
Program Guide (129)
Children categories
Formatting numbers in Excel cells is a critical step when working with spreadsheets, especially in professional or data-driven environments. Proper number formatting ensures that data is presented clearly, consistently, and in a way that aligns with its purpose—whether it's financial data, percentages, dates, or scientific values. When automating Excel tasks using Java, applying the correct number format programmatically can save time, reduce errors, and enhance the readability of reports or dashboards. This article explores how to use Spire.XLS for Java to set number formats in Excel cells, enabling you to create polished and well-structured spreadsheets with ease.
- How to Set Number Formats in Excel with Java
- Add Values in Specified Number Formats to Excel Cells with Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
How to Set Number Formats in Excel with Java
Spire.XLS for Java provides the CellRange.setNumberFormat() method, enabling developers to set number formats for cells using Excel's number format codes. The table below highlights commonly used symbols in Excel number format codes and their functions:
| Symbols | Description |
| 0 and # | 0 forces display of digit places, padding with zeros if necessary; # shows digits only when needed. |
| ? | Placeholder for aligning numbers, leaves space but does not display anything if not used. |
| , and . | , serves as a thousands separator and can also indicate division by 1000; . is the decimal point. |
| % | Multiplies the number by 100 and adds a percent sign. |
| E+ / E- | Scientific notation, for positive and negative exponents respectively. |
| Currency ($, €, ¥, etc.) | Displays the respective currency symbol. |
| [Color] | Sets text color (e.g., [Red], [Blue]). |
| @ | Text placeholder, used to represent text in custom formats. |
| Date/Time (yyyy, mmmm, mm, dd, hh, ss, AM/PM) | Represent year, full month name, month, day, hour, minute, second, and 12-hour clock markers respectively. |
The detailed steps for setting number formats of Excel cells with Java are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object to create a new Excel workbook.
- Get the first default worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Add values using the CellRange.setValue() method or add numeric values using the CellRange.setNumberValue() method.
- Set the number formats using the CellRange.setNumberFormat() method.
- Save the workbook using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class SetNumberFormat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Add a title
sheet.getCellRange("B1").setText("NUMBER FORMATTING");
sheet.getCellRange("B1").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().isBold(true);
sheet.getCellRange("B1:C1").merge(); // Merge cells B1 and C1
sheet.getCellRange("B1:C1").setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Center); // Center align the text
// Add number format examples and corresponding values
// Add positive number formats
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B3", "C3", "0", "1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B4", "C4", "0.00", "1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B5", "C5", "#,##0.00", "1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B6", "C6", "$#,##0.00", "1234.5678");
// Add negative number formats
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B7", "C7", "0;[Red]-0", "-1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B8", "C8", "0.00;[Red]-0.00", "-1234.5678");
// Add scientific notation and percentage formats
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B9", "C9", "0.00E+00", "1234.5678");
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B10", "C10", "0.00%", "0.5678");
// Add date and time formats
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B11", "C11", "yyyy-MM-dd", "44930.0"); // Excel date value for 2023-01-01
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B12", "C12", "HH:mm:ss", "0.75"); // Excel time value for 18:00:00
// Add text format
addNumberFormatExample(sheet, "B13", "C13", "@", "Text Example");
// Set the formatting
sheet.getCellRange("B3:B13").getCellStyle().setKnownColor(ExcelColors.Gray25Percent);
sheet.getCellRange("C3:C13").getCellStyle().setKnownColor(ExcelColors.Gray50Percent);
sheet.setColumnWidth(2, 24); // Column B
sheet.setColumnWidth(3, 24); // Column C
// Save the workbook to a file
workbook.saveToFile("output/SetExcelNumberFormat.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
/**
* Adds a number format example to the specified cells in the worksheet.
*
* @param sheet The worksheet to modify.
* @param textCell The cell for displaying the number format string.
* @param valueCell The cell for displaying the formatted value.
* @param format The number format code.
* @param value The numeric value to format.
*/
private static void addNumberFormatExample(Worksheet sheet, String textCell, String valueCell, String format, String value) {
sheet.getCellRange(textCell).setText(format); // Display the number format code
sheet.getCellRange(valueCell).setValue(value); // Add the value
// sheet.getCellRange(valueCell).setNumberValue(Double); // Or set numeric value with setNumberValue() method
sheet.getCellRange(valueCell).setNumberFormat(format); // Apply the number format
}
}

Add Values in Specified Number Formats to Excel Cells with Java
Spire.XLS for Java also supports directly adding data with specific number formats to Excel cells with methods under the CellRange class. The following table outlines the methods for adding data with common number formats to cells and their corresponding data types:
| Method | Description |
| setText(String text) | Sets a text value in a cell or range of cells. |
| setNumberValue(double numberValue) | Sets a numeric value in a cell or range of cells. |
| setBooleanValue(boolean booleanValue) | Sets a boolean value (true/false) in a cell or range of cells. |
| setDateTimeValue(java.util.Date dateTime) | Sets a date and time value in a cell or range of cells. |
| setHtmlString(String htmlCode) | Sets an HTML-formatted string in a cell or range of cells. |
The detailed steps for adding values with number formats to Excel cells are as follows:
- Create an instance of the Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get a cell or cell range using the Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Add values in specific number formats using the methods under the CellRange class.
- Set the cell styles as needed.
- Save the workbook using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class AddFormattedDataExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
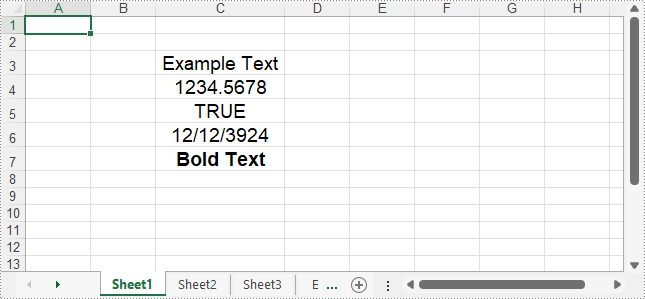
// Add a text value
sheet.getCellRange("C3").setText("Example Text");
// Add number value
sheet.getCellRange("C4").setNumberValue(1234.5678);
// Add boolean value
sheet.getCellRange("C5").setBooleanValue(true);
// Add date time value
sheet.getCellRange("C6").setDateTimeValue(new Date(2024, Calendar.DECEMBER, 12));
// Add HTML string
sheet.getCellRange("C7").setHtmlString("Bold Text");
// Format the cells
sheet.getCellRange("C3:C7").setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Center);
sheet.getCellRange("C3:C7").setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType.Center);
sheet.getCellRange("C3:C7").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().setSize(14);
for (int i = 3; i <= 7; i++) {
sheet.autoFitColumn(i);
}
// Save the workbook
workbook.saveToFile("output/AddFormattedDataExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Apply Color to Alternate Rows in Excel Using Conditional Formatting
2022-09-14 07:45:00 Written by KoohjiApplying different background colors to alternate rows of Excel can improve the readability of data and make the spreadsheet appear more professional. There many ways to set row color, among which using conditional formatting is a good choice. It can not only set colors in batches, but also define more flexible rules, such as alternating every three rows. In this article, you will learn how to alternate row color in Excel using conditional formatting using Spire.XLS for Java.
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Apply Color to Alternate Rows in Excel Using Conditional Formatting
The following are the steps to add color to alternative rows in Excel using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook using Workbook.getWorsheets().get(index) method.
- Add a conditional formatting to the worksheet using Worksheet.getConditionalFormats().add() method and return an object of XlsConditionalFormats class.
- Set the cell range where the conditional formatting will be applied using XlsConditionalFormats.addRange() method.
- Add a condition using XlsConditionalFormats.addCondition() method, then set the conditional formula and the cell color of even rows.
- Add another condition to change the format of the cells of odd rows.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ConditionalFormatType;
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import com.spire.xls.core.IConditionalFormat;
import com.spire.xls.core.spreadsheet.collections.XlsConditionalFormats;
import java.awt.*;
public class AlternateRowColors {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Add a conditional format to the worksheet
XlsConditionalFormats format = sheet.getConditionalFormats().add();
//Set the range where the conditional format will be applied
format.addRange(sheet.getRange().get(2,1,sheet.getLastRow(),sheet.getLastColumn()));
//Add a condition to change the format of the cells based on formula
IConditionalFormat condition1 = format.addCondition();
condition1.setFirstFormula("=MOD(ROW(),2)=0");
condition1.setFormatType(ConditionalFormatType.Formula);
condition1.setBackColor(Color.YELLOW);
//Add another condition to change the format of the cells based on formula
IConditionalFormat condition2 = format.addCondition();
condition2.setFirstFormula("=MOD(ROW(),2)=1");
condition2.setFormatType(ConditionalFormatType.Formula);
condition2.setBackColor(new Color(32,178, 170));
//Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.saveToFile("output/AlternateRowColors.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In Excel, the border is a line around a cell or a range of cells. Adding cell borders can help distinguish different sections, highlight summarized values, or separate specific data in a worksheet. In this article, you will learn how to add borders with different line styles and colors to Excel cells using Spire.XLS for Java.
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add Cell Borders in Excel
Spire.XLS for Java provides the CellRange.borderInside() and CellRange.borderAround() methods to add inside and around borders to a specified cell range. To add top, bottom, left, right and diagonal borders, you can use the BordersCollection.getByBordersLineType(BordersLineType index).setLineStyle (LineStyleType lineStyleType) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get a specified cell range using Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Add inside and around borders with specific line styles and colors to the specified range using CellRange.borderInside(LineStyleType borderLine, Color borderColor) and CellRange.borderAround (LineStyleType borderLine, Color borderColor) methods.
- Get a borders collection that represents the borders of the specified cell range using CellRange.getBorders() method.
- Set the border line style and color for the specified range using BordersCollection.setLineStyle() and BordersCollection.setColor() methods.
- Set the diagonal border line style for the specified range using BordersCollection.getByBordersLineType(BordersLineType index).setLineStyle (LineStyleType lineStyleType) method.
- Save the document to another file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class AddBorders {
public static void main(String[] args){
//Create a workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel document
workbook.loadFromFile("D:\\Files\\Input.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Add border to range "B2:F9"
CellRange range1= sheet.getCellRange("B2:F9");
range1.borderInside(LineStyleType.Thin, Color.BLUE);
range1.borderAround(LineStyleType.Medium, Color.BLUE);
//Add border to range "B14:F14"
CellRange range2= sheet.getCellRange("B14:F14");
range2.getBorders().setLineStyle(LineStyleType.Double);
range2.getBorders().setColor(Color.RED);
//Set the diagonal border line style for range "B14:F14"
range2.getBorders().getByBordersLineType(BordersLineType.DiagonalDown).setLineStyle(LineStyleType.None);
range2.getBorders().getByBordersLineType(BordersLineType.DiagonalUp).setLineStyle(LineStyleType.None);
//Save the file
workbook.saveToFile("SetBorder.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Consistent text alignment and orientation throughout an Excel worksheet create a sense of order and professionalism. It makes the data presentation more organized and aesthetically pleasing, which is especially important when sharing a spreadsheet with others or presenting to clients. A well-designed worksheet with proper text formatting can leave a good impression and facilitate data reading and analyzing. In this article, you will learn how to set text alignment and orientation in Excel cells in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Set Text Alignment and Orientation in Excel in Java
The CellRange.getCellStyle().setHorizontalAlignment() and CellRange.getCellStyle().setVerticalAlignment() methods allows you to set the horizontal and vertical alignment of text in an Excel cell or cell range. To change the orientation of text, you can use the CellRange.getCellStyle().setRotation(int rotation) method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get a specified cell using Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Set the horizontal alignment of text in specified cell using CellRange.getCellStyle().setHorizontalAlignment() method.
- Set the vertical alignment of text in specified cell using CellRange.getCellStyle().setVerticalAlignment() method.
- Rotate the text in specific cell to a desired degree using CellRange.getCellStyle().setRotation() method.
- Set the indentation of text in specific cell using CellRange.getCellStyle().setIndentLevel() method.
- Save the result document using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class AlignText {
public static void main(String[] args){
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Text.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
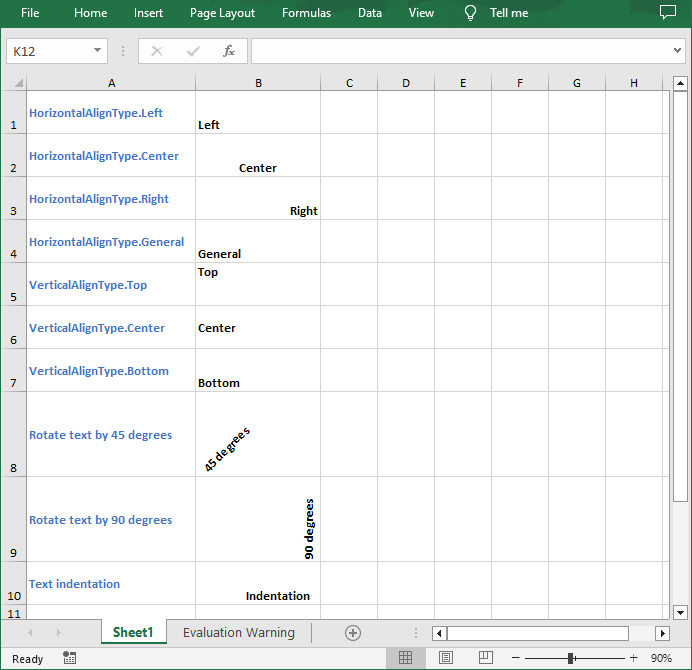
// Set the horizontal alignment of text in a specified cell to Left
sheet.getCellRange("B1").getCellStyle().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Left);
// Set the horizontal alignment of text in a specified cell to Center
sheet.getCellRange("B2").getCellStyle().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Center);
// Set the horizontal alignment of text in a specified cell to Right
sheet.getCellRange("B3").getCellStyle().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.Right);
// Set the horizontal alignment of text in a specified cell to General
sheet.getCellRange("B4").getCellStyle().setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignType.General);
// Set the vertical alignment of text in a specified cell to Top
sheet.getCellRange("B5").getCellStyle().setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType.Top);
// Set the vertical alignment of text in a specified cell to Center
sheet.getCellRange("B6").getCellStyle().setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType.Center);
// Set the vertical alignment of text in a specified cell to Bottom
sheet.getCellRange("B7").getCellStyle().setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignType.Bottom);
// Rotate the text to specified degrees
sheet.getCellRange("B8").getCellStyle().setRotation(45);
sheet.getCellRange("B9").getCellStyle().setRotation(90);
// Set the text indentation
sheet.getCellRange("B10").getCellStyle().setIndentLevel(6);
// Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("TextAlignment.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Java without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
We have already demonstrated how to protect the Excel file in Java; this article will show you how to unprotect the Excel workbook or a single worksheet in Java applications.
Unprotect the Excel workbook:
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class UnprotectExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Use the password to open the sample document
workbook.setOpenPassword("E-iceblue");
workbook.loadFromFile("ProtectWorkbook.xlsx");
//Unprotect the whole workbook
workbook.unProtect();
//Save the document to file
workbook.saveToFile("UnprotectWb.xlsx");
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Unprotect a single Excel worksheet:
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class UnprotectExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a workbook and load a sample file with protected worksheet
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.loadFromFile("ProtectWS.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Unprotect the first worksheet
sheet.unprotect("iceblue");
//Save the document to file
workbook.saveToFile("Unprotectworksheet.xlsx");
workbook.dispose();
}
}
As you create or review a worksheet, you may want to change the font style in some cells to make them stand out. For example, you can apply a different font type, font color, and font size to text, as well as make text bold. In this article, you will learn how to apply font styles to Excel cells using Spire.XLS for Java.
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you’re required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Apply Different Fonts to Different Cells
Spire.XLS provides the ExcelFont class which you can use to set or change the font name, color, size, and style in a cell easily. The following are the steps to apply a font style to a specific cell using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get a specific cell using Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Set the value of the cell using CellRange.setText() method.
- Set the font name, color, size and style of the cell value using setFontName(), setFontColor(), setFontSize(), isBlod() methods under the ExcelFont object.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.FontUnderlineType;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import java.awt.*;
public class ApplyFontToCell {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first sheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Set font name
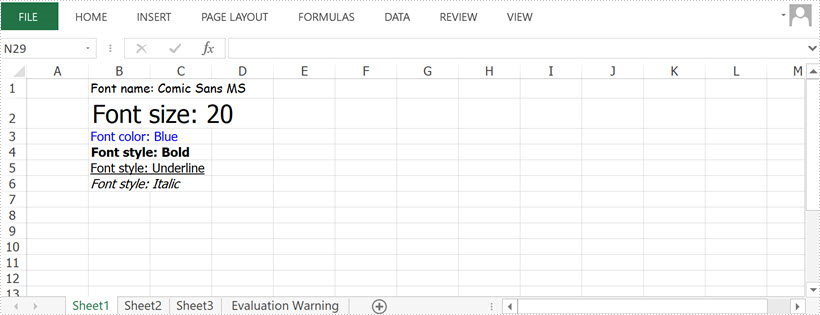
sheet.getCellRange("B1").setText("Font name: Comic Sans MS");
sheet.getCellRange("B1").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().setFontName("Comic Sans MS");
//Set font size
sheet.getCellRange("B2").setText("Font size: 20");
sheet.getCellRange("B2").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().setSize(20);
//Set font color
sheet.getCellRange("B3").setText("Font color: Blue");
sheet.getCellRange("B3").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().setColor(Color.blue);
//Make text bold
sheet.getCellRange("B4").setText("Font style: Bold");
sheet.getCellRange("B4").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().isBold(true);
//Make text italic
sheet.getCellRange("B5").setText("Font style: Italic");
sheet.getCellRange("B5").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().isItalic(true);
//Underline text
sheet.getCellRange("B6").setText("Font style: Underline");
sheet.getCellRange("B6").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().setUnderline(FontUnderlineType.Single);
//Strikethrough text
sheet.getCellRange("B7").setText("Font style: Strikethrough");
sheet.getCellRange("B7").getCellStyle().getExcelFont().isStrikethrough(true);
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("output/ApplyFontToCell.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Apply Multiple Fonts to a Single Cell
Mixing different font styles can help you emphasize some specific characters in a cell. The following are the steps to apply multiple fonts in a cell using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Create two ExcelFont objects using Workbook.createFont() method.
- Get a specific cell using Worksheet.getCellRange() method, and set the rich text content of the cell using CellRange.getRichText().setText() method.
- Apply the two ExcelFont objects to the rich text using RichText.setFont() method.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class ApplyMultipleFontsToCell {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Create one Excel font
ExcelFont font1 = wb.createFont();
font1.setFontName("Arial Black");
font1.setColor(Color.blue);
font1.setSize(13f);
font1.isBold(true);
//Create another Excel font
ExcelFont font2 = wb.createFont();
font2.setFontName("Algerian");
font2.setColor(Color.red);
font2.setSize(15f);
font2.isBold(true);
font2.isItalic(true);
//Insert text to cell B5
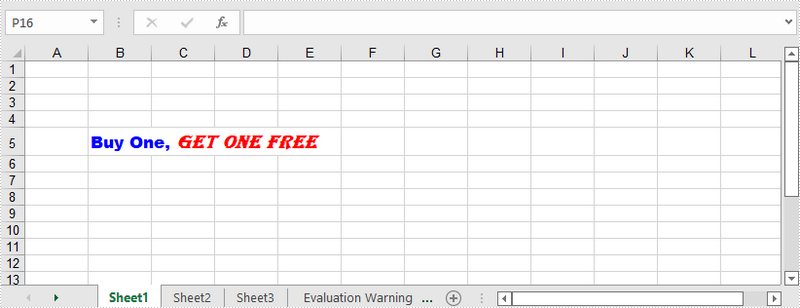
RichText richText = sheet.getCellRange("B5").getRichText();
richText.setText("Buy One, Get One Free");
//Apply two fonts to the text in the cell B5
richText.setFont(0, 8, font1);
richText.setFont(9, 21, font2);
//Save the document
wb.saveToFile("output/ApplyMultipleFontsToCell.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Images are universally supported and can be seamlessly embedded and displayed in a variety of web platforms and documents. When you intend to publish Excel charts on websites or include them in videos or presentations, converting them to images is a practical option. By doing so, you can eliminate any potential compatibility issues and ensure that these charts are accessible to a wider audience. In this article, we will demonstrate how to convert Excel charts to images in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to an Image in Java
- Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Java
- Convert a Chart Sheet to an Image in Excel in Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to an Image in Java
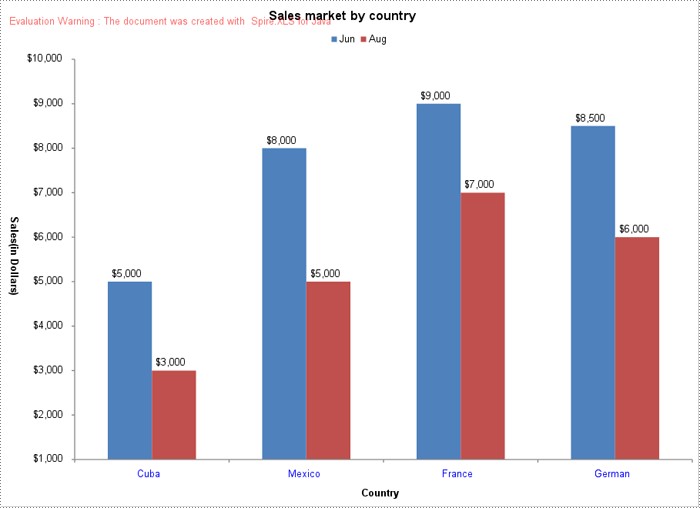
Spire.XLS for Java provides the Workbook.saveChartAsImage(Worksheet worksheet, int chartIndex) method to convert a specific chart in a worksheet as an image. The following are the detailed steps:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using Workbook.getWorksheets().get(int index) method.
- Save a specific chart in the worksheet as an image using Workbook.saveChartAsImage(Worksheet worksheet, int chartIndex) method.
- Save the image to a PNG file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConvertAExcelChartToImage {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Charts.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Save the first chart in the first worksheet as an image
BufferedImage image = workbook.saveChartAsImage(sheet, 0);
//Save the image to a .png file
ImageIO.write(image, "PNG", new File("output\\chart.png"));
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Java
To convert all charts in an Excel worksheet to images, you can use the Workbook.saveChartAsImage(Worksheet worksheet) method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using Workbook.getWorksheets().get(int index) method.
- Save all charts in the worksheet as images using Workbook.saveChartAsImage(Worksheet worksheet) method.
- Save the images to PNG files.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConvertAllExcelChartsToImage {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("Charts.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Save all charts in the first worksheet as images
BufferedImage[] imgs = workbook.saveChartAsImage(sheet);
//Save the images to .png files
for (int i = 0; i < imgs.length; i++)
{
File file = new File("output\\" + String.format(("chart-%d.png"), i));
ImageIO.write(imgs[i], "PNG", file);
}
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Convert a Chart Sheet to an Image in Excel in Java
A chart sheet in Excel is a separate sheet dedicated solely to displaying a chart. You can use the Workbook.saveChartAsImage(ChartSheet chartSheet) method to convert a chart sheet in an Excel workbook to an image. The following are the detailed steps:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific chart sheet by its index using Workbook.getChartsheets().get(int index) method.
- Save the chart sheet as an image using Workbook.saveChartAsImage(ChartSheet chartSheet) method.
- Save the image to a .png file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ChartSheet;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConvertExcelChartSheetToImage {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("ChartSheet.xlsx");
//Get the first chart sheet
ChartSheet chartSheet = workbook.getChartsheets().get(0);
//Save the first chart sheet as an image
BufferedImage image = workbook.saveChartAsImage(chartSheet);
//Save the image to a .png file
ImageIO.write(image, "PNG", new File("output\\chartSheet.png"));
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Headers and footers in Excel are the text or images placed at the top and bottom of each page, respectively. These texts/images give basic information about the pages or document, such as the file name, company logo, page number, date/time, and so on. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically add text, images, as well as fields (like page number) to Excel headers or footers using Spire.XLS for Java.
Spire.XLS for Java provides the PageSetup class to work with the page setup in Excel including headers and footers. Specifically, it offers the setLeftHeader() method, setCenterHeader() method, setRightHeader() method, setLeftFooter() method, etc. to add content to the left section, center section and right section of a header or footer. To add fields to headers or footers, or to apply formatting to text, you'll need to use the scripts listed in the following table.
| Script | Description |
| &P | The current page numbers. |
| &N | The total number of pages. |
| &D | The current data. |
| &T | The current time. |
| &G | A picture. |
| &A | The worksheet name. |
| &F | The file name. |
| &B | Make text bold. |
| &I | Italicize text. |
| &U | Underline text. |
| &"font name" | Represents a font name, for example, &"Arial". |
| & + Integer | Represents font size, for example, &12. |
| &K + Hex color code | Represents font color, for example, &KFF0000. |
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you’re required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
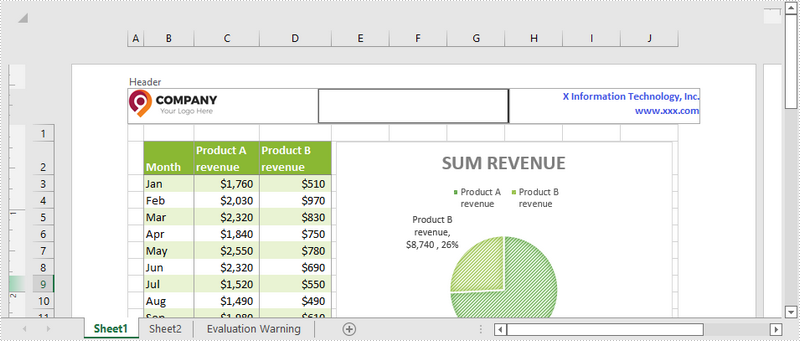
Add Images and Formatted Text to Header
The steps to add images and formatted text an Excel header using Spire.XLS for Java are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Load an image using ImageIO.read() method.
- Set the image as the image source of the header’s left section using PageSetup.setLeftHeaderImage() method.
- Display image in the left header section by passing the value “&G” to PageSetup.setLeftHeader() method as a parameter.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class AddImageAndTextToHeader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Load an existing Excel file
wb.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Load an image
BufferedImage bufferedImage = ImageIO.read(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\your-logo.png"));
//Add image to header’s left section
sheet.getPageSetup().setLeftHeaderImage(bufferedImage,0.4f);
sheet.getPageSetup().setLeftHeader("&G");
//Add formatted text to header’s right section
sheet.getPageSetup().setRightHeader("&\"Calibri\"&B&10&K4253E2X Information Technology, Inc. \n www.xxx.com");
//Save the file
wb.saveToFile("output/Header.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Add the Current Date and Page Number to Footer
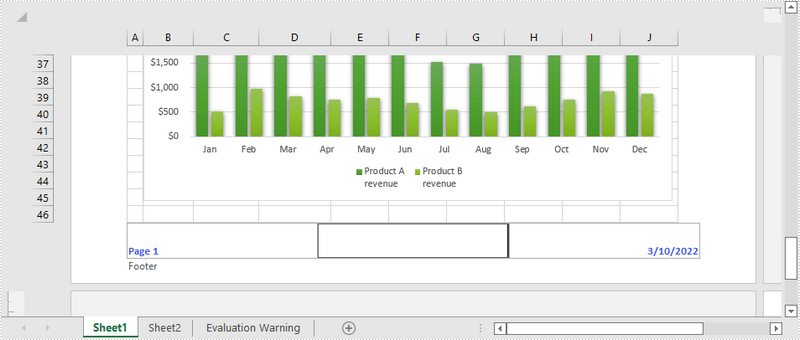
The following are the steps to add the current date and page number to an Excel footer using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets.get() method.
- Add page numbers with formatting to the footer’s left section by passing the value “&\"Calibri\"&B&10&K4253E2Page &P” to PageSetup.setLeftFooter() method. You can customize the page numbers’ formatting according to your preference.
- Add the current date to the footer’s right section by passing the value “&\"Calibri\"&B&10&K4253E2&D” to PageSetup.setRightFooter() method. Likewise, you can change the appearance of the date string as desired.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class AddDateAndPageNumberToFooter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Load an existing Excel file
wb.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Add page number to footer's left section
sheet.getPageSetup().setLeftFooter("&\"Calibri\"&B&10&K4253E2Page &P");
//Add current date to footer's right section
sheet.getPageSetup().setRightFooter("&\"Calibri\"&B&10&K4253E2&D");
//Save the file
wb.saveToFile("output/Footer.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
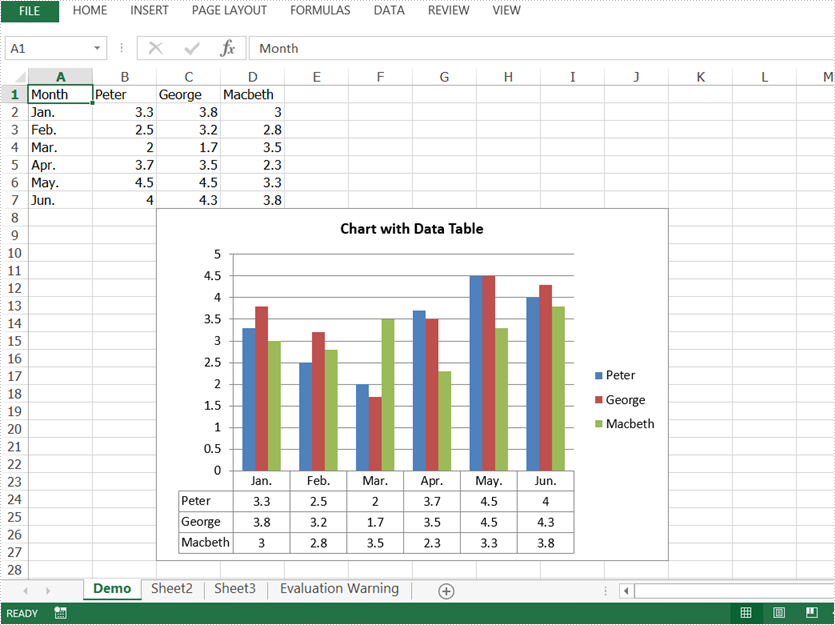
In Excel, we could use charts to visualize and compare data. However, once the charts are created, it becomes much difficult for us to read the data precisely from charts, adding a data table below the chart is a good solution. This article is going to introduce how to add a data table to an Excel chart in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.charts.ChartSerie;
public class AddDataTableToChart {
public static void main(String[] args){
//Create a new workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Set sheet name
sheet.setName("Demo");
//Add Data to the sheet
sheet.getRange().get("A1").setValue("Month");
sheet.getRange().get("A2").setValue("Jan.");
sheet.getRange().get("A3").setValue("Feb.");
sheet.getRange().get("A4").setValue("Mar.");
sheet.getRange().get("A5").setValue("Apr.");
sheet.getRange().get("A6").setValue("May.");
sheet.getRange().get("A7").setValue("Jun.");
sheet.getRange().get("B1").setValue("Peter");
sheet.getRange().get("B2").setNumberValue(3.3);
sheet.getRange().get("B3").setNumberValue(2.5);
sheet.getRange().get("B4").setNumberValue(2.0);
sheet.getRange().get("B5").setNumberValue(3.7);
sheet.getRange().get("B6").setNumberValue(4.5);
sheet.getRange().get("B7").setNumberValue(4.0);
sheet.getRange().get("C1").setValue("George");
sheet.getRange().get("C2").setNumberValue(3.8);
sheet.getRange().get("C3").setNumberValue(3.2);
sheet.getRange().get("C4").setNumberValue(1.7);
sheet.getRange().get("C5").setNumberValue(3.5);
sheet.getRange().get("C6").setNumberValue(4.5);
sheet.getRange().get("C7").setNumberValue(4.3);
sheet.getRange().get("D1").setValue("Macbeth");
sheet.getRange().get("D2").setNumberValue(3.0);
sheet.getRange().get("D3").setNumberValue(2.8);
sheet.getRange().get("D4").setNumberValue(3.5);
sheet.getRange().get("D5").setNumberValue(2.3);
sheet.getRange().get("D6").setNumberValue(3.3);
sheet.getRange().get("D7").setNumberValue(3.8);
//Add a chart to the sheet
Chart chart = sheet.getCharts().add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
//Set chart data
chart.setDataRange(sheet.getRange().get("B1:D7"));
chart.setSeriesDataFromRange(false);
//Set chart position
chart.setTopRow(8);
chart.setBottomRow(28);
chart.setLeftColumn(3);
chart.setRightColumn(11);
//Set chart title
chart.setChartTitle("Chart with Data Table");
chart.getChartTitleArea().isBold(true);
chart.getChartTitleArea().setSize(12);
//Set category labels for the first series of the chart
ChartSerie cs1 = chart.getSeries().get(0);
cs1.setCategoryLabels(sheet.getRange().get("A2:A7"));
//Add data table to the chart
chart.hasDataTable(true);
//Save the result file
workbook.saveToFile("AddDataTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
Output:
Adjusting row heights and column widths allows users to optimize the display of their data in a spreadsheet. Whether you're working with a large dataset or preparing a report, customizing these dimensions can help ensure that your information is presented clearly and concisely. Excel provides several ways to change row height and column width, including manual adjustments and automatic fitting options.
In this article, you will learn how to programmatically change row height and column width in Excel in Java using the Spire.XLS for Java library.
- Change Row Height and Column Width for a Specific Row and Column
- Change Row Height and Column Width for All Rows and Columns
- Automatically Adjust Row Height and Column Width for a Specific Row and Column
- Automatically Adjust Row Height and Column Width in a Cell Range
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Change Row Height and Column Width for a Specific Row and Column
Spire.XLS for Java provides the Worksheet.setRowHeight() and Worksheet.setColumnWidth() methods for adjusting the height of a specific row and the width of a specific column in a worksheet. Here are the detailed steps to accomplish this task.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Change the height of a specific row using Worksheet.setRowHeight() method.
- Change the width of a specific column using Worksheet.setColumnWidth() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class SetRowHeightAndColumnWidth {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Set the height of a selected row to 20
worksheet.setRowHeight(1,20);
// Set the width of a selected column to 30
worksheet.setColumnWidth(4, 30);
//Save to file.
workbook.saveToFile("output/SetHeightAndWidth.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Change Row Height and Column Width for All Rows and Columns
To modify the row height and column width for all rows and columns in a worksheet, you can utilize the Worksheet.setDefaultRowHeight() and Worksheet.setDefaultColumnWidth() methods. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Change the height for all rows using Worksheet.setDefaultRowHeight() method.
- Change the width for all columns using Worksheet.setDefaultColumnWidth() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class SetRowHeightColumnWidthForAll {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Set the default row height to 18
worksheet.setDefaultRowHeight(18);
// Set the default column width to 15
worksheet.setDefaultColumnWidth(15);
//Save to file.
workbook.saveToFile("output/SetHeightAndWidthForAll.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Automatically Adjust Row Height and Column Width for a Specific Row and Column
To automatically adjust the row height and column width to fit the content of a specific row and column in a worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.autoFitRow() and Worksheet.autoFitColumn() methods. The steps to autofit row height and column width are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Automatically adjust the height of a specific row using Worksheet.autoFitRow() method.
- Automatically adjust the width of a specific column using Worksheet.autoFitColumn() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class AutoFitRowHeightAndColumnWidth {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Autofit the first row
worksheet.autoFitRow(1);
// Autofit the second column
worksheet.autoFitColumn(2);
// Save the document
workbook.saveToFile("output/AutoFit.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Automatically Adjust Row Height and Column Width in a Cell Range
To automatically adjust the row height and column width within a specific cell range in your worksheet, you can utilize the CellRange.autoFitRows() and CellRange.autoFitColumns() methods respectively. Below are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Get a cell range using Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Automatically adjust the row height in the range using CellRange.autoFitRow() method.
- Automatically adjust the column width in the range using CellRange.autoFitColumn() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.CellRange;
import com.spire.xls.ExcelVersion;
import com.spire.xls.Workbook;
import com.spire.xls.Worksheet;
public class AutoFitInRange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
workbook.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the used range
CellRange cellRange = worksheet.getAllocatedRange();
// Or, you can get a desired cell range
// CellRange cellRange = worksheet.getCellRange(1,1,6,4)
// Autofit rows and columns in the range
cellRange.autoFitRows();
cellRange.autoFitColumns();
// Save the document
workbook.saveToFile("output/AutoFit.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
