Python: Create a Fillable Form in Word
Creating a fillable form in Word allows you to design a document that can be easily completed and customized by others. Whether you need to collect information, gather feedback, or create an interactive document, fillable forms provide a convenient way to capture data electronically. By adding various elements such as text fields, checkboxes, dropdown menus, and more, you can tailor the form to your specific requirements.
To create a fillable form in Word, you probably need to use the following tools.
- Content Controls: The areas where users input information in a form.
- Tables: Tables are used in forms to align text and form fields, and to create borders and boxes.
- Protection: Allows users to populate fields but not to make changes to the rest of the document.
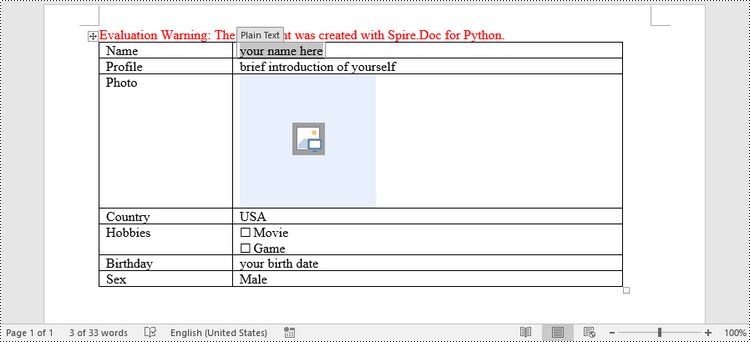
In Word, content controls serve as containers for structured documents, allowing users to organize content within a document. Word 2013 provides ten types of content controls. This article introduces how to create a fillable form in Word that includes the following seven commonly-used content controls using Spire.Doc for Python.
| Content Control | Description |
| Plain Text | A text field limited to plain text, so no formatting can be included. |
| Rich Text | A text field that can contain formatted text or other items, such as tables, pictures, or other content controls. |
| Picture | Accepts a single picture. |
| Drop-Down List | A drop-down list displays a predefined list of items for the user to choose from. |
| Combo Box | A combo box enables users to select a predefined value in a list or type their own value in the text box of the control. |
| Check Box | A check box provides a graphical widget that allows the user to make a binary choice: yes (checked) or no (not checked). |
| Date Picker | Contains a calendar control from which the user can select a date. |
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create a Fillable Form in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the StructureDocumentTagInline class, which is utilized to generate structured document tags within a paragraph. By utilizing the SDTProperties property and SDTContent property of this class, one can define the properties and content of the current structured document tag. Below are the step-by-step instructions for creating a fill form in a Word document in Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a table using Section.AddTable() method.
- Add a paragraph to a specific table cell using TableCell.AddParagraph() method.
- Create an instance of StructureDocumentTagInline class, and add it to the paragraph as a child object using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Add() method.
- Specify the type, content and other attributes of the structured document tag through the SDTProperties property and the SDTContent property of the StructureDocumentTagInline object.
- Prevent users from editing content outside form fields using Document.Protect() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Add a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
table.ResetCells(7, 2)
table.SetColumnWidth(0, 120, CellWidthType.Point)
table.SetColumnWidth(1, 350, CellWidthType.Point)
# Add text to the cells of the first column
paragraph = table.Rows.get_Item(0).Cells.get_Item(0).AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Name")
paragraph = table.Rows[1].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Profile")
paragraph = table.Rows[2].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Photo")
paragraph = table.Rows[3].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Country")
paragraph = table.Rows[4].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Hobbies")
paragraph = table.Rows[5].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Birthday")
paragraph = table.Rows[6].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Sex")
# Add a plain text content control to the cell (0,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[0].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.Text
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Plain Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Plain Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.IsShowingPlaceHolder = True
text = SdtText(True)
text.IsMultiline = False
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = text
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "your name here"
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
# Add a rich text content control to the cell (1,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[1].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.RichText
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Rich Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Rich Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.IsShowingPlaceHolder = True
text = SdtText(True)
text.IsMultiline = False
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = text
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "brief introduction of yourself"
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange )
# Add a picture content control to the cell (2,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[2].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.Picture
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Picture"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Picture"
sdtPicture = SdtPicture(True)
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = sdtPicture
pic = DocPicture(doc)
pic.LoadImage("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\placeHolder.png")
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(pic)
# Add a dropdown list content control to the cell (3,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[3].Cells[1].AddParagraph();
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.DropDownList
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Dropdown List"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Dropdown List"
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
stdList = SdtDropDownList()
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("USA", "1"))
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("China", "2"))
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Briza", "3"))
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Austrilia", "4"))
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = stdList;
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange .Text = stdList.ListItems[0].DisplayText
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange )
# Add two check box content controls to the cell (4,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[4].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.CheckBox
sdtCheckBox = SdtCheckBox()
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = sdtCheckBox
textRange = TextRange(doc)
sdt.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
sdtCheckBox.Checked = False
paragraph.AppendText(" Movie")
paragraph = table.Rows[4].Cells[1].AddParagraph();
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.CheckBox
sdtCheckBox = SdtCheckBox()
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = sdtCheckBox
textRange = TextRange(doc)
sdt.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
sdtCheckBox.Checked = False
paragraph.AppendText(" Game")
# Add a date picker content control to the cell (5,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[5].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.DatePicker
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Date Picker"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Date Picker"
stdDate = SdtDate()
stdDate.CalendarType = CalendarType.Default
stdDate.DateFormat = "yyyy.MM.dd"
stdDate.FullDate = DateTime.get_Now()
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = stdDate
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "your birth date"
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
# Add a combo box content control to the cell (6,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[6].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.ComboBox
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Combo Box"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Combo Box"
stdComboBox = SdtComboBox()
stdComboBox.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Male"))
stdComboBox.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Female"))
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = stdComboBox
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = stdComboBox.ListItems[0].DisplayText
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
# Allow users to edit the form fields only
doc.Protect(ProtectionType.AllowOnlyFormFields, "permission-psd")
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Form.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add, Edit, or Delete Bookmarks in PDF
PDF bookmarks are navigational aids that allow users to quickly locate and jump to specific sections or pages in a PDF document. Through a simple click, users can arrive at the target location, which eliminates the need to manually scroll or search for specific content in a lengthy document. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically add, modify and delete bookmarks in PDF files using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add Bookmarks to a PDF Document
- Edit Bookmarks in a PDF Document
- Delete Bookmarks from a PDF Document
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add Bookmarks to a PDF Document in Python
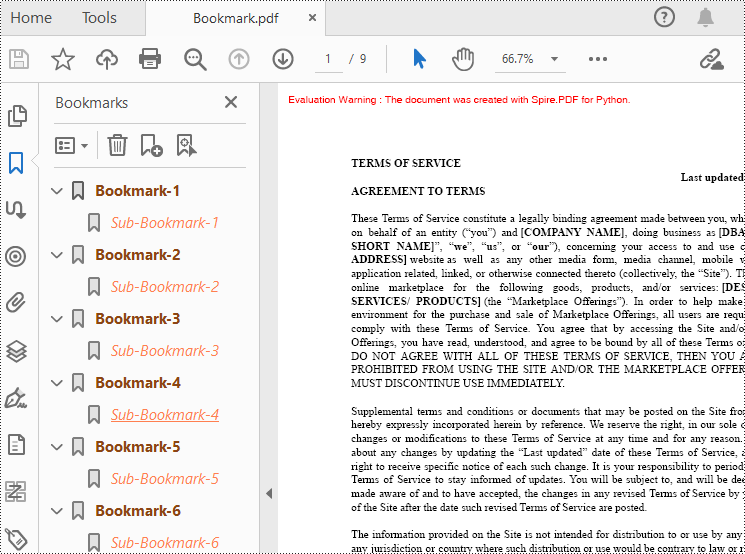
Spire.PDF for Python provides a method to add bookmarks to a PDF document: PdfDocument. Bookmarks.Add(). You can use this method to create primary bookmarks for the PDF document and use the PdfBookmarkCollection.Add() method to add sub-bookmarks to the primary bookmarks. Additionally, the PdfBookmark class offers other methods to set properties such as destination, text color, and text style for the bookmarks. The following are the detailed steps for adding bookmarks to a PDF document.
- Create a PdfDocument class instance.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a parent bookmark to the document using PdfDocument.Bookmarks.Add() method.
- Create a PdfDestination class object and set the destination of the parent bookmark using PdfBookmark.Action property.
- Set the text color and style of the parent bookmark.
- Create a PdfBookmarkCollection class object to add sub-bookmark to the parent bookmark using PdfBookmarkCollection.Add() method.
- Use the above methods to set the destination, text color, and text style of the sub-bookmark.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Terms of service.pdf")
# Loop through the pages in the PDF file
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Set the title and destination for the bookmark
bookmarkTitle = "Bookmark-{0}".format(i+1)
bookmarkDest = PdfDestination(page, PointF(0.0, 0.0))
# Create and configure the bookmark
bookmark = doc.Bookmarks.Add(bookmarkTitle)
bookmark.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_SaddleBrown())
bookmark.DisplayStyle = PdfTextStyle.Bold
bookmark.Action = PdfGoToAction(bookmarkDest)
# Create a collection to hold child bookmarks
bookmarkColletion = PdfBookmarkCollection(bookmark)
# Set the title and destination for the child bookmark
childBookmarkTitle = "Sub-Bookmark-{0}".format(i+1)
childBookmarkDest = PdfDestination(page, PointF(0.0, 100.0))
# Create and configure the child bookmark
childBookmark = bookmarkColletion.Add(childBookmarkTitle)
childBookmark.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Coral())
childBookmark.DisplayStyle = PdfTextStyle.Italic
childBookmark.Action = PdfGoToAction(childBookmarkDest)
# Save the PDF file
outputFile = "Bookmark.pdf"
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
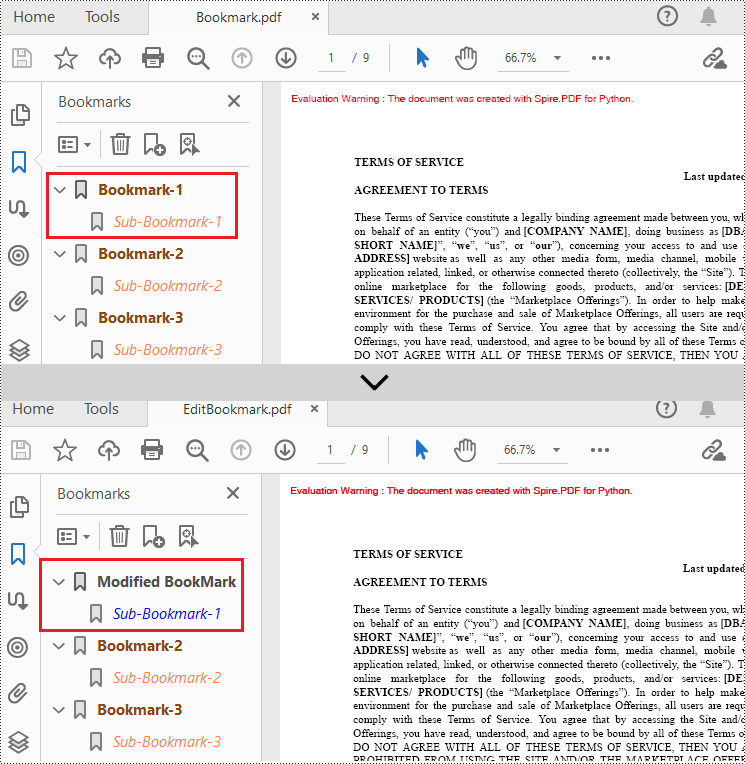
Edit Bookmarks in a PDF Document
If you need to update the existing bookmarks, you can use the methods of PdfBookmark class to rename the bookmarks and change their text color, text style. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument class instance.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified bookmark using PdfDocument.Bookmarks[] property.
- Change the title of the bookmark using PdfBookmark.Title property.
- Change the font color of the bookmark using PdfBookmark.Color property.
- Change the text style of the bookmark using PdfBookmark.DisplayStyle property.
- Change the text color and style of the sub-bookmark using the above methods.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Bookmark.pdf")
# Get the first bookmark
bookmark = doc.Bookmarks.get_Item(0)
# Change the title of the bookmark
bookmark.Title = "Modified BookMark"
# Set the color of the bookmark
bookmark.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Black())
# Set the outline text style of the bookmark
bookmark.DisplayStyle = PdfTextStyle.Bold
# Edit child bookmarks of the parent bookmark
pBookmark = PdfBookmarkCollection(bookmark)
for i in range(pBookmark.Count):
childBookmark = pBookmark.get_Item(i)
childBookmark.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
childBookmark.DisplayStyle = PdfTextStyle.Regular
# Save the PDF document
outputFile = "EditBookmark.pdf"
# Close the document
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile)
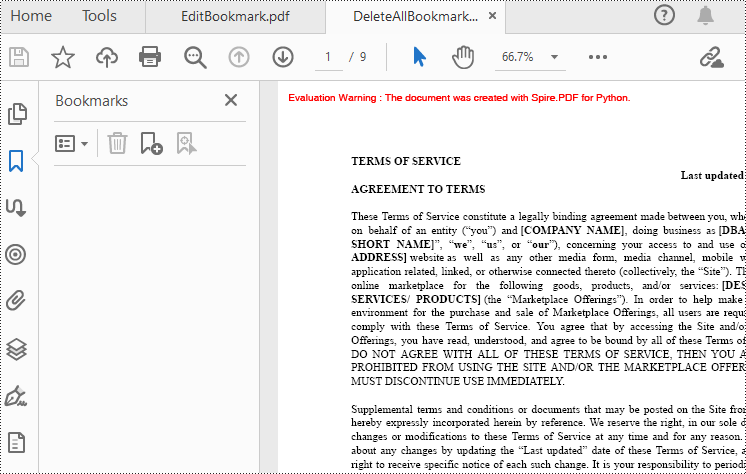
Delete Bookmarks from a PDF Document
Spire.PDF for Python also provides methods to delete any bookmark in a PDF document. PdfDocument.Bookmarks.RemoveAt() method is used to remove a specific primary bookmark, PdfDocument.Bookmarks.Clear() method is used to remove all bookmarks, and PdfBookmarkCollection.RemoveAt() method is used to remove a specific sub-bookmark of a primary bookmark. The detailed steps of removing bookmarks form a PDF document are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument class instance.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first bookmark using PdfDocument.Bookmarks[] property.
- Remove a specified sub-bookmark of the first bookmark using PdfBookmarkCollection.RemoveAt() method.
- Remove a specified bookmark including its sub-bookmarks using PdfDocument.Bookmarks.RemoveAt() method.
- Remove all bookmarks in the PDF file using PdfDocument.Bookmarks.Clear() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Bookmark.pdf")
# # Delete the first bookmark
# doc.Bookmarks.RemoveAt(0)
# # Get the first bookmark
# bookmark = doc.Bookmarks.get_Item(0)
# # Remove the first child bookmark from first parent bookmark
# pBookmark = PdfBookmarkCollection(bookmark)
# pBookmark.RemoveAt(0)
#Remove all bookmarks
doc.Bookmarks.Clear()
# Save the PDF document
output = "DeleteAllBookmarks.pdf"
doc.SaveToFile(output)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Convert SVG to PDF
SVG files are commonly used for web graphics and vector-based illustrations because they can be scaled and adjusted easily. PDF, on the other hand, is a versatile format widely supported across different devices and operating systems. Converting SVG to PDF allows for easy sharing of graphics and illustrations, ensuring that recipients can open and view the files without requiring specialized software or worrying about browser compatibility issues. In this article, we will demonstrate how to convert SVG files to PDF format in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert SVG to PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.LoadFromSvg() method, which allows users to load an SVG file. Once loaded, users can use the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method to save the SVG file as a PDF file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load an SVG file using PdfDocument.LoadFromSvg() method.
- Save the SVG file to PDF format using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load an SVG file
doc.LoadFromSvg("Sample.svg")
# Save the SVG file to PDF format
doc.SaveToFile("ConvertSvgToPdf.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
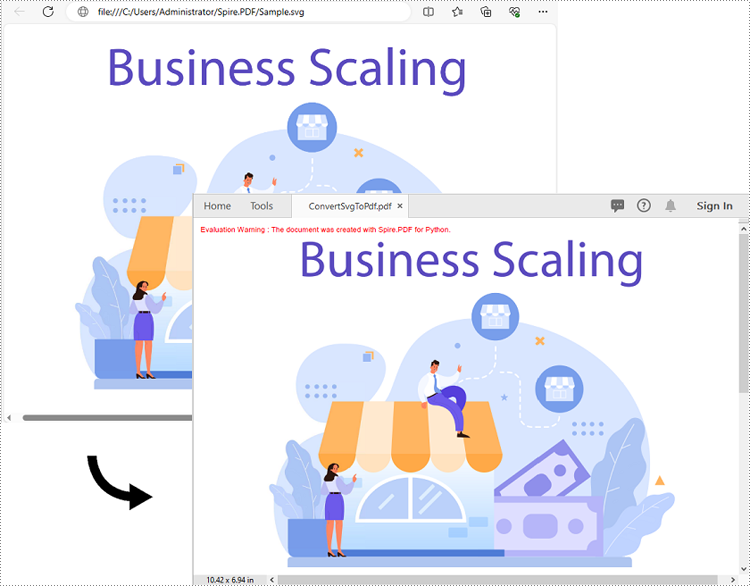
Add SVG to PDF in Python
In addition to converting SVG to PDF directly, Spire.PDF for Python also supports adding SVG files to specific locations in PDF. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load an SVG file using PdfDocument.LoadFromSvg() method.
- Create a template based on the content of the SVG file using PdfDocument. Pages[].CreateTemplate() method.
- Get the width and height of the template.
- Create another object of the PdfDocument class and load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Draw the template with a custom size at a specific location in the PDF file using PdfDocument.Pages[].Canvas.DrawTemplate() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc1 = PdfDocument()
# Load an SVG file
doc1.LoadFromSvg("Sample.svg")
# Create a template based on the content of the SVG
template = doc1.Pages.get_Item(0).CreateTemplate()
# Get the width and height of the template
width = template.Width
height = template.Height
# Create another PdfDocument object
doc2 = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc2.LoadFromFile(""Sample.pdf"")
# Draw the template with a custom size at a specific location on the first page of the loaded PDF file
doc2.Pages.get_Item(0).Canvas.DrawTemplate(template, PointF(10.0, 100.0), SizeF(width*0.8, height*0.8))
# Save the result file
doc2.SaveToFile("AddSvgToPdf.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Close the PdfDocument objects
doc2.Close()
doc1.Close()
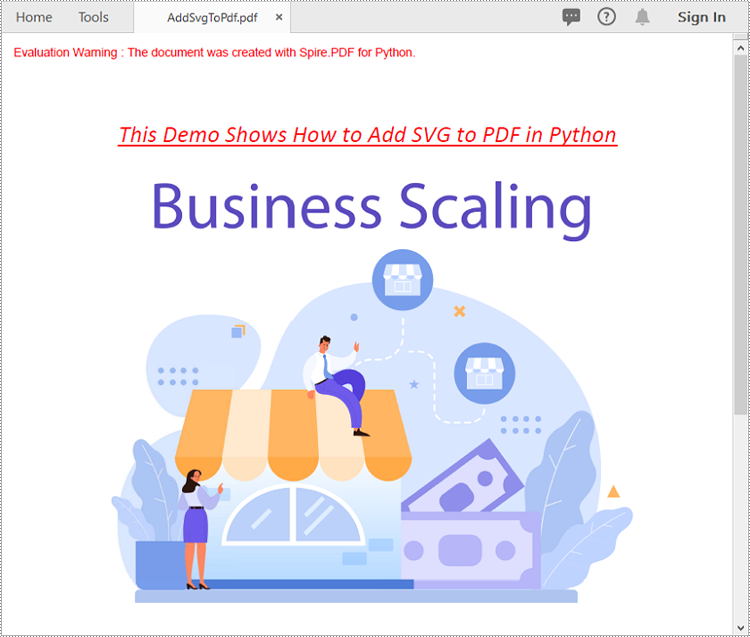
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Insert Headers and Footers in Word
Headers and footers in Word are sections at the top and bottom margins of each page. They can contain additional information such as page numbers, document titles, dates, author names, and other identifying details. By default, the headers or footers on all pages are the same, but in certain scenarios, you can also insert different headers or footers on the first page, odd pages, or even pages. This article will demonstrate how to insert headers and footers into a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Insert Headers and Footers into a Word Document
- Add Different Headers and Footers for the First Page and Other Pages
- Add Different Headers and Footers for Odd and Even Pages
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert Headers and Footers into a Word Document in Python
To insert a header or a footer into a Word document, you first need to get them through the Section.HeadersFooters.Header and Section.HeadersFooters.Footer properties, and then add paragraphs to them to insert pictures, text, page numbers, dates, or other information.
The following are steps to add headers and footers in Word:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Add Header
- Get header using Section.HeadersFooters.Header property.
- Add a paragraph to the header using HeaderFooter.AddParagraph() method and set paragraph alignment.
- Add an image to the header paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method, and then set the text wrapping style and position of the image.
- Add text to the header paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method, and then set the font name, size, color, etc.
- Add Footer
- Get footer using Section.HeadersFooters.Footer property.
- Add a paragraph to the footer and then add text to the footer paragraph.
- Get the borders of the footer paragraph using Paragraph.Format.Borders property, and then set the top border style and space.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get header
header = section.HeadersFooters.Header
# Add a paragraph to the header and set its alignment style
headerParagraph = header.AddParagraph()
headerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
# Add an image to the header paragraph and set its text wrapping style, position
headerPicture = headerParagraph.AppendPicture("Logo.png")
headerPicture.TextWrappingStyle = TextWrappingStyle.Square
headerPicture.VerticalOrigin = VerticalOrigin.Line
headerPicture.VerticalAlignment = ShapeVerticalAlignment.Center
# Add text to the header paragraph and set its font style
text = headerParagraph.AppendText("E-iceblue Co. Ltd."+ "\nYour Office Development Master")
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 10
text.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
text.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
# Get footer
footer = section.HeadersFooters.Footer
# Add a paragraph to the footer paragraph and set its alignment style
footerParagraph = footer.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Add text to the footer paragraph and set its font style
text = footerParagraph.AppendText("Copyright © 2013 e-iceblue. All Rights Reserved.")
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 10
# Set the border of the footer paragraph
footerParagraph.Format.Borders.Top.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
footerParagraph.Format.Borders.Top.Space = 0.05
# Save the result file
document.SaveToFile("HeaderAndFooter.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
document.Close()
Add Different Headers and Footers for the First Page and Other Pages in Word in Python
Sometimes you may need to insert a header and footer only on the first page, or you may want the header and footer on the first page different from other pages.
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Section.PageSetup.DifferentFirstPageHeaderFooter property to enable a different first page header or footer. The following are the detailed steps to accomplish the task.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Enable different headers and footers for the first page and other pages by setting the Section.PageSetup.DifferentFirstPageHeaderFooter property to True.
- Get the first page header using Section.HeadersFooters.FirstPageHeader property.
- Add a paragraph to the first page header and then add an image to the header paragraph.
- Get the first page footer using Section.HeadersFooters.FirstPageFooter property.
- Add a paragraph to the first page footer and then add text to the footer paragraph.
- Set headers and footers for other pages. (There's no need to set this if you only need the header & footer for the first page.)
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Enable different headers and footers for the first page and other pages
section.PageSetup.DifferentFirstPageHeaderFooter = True
# Add a paragraph to the first page header and set its alignment style
headerParagraph = section.HeadersFooters.FirstPageHeader.AddParagraph()
headerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Right
# Add an image to the header paragraph
headerimage = headerParagraph.AppendPicture("E-iceblue.png")
# Add a paragraph to the first page footer and set its alignment style
footerParagraph = section.HeadersFooters.FirstPageFooter.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Add text to the footer paragraph and set its font style
text = footerParagraph.AppendText("Different First Page Footer")
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11
# Set the header & footer for other pages. If you only headers & footers for the first page, don't set this.
para = section.HeadersFooters.Header.AddParagraph()
para.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
paraText = para.AppendText("A Professional Word Python API")
paraText.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
paraText.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DeepPink()
para.Format.Borders.Bottom.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
para.Format.Borders.Bottom.Space = 0.05
paragraph = section.HeadersFooters.Footer.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paraText = paragraph.AppendText("E-iceblue Co. Ltd.")
paraText.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
paraText.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
paraText.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DodgerBlue()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("DifferentFirstPage.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
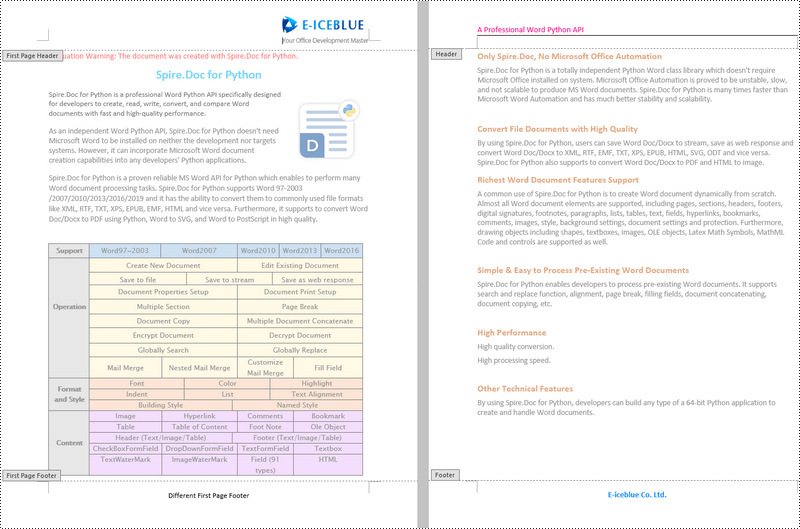
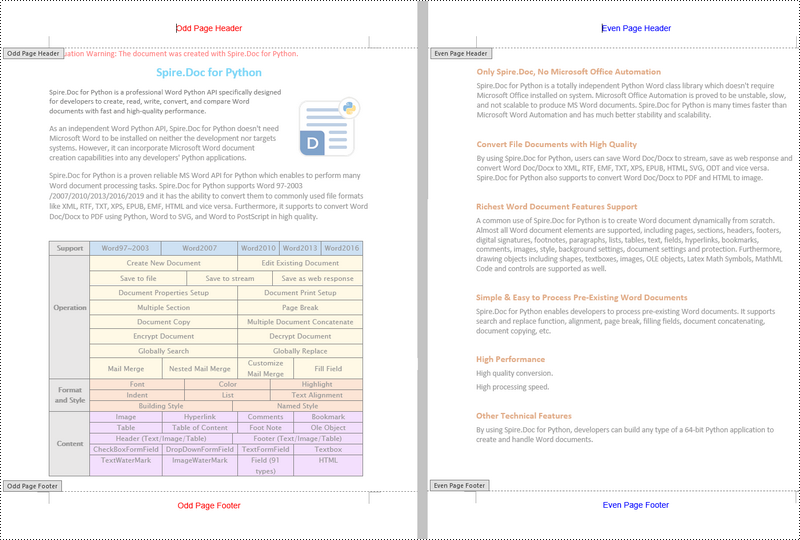
Add Different Headers and Footers for Odd and Even Pages in Word in Python
To have different headers and footers on odd and even pages, Spire.Doc for Python provides the Section.PageSetup.DifferentOddAndEvenPagesHeaderFooter property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Enable different headers and footers for the odd and even pages by setting the Section.PageSetup.DifferentOddAndEvenPagesHeaderFooter property to True.
- Get the header and footer of odd pages using Section.HeadersFooters.OddHeader and Section.HeadersFooters.OddFooter properties.
- Add paragraphs to the header and footer of odd pages and then add text to them.
- Get the header and footer of even pages using Section.HeadersFooters.EvenHeader and Section.HeadersFooters.EvenFooter properties.
- Add paragraphs to the header and footer of even pages and then add text to them.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Enable different headers and footers for the odd and even pages
section.PageSetup.DifferentOddAndEvenPagesHeaderFooter = True
# Add headers and footers to odd pages
OHpara = section.HeadersFooters.OddHeader.AddParagraph()
OHtext = OHpara.AppendText("Odd Page Header")
OHpara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
OHtext.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
OHtext.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
OHtext.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
OFpara = section.HeadersFooters.OddFooter.AddParagraph()
OFtext = OFpara.AppendText("Odd Page Footer")
OFpara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
OFtext.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
OFtext.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
OFtext.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
# Add headers and footers to even pages
EHpara = section.HeadersFooters.EvenHeader.AddParagraph()
EHtext = EHpara.AppendText("Even Page Header")
EHpara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
EHtext.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
EHtext.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
EHtext.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
EFpara = section.HeadersFooters.EvenFooter.AddParagraph()
EFtext = EFpara.AppendText("Even Page Footer")
EFpara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
EFtext.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
EFtext.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
EFtext.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("OddAndEvenHeaderFooter.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Set or Change Fonts in PowerPoint
In a PowerPoint document, the choice of fonts plays a significant role in enhancing the overall visual appeal and effectiveness of the presentation. Different fonts can be used to establish a visual hierarchy, allowing you to emphasize key points, headings, or subheadings in your presentation and guide the audience's attention. This article introduces how to set or change fonts in a PowerPoint document in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Set Fonts when Creating a New PowerPoint Document in Python
- Change Fonts in an Existing PowerPoint Document in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Set Fonts when Creating a New PowerPoint Document in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python offers the TextRange class to represent a range of text. A paragraph can consist of one or more text ranges. To apply font formatting to the characters in a text range, you can use the properties like LatinFont, IsBold, IsItalic, and FontHeight of the TextRange class. The following are the steps to set fonts when creating a new PowerPoint document in Python.
- Create a Presentation object.
- Get the first slide through Presentation.Slides[0] property.
- Add a shape to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendShape() method.
- Add text to the shape using IAutoShape.AppendTextFrame() method.
- Get TextRange object through IAutoShape.TextFrame.TextRange property.
- Set the font information such as font name, font size, bold, italic, underline, and text color through the properties under the TextRange object.
- Save the presentation to a PPTX file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
import math
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Set slide size type
presentation.SlideSize.Type = SlideSizeType.Screen16x9
# Add a shape to the first slide
rec = RectangleF.FromLTRB (30, 100, 900, 250)
shape = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, rec)
# Set line color and fill type of the shape
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_Transparent()
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Add text to the shape
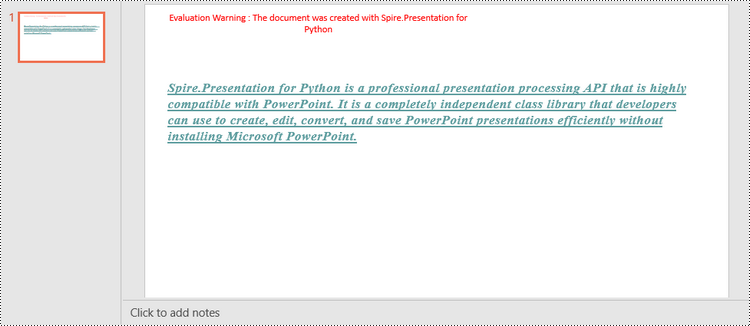
shape.AppendTextFrame("Spire.Presentation for Python is a professional presentation processing API that \
is highly compatible with PowerPoint. It is a completely independent class library that developers can \
use to create, edit, convert, and save PowerPoint presentations efficiently without installing Microsoft PowerPoint.")
# Get text of the shape as a text range
textRange = shape.TextFrame.TextRange
# Set font name
textRange.LatinFont = TextFont("Times New Roman")
# Set font style (bold & italic)
textRange.IsBold = TriState.TTrue
textRange.IsItalic = TriState.TTrue
# Set underline type
textRange.TextUnderlineType = TextUnderlineType.Single
# Set font size
textRange.FontHeight = 22
# Set text color
textRange.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
textRange.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_CadetBlue()
# Set alignment
textRange.Paragraph.Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Left
# Set line spacing
textRange.LineSpacing = 0.5
# Save to file
presentation.SaveToFile("output/SetFont.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2019)
presentation.Dispose()
Change Fonts in an Existing PowerPoint Document in Python
To change the font for a specific paragraph, we need to get the paragraph from the document. Then, iterate through the text ranges in the paragraph and reset the font information for each text range. Below are the steps to change the font of a paragraph in an existing PowerPoint document using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Create a Presentation object.
- Get a specific slide through Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Get a specific shape through ISlide.Shapes[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph of the shape through IAutoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Iterate through the text ranges in the paragraph.
- Set the font information such as font name, font size, bold, italic, underline, and text color of a specific text range through the properties under the TextRange object.
- Save the presentation to a PPTX file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint file
presentation.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
"# Get the first shape on the slide
shape = (IAutoShape)(slide.Shapes[0])
# Get the first paragraph of the shape
paragraph = shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0]
# Get the first paragraph of the shape
paragraph = shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0]
# Create a font
newFont = TextFont("Times New Roman")
# Loop through the text ranges in the paragraph
for textRange in paragraph.TextRanges:
# Apply font to a specific text range
textRange.LatinFont = newFont
# Set font to Italic
textRange.Format.IsItalic = TriState.TTrue
# Set font size
textRange.FontHeight = 25
# Set font color
textRange.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
textRange.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Purple()
# Save to file
presentation.SaveToFile("output/ChangeFont.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2019)
presentation.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add Hyperlinks to PDF
Hyperlinks in PDF are interactive elements that, when clicked, can jump to a specific location in the document, to an external website, or to other resources. By inserting hyperlinks in a PDF document, you can provide supplementary information and enhance the overall integrity of the document. This article will demonstrate how to add hyperlinks to PDF files in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add Hyperlinks to a PDF Document in Python
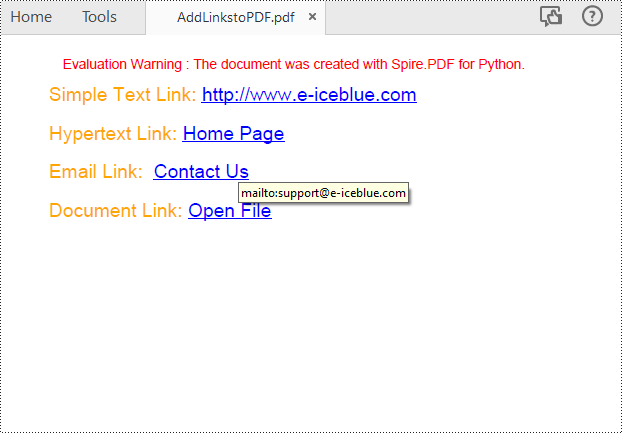
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can add web links, email links and file links to a PDF document. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a pdf document and add a page to it.
- Specify a URL address and draw it directly on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Create a PdfTextWebLink object.
- Set the link's display text, URL address, and the font and brush used to draw it using properties of PdfTextWebLink class.
- Draw the link on the page using PdfTextWebLink.DrawTextWebLink() method.
- Create a PdfFileLinkAnnotation object and with a specified file.
- Add the file link to the page annotations using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add(PdfFileLinkAnnotation) method.
- Draw hypertext of the file link using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Initialize x, y coordinates
y = 30.0
x = 10.0
# Create true type fonts
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0,PdfFontStyle.Regular,True)
font1 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Underline,True)
# Add a simply link
label = "Simple Text Link: "
format = PdfStringFormat()
format.MeasureTrailingSpaces = True
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
url = "http://www.e-iceblue.com"
page.Canvas.DrawString(url, font1, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
y = y + 28
# Add a hypertext link
label = "Hypertext Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
webLink = PdfTextWebLink()
webLink.Text = "Home Page"
webLink.Url = url
webLink.Font = font1
webLink.Brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
webLink.DrawTextWebLink(page.Canvas, PointF(x, y))
y = y + 28
# Add an Email link
label = "Email Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
link = PdfTextWebLink()
link.Text = "Contact Us"
link.Url = "mailto:support@e-iceblue.com"
link.Font = font1
link.Brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
link.DrawTextWebLink(page.Canvas, PointF(x, y))
y = y + 28
# Add a file link
label = "Document Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
text = "Open File"
location = PointF(x, y)
size = font1.MeasureString(text)
linkBounds = RectangleF(location, size)
fileLink = PdfFileLinkAnnotation(linkBounds,"C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Report.xlsx")
fileLink.Border = PdfAnnotationBorder(0.0)
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(fileLink)
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font1, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
#Save the result pdf file
pdf.SaveToFile("AddLinkstoPDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
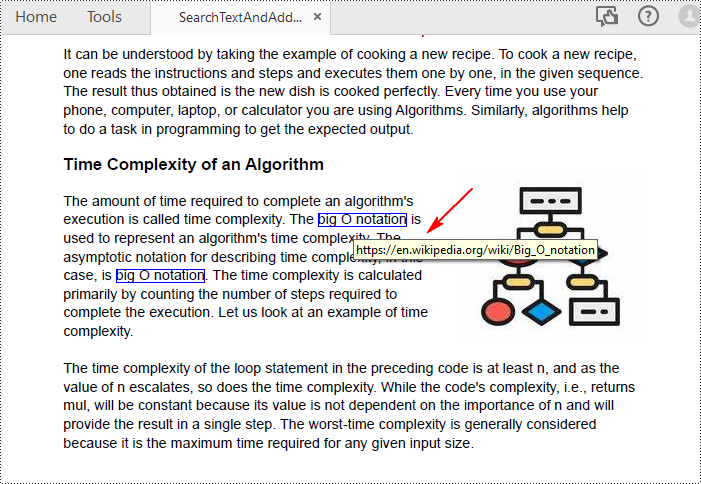
Insert Hyperlinks into Existing Text in PDF in Python
Adding a hyperlink to existing text in a PDF document requires locating the text first. Once the location has been obtained, an object of PdfUriAnnotation class with the link can be created and added to the position. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first page using PdfDocument.Pages property.
- Find all occurrences of the specified text on the page using PdfPageBase.FindText() method.
- Loop through all occurrences of the found text and create a PdfUriAnnotation instance based on the text bounds of each occurrence.
- Set the hyperlink URL, border, and border color using properties under PdfUriAnnotation class.
- Insert the hyperlink to the page annotations using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add(PdfUriAnnotation) method.
- Save the PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("input.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Find all occurrences of the specified text on the page
collection = page.FindText("big O notation", TextFindParameter.IgnoreCase)
# Loop through all occurrences of the specified text
for find in collection.Finds:
# Create a hyperlink annotation
uri = PdfUriAnnotation(find.Bounds)
# Set the URL of the hyperlink
uri.Uri = "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_O_notation"
# Set the border of the hyperlink annotation
uri.Border = PdfAnnotationBorder(1.0)
# Set the color of the border
uri.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
# Add the hyperlink annotation to the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(uri)
#Save the result file
pdf.SaveToFile("SearchTextAndAddHyperlink.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add, Hide, or Remove Layers in PDF
Layers in PDF are similar to layers in image editing software, where different elements of a document can be organized and managed separately. Each layer can contain different content, such as text, images, graphics, or annotations, and can be shown or hidden independently. PDF layers are often used to control the visibility and positioning of specific elements within a document, making it easier to manage complex layouts, create dynamic designs, or control the display of information. In this article, you will learn how to add, hide, remove layers in a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add a Layer to PDF in Python
- Set Visibility of a Layer in PDF in Python
- Remove a Layer from PDF in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add a Layer to PDF in Python
A layer can be added to a PDF document using the Document.Layers.AddLayer() method. After the layer object is created, you can draw text, images, fields, or other elements on it to form its appearance. The detailed steps to add a layer to PDF using Spire.PDF for Java are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a layer using Document.Layers.AddLayer() method.
- Get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Create a canvas for the layer based on the page using PdfLayer.CreateGraphics() method.
- Draw text on the canvas using PdfCanvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def AddLayerWatermark(doc):
# Create a layer named "Watermark"
layer = doc.Layers.AddLayer("Watermark")
# Create a font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Bodoni MT Black", 50.0, 1, True)
# Specify watermark text
watermarkText = "DO NOT COPY"
# Get text size
fontSize = font.MeasureString(watermarkText)
# Get page count
pageCount = doc.Pages.Count
# Loop through the pages
for i in range(0, pageCount):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create canvas for layer
canvas = layer.CreateGraphics(page.Canvas)
# Draw sting on the graphics
canvas.DrawString(watermarkText, font, PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), (canvas.Size.Width - fontSize.Width)/2, (canvas.Size.Height - fontSize.Height)/2 )
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Invoke AddLayerWatermark method to add a layer
AddLayerWatermark(doc)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Set Visibility of a Layer in PDF in Python
To control the visibility of layers in a PDF document, you can use the PdfDocument.Layers[index].Visibility property. Set it to off to hide a layer, or set it to on to unhide a layer. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the visibility of a certain layer through Document.Layers[index].Visibility property.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Layer.pdf")
# Hide a layer by setting the visibility to off
doc.Layers.get_Item(0).Visibility = PdfVisibility.Off
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/HideLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Remove a Layer from PDF in Python
If a layer is no more wanted, you can remove it using the PdfDocument.Layers.RmoveLayer() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific layer through PdfDocument.Layers[index] property.
- Remove the layer from the document using PdfDcument.Layers.RemoveLayer(PdfLayer.Name) method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Layer.pdf")
# Delete the specific layer
doc.Layers.RemoveLayer(doc.Layers.get_Item(0).Name)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Insert or Remove Footnotes in Word
Footnotes are a valuable tool in Microsoft Word that allows you to enhance the content of your documents by providing additional information, references, or citations at the bottom of a page. For example, you can use footnotes to provide in-depth explanations of complex concepts, cite sources to support your arguments, or offer tangential information that might be interesting to your readers. Whether you're working on an academic paper, a book, or any document that requires citations or explanations, footnotes offer a convenient way to maintain a clean and organized layout while presenting supplementary details. In this article, we will explain how to insert or remove footnotes in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Insert a Footnote for a Specific Paragraph in Word in Python
- Insert a Footnote for a Specific Text in Word in Python
- Remove Footnotes in a Word Document in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert a Footnote for a Specific Paragraph in Word in Python
You can use the Paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python to easily add a footnote for a specific paragraph. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section in the document using Document.Section[int] property and then get a specific paragraph of the section using Section.Paragraphs[int] property.
- Add a footnote at the end of the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote) method.
- Set the text content of the footnote, and then set the font and color for the footnote text and the footnote reference mark.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(3)
# Add a footnote at the end of the paragraph
footnote = paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote)
# Set the text content of the footnote
text = footnote.TextBody.AddParagraph().AppendText("The industry code list is available online.")
# Set the text font and color
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
text.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkBlue()
# Set the font and color of the footnote reference mark
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri"
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontSize = 15
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.Bold = True
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkCyan()
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AddFootnoteForParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Insert a Footnote for a Specific Text in Word in Python
To add a footnote for a specific text, you need to find the text in the document, get the location of the text in its owner paragraph, and then insert the footnote after the text. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find a specific text using Document.FindString() method.
- Get the found text as a single text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method.
- Get the paragraph where the text range is located using TextRange.OwnerParagraph property.
- Get the index position of the text range in the paragraph using Paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf() method.
- Add a footnote to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote) method, and then insert the footnote after the specific text using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method.
- Set the text content of the footnote, and then set the font and color for the footnote text and the footnote reference mark.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Find a specific text
selection = document.FindString("major players", False, True)
# Get the found text as a single text range
textRange = selection.GetAsOneRange()
# Get the paragraph where the text range is located
paragraph = textRange.OwnerParagraph
# Get the index position of the text range in the paragraph
index = paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(textRange)
# Add a footnote to the paragraph
footnote = paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote)
# Insert the footnote after the text range
paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(index + 1, footnote)
# Set the text content of the footnote
text = footnote.TextBody.AddParagraph().AppendText("Including suppliers, competitors, and customers")
# Set the text font and color
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
text.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkBlue()
# Set the font and color of the footnote reference mark
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri"
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontSize = 15
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.Bold = True
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkGreen()
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AddFootnoteForText.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Remove Footnotes in a Word Document in Python
When the footnotes of a Word document are no longer needed, you can remove them to make the document neater. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[int] property.
- Loop through each paragraph in the section to find the footnotes.
- Remove the footnotes using Paragraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("AddFootnoteForParagraph.docx")
# Get the first section of the document
section = document.Sections[0]
# Loop through the paragraphs in the section
for y in range(section.Paragraphs.Count):
para = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(y)
index = -1
i = 0
cnt = para.ChildObjects.Count
while i < cnt:
pBase = para.ChildObjects[i] if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[i], ParagraphBase) else None
if isinstance(pBase, Footnote):
index = i
break
i += 1
if index > -1:
# Remove the footnotes from the paragraph
para.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(index)
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveFootnotes.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
document.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Create Tables in a Word Document
A table is a powerful tool in a Word document that allows you to organize and present information in a structured manner. It consists of rows and columns, forming a grid-like structure. Tables are commonly used for various purposes, such as creating schedules, comparing data, or displaying data in a neat and organized format. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create tables in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Simple Table in Word in Python
- Create a Table from an HTML String in Python
- Merge and Split Cells in a Table in Python
- Fill a Table with Data in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Prerequisite Knowledge
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Table class to represent a table in a Word document. You can create table objects either through the constructor or the Section.AddTable() method. After the table object is created, you can use the Table.AddRow() method to dynamically add rows to the table, or specify the number of rows and columns of the table, and then populate it with data in a single pass.
Also, Spire.Doc for Python supports creating tables from an HTML string. This method does not return an object of Table. Therefore, you cannot use the properties or methods under the Table class to deal with the table created from an HTML string. You need to set up the content and style of the table in the HTML string.
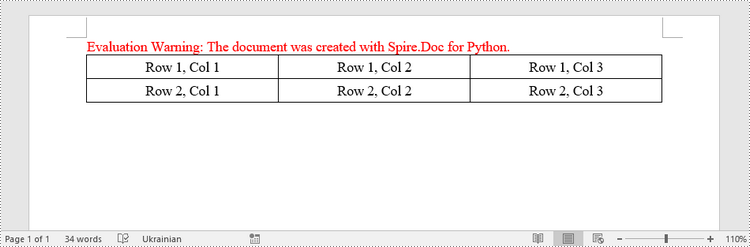
Create a Simple Table in Word in Python
This example demonstrates how to create a simple plain table using the Table class and how to add rows one by one. Here are the main steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section to it using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a Table object.
- Add a row to it using Table.AddRow() method.
- Get a specific cell of the row through Row.Cells[index] property.
- Add text to the cell using TableCell.AddParagraph().AppendText() method.
- Add the table to the document using Section.AddTable() method.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a table
table = Table(doc, True)
# Set the width of table
table.PreferredWidth = PreferredWidth(WidthType.Percentage, int(100))
# Set the border of table
table.TableFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
table.TableFormat.Borders.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Add a row
row = table.AddRow(False, 3)
row.Height = 20.0
# Add data to the cells
cell = row.Cells[0]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 1, Col 1")
cell = row.Cells[1]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 1, Col 2")
cell = row.Cells[2]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 1, Col 3")
# Add the second row
row = table.AddRow(False, 3)
row.Height = 20.0
cell = row.Cells[0]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 2, Col 1")
cell = row.Cells[1]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 2, Col 2")
cell = row.Cells[2]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 2, Col 3")
# Add the table to the section
section.Tables.Add(table)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/CreateTable.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()
Create a Table from an HTML String in Python
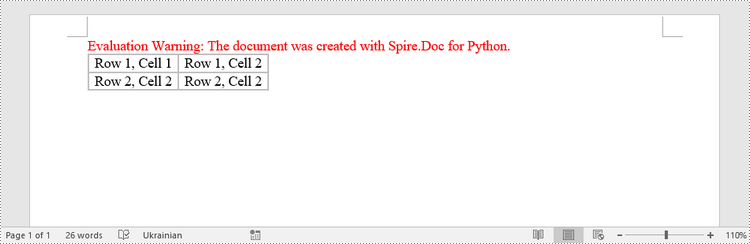
To create a table from an HTML string, use the Paragraph.AppendHTML() method. The following are the steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section to it using Document.AddSection() method.
- Specify the HTML string for generating the table.
- Add a paragraph using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add the HTML table to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendHTML() method.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Add a section
section = document.AddSection()
# Specify HTML string
HTML = "<table border='2px'>" + "<tr>" + "<td>Row 1, Cell 1</td>" + "<td>Row 1, Cell 2</td>" + \
"</tr>" + "<tr>" + "<td>Row 2, Cell 2</td>" + \
"<td>Row 2, Cell 2</td>" + "</tr>" + "</table>"
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Append HTML string to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendHTML(HTML)
# Save to Word document
document.SaveToFile("output/HtmlTable.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
Merge and Split Cells in a Table in Python
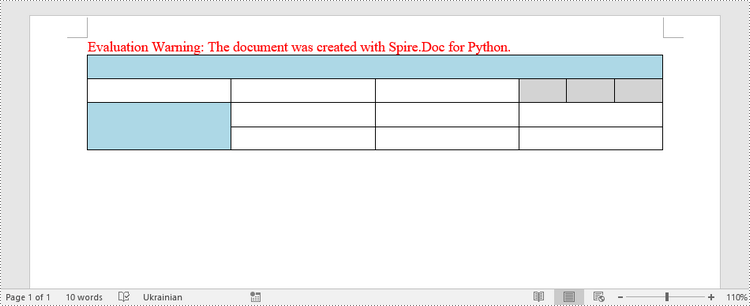
When working with tables, the ability to merge or split cells provides a powerful way to customize and format data. This example shows you how to combine adjacent cells into a single cell and how to divide a single cell into multiple smaller cells using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a table using Section.AddTable() method.
- Set the column number and row number of the table using Table.ResetCells() method.
- Horizontally merge cells using Table.ApplyHorizontalMerge() method.
- Vertically merge cells using Table.ApplyVerticalMerge() method.
- Split a cell into multiple smaller cells using TableCell.SplitCell() method.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Add a section
section = document.AddSection()
# Create a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
# Set the row number and column number of table
table.ResetCells(4, 4)
# Set the width of table
table.PreferredWidth = PreferredWidth(WidthType.Percentage, int(100))
# Set row height
for i in range(0, table.Rows.Count):
table.Rows[i].Height = 20.0
# Horizontally merge cells
table.ApplyHorizontalMerge(0, 0, 3)
# Vertically merge cells
table.ApplyVerticalMerge(0, 2, 3)
# Get a cell
cell = table.Rows.get_Item(1).Cells.get_Item(3)
# Split the cell into 3 smaller cells
cell.SplitCell(3, 0)
# Fill specified cells with color
table.Rows[0].Cells[0].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightBlue()
table.Rows[2].Cells[0].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightBlue()
table.Rows[1].Cells[3].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
table.Rows[1].Cells[4].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
table.Rows[1].Cells[5].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
# Save to Word document
document.SaveToFile("output/MergeAndSplit.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
Fill a Table with Data in Word in Python
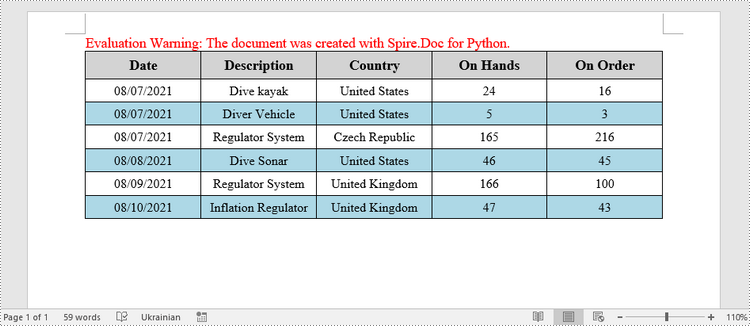
This example creates a 5x7 table, writes the data from lists into the cells, and applies different formatting to the header row and other rows. The following are the main steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a table using Section.AddTable() method.
- Specify the data for filling the table in two lists.
- Reset the row number and column number of the table depending on the height and width of the data using Table.ResetCells() method.
- Write data into the corresponding cells using TableCell.AddParagraph().AppendText() method.
- Apply different colors to different rows through TableCell.CellFormat.BackColor property.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
import math
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
# Specify table data
header_data = ["Date", "Description", "Country", "On Hands", "On Order"]
row_data = [ ["08/07/2021","Dive kayak","United States","24","16"],
["08/07/2021","Diver Vehicle","United States","5","3"],
["08/07/2021","Regulator System","Czech Republic","165","216"],
["08/08/2021","Dive Sonar","United States","46","45"],
["08/09/2021","Regulator System","United Kingdom","166","100"],
["08/10/2021","Inflation Regulator","United Kingdom","47","43"]]
# Set the row number and column number of table
table.ResetCells(len(row_data) + 1, len(header_data))
# Set the width of table
table.PreferredWidth = PreferredWidth(WidthType.Percentage, int(100))
# Get header row
headerRow = table.Rows[0]
headerRow.IsHeader = True
headerRow.Height = 23
headerRow.RowFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
# Fill the header row with data and set the text formatting
i = 0
while i < len(header_data):
headerRow.Cells[i].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = headerRow.Cells[i].AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
txtRange = paragraph.AppendText(header_data[i])
txtRange.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
i += 1
# Fill the rest rows with data and set the text formatting
r = 0
while r < len(row_data):
dataRow = table.Rows[r + 1]
dataRow.Height = 20
dataRow.HeightType = TableRowHeightType.Exactly
c = 0
while c < len(row_data[r]):
dataRow.Cells[c].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = dataRow.Cells[c].AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
txtRange = paragraph.AppendText(row_data[r][c])
txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11
c += 1
r += 1
# Alternate row color
for j in range(1, table.Rows.Count):
if math.fmod(j, 2) == 0:
row2 = table.Rows[j]
for f in range(row2.Cells.Count):
row2.Cells[f].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightBlue()
# Set the border of table
table.TableFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
table.TableFormat.Borders.LineWidth = 1.0
table.TableFormat.Borders.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/Table.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add Stamps to a PDF Document
Stamps are a powerful tool in PDF documents that allow users to mark and annotate specific areas or sections of a PDF file. Often used for approval, review, or to indicate a specific status, stamps can greatly enhance collaboration and document management. In PDF, stamps can take various forms, such as a simple checkmark, a customized graphic, a date and time stamp, or even a signature. In this article, you will learn how to add image stamps and dynamic stamps to a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
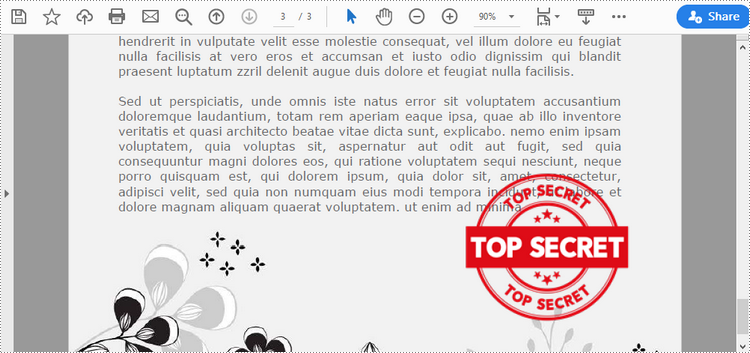
Add an Image Stamp to PDF Documents in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfRubberStampAnnotation class to represent a rubber stamp in a PDF document. In order to create the appearance of a rubber stamp, the PdfTemplate class is used. The PdfTemplate is a piece of canvas on which you can draw whatever information you want, such as text, images, date, and time.
Image stamps can include logos, signatures, watermarks, or any other custom graphics that you want to overlay onto your PDFs. The main steps to add an image stamp to PDF using Spire.PDF for Python are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Load an image that you want to stamp on PDF using PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Create a PdfTemplate object with the dimensions of the image.
- Draw the image on the template using PdfTemplate.Graphics.DrawImage() method.
- Create a PdfRubberStampAnnotation object, and set the template as its appearance.
- Add the stamp to a specific PDF page using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(2)
# Load an image file
image = PdfImage.FromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\secret.png")
# Get the width and height of the image
width = (float)(image.Width)
height = (float)(image.Height)
# Create a PdfTemplate object based on the size of the image
template = PdfTemplate(width, height, True)
# Draw image on the template
template.Graphics.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0, width, height)
# Create a rubber stamp annotation, specifying its location and position
rect = RectangleF((float) (page.ActualSize.Width - width - 50), (float) (page.ActualSize.Height - height - 40), width, height)
stamp = PdfRubberStampAnnotation(rect)
# Create a PdfAppearance object
pdfAppearance = PdfAppearance(stamp)
# Set the template as the normal state of the appearance
pdfAppearance.Normal = template
# Apply the appearance to the stamp
stamp.Appearance = pdfAppearance
# Add the stamp annotation to PDF
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(stamp)
# Save the file
doc.SaveToFile("output/ImageStamp.pdf")
doc.Close()
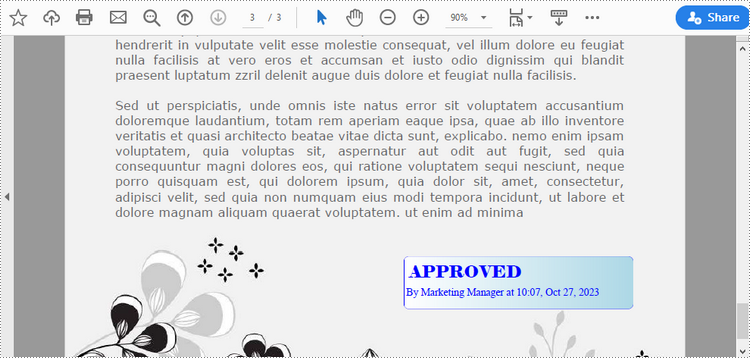
Add a Dynamic Stamp to PDF in Python
Unlike static stamps, dynamic stamps can contain variable information such as the date, time, or user input. The following are the steps to create a dynamic stamp in PDF using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PdfTemplate object with desired size.
- Draw strings on the template using PdfTemplate.Graphics.DrawString() method.
- Create a PdfRubberStampAnnotation object, and set the template as its appearance.
- Add the stamp to a specific PDF page using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(2)
# Create a PdfTemplate object
template = PdfTemplate(220.0, 50.0, True)
# Create two fonts
font1 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Elephant", 16.0, 0, True)
font2 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 10.0, 0, True)
# Create a solid brush and a gradient brush
solidBrush = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue()))
rectangle1 = RectangleF(PointF(0.0, 0.0), template.Size)
linearGradientBrush = PdfLinearGradientBrush(rectangle1, PdfRGBColor(Color.get_White()), PdfRGBColor(Color.get_LightBlue()), PdfLinearGradientMode.Horizontal)
# Create a pen
pen = PdfPen(solidBrush)
# Create a rounded rectangle path
CornerRadius = 10.0
path = PdfPath()
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 180.0, 90.0)
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X + template.Width - CornerRadius, template.GetBounds().Y, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 270.0, 90.0)
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X + template.Width - CornerRadius, template.GetBounds().Y + template.Height - CornerRadius, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 0.0, 90.0)
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y + template.Height - CornerRadius, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 90.0, 90.0)
path.AddLine(template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y + template.Height - CornerRadius, template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y + CornerRadius / 2)
# Draw path on the template
template.Graphics.DrawPath(pen, path)
template.Graphics.DrawPath(linearGradientBrush, path)
# Draw text on the template
string1 = "APPROVED\n"
string2 = "By Marketing Manager at " + DateTime.get_Now().ToString("HH:mm, MMM dd, yyyy")
template.Graphics.DrawString(string1, font1, solidBrush, PointF(5.0, 5.0))
template.Graphics.DrawString(string2, font2, solidBrush, PointF(2.0, 28.0))
# Create a rubber stamp, specifying its size and location
rectangle2 = RectangleF((float) (page.ActualSize.Width - 220.0 - 50.0), (float) (page.ActualSize.Height - 50.0 - 100.0), 220.0, 50.0)
stamp = PdfRubberStampAnnotation(rectangle2)
# Create a PdfAppearance object and apply the template as its normal state
apprearance = PdfAppearance(stamp)
apprearance.Normal = template
# Apply the appearance to stamp
stamp.Appearance = apprearance
# Add the stamp annotation to annotation collection
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(stamp)
# Save the file
doc.SaveToFile("output/DynamicStamp.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.