
.NET (1317)
Children categories
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is an image file format and it has the advantage of be edited and indexed easily. It is widely used for interactivity and animation. Starts from Spire.Doc V5.8, Spire.Doc offers a method doc.SaveToFile() to enable developers to save the word document to SVG file format in C# easily. This article will focus on demonstrate how to convert word document to SVG with the help of Spire.Doc by using a simple line of code in C#.
Firstly, please view the original word document:
Step 1: Create a C# project in visual studio, then add a reference to Spire.Doc.dll and use the following namespace.
using Spire.Doc;
Step 2: Create a word instance and load the source word document from file.
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
Step 3: Save the document to SVG file.
doc.SaveToFile("result.svg", FileFormat.SVG);
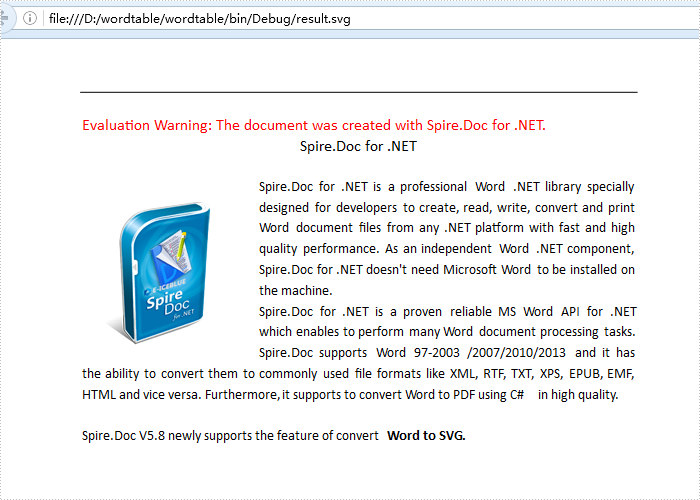
After running the code, we'll get the effective screenshot of the following result SVG file from word document:
Full codes:
using Spire.Doc;
namespace wordconversion.Case
{
class WordtoSVG
{
public WordtoSVG()
{
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
doc.SaveToFile("result.svg", FileFormat.SVG);
}
}
}
Videos are common elements in PowerPoint, sometimes developers need to extract videos from PowerPoint documents and save them to disk programmatically. Spire.Presentation provides developers many flexible functions to manipulate PowerPoint documents including extract Videos. This article will explain how to achieve this task in C# and VB.NET using Spire.Presentation.
Note: Before start, please download and install Spire.Presentation correctly, after that add a reference to Spire.Presentation.dll in your project.
Detail steps:
Step 1: Instantiate an object of Presentation class and load the sample document.
Presentation presentation = new Presentation(); presentation.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Sample.pptx");
Step 2: Loop through all shapes on the slides, find out the videos and then call VideoData.SaveToFile(string fileName) method to save them to disk.
int i = 0;
foreach (ISlide slide in presentation.Slides)
{
foreach (IShape shape in slide.Shapes)
{
if (shape is IVideo)
{
(shape as IVideo).EmbeddedVideoData.SaveToFile(string.Format(@"Video\Video-{0}.mp4",i));
i++;
}
}
}
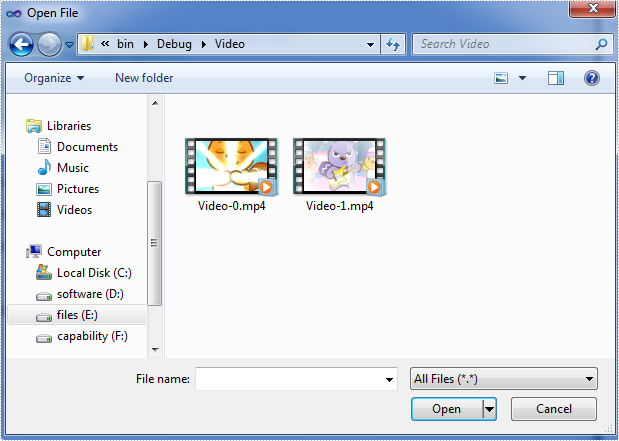
Below are the extracted videos from the PowerPoint document:
Full code:
using Spire.Presentation;
namespace Extract_Video
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
presentation.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Sample.pptx");
int i = 0;
foreach (ISlide slide in presentation.Slides)
{
foreach (IShape shape in slide.Shapes)
{
if (shape is IVideo)
{
(shape as IVideo).EmbeddedVideoData.SaveToFile(string.Format(@"Video\Video-{0}.mp4",i));
i++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Presentation
Namespace Extract_Video
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim presentation As New Presentation()
presentation.LoadFromFile("C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Sample.pptx")
Dim i As Integer = 0
For Each slide As ISlide In presentation.Slides
For Each shape As IShape In slide.Shapes
If TypeOf shape Is IVideo Then
TryCast(shape, IVideo).EmbeddedVideoData.SaveToFile(String.Format("Video\Video-{0}.mp4", i))
i += 1
End If
Next
Next
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Required fields force the user to fill in the selected form field. If the user attempts to submit the form while a required field is blank, an error message appears and the empty required form field is highlighted.
Using Spire.PDF, we're able to enforce a form field as "Required" or determine which fields are required in an existing PDF document. This article mainly introduce how to detect the required form fields in C# and VB.NET.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize an instance of PdfDocument class and load a sample PDF file that contains some form fields.
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument(); doc.LoadFromFile(@"C: \Users\Administrator\Desktop\PdfFormExample.pdf");
Step 2: Get all form widgets from the PDF document.
PdfFormWidget formWidget = doc.Form as PdfFormWidget;
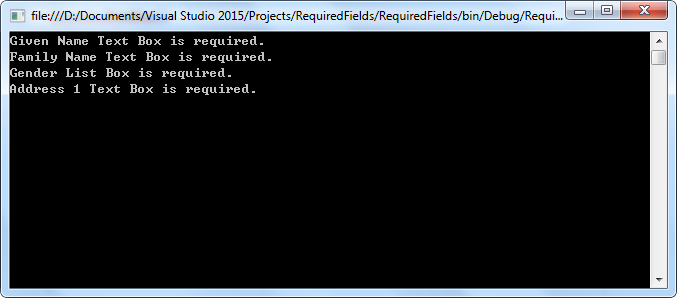
Step 3: Traverse the form widgets to find the form field that is required and print all results on console.
for (int i = 0; i < formWidget.FieldsWidget.List.Count; i++)
{
PdfField field = formWidget.FieldsWidget.List[i] as PdfField;
string fieldName = field.Name;
bool isRequired = field.Required;
if (isRequired)
{
Console.WriteLine(fieldName + " is required.");
}
}
Output:
Full Code:
using Spire.Pdf;
using Spire.Pdf.Fields;
using Spire.Pdf.Widget;
using System;
namespace Detect
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string []args)
{
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.LoadFromFile(@"C: \Users\Administrator\Desktop\PdfFormExample.pdf");
PdfFormWidget formWidget = doc.Form as PdfFormWidget;
for (int i = 0; i < formWidget.FieldsWidget.List.Count; i++)
{
PdfField field = formWidget.FieldsWidget.List[i] as PdfField;
string fieldName = field.Name;
bool isRequired = field.Required;
if (isRequired)
{
Console.WriteLine(fieldName + " is required.");
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Pdf
Imports Spire.Pdf.Fields
Imports Spire.Pdf.Widget
Namespace Detect
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim doc As New PdfDocument()
doc.LoadFromFile("C: \Users\Administrator\Desktop\PdfFormExample.pdf")
Dim formWidget As PdfFormWidget = TryCast(doc.Form, PdfFormWidget)
For i As Integer = 0 To formWidget.FieldsWidget.List.Count - 1
Dim field As PdfField = TryCast(formWidget.FieldsWidget.List(i), PdfField)
Dim fieldName As String = field.Name
Dim isRequired As Boolean = field.Required
If isRequired Then
Console.WriteLine(fieldName & Convert.ToString(" is required."))
End If
Next
Console.ReadKey()
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
A pie chart helps show proportions and percentages between categories, by dividing a circle into proportional segments. This article will introduce how to create a pie chart that looks like the below screenshot in PowerPoint document using Spire.Presentation in C#.
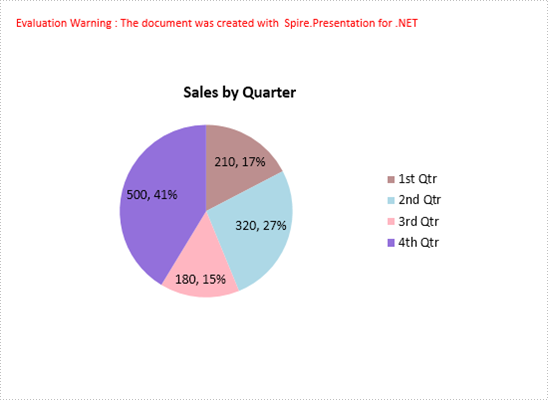
Code Snippets:
Step 1: Initialize an instance of Presentation class.
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
Step 2: Insert a Pie chart to the first slide by calling the AppendChart() method and set the chart title.
RectangleF rect1 = new RectangleF(40, 100, 550, 320); IChart chart = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendChart(ChartType.Pie, rect1, false); chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Sales by Quarter"; chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.IsCentered = true; chart.ChartTitle.Height = 30; chart.HasTitle = true;
Step 3: Define some data.
string[] quarters = new string[] { "1st Qtr", "2nd Qtr", "3rd Qtr", "4th Qtr" };
int[] sales = new int[] { 210, 320, 180, 500 };
Step 4: Append data to ChartData, which represents a data table where the chart data is stored.
chart.ChartData[0, 0].Text = "Quarters";
chart.ChartData[0, 1].Text = "Sales";
for (int i = 0; i < quarters.Length; ++i)
{
chart.ChartData[i + 1, 0].Value = quarters[i];
chart.ChartData[i + 1, 1].Value = sales[i];
}
Step 5: Set category labels, series label and series data.
chart.Series.SeriesLabel = chart.ChartData["B1", "B1"]; chart.Categories.CategoryLabels = chart.ChartData["A2", "A5"]; chart.Series[0].Values = chart.ChartData["B2", "B5"];
Step 6: Add data points to series and fill each data point with different color.
for (int i = 0; i < chart.Series[0].Values.Count; i++)
{
ChartDataPoint cdp = new ChartDataPoint(chart.Series[0]);
cdp.Index = i;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.Add(cdp);
}
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.RosyBrown;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[1].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[1].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.LightBlue;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[2].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[2].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.LightPink;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[3].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[3].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.MediumPurple;
Step 7: Set the data labels to display label value and percentage value.
chart.Series[0].DataLabels.LabelValueVisible = true; chart.Series[0].DataLabels.PercentValueVisible = true;
Step 8: Save the file.
ppt.SaveToFile("PieChart.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
Full Code:
using Spire.Presentation;
using Spire.Presentation.Charts;
using Spire.Presentation.Drawing;
using System.Drawing;
namespace CreatePieChartInPowerPoint
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
RectangleF rect1 = new RectangleF(40, 100, 550, 320);
IChart chart = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendChart(ChartType.Pie, rect1, false);
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Sales by Quarter";
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.IsCentered = true;
chart.ChartTitle.Height = 30;
chart.HasTitle = true;
string[] quarters = new string[] { "1st Qtr", "2nd Qtr", "3rd Qtr", "4th Qtr" };
int[] sales = new int[] { 210, 320, 180, 500 };
chart.ChartData[0, 0].Text = "Quarters";
chart.ChartData[0, 1].Text = "Sales";
for (int i = 0; i < quarters.Length; ++i)
{
chart.ChartData[i + 1, 0].Value = quarters[i];
chart.ChartData[i + 1, 1].Value = sales[i];
}
chart.Series.SeriesLabel = chart.ChartData["B1", "B1"];
chart.Categories.CategoryLabels = chart.ChartData["A2", "A5"];
chart.Series[0].Values = chart.ChartData["B2", "B5"];
for (int i = 0; i < chart.Series[0].Values.Count; i++)
{
ChartDataPoint cdp = new ChartDataPoint(chart.Series[0]);
cdp.Index = i;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.Add(cdp);
}
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.RosyBrown;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[1].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[1].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.LightBlue;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[2].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[2].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.LightPink;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[3].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints[3].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.MediumPurple;
chart.Series[0].DataLabels.LabelValueVisible = true;
chart.Series[0].DataLabels.PercentValueVisible = true;
ppt.SaveToFile("PieChart.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("PieChart.pptx");
}
}
}
Hyperlinks in Word documents are clickable links that allow readers to navigate to a website or another document. While hyperlinks can provide valuable supplemental information, sometimes they can also be distracting or unnecessarily annoying, so you may want to remove them. In this article, you will learn how to remove hyperlinks from a Word document in C# and VB.NET using Spire.Doc for .NET.
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Remove All the Hyperlinks in a Word Document
To delete all hyperlinks in a Word document at once, you'll need to find all the hyperlinks in the document and then create a custom method FlattenHyperlinks() to flatten them. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a sample Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find all the hyperlinks in the document using custom method FindAllHyperlinks().
- Loop through the hyperlinks and flatten all of them using custom method FlattenHyperlinks().
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using System.Drawing;
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace removeWordHyperlink
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document instance
Document doc = new Document();
//Load a sample Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Hyperlink.docx");
//Find all hyperlinks
List<Field> hyperlinks = FindAllHyperlinks(doc);
//Flatten all hyperlinks
for (int i = hyperlinks.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
FlattenHyperlinks(hyperlinks[i]);
}
//Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("RemoveHyperlinks.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
//Create a method FindAllHyperlinks() to get all the hyperlinks from the sample document
private static List<Field> FindAllHyperlinks(Document document)
{
List<Field> hyperlinks = new List<Field>();
//Iterate through the items in the sections to find all hyperlinks
foreach (Section section in document.Sections)
{
foreach (DocumentObject sec in section.Body.ChildObjects)
{
if (sec.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph)
{
foreach (DocumentObject para in (sec as Paragraph).ChildObjects)
{
if (para.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Field)
{
Field field = para as Field;
if (field.Type == FieldType.FieldHyperlink)
{
hyperlinks.Add(field);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return hyperlinks;
}
//Create a method FlattenHyperlinks() to flatten the hyperlink field
private static void FlattenHyperlinks(Field field)
{
int ownerParaIndex = field.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field.OwnerParagraph);
int fieldIndex = field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field);
Paragraph sepOwnerPara = field.Separator.OwnerParagraph;
int sepOwnerParaIndex = field.Separator.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field.Separator.OwnerParagraph);
int sepIndex = field.Separator.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field.Separator);
int endIndex = field.End.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field.End);
int endOwnerParaIndex = field.End.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field.End.OwnerParagraph);
FormatFieldResultText(field.Separator.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody, sepOwnerParaIndex, endOwnerParaIndex, sepIndex, endIndex);
field.End.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(endIndex);
for (int i = sepOwnerParaIndex; i >= ownerParaIndex; i--)
{
if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex && i == ownerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex; j >= fieldIndex; j--)
{
field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j);
}
}
else if (i == ownerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.Count - 1; j >= fieldIndex; j--)
{
field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j);
}
}
else if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex; j >= 0; j--)
{
sepOwnerPara.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j);
}
}
else
{
field.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(i);
}
}
}
//Create a method FormatFieldResultText() to remove the font color and underline format of the hyperlinks
private static void FormatFieldResultText(Body ownerBody, int sepOwnerParaIndex, int endOwnerParaIndex, int sepIndex, int endIndex)
{
for (int i = sepOwnerParaIndex; i <= endOwnerParaIndex; i++)
{
Paragraph para = ownerBody.ChildObjects[i] as Paragraph;
if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex && i == endOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex + 1; j < endIndex; j++)
{
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j] as TextRange);
}
}
else if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex + 1; j < para.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j] as TextRange);
}
}
else if (i == endOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = 0; j < endIndex; j++)
{
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j] as TextRange);
}
}
else
{
for (int j = 0; j < para.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j] as TextRange);
}
}
}
}
//Create a method FormatText() to change the color of the text to black and remove the underline
private static void FormatText(TextRange tr)
{
//Set the text color to black
tr.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Black;
//Set the text underline style to none
tr.CharacterFormat.UnderlineStyle = UnderlineStyle.None;
}
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is an image file format used for rendering two-dimensional images on the web. Comparing with other image file formats, SVG has many advantages such as supporting interactivity and animation, allowing users to search, index, script, and compress/enlarge images without losing quality. Occasionally, you may need to convert PDF files to SVG file format, and this article will demonstrate how to accomplish this task using Spire.PDF for .NET.
- Convert a PDF File to SVG in C#/VB.NET
- Convert Selected PDF Pages to SVG in C#/VB.NET
- Convert a PDF File to SVG with Custom Width and Height in C#/VB.NET
Install Spire.PDF for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.PDF for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLLs files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.PDF
Convert a PDF File to SVG in C#/VB.NET
Spire.PDF for .NET offers the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(String, FileFormat) method to convert each page in a PDF file to a single SVG file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert the PDF file to SVG using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(String, FileFormat) method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Pdf;
namespace ConvertPDFtoSVG
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument document = new PdfDocument();
//Load a sample PDF file
document.LoadFromFile("input.pdf");
//Convert PDF to SVG
document.SaveToFile("PDFtoSVG.svg", FileFormat.SVG);
}
}
}
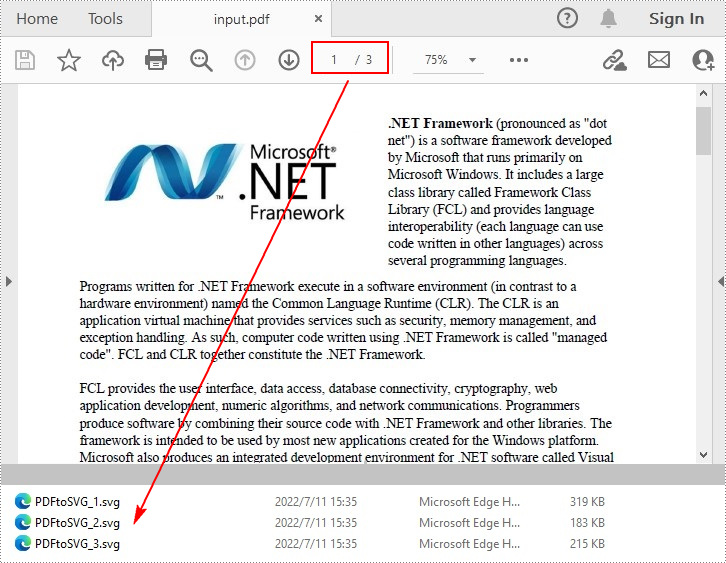
Convert Selected PDF Pages to SVG in C#/VB.NET
The PdfDocument.SaveToFile(String, Int32, Int32, FileFormat) method allows you to convert the specified pages in a PDF file to SVG files. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert selected PDF pages to SVG using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(String, Int32, Int32, FileFormat) method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Pdf;
namespace PDFPagetoSVG
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
//Load a sample PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("input.pdf");
//Convert selected PDF pages to SVG
doc.SaveToFile("PDFPagetoSVG.svg", 1, 2, FileFormat.SVG);
}
}
}

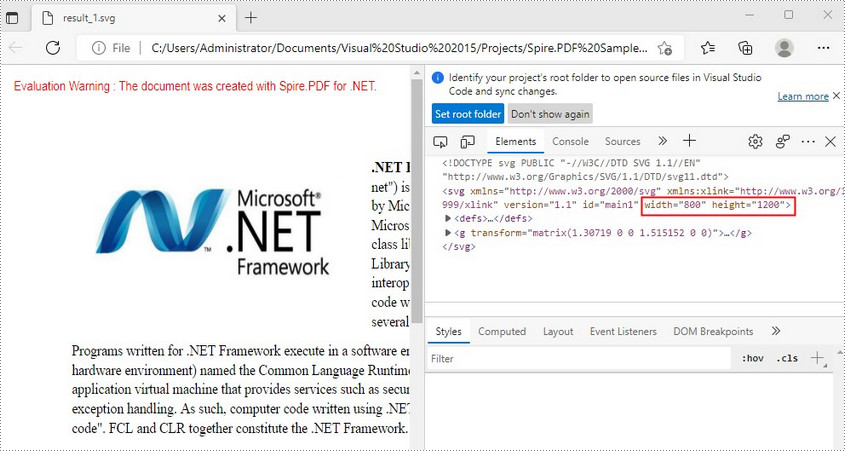
Convert a PDF File to SVG with Custom Width and Height in C#/VB.NET
The PdfConvertOptions.SetPdfToSvgOptions() method offered by Spire.PDF for .NET allows you to specify the width and height of output SVG file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set PDF convert options using PdfDocument.ConvertOptions property.
- Specify the width and height of output SVG file using PdfConvertOptions.SetPdfToSvgOptions() method.
- Convert the PDF file to SVG using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Pdf;
namespace PDFtoSVG
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument document = new PdfDocument();
//Load a sample PDF file
document.LoadFromFile("input.pdf");
//Specify the width and height of output SVG file
PdfToSvgConverter converter = new PdfToSvgConverter(inputFile);
converter.SvgOptions.ScaleX = (float)0.5;
converter.SvgOptions.ScaleY = (float)0.5;
converter.Convert(outputFile);
//Convert PDF to SVG
document.SaveToFile("result.svg", FileFormat.SVG);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In this article, we will explain how to copy an existing chart within the same PowerPoint document or between PowerPoint documents by using Spire.Presentation. Below example called a main method public IChart CreateChart(IChart baseChart, RectangleF rectangle, int nIndex).
There are three Parameters passed in this method:
- baseChart: The source chart.
- rectangle: The area that the chart will be copied to.
- nIndex: The index of the rectangle shape. For example, -1 means append it as the last shape of the slide, 0 means append as the first shape.
Now refer to the following steps:
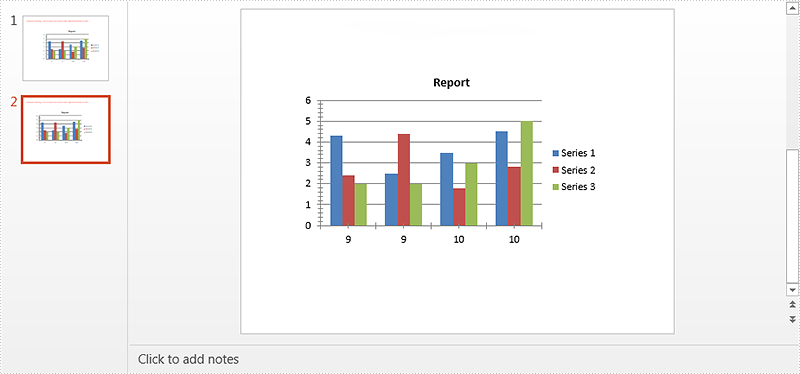
Copy chart within the same PowerPoint document
Step 1: Instantiate a Presentation object and load the PowerPoint document.
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
Step 2: Get the chart that is going to be copied.
IChart chart = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes[0] as IChart;
Step 3: Copy the chart from the first slide to the specified location of the second slide within the same document.
ppt.Slides[1].Shapes.CreateChart(chart, new RectangleF(100, 100, 500, 300), 0);
Step 4: Save the document.
ppt.SaveToFile("TestResult.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
Screenshot of copying chart within the same PowerPoint document:
Copy chart between PowerPoint documents
Step 1: Load the first PowerPoint document.
Presentation ppt1 = new Presentation();
ppt1.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
Step 2: Get the chart that is going to be copied.
IChart chart = ppt1.Slides[0].Shapes[0] as IChart;
Step 3: Load the second PowerPoint document.
Presentation ppt2 = new Presentation();
ppt2.LoadFromFile("Dest.pptx");
Step 4: Copy chart from the first document to the specified location of the second document.
ppt2.Slides[0].Shapes.CreateChart(chart, new RectangleF(100, 100, 500, 300), -1);
Step 5: Save the second document.
ppt2.SaveToFile("TestResult2.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
Screenshot of copying chart between PowerPoint documents:

Full code:
Copy chart within the same PowerPoint document
using System.Drawing;
using Spire.Presentation;
using Spire.Presentation.Charts;
namespace Copy_Chart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
IChart chart = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes[0] as IChart;
ppt.Slides[1].Shapes.CreateChart(chart, new RectangleF(100, 100, 500, 300), 0);
ppt.SaveToFile("TestResult.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
}
}
}
Copy chart between PowerPoint documents
using System.Drawing;
using Spire.Presentation;
using Spire.Presentation.Charts;
namespace Copy_Chart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Presentation ppt1 = new Presentation();
ppt1.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
IChart chart = ppt1.Slides[0].Shapes[0] as IChart;
Presentation ppt2 = new Presentation();
ppt2.LoadFromFile("Dest.pptx");
ppt2.Slides[0].Shapes.CreateChart(chart, new RectangleF(100, 100, 500, 300), -1);
ppt2.SaveToFile("TestResult2.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
}
}
}
Spire.XLS enable programmers to insert, modify as well as format comments in Excel. Also, it allows users to fill a comment with solid color, gradient, pattern or a picture to change the look of the comment. This article is going to introduce how to set background image for a comment in Excel using Spire.XLS.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize an instance of Wordbook and get the first worksheet.
Workbook wb = new Workbook(); Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Fill the comment with a customized background picture.
Image image = Image.FromFile(@"C: \Users\Administrator\Desktop\logo.png"); sheet.Range["C6"].Comment.Fill.CustomPicture(image, "logo.png");
Step 3: Re-set the size of comment box.
sheet.Range["C6"].Comment.Height = image.Height; sheet.Range["C6"].Comment.Width = image.Width;
Step 4: Save the file.
wb.SaveToFile("PicFillComment.xls", ExcelVersion.Version97to2003);
Output:
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
namespace SetPictureFill
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
{
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
Image image = Image.FromFile(@"C: \Users\Administrator\Desktop\logo.png");
sheet.Range["C6"].Comment.Fill.CustomPicture(image, "logo.png");
sheet.Range["C6"].Comment.Height = image.Height;
sheet.Range["C6"].Comment.Width = image.Width;
wb.SaveToFile("PicFill.xls", ExcelVersion.Version97to2003);
}
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports System.Drawing
Namespace SetPictureFill
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
If True Then
Dim wb As New Workbook()
Dim sheet As Worksheet = wb.Worksheets(0)
Dim image__1 As Image = Image.FromFile("C: \Users\Administrator\Desktop\logo.png")
sheet.Range("C6").Comment.Fill.CustomPicture(image__1, "logo.png")
sheet.Range("C6").Comment.Height = image__1.Height
sheet.Range("C6").Comment.Width = image__1.Width
wb.SaveToFile("PicFill.xls", ExcelVersion.Version97to2003)
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Apart from creating chart with continuous data range, Spire.XLS also supports to create chart with discontinuous data range by calling the XlsRange.AddCombinedRange(CellRange cr) method. This example explains a quick solution of how to achieve this task in C# with the help of Spire.XLS.
For demonstration, here we used a template excel document, in which you can see there are some blank rows among the data, in other words, the data range is discontinuous.
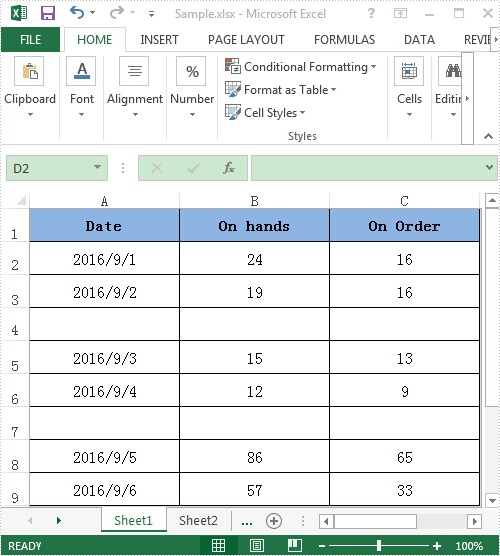
Here comes to the detail steps:
Step 1: Instantiate a Wordbook object, load the excel document and get its first worksheet.
Workbook book = new Workbook();
book.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Add a column chart to the first worksheet and set the position of the chart.
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered); chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false; //Set chart position chart.LeftColumn = 5; chart.TopRow = 1; chart.RightColumn = 13; chart.BottomRow = 10;
Step 3: Add two series to the chart, set data source for category labels and values of the series with discontinuous data range.
//Add the first series var cs1 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series.Add(); //Set name of the serie cs1.Name = sheet.Range["B1"].Value; //Set data source for Category Labels and Values of the serie with discontinuous data range cs1.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A5:A6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A8:A9"]); cs1.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["B5:B6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["B8:B9"]); //Specify the serie type cs1.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered; //Add the second series var cs2 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series.Add(); cs2.Name = sheet.Range["C1"].Value; cs2.CategoryLabels = cs2.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A5:A6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A8:A9"]); cs2.Values = sheet.Range["C2:C3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["C5:C6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["C8:C9"]); cs2.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered;
Step 4: Save the excel document.
book.SaveToFile("Result.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2010);
After executing the above example code, a column chart with discontinuous data range was added to the worksheet as shown below.
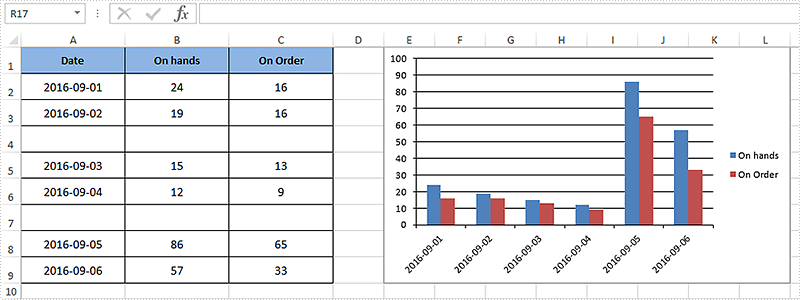
Full code:
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
namespace Assign_discontinuous_range_for_chart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook book = new Workbook();
book.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
chart.LeftColumn = 5;
chart.TopRow = 1;
chart.RightColumn = 13;
chart.BottomRow = 10;
var cs1 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series.Add();
cs1.Name = sheet.Range["B1"].Value;
cs1.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A5:A6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A8:A9"]);
cs1.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["B5:B6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["B8:B9"]);
cs1.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered;
var cs2 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series.Add();
cs2.Name = sheet.Range["C1"].Value;
cs2.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A5:A6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A8:A9"]);
cs2.Values = sheet.Range["C2:C3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["C5:C6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["C8:C9"]);
cs2.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered;
chart.ChartTitle = string.Empty;
book.SaveToFile("Result.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Result.xlsx");
}
}
}
Set Different Header or Footer for Odd and Even Pages in Excel in C#, VB.NET
2016-09-22 00:59:10 Written by KoohjiHeaders or footers are added to a worksheet to deliver some extra information about each page. By default, the headers or footers on odd and even pages are the same. However, we are able to set different headers or footers for odd and even pages to display different information.
Following sections demonstrate how to create different odd and even page headers/footers using Spire.XLS.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize an instance of Workbook and get the first worksheet.
Workbook wb = new Workbook(); Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Set the value of DifferentOddEven as 1, which indicates that headers/footers for odd and even pages are different.
sheet.PageSetup.DifferentOddEven = 1;
Step 3: Set header and footer string for odd pages, and format the string.
sheet.PageSetup.OddHeaderString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Header"; sheet.PageSetup.OddFooterString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Footer";
Step 4: Set different header and footer string for even pages, and format the string with different color.
sheet.PageSetup.EvenHeaderString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFF0000Even_Header"; sheet.PageSetup.EvenFooterString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFF0000Even_Footer";
Step 5: Save the file.
wb.SaveToFile("OddEvenHeaderFooter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
Output:
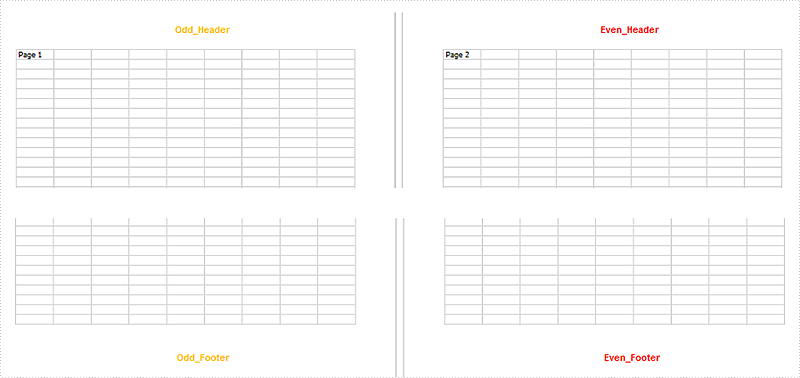
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetDifferentHeaderorFooter
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Page 1";
sheet.Range["J1"].Text = "Page 2";
sheet.PageSetup.DifferentOddEven = 1;
sheet.PageSetup.OddHeaderString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Header";
sheet.PageSetup.OddFooterString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Footer";
sheet.PageSetup.EvenHeaderString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFF0000Even_Header";
sheet.PageSetup.EvenFooterString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFF0000Even_Footer";
wb.SaveToFile("OddEvenHeaderFooter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace SetDifferentHeaderorFooter
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim wb As New Workbook()
Dim sheet As Worksheet = wb.Worksheets(0)
sheet.Range("A1").Text = "Page 1"
sheet.Range("J1").Text = "Page 2"
sheet.PageSetup.DifferentOddEven = 1
sheet.PageSetup.OddHeaderString = "&""Arial""&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Header"
sheet.PageSetup.OddFooterString = "&""Arial""&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Footer"
sheet.PageSetup.EvenHeaderString = "&""Arial""&12&B&KFF0000Even_Header"
sheet.PageSetup.EvenFooterString = "&""Arial""&12&B&KFF0000Even_Footer"
wb.SaveToFile("OddEvenHeaderFooter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
