, PdfMargins margins) method to insert a new page that is the same size as the first page to the specified location of doc2, next draw the template to the new page.
doc2.Pages.Insert(1, size, new PdfMargins(0,0)); doc2.Pages[1].Canvas.DrawTemplate(template,new PointF(0,0));
If you want to copy the page to doc2 as its last page, please use the following code to add a new page to the end of doc2, then draw the template to the new page.
doc2.Pages.Add(size, new PdfMargins(0, 0));
Step 5: Save and launch the file.
doc2.SaveToFile("copyBetween.pdf");
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("copyBetween.pdf");
Effective Screenshot:
Full codes:
Copy page within a pdf file:
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
PdfDocument doc1 = new PdfDocument();
doc1.LoadFromFile("Stories.pdf");
PdfPageBase page = doc1.Pages[0];
SizeF size = page.Size;
PdfTemplate template = page.CreateTemplate();
page = doc1.Pages.Add(size, new PdfMargins(0,0));
page.Canvas.DrawTemplate(template, new PointF(0,0));
doc1.SaveToFile("copyWithin.pdf");
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("copyWithin.pdf");
}
Copy page between pdf files:
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
PdfDocument doc1 = new PdfDocument();
doc1.LoadFromFile("Stories.pdf");
PdfDocument doc2 = new PdfDocument();
doc2.LoadFromFile("Instruction.pdf");
PdfPageBase page = doc1.Pages[0];
SizeF size = page.Size;
PdfTemplate template = page.CreateTemplate();
doc2.Pages.Insert(1, size, new PdfMargins(0,0));
doc2.Pages[1].Canvas.DrawTemplate(template, new PointF(0,0));
doc2.SaveToFile("copyBetween.pdf");
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("copyBetween.pdf");
}
How to highlight different searched texts with different colors in WPF
2016-04-28 01:44:46 Written by KoohjiNowadays, many files are saved as PDF format. PDF has many advantages and its Find and Highlight feature makes it easier for us to find important information inside a lengthy PDF document.
In the following sections, I will demonstrate how to highlight different searched texts with different colors in WPF.
The code snippets are as followed:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of PdfDocument class and load the PDF document from the file.
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument("ToHelen.pdf");
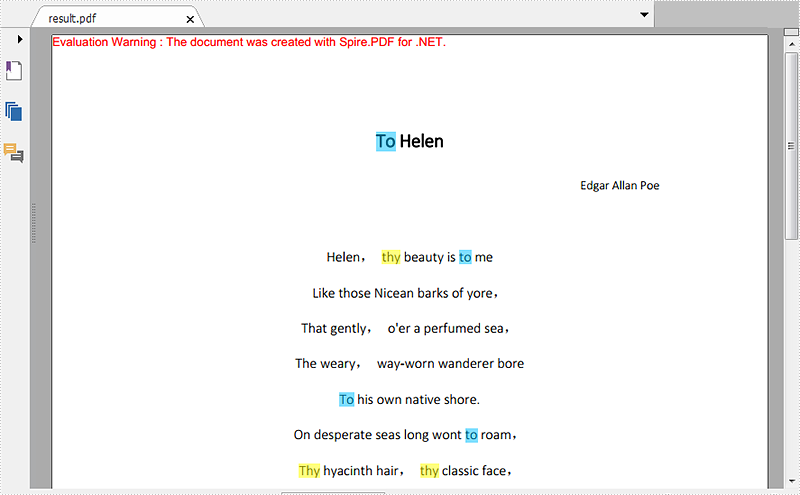
Step 2: Call FindText() method to search the string "thy" in the first page of the file, then return to Result1. Traverse result1 and call ApplyHighLight() method to highlight all elements in result1. Set the highlight color as yellow.
PdfTextFind[] result1 = null;
result1 = pdf.Pages[0].FindText("thy").Finds;
foreach (PdfTextFind find in result1)
{
find.ApplyHighLight(System.Drawing.Color.Yellow);
}
Step 3: Repeat step 2 to highlight all the texts "to" on Page 1 with the color of DeepSkyBlue.
PdfTextFind[] result2 = null;
result2 = pdf.Pages[0].FindText("to").Finds;
foreach (PdfTextFind find in result2)
{
find.ApplyHighLight(System.Drawing.Color.DeepSkyBlue);
}
Step 4: Save the PDF document and launch the file.
pdf.SaveToFile("HighlightedToHelen.pdf", Spire.Pdf.FileFormat.PDF);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("HighlightedToHelen.pdf");
Effective screenshot:
Full Codes:
//load the PDF document from the file
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument("ToHelen.pdf");
//highlight searched text "thy" with Yellow
PdfTextFind[] result1 = null;
result1 = pdf.Pages[0].FindText("thy").Finds;
foreach (PdfTextFind find in result1)
{
find.ApplyHighLight(System.Drawing.Color.Yellow);
}
//highlight searched text “to” with DeepSkyBlue
PdfTextFind[] result2 = null;
result2 = pdf.Pages[0].FindText("to").Finds;
foreach (PdfTextFind find in result2)
{
find.ApplyHighLight(System.Drawing.Color.DeepSkyBlue);
}
//save and launch the file
pdf.SaveToFile("HighlightedToHelen.pdf", Spire.Pdf.FileFormat.PDF);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("HighlightedToHelen.pdf");
'load the PDF document from the file
Dim pdf As New PdfDocument("ToHelen.pdf")
'highlight searched text "thy" with Yellow
Dim result1 As PdfTextFind() = Nothing
result1 = pdf.Pages(0).FindText("thy").Finds
For Each find As PdfTextFind In result1
find.ApplyHighLight(System.Drawing.Color.Yellow)
Next
'highlight searched text "to" with DeepSkyBlue
Dim result2 As PdfTextFind() = Nothing
result2 = pdf.Pages(0).FindText("to").Finds
For Each find As PdfTextFind In result2
find.ApplyHighLight(System.Drawing.Color.DeepSkyBlue)
Next
'save and launch the file
pdf.SaveToFile("HighlightedToHelen.pdf", Spire.Pdf.FileFormat.PDF)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("HighlightedToHelen.pdf")
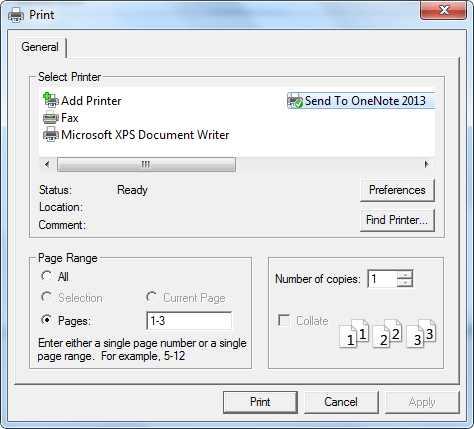
Spire.XLS supports to silently print an Excel file as well as print document with a print dialog, which is provided by System.Windows.Controls namespace in WPF, allowing users to select a specified printer and also the print pages. This article demonstrates how to print Excel file from a WPF application by invoking the print dialog in C# and VB.NET.
Necessary Namespaces:
using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Controls; using System.Drawing.Printing; using Spire.Xls;
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize an instance of Workbook and load a sample Excel file that you want to print.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
Step 2: Create a new object of PrintDialog and set its properties such as PageRangeSelection and UserPageRangeEnabled.
PrintDialog dialog = new PrintDialog(); dialog.UserPageRangeEnabled = true; PageRange rang = new PageRange(1, 3); dialog.PageRange = rang; PageRangeSelection seletion = PageRangeSelection.UserPages; dialog.PageRangeSelection =seletion;
Step 3: Get the print document and invoke the print dialog to print.
PrintDocument pd = workbook.PrintDocument;
if (dialog.ShowDialog() == true)
{
pd.Print();
}
Output:
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Printing;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
namespace WpfApplication1
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
PrintDialog dialog = new PrintDialog();
dialog.UserPageRangeEnabled = true;
PageRange rang = new PageRange(1, 3);
dialog.PageRange = rang;
PageRangeSelection seletion = PageRangeSelection.UserPages;
dialog.PageRangeSelection = seletion;
PrintDocument pd = workbook.PrintDocument;
if (dialog.ShowDialog() == true)
{
pd.Print();
}
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System.Drawing.Printing
Imports System.Windows
Imports System.Windows.Controls
Namespace WpfApplication1
Public Partial Class MainWindow
Inherits Window
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Sub button1_Click(sender As Object, e As RoutedEventArgs)
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx")
Dim dialog As New PrintDialog()
dialog.UserPageRangeEnabled = True
Dim rang As New PageRange(1, 3)
dialog.PageRange = rang
Dim seletion As PageRangeSelection = PageRangeSelection.UserPages
dialog.PageRangeSelection = seletion
Dim pd As PrintDocument = workbook.PrintDocument
If dialog.ShowDialog() = True Then
pd.Print()
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
It's well known that we can add a variety of bullet styles to paragraphs in Word, such as various symbols, pictures, fonts and numbers. Bullet makes these paragraphs to be a bulleted list, so that we can easily create a well-structured and professional document.
This article will demonstrate how to set bullet style for word paragraphs in WPF applications using Spire.Doc for WPF.
Below is the effective screenshot after setting bullet style:

Code snippets:
Use namespace:
using System.Windows; using Spire.Doc; using Spire.Doc.Documents;
Step 1: Create a new instance of Document class and load the sample word document from file.
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("Instruction.docx");
Step 2: Create a bulleted list.
Get the first section, then apply bullet style to paragraphs from 5th to 13th and set bullet position.
Section sec = doc.Sections[0];
for (int i = 4; i < 13; i++)
{
Paragraph paragraph = sec.Paragraphs[i];
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyBulletStyle();
paragraph.ListFormat.CurrentListLevel.NumberPosition = -20;
}
In addition, we can also use following code to create a numbered list:
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyNumberedStyle();
Step 3: Save and launch the file.
doc.SaveToFile("Bullet.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Bullet.docx");
Full codes:
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
//Load Document
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("Instruction.docx");
//Set Bullet Style
Section sec = doc.Sections[0];
for (int i = 4; i < 13; i++)
{
Paragraph paragraph = sec.Paragraphs[i];
//Create a bulleted list
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyBulletStyle();
//Create a numbered list
// paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyNumberedStyle();
paragraph.ListFormat.CurrentListLevel.NumberPosition = -20;
}
//Save and Launch
doc.SaveToFile("Bullet.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Bullet.docx");
}
