
.NET (1317)
Children categories
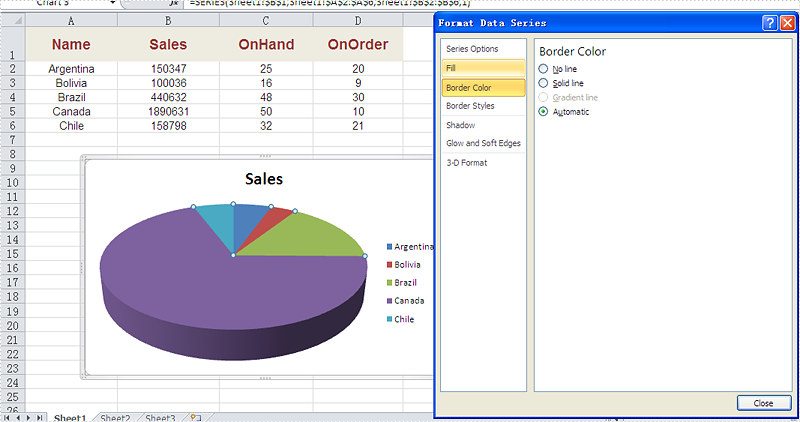
The different border color and styles on the Excel Chart can distinguish the chart categories easily. Spire.XLS offers a property of LineProperties to enables developers to set the color and styles for the data point. This article is going to introduce the method of how to format data series for Excel charts in C# using Spire.XLS.
Note: Before Start, please download the latest version of Spire.XLS and add Spire.xls.dll in the bin folder as the reference of Visual Studio.
Firstly, please check the original screenshot of excel chart with the automatic setting for border.
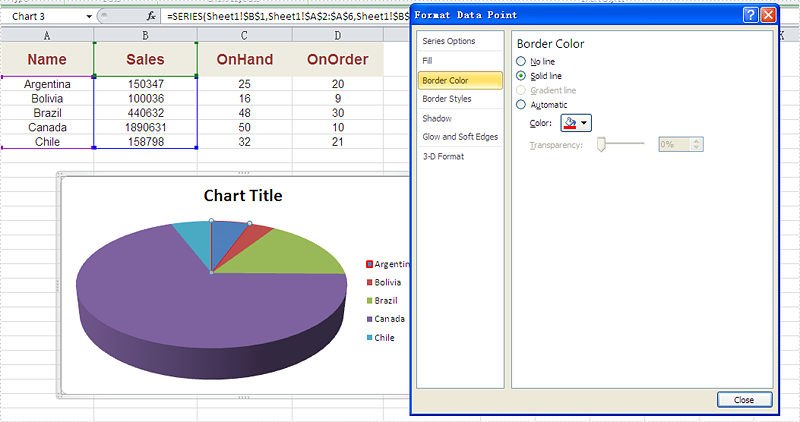
Code Snippet of how to set the border color and border styles for Excel chart data series.
Step 1: Create a new workbook and load from file.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
Step 2: Get the first worksheet from workbook and then get the first chart from the worksheet.
Worksheet ws = workbook.Worksheets[0]; Chart chart = ws.Charts[0];
Step 3: Set CustomLineWeight property for Series line.
(chart.Series[0].DataPoints[0].DataFormat.LineProperties as XlsChartBorder).CustomLineWeight = 1.5f;
Step 4: Set Color property for Series line.
(chart.Series[0].DataPoints[0].DataFormat.LineProperties as XlsChartBorder).Color = Color.Red;
Step 5: Save the document to file.
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
Effective screenshot after set the color and width of excel chart border.
Full codes:
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
using Spire.Xls.Core.Spreadsheet.Charts;
using System.Drawing;
namespace SetBoarderColor
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
Worksheet ws = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Chart chart = ws.Charts[0];
(chart.Series[0].DataPoints[0].DataFormat.LineProperties as XlsChartBorder).CustomLineWeight = 1.5f;
(chart.Series[0].DataPoints[0].DataFormat.LineProperties as XlsChartBorder).Color = Color.Red;
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
}
How to Adjust the Spaces between Bars in Excel Chart in C#, VB.NET
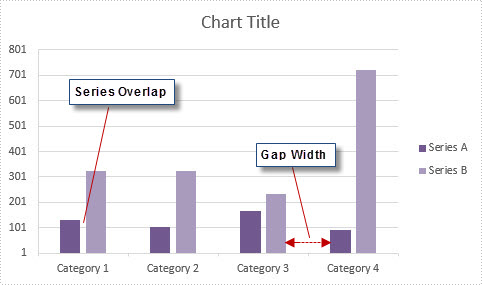
2015-12-30 07:34:49 Written by KoohjiIn MS Excel, the spaces between data bars have been defined as Series Overlap and Gap Width.
- Series Overlap: Spaces between data series within a single category.
- Gap Width: Spaces between two categories.
Check below picture, you'll have a better understanding of these two concepts. Normally the spaces are automatically calculated based on the date and chart area, the space may be very narrow or wide depending on how many date series you have in a fixed chart area. In this article, we'll introduce how to adjust the spaces between data bars using Spire.XLS.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Wordbook class and load the sample Excel file that contains some data in A1 to C5.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
Step 2: Create a Column chart based on the data in cell range A1 to C5.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered); chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]; chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridLines.LineProperties.Color = Color.LightGray;
Step 3: Set chart position.
chart.LeftColumn = 5; chart.TopRow = 7; chart.RightColumn = 13; chart.BottomRow = 21;
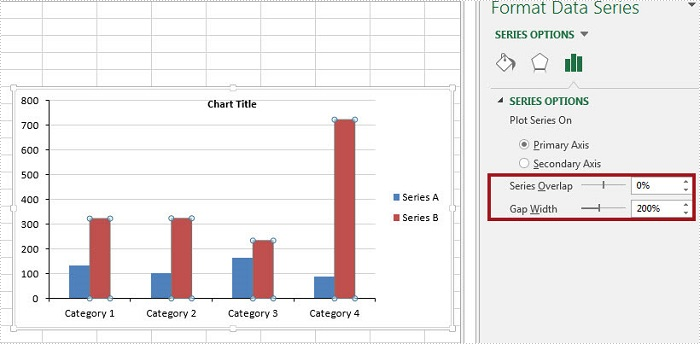
Step 4: The ChartSerieDataFormat class has two properties - GapWidth property and Overlap property to handle the Gap Width and Series Overlap respectively. The value of GapWidth varies from 0 to 500, and the value of Overlap varies from -100 to 100.
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.Format.Options.GapWidth = 200;
cs.Format.Options.Overlap = 0;
}
Step 5: Save and launch the file.
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
Output:
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
namespace AdjustSpaces
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridLines.LineProperties.Color = Color.LightGray;
chart.LeftColumn = 5;
chart.TopRow = 7;
chart.RightColumn = 13;
chart.BottomRow = 21;
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.Format.Options.GapWidth = 200;
cs.Format.Options.Overlap = 0;
}
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports Spire.Xls.Charts
Namespace AdjustSpaces
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx")
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim chart As Chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered)
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range("A1:C5")
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridLines.LineProperties.Color = Color.LightGray
chart.LeftColumn = 5
chart.TopRow = 7
chart.RightColumn = 13
chart.BottomRow = 21
For Each cs As ChartSerie In chart.Series
cs.Format.Options.GapWidth = 200
cs.Format.Options.Overlap = 0
Next
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
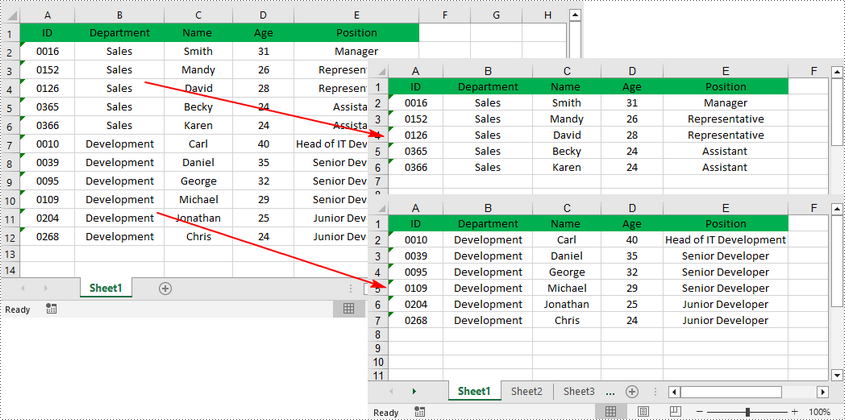
When dealing with an Excel worksheet containing a large amount of data, splitting it into several separate Excel files based on specific criteria can be beneficial. By dividing the worksheet into smaller, more manageable files, you can improve your work efficiency and make data analysis easier. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically split an Excel worksheet into multiple Excel files using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Split an Excel Sheet into Multiple Files in C# and VB.NET
The Worksheet.Copy(CellRange sourceRange, CellRange destRange) method provided by Spire.XLS for .NET allows you to split a worksheet by copying a specified cell range from the original Excel file to a new Excel file. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get the header row and the specified cell ranges using Worksheet.Range property.
- Create a new workbook and get its first worksheet.
- Copy the header row and specified cell range to the first worksheet of the new workbook using Worksheet.Copy(CellRange sourceRange, CellRange destRange) method.
- Copy the column width from the original workbook to the new workbook, and then save the new workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Create another new workbook, and then repeat the above steps to copy the header row and specified cell range into the new workbook.
- Save the new workbook to another Excel file.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace splitworksheet
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook originalBook= new Workbook();
//Load the original Excel document from file
originalBook.LoadFromFile("Info.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = originalBook.Worksheets[0];
//Get the header row
CellRange headerRow = sheet.Range[1, 1, 1,5];
//Get two cell ranges
CellRange range1 = sheet.Range[2, 1, 6, sheet.LastColumn];
CellRange range2 = sheet.Range[7, 1, sheet.LastRow, sheet.LastColumn];
//Create a new workbook
Workbook newBook1 = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet of new workbook
Worksheet newSheet1 = newBook1.Worksheets[0];
//Copy the header row and range 1 to the first worksheet of the new workbook
sheet.Copy(headerRow, newSheet1.Range[1, 1]);
sheet.Copy(range1, newSheet1.Range[2, 1]);
//Copy the column width from the original workbook to the new workbook
for (int i = 0; (i < sheet.LastColumn); i++)
{
newBook1.Worksheets[0].SetColumnWidth(i + 1, sheet.GetColumnWidth(i + 1));
}
//Save the new workbook to an Excel file
newBook1.SaveToFile("Sales Depart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
//Create another new workbook
Workbook newBook2 = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet of new workbook
Worksheet newSheet2 = newBook2.Worksheets[0];
//Copy the header row and range 2 to the first worksheet of the new workbook
sheet.Copy(headerRow, newSheet2.Range[1, 1]);
sheet.Copy(range2, newSheet2.Range[2, 1]);
//Copy the column width from the original workbook to the new workbook
for (int i = 0; (i < sheet.LastColumn); i++)
{
newBook2.Worksheets[0].SetColumnWidth(i + 1, sheet.GetColumnWidth(i + 1));
}
//Save the new workbook to another Excel file
newBook2.SaveToFile("Development Depart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Gridlines are often added to charts to help improve the readability of the chart itself, but it is not a necessary to display the gridlines in every chart especially when we do not need to know the exact value of each data point from graphic. This article will present how to hide gridlines in Excel chart using Spire.XLS.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Workbook class and load a sample Excel file that contains some data in A1 to C5.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx");
Step 2: Create a Column chart based on the data in cell range A1 to C5.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered); chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]; chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
Step 3: Set chart position.
chart.LeftColumn = 1; chart.TopRow = 6; chart.RightColumn = 8 chart.BottomRow = 19;
Step 4: Set the PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines property to false.
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
Step 5: Save and launch the file.
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
Output:
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace HideGridLine
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
chart.LeftColumn = 1;
chart.TopRow = 6;
chart.RightColumn = 8;
chart.BottomRow = 19;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace HideGridLine
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx")
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim chart As Chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered)
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range("A1:C5")
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 8
chart.BottomRow = 19
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
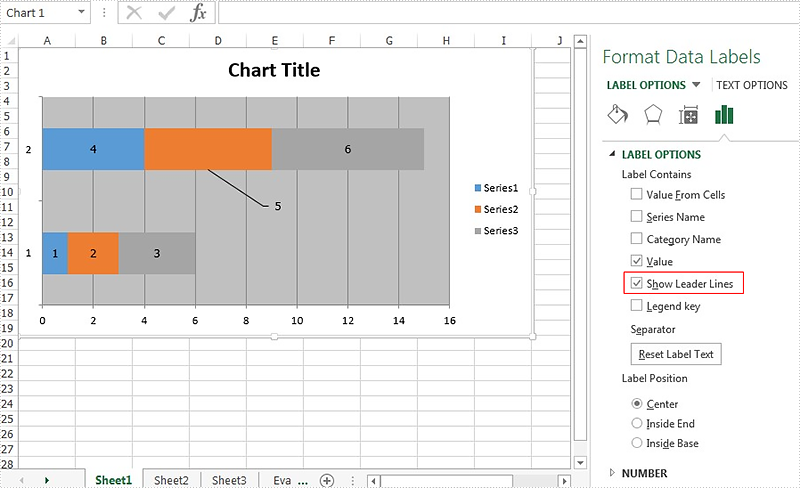
The leader line on Excel chart is very helpful since it gives a visual connection between a data label and its corresponding data point. Spire.XLS offers a property of DataLabels.ShowLeaderLines to enable developers to show or hide the leader lines easily. This article will focus on demonstrating how to show the leader line on Excel stacked bar chart in C#.
Note: Before Start, please ensure that you have download the latest version of Spire.XLS (V7.8.64 or above) and add Spire.xls.dll in the bin folder as the reference of Visual Studio.
Here comes to the code snippet of how to show the leader line on Excel stacked bar chart in C#.
Step 1: Create a new excel document instance and get the first worksheet.
Workbook book = new Workbook(); Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Add some data to the Excel sheet cell range.
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "1"; sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "2"; sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "3"; sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "4"; sheet.Range["B2"].Value = "5"; sheet.Range["B3"].Value = "6";
Step 3: Create a bar chart and define the data for it.
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.BarStacked); chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:B3"];
Step 4: Set the property of HasValue and ShowLeaderLines for DataLabels.
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = true;
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.ShowLeaderLines = true;
}
Step 5: Save the document to file and set the excel version.
book.Version = ExcelVersion.Version2013;
book.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
Effective screenshots:
Full codes:
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
using Spire.Xls.Core.Spreadsheet.Charts;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ShowLeaderLine
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook book = new Workbook();
Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "1";
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "2";
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "3";
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "4";
sheet.Range["B2"].Value = "5";
sheet.Range["B3"].Value = "6";
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.BarStacked);
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:B3"];
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = true;
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.ShowLeaderLines = true;
}
book.Version = ExcelVersion.Version2013;
book.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
}
Simple introduction about Word XML
Word XML is a special XML format, which makes Word be able to manipulate the Word documents stored in XML format. It can be divided into two types: WordML(supported by Word 2003) and WordXML(supported by Word 2007). If external applications support Word XML and the generated data follow the Word XML structure, then the data can be processed by Word. In this way, Word XML has become the bridge between Word and other external applications, any XML- formatted document based on Word XML structure can be opened, edited and saved in Word.
Using C#/VB.NET to convert Word to Word XML via Spire.Doc
Spire.Doc enables users to convert word document to Word XML format easily by using the doc.SaveToFile() method. Now, please follow the detail steps below:
Note: Before start, please download Spire.Doc and install it correctly, then add Spire.Doc.dll file from Bin folder as the reference of your project.
This is the screenshot of the original word document:
Step 1: Create a new document instance.
Document doc = new Document();
Step 2: Load the sample word document from file.
doc.LoadFromFile("Spire.Doc for .NET.docx");
Step 3: Save the word document as Word XML format.
For word 2003:
doc.SaveToFile("DocxToWordML.xml", FileFormat.WordML);
For word 2007:
doc.SaveToFile("DocxToWordXML.xml", FileFormat.WordXml);
Effective screenshot:
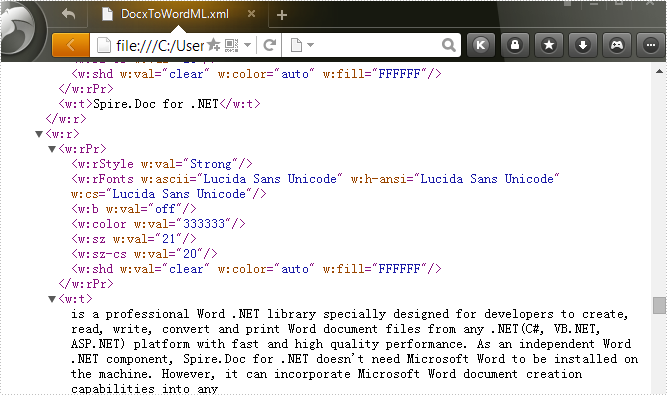
Full codes:
using Spire.Doc;
namespace Convert_Word_to_Word_XML
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("Spire.Doc for .NET.docx");
doc.SaveToFile("DocxToWordML.xml", FileFormat.WordML);
//doc.SaveToFile("DocxToWordXML.xml", FileFormat.WordXml);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Namespace Convert_Word_to_Word_XML
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim doc As New Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Spire.Doc for .NET.docx")
doc.SaveToFile("DocxToWordML.xml", FileFormat.WordML)
'doc.SaveToFile("DocxToWordXML.xml", FileFormat.WordXml);
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
After a PDF document is digitally signed with signature, the PDF has been locked to prevent changes or allow the detection of changes. In this article, we'll introduce how to detect if a signed PDF was modified using Spire.PDF.
In order to test this function, we created a PDF document and signed the PDF with digital signature, then changed the word 'PDF' in the sample document into 'Pdf' and saved it as another file. Here is what the modified PDF document looking like:
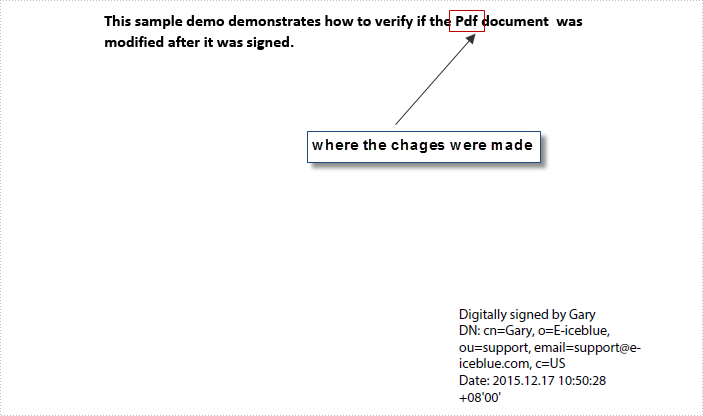
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Create a Window Forms Application and design form1 as following.
Step 2: Double click 'Load' button to write following code, which will allow us to find a PDF file from folder and return the file path in textBox1.Text.
private void btnLoad_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog fileName = new OpenFileDialog();
fileName.InitialDirectory = Application.StartupPath;
fileName.Filter = "All files|*.pdf";
if (fileName.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
string Path = fileName.FileName.ToString();
textBox1.Text = Path;
}
}
Step 3: Enter following code to the button of 'Check'. In this part, we get all signatures in the PDF document, and then call PdfSignature.VerifyDocModified() method to detect if the document was altered after signed. If it was modified return true, otherwise false.
private void btnCheck_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//get signatures from PDF
List signatures = new List();
using (PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument(textBox1.Text))
{
PdfFormWidget form = pdf.Form as PdfFormWidget;
for (int i = 0; i < form.FieldsWidget.Count; i++)
{
PdfSignatureFieldWidget field = form.FieldsWidget[i] as PdfSignatureFieldWidget;
if (field != null && field.Signature != null)
{
PdfSignature signature = field.Signature;
signatures.Add(signature);
}
}
PdfSignature signatureOne = signatures[0];
//detect if the PDF was modified
bool modified = signatureOne.VerifyDocModified();
if (modified == true)
{
MessageBox.Show("The document was modified");
}
}
}
Run the program and load the modified document, you'll get following output after clicking 'Check' button.
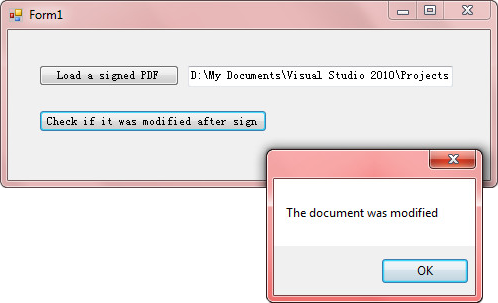
Full Code:
private void btnLoad_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog fileName = new OpenFileDialog();
fileName.InitialDirectory = Application.StartupPath;
fileName.Filter = "All files|*.pdf";
if (fileName.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
string Path = fileName.FileName.ToString();
textBox1.Text = Path;
}
}
private void btnCheck_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//get signatures from PDF
List signatures = new List();
using (PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument(textBox1.Text))
{
PdfFormWidget form = pdf.Form as PdfFormWidget;
for (int i = 0; i < form.FieldsWidget.Count; i++)
{
PdfSignatureFieldWidget field = form.FieldsWidget[i] as PdfSignatureFieldWidget;
if (field != null && field.Signature != null)
{
PdfSignature signature = field.Signature;
signatures.Add(signature);
}
}
PdfSignature signatureOne = signatures[0];
//detect if the PDF was modified
bool modified = signatureOne.VerifyDocModified();
if (modified == true)
{
MessageBox.Show("The document was modified");
}
}
}
The colorful excel font makes the whole excel document attractive and it is easy to give more importance to some data we'd like to show to others. With the help of Spire.XLS, developers can easily set Excel font and copy formatting from one place and apply it to another. This article will focus on demonstrating how to clone Excel font style directly when adding the new text to Excel worksheet in C#.
Note: Before Start, please ensure that you have download the latest version of Spire.XLS (V7.8.64 or above) and add Spire.xls.dll in the bin folder as the reference of Visual Studio.
Here comes to the code snippet of how to clone cell style for the text in Excel worksheets.
Step 1: Create a new excel document instance and get the first worksheet.
Workbook book = new Workbook(); Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Add the text to the Excel sheet cell range A1.
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Text1";
Step 3: Set A1 cell range's CellStyle.
CellStyle style = book.Styles.Add("style");
style.Font.FontName = "Calibri";
style.Font.Color = Color.Red;
style.Font.Size = 12;
style.Font.IsBold = true;
style.Font.IsItalic = true;
sheet.Range["A1"].CellStyleName = style.Name
Step 4: Use the method style.clone() to clone the same style for B2 cell range.
CellStyle csOrieign = style.clone(); sheet.Range["B2"].Text = "Text2"; sheet.Range["B2"].CellStyleName = csOrieign.Name;
Step 5: Clone the same style for C3 cell range and then reset the font color for the text.
CellStyle csGreen = style.clone(); csGreen.Font.Color = Color.Green; sheet.Range["C3"].Text = "Text3"; sheet.Range["C3"].CellStyleName = csGreen.Name;
Step 6: Save the document to file and set the excel version.
book.SaveToFile("sample2.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Effective screenshots:
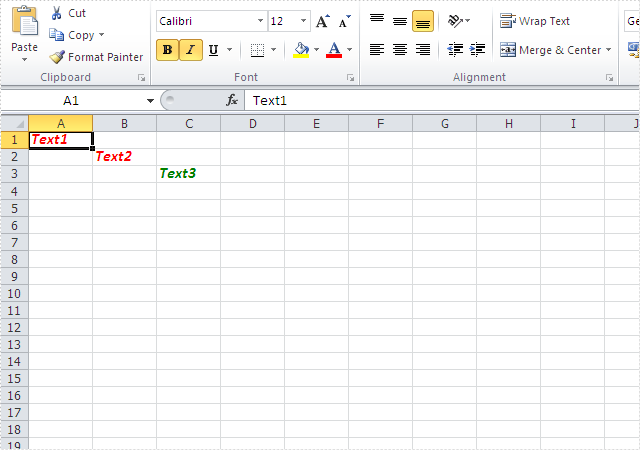
Full codes:
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
namespace CloneExcelFont
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook book = new Workbook();
Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Text1";
CellStyle style = book.Styles.Add("style");
style.Font.FontName = "Calibri";
style.Font.Color = Color.Red;
style.Font.Size = 12;
style.Font.IsBold = true;
style.Font.IsItalic = true;
sheet.Range["A1"].CellStyleName = style.Name;
CellStyle csOrieign = style.clone();
sheet.Range["B2"].Text = "Text2";
sheet.Range["B2"].CellStyleName = csOrieign.Name;
CellStyle csGreen = style.clone();
csGreen.Font.Color = Color.Green;
sheet.Range["C3"].Text = "Text3";
sheet.Range["C3"].CellStyleName = csGreen.Name;
book.SaveToFile("sample2.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
}
Retrieve data from one excel worksheet and extract to a new excel file in C#
2015-12-14 02:47:26 Written by KoohjiSearching data is a powerful data processing function of Microsoft excel, but it doesn't allow users to extract the selected data to a new excel file directly. It's almost impossible for us to copy data row by row manually from one excel file to another, so it cannot entirely meet our requirements especially when we want to retrieve and extract the interesting data from a large excel file.
This article will demonstrate how to retrieve data from one excel worksheet and extract to a new excel file with Spire.XLS in C#.
Note: Before start, please download and install Spire.XLS correctly. Then add Spire.XLS.dll file as reference of your project.
Below is the screenshot of the original excel worksheet:
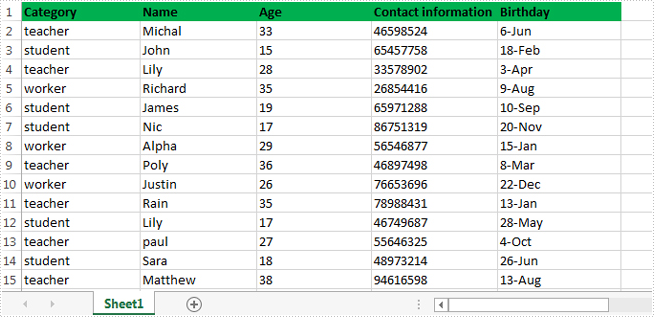
In this sample, all of the data related to teacher were extracted to a new excel file.
Detail steps overview:
Step 1: Create a new workbook instance and get the first worksheet.
Workbook newBook = new Workbook(); Worksheet newSheet = newBook.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Create a new workbook instance and load the sample excel file.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("Information.xlsx");
Step 3: Get the worksheet where you want to retrieve and extract data from. In this sample, it's the first worksheet.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Step 4: Retrieve data and extract to the first worksheet of the new excel workbook.
int i = 1;
int columnCount = sheet.Columns.Count();
foreach (CellRange range in sheet.Columns[0])
{
if (range.Text == "teacher")
{
CellRange sourceRange = sheet.Range[range.Row, 1, range.Row, columnCount];
CellRange destRange = newSheet.Range[i, 1, i, columnCount];
sheet.Copy(sourceRange, destRange, true);
i++;
}
}
Step 5: Save the target file as NewForm.xlsx.
newBook.SaveToFile("NewForm.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Effective screenshot:
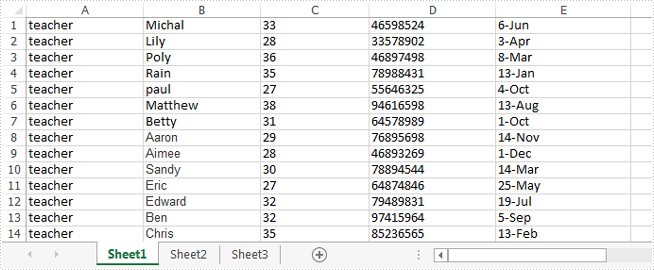
Full codes:
using System.Linq;
using Spire.Xls;
namespace Retrieve_and_extract_data
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook newBook = new Workbook();
Worksheet newSheet = newBook.Worksheets[0];
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("Information.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
int i = 1;
int columnCount = sheet.Columns.Count();
foreach (CellRange range in sheet.Columns[0])
{
if (range.Text == "teacher")
{
CellRange sourceRange = sheet.Range[range.Row, 1, range.Row, columnCount];
CellRange destRange = newSheet.Range[i, 1, i, columnCount];
sheet.Copy(sourceRange, destRange, true);
i++;
}
}
newBook.SaveToFile("NewForm.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
}
MS Word allows users to select a shape from shapes menu, drag and place it to any desired location on the page. From Spire.Doc Version 6.0 or above, we added a new feature to work with shape using code. The following section will present how to insert shapes and shape group in a Word document at the specified locations using Spire.Doc.
Code Snippets:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Document class.
Document doc = new Document();
Step 2: Add a new section to Word document, and add a paragraph to the section.
Section sec = doc.AddSection(); Paragraph para1 =sec.AddParagraph();
Step 3: Add shapes to the paragraph by calling AppendShape() method. In order to locate where the shape will be placed, you can just set the HorizontalPosition and VerticalPosition properties of ShapeObject class. We can also format the shape by set the FillColor,StrokeColor and LineStyle properties.
ShapeObject shape1 = para1.AppendShape(50, 50, ShapeType.Heart);
shape1.FillColor = Color.Red;
shape1.StrokeColor = Color.Red;
shape1.HorizontalPosition = 200;
shape1.VerticalPosition = 100;
ShapeObject shape2 = para1.AppendShape(100, 100, ShapeType.Arrow);
shape2.FillColor = Color.Purple;
shape2.StrokeColor = Color.Black;
shape2.LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.Double;
shape2.StrokeWeight = 3;
shape2.HorizontalPosition = 200;
shape2.VerticalPosition = 200;
Step 4: Add a new paragraph and insert a shape group to the paragraph by calling AppendShapeGroup() method.
Paragraph para2 = sec.AddParagraph();
ShapeGroup shapegr = para2.AppendShapeGroup(200, 400);
shapegr.ChildObjects.Add(new ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.Rectangle)
{
Width = 500,
Height = 300,
LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.ThickThin,
StrokeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue,
StrokeWeight = 1.5,
});
shapegr.ChildObjects.Add(new ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.RightTriangle)
{
Width = 500,
Height = 300,
VerticalPosition = 301,
LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.ThickThin,
StrokeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Green,
StrokeWeight = 1.5,
});
shapegr.ChildObjects.Add(new ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.QuadArrow)
{
Width = 500,
Height = 300,
VerticalPosition = 601,
LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.ThickThin,
StrokeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue,
StrokeWeight = 1.5,
});
Step 5: Save the document to file.
doc.SaveToFile("InsertShapes.docx", FileFormat.Docx2010);
Result:
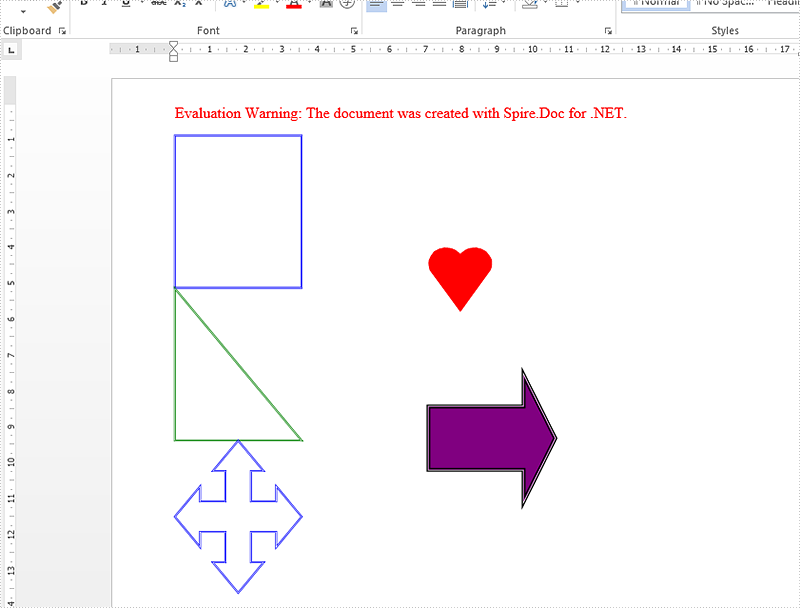
Full code:
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System.Drawing;
namespace InsertShape
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document doc = new Document();
Section sec = doc.AddSection();
Paragraph para1 = sec.AddParagraph();
ShapeObject shape1 = para1.AppendShape(50, 50, ShapeType.Heart);
shape1.FillColor = Color.Red;
shape1.StrokeColor = Color.Red;
shape1.HorizontalPosition = 200;
shape1.VerticalPosition = 100;
ShapeObject shape2 = para1.AppendShape(100, 100, ShapeType.Arrow);
shape2.FillColor = Color.Purple;
shape2.StrokeColor = Color.Black;
shape2.LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.Double;
shape2.StrokeWeight = 3;
shape2.HorizontalPosition = 200;
shape2.VerticalPosition = 200;
Paragraph para2 = sec.AddParagraph();
ShapeGroup shapegr = para2.AppendShapeGroup(200, 400);
shapegr.ChildObjects.Add(new ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.Rectangle)
{
Width = 500,
Height = 300,
LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.ThickThin,
StrokeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue,
StrokeWeight = 1.5,
});
shapegr.ChildObjects.Add(new ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.RightTriangle)
{
Width = 500,
Height = 300,
VerticalPosition = 301,
LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.ThickThin,
StrokeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Green,
StrokeWeight = 1.5,
});
shapegr.ChildObjects.Add(new ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.QuadArrow)
{
Width = 500,
Height = 300,
VerticalPosition = 601,
LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.ThickThin,
StrokeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue,
StrokeWeight = 1.5,
});
doc.SaveToFile("InsertShapes.docx", FileFormat.Docx2010);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Imports Spire.Doc.Documents
Imports Spire.Doc.Fields
Imports System.Drawing
Namespace InsertShape
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim doc As New Document()
Dim sec As Section = doc.AddSection()
Dim para1 As Paragraph = sec.AddParagraph()
Dim shape1 As ShapeObject = para1.AppendShape(50, 50, ShapeType.Heart)
shape1.FillColor = Color.Red
shape1.StrokeColor = Color.Red
shape1.HorizontalPosition = 200
shape1.VerticalPosition = 100
Dim shape2 As ShapeObject = para1.AppendShape(100, 100, ShapeType.Arrow)
shape2.FillColor = Color.Purple
shape2.StrokeColor = Color.Black
shape2.LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.[Double]
shape2.StrokeWeight = 3
shape2.HorizontalPosition = 200
shape2.VerticalPosition = 200
Dim para2 As Paragraph = sec.AddParagraph()
Dim shapegr As ShapeGroup = para2.AppendShapeGroup(200, 400)
shapegr.ChildObjects.Add(New ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.Rectangle) With { _
Key .Width = 500, _
Key .Height = 300, _
Key .LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.ThickThin, _
Key .StrokeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue, _
Key .StrokeWeight = 1.5 _
})
shapegr.ChildObjects.Add(New ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.RightTriangle) With { _
Key .Width = 500, _
Key .Height = 300, _
Key .VerticalPosition = 301, _
Key .LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.ThickThin, _
Key .StrokeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Green, _
Key .StrokeWeight = 1.5 _
})
shapegr.ChildObjects.Add(New ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.QuadArrow) With { _
Key .Width = 500, _
Key .Height = 300, _
Key .VerticalPosition = 601, _
Key .LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.ThickThin, _
Key .StrokeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue, _
Key .StrokeWeight = 1.5 _
})
doc.SaveToFile("InsertShapes.docx", FileFormat.Docx2010)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
